Economic Performance Indicators - Unemployment, CPI, GDP
|
|
|
- Darcy Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supply and Demand law of demand income effect substitution effect change in quantity demanded vs. change in demand determinants of demand (TRIBE) normal vs. inferior goods supplied vs. change in supply determinants of supply (TIGERS) equilibrium surplus/shortage effects of double shifts price controls: ceiling and floors law of supply change in quantity
2 Economic Performance Indicators - Unemployment, CPI, GDP Labor Force and Unemployment who is in/excluded in the labor force LFPR and UR formulas types of unemployment -frictional, structural, cyclical underemployment discouraged workers full employment/natural rate of unemployment CPI and Inflation consumer price index and the inflation rate formulas demand-pull, cost-push, quantity theory the costs of inflation -menu, shoe leather, unit of account costs. winners and losers of unanticipated inflation nominal v s. real interest rates producer price index deflation Gross Domestic Product goods/services in/excluded in GDP nominal vs. real GDP real gdp per capita calculating GDP: income vs. expenditure approach expenditure components -consumption, investment gov ernment spending, net exports gdp deflator
3 Aggregate Supply and Demand Model, Business Cycles, Philips Curve, Classical vs. Keynesian Theory and Fiscal Policy Fluctuations in Economy Business Cycle 4 Phases: expansionary, peak, contractionary, trough Slope of AD wealth, interest-rate, netex port effects Determinants of AD changes in C, I, G, Nx Slope of SRAS sticky wages Determinants of SRAS input costs, productivity, government influence and ex pectations of inflation Slope of LRAS quantity and quality of factors of production Recessionary gap Inflationary gap Stagflation Philips Curve Slope of SR and LR Philips curve Relationship between shifts of AD/SRAS and the SR Philips curve Relationship between shifts of LRAS and LRPC Role of Government: Classical vs. Keynesian LR equilibrium according to Classical Theory For ALL LR problems, apply classical theory. Output will return to the initial level and only PL will change. Say s Law Rational Ex pectations Theory Keynesian Theory prices, wages, interest rates Three ranges of AS Automatic/Discretionary Stabilizers Expansionary/Contractionary Fiscal Policy Marginal Propensity to Consume/Save Multiplier Effect Spending and tax multiplier formulas Supply-side economics recognition, administrative, implementation lags crowding out other problems associated with fiscal policy
4 AD/AS, Fiscal Policy Practice MCQ KEY 1. D or E (if you view III as the net-export effect) 2. A 3. E 4. D 5. E 6. D 7. B 8. B 9. C 10.A 11.E 12.B 13.E 14.B 15.B 16.D 17.B 18.E 19.C 20.B 21.C 22.B 23.A
5 Money and Monetary Policy Types and Functions of Money Money supply M1 and M2 Monetary base Time value of money present and future Bond prices and interest rates (inv ersely related) The Fed and Monetary Policy Structure of the Fed Federal Open Market Com mittee Contractionary vs. Expansionary MP Tools: RRR, Discount Rate, Federal Funds Rate (Open Market Operations) Banks and Money Creation Money Multiplier Money Creation Calculate maximum amount of New loans Loans over time Dem and deposits over time T-accounts Assets and liabilities Net worth and owner s equity Money Market Graph Money demand and money supply Axis and slope Shifters Loanable Funds Demand for and Supply of Axis and slope Shifters Crowding-out effect Equat ion of Exchange Classical vs. Monetarist vs. Keynesian view of government involvement Quantity Theory of Money Money Neutrality Monetary Rule Rational Expectations Theory
6 Production Possibilities Curve/Frontier Slope and shifters Allocative/Productive Efficiency Increasing/Constant Opportunity Costs Absolute/Comparative Advantage Specialization and Terms of Trade Capital vs Consumer Goods Int ernational Trade International Trade and Forex Market Protectionism Policies and their effects Balance of Trade vs. Balance of Payments Current vs. Capital Account Current Account + Capital Account = 0 FOREX Graph Slopes and Shifters Capital Inflow/Outflow and the Loanable Funds Market Appreciation vs. Depreciation Effect of Appreciation/Deprecation on Export and Imports and AD (PL and Q) Fixed/Pegged Exchange Rates Gov t Intervention buy/sell currency, adjust interest rates, trade controls Nominal vs. Real Exchange Rates Theory of Purchasing Power Parity Economic Systems 3 Basic Economic Questions Factors of Production Market vs. Com mand Econom ies Economic Growth PPC and LRAS shifters Real GDP/capita
AP Macroeconomics review. By: Maria Villasmil. Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity.
