Syllabus. Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2013
|
|
|
- Lindsay Short
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2013
2
3 Contents Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code Introduction Why choose Cambridge? 1.2 Why choose Cambridge A & AS Level Accounting? 1.3 Cambridge Advanced International Certificate of Education (AICE) 1.4 How can I find out more? 2. Assessment at a glance Syllabus aims and objectives Aims 3.2 Assessment objectives and their weighting in the exam papers 4. Curriculum content Core content: AS Level 4.2 Core content: A Level 5. Appendix Summary of commonly used ratios (AS and A Level) 5.2 Resource list 5.3 International standards terminology 6. Additional information Guided learning hours 6.2 Recommended prior learning 6.3 Progression 6.4 Component codes 6.5 Grading and reporting 6.6 Resources UCLES 2010
4 1. Introduction 1.1 Why choose Cambridge? University of Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) is the world s largest provider of international qualifications. Around 1.5 million students from 150 countries enter Cambridge examinations every year. What makes educators around the world choose Cambridge? Recognition A Cambridge International A or AS Level is recognised around the world by schools, universities and employers. The qualifications are accepted as proof of academic ability for entry to universities worldwide, though some courses do require specific subjects. Cambridge International A Levels typically take two years to complete and offer a flexible course of study that gives students the freedom to select subjects that are right for them. Cambridge International AS Levels often represent the first half of an A Level course but may also be taken as a freestanding qualification. They are accepted in all UK universities and carry half the weighting of an A Level. University course credit and advanced standing is often available for Cambridge International A/AS Levels in countries such as the USA and Canada. Learn more at Support CIE provides a world-class support service for teachers and exams officers. We offer a wide range of teacher materials to Centres, plus teacher training (online and face-to-face) and student support materials. Exams officers can trust in reliable, efficient administration of exams entry and excellent, personal support from CIE Customer Services. Learn more at Excellence in education Cambridge qualifications develop successful students. They build not only understanding and knowledge required for progression, but also learning and thinking skills that help students become independent learners and equip them for life. Not-for-profit, part of the University of Cambridge CIE is part of Cambridge Assessment, a not-for-profit organisation and part of the University of Cambridge. The needs of teachers and learners are at the core of what we do. CIE invests constantly in improving its qualifications and services. We draw upon education research in developing our qualifications. 2
5 1. Introduction 1.2 Why choose Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting? Cambridge A and AS Level Accounting is accepted by universities and employers as proof of an understanding of the main principles of accounting. Successful A and AS Level candidates gain lifelong skills, including: an ability to apply accounting concepts, principles and practices an understanding of the role of accounting as an information system for monitoring, problem-solving and decision making and the place of accounting in changing economic, social and technological environments an ability to examine and evaluate accounting policies and practices critically and analytically improved skills of communication, analysis, interpretation and presentation of both qualitative and quantitative accounting information 1.3 Cambridge Advanced International Certificate of Education (AICE) Cambridge AICE is the group award of Cambridge International Advanced Supplementary Level and Advanced Level (AS Level and A Level). Cambridge AICE involves the selection of subjects from three curriculum groups Mathematics and Science; Languages; Arts and Humanities. An A Level counts as a double-credit qualification and an AS Level as a single-credit qualification within the Cambridge AICE award framework. To be considered for an AICE Diploma, a candidate must earn the equivalent of six credits by passing a combination of examinations at either double credit or single credit, with at least one course coming from each of the three curriculum areas. The examinations are administered in May/June and October/November sessions each year. Accounting (9706) falls into Group C, Arts and Humanities. Learn more about AICE at 3
6 1. Introduction 1.4 How can I find out more? If you are already a Cambridge Centre You can make entries for this qualification through your usual channels, e.g. CIE Direct. If you have any queries, please contact us at international@cie.org.uk. If you are not a Cambridge Centre You can find out how your organisation can become a Cambridge Centre. us at international@cie.org.uk. Learn more about the benefits of becoming a Cambridge Centre at 4
7 2. Assessment at a glance Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 AS Level candidates take only Papers 1 and 2. A Level candidates have two choices. Candidates who want to take the whole of the A Level qualification at the end of a course of study take all four papers together. Candidates who want to get the A Level qualification in two stages take the AS Level first. If they pass AS Level, they then only need to take Papers 3 and 4 in order to complete the A Level. AS Level Paper 1 1 hour Paper 2 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates answer 30 multiple choice questions on AS topics; there are 30 marks for this paper. Candidates answer 3 structured questions on AS topics; there are 90 marks for this paper. The first question in Paper 2 is always about the final accounts of sole proprietors, partnerships or private limited companies. 30% of total marks 70% of total marks A Level Paper 1 1 hour Paper 2 1 hour 30 minutes Paper 1 for A Level is the same as Paper 1 for AS Level. Paper 2 for A Level is the same as Paper 2 for AS Level. 15% of total marks 35% of total marks Paper 3 1 hour Paper 4 2 hours Candidates answer 30 multiple choice questions; there are 30 marks for this paper. Each item on Paper 3 tests a topic in the A Level Supplement part of the syllabus, but may also require a knowledge and understanding of the AS Level syllabus. Candidates answer 3 problem solving questions; there are 120 marks for this paper. Each question in Paper 4 tests a topic or topics in the A Level Supplement part of the syllabus, but may also require a knowledge and understanding of the AS Level syllabus. 15% of total marks 35% of total marks 5
8 2. Assessment at a glance Availability This syllabus is examined in the May/June examination session and the October/November examination session. This syllabus is available to private candidates. Centres in the UK that receive government funding are advised to consult the CIE website for the latest information before beginning to teach this syllabus. Combining this with other syllabuses Candidates can combine this syllabus in an examination session with any other CIE syllabus, except: syllabuses with the same title at the same level 7110 Principles of Accounts 9372 Principles of Accounting (Singapore) 6
9 3. Syllabus aims and objectives 3.1 Aims The syllabus is intended to encourage courses that will enable candidates to: develop an ability to apply accounting concepts, principles and practices understand the role of accounting as an information system for monitoring, problem-solving and decision making and the place of accounting in changing economic, social and technological environments develop a critical and analytical approach to examining and evaluating accounting policies and practices develop skills of communication, analysis, interpretation and presentation of both qualitative and quantitative accounting information 3.2 Assessment objectives and their weighting in the exam papers To pass A and AS Level Accounting, candidates must demonstrate the following: AO1: knowledge and understanding of the accounting procedures and practices in the specified content and the principles which these are based on AO2: an ability to apply knowledge and understanding of accounting procedures, practices and principles to familiar and new situations AO3: an ability to select, order, analyse and present information in an appropriate accounting form AO4: an ability to present reasoned explanations, understand implications and communicate them in a clear and logical manner AO5: an ability to make judgements, recommendations and decisions based on accounting information and principles The multiple choice papers (Papers 1 and 3) test assessment objectives 1, 2 and 3. The written papers (Papers 2 and 4) mainly test assessment objectives 1, 2 and 3, but also, to a lesser extent, test assessment objectives 4 and 5. 7
10 4. Curriculum content Overview of the curriculum for A & AS Level Accounting Topic AS Level A Level THE ACCOUNTING SYSTEM A Recording Financial Information B Accounting Principles C Control Systems FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING D Preparation of Financial Statements E Capital (Equity) F Business Purchase G Published Company Accounts FINANCIAL REPORTING AND INTERPRETATION H Interpretation and Analysis I Company Financing ELEMENTS OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING J Costing Principles and Systems K Budgeting L Standard Costing M Investment Appraisal Examined at AS Examined at AS Examined at AS Examined at AS Examined at AS Examined at AS Examined at AS Examined at AS May be examined at A Level May be examined at A Level May be examined at A Level Includes additional content at A Level Includes additional content at A Level Examined at A Level Examined at A Level Includes additional content at A Level Examined at A Level Includes additional content at A Level Includes additional content at A Level Examined at A Level Examined at A Level 8
