INSTITUTIONS. After reading this unit, you should be able to: 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Participants in Money Markets
|
|
|
- Damian Christian Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Markets and Services UNIT 2 FINANCIAL MARKETS AND INSTITUTIONS Objectives After reading this unit, you should be able to: r recognise the various instruments of Financial Market; and r identify various participants in Money Market and Capital Market. Structure 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Participants in Money Markets Central Bank Commercial Banks Indigenous Financial Agencies Discount Houses Acceptance Houses 2.3 Participants in Capital Markets Banking Institutions Non-Banking Financial Institutions 2.4 Summary 2.5 Self Assessment Questions 2.6 Further Readings 2.1 INTRODUCTION The basic function of financial market is to exchange funds, from one party to another. In business world, the demand for funds arises for different purposes and periods. For example, funds for working capital may be required for short period ranging from one month to one year whereas, for fixed assets the funds maturing ten to twenty years may be needed. Hence, there are, in fact, dozens of financial market; markets for corporate bonds and equity shares, Government and semi-government securities, mutual funds, markets like; foreign securities, public sector bonds and equities, etc. In fact, the markets in which these funds or securities are traded reflect difference in purposes, maturities and risks. On such basis, the financial markets can be classified into two broad categories which are as under: 1) Money Market 2) Capital Market. Money Market 24 The term Money Market is a little bit misleading term. It does not mean the market where different currencies are traded or exchanged, that is called foreign exchange market. In fact, money market is related with short term loans or securities, normally maturing within one year. In simple term, money market is that market where short term financial instruments that mature within a year or earlier are traded. For example, short term loans or deposits of banks, commercial papers, certificates of deposits of banks, commercial papers, treasury bills and notes, etc.
2 Money Market instruments or short-term financial assets are near substitutes for money. The risk of capital losses (money risk) and risk of default are very low in comparison to capital market. Since the change in interest rates does not affect their prices very much due to short period maturity, money market risk is very low. Further, the default risk is also very low because major participants in this market are governments, central bank, commercial banks and other important institutions. That is why money market instruments are most liquid and can be turned over quickly at low transaction cost without loss. Financial Markets and Institutions The other objective of money market is to provide the means by which individuals, institutions and governments may be able to rapidly adjust their actual liquidity position to the amount desired. It is the place where temporary cash surpluses are adjusted with temporary cash deficits. So it assures the borrowers that they can obtain shortterm funds quickly and the lenders to convert their short term financial assets into cash. The Central Bank of the country is responsible for regulating and controlling the money supply and operations in the money market. Hence, Central Bank is a major participant in the money market. Capital Market As the name indicates, a capital market is a market which provides capital funds to the needy persons or firms. It means the capital market deals in capital which can be used to mean the money value of the instruments of ownership and of long term claims to assets. In other words the capital market is the place where such financial instruments which provide long term and medium term funds are traded. Various institutions and firms, popularly known as financial institutions, assist in this process. It is noted that capital markets are the complex of various institutions and mechanism through which available long term resources are pooled and transferred to the interested business firms, governments, individuals and other agencies. These funds are made available on the basis of purpose and requirement of the borrowers. Therefore, the capital market can further be classified into various categories like primary and secondary market, equity and debt market, mortgage market, stock market, securities market and so on. In the capital market, much investment is direct and internally financed. For example, a lot of funds are internally generated by the business units from their business earning and directly invested in the long term fixed assets like plant and machinery, equipments, premises and other assets. These funds are directly employed by the borrowers without the help of financial institutions. Further, it is also noted that in the capital market the individual investors (oftenly known as household investors) also meet the long term funds requirement of the borrowing firms. Sometimes, they directly invest through primary markets and sometimes through other financial institutions; popularly known as indirect financing. 2.2 PARTICIPANTS IN MONEY MARKETS As stated earlier, the money market is the place or mechanism where short term funds are raised. These funds are obtained at the varying rates depending upon the sources of funds, the credit standing of the borrowers, maturity period, etc. There is also a secondary market where old outstanding short term claims or securities are traded at the rates determined by demand and supply position of these assets. Money market consists of specialised sub-markets which deal with specific type of short term funds and instruments. Important among these are call money market, treasury bills market, commercial bills market; short term loan market. On the basis of these specialised sub-markets, the important participants in the money market are: 25
3 Markets and Services Central Bank The Central Bank of any country is the apex monetary institution in the money market. It regulates and makes policy relating to monetary management in the country. It serves as the government bank because it performs the major financial operations of the government. It is one of the major participants in the money market because it also participates in a big way in the market to purchase and sell various securities, specifically those issued by the Government. In brief, the Central bank is an organ of the government which participates in financial markets in different ways. These are: a) By issuing of currency notes which is directly and solely under the purview of the Central Bank. For example, in our country Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has been given the sole authority to issue various currency notes except one rupee notes and coins and subsidiary coins. For this purpose, the RBI maintains a separate department known as the Issue Department. b) By working as the agent and adviser of the Government specifically concerning to the financial matters, such as loans, advances, servicing of debts, etc. It also performs such functions of the Government Departments, Government Boards and public undertakings. It also makes arrangements to meet the financial requirements; both short term as well as long term in anticipation of the collection of taxes or raising funds from the public. Further, the Central Bank also advises the government in formulation of its economic and financial policies on national as well as international matters. c) By acting as bankers bank in the financial market the Central Bank regulates the banking operations in the country. How much rate of interest would be charged and paid on advances and deposits by the bankers is regulated by the Central Bank. Undoubtedly, the Central Bank holds a privileged position and all the commercial banks have to deposit a pre-decided fixed percentage of their deposits with it. The Central Bank has the power to increase or decrease this percentage upto the specific limit. d) By maintaining adequate foreign exchange reserve for meeting the requirements of foreign trade and servicing of foreign debts. It also ensures the stability of the currency at international level. For these purposes, the Central Bank has to participate in a big way in domestic as well as foreign financial markets. From the above, it is evident that Central Bank of the country plays a significant role in money market by participating in different capacities Commercial Banks 26 Another significant participant in the money market of a country is commercial bank. A major portion of the total operations of the money markets is conducted through the commercial banks. The basic functions of commercial banks are borrowing and lending of money. They borrow money by accepting all kinds of deposits from the public at large, repayable on demand or otherwise. These deposits can be withdrawn by cheques, drafts, pay order or otherwise. The banks employ these pooled funds in the form of loans and advances to those who are in need of them. The commercial banks assist in mobilising the public savings which are normally in the form of small holdings and then combining the same into a huge lot for the purpose of investment into business sector. In general, these banks meet the short term financial needs (working capital needs) of the business firms through the mechanism of cash credit, discounting bills, hundies, promissory notes, overdraft facility and other short-term debt instruments.
4 Besides accepting deposits and granting loans and advances, the commercial banks also provide a range of other services in the capacity of agent, for their clients. They undertake the payment of subscription, insurance premium, rent, royalty, interest dividend, etc. on behalf of their clients. They also collect the amounts arisen due to interest, dividend, rent, salary and wages, commission for their customers. These banks also, sometimes, advise their clients relating to sale and purchase of various securities and in designing their investment portfolio. This service is popularly known as Portfolio Management Service. Financial Markets and Institutions Indigenous Financial Agencies Indigenous financial agencies are important participants in money market, specially in unorganised sector. They comprise of money lenders (Village Sahukars) and indigenous bankers. Money lenders are normally referred to those persons whose main business is to provide financial assistance to rural farmers, artisans and others. On the other hand, indigenous banker is referred to an individual or private firm receiving deposits and dealing in hundies or lending money. However, it is very difficult to draw a line between money lenders and indigenous bankers. The banking commission has pointed out in this regard as, while the former lends his own funds, the latter acts as a financial intermediary by accepting deposits, or avails himself of bank credit. The basic function of these agencies is to provide usually short term loans to both urban as well as rural borrowers. Normally they finance in land trade including the movement of agricultural commodities such as cotton, oil seeds, sugar and others. The main technique of their financing is discounting of hundies and bills. Sometime, they also lend money by mortgaging immovable property like houses, land, fixed assets, etc. The rate of interest charged by them is normally very high in comparison to the banks. As stated above, money lender s lending policy is flexible and informal which is based upon their personal contacts with the clients. So their policies are not uniform and vary from place to place. Since the loans are provided mostly on the personal security, so the size of loan and the rate of interest to be charged also differ from client to client. In some cases, they charge a very high rate of interest to cover the risk. In brief, indigenous financial agencies provide financial assistance, usually short term, to rural and semi-urban borrowers at the different rate of interest depending upon the personal capability and risk involved Discount Houses Discount houses are important constituents of the money market. The major function of these houses is to discount trade bills of traders so as to provide adequate liquidity in the market. These houses are normally found in the developed money market, e.g. London Money Market. There are about twelve discount houses in the London money market. The organisational structure of these houses is very simple. Normally they are set up in public limited company form and the number of persons employed by them are not very large. They work independent of other financial institutions. Since their main activities are concerned with discounting of traders bills, so the size of their capital is relatively small. They usually rely on borrowed funds. Discount houses play a significant role in business world specifically in money market. They assist the market making more liquid by discounting the trade bills. Further, by endorsing these bills, they sell these bills to commercial banks to raise funds so that they can facilitate this service further to the traders. Besides this, they 27
5 Markets and Services also provide guarantee to the bankers for payment of bills on maturity by the traders. In case of default, they take the responsibility of payment. In this way, discount houses provide very flexible instrument whereby the bankers are able to adjust their cash positions through these houses. Besides discounting the trade bills, these houses also deal in short term government securities. From the past practice of the discount houses of London, it is observed that these houses also invest in Treasury Bills, commercial bills, other Government securities, bonds and certificates issued by the Local Authorities and public corporations. Hence, major portion of the earnings of these houses is derived from commission received on discounting of the trade bills and interest accrued on investment. In brief, a discount house is an important organ of a developed money market. However, in India, such discount houses which are specifically engaged in this service are not existed. This facility is normally provided by the commercial banks and other financial institutions in our country Acceptance Houses Another important participant in the money market is Acceptance house. They play a significant role in providing more liquidity in the money market through borrowing short term loans from the banks and lending the same to the traders. In other words, the acceptance houses accept the bills of exchange which are drawn on them either by the seller or the buyer of the goods so that the accepted bill can further be discounted from the discount house. Acceptance house is an important organ of a developed money market. They not only accept the bills which are drawn on them, but also performs some other functions like normal banking facilities; both domestic and foreign, short term loans to the traders, regulating their clients open credit, advising on shipping and insurance problems arising out of the financing of trade, etc. Further, it has been noticed that some acceptance houses have also started medium as well as long term financing for major projects. In brief, acceptance houses provide adequate liquidity in the secondary market through accepting the bills so that these (bills) can easily be discounted by the discount houses and other banks. By doing this, they enhance the credit worthiness of their clients (traders) in the money market. However, the existence of these houses are very rare and is seen only in developed money market like London money market. In India, the market is still in its infancy stage of such participants. Activity 1 a) List the participants in the Money Market? b) Define: i) Discount House.