 AP Macroeconomics review By: Maria Villasmil Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity. Factors of Production: 1)Land: natural resources 2) Labor:
AP Macroeconomics review By: Maria Villasmil Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity. Factors of Production: 1)Land: natural resources 2) Labor:
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP MACROECONOMICS-2018 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/21 st (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/20 th (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP MACROECONOMICS-2018 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/21 st (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/20 th (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
Name Date Per. Part 1: Aggregate Demand
 Name Date Per Part 1: Aggregate Demand 1. Aggregate means. When we use aggregates, we combine. Aggregate Demand is all the goods and services ( ) that buyers are willing and able to purchase at different
Name Date Per Part 1: Aggregate Demand 1. Aggregate means. When we use aggregates, we combine. Aggregate Demand is all the goods and services ( ) that buyers are willing and able to purchase at different
Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics
 Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics Instructional Philosophy The Advanced Placement Macroeconomics curriculum is a full year program designed to provide both an overview of economics. Economics
Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics Instructional Philosophy The Advanced Placement Macroeconomics curriculum is a full year program designed to provide both an overview of economics. Economics
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP MACROECONOMICS-2017 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/22 nd (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/21 st (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP MACROECONOMICS-2017 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/22 nd (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/21 st (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
Unit 3 Exam Review. Formulas to Know: Output gap = YA YP/YP (x 100) MPC = Consumption/ Yd. MPS = Savings/ Yd
 Unit 3 Exam Review Income and Expenditure 1. Explain relationship between MPC and the multiplier. Direct relationship, the higher the MPC, the greater the multiplier. 2. Understand the concept of autonomous
Unit 3 Exam Review Income and Expenditure 1. Explain relationship between MPC and the multiplier. Direct relationship, the higher the MPC, the greater the multiplier. 2. Understand the concept of autonomous
Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply
 Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply 1 Aggregate Demand AD = C + I + G + NX The sum of planned consumption, investment, government, and net exports expenditures on final goods and services 2 Aggregate Demand
Aggregate Demand & Aggregate Supply 1 Aggregate Demand AD = C + I + G + NX The sum of planned consumption, investment, government, and net exports expenditures on final goods and services 2 Aggregate Demand
Eco202 Review, April 2011, Prof. Bill Even. I. Introduction. A. The causes of the great recession B. Government responses to great recession
 Eco202 Review, April 2011, Prof. Bill Even I. Introduction. A. The causes of the great recession B. Government responses to great recession II. III. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth A. Definition
Eco202 Review, April 2011, Prof. Bill Even I. Introduction. A. The causes of the great recession B. Government responses to great recession II. III. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth A. Definition
Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts
 Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts Key Terms- Define the following: 3 Economic Systems 1. Scarcity 1. Centrally Planned Economies Individuals, businesses, and governments have Economic system
Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts Key Terms- Define the following: 3 Economic Systems 1. Scarcity 1. Centrally Planned Economies Individuals, businesses, and governments have Economic system
2.2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply
 The business cycle Short-term fluctuations and long-term trend Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the
The business cycle Short-term fluctuations and long-term trend Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the
INDIAN HILL EXEMPTED VILLAGE SCHOOL DISTRICT Social Studies Curriculum - May 2009 AP Economics
 Course Description: This full-year college-level course begins with basic economic concepts and proceeds to examine both microeconomics and macroeconomics in greater detail. There are five units which
Course Description: This full-year college-level course begins with basic economic concepts and proceeds to examine both microeconomics and macroeconomics in greater detail. There are five units which
Eco202 Review, April 2013, Prof. Bill Even. I. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth
 Eco202 Review, April 2013, Prof. Bill Even I. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth A. Definition of GDP B. Measuring GDP 1. Expenditure side a) C+I+G+NX b) Definition of each component 2. Income
Eco202 Review, April 2013, Prof. Bill Even I. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth A. Definition of GDP B. Measuring GDP 1. Expenditure side a) C+I+G+NX b) Definition of each component 2. Income
Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand ECO 301: Money and Banking 1 1.1 Goals Goals Specific Goals Be able to explain GDP fluctuations when the price level is also flexible. Explain how real GDP and the
Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand ECO 301: Money and Banking 1 1.1 Goals Goals Specific Goals Be able to explain GDP fluctuations when the price level is also flexible. Explain how real GDP and the
AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition
 AP Macroeconomics Mrs. Cook 1 st Period Room 210 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition Unit One: Basic Economic
AP Macroeconomics Mrs. Cook 1 st Period Room 210 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition Unit One: Basic Economic
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.
![Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.](/thumbs/77/76534172.jpg) Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Name Date Per Part 1: Aggregate Demand
 Name Date Per Part 1: Aggregate Demand 1. Aggregate means. When we use aggregates, we combine. Aggregate Demand is all the goods and services ( ) that buyers are willing and able to purchase at different
Name Date Per Part 1: Aggregate Demand 1. Aggregate means. When we use aggregates, we combine. Aggregate Demand is all the goods and services ( ) that buyers are willing and able to purchase at different
AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers
 AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve
AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve
Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy
 Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Aggregate Demand 2 What is Aggregate Demand? Aggregate means added all together. When we use aggregates we combine all prices and all quantities.
Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Aggregate Demand 2 What is Aggregate Demand? Aggregate means added all together. When we use aggregates we combine all prices and all quantities.
ECNS Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity
 ECNS 202 -- Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity Mark the answer on the provided scantron sheet using a #2 lead pencil. Erase completely. I am not responsible for poorly marked or poorly erased asnwers.
ECNS 202 -- Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity Mark the answer on the provided scantron sheet using a #2 lead pencil. Erase completely. I am not responsible for poorly marked or poorly erased asnwers.
AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview
 AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve requirement).
AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve requirement).
Economics 102 Discussion Handout Week 14 Spring Aggregate Supply and Demand: Summary
 Economics 102 Discussion Handout Week 14 Spring 2018 Aggregate Supply and Demand: Summary The Aggregate Demand Curve The aggregate demand curve (AD) shows the relationship between the aggregate price level
Economics 102 Discussion Handout Week 14 Spring 2018 Aggregate Supply and Demand: Summary The Aggregate Demand Curve The aggregate demand curve (AD) shows the relationship between the aggregate price level
Monetary Policy Tools?