11 4. Curriculum content 4.1 Core content: AS Level Content Notes THE ACCOUNTING SYSTEM A. Recording financial information The recording and processing of accounting data based on the double-entry system of accounting. Double-entry book-keeping, journal entries, other payables, other receivables, bad debts and the provision for doubtful debts. The distinction between capital and revenue incomes and expenditures and the treatment of tangible non-current assets including their depreciation, disposal and revaluation. The treatment of current assets, current liabilities, non-current liabilities, equity and reserves. B. Accounting principles The recognition and application of accounting concepts. The principles, concepts and conventions which underlie the accounting process including going concern, matching, other payables, other receivables, consistency, materiality, aggregation, offsetting and comparative information. The importance of a true and fair view, and of prudence and substance over form. The use of the business entity, historical cost and revaluation as features of the recording system. C. Control systems Principles of accounting control systems. The trial balance, bank reconciliations, suspense accounts, control accounts and the correction of errors and consequent adjustments to the profit and loss account or income statement and balance sheet. 9
12 4. Curriculum content FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING D. Preparation of financial statements The periodic determination of profit (or earnings) and overall financial position based on historical cost data and generally accepted accounting principles and policies, conventions and practices which relate to each type of organisation listed below: (a) Sole Proprietors and Private Limited Companies (b) Partnerships This section covers the preparation of final accounts (financial statements), namely: manufacturing, trading, departmental, income statements, profit and loss accounts, appropriation accounts, balance sheets and simple cash flow, in good style and format. Manufacturing, trading, departmental, profit and loss accounts, income statements and balance sheets. The AS Level curriculum does not include published accounts of PLCs. The preparation of partnership appropriation accounts, current accounts and capital accounts. Changes in partnership incoming and outgoing partners. Changes in profit sharing ratio. (c) Non-profit making (not for profit) organisations (d) Accounts prepared from incomplete records or where financial records are deficient or incorrect Intangible assets (Goodwill) adjustments in partners capital accounts: (i) with the introduction of a goodwill (intangible assets) account in the firm s books, and (ii) when no goodwill (intangible assets) account is to be introduced. For example, clubs and societies. 10
13 4. Curriculum content A general knowledge and understanding of the accepted principles and application of stock valuation (inventory), depreciation and goodwill (intangible assets) as it applies to the above. Valuation of inventory The calculation of the value of closing inventory using the FIFO and AVCO methods (perpetual and periodic). The effect of different methods of valuing inventory on profit and the valuation of inventory in the balance sheet. The different characteristics, and the appropriateness, of using FIFO and AVCO. Detailed calculations of the value of inventory using LIFO will not be set. The principle of applying the lower of cost or net realisable value when valuing closing inventory. There are no questions on long-term contracts. Depreciation The causes of depreciation: physical deterioration, economic factors, obsolescence, inadequacy and the passage of time. The terminology used in accounting for depreciation: cost, useful asset life, residual (scrap) value and carrying amount. The reasons for accounting for depreciation and the application of relevant accounting concepts. The calculation of depreciation: reducing balance, straight-line and revaluation methods. The calculation of profit or loss on disposal of noncurrent assets; ledger accounts and journal entries for non-current assets, depreciation and disposal; the application of relevant accounting concepts. 11
14 4. Curriculum content Intangible assets The concept and treatment of intangible assets as it applies to Sole Proprietors and Limited Companies. (Partnership treatment of intangible assets is in A Level only) It is not necessary to know about taxation. There are no questions on any aspects of: Brand names (although this may be included at A level) Container accounts Joint ventures Royalties Investment accounts involving the apportionment of income and capital Piecemeal dissolution of partnership, or the rule in Garner versus Murray Bills of exchange Group or consolidated accounts Hire purchase accounts or branch and consignment accounts. E. Capital (equity) The raising of capital. The main types of share capital: ordinary shares; preference shares (cumulative, non-cumulative, participating and redeemable). The principles of overdrafts; trade credit and factoring; loans and debentures. The effect on the balance sheet of the issue of shares. There are no questions on: forfeiture of shares, redemption and purchase of own shares by a company, or on convertible loan stock. the detailed procedure of book-keeping entries for share issues. the published accounts of Limited Companies. F. Business purchase This topic is not in the AS Level syllabus. 12
15 4. Curriculum content G. Published company accounts This topic is not in the AS Level syllabus. FINANCIAL REPORTING AND INTERPRETATION H. Interpretation and analysis Users of financial statements. Calculation of ratios. The differing requirements for information of user groups including management, shareholders, employees, potential investors, creditors, government, public and environmental bodies. See the ratios on pages Ratios to aid the appraisal of profitability, liquidity and efficiency. Analysis and interpretation of accounting information Limitations of accounting information Calculation of the following specific ratios: Gross profit ratio (margin) Mark up Net profit ratio (percentage) Return on capital employed Expenses to sales ratio Non-current Asset Turnover Current ratio Liquid (acid test) ratio Trade receivables turnover (days) Trade payables turnover (days) Inventory turnover (days) Inventory turnover (times) The presentation, analysis and interpretation of accounting information as an aid to decision making by user groups; inter-firm comparisons and trend analyses. The limitations of accounting information. The difficulties of comparison presented by subjectivity, time lapse, monetary measurement and other external factors. I. Company financing This topic is not in the AS Level syllabus. 13
16 4. Curriculum content ELEMENTS OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING J. Costing principles and systems Cost accounting for material, labour and overheads. The elements of cost: cost classification and ascertainment of fixed, variable and semi-variable costs, stepped costs, total costs, unit costs and sunk costs. Availability of materials and labour and limiting factors relating to production and capacity. Preparation of cash budgets and forecasts in good style and format to aid decision making. Marginal (variable) costing Making simple business decisions using marginal costing e.g. make or buy. The concept of contribution and its application to the calculation of revenue, cost and profit data. The calculation of the break-even point, contribution to sales (revenue) ratio and margin of safety, the preparation and use of break-even graphs and contribution to sales (revenue) (profit/volume) graphs. The advantages and limitations of cost-volumeprofit analysis. The evaluation and interpretation of costvolume-profit data and its value as a support for management decision making. 14
17 4. Curriculum content Absorption (total) costing Making simple business decisions using absorption costing. The classification of direct and indirect material and labour costs, other direct expenses and overhead expenditure. The allocation and apportionment of overhead expenditure between production and service departments and the calculation of overhead absorption rates; under absorption and over absorption of overheads. The uses and limitations of marginal costing and absorption costing. Valuation of inventory using absorption and marginal cost principles. Costing systems Costing systems as used for job, unit, and batch costing, including the calculation of the value of inventory. There are no questions on process costing. K. Budgets Preparation of simple cash budgets to aid decision making L. Standard costing This topic is not in the AS Level syllabus. M. Investment appraisal This topic is not in the AS Level syllabus. 15
18 4. Curriculum content 4.2 Core content: A Level Content Notes THE ACCOUNTING SYSTEM A Level candidates need to be familiar with all the material in the AS Level syllabus, although there are no questions testing this in detail. FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING D. Preparation of financial statements Knowledge of all the material in the AS Level syllabus is necessary. Cash flow statements As for the AS Level syllabus, plus: The preparation of statement of cash flows in good style and format and in accordance with current accounting standards such as IAS7. The internal financial statements of Limited Companies. Partnership changes As for the AS Level syllabus plus: Dissolution of partnership. Effects of asset and liability revaluation. E. Capital (Equity) The whole of the AS Level syllabus, plus the following: (a) Premium on redemption of shares and the capital redemption reserve. (b) Repayment of share capital. (c) Redemption and purchase of own shares. (d) Repayment of debentures. (e) Convertible loan stock. (f) Distributable profits. As for the AS Level syllabus, plus the following: The effect on the balance sheet of the redemption of shares, capital reductions and reconstructions. The effect on the balance sheet of bonus and rights issues. Revenue and capital reserves. There are no questions on forfeiture of shares. A knowledge of share issues, capital reductions and reconstructions. There are no questions involving the detailed procedure of book-keeping entries required in the journal or in ledger accounts for share issues, capital reductions or reconstructions. 16