6 ii) iii) Acceptance House. Indigenous Financial Agencies. Financial Markets and Institutions 2.3 PARTICIPANTS IN CAPITAL MARKETS In this section, only such financial institutions and other agencies which are actively participating in capital market or facilitating the capital market process are described here. These institutions can be classified into two categories: a) Banking institutions b) Non-banking financial institutions Banking Institutions Though there is no hard and fast rule to distinguish between banking and non-banking institutions, however in this section, banking institutions simply refer to such banks which accept the long term deposits from the public and then lend to the borrowing community. Various forms of these Banking Institutions are: commercial banks, cooperative banks, land development banks, foreign banks, regional rural banks, etc. Some of the important activities of these banks are discussed below in brief: Commercial banks, besides meeting short term funds requirement of the borrowers, now they also participate in capital market activities. These banks accept long term deposits from the public at large providing opportunity to invest their savings. Further, now these commercial banks also meet long term funds requirement of all types of business undertakings like tiny, small, medium and large units. They also provide long term finance to transport operators for buying the vehicles, dealers in various goods, farmers, professionals and self-employed persons, etc. Banks also provide long term finance for special purposes like advances against fixed deposits receipts, advances against gold and gold ornaments, advances for durable goods like vehicles, televisions, refrigerators, washing machines, furniture, etc. They also assist for construction of houses, purchase of plots and expansion or renovation of the existing building. In brief, the commercial banks take active part in providing long term funds to different borrowers. Another important constituent of banking system which facilitates the capital market activities is cooperative banks. The basic function of these banks is to provide financial assistance to agriculturalists and others, normally through cooperative societies. In addition to this, they also carry on commercial banking activities like acceptance of deposits, loans on securities, gold and other goods, working as agents on behalf of their clients, etc. Further, they also act as balancing Centres making available temporary excess funds of one primary society to another which are in need of them. In fact, these banks normally focus on providing short and medium term financial requirements to agriculturists, artisans and others. Land development banks meet long-term and medium term funds requirement of agriculturists to purchase agricultural machinery and implements, affecting permanent improvement in land, liquidating old debts etc. Further, in this regard, regional rural 29
7 Markets and Services banks are also providing credit and other facilities specially to the small and marginal farmers, agricultural labourers, artisans and small entrepreneurs in rural areas Non-Banking Financial Institutions Apart from some banking concerns described above, a lot of capital market activities are performed by the other financial institutions which are of non-banking nature. They actively participate in capital transformation process from savers to investors in an economy. They collect funds by accepting deposits from individuals and others and lend them to trade, industries, government, etc. They buy and sell instruments and also create new instruments as per different needs of the savers. The various forms of non-banking Financial Institutions and their role in Financial Markets are described hereunder: Investment Banks Investment banking institution may be defined as financial intermediary which is responsible for garnering the savings of thrifty people and directing these funds into the business enterprise. The basic functions of these investment banks are: long term financing of business undertakings marketing of shares and debentures acting as security middlemen advising in marketing of an issue acting as an insurer instead of outright purchase of security etc. Investment banks are very much popular in developed countries specifically in USA. The functions of investment bankers in USA, are classified into two broad groups: (1) Functions relating to formation of new capital; (2) Functions subordinate to capital formation. The function concerning formation of a new capital is related with the participation in formation of new capital for both new as well as old undertakings. It includes all such activities like originating, under-writing, purchase and sale of securities, etc., in the first category whereas in the second category, it comprises of working as broker or dealer, offering security, counselling, advising, security substitutions and other allied services. In brief, these institutions play a significant role by providing the necessary capital for the long term needs of business world. That is why, these are also known as the entrepreneurs of entrepreneurs. Some of these functions have been taken over by merchant banks in India. 30 Merchant Banks Merchant banking activities were firstly developed in early nineteenth centuries in the U.K. when trade between countries was financed by bills of exchange drawn on the principal merchant houses. Recently, it has attracted the attention of all financial and consultancy firms. Merchant banks, in essence, are financial institutions providing specific services like acceptance of bills of exchange, corporate issue management, portfolio management services, project counselling and financing, corporate restructuring, etc. Needless to say that the scope of merchant banking activities is too vast and there would be more and more challenges ahead. Basically merchant banking activity is an institutional arrangement providing financial advisory and intermediary services to the corporate sector. One merchant banker may specialise in one activity only, simultaneously he may take up other supportive or complimentary activity. In fact, there is a wide range of financial activities which come under the purview of merchant banking, a few among these are narrated below:
8 i) Corporate Counselling: The major function of a merchant banker is to advise the corporate sector units on various matters like in locating area/activities of growth and diversification, appraising product lines and future trends, rejuvenating old company and ailing sick units by appraising their technology, process, etc. Financial Markets and Institutions ii) Project Counselling: Project counselling is another important merchant banking activity which includes preparation of economic, technical, financial and feasibility reports. Further, it also covers project viability and procedural steps for its implementation. Besides these, project counselling may include identification of potential investment avenues and pattern of financing. iii) Capital Restructuring: The basic objective of capital restructuring is to advise the management of the unit in designing its capital structure in such a way that it could achieve maximum potential out of its financial resources. This may include redesign of debt-equity ratio, reserve and surplus, capitalisation of reserve, asset structure ratio, debt servicing with overall impact on funds generating capacity of corporate unit. iv) Issue Management: The basic objective of issue management activity is to make all arrangements for mobilising resources from the capital market for its client by issuing securities like equity shares, preference shares, debentures, etc. This includes taking consent/approval of the Government Agencies, drafting of prospectus, selection of brokers, under-writers, bankers, registrar, advertising agency, etc. v) Portfolio Management: Merchant bankers render expert advice on matters pertaining to portfolio management of their clients. They advise which securities should be purchased or sold and assist in designing optimum portfolio within the purview of risk, return and tax bracket of the investors, vi) Credit syndication: The merchant bankers make arrangement of credit procurement and project finance for their client units. In this regards, they contact with banks and other financial institutions both in India and abroad for raising rupee and foreign currency loans. Sometimes, they also arrange bridge finance and other funds for cost escalations or cost over-runs. vii) Corporate restructuring: External restructuring for the overall better performance of corporate units is another important service rendered by the merchant banks. In this regard, merger, acquisition, amalgamation, takeover; alliances, reconstruction etc. are various possibilities, which can be explored among the interested units. The merchant banks assist in such negotiation and also guides in legal documentations, official approval, tax matters, etc. of the proposed merged unit. viii) Working capital finance: The merchant banks assist in arranging working capital finance for their clients. They advice the possible sources from where the working capital finance can be arranged, Further, sometimes, they also manage to enhance cash credit facilities for their clients. ix) Credit Bills Discounting: This is one of the major service which is rendered by the merchant banks specially in developed countries like U.S.A., U.K. etc. They make arrangement for providing bills discounting facilities for their clients after contacting the acceptance houses and discount houses. In this regard, reputation and creditability of the merchant bankers also play a significant role in this arrangement. Merchant banking in India is also gaining popularity. Various public financial institutions, commercial banks and their subsidiaries, foreign banks, state financial corporations, state industrial developmental corporations, private non-banking finance companies, etc. are engaged in at a large scale in this service. 31
9 Markets and Services 32 Investment Companies Investment companies are such institutions which collect the funds from the people (generally house-hold savers) through a specific financial instrument, i.e. unit, share, debenture, etc. and then invest these pooled funds in the suitable securities depending upon the objective of that scheme. In general, the basic objective of such investment companies is to get enhanced benefits of large and pooled resources through low risk and expertise. Investment management in these days has become a complicated and risky task. A lot of information and adequate knowledge are required for successful investment of funds. Further, these incur a huge cost for collecting information and hiring experts of this field. All this is not possible in case of small investors who has limited resources, inadequate knowledge and limited information. As a result, the establishment of investment trust or companies can be useful in this regard. The major investment type companies include investment trusts, mutual funds, common trust funds of commercial banks, management investment companies, unit trusts, etc. The mutual funds have had a mushroom growth in Indian investment market. These investment companies can be classified into two categories: a) Management Investment Companies b) Unit Trusts. a) Management Investment Companies: These companies are also known as Discretionary trusts or mutual funds. The managements of these trusts enjoy wide discretionary powers relating to selection of various securities for designing of their investment portfolio. In other words, the investment pattern of such trust will not be fixed but be rather flexible depending upon development of the market. These companies can further be divided into two categories; close ended and open ended. In the first category, the capitalisation of the company is fixed and not changed before a particular period. In other words, share holders cannot get back their investment from these companies before a particular period. Whereas in the case of open ended companies, the investors can sell and buy their shares from the company, and hence, no limit to capitalisation. In other words, such companies make a continuous offering of new shares at prices near to their net asset value and shares are redeemable at net asset value on short notice. b) Unit Trust : This is a specific type of investment company which is normally established under a particular Act. The funds are raised from the large number of investors through selling of units, and the persons to whom the units are sold are called the unit holders. The holders of these units are the owners of the trust who have a real interest in securities, which constitute the trust fund. A certificate of units is issued to each unit holder which represent their holdings in the trust s property. Normally, a unit trust is established as an open-end investment company. Unit Trust of India is an example for this. In brief, investment companies are important participants in the capital markets. They mobilise funds from a large number of investors and channelise the same for productive purpose through financial markets.. Insurance Companies Insurance companies have emerged as prominent participants in the capital markets because of the availability of huge funds at their disposal for investment purpose. These companies can be classified into various categories such as Life insurance companies, general insurance companies, marine insurance companies which cover risk arising from fire, accidents, natural calamities for human lives, vehicles, houses, durable goods, fixed assets, etc. Among these life insurance companies are dominant due to their large size and protection from state.