 EQ: What is the Federal Reserve System? In the U.S., the Federal Reserve System was established in 1913 to discharge the function of a central bank and provide a strengthened framework of regulatory control
EQ: What is the Federal Reserve System? In the U.S., the Federal Reserve System was established in 1913 to discharge the function of a central bank and provide a strengthened framework of regulatory control
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 2
 Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 2 Concept / Topic To Teach: Specific Objectives: Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Unit 3 Module 16 INCOME AND EXPENDITURES Comprehend the nature
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 2 Concept / Topic To Teach: Specific Objectives: Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Unit 3 Module 16 INCOME AND EXPENDITURES Comprehend the nature
3. Explain what the APS tells us about people s spending and saving habits.
 National Income and Price Determination Reading Guide Chapters 9, 10 and 11 Chapter 9: Building the Aggregate Expenditures Model Objective... 1. Explain how the consumption schedule helps us find equilibrium
National Income and Price Determination Reading Guide Chapters 9, 10 and 11 Chapter 9: Building the Aggregate Expenditures Model Objective... 1. Explain how the consumption schedule helps us find equilibrium
Aggregate Demand I, II March 22-31
 March 22-31 The Keynesian Cross Y=C(Y-T)+I+G with I, T, and G fixed Government-purchases multiplier Y/ G (if interest rate is fixed) Tax multiplier Y/ T (if interest rate is fixed) Marginal propensity
March 22-31 The Keynesian Cross Y=C(Y-T)+I+G with I, T, and G fixed Government-purchases multiplier Y/ G (if interest rate is fixed) Tax multiplier Y/ T (if interest rate is fixed) Marginal propensity
All the graphs (and some other stuff) you need to know for Macro
 All the graphs (and some other stuff) you need to know for Macro IGNORE THE LAFFER CURVE! Correctly drawing and labeling graphs is critical in answering the free response questions (FRQs). For an interactive
All the graphs (and some other stuff) you need to know for Macro IGNORE THE LAFFER CURVE! Correctly drawing and labeling graphs is critical in answering the free response questions (FRQs). For an interactive
Practice Problems 30-32
 Practice Problems 30-32 1. The budget balance is calculated as: A. T G TR B. T + G TR C. T G + TR D. T + G + TR E. TR T G 2. The government budget balance equals: A. Taxes + Government purchases + Government
Practice Problems 30-32 1. The budget balance is calculated as: A. T G TR B. T + G TR C. T G + TR D. T + G + TR E. TR T G 2. The government budget balance equals: A. Taxes + Government purchases + Government
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to Exam #3. Section A: Multiple Choice Questions. (30 points; 2 pts each)
 ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to Exam #3 Section A: Multiple Choice Questions. (30 points; 2 pts each) #1. In an open economy where government spending was $30 billion, consumption was
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to Exam #3 Section A: Multiple Choice Questions. (30 points; 2 pts each) #1. In an open economy where government spending was $30 billion, consumption was
EQ: What happens to equilibrium price and quantity when there is a change in supply or demand?
 EQ: What happens to equilibrium price and quantity when there is a change in supply or demand? The main thing that affects Supply is production costs. Costs of factors of production affect supply: Employee
EQ: What happens to equilibrium price and quantity when there is a change in supply or demand? The main thing that affects Supply is production costs. Costs of factors of production affect supply: Employee
Module 4: Applications of Supply and Demand
 The following list shows a summary of the topics covered in the macroeconomics course. Module 1: Economic Thinking Understanding Economics and Scarcity The Concept of Opportunity Cost Labor, Markets, and
The following list shows a summary of the topics covered in the macroeconomics course. Module 1: Economic Thinking Understanding Economics and Scarcity The Concept of Opportunity Cost Labor, Markets, and
Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy
 Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Demand and Supply Review 1. Define Demand and the Law of Demand. 2. Identify the three concepts that explain why demand is downward sloping. 3. Identify
Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Demand and Supply Review 1. Define Demand and the Law of Demand. 2. Identify the three concepts that explain why demand is downward sloping. 3. Identify
Econ 102 Discussion Section 8 (Chapter 12, 13) March 20, 2015
 Econ 102 Discussion Section 8 (Chapter 12, 13) March 20, 2015 The Multiplier and Shifting the Aggregate Expenditures Function The multiplier effect describes how changes in autonomous expenditures lead
Econ 102 Discussion Section 8 (Chapter 12, 13) March 20, 2015 The Multiplier and Shifting the Aggregate Expenditures Function The multiplier effect describes how changes in autonomous expenditures lead
Disposable income (in billions)
 Section 4 version 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An increase in the MPC: A. increases the multiplier. B. shifts the autonomous investment
Section 4 version 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An increase in the MPC: A. increases the multiplier. B. shifts the autonomous investment
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Mr. Jonker Room 212
 Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Mr. Jonker Room 212 Phone Number/Voice Mail: 231-348-2144 Conference Period: 1 st Hour Website: http://www.petoskeyschools.org/jonker.zp.t/ Twitter: http://twitter.com/ap_economics