19 4. Curriculum content F. Business purchase The purchase of an unincorporated business by a limited company. The purchase of assets, and the assumption of liabilities of one business by another, or by a new company which buys one or more existing businesses. Merger of unincorporated businesses to form a partnership or limited company. Evaluating a business with a view to acquiring it. G. Published company accounts Principles governing the disclosure requirements of company annual reports covering: (a) The Directors Report; (b) Income statement (statement of comprehensive income); (c) Balance sheet (statement of financial position); (d) Statement of cash flows; (e) Statement of changes in equity (total recognised gains and losses). An appreciation of return on investment; calculation of goodwill (intangible assets) and negative goodwill (intangible assets); purchase of a business by issue of shares, debentures, and by cash. Mergers by means of combining or purchasing assets and liabilities. Valuation of a business by book value and net equity methods. The main disclosure requirements relating to published corporate reports. Disclosure of accounting policies. Familiarity with the requirements to disclose details concerning fixed assets, depreciation. Treatment of intangible assets. There are no questions which rely wholly or mainly on the Companies Acts concerning the format of published accounts. There are no questions on corporate governance, reports of audit committees, remuneration committees, interim reports, segmental information and foreign exchange. FINANCIAL REPORTING AND INTERPRETATION H. Interpretation and analysis Builds on the whole of the AS Level syllabus. There may be questions on all ratios in the syllabus (both AS and A Level). See ratios given on pages Ratios to aid the appraisal of financial structure; gearing and Stock Exchange ratios. 17
20 4. Curriculum content I. Company financing The financing of companies including capital gearing, capital structures, and loan capital. The bases of modern financial reporting and its limitations. Rights and bonus issues. An understanding of the disclosure standards adopted by quoted companies. A basic knowledge of the following standards and how these standards relate to topics in the syllabus: IAS IAS 1 IAS 2 IAS 7 IAS 8 IAS 10 IAS 16 IAS 18 IAS 23 IAS 33 IAS 36 IAS 37 IAS 38 Topic Presentation of financial statements Inventories (not long-term contracts) Statement of cash flows Accounting policies Events after the reporting period Property, plant and equipment Revenue Borrowing costs Earnings per share Impairment of assets Provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets Intangible assets ELEMENTS OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING J. Costing principles and systems A Level Candidates need to be familiar with all the material in the AS Level syllabus, plus: Process costing, including by-products and waste products and the calculation of work in progress. Process costing involving normal wastage and joint products, but not involving more than three processes. Valuation of inventory using absorption and marginal costing principles. Relevant costs and the preparation of costing reports for use in decision-making. Availability of materials and labour and limiting factors relating to production and capacity. 18
21 4. Curriculum content K. Budgets Advantages of using budgets. The preparation of the following budgets: Master budget budgeted profit and loss accounts, income statements and balance sheets Production Purchases Expenditure Trade receivables Trade payables Cash Sales. Principal budget factors and the flexing of budgets. Behavioural aspects of budgeting. Limitations of budgets. L. Standard costing Establishing cost standards for unit costs, and variance analysis involving usage and price variances. Types of cost standard. Standard hours and calculation of a standard unit price. Calculation of sales volume and price variances; materials usage and price variances; labour efficiency and rate variances. Candidates do not need to calculate overhead and sales mix variances. There are no questions on standard costing involving several processes through which a product may pass. 19
22 4. Curriculum content M. Investment appraisal The elements of investment appraisal including discounted cash flow methods. Capital investment appraisal to include: Ascertainment of future net cash flows Payback Discounted payback Accounting rate of return (ARR). Discounting methods for calculating the net present value and internal rate of return. Discount factors are given. Advantages and disadvantages of using different methods of investment appraisal. Treatment of working capital required. Capital rationing and selection of appropriate projects. (Discount factors are given.) Other factors affecting investment decisions. Sensitivity analysis. Critical changes in initial outlay and future net cash flows. 20
23 5. Appendix 5.1 Summary of commonly used ratios (AS and A Level) Profitability ratios Gross Profit (i) Gross Profit Ratio (margin) (also known as Gross Profit percentage) = 100 Net Sales/Revenue GrossProfit Mark up = 100 Cost of Sales NPBI (ii) Net Profit Ratio (also known as Net Profit percentage) = 100 Net Sales Revenue can also be expressed as Net Profit Net Sales/Revenue (after interest) [Uses NPBI Net Profit before interest, i.e. add back interest] NPBI (iii) Return on Capital Employed = 100 CapitalEmployed [Capital Employed = Issued Shares + Reserves + Non-Current Liabilities] Net Profit after Preference Dividends (iv) Return on Equity = 100 Equity [Equity = Issued Ordinary Shares + Reserves] NPBI (v) Return on Total Assets = 100 Total Assets [Total Assets = Non-Current Assets + Current Assets] Operating Expenses (vi) Operating expenses to Revenue Ratio = 100 Revenue (vii) Non-Current Asset Turnover = Total Net Book Net Sales Revenue Value of Non-Current Assets 21
24 5. Appendix Liquidity (i) Current Ratio = Current Assets Current Liabilities (ii) Liquid Ratio = Current Assets Inventory Current Liabilities (Also known as Acid Test or Quick Ratio ) (iii) Trade Receivables Turnover = Trade Receivables 365 days Credit Sales (Also known as Average Collection Period) (iv) Trade Payables Turnover = Trade Payables Credit Purchases 365 days (Also known as Average Payment Period) (v) Inventory Turnover = Average Inventory Cost of Goods Sold 365 days Or Rate of Inventory Turnover = Cost of Goods Sold Average Inventory (answer given in times) 22
25 5. Appendix A Level only (vi) Working Capital Cycle (in days) = Trade Receivables Turnover (in days) + Inventory Turnover (in days) Trade Payables Turnover (in days) Or Working Capital Cycle (in days) = Average Collection Period + Inventory Turnover (in days) Average Payment Period Net Working Assets (vii) 100 Sales/Revenue Net Working Assets = Inventories plus Trade Receivables less Trade Payables Interest Expense (viii) Income Gearing = 100 Profit Before Interest and Tax (PBIT) (ix) Gearing Ratio = Which is: Fixed Cost Capital Total Capital Non-Current Liabilities + Preference Share Capital Issued Ordinary Share Capital + AllReserves + Non-Current Liabilities + Preference Shares Investment ratios (stock exchange ratios) A Level only (i) Earnings per share = Net Profit Preference Share Dividend No. of issued Ordinary Shares (ii) Price Earnings Ratio = Market Price per share Earnings per share (iii) Dividend yield = Dividend paid and proposed Market Price of share (iv) Dividend cover = (v) Dividend per share = Profit available to pay ordinary dividend Ordinary dividend paid Ordinary dividend paid Number of issued ordinary shares 23
26 5. Appendix Cash flow ratios Operating Cash Flow (i) Cash margin on sales = 100 Sales Revenue Operating Cash Flow (ii) Cash liquidity ratio = 100 Current Liabilities (iii) Interest cover on a cash basis = (iv) Dividend cover on a cash basis = Trade Payables Credit Purchases 365 days Operating Cash Flow lessinterest, Taxation and Preference Dividend Ordinary shareholders Dividend 100 Calculate ratios using year-end balances where appropriate, unless the question specifies the use of average figures. Calculate ratios to the number of decimal places required by the question. 24
27 5. Appendix 5.2 Resource list This is NOT a list of prescribed texts, but a range of alternative texts from which teachers may wish to choose. Student textbooks Author Title Publisher ISBN Date Harold Randall Accounting: A Level and AS Level *Endorsed Textbook* CUP David Cox Business Accounts Osborne Ian Harrison Advanced Accounting for A2 Hodder Education Ian Harrison Introducing Accounting for AS Hodder and Stoughton Ian Harrison The Complete A-Z Accounting Handbook Hodder and Stoughton Ian Harrison A Level Study Guide: Accounting Letts Rob Jones Business Accounting Causeway Press Riad Izhar and Janet Hontoir Accounting, Costing and Management OUP Harold Randall A Level Accounting (3rd edition) Letts Educational Frank Wood A Level Accounting FT Prentice Hall Teacher s resources Author Title Publisher ISBN Date Catherine Coucom Professional Development for Teachers: Teaching and Assessing Skills in Accounting CUP Ian Harrison The Complete A-Z Accounting Hodder and Stoughton Frank Wood and Alan Sangster Frank Wood and Alan Sangster Business Accounting 1 (10th edition) Business Accounting 2 (10th edition) Prentice Hall Prentice Hall
28 5. Appendix Online resources: 1 If problems are experienced with this site, select then select Student Resources, Select Accounting and Finance and the Select Accounting Documents.pdf) (useful to focus searching to relevant areas) 9 (Company Annual Reports Online site; commercial final accounts) 10 (covers aspects of the syllabus) 11 (Business Studies but some relevant resources for Accounting) 12 (Business Studies but relevant resources for Accounting) 13 (Business Studies but some relevant resources for Accounting) 14 (ACCA Student Accountant site with some relevant articles) International standards: 15 (Click on the standards button in the heading and then scroll down) 16 (Then insert the relevant IAS in the heading) 17 (Use the search facility to find individual IAS e.g. IAS 1: Presentation of Financial Statements. Wikipedia is also available in other languages scroll down to the languages section on the Main Page.) 26