10 Life insurance companies perform two major functions; firstly, protection of policy holders against loss due to pre-mature death and secondly investment of funds in various financial instruments. The major source of funds of these companies is premium received from the policy holders. Being the custodians of policy holder s savings, the responsibility of these companies to the public is very high. Hence the investment policy is usually different from that of other institutions. The major portion of the fund is normally invested in Government and Semi-Government securities, fixed income securities of public sector units and other corporate sector units. For example, in India, Life Insurance Corporation of India has been allowed to invest not less than 50 per cent of its total investible funds in marketable securities of Central Government, State Government and guaranteed by the Central Government. Financial Markets and Institutions Apart from life insurance companies, general companies which are in insurance business of fire, marine and others also have huge investible funds to employ in the business sector. For example, General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC) is participating, actively in the capital market. In brief, insurance companies recently have become an important constituent of capital markets all over the world. Development Banks Development banks which came into existence after the second world war are now most active participant in the capital markets all over the world. Their main objective is to hasten the pace of industrialisation by supplying basic ingredients of development like finance, knowledge and entrepreneurship skills. So a development bank is a hybrid institution which combines in itself the objectives of finance corporation as well as of development corporation. Development banks, also known as financial institutions, are primarily engaged in providing long term financial assistance to the industrial units, usually of all categories. The financial assistance is provided in various forms like extending term loans, subscription to shares and debentures, underwriting capital issues, guarantee of term loans, guarantee in respect of deferred payments by importers, etc. In India, some major development banks are : Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), State Financial Corporations (SFCs), State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDCs), Industrial Reconstruction Bank of India (IRBI). IDBI and ICICI which were orginally started as developmental banks got converted themselves into universal banks in order to face the challenges in the liberalised environment. Pension Funds Pension funds and retirement plans of all types have become important investors and participants in the capital markets recently. These constitute huge investible funds which needs judicious selection of investment outlets as per the requirement of particular fund or plan. In developed countries, private pension plans or corporate pension funds have become major constituent of the capital market largely in the second half of the twentieth century. In a pension plan, pension holders are provided with a fixed amount in particular currency each month, often calculated as a multiple of the number of years worked in that organisation. Sometimes, the terms and conditions of plan agreements may differ, however, mostly pension payments are fixed for a period of time. Because contributions are usually made by the employers, so they should select such investment outlets which could provide them high rate of return, and at the same time are not very risky. It has been observed that assets in pension funds grow over long period because most of the employees who come under a plan are a number of years from retirement. So, for longer period, contributions made by those who are employed exceed the payments of those who have retired. Therefore, adequate precautions should be taken while selecting investment avenues for such funds. 33
11 Markets and Services Finance Companies Another important participant in the capital market is private sector finance companies. These companies collect funds from the people through shares, debentures, fixed deposits and short term loans from banks and other corporate units. Sometimes, a huge fund is also raised through inter-corporate deposits. In some cases, it is noticed that they raise fund at a very high rate of interest. So, these companies have a quite different liability and capital structure from that of other public financial institutions. Relatively they have large proportion of equity capital. It has been further observed that in these companies, a large part of outstanding liabilities is unsecured. Most of the finance companies go for financing of consumer durable goods, automobiles, furniture, etc; normally on instalment basis. Besides, they also provide short term business credit to the business firms and professionals. Thus, these finance companies have to compete with commercial banks and other financial institutions which provide such loans. Undoubtedly, their rate of interest on the loan is very high in comparison to the bankers, but still consumers prefer to go to these units due to easy availability and less formalities. In brief, finance companies play a significant role in capital market fulfilling financial needs of specific section of the society. Further, they borrow in both money market and capital market, so they create a link between these markets and relationship between long term and short term interest rates. Unfortunately, the performance of these companies, recently in India, is not found satisfactory. Activity 2 a) List the participants in a Capital Market b) Distinguish between an: i) Investment Company and Finance Company. ii) Investment Bank and Merchant Bank. iii) Investment Bank and Commercial Bank.
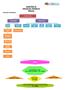
12 2.4 SUMMARY Financial Markets and Institutions Financial markets facilitate trading in financial assets. These assets are also referred to as financial instruments or securities. Since financial assets are not consumed, what is bought and sold is their use for a particular period of time. There are many agencies which are participating in the financial market operations and are facilitating the process of transfer of funds from surplus units to deficit units. Financial Markets can be classified as money markets and capital markets. In this unit, Participants in each of these segments of the financial market are discussed separately. The major participants in the money market segment are; the Central Bank, the Commercial Banks, indigenous Financial Agencies, Discount Houses and Acceptance Houses. The major players in the Capital Market are; the Banking Institutions and the non- Banking Institutions. Figure. 2.1 gives bird s eyeview of the various participants in Financial Markets. Participants in Financial Markets Money Market Prticipants Capital Market Participants Central Commercial Indegenous Discount Acceptance Banking Non-Banking Bank Bank Financial Houses Houses Institution Financial Institutions Agencies Commercial Coop- Regional Land Foreign Bank erative Rural Develop- Banks Banks Banks Ment Banks Investment Merchant Investment Develop- Insurance Pension Finance Banks Banks Companies ment Companies Funds Companies Banks Figure 2.1: Participants in the Financial Markets 2.5 SELF ASSESSMENT QUESTIONS 1) Explain the term Money Market and who are the different participants in a money market? 2) Explain the term Capital Market. Who are the various participants in capital market. 3) What are the various non-banking finance institutions that are involved in the Capital Market operations. 4) Describe the role of the Central Bank in Financial market operations. 5) Enumerate the various financial activities that are undertaken by a merchant banker. 35
13 Markets and Services 2.6 FURTHER READINGS Avadhani V.A., 1997, Capital Market Management, Himalaya Publishing House, Bombay. Bhole L.M., 1992, Financial Institutions and Markets, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd., New Delhi. Dougall E. Herbert and Gaumnitz. E. Jack. 1980, Capital Market and Institutions, Prentice Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey. Hennings N. Charles, Pigott William & Scott Haney Robert, 1975, Financial Markets and the Economy, Prentice Hall, Inc. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey. Kohn Meir, 1996, Financial Institutions and Markets, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Company Ltd., New Delhi. Krishan Bal & Narta S.S., Security Markets in India, Kanishka Publishers Distributors, New Delhi. Shekhar K.C., 1992, Banking Theory and Practice, Vikas Publishing House Private Ltd. New Delhi. 36
ANSWER KEY C F.Y.B. Com. (FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT) (CHOICE BASE) SEMESTER - I / C Indian Financial System
 ANSWER KEY-00135 C0921 - F.Y.B. Com. (FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT) (CHOICE BASE) SEMESTER - I / C0584 - Indian Financial System Q1) a) Answer whether the below statements are True or False: (Attempt any 8) (8
ANSWER KEY-00135 C0921 - F.Y.B. Com. (FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT) (CHOICE BASE) SEMESTER - I / C0584 - Indian Financial System Q1) a) Answer whether the below statements are True or False: (Attempt any 8) (8
COMMERCIAL BANKING INTRODUCTION
 1 COMMERCIAL BANKING INTRODUCTION Banking occupies one of the most important positions in the modern economic world. It is necessary for trade and industry. Hence it is one of the great agencies of commerce.