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Mr. Jonker Room 212 Phone Number/Voice Mail: 231-348-2144 Conference Period: 1 st Hour Website: http://www.petoskeyschools.org/jonker.zp.t/ Twitter: http://twitter.com/ap_economics
Introduction to Economic Fluctuations
 Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations slide 0 In this chapter, you will learn facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an
Chapter 9 Introduction to Economic Fluctuations slide 0 In this chapter, you will learn facts about the business cycle how the short run differs from the long run an introduction to aggregate demand an
Aggregate Supply and Demand Model
 THE AGGREGATE MODEL Aggregate Supply and Demand Model The AS-AD model helps us understand aggregate output (RGDP), employment, prices and the business cycle. Aggregate Demand shows the quantity of goods
THE AGGREGATE MODEL Aggregate Supply and Demand Model The AS-AD model helps us understand aggregate output (RGDP), employment, prices and the business cycle. Aggregate Demand shows the quantity of goods
graphing ad & as 25 Points Total
 graphing ad & as 25 Points Total 2 Points Each (1 pt. for the graph, 1 pt. for the results) 1. AD increases (shifts right), consumer spending, inflationary gap 2. AS decreases (shifts left), government
graphing ad & as 25 Points Total 2 Points Each (1 pt. for the graph, 1 pt. for the results) 1. AD increases (shifts right), consumer spending, inflationary gap 2. AS decreases (shifts left), government
ECON Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory
 ECON 3510 - Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory Fall 2015 Mankiw, Macroeconomics, 8th ed., Chapter 12 Chapter 12: Aggregate Demand 2: Applying the IS-LM Model Key points: Policy in the IS LM model: Monetary
ECON 3510 - Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory Fall 2015 Mankiw, Macroeconomics, 8th ed., Chapter 12 Chapter 12: Aggregate Demand 2: Applying the IS-LM Model Key points: Policy in the IS LM model: Monetary
Archimedean Upper Conservatory Economics, November 2016 Quiz, Unit VI, Stabilization Policies
 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The federal budget tends to move toward _ as the economy. A. deficit; contracts B. deficit; expands C.
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The federal budget tends to move toward _ as the economy. A. deficit; contracts B. deficit; expands C.
Economics 102 Discussion Handout Week 14 Spring Aggregate Supply and Demand: Summary
 Economics 102 Discussion Handout Week 14 Spring 2018 Aggregate Supply and Demand: Summary The Aggregate Demand Curve The aggregate demand curve (AD) shows the relationship between the aggregate price level
Economics 102 Discussion Handout Week 14 Spring 2018 Aggregate Supply and Demand: Summary The Aggregate Demand Curve The aggregate demand curve (AD) shows the relationship between the aggregate price level
Archimedean Upper Conservatory Economics, October 2016
 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to: A. the proportion of consumer spending as a function of
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to: A. the proportion of consumer spending as a function of
Webnote 228. Aggregate demand (AD) U-tube. Item hl sl Must Know Must know very well! Here are the details of what you need to know.
 Webnote 228 2.2 Aggregate demand and Big Questions: 1. What factors cause changes (shifts + movements) in AS and AD? 2. What can the AS/AD model show in the macro economy?. Draw + explain the 2 schools
Webnote 228 2.2 Aggregate demand and Big Questions: 1. What factors cause changes (shifts + movements) in AS and AD? 2. What can the AS/AD model show in the macro economy?. Draw + explain the 2 schools
AP Econ Practice Test Unit 5
 DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST! AP Econ Practice Test Unit 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to:
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST! AP Econ Practice Test Unit 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to:
Unemployment Inflation
 See webnotes: 235 236 237 238 2.3 Big Ideas Unemployment Inflation Read the syllabus items to understand the IB focus for this economic theory! Growth Distribution Big Idea Big Idea Big Idea Big Idea Big
See webnotes: 235 236 237 238 2.3 Big Ideas Unemployment Inflation Read the syllabus items to understand the IB focus for this economic theory! Growth Distribution Big Idea Big Idea Big Idea Big Idea Big
Consumption expenditure The five most important variables that determine the level of consumption are:
 The aggregate expenditure model: A macroeconomic model that focuses on the relationship between total spending and real GDP, assuming the price level is constant. Macroeconomic equilibrium: AE = GDP Consumption
The aggregate expenditure model: A macroeconomic model that focuses on the relationship between total spending and real GDP, assuming the price level is constant. Macroeconomic equilibrium: AE = GDP Consumption
4: AGGREGATE D/S & FISCAL POLICY
 4: AGGREGATE D/S & FISCAL POLICY VOCABULARY (with some additional terms) Aggregate Demand curve that shows the amounts of real output that buyers collectively desire to purchase at each possible price
4: AGGREGATE D/S & FISCAL POLICY VOCABULARY (with some additional terms) Aggregate Demand curve that shows the amounts of real output that buyers collectively desire to purchase at each possible price
AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016
 AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016 Ms. Huynh ( Win ), Room 126 Phone: (626) 441-5820 Ext 2126 Email: Thuynh@spusd.net Curricular Overview This semester long course will introduce students to the principles
AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016 Ms. Huynh ( Win ), Room 126 Phone: (626) 441-5820 Ext 2126 Email: Thuynh@spusd.net Curricular Overview This semester long course will introduce students to the principles