29 5. Appendix 5.3 International standards terminology The list below identifies the international standards terminology used in CIE accounting syllabuses. CIE anticipates including well-known standards, which are relevant to the level of study, in question papers, mark schemes and associated documents. Centres should use the new terminology in their teaching and learning materials so that candidates are familiar with the terms. Candidates will not lose marks for using different terms. International usage Statement of financial position (balance sheet) Bank (and other) loans/ Interest bearing loans and borrowing Bank overdrafts and loans/ Interest bearing loans and borrowing Capital or equity/shareholders equity Cash (and cash equivalents) Cost of sales Current assets Current liabilities Finance costs Finance income/investment revenues Financial statements Gross profit Income statement (statement of comprehensive income) Intangible assets Inventory/inventories (of raw materials and finished goods) Investment property Non-current assets Current CIE/UK usage Balance sheet Loans repayable after 12 months Loans repayable within 12 months Capital Bank and cash Cost of goods sold Current assets Current liabilities/ Creditors: amounts due within 12 months Interest payable Interest receivable Final accounts Gross profit Trading and profit and loss account Goodwill etc. Stock Investments Fixed assets 27
30 5. Appendix Non-current liabilities Other operating expenses Other operating income Other payables Other receivables Plant and equipment Profit (before tax) for the year Property Raw materials Ordinary goods purchased Revenue Share capital Trade payables Trade receivables Work in progress Long term liabilities/ Creditors: amounts falling due after more than one year Sundry expenses (administration and distribution) Sundry income Accruals Prepayments Plant and equipment Net profit Land and buildings Purchases Sales Share capital Creditors Debtors Work in progress 28
31 6. Additional information 6.1 Guided learning hours Advanced Level ( A Level ) syllabuses are designed on the assumption that candidates have about 360 guided learning hours per subject over the duration of the course. Advanced Subsidiary Level ( AS Level ) syllabuses are designed on the assumption that candidates have about 180 guided learning hours per subject over the duration of the course. ( Guided learning hours include direct teaching and any other supervised or directed study time. They do not include private study by the candidate.) However, these figures are for guidance only, and the number of hours required may vary according to local curricular practice and the candidates prior experience of the subject. 6.2 Recommended prior learning We recommend that candidates who are beginning this course should have previously completed an O Level or IGCSE course in Accounting or the equivalent. 6.3 Progression Cambridge International A Level Accounting provides a suitable foundation for the study of Accounting or related courses in higher education. Equally it is suitable for candidates intending to pursue careers or further study in Accounting, or as part of a course of general education. Cambridge International AS Level Accounting constitutes the first half of the Cambridge International A Level course in Accounting and therefore provides a suitable foundation for the study of Accounting at A Level and thence for related courses in higher education. Depending on local university entrance requirements, it may permit or assist progression directly to university courses in Accounting or some other subjects. It is also suitable for candidates intending to pursue careers or further study in Accounting, or as part of a course of general education. 6.4 Component codes Because of local variations, in some cases component codes will be different in instructions about making entries for examinations and timetables from those printed in this syllabus, but the component names will be unchanged to make identification straightforward. 29
32 6. Additional information 6.5 Grading and reporting A Level results are shown by one of the grades A*, A, B, C, D or E indicating the standard achieved, Grade A* being the highest and Grade E the lowest. Ungraded indicates that the candidate has failed to reach the standard required for a pass at either A Level or AS Level. Ungraded will be reported on the statement of results but not on the certificate. If a candidate takes an A Level and fails to achieve grade E or higher, an AS Level grade will be awarded if both of the following apply: the components taken for the A Level by the candidate in that session included all the components making up an AS Level the candidate s performance on these components was sufficient to merit the award of an AS Level grade. For languages other than English, CIE also reports separate speaking endorsement grades (Distinction, Merit and Pass), for candidates who satisfy the conditions stated in the syllabus. Percentage uniform marks are also provided on each candidate s statement of results to supplement their grade for a syllabus. They are determined in this way: A candidate who obtains the minimum mark necessary for a Grade A* obtains a percentage uniform mark of 90%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade A obtains a percentage uniform mark of 80%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade B obtains a percentage uniform mark of 70%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade C obtains a percentage uniform mark of 60%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade D obtains a percentage uniform mark of 50%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade E obtains a percentage uniform mark of 40%. no marks receives a percentage uniform mark of 0%. Candidates whose mark is none of the above receive a percentage mark in between those stated according to the position of their mark in relation to the grade thresholds (i.e. the minimum mark for obtaining a grade). For example, a candidate whose mark is halfway between the minimum for a Grade C and the minimum for a Grade D (and whose grade is therefore D) receives a percentage uniform mark of 55%. The uniform percentage mark is stated at syllabus level only. It is not the same as the raw mark obtained by the candidate, since it depends on the position of the grade thresholds (which may vary from one session to another and from one subject to another) and it has been turned into a percentage. 30
33 6. Additional information AS Level results are shown by one of the grades a, b, c, d or e indicating the standard achieved, Grade a being the highest and Grade e the lowest. Ungraded indicates that the candidate has failed to reach the standard required for a pass at AS Level. Ungraded will be reported on the statement of results but not on the certificate. For languages other than English, CIE will also report separate speaking endorsement grades (Distinction, Merit and Pass) for candidates who satisfy the conditions stated in the syllabus. The content and difficulty of an AS Level examination is equivalent to the first half of a corresponding A Level. Percentage uniform marks are also provided on each candidate s statement of results to supplement their grade for a syllabus. They are determined in this way: A candidate who obtains the minimum mark necessary for a Grade a obtains a percentage uniform mark of 80%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade b obtains a percentage uniform mark of 70%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade c obtains a percentage uniform mark of 60%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade d obtains a percentage uniform mark of 50%. the minimum mark necessary for a Grade e obtains a percentage uniform mark of 40%. no marks receives a percentage uniform mark of 0%. Candidates whose mark is none of the above receive a percentage mark in between those stated according to the position of their mark in relation to the grade thresholds (i.e. the minimum mark for obtaining a grade). For example, a candidate whose mark is halfway between the minimum for a Grade c and the minimum for a Grade d (and whose grade is therefore d) receives a percentage uniform mark of 55%. The uniform percentage mark is stated at syllabus level only. It is not the same as the raw mark obtained by the candidate, since it depends on the position of the grade thresholds (which may vary from one session to another and from one subject to another) and it has been turned into a percentage. 31
34 6. Additional information 6.6 Resources Copies of syllabuses, the most recent question papers and Principal Examiners reports for teachers are available on the Syllabus and Support Materials CD-ROM, which is sent to all CIE Centres. Resources are also listed on CIE s public website at Please visit this site on a regular basis as the Resource lists are updated through the year. Access to teachers discussion groups, suggested schemes of work and regularly updated resource lists may be found on the CIE Teacher Support website at This website is available to teachers at registered CIE Centres. 32
35 University of Cambridge International Examinations 1 Hills Road, Cambridge, CB1 2EU, United Kingdom Tel: +44 (0) Fax: +44 (0) international@cie.org.uk Website: University of Cambridge International Examinations 2010
Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011
 www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011 Note for Exams Officers: Before making Final Entries, please check
www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011 Note for Exams Officers: Before making Final Entries, please check
Syllabus. General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level ACCOUNTING 9706
 General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus ACCOUNTING 9706 For examination in June and November 2009 CIE provides syllabuses,
General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus ACCOUNTING 9706 For examination in June and November 2009 CIE provides syllabuses,
SYLLABUS. Cambridge International AS and A Level Accounting.