1 COMMERCIAL BANKING INTRODUCTION Banking occupies one of the most important positions in the modern economic world. It is necessary for trade and industry. Hence it is one of the great agencies of commerce.
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
 CHAPTER - VIII CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS The main function of IDBI, as its name suggests, is to finance industrial enterprises such as manufacturing, mining, processing, shipping and other transport
CHAPTER - VIII CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS The main function of IDBI, as its name suggests, is to finance industrial enterprises such as manufacturing, mining, processing, shipping and other transport
In the previous lesson you learnt about the various methods of raising long-term
 16 SOURCES OF LONG-TERM FINANCE In the previous lesson you learnt about the various methods of raising long-term finance. Normally the methods of raising finance are also termed as the sources of finance.
16 SOURCES OF LONG-TERM FINANCE In the previous lesson you learnt about the various methods of raising long-term finance. Normally the methods of raising finance are also termed as the sources of finance.
The nature of function of a central bank differs in a developed economy as compared to those in a developing economy.
 Chapter# Central Bank & Commercial Banks Meaning of Central Bank In every country there is one bank which acts as the leader of the money market, supervising, controlling and regulating the activities
Chapter# Central Bank & Commercial Banks Meaning of Central Bank In every country there is one bank which acts as the leader of the money market, supervising, controlling and regulating the activities
IJMSS Vol.03 Issue-01, (January 2015) ISSN: Impact Factor
 Indian Financial System- Structure and Function Dr Ritu Chandna Associate Professor in Commerce Sant Mohan Singh Khalsa Labana Girls College Barara Introduction Financial System is a set of institutional
Indian Financial System- Structure and Function Dr Ritu Chandna Associate Professor in Commerce Sant Mohan Singh Khalsa Labana Girls College Barara Introduction Financial System is a set of institutional
In the words of Charles T Horngren, Capital budgeting is a long term planning for making and financing proposed capital outlays.
 Capital budgeting I) Meaning of Capital Budgeting: Capital budgeting can be defined as the planning, evaluation and selection of capital expenditure proposals. Capital budgeting is important for firms
Capital budgeting I) Meaning of Capital Budgeting: Capital budgeting can be defined as the planning, evaluation and selection of capital expenditure proposals. Capital budgeting is important for firms
MVSR ENGINEERING COLLEGE MBA DEPARTMNET. Concepts in Financial Services and Systems
 MVSR ENGINEERING COLLEGE MBA DEPARTMNET Concepts in Financial Services and Systems 1. Financial System: The Financial system is a broader term which brings under its fold the financial markets and the
MVSR ENGINEERING COLLEGE MBA DEPARTMNET Concepts in Financial Services and Systems 1. Financial System: The Financial system is a broader term which brings under its fold the financial markets and the
Section A (Short Answer Type Questions)
 B.Com. (Hons.) V Semester Paper Title: Paper Code: AS-2640 *(Prepared by Mr. Amit Manglani, Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce, GGV) Note: These model answers are a depiction of important points
B.Com. (Hons.) V Semester Paper Title: Paper Code: AS-2640 *(Prepared by Mr. Amit Manglani, Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce, GGV) Note: These model answers are a depiction of important points
DOMESTIC SAVING. National Accounts Statistics Sources & Methods, 2007 CHAPTER 24. quasi government bodies and nondepartmental
 DOMESTIC SAVING Introduction 24.1 Saving represents the excess of current income over current expenditure and is the balancing item of: the income and outlay accounts (as per 1968 SNA) and use of disposable
DOMESTIC SAVING Introduction 24.1 Saving represents the excess of current income over current expenditure and is the balancing item of: the income and outlay accounts (as per 1968 SNA) and use of disposable
CHAPTER 10 Financial Market
 CHAPTER 10 Financial Market A financial market refers to a market where the creation and exchange of financial assets (such as shares and debentures) takes place. Allocative Function of Financial Market
CHAPTER 10 Financial Market A financial market refers to a market where the creation and exchange of financial assets (such as shares and debentures) takes place. Allocative Function of Financial Market
Money and Banking, Commercial Banks. General Economics
 Money and Banking, Commercial Banks General Economics Money Money is an important and indispensable element of modern civilization. In ordinary usage, what we use to pay for things is called money. To
Money and Banking, Commercial Banks General Economics Money Money is an important and indispensable element of modern civilization. In ordinary usage, what we use to pay for things is called money. To
B Com/BBA/MBA/M.COM (Specialization - Finance) EASY NOTES4U Makes You Exams Easy
 FINANCIAL SERVICES B Com/BBA/MBA/M.COM (Specialization - Finance) EASY NOTES4U www.easynotes4u.com Makes You Exams Easy www.easynotes4u.com MODULE CONTENTS PAGE NO. 1 FINANCIAL SERVICES 5 2 MERCHANT BANKING
FINANCIAL SERVICES B Com/BBA/MBA/M.COM (Specialization - Finance) EASY NOTES4U www.easynotes4u.com Makes You Exams Easy www.easynotes4u.com MODULE CONTENTS PAGE NO. 1 FINANCIAL SERVICES 5 2 MERCHANT BANKING
UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS
 UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS Introduction : Financial Market is a market for creation and exchange of financial assets like share, bonds etc. It helps in mobilising savings and channelising them into the
UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS Introduction : Financial Market is a market for creation and exchange of financial assets like share, bonds etc. It helps in mobilising savings and channelising them into the
Development Financial Institutions
 CHAPTER 10 Development Financial Institutions LEARNING OBJECTIVES: After studying the chapter you should be able to understand: overview of development financial institutions in india Role of DFis in indian
CHAPTER 10 Development Financial Institutions LEARNING OBJECTIVES: After studying the chapter you should be able to understand: overview of development financial institutions in india Role of DFis in indian
CPW2A THEORY OF MONEY AND BANKING. Unit : I
 THEORY OF MONEY AND BANKING Unit : I Unit: I Introduction to money Kinds functions and significance Demand for and supply of Money Monetary standards Gold standard Bimetallism and paper currency systems
THEORY OF MONEY AND BANKING Unit : I Unit: I Introduction to money Kinds functions and significance Demand for and supply of Money Monetary standards Gold standard Bimetallism and paper currency systems
Financial Reporting for Financial Institutions
 CHAPTER 8 Financial Reporting for Financial Institutions BASIC CONCEPTS MUTUAL FUNDS In India, mutual funds are regulated by SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations, 1996. According to the SEBI (Mutual Funds)
CHAPTER 8 Financial Reporting for Financial Institutions BASIC CONCEPTS MUTUAL FUNDS In India, mutual funds are regulated by SEBI (Mutual Funds) Regulations, 1996. According to the SEBI (Mutual Funds)
Ch. 2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
 Ch. 2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM To "finance" something means to pay for it. Since money (or credit) is the means of payment, "financial" basically means "pertaining to money or credit." Financial
Ch. 2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM To "finance" something means to pay for it. Since money (or credit) is the means of payment, "financial" basically means "pertaining to money or credit." Financial
THE COMPANIES ACT, COMPANY LIMITED BY SHARES (Incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956) MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION
 THE COMPANIES ACT, 2013 COMPANY LIMITED BY SHARES (Incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956) MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION OF U.P. STOCK AND CAPITAL LIMITED I. The name of the company is U.P. STOCK AND CAPITAL
THE COMPANIES ACT, 2013 COMPANY LIMITED BY SHARES (Incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956) MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION OF U.P. STOCK AND CAPITAL LIMITED I. The name of the company is U.P. STOCK AND CAPITAL
An Evaluation of Investors Grievances and Redressal Mechanism in Indian Capital Market
 An Evaluation of Investors Grievances and Redressal Mechanism in Indian Capital Market 1 Ch. Balaji, 2 Dr. Praveen Kumar 1,2 Rayalaseema University, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India Abstract This paper explains
An Evaluation of Investors Grievances and Redressal Mechanism in Indian Capital Market 1 Ch. Balaji, 2 Dr. Praveen Kumar 1,2 Rayalaseema University, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India Abstract This paper explains
Meaning. In a broad sense the term Financial Services means Mobilising and allocating savings. It can also be called Financial Intermediation
 Financial Services Meaning Classification of Fin. Service Industry Scope of Financial Services Sources of Revenue Causes for Financial Innovation New Financial Products & Services Innovative Financial
Financial Services Meaning Classification of Fin. Service Industry Scope of Financial Services Sources of Revenue Causes for Financial Innovation New Financial Products & Services Innovative Financial