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam
 ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam Section A: Multiple Choice Questions. (120 points; 3 pts each) #1. The opportunity cost of something is: a) greater during periods of
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to the Final Exam Section A: Multiple Choice Questions. (120 points; 3 pts each) #1. The opportunity cost of something is: a) greater during periods of
Buchholz, Todd. New Ideas From Dead Economists. New York: Plame, 1999
 AP MACROECONOMICS COURSE SYLLABUS AP Macroeconomics is a one semester college level course. The AP Macroeconomics course is designed as an initial college level course in macroeconomics and as a foundation
AP MACROECONOMICS COURSE SYLLABUS AP Macroeconomics is a one semester college level course. The AP Macroeconomics course is designed as an initial college level course in macroeconomics and as a foundation
III. 9. IS LM: the basic framework to understand macro policy continued Text, ch 11
 Objectives: To apply IS-LM analysis to understand the causes of short-run fluctuations in real GDP and the short-run impact of monetary and fiscal policies on the economy. To use the IS-LM model to analyse
Objectives: To apply IS-LM analysis to understand the causes of short-run fluctuations in real GDP and the short-run impact of monetary and fiscal policies on the economy. To use the IS-LM model to analyse
4. (Figure: Monetary Policy 1) If the money market is initially at E 2 and the central bank chooses
 Name: Date: Use the following to answer questions 1-6. Figure: Monetary Policy 1 1. (Figure: Monetary Policy 1) If the money market is initially at E 1 and the central bank chooses to sell bonds, then:
Name: Date: Use the following to answer questions 1-6. Figure: Monetary Policy 1 1. (Figure: Monetary Policy 1) If the money market is initially at E 1 and the central bank chooses to sell bonds, then:
Velocity of Money and the Equation of Exchange
 Velocity of Money and the Equation of Exchange Velocity of Money the rate at which the dollar travels around the economy from consumer to consumer. measures the economic activity of a nation V = P x Y
Velocity of Money and the Equation of Exchange Velocity of Money the rate at which the dollar travels around the economy from consumer to consumer. measures the economic activity of a nation V = P x Y
Disputes In Macroeconomics
 No G G & T 3-5% Monetary Rule Expectations negate fiscal and monetary Policy. Adam Smith John M. Keynes Milton Friedman Classicals Keynesians Monetarists Robert Lucas Get the G off of our backs. Ronald
No G G & T 3-5% Monetary Rule Expectations negate fiscal and monetary Policy. Adam Smith John M. Keynes Milton Friedman Classicals Keynesians Monetarists Robert Lucas Get the G off of our backs. Ronald
Aggregate Supply and Demand Model
 THE AGGREGATE MODEL Aggregate Supply and Demand Model The AS-AD model helps us understand aggregate output (RGDP), employment, prices and the business cycle. Aggregate Demand shows the quantity of goods
THE AGGREGATE MODEL Aggregate Supply and Demand Model The AS-AD model helps us understand aggregate output (RGDP), employment, prices and the business cycle. Aggregate Demand shows the quantity of goods
Macroeconomics Study Sheet
 Macroeconomics Study Sheet MACROECONOMICS Macroeconomics studies the determination of economic aggregates. Output tends to rise in the long run (longterm economic growth), but fluctuates in the short run
Macroeconomics Study Sheet MACROECONOMICS Macroeconomics studies the determination of economic aggregates. Output tends to rise in the long run (longterm economic growth), but fluctuates in the short run
Principles of Macroeconomics
 Principles of Macroeconomics 978-1-63545-094-1 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Senior Contributing Authors:
Principles of Macroeconomics 978-1-63545-094-1 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Senior Contributing Authors:
READ CAREFULLY Failure to read has been a problem on the exams
 Introduction to Agricultural Economics Agricultural Economics 105 Fall 2009 Third Hour Exam Version 1 READ CAREFULLY Failure to read has been a problem on the exams Name Section -3 points for wrong section
Introduction to Agricultural Economics Agricultural Economics 105 Fall 2009 Third Hour Exam Version 1 READ CAREFULLY Failure to read has been a problem on the exams Name Section -3 points for wrong section
Everyone Loves Econ Notes
 Unit 1: Economic Fundamentals Everyone Loves Econ Notes Scarcity - the lack of resources for our unlimited wants. Ceteris Paribus Economists hold factors constant, except for what s being considered Goods
Unit 1: Economic Fundamentals Everyone Loves Econ Notes Scarcity - the lack of resources for our unlimited wants. Ceteris Paribus Economists hold factors constant, except for what s being considered Goods
Assumptions of the Classical Model
 Meridian Notes By Tim Qi, Amy Young, Willy Zhang Economics AP Unit 4: Keynes, the Multiplier, and Fiscal Policy Covers Ch 11-13 Classical and Keynesian Macro Analysis The Classic Model the old economic
Meridian Notes By Tim Qi, Amy Young, Willy Zhang Economics AP Unit 4: Keynes, the Multiplier, and Fiscal Policy Covers Ch 11-13 Classical and Keynesian Macro Analysis The Classic Model the old economic
Textbook Media Press. CH 27 Taylor: Principles of Economics 3e 1
 CH 27 Taylor: Principles of Economics 3e 1 The Building Blocks of Keynesian Analysis Keynesian economics is based on two main ideas: a) aggregate demand is more likely than aggregate supply to be the primary
CH 27 Taylor: Principles of Economics 3e 1 The Building Blocks of Keynesian Analysis Keynesian economics is based on two main ideas: a) aggregate demand is more likely than aggregate supply to be the primary
EQ: What are the Assumptions of Keynesian Economic Theory?