 SYLLABUS Cambridge International AS and A Level Accounting 9706 For examination in June and November 2014 University of Cambridge International Examinations retains the copyright on all its publications.
SYLLABUS Cambridge International AS and A Level Accounting 9706 For examination in June and November 2014 University of Cambridge International Examinations retains the copyright on all its publications.
Syllabus. General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level ACCOUNTING 9706
 General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus ACCOUNTING 9706 For examination in June and November 2010 CIE provides syllabuses,
General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus ACCOUNTING 9706 For examination in June and November 2010 CIE provides syllabuses,
Syllabus Cambridge IGCSE Accounting Syllabus code 0452 For examination in June and November 2012
 www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus Cambridge IGCSE Accounting Syllabus code 0452 For examination in June and November 2012 Contents Cambridge IGCSE Accounting Syllabus code 0452 1. Introduction... 2 1.1 Why
www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus Cambridge IGCSE Accounting Syllabus code 0452 For examination in June and November 2012 Contents Cambridge IGCSE Accounting Syllabus code 0452 1. Introduction... 2 1.1 Why
Syllabus. Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus code 7110 For examination in June and November 2013
 Syllabus Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus code 7110 For examination in June and November 2013 Contents Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus code 7110 1. Introduction... 2
Syllabus Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus code 7110 For examination in June and November 2013 Contents Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus code 7110 1. Introduction... 2
MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION
 ZIMBABWE MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS FORMS 5-6 2015 2022 Curriculum Development Unit P.O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant Harare All rights reserved 2015 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The
ZIMBABWE MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS FORMS 5-6 2015 2022 Curriculum Development Unit P.O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant Harare All rights reserved 2015 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 7110 GCE O Level FOR EXAMINATION IN Exclusions
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 7110 GCE O Level FOR EXAMINATION IN 2008 Exclusions This syllabus must not be offered in the same session with any of the following syllabuses: 0452 Accounting 0614 Accounting (Botswana)
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 7110 GCE O Level FOR EXAMINATION IN 2008 Exclusions This syllabus must not be offered in the same session with any of the following syllabuses: 0452 Accounting 0614 Accounting (Botswana)
LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
 LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Lesotho General Certificate of Secondary Education Syllabus Accounting 0187 For examination in November 2018 National Curriculum Development Centre in
LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Lesotho General Certificate of Secondary Education Syllabus Accounting 0187 For examination in November 2018 National Curriculum Development Centre in
AM Syllabus ( ): Accounting AM SYLLABUS ( ) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS
 AM SYLLABUS (2008-2013) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM 01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus builds on the topics set for the SEC
AM SYLLABUS (2008-2013) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM 01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus builds on the topics set for the SEC
AM01 Syllabus (2019): Accounting AM SYLLABUS (2019) SYLLABUS
 ACCOUNTING AM SYLLABUS (2019) AM01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop the students financial literacy,
ACCOUNTING AM SYLLABUS (2019) AM01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop the students financial literacy,
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ)
 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ) (ASE3012X) L3 SPECIFICATION Issue 2 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ) (ASE3012X) Specification Issue 2 Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ) (ASE3012X) L3 SPECIFICATION Issue 2 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ) (ASE3012X) Specification Issue 2 Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications
IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS
 IM Syllabus (2020): Accounting IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial
IM Syllabus (2020): Accounting IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION
 Republic of Namibia MINISTRY OF EDUCATION NAMIBIA SENIOR SECONDARY CERTIFICATE (NSSC) ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS HIGHER LEVEL SYLLABUS CODE: 8335 GRADES 11-12 2010 DEVELOPED IN COLLABORATION WITH UNIVERSITY OF
Republic of Namibia MINISTRY OF EDUCATION NAMIBIA SENIOR SECONDARY CERTIFICATE (NSSC) ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS HIGHER LEVEL SYLLABUS CODE: 8335 GRADES 11-12 2010 DEVELOPED IN COLLABORATION WITH UNIVERSITY OF
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding
Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting
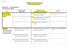 Suggested Revised BAFS Curriculum Draft as at 30 January 2013 Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting Topic Books of Original Entry and Types of Ledgers Explanatory Notes (original
Suggested Revised BAFS Curriculum Draft as at 30 January 2013 Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting Topic Books of Original Entry and Types of Ledgers Explanatory Notes (original
IM SYLLABUS (2018) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS
 IM SYLLABUS (2018) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial literacy, and the presentation
IM SYLLABUS (2018) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial literacy, and the presentation
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding of accounting
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding of accounting
Level 3 Certificate in Accounting
 Level 3 Certificate in Accounting Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after 1 January 2008 (UK Accreditation No: 100/1450/0) ASP 0047 ALSG >f0t@wjy2`?h:y3]0t9]@w>q0z# Vision Statement Our vision
Level 3 Certificate in Accounting Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after 1 January 2008 (UK Accreditation No: 100/1450/0) ASP 0047 ALSG >f0t@wjy2`?h:y3]0t9]@w>q0z# Vision Statement Our vision
SEC Syllabus (2020) Accounting
 SEC SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING SEC 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting SEC 01 Syllabus (not available in September) Paper 1 (2hrs) + Paper II (2 hrs) The aims of the syllabus are to enable students: 1. To understand
SEC SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING SEC 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting SEC 01 Syllabus (not available in September) Paper 1 (2hrs) + Paper II (2 hrs) The aims of the syllabus are to enable students: 1. To understand
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION
 Republic of Namibia MINISTRY OF EDUCATION NAMIBIA SENIOR SECONDARY CERTIFICATE (NSSC) ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS ORDINARY LEVEL SYLLABUS CODE: 4345 GRADES 11-12 2010 DEVELOPED IN COLLABORATION WITH UNIVERSITY
Republic of Namibia MINISTRY OF EDUCATION NAMIBIA SENIOR SECONDARY CERTIFICATE (NSSC) ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS ORDINARY LEVEL SYLLABUS CODE: 4345 GRADES 11-12 2010 DEVELOPED IN COLLABORATION WITH UNIVERSITY
Activity to Develop and Demonstrate Competence. Describe the nature, scope and purposes of financial statements and their related records and accounts
 Paper 1 Financial Accounting Aim This paper aims at testing students understanding of the basic accounting principles, and their ability to apply concepts of financial accounting and methods to record
Paper 1 Financial Accounting Aim This paper aims at testing students understanding of the basic accounting principles, and their ability to apply concepts of financial accounting and methods to record
Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (IAS) Effective for examinations to be held after January 2008
 LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (IAS) Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after January 2008 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909
LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (IAS) Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after January 2008 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909
OUTLINE ANSWERS TO EXERCISES
 OUTLINE ANSWERS TO EXERCISES 437 2.1 Cash account balance carried forward 1,680 2.2 Rent account Credit balance carried forward 300 Profit and loss charge 1,050 Rates account Debit balance carried forward
OUTLINE ANSWERS TO EXERCISES 437 2.1 Cash account balance carried forward 1,680 2.2 Rent account Credit balance carried forward 300 Profit and loss charge 1,050 Rates account Debit balance carried forward
Cambridge IGCSE Accounting (0452)
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge IGCSE Accounting (0452) International Accounting Standards (IAS) Guidance for Teachers Contents Introduction... 2 Use of this document... 2 Users of financial statements...