Sources of Business Finance
 Sources of Business Finance Multiple Choice Questions Tick ( ) the correct answer out of the given alternatives: Question 1. Equity shareholders are called: (a) Owners of the company (b) Partners of the
Sources of Business Finance Multiple Choice Questions Tick ( ) the correct answer out of the given alternatives: Question 1. Equity shareholders are called: (a) Owners of the company (b) Partners of the
CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks
 CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks Key Concepts in nutshell: CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL MARKET: It refers to the market which creates and exchanges financial assets. FUNCTIONS OF FINANICIAL
CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks Key Concepts in nutshell: CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL MARKET: It refers to the market which creates and exchanges financial assets. FUNCTIONS OF FINANICIAL
1 ANNA UNIVERSITY, CHENNAI REGULATION 2013 BA7022 MERCHANT BANKING AND FINANCIAL SERVICES PROF. I. ARUL EDISON ANTHONY RAJ,
 Page 1 QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWER KEY Page 1 TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWER KEY UNIT-I 1. What do you mean by financial system? A financial system or financial sector functions as an intermediary and facilitates
Page 1 QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWER KEY Page 1 TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWER KEY UNIT-I 1. What do you mean by financial system? A financial system or financial sector functions as an intermediary and facilitates
Financial Intermediaries in India. Samir K Mahajan
 Financial Intermediaries in India Financial Institutions are intermediaries that mobilizes saving and channelize the funds to the productive investment. These are responsible for efficient allocation and
Financial Intermediaries in India Financial Institutions are intermediaries that mobilizes saving and channelize the funds to the productive investment. These are responsible for efficient allocation and
RoleofPrimaryAgriculturalCoOperativeSocietyPacsinAgriculturalDevelopmentinIndia
 Global Journal of Management and Business Research: C Finance Volume 17 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2017 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA)
Global Journal of Management and Business Research: C Finance Volume 17 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2017 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA)
An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market. Manendra Singh*
 Article 222 KNOWLEDGE RESOURCE [Vol. 38 An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market Manendra Singh* The growth of financial sector in India at present is
Article 222 KNOWLEDGE RESOURCE [Vol. 38 An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market Manendra Singh* The growth of financial sector in India at present is
International Capital Market
 J B GUPTA CLASSES 98184931932, drjaibhagwan@gmail.com, www.jbguptaclasses.com Copyright: Dr JB Gupta 16 International Capital Market Global Depository Receipts American Depository Receipts External Commercial
J B GUPTA CLASSES 98184931932, drjaibhagwan@gmail.com, www.jbguptaclasses.com Copyright: Dr JB Gupta 16 International Capital Market Global Depository Receipts American Depository Receipts External Commercial
Paper 3.4: PROJECT FINANCING. Financial institutions of India Introduction Institutional framework Types of Assistance Project financing scheme IDBI
 Paper 3.4: PROJECT FINANCING UNIT 1 Financial institutions of India Introduction Institutional framework Types of Assistance Project financing scheme IDBI UNIT 2 Project Financing Estimating the Total
Paper 3.4: PROJECT FINANCING UNIT 1 Financial institutions of India Introduction Institutional framework Types of Assistance Project financing scheme IDBI UNIT 2 Project Financing Estimating the Total
BFF1001 Week 1 Topic 1: What is finance
 BFF1001 Week 1 Topic 1: What is finance Definitions Deficit A deficit unit saves less money than it invests A deficit unit needs funds If saving is less than investment, a deficit occurs Surplus A surplus
BFF1001 Week 1 Topic 1: What is finance Definitions Deficit A deficit unit saves less money than it invests A deficit unit needs funds If saving is less than investment, a deficit occurs Surplus A surplus
TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: BANKING AND FINANCE COURSE: BFN 121
 TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: BANKING AND FINANCE COURSE: BFN 121 i DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the undergraduate level. The materials
TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: BANKING AND FINANCE COURSE: BFN 121 i DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the undergraduate level. The materials
INDIAN BANKING SYSTEM (UNIT-4) REGIONAL RURAL BANKS IN INDIA (PART-1)
 INDIAN BANKING SYSTEM (UNIT-4) REGIONAL RURAL BANKS IN INDIA (PART-1) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers welcome to the lecture series on Indian Banking System. Today we shall take up unit 4 and we shall discuss
INDIAN BANKING SYSTEM (UNIT-4) REGIONAL RURAL BANKS IN INDIA (PART-1) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers welcome to the lecture series on Indian Banking System. Today we shall take up unit 4 and we shall discuss
1 SOURCES OF FINANCE
 1 SOURCES OF FINANCE 2 3 TRADE CREDIT Trade credit is a form of short-term finance. It has few costs and security is not required. Normally a supplier will allow business customers a period of time after
1 SOURCES OF FINANCE 2 3 TRADE CREDIT Trade credit is a form of short-term finance. It has few costs and security is not required. Normally a supplier will allow business customers a period of time after
(a) Bonus/capitalisation issues which represent only book keeping entries.
 What are the Chief Functions of the New Issue Market? The main function of the New Issue Market is to facilitate the transfer of resources from savers to users. Conceptually, however, the New Issue Market
What are the Chief Functions of the New Issue Market? The main function of the New Issue Market is to facilitate the transfer of resources from savers to users. Conceptually, however, the New Issue Market
Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101
![Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101 Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101](/thumbs/96/128932629.jpg) Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101 P. G. D. F. S. (Semester - I) Examination - 2010 FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 70 (1)
Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101 P. G. D. F. S. (Semester - I) Examination - 2010 FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 70 (1)
EOCNOMICS- MONEY AND CREDIT
 EOCNOMICS- MONEY AND CREDIT Banks circulate the money deposited by customers in the banks by lending it out to businesses at a rate of interest as a credit, which then acts as the income of the bank....
EOCNOMICS- MONEY AND CREDIT Banks circulate the money deposited by customers in the banks by lending it out to businesses at a rate of interest as a credit, which then acts as the income of the bank....
GOYAL BROTHERS PRAKASHAN
 Question Bank in Social Science (Economics) Class-X (Term-II) 3 MONEY AND CREDIT CONCEPT Money is anything which is commonly accepted as a medium of exchange and in discharge of debts. People exchange
Question Bank in Social Science (Economics) Class-X (Term-II) 3 MONEY AND CREDIT CONCEPT Money is anything which is commonly accepted as a medium of exchange and in discharge of debts. People exchange
Indirect Taxes Cooperative Banks / Housing. Milind V. Sahasrabudhe, M A Y & Co
 Indirect Taxes Cooperative Banks / Housing Milind V. Sahasrabudhe, M A Y & Co. 9821045049 milind@camay.net Co-operatives the key distinguishing factor. Co-operative is normally considered to be an entity
Indirect Taxes Cooperative Banks / Housing Milind V. Sahasrabudhe, M A Y & Co. 9821045049 milind@camay.net Co-operatives the key distinguishing factor. Co-operative is normally considered to be an entity
VISION PAYUMAGIC MULTISERVICES PRIVATE LIMITED
 THE COMPANIES ACT 1956 COMPANY LIMITED BY SHARES MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION OF VISION PAYUMAGIC MULTISERVICES PRIVATE LIMITED I The name of the Company is VISION PAYUMAGIC MULTISERVICES PRIVATE LIMITED
THE COMPANIES ACT 1956 COMPANY LIMITED BY SHARES MEMORANDUM OF ASSOCIATION OF VISION PAYUMAGIC MULTISERVICES PRIVATE LIMITED I The name of the Company is VISION PAYUMAGIC MULTISERVICES PRIVATE LIMITED
Full file at CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE
 CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS: 1. The saving-investment cycle consists of net savers (surplus spending units) transferring funds to net investors (deficit
CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS: 1. The saving-investment cycle consists of net savers (surplus spending units) transferring funds to net investors (deficit
CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE
 CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS: 1. a. A multinational corporation is a firm that has investments in manufacturing and/or distribution facilities in
CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS: 1. a. A multinational corporation is a firm that has investments in manufacturing and/or distribution facilities in
Notes from Business Environment SIGNIFICANCE OF BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT
 UNIT-1 Notes from Business Environment SIGNIFICANCE OF BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT The survival and success of any enterprise depends upon its inherent capabilities (Physical, financial, human and other resources)
UNIT-1 Notes from Business Environment SIGNIFICANCE OF BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT The survival and success of any enterprise depends upon its inherent capabilities (Physical, financial, human and other resources)
IMPACT OF NON-BANKING FINANCIAL COMPANIES (NBFCS) IN INDIAN ECONOMY GROWTH
 EPRA International Journal of Economic and Business Review Inno Space (SJIF) Impact Factor : 5.509(Morocco) e-issn : 2347-9671, p- ISSN : 2349-0187 Vol - 4, Issue- 3, March 2016 ISI Impact Factor : 1.259
EPRA International Journal of Economic and Business Review Inno Space (SJIF) Impact Factor : 5.509(Morocco) e-issn : 2347-9671, p- ISSN : 2349-0187 Vol - 4, Issue- 3, March 2016 ISI Impact Factor : 1.259
P.G.D.C.M.M. Examination, : MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES (New) (2008 Pattern)
 *3991101* [3991] 101 101 : MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES (New) (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 70 Instructions : a) Attempt any five questions. b) Each question carry equal marks. 1. Describe
*3991101* [3991] 101 101 : MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES AND PRACTICES (New) (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 70 Instructions : a) Attempt any five questions. b) Each question carry equal marks. 1. Describe
Study Material FREE MASTER CLASS SERIES. Downloaded from Vedantu. About Vedantu. Awesome Master Teachers. 95% Top Results. 3,13,100+ Happy Students
 Downloaded from Vedantu Study Material About Vedantu FREE LIVE ONLINE MASTER CLASSES FREE Webinars by Expert Teachers Vedantu is India s largest LIVE online teaching platform with best teachers from across
Downloaded from Vedantu Study Material About Vedantu FREE LIVE ONLINE MASTER CLASSES FREE Webinars by Expert Teachers Vedantu is India s largest LIVE online teaching platform with best teachers from across
MONEY AND CREDIT VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [1 MARK]
![MONEY AND CREDIT VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [1 MARK] MONEY AND CREDIT VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [1 MARK]](/thumbs/76/74334829.jpg) MONEY AND CREDIT VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [1 MARK] 1. What is collateral? Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, deposits with the banks and uses
MONEY AND CREDIT VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [1 MARK] 1. What is collateral? Collateral is an asset that the borrower owns such as land, building, vehicle, livestock, deposits with the banks and uses
Financial Framework in India
 Financial Framework in India For Finance related courses and CSE Main Optional Paper on Finance 10x10 Learning TM 1 10x10 Learning TM 2 Laws applicable to the Financial Sector : Act = 15. Rules = 10. Regulations
Financial Framework in India For Finance related courses and CSE Main Optional Paper on Finance 10x10 Learning TM 1 10x10 Learning TM 2 Laws applicable to the Financial Sector : Act = 15. Rules = 10. Regulations
CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE
 CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS: 1. The saving-investment cycle consists of net savers (surplus spending units) transferring funds to net investors (deficit
CHAPTER 2 THE DOMESTIC AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MARKETPLACE ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS: 1. The saving-investment cycle consists of net savers (surplus spending units) transferring funds to net investors (deficit
 7 FORMATION OF JOINT STOCK COMPANY You have learnt that formation of a sole proprietorship organisation or a partnership firm does not involve much formalities so much so that even the registration is
7 FORMATION OF JOINT STOCK COMPANY You have learnt that formation of a sole proprietorship organisation or a partnership firm does not involve much formalities so much so that even the registration is
ICSE Board Class X - Economics Board Paper 2018 Solution
 ICSE Board Class X - Economics SECTION A Answer 1 a) The division of labour is an advantage to the producer because it increases the efficiency of labour. This leads to an increase in the quantity of output
ICSE Board Class X - Economics SECTION A Answer 1 a) The division of labour is an advantage to the producer because it increases the efficiency of labour. This leads to an increase in the quantity of output
Polk County Wisconsin. Policy 913 Effective Date: Revision Date: , ,
 Polk County Wisconsin INVESTMENT POLICY Policy 913 Effective Date: 06-19-2000 Revision Date: 5-20-2003, 7-18-2006, 01-16-07 POLK COUNTY INVESTMENT POLICY 1.0 Policy: The County Board Chairperson, Polk
Polk County Wisconsin INVESTMENT POLICY Policy 913 Effective Date: 06-19-2000 Revision Date: 5-20-2003, 7-18-2006, 01-16-07 POLK COUNTY INVESTMENT POLICY 1.0 Policy: The County Board Chairperson, Polk
The financial corporations sector and its subsectors
 The financial corporations sector and its subsectors IFC Workshop on Developing and Improving Sectoral Financial Accounts 20-21 January 2016 Algiers, Algeria United Nations Statistics Division Outline
The financial corporations sector and its subsectors IFC Workshop on Developing and Improving Sectoral Financial Accounts 20-21 January 2016 Algiers, Algeria United Nations Statistics Division Outline
Products and Services
 Products and Services Everyday Banking Citigold Private Client Centres The Citigold Private Client Centre is an exclusive, cultured and professional environment presenting our valued clients with personalised
Products and Services Everyday Banking Citigold Private Client Centres The Citigold Private Client Centre is an exclusive, cultured and professional environment presenting our valued clients with personalised
MMS MBA Semester IV Examination, M (Printed Pages 3) Entrepreneurship & Project Management. Note : Answer all the questions.
 M (Printed Pages 3) Roll No. MMS-0401 MBA Semester IV Examination, 2017 Entrepreneurship & Project Management Time Allowed : Three Hours ] [ Maximum Marks : 70 Note : Answer all the questions. 1. Attempt
M (Printed Pages 3) Roll No. MMS-0401 MBA Semester IV Examination, 2017 Entrepreneurship & Project Management Time Allowed : Three Hours ] [ Maximum Marks : 70 Note : Answer all the questions. 1. Attempt
Financial Management Questions
 Financial Management Questions Question 1. What Is The Financial Management Reform? The Financial Management Reform is the new policy framework that had been adopted by the Fiji Government to improve performance
Financial Management Questions Question 1. What Is The Financial Management Reform? The Financial Management Reform is the new policy framework that had been adopted by the Fiji Government to improve performance
BANK EXAMS GENERAL AWARENESS Kinds of Banks in India
 BANK EXAMS GENERAL AWARENESS Kinds of s in India The Financial Requirements in a modern economy are of a diverse nature, distinctive variety and large magnitude. These banks satisfy the various needs of
BANK EXAMS GENERAL AWARENESS Kinds of s in India The Financial Requirements in a modern economy are of a diverse nature, distinctive variety and large magnitude. These banks satisfy the various needs of
Annexure - XV (Paragraph ) Suggested format of Balance Sheet of UCBs
 Annexure - XV (Paragraph - 8.33) Suggested format of Balance Sheet of UCBs Balance Sheet of (here enter name of the bank) as on 31st March (Year). Capital and Liabilities Schedule Capital 1 Reserve and
Annexure - XV (Paragraph - 8.33) Suggested format of Balance Sheet of UCBs Balance Sheet of (here enter name of the bank) as on 31st March (Year). Capital and Liabilities Schedule Capital 1 Reserve and
Chapter 2 The Domestic and International Financial Marketplace
 Download Solution Manual for Contemporary Financial Management 13th Edition by Moyer Link full: https://testbankservice.com/download/solutionmanual-for-contemporary-financial-management-13th-editionby-moyer/
Download Solution Manual for Contemporary Financial Management 13th Edition by Moyer Link full: https://testbankservice.com/download/solutionmanual-for-contemporary-financial-management-13th-editionby-moyer/
Basic Accounting Terms. Samir K Mahajan
 Basic Accounting Terms Business Entity A business entity is a commercial (corporate or other) organisation that is formed in order to engage in business activities, usually for the sale of a product or
Basic Accounting Terms Business Entity A business entity is a commercial (corporate or other) organisation that is formed in order to engage in business activities, usually for the sale of a product or
CHAPTER 8 SPECIALIST DEBT SECURITIES
 CHAPTER 8 SPECIALIST DEBT SECURITIES Contents This chapter sets out the conditions for listing and the information which is required to be included in the listing document for specialist debt securities
CHAPTER 8 SPECIALIST DEBT SECURITIES Contents This chapter sets out the conditions for listing and the information which is required to be included in the listing document for specialist debt securities
FUNCTIONS AND STRUCTURE OF THE PLANNING COMMISSION ( IN BRIEF )
 FUNCTIONS AND STRUCTURE OF THE PLANNING COMMISSION ( IN BRIEF ) Planning Commission was set up in March, 1950. A copy of the Resolution of Government of India has been given in Unit I of this document.
FUNCTIONS AND STRUCTURE OF THE PLANNING COMMISSION ( IN BRIEF ) Planning Commission was set up in March, 1950. A copy of the Resolution of Government of India has been given in Unit I of this document.