 EQ: How is Keynesian Theory Different from Classical Theory? Classical Theory Supply-Focused (SRAS) Say s Law Economy is self-regulating Laissez-Faire Wages can go up or down Businesses will borrow & invest
EQ: How is Keynesian Theory Different from Classical Theory? Classical Theory Supply-Focused (SRAS) Say s Law Economy is self-regulating Laissez-Faire Wages can go up or down Businesses will borrow & invest
Revision Sheets. AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context. Revision Sheets
 2018 http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/150000/velka/uk-map.jpg AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context Macroeconomic Objectives Low unemployment Improve external performance Objectives
2018 http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/150000/velka/uk-map.jpg AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context Macroeconomic Objectives Low unemployment Improve external performance Objectives
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics
 Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Introduction Welcome to AP Macroeconomics! This is a challenging course; taught at the college level, this course requires that you operate at a level higher than what
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Introduction Welcome to AP Macroeconomics! This is a challenging course; taught at the college level, this course requires that you operate at a level higher than what
Expansionary Fiscal Policy 2. If the economy is experiencing a recession what type of fiscal policy would be in order?
 Stabilization Policies Reading Guide Chapters 12, 16, and 18 Chapter 12: Fiscal Policy 1. Assess the effect of fiscal policy on real output, price level, and the level of employment in the long run and
Stabilization Policies Reading Guide Chapters 12, 16, and 18 Chapter 12: Fiscal Policy 1. Assess the effect of fiscal policy on real output, price level, and the level of employment in the long run and
A. Regular attendance is crucial to success in this class. Poor attendance will harm your participation grade. Grade categories are as follows:
 AP Macroeconomics JOHNSON Spring 11 AP Macroeconomics is a one-semester, college-level course. Each student is expected to take the AP Macroeconomics Exam that is administered in May. Successful achievement
AP Macroeconomics JOHNSON Spring 11 AP Macroeconomics is a one-semester, college-level course. Each student is expected to take the AP Macroeconomics Exam that is administered in May. Successful achievement
SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ February 2012
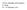 SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 13 17 February 2012 SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 14 February 2012 Key terms / chapter 23: Aggregate demand Wealth effects Interest rate effects Exchange
SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 13 17 February 2012 SV151, Principles of Economics K. Christ 14 February 2012 Key terms / chapter 23: Aggregate demand Wealth effects Interest rate effects Exchange
Discussion Handout 7 7/12/2016 TA: Anton Babkin
 Aggregate Supply and Demand: Summary The Aggregate Demand Curve The aggregate demand curve (AD) shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output demanded by
Aggregate Supply and Demand: Summary The Aggregate Demand Curve The aggregate demand curve (AD) shows the relationship between the aggregate price level and the quantity of aggregate output demanded by
14 MONETARY POLICY Part 2
 14 MONETARY POLICY Part 2 The Conduct of Monetary Policy The Fed s Decision-Making Strategy The decision to change the target Federal Funds rate begins with an assessment of the current state of the economy.
14 MONETARY POLICY Part 2 The Conduct of Monetary Policy The Fed s Decision-Making Strategy The decision to change the target Federal Funds rate begins with an assessment of the current state of the economy.
Answers and Explanations
 Answers and Explanations 1. The correct answer is (E). A change in the composition of output causes a movement along the production possibilities curve. A shift in the curve is caused by changes in technology,
Answers and Explanations 1. The correct answer is (E). A change in the composition of output causes a movement along the production possibilities curve. A shift in the curve is caused by changes in technology,
Basic Concepts. MICROECONOMICS: deals with specific economic units and a detailed consideration of these individual units.
 Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
Review Session: ECON220F/G Introductory Macroeconomics
 Review Session: ECON220F/G Introductory Macroeconomics Yulei Luo SEF of HKU April 25, 2016 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON1220F/G April 25, 2016 1 / 13 The Structure of Macroeconomics Key Macroeconomic Variables:
Review Session: ECON220F/G Introductory Macroeconomics Yulei Luo SEF of HKU April 25, 2016 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON1220F/G April 25, 2016 1 / 13 The Structure of Macroeconomics Key Macroeconomic Variables:
AP Macro: Economic Models and Graphs Study Guide. Economic Conditions. Price Level. LRAS SRAS Price Level. Y F Y 1 Real GDP
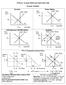 AP Macro: Economic Models and Graphs Study Guide Economic Conditions Recession LRAS SRAS Serious Inflation LRAS SRAS AD AD Y 1 Y F Real GDP Y F Y 1 Real GDP Full Employment with Mild Inflation LRAS SRAS
AP Macro: Economic Models and Graphs Study Guide Economic Conditions Recession LRAS SRAS Serious Inflation LRAS SRAS AD AD Y 1 Y F Real GDP Y F Y 1 Real GDP Full Employment with Mild Inflation LRAS SRAS
Final Exam. ECON 010, Fall /19/12
 Final Exam ECON 010, Fall 2012 12/19/12 Total Score NAME: Recitation Section/ Time: INSTRUCTIONS Please put your name on all pages. There are 4 parts. There are 100 total points. Plan your time accordingly.
Final Exam ECON 010, Fall 2012 12/19/12 Total Score NAME: Recitation Section/ Time: INSTRUCTIONS Please put your name on all pages. There are 4 parts. There are 100 total points. Plan your time accordingly.