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge IGCSE Accounting (0452) International Accounting Standards (IAS) Guidance for Teachers Contents Introduction... 2 Use of this document... 2 Users of financial statements...
Unit 4: Elements of Managerial Accounting Syllabus Section Absorption (Total) costing
 www.xtremepapers.com Unit 4: Elements of Managerial Accounting Syllabus Section Absorption (Total) costing Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities Resources Online Resources Students will learn
www.xtremepapers.com Unit 4: Elements of Managerial Accounting Syllabus Section Absorption (Total) costing Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities Resources Online Resources Students will learn
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS OBJECTIVE The objective of the examination is to test candidates understanding of the basic principles and methods of accounting and their application to practical situations. THE
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS OBJECTIVE The objective of the examination is to test candidates understanding of the basic principles and methods of accounting and their application to practical situations. THE
Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting
 Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FA2-MA2.X Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Intermediate course orientation
Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FA2-MA2.X Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Intermediate course orientation
Level 2 Cost Accounting
 Level 2 Cost Accounting Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after 1 January 2008 ASPE0483 >f0t@wjy9w2`4s3dpd# Vision Statement Our vision is to contribute to the achievements of learners around
Level 2 Cost Accounting Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after 1 January 2008 ASPE0483 >f0t@wjy9w2`4s3dpd# Vision Statement Our vision is to contribute to the achievements of learners around
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9706 ACCOUNTING. 9706/11 Paper 1 (Multiple Choice Core), maximum raw mark 30
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/11 Paper 1 (Multiple Choice Core), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/11 Paper 1 (Multiple Choice Core), maximum
ACCOUNTS (858) CLASS XI
 ACCOUNTS (858) Aims: 1. To provide an understanding of the principles of accounts and practice in recording transactions and interpreting individual as well as company accounts. 2. To develop an understanding
ACCOUNTS (858) Aims: 1. To provide an understanding of the principles of accounts and practice in recording transactions and interpreting individual as well as company accounts. 2. To develop an understanding
Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019
 Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
PAPER C01 Fundamentals of Management Accounting Acorn chapters
 PAPER C01 Fundamentals of Management Accounting Acorn chapters 1 Classification of costs 2 The context of management accounting 3 Absorbing fixed production overhead 4 Absorption and marginal costing 5
PAPER C01 Fundamentals of Management Accounting Acorn chapters 1 Classification of costs 2 The context of management accounting 3 Absorbing fixed production overhead 4 Absorption and marginal costing 5
Student Guidance Notes
 Student Guidance Notes Guide C01 September 2004 Guidance notes for students planning to sit C01 Fundamentals of Management Accounting of the new 2006 CIMA Certificate in Business Accounting syllabus This
Student Guidance Notes Guide C01 September 2004 Guidance notes for students planning to sit C01 Fundamentals of Management Accounting of the new 2006 CIMA Certificate in Business Accounting syllabus This
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 *5783442697* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/11 Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2017 Additional Materials: Multiple
*5783442697* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/11 Paper 1 Multiple Choice May/June 2017 Additional Materials: Multiple
Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016)
 Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016) This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide
Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016) This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide
Principles of Accounting
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING 1 Principles of Accounting Lecturer: Kondrakhina Olesya Class teachers: Kondrakhina S. Olesya, Victoria V. Poleschuk, Tatyana S. Shurchkova, Kristina S. Pogosbekyan Course description
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING 1 Principles of Accounting Lecturer: Kondrakhina Olesya Class teachers: Kondrakhina S. Olesya, Victoria V. Poleschuk, Tatyana S. Shurchkova, Kristina S. Pogosbekyan Course description
Annual Qualification Review
 LCCI International Qualifications Level 2 Certificate in Book-Keeping and Accounts Annual Qualification Review 2008 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. enquiries@ediplc.com
LCCI International Qualifications Level 2 Certificate in Book-Keeping and Accounts Annual Qualification Review 2008 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. enquiries@ediplc.com
Dawood Public School. Course Outline for Principles of Accounts. Class X
 Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus Code 7110 Course Books: Dawood Public School Course Outline for 2013-2014 Principles of Accounts Class X 1. Wood, Frank, Business Accounting, FT Pitman
Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus Code 7110 Course Books: Dawood Public School Course Outline for 2013-2014 Principles of Accounts Class X 1. Wood, Frank, Business Accounting, FT Pitman
Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (VRQ)
 L2 Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20093) SPECIFICATION Issue 3 First teaching from September 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting
L2 Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20093) SPECIFICATION Issue 3 First teaching from September 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting
Level 3 Certificate in Advanced Business Calculations
 LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Advanced Business Calculations Syllabus Effective from 2001 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. enquiries@ediplc.com
LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Advanced Business Calculations Syllabus Effective from 2001 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. enquiries@ediplc.com
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. Duration 10 weeks ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Course orientation Start of course survey Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2:
Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. Duration 10 weeks ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Course orientation Start of course survey Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2:
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9706 ACCOUNTING
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/21
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/21
IAB LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING TO INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS (Qualification Accreditation Number 500/3370/
 IAB LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING TO INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS (Qualification Accreditation Number 500/3370/ INTRODUCTION The overall aim of this qualification is to accredit candidates knowledge and understanding
IAB LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING TO INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS (Qualification Accreditation Number 500/3370/ INTRODUCTION The overall aim of this qualification is to accredit candidates knowledge and understanding
Financial Accounting (FA)/FFA September 2018 to August 2019
 Financial Accounting (FA)/FFA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Financial Accounting (FA)/FFA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Financial Accounting (VRQ)
 Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Financial Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20101) L4 SPECIFICATION Issue 4 First teaching from September 2015 Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications
Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Financial Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20101) L4 SPECIFICATION Issue 4 First teaching from September 2015 Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications
MARK SCHEME for the November 2004 question paper 9706 ACCOUNTING
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the November 2004 question paper 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics), maximum raw
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the November 2004 question paper 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics), maximum raw
(F2/FMA) December 2011
 Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Financial Accounting (F3/FFA) February 2013 to January 2014
 Financial Accounting (F3/FFA) February 2013 to January 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be
Financial Accounting (F3/FFA) February 2013 to January 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be
Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Financial Accounting (VRQ)
 Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Financial Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20101) L4 SPECIFICATION Issue 3 First teaching from September 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Financial Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20101)
Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Financial Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20101) L4 SPECIFICATION Issue 3 First teaching from September 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Financial Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20101)
(F2/FMA) December 2011
 Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Institute of Certified Bookkeepers
 Institute of Certified Bookkeepers Level III Diploma in Costing and Budgeting Introduction: Financial Accounting is the reporting of financial information to users of Financial Statements both internal
Institute of Certified Bookkeepers Level III Diploma in Costing and Budgeting Introduction: Financial Accounting is the reporting of financial information to users of Financial Statements both internal
Annual Qualification Review 2010
 LCCI International Qualifications Level 2 Book-keeping & Accounts Annual Qualification Review 2010 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. enquiries@ediplc.com www.lcci.org.uk
LCCI International Qualifications Level 2 Book-keeping & Accounts Annual Qualification Review 2010 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. enquiries@ediplc.com www.lcci.org.uk
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS GCE ORDINARY LEVEL (SYLLABUS 7092) INTRODUCTION The syllabus aims to develop an understanding of the principles and concepts of accounting and their applications in a variety of
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS GCE ORDINARY LEVEL (SYLLABUS 7092) INTRODUCTION The syllabus aims to develop an understanding of the principles and concepts of accounting and their applications in a variety of
Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level 9706 Accounting June 2015 Principal Examiner Report for Teachers
 Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING Paper 9706/11 Multiple Choice Question Number Key Question Number Key 1 D 16 A 2 C 17 A 3 D 18 B 4 B 19 A 5 D 20 D 6 A 21
Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING Paper 9706/11 Multiple Choice Question Number Key Question Number Key 1 D 16 A 2 C 17 A 3 D 18 B 4 B 19 A 5 D 20 D 6 A 21
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9706 ACCOUNTING
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of
+44 (0) International Accounting Standards (IAS) Guidance: Terminology and Presentation
 internationalenquiries@ediplc.com +44 (0) 2476 518951 www.lcci.org.uk International Accounting Standards (IAS) Guidance: Terminology and Presentation Contents Introduction 3 1 First Level 4 1.1 Terminology
internationalenquiries@ediplc.com +44 (0) 2476 518951 www.lcci.org.uk International Accounting Standards (IAS) Guidance: Terminology and Presentation Contents Introduction 3 1 First Level 4 1.1 Terminology
Introduction Financial record keeping Income statements The balance sheet Further adjustments to the income statement 47
 CONTENTS Introduction 1 01 Financial record keeping 3 Introduction 3 Single-entry bookkeeping 4 Double-entry bookkeeping 6 Balancing accounts 10 The trial balance 13 Daybooks and ledgers 15 Modern double-entry
CONTENTS Introduction 1 01 Financial record keeping 3 Introduction 3 Single-entry bookkeeping 4 Double-entry bookkeeping 6 Balancing accounts 10 The trial balance 13 Daybooks and ledgers 15 Modern double-entry
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Cost and Management Accounting (VRQ)
 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Cost and Management Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20098) L3 SPECIFICATION Issue 2 First teaching from September 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Cost and Management
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Cost and Management Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20098) L3 SPECIFICATION Issue 2 First teaching from September 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Cost and Management
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Introduction course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: What, when and why? Lesson
Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Introduction course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: What, when and why? Lesson
Intermediate Management Accounting
 Intermediate Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. Course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: Getting your diploma Lesson 3: How do I study this course? Unit
Intermediate Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. Course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: Getting your diploma Lesson 3: How do I study this course? Unit
9706 ACCOUNTING. 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics), maximum raw mark 120
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the June 2005 question paper 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics), maximum raw mark
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the June 2005 question paper 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics), maximum raw mark
Level 2 Certificate in Book-Keeping and Accounts
 LCCI International Qualifications Level 2 Certificate in Book-Keeping and Accounts Extended Syllabus Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after 1 January 2008 For further information contact
LCCI International Qualifications Level 2 Certificate in Book-Keeping and Accounts Extended Syllabus Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after 1 January 2008 For further information contact
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 *1560424483* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/43 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics) May/June 2015 2 s No Additional
*1560424483* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/43 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics) May/June 2015 2 s No Additional
9706 ACCOUNTING. 9706/01 Paper 1 (Multiple Choice), maximum raw mark /02 Paper 2 (Structured Questions), maximum raw mark 90
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the June 2004 question papers 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/01 Paper 1 (Multiple Choice), maximum raw
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the June 2004 question papers 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/01 Paper 1 (Multiple Choice), maximum raw
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BUS245 COST ACCOUNTING. 3 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Mary E. Baricevic, Ph.D. April 18, 2013
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BUS245 COST ACCOUNTING 3 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mary E. Baricevic, Ph.D. April 18, 2013 Updated by: Mary E. Baricevic, Ph.D. November 4, 2018 Dr. Terry Kite, Interim
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BUS245 COST ACCOUNTING 3 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mary E. Baricevic, Ph.D. April 18, 2013 Updated by: Mary E. Baricevic, Ph.D. November 4, 2018 Dr. Terry Kite, Interim
Example Candidate Responses
 Example Candidate Responses Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts 7110 Cambridge Secondary 2 In order to help us develop the highest quality Curriculum Support resources, we are undertaking a continuous
Example Candidate Responses Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts 7110 Cambridge Secondary 2 In order to help us develop the highest quality Curriculum Support resources, we are undertaking a continuous
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS GCE Ordinary Level (2017) (Syllabus 7175) CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 2 AIMS 2 ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES 3 SCHEME OF ASSESSMENT 4 USE OF CALCULATORS 4 SYLLABUS OUTLINE 5 SUBJECT CONTENT
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS GCE Ordinary Level (2017) (Syllabus 7175) CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 2 AIMS 2 ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES 3 SCHEME OF ASSESSMENT 4 USE OF CALCULATORS 4 SYLLABUS OUTLINE 5 SUBJECT CONTENT
Contents. 1 - Finance Financial Statements 4. 3 Accounting Concept & Conventions 5. 4 Capital & Revenue Expenditure 8
 Contents 1 - Finance 3 2 - Financial Statements 4 3 Accounting Concept & Conventions 5 4 Capital & Revenue Expenditure 8 5 - Financial Statements Analysis 15 6 - Management Accounting 21 7 - Working Capital
Contents 1 - Finance 3 2 - Financial Statements 4 3 Accounting Concept & Conventions 5 4 Capital & Revenue Expenditure 8 5 - Financial Statements Analysis 15 6 - Management Accounting 21 7 - Working Capital
O & A Level Accounting Online Lectures By Waseem Hassan Gul
 O & A Level Accounting Online Lectures By Waseem Hassan Gul whg4gul@gmail.com : (For E. Mail & Text Chat) whg4gul : (Skype: Voice Call) 0092-333-4374592 : (Voice Call) http://whg.awardspace.com : (For
O & A Level Accounting Online Lectures By Waseem Hassan Gul whg4gul@gmail.com : (For E. Mail & Text Chat) whg4gul : (Skype: Voice Call) 0092-333-4374592 : (Voice Call) http://whg.awardspace.com : (For
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education 0452 Accounting June 2014 Principal Examiner Report for Teachers
 ACCOUNTING Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education Paper 0452/11 Paper 11 Key Messages Question 1 consisted of ten multiple choice items covering topics across the whole syllabus.
ACCOUNTING Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education Paper 0452/11 Paper 11 Key Messages Question 1 consisted of ten multiple choice items covering topics across the whole syllabus.