Function of Financial Markets
 Chapter 2 An Overview of the Financial System Function of Financial Markets Perform the essential function of channeling funds from economic players (households, firms and govt.) that have saved surplus
Chapter 2 An Overview of the Financial System Function of Financial Markets Perform the essential function of channeling funds from economic players (households, firms and govt.) that have saved surplus
Muthoot Finance Limited Public Issue Of Secured Redeemable & Unsecured Redeemable Non-Convertible Debentures
 Note: Edelweiss Broking Ltd. is a Lead Broker to the issue; accordingly, this note is prepared based on the Prospectus for informative purpose only. Issue Highlights Muthoot Finance Limited Public Issue
Note: Edelweiss Broking Ltd. is a Lead Broker to the issue; accordingly, this note is prepared based on the Prospectus for informative purpose only. Issue Highlights Muthoot Finance Limited Public Issue
PUBLIC ISSUE OF SECURED AND UNSECURED NON-CONVERTIBLE DEBENTURES OF MUTHOOT FINANCE LIMITED of face value Rs. 1,000 upto ` 5,000 million
 PUBLIC ISSUE OF SECURED AND UNSECURED NON-CONVERTIBLE DEBENTURES OF MUTHOOT FINANCE LIMITED of face value Rs. 1,000 upto ` 5,000 million Issue Opening December 11, 2015 Issue Closing January 11, 2015*
PUBLIC ISSUE OF SECURED AND UNSECURED NON-CONVERTIBLE DEBENTURES OF MUTHOOT FINANCE LIMITED of face value Rs. 1,000 upto ` 5,000 million Issue Opening December 11, 2015 Issue Closing January 11, 2015*
Week 1 Surplus economic units: Individuals, households, companies with more funds than required for immediate expenditure Saver Potential lenders
 Week 1 Surplus economic units: Individuals, households, companies with more funds than required for immediate expenditure Saver Potential lenders Deficit economic units Individuals, households, companies
Week 1 Surplus economic units: Individuals, households, companies with more funds than required for immediate expenditure Saver Potential lenders Deficit economic units Individuals, households, companies
Chapter - I Introduction
 Chapter - I Introduction 1.1 The Background The most important thing for people is the protection of their lives and their assets. Whenever one thinks about the security of his assets, the thought of general
Chapter - I Introduction 1.1 The Background The most important thing for people is the protection of their lives and their assets. Whenever one thinks about the security of his assets, the thought of general
Other U.S. Financial Institutions
 In addition to the commercial banking institutions, the following are also part of the United States financial system (Rose, 2008): Representative Offices Representative offices of U.S. commercial banks
In addition to the commercial banking institutions, the following are also part of the United States financial system (Rose, 2008): Representative Offices Representative offices of U.S. commercial banks
MERCHANT BANKING OBJECTIVES
 MERCHANT BANKING OBJECTIVES : Objective of this lesson is to get an idea regarding merchant banking STRUCTURE : 1.1.1 Introduction 1.1.2 Definition 1.1.3 Origin 1.1.4 Merchant Banking in India 1.1.5 Merchant
MERCHANT BANKING OBJECTIVES : Objective of this lesson is to get an idea regarding merchant banking STRUCTURE : 1.1.1 Introduction 1.1.2 Definition 1.1.3 Origin 1.1.4 Merchant Banking in India 1.1.5 Merchant
NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES
 National Income and Related Aggregates MODULE - 9 National Income Accounting 24 NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The main objective of an economy is to provide goods and services for the satisfaction
National Income and Related Aggregates MODULE - 9 National Income Accounting 24 NATIONAL INCOME AND RELATED AGGREGATES The main objective of an economy is to provide goods and services for the satisfaction
Dr. P.Velusamy Assistant Professor, Department of co operation, Sri Ramakrishna mission Vidyalaya College of arts and science, Coimbatore.
 ATTAINING THE MARKET THROUGH INNOVATIVE STRATEGIES A CASE STUDY ON KARIAMPALAYAM PRIMARY AGRICULTURAL COOPERATIVE SOCIETY-COIMBATORE DISTRICT-TAMILNADU Dr. P.Velusamy Assistant Professor, Department of
ATTAINING THE MARKET THROUGH INNOVATIVE STRATEGIES A CASE STUDY ON KARIAMPALAYAM PRIMARY AGRICULTURAL COOPERATIVE SOCIETY-COIMBATORE DISTRICT-TAMILNADU Dr. P.Velusamy Assistant Professor, Department of
PERFORMANCE OF LEAD BANK SCHEME IN VIRUDHUNAGAR DISTRICT OF TAMILNADU
 PERFORMANCE OF LEAD BANK SCHEME IN VIRUDHUNAGAR DISTRICT OF TAMILNADU A.Surendran 1 and Dr. B.Manoharan 2 1 Assistant Professor in Commerce, Rajapalayam Rajus College, Rajapalayam Email: surendran.ayyan@gmail.com
PERFORMANCE OF LEAD BANK SCHEME IN VIRUDHUNAGAR DISTRICT OF TAMILNADU A.Surendran 1 and Dr. B.Manoharan 2 1 Assistant Professor in Commerce, Rajapalayam Rajus College, Rajapalayam Email: surendran.ayyan@gmail.com
Money and Banking Prof. Dr. Surajit Sinha Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur.
 Money and Banking Prof. Dr. Surajit Sinha Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 39 What I am going to start today is the cooperative banks its amazing
Money and Banking Prof. Dr. Surajit Sinha Department of Humanities and Social Sciences Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 39 What I am going to start today is the cooperative banks its amazing
The Financial Sector Functions of money Medium of exchange Measure of value Store of value Method of deferred payment
 The Financial Sector Functions of money Medium of exchange - avoids the double coincidence of wants Measure of value - measures the relative values of different goods and services Store of value - kept
The Financial Sector Functions of money Medium of exchange - avoids the double coincidence of wants Measure of value - measures the relative values of different goods and services Store of value - kept
THIS CHAPTER COMPRISES OF. Working knowledge of : AS 1, AS2, AS 3, AS 6, AS 7, AS 9, AS 10, AS 13, AS 14.
 Star Rating On the basis of Maximum marks from a chapter On the basis of Questions included every year from a chapter On the basis of Compulsory questions from a chapter CHAPTER 1 Accounting Standards
Star Rating On the basis of Maximum marks from a chapter On the basis of Questions included every year from a chapter On the basis of Compulsory questions from a chapter CHAPTER 1 Accounting Standards
SYLLABUS B.B.A. V SEM. Subject Indian Financial Systems
 SYLLABUS B.B.A. V SEM Subject Indian Financial Systems UNIT I CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL SYSTEM; Formal and informal financial systems, Functions of financial system, Nature and Role of financial institutions
SYLLABUS B.B.A. V SEM Subject Indian Financial Systems UNIT I CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL SYSTEM; Formal and informal financial systems, Functions of financial system, Nature and Role of financial institutions
BANK DEPOSITS & DEPOSIT MANAGEMENT
 BANK DEPOSITS & DEPOSIT MANAGEMENT Samir K Mahajan Bank Deposits Banks accepts deposits from the public. Banks deposits are classified by type of customers, the tenure and its cost to the bank. Based on
BANK DEPOSITS & DEPOSIT MANAGEMENT Samir K Mahajan Bank Deposits Banks accepts deposits from the public. Banks deposits are classified by type of customers, the tenure and its cost to the bank. Based on
Seat No. Total No. of Questions : 6] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [4185]-101
![Seat No. Total No. of Questions : 6] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [4185]-101 Seat No. Total No. of Questions : 6] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [4185]-101](/thumbs/95/124619348.jpg) Total of Questions : 6] [Total of Printed Pages : 2 [4185]-101 P. G. D. F. S. (Semester - I) Examination - 2012 FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 70 (1) Answer
Total of Questions : 6] [Total of Printed Pages : 2 [4185]-101 P. G. D. F. S. (Semester - I) Examination - 2012 FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 70 (1) Answer
Conflicts of Interest Disclosure
 Conflicts of Interest Disclosure April 2017 An investment in the Company or a Fund is subject to a number of actual or potential conflicts of interest. The description of conflicts of interests below,
Conflicts of Interest Disclosure April 2017 An investment in the Company or a Fund is subject to a number of actual or potential conflicts of interest. The description of conflicts of interests below,
13 Audit of Co-operative Societies
 13 Audit of Co-operative Societies Question 1 An auditor of a Co-operative Society governed by Cooperative Societies Act, 1912 is required to attach schedules giving certain information. Please list the
13 Audit of Co-operative Societies Question 1 An auditor of a Co-operative Society governed by Cooperative Societies Act, 1912 is required to attach schedules giving certain information. Please list the
REGIONAL RURAL BANKS The need for evolving a hybrid type of credit agency which combines the resource orientation of the commercial banks and the
 REGIONAL RURAL BANKS The need for evolving a hybrid type of credit agency which combines the resource orientation of the commercial banks and the rural orientation of the co-operatives has been expressed
REGIONAL RURAL BANKS The need for evolving a hybrid type of credit agency which combines the resource orientation of the commercial banks and the rural orientation of the co-operatives has been expressed
PRIORITY SECTOR LENDING - RRB
 PRIORITY SECTOR LENDING - RRB Priority Sector lending includes lending to those sectors that impact large sections of the population, the weaker sections and the sectors which are employment-intensive