The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy on Aggregate Demand. Lecture
 The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy on Aggregate Demand Lecture 10 28.4.2015 Previous Lecture Short Run Economic Fluctuations Short Run vs. Long Run The classical dichotomy and monetary neutrality
The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy on Aggregate Demand Lecture 10 28.4.2015 Previous Lecture Short Run Economic Fluctuations Short Run vs. Long Run The classical dichotomy and monetary neutrality
The Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model
 CHAPTER 27 The Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model The Theory of Economics... is a method rather than a doctrine, an apparatus of the mind, a technique of thinking which helps its possessor to draw
CHAPTER 27 The Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply Model The Theory of Economics... is a method rather than a doctrine, an apparatus of the mind, a technique of thinking which helps its possessor to draw
AP Macroeconomics. Scoring Guidelines
 2018 AP Macroeconomics Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online
2018 AP Macroeconomics Scoring Guidelines College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP, AP Central, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. AP Central is the official online
!&Z -** -. oremacroeconorracs. Gerald W. Stone Metropolitan State College of Denver. Worth Publishers
 V -** -.!&Z oremacroeconorracs 1 Gerald W. Stone Metropolitan State College of Denver Worth Publishers BRIEF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 Exploring Economics 1 CHAPTEFL2 j Production, Economic Growth, and Trade
V -** -.!&Z oremacroeconorracs 1 Gerald W. Stone Metropolitan State College of Denver Worth Publishers BRIEF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 Exploring Economics 1 CHAPTEFL2 j Production, Economic Growth, and Trade
QUICK REVISION. CFA level 1
 ECONOMICS QUICK REVISION NOTES CFA level 1 Edited By Sam Economics Keynes: Sticky prices, so if Demand falls, Supply will fall, and employment falls Expenditures GDP: Consumer Spending, Private Investment,
ECONOMICS QUICK REVISION NOTES CFA level 1 Edited By Sam Economics Keynes: Sticky prices, so if Demand falls, Supply will fall, and employment falls Expenditures GDP: Consumer Spending, Private Investment,
Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION
 Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION Ch 26: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply Purpose of aggregate supply: aggregate demand model is to explain
Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION Ch 26: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply Purpose of aggregate supply: aggregate demand model is to explain
Lecture 22. Aggregate demand and aggregate supply
 Lecture 22 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply By the end of this lecture, you should understand: three key facts about short-run economic fluctuations how the economy in the short run differs from the
Lecture 22 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply By the end of this lecture, you should understand: three key facts about short-run economic fluctuations how the economy in the short run differs from the
Inflation and the Phillips Curve
 CHAPTER 33 Inflation and the Phillips Curve The first few months or years of inflation, like the first few drinks, seem just fine. Everyone has more money to spend and prices aren t rising quite as fast
CHAPTER 33 Inflation and the Phillips Curve The first few months or years of inflation, like the first few drinks, seem just fine. Everyone has more money to spend and prices aren t rising quite as fast
AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus
 Contact Information AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus Teacher: Edmund Ned Maino Email: emaino@teh.k12.ca.us (I check email until 5pm, Monday-Friday) Phone: 661-822-2130 ext. 1701 (Please call between
Contact Information AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus Teacher: Edmund Ned Maino Email: emaino@teh.k12.ca.us (I check email until 5pm, Monday-Friday) Phone: 661-822-2130 ext. 1701 (Please call between
HCCS 2011 REVIEW FOR TEST II Covering chapters from Case, Fair, Oster text. GDP and the Standard of Living
 HCCS 2011 REVIEW FOR TEST II Covering chapters 20 -- 24 from Case, Fair, Oster text GDP and the Standard of Living What is Gross Domestic Product and how is it measured? Expenditure Approach (C+I+G+NX)
HCCS 2011 REVIEW FOR TEST II Covering chapters 20 -- 24 from Case, Fair, Oster text GDP and the Standard of Living What is Gross Domestic Product and how is it measured? Expenditure Approach (C+I+G+NX)
Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403
 Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403 http//vustudents.ning.com Actual budget The amount spent by the Federal government (to purchase goods and services and for transfer payments) less the amount of tax
Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403 http//vustudents.ning.com Actual budget The amount spent by the Federal government (to purchase goods and services and for transfer payments) less the amount of tax
ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS
 ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Instructor: James J. Sostack Jr. Department: Social Studies Length of Course: Full Year (A/B Block format) Weight 1.20 Grade Level
ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Instructor: James J. Sostack Jr. Department: Social Studies Length of Course: Full Year (A/B Block format) Weight 1.20 Grade Level
AS-AD Model. Prof. Irina A. Telyukova UBC Economics 345 Fall 2008
 AS-AD Model Prof. Irina A. Telyukova UBC Economics 345 Fall 2008 Outline Now that we know how to model money supply and money demand, we take a quick look at one model of the aggregate economy. Aggregate
AS-AD Model Prof. Irina A. Telyukova UBC Economics 345 Fall 2008 Outline Now that we know how to model money supply and money demand, we take a quick look at one model of the aggregate economy. Aggregate
LECTURE 18. AS/AD in demand-deficient Ireland: Unemployment and Deflation
 LECTURE 18 AS/AD in demand-deficient Ireland: Unemployment and Deflation THE AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE Aggregate supply curve Each possible price level Quantity of goods & services All nation s businesses
LECTURE 18 AS/AD in demand-deficient Ireland: Unemployment and Deflation THE AGGREGATE SUPPLY CURVE Aggregate supply curve Each possible price level Quantity of goods & services All nation s businesses
Lecture 12: Economic Fluctuations. Rob Godby University of Wyoming
 Lecture 12: Economic Fluctuations Rob Godby University of Wyoming Short-Run Economic Fluctuations Economic activity fluctuates from year to year. In some years, the production of goods and services rises.