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9706 ACCOUNTING
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 (Problem Solving
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 (Problem Solving
Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level 9706 Accounting November 2014 Principal Examiner Report for Teachers
 Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING www.xtremepapers.com Paper 9706/11 Multiple Choice 1 B 16 B 2 B 17 B 3 B 18 D 4 C 19 D 5 C 20 C 6 D 21 C 7 B 22 C 8 B 23
Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING www.xtremepapers.com Paper 9706/11 Multiple Choice 1 B 16 B 2 B 17 B 3 B 18 D 4 C 19 D 5 C 20 C 6 D 21 C 7 B 22 C 8 B 23
PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING I ACC 2110
 PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING I ACC 2110 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0 Laboratory Hours: 0.0 Date Revised: Fall 1999 Catalog Course Description:
PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTING I ACC 2110 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0 Laboratory Hours: 0.0 Date Revised: Fall 1999 Catalog Course Description:
IAB Level 4 Certificate in International Accounting Standards and IFRS 603/3017/X. Qualification Specification
 IAB Level 4 Certificate in International Accounting Standards and IFRS 603/3017/X Qualification Specification Contents 1 Introduction to the qualification... 2 2 Statement of level... 2 3 Aims... 2 4 Target
IAB Level 4 Certificate in International Accounting Standards and IFRS 603/3017/X Qualification Specification Contents 1 Introduction to the qualification... 2 2 Statement of level... 2 3 Aims... 2 4 Target
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Advanced Business Calculations (ASE3003)
 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Advanced Business Calculations (ASE3003) Specification First teaching from 2001 Issue 2 Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications are
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Advanced Business Calculations (ASE3003) Specification First teaching from 2001 Issue 2 Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications are
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics) October/November
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics) October/November
Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Management Accounting (VRQ)
 Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Management Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20102) L4 SPECIFICATION First teaching from January 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Management Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20102)
Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Management Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20102) L4 SPECIFICATION First teaching from January 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 4 Certificate in Management Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20102)
Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level 9706 Accounting November 2013 Principal Examiner Report for Teachers
 ACCOUNTING www.xtremepapers.com Paper 9706/11 Multiple Choice Question Number Key Question Number Key 1 D 16 D 2 C 17 B 3 C 18 B 4 B 19 A 5 C 20 B 6 B 21 C 7 C 22 D 8 C 23 D 9 C 24 C 10 A 25 B 11 A 26
ACCOUNTING www.xtremepapers.com Paper 9706/11 Multiple Choice Question Number Key Question Number Key 1 D 16 D 2 C 17 B 3 C 18 B 4 B 19 A 5 C 20 B 6 B 21 C 7 C 22 D 8 C 23 D 9 C 24 C 10 A 25 B 11 A 26
Level 3 Management Accounting
 Level 3 Management Accounting Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after 1 January 2008 ASPE0483 >f0t@wjy9w2`4s3dpd# Vision Statement Our vision is to contribute to the achievements of learners
Level 3 Management Accounting Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after 1 January 2008 ASPE0483 >f0t@wjy9w2`4s3dpd# Vision Statement Our vision is to contribute to the achievements of learners
9706 ACCOUNTING. Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for Teachers.
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/43 Paper 4 (Problem Solving Supplement), maximum raw mark 120 This mark scheme is published
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2013 series 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/43 Paper 4 (Problem Solving Supplement), maximum raw mark 120 This mark scheme is published
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9706 ACCOUNTING
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9706 ACCOUNTING
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level and GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9706 ACCOUNTING
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education 0452 Accounting November 2014 Principal Examiner Report for Teachers
 ACCOUNTING Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education Paper 0452/11 Paper 11 Key Messages Questions can be set on any section of the syllabus and a good knowledge of all sections
ACCOUNTING Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education Paper 0452/11 Paper 11 Key Messages Questions can be set on any section of the syllabus and a good knowledge of all sections
RELATIONAL DIAGRAM OF MAIN CAPABILITIES
 Syllabus MAIN CAPABILITIES APM (P5) On successful completion of this paper, candidates should be able to: A Explain the nature and purpose of cost and management accounting PM (F5) FM (F9) B Describe costs
Syllabus MAIN CAPABILITIES APM (P5) On successful completion of this paper, candidates should be able to: A Explain the nature and purpose of cost and management accounting PM (F5) FM (F9) B Describe costs
 *7676554572* www.students-resource.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem
*7676554572* www.students-resource.com UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/33 Paper 3 Structured Questions May/June 2017 3 hours No Additional Materials are required.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/33 Paper 3 Structured Questions May/June 2017 3 hours No Additional Materials are required.
O & A Level Accounting Online Lectures By Waseem Hassan Gul
 O & A Level Accounting Online Lectures By Waseem Hassan Gul whg4gul@gmail.com : (For E. Mail & Text Chat) whg4gul : (Skype: Voice Call) 0092-333-4374592 : (Voice Call) http://whg.awardspace.com : (For
O & A Level Accounting Online Lectures By Waseem Hassan Gul whg4gul@gmail.com : (For E. Mail & Text Chat) whg4gul : (Skype: Voice Call) 0092-333-4374592 : (Voice Call) http://whg.awardspace.com : (For
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9706 ACCOUNTING
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/42 Paper 4 (Problem Solving Supplement), maximum raw mark
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/42 Paper 4 (Problem Solving Supplement), maximum raw mark
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9706 ACCOUNTING
 www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/41 Paper 4 (Problem Solving Supplement),
www.onlineexamhelp.com CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2014 series 9706 ACCOUNTING 9706/41 Paper 4 (Problem Solving Supplement),
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics) May/June 2003 Additional
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/04 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics) May/June 2003 Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/32 Paper 3 A Level Structured Questions MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 150 Published This
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/32 Paper 3 A Level Structured Questions MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 150 Published This
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Management Accounting (ASE3024)
 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Management Accounting (ASE3024) Annual Qualification Review 2013/2014 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 247 6518951 Email. internationalenquiries@pearson.com
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Management Accounting (ASE3024) Annual Qualification Review 2013/2014 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 247 6518951 Email. internationalenquiries@pearson.com
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level
 *9318495000* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/41 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics) October/November 2015
*9318495000* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level ACCOUNTING 9706/41 Paper 4 Problem Solving (Supplementary Topics) October/November 2015
Examiners commentaries 2015
 Examiners commentaries 2015 AC3091 Financial reporting Important note This commentary reflects the examination and assessment arrangements for this course in the academic year 2014 15. The format and structure
Examiners commentaries 2015 AC3091 Financial reporting Important note This commentary reflects the examination and assessment arrangements for this course in the academic year 2014 15. The format and structure
COST ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
 STUDY MATERIAL Intermediate (IPC) Course PAPER : 3 COST ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Part 1 : Cost Accounting VOLUME I BOARD OF STUDIES THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA This study
STUDY MATERIAL Intermediate (IPC) Course PAPER : 3 COST ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Part 1 : Cost Accounting VOLUME I BOARD OF STUDIES THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA This study
FOREWORD... 1 ACCOUNTING... 2
 FOREWORD... 1 ACCOUNTING... 2 GCE Advanced Level and GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level... 2 Paper 9706/01 Multiple Choice (Core)... 2 Paper 9706/02 Structured Questions... 3 Paper 9706/03 Multiple Choice (Extension)...
FOREWORD... 1 ACCOUNTING... 2 GCE Advanced Level and GCE Advanced Subsidiary Level... 2 Paper 9706/01 Multiple Choice (Core)... 2 Paper 9706/02 Structured Questions... 3 Paper 9706/03 Multiple Choice (Extension)...
LCCI International Qualifications. Accounting (IAS) Level 3. Model Answers Series (3902)
 LCCI International Qualifications Accounting (IAS) Level 3 Model Answers Series 2 2012 (3902) For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. enquiries@ediplc.com www.lcci.org.uk Accounting
LCCI International Qualifications Accounting (IAS) Level 3 Model Answers Series 2 2012 (3902) For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909 Email. enquiries@ediplc.com www.lcci.org.uk Accounting
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2010 question paper for the guidance of teachers 0452 ACCOUNTING. 0452/23 Paper 2, maximum raw mark 120
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November question paper for the guidance of teachers 0452 ACCOUNTING
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the October/November question paper for the guidance of teachers 0452 ACCOUNTING
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BUS245 COST ACCOUNTING. 3 Credit Hours. Prepared by Mary E. Baricevic April 18, 2013
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BUS245 COST ACCOUNTING 3 Credit Hours Prepared by Mary E. Baricevic April 18, 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Math, Science and Business Division Chair Ms. Shirley Davenport,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BUS245 COST ACCOUNTING 3 Credit Hours Prepared by Mary E. Baricevic April 18, 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Math, Science and Business Division Chair Ms. Shirley Davenport,
 All questions copyright of Cambridge International Examinations 1 Page 1 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper A AND AS LEVEL JUNE 2003 9706 1 Question Question Key Number Number Key 1 D 16 B 2 A 17 A 3 A 18 A 4
All questions copyright of Cambridge International Examinations 1 Page 1 Mark Scheme Syllabus Paper A AND AS LEVEL JUNE 2003 9706 1 Question Question Key Number Number Key 1 D 16 B 2 A 17 A 3 A 18 A 4