PRIORITY SECTOR LENDING - RRB Priority Sector lending includes lending to those sectors that impact large sections of the population, the weaker sections and the sectors which are employment-intensive
CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD
 CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD PART I: ELIGIBILITY REQUIREMENTS Reference date 4. Unless otherwise provided in this Chapter, an issuer making an initial public offer of specified securities
CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD PART I: ELIGIBILITY REQUIREMENTS Reference date 4. Unless otherwise provided in this Chapter, an issuer making an initial public offer of specified securities
SECTION IIIB - INTERNATIONAL ISSUERS - DEBT SECURITIES
 LISTING REGULATIONS - INTERNATIONAL ISSUERS - DEBT SECURITIES Millennium Edition January 2002 THE BERMUDA STOCK EXCHANGE All rights reserved Bermuda Stock Exchange 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 4... 4 QUALIFICATIONS
LISTING REGULATIONS - INTERNATIONAL ISSUERS - DEBT SECURITIES Millennium Edition January 2002 THE BERMUDA STOCK EXCHANGE All rights reserved Bermuda Stock Exchange 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 4... 4 QUALIFICATIONS
Question 1. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 Question 1 PAPER 2 : STRATEGIC FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. Wherever appropriate, suitable assumption should be made by the candidates. (a) XY
Question 1 PAPER 2 : STRATEGIC FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. Wherever appropriate, suitable assumption should be made by the candidates. (a) XY
Topic 5 Sources of Finance. N5 Business Management
 Topic 5 Sources of Finance N5 Business Management 1 Learning Intentions / Success Criteria Learning Intentions Sources of finance Success Criteria By end of this topic you will be able to describe: sources
Topic 5 Sources of Finance N5 Business Management 1 Learning Intentions / Success Criteria Learning Intentions Sources of finance Success Criteria By end of this topic you will be able to describe: sources
Influencing Factors in Determining Credit Terms
 International Journal of Management, IT & Engineering Vol. 7 Issue 11, November 2017, ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International
International Journal of Management, IT & Engineering Vol. 7 Issue 11, November 2017, ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International
ISSUE STRUCTURE. Strategies
 PUBLIC ISSUE OF SECURED AND UNSECURED NON-CONVERTIBLE DEBENTURES OF MUTHOOT FINANCE LIMITED of face value Rs. 1,000 upto ` 4,000 million Issue Opening November 19, 2014 Issue Closing December 18, 2014*
PUBLIC ISSUE OF SECURED AND UNSECURED NON-CONVERTIBLE DEBENTURES OF MUTHOOT FINANCE LIMITED of face value Rs. 1,000 upto ` 4,000 million Issue Opening November 19, 2014 Issue Closing December 18, 2014*
6 Amalgamation. 1. Meaning of Amalgamation. Learning Objectives. After studying this chapter, you will be able to
 6 Amalgamation After studying this chapter, you will be able to Learning Objectives Understand the term Amalgamation and the methods of accounting for amalgamations. Appreciate the concept of transferee
6 Amalgamation After studying this chapter, you will be able to Learning Objectives Understand the term Amalgamation and the methods of accounting for amalgamations. Appreciate the concept of transferee
Bonanza Portfolio Ltd
 Public Issue of Tax Free Secured Redeemable Non-Convertible Bonds issued by HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS In exercise of the powers conferred by item (h) of sub-clause (iv) of clause (15) of Section 10 of
Public Issue of Tax Free Secured Redeemable Non-Convertible Bonds issued by HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS In exercise of the powers conferred by item (h) of sub-clause (iv) of clause (15) of Section 10 of
A Study of Investors Attitude towards Mutual Fund
 A Study of Investors Attitude towards Mutual Fund Mr. Erram Ramesh Asst.Professor, SR Engineering College, Ananthasagar, Warangal, Telangana District. ABSTRACT: The paper consists of mutual fund structure,
A Study of Investors Attitude towards Mutual Fund Mr. Erram Ramesh Asst.Professor, SR Engineering College, Ananthasagar, Warangal, Telangana District. ABSTRACT: The paper consists of mutual fund structure,
FINANCIAL ECONOMICS GENERAL COMMENTS. The following table shows the distribution of candidate by scores: Overall Performance of Candidates
 GENERAL COMMENTS FINANCIAL ECONOMICS The following table shows the distribution of candidate by scores: Overall Performance of Candidates Grade Marks No of Candidates % of Candidates Distinction 71 100
GENERAL COMMENTS FINANCIAL ECONOMICS The following table shows the distribution of candidate by scores: Overall Performance of Candidates Grade Marks No of Candidates % of Candidates Distinction 71 100
(i) A company with a cash flow problem that is having difficulty collecting its debts.
 Answer on question #41311 - Management - Other For each of the following situations, explain what the most suitable source of finance is: (i) A company with a cash flow problem that is having difficulty
Answer on question #41311 - Management - Other For each of the following situations, explain what the most suitable source of finance is: (i) A company with a cash flow problem that is having difficulty
SYLLABUS B.B.A. V SEM. Subject Indian Financial Systems
 SYLLABUS B.B.A. V SEM Subject Indian Financial Systems UNIT I CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL SYSTEM; Formal and informal financial systems, Functions of financial system, Nature and Role of financial institutions
SYLLABUS B.B.A. V SEM Subject Indian Financial Systems UNIT I CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL SYSTEM; Formal and informal financial systems, Functions of financial system, Nature and Role of financial institutions
GROWTH OF RESOURCE MOBILISATION BY INDIAN MUTUAL FUND INDUSTRY: AN EMPIRICALANALYSIS
 Volume 118 No. 18 2018, 4357-4371 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu GROWTH OF RESOURCE MOBILISATION BY INDIAN MUTUAL FUND INDUSTRY:
Volume 118 No. 18 2018, 4357-4371 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu GROWTH OF RESOURCE MOBILISATION BY INDIAN MUTUAL FUND INDUSTRY:
LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1. Learning outcomes
 LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1 Learning outcomes After studying this unit, you should be able to: Define foreign exchange Know foreign exchange markets functions of foreign exchange market methods affecting
LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1 Learning outcomes After studying this unit, you should be able to: Define foreign exchange Know foreign exchange markets functions of foreign exchange market methods affecting
Limited Companies Question: Explain the meaning of the following terms so as to make clear the differences between them: Ordinary Shares are
 Limited Companies Explain the meaning of the following terms so as to make clear the differences between them: Ordinary Shares are certificates of ownership to a company. They are issued to shareholders
Limited Companies Explain the meaning of the following terms so as to make clear the differences between them: Ordinary Shares are certificates of ownership to a company. They are issued to shareholders
1. Primary markets are markets in which users of funds raise cash by selling securities to funds' suppliers.
 Test Bank Financial Markets and Institutions 6th Edition Saunders Complete download Financial Markets and Institutions 6th Edition TEST BANK by Saunders, Cornett: https://testbankarea.com/download/financial-markets-institutions-6th-editiontest-bank-saunders-cornett/
Test Bank Financial Markets and Institutions 6th Edition Saunders Complete download Financial Markets and Institutions 6th Edition TEST BANK by Saunders, Cornett: https://testbankarea.com/download/financial-markets-institutions-6th-editiontest-bank-saunders-cornett/
"OFFSHORE FUNDING" THE OVERSEAS BANKER'S ROLE by W. P. Bonds Assistant Vice President, Wells Fargo Bank n.a.
 Offshore Funding -The Overseas Banker's Role 3 "OFFSHORE FUNDING" A Seminar sponsored by The Securities Institute of Australia, New South Wales Division, on September 7, 1978, in Sydney. The three papers
Offshore Funding -The Overseas Banker's Role 3 "OFFSHORE FUNDING" A Seminar sponsored by The Securities Institute of Australia, New South Wales Division, on September 7, 1978, in Sydney. The three papers
ROLE OF RRB IN RURAL DEVELOPMENT. G.K.Lavanya, Assistant Professor, St.Joseph scollege
 ROLE OF RRB IN RURAL DEVELOPMENT G.K.Lavanya, Assistant Professor, St.Joseph scollege ABSTRACT: The importance of the rural banking in the economic development of a country cannot be overlooked. The objective
ROLE OF RRB IN RURAL DEVELOPMENT G.K.Lavanya, Assistant Professor, St.Joseph scollege ABSTRACT: The importance of the rural banking in the economic development of a country cannot be overlooked. The objective
LISTINGS RULES OF THE NIGERIAN STOCK EXCHANGE CHAPTER [ ] LISTING OF DEPOSITARY RECEIPTS 1. Introduction
![LISTINGS RULES OF THE NIGERIAN STOCK EXCHANGE CHAPTER [ ] LISTING OF DEPOSITARY RECEIPTS 1. Introduction LISTINGS RULES OF THE NIGERIAN STOCK EXCHANGE CHAPTER [ ] LISTING OF DEPOSITARY RECEIPTS 1. Introduction](/thumbs/76/74209471.jpg) LISTINGS RULES OF THE NIGERIAN STOCK EXCHANGE CHAPTER [ ] LISTING OF DEPOSITARY RECEIPTS 1 Introduction This Chapter sets out The Exchange s requirements relating to Depositary Receipts (DRs). The aim
LISTINGS RULES OF THE NIGERIAN STOCK EXCHANGE CHAPTER [ ] LISTING OF DEPOSITARY RECEIPTS 1 Introduction This Chapter sets out The Exchange s requirements relating to Depositary Receipts (DRs). The aim