Lecture 12: Economic Fluctuations Rob Godby University of Wyoming Short-Run Economic Fluctuations Economic activity fluctuates from year to year. In some years, the production of goods and services rises.
Unit 3.3 Macroeconomic Models Unit Overview
 Unit 3.3 Unit Overview 3.3 Macroeconomic models Aggregate demand - components Aggregate supply >>short-run >>long-run (Keynesian versus neo-classical approach) Full employment level of national income
Unit 3.3 Unit Overview 3.3 Macroeconomic models Aggregate demand - components Aggregate supply >>short-run >>long-run (Keynesian versus neo-classical approach) Full employment level of national income
AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas
 AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas 1. Rule of 70: Used to determine how many years it takes for a value to double, given a particular annual growth rate. For example, if you put $20,000
AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas 1. Rule of 70: Used to determine how many years it takes for a value to double, given a particular annual growth rate. For example, if you put $20,000
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
 Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply The Learning Objectives in this presentation are covered in Chapter 20: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply The Learning Objectives in this presentation are covered in Chapter 20: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Putting AD and AS together to get Equilibrium Price Level and Output. Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy
 1 Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Shifters of Aggregate Demand = C + I + G + X Change in Consumer Spending Change in Investment Spending Change in Government Spending Net EXport
1 Unit 3: Aggregate Demand and Supply and Fiscal Policy 1 Shifters of Aggregate Demand = C + I + G + X Change in Consumer Spending Change in Investment Spending Change in Government Spending Net EXport
Review Session: ECON1002 Introduction to Economics II
 Review Session: ECON1002 Introduction to Economics II Yulei Luo SEF of HKU April 26, 2012 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON1002 April 26, 2012 1 / 12 The Structure of Macroeconomics Key Macroeconomic Variables:
Review Session: ECON1002 Introduction to Economics II Yulei Luo SEF of HKU April 26, 2012 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON1002 April 26, 2012 1 / 12 The Structure of Macroeconomics Key Macroeconomic Variables:
AGEC 105 Test 3 Spring 2013
 AGEC 105 Test 3 Spring 2013 Name There is only ONE correct answer per multiple choice question. Please put your answer on the attached sheet. DO NOT RIP THE ANSWER SHEET FROM THE TEST. 1. Assume a producer
AGEC 105 Test 3 Spring 2013 Name There is only ONE correct answer per multiple choice question. Please put your answer on the attached sheet. DO NOT RIP THE ANSWER SHEET FROM THE TEST. 1. Assume a producer
Econ 102 Exam 2 Name ID Section Number
 Econ 102 Exam 2 Name ID Section Number 1. In a closed economy government spending was $30 billion, consumption was $70 billion, taxes were $20 billion, and GDP was $110 billion this year. Investment spending
Econ 102 Exam 2 Name ID Section Number 1. In a closed economy government spending was $30 billion, consumption was $70 billion, taxes were $20 billion, and GDP was $110 billion this year. Investment spending
Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory / Macroeconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Midterm Exam (Answers)
 Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory / Macroeconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Midterm Exam (Answers) Part A (15 points) State whether you think each of the following questions is true (T), false (F), or
Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory / Macroeconomic Analysis (ECON 3560/5040) Midterm Exam (Answers) Part A (15 points) State whether you think each of the following questions is true (T), false (F), or
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam
 ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 2 pts each) #1. Which of the following is a stock variable? a) wealth b) consumption c) investment d) income #2.
ECON 3010 Intermediate Macroeconomics Final Exam Multiple Choice Questions. (60 points; 2 pts each) #1. Which of the following is a stock variable? a) wealth b) consumption c) investment d) income #2.
Macroeconomics CHAPTER 10. Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
 Macroeconomics CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand What you will learn in this chapter: How the aggregate supply curve illustrates the relationship between the aggregate price level and the
Macroeconomics CHAPTER 10 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand What you will learn in this chapter: How the aggregate supply curve illustrates the relationship between the aggregate price level and the
PART ONE INTRODUCTION
 CONTENTS Chapter-1 The Nature and Scope of Macroeconomics Nature of Macroeconomic Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Dependence of Microeconomic Theory on Macroeconomics Dependence of
CONTENTS Chapter-1 The Nature and Scope of Macroeconomics Nature of Macroeconomic Difference Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Dependence of Microeconomic Theory on Macroeconomics Dependence of
Chapter 9 Chapter 10
 Assignment 4 Last Name First Name Chapter 9 Chapter 10 1 a b c d 1 a b c d 2 a b c d 2 a b c d 3 a b c d 3 a b c d 4 a b c d 4 a b c d 5 a b c d 5 a b c d 6 a b c d 6 a b c d 7 a b c d 7 a b c d 8 a b
Assignment 4 Last Name First Name Chapter 9 Chapter 10 1 a b c d 1 a b c d 2 a b c d 2 a b c d 3 a b c d 3 a b c d 4 a b c d 4 a b c d 5 a b c d 5 a b c d 6 a b c d 6 a b c d 7 a b c d 7 a b c d 8 a b
