Iranian Journal of Economic Studies. The Welfare Effects of Rising Imported Food Prices in Iran
|
|
|
- Candice Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes Journal homepage: es.shrazu.ac.r The Welfare Effects of Rsng Imported Food Prces n Iran Zakarya Farazadeh, Abdoulkarm Esmael Department of Agrcultural Economcs, Shraz Unversty, Shraz, Iran. Artcle Hstory Receved date: 20 Aprl 2017 Revsed date: 6 November 2017 Accepted date: 13 November 2017 Avalable onlne: 5 December 2017 JEL Classfcaton: F14 Q17 Q18 Keywords: Import Demand QAIDS Welfare Effects Food Abstract Imports of food products account for a sgnfcant amount of total mports nto Iran. Despte a rse n prce of food products over the last two decades, there has been a rse n ther mports. The present study was an attempt to analyze the mport demand for foodstuffs through the use of a Quadratc AIDS model. Welfare mpacts were also measured usng compensated varaton. The fndngs revealed ownprce nelastc demand for all products, except for tea and cheese. The prce response of food mports was found to be low. Overall, the rse n prce of food products as hgh as ther trend over the last two decades has resulted n an annual welfare loss of 2.2 percent. 1. Introducton Irrespectve of ther level of development, almost all governments have some plans to provde the socety, especally the most vulnerable members of socety wth basc foodstuffs. Subsdzng some foodstuffs can be consdered as one of these plans (Gharbnavaz & Waschk, 2015). The mplementaton of food subsdy programs n Iran can be traced back to the famnes caused by World War II, when a substantal amount of wheat was suppled by the Iranan government through the use of a ratonng system (Farazadeh & Naaf, 2005). Durng the last decades, a sgnfcant porton of some foodstuffs has been provded va mports nto the country and the subsdy system of consumpton has nduced a growng trend of food mports. Although domestc agrcultural output was hgh, consderng populaton growth over , food mports ncreased due to the ncrease n the country's populaton and per capta food consumpton (Esmael & Farazadeh, 2016). 1.1 Some stylzed facts Consderng nomnal values, Iran's mport of agrcultural products grew by 8.8% annually durng , ncreasng from 0.12 to over 5 bllon USD (FAO, 2012). Although a decrease can be observed n some perods, the general zakarafarazadeh@gmal.com DOI: /es , Shraz Unversty, All rght reserved
2 190 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, trend ndcates an ncrease. Unlke the nomnal value of mport, there were consderable changes n the real mport value. Imports ncreased by an annual rate of 21.6%, durng 1965 to 1975; however, a 6% decrease was observed durng 1975 to In general, the real value of mports grew by 1.9% annually durng the years Borenszten and Renhart (1994) reported a decreasng trend n prces for agrcultural commodtes n developng countres. The real prce of the Iran's agrcultural mport bundle shows a decrease before 1990s. Durng the last two decades, however, as ndcated by FAO (2012) and llustrated n Fgure 1, there has been an ncrease n the food prce ndex. Indeed, an annual 1.45 % ncrease n the food prce ndex can be observed durng the years Smlarly, an ncrease n the food prce has been reported for the UAE (Azzam & Rettab, 2012) and Mexco (Attanaso et al., 2013) over the same perod of tme. As t can be seen from Fgure 1, there has been an ncrease n the general trend n the prce ndex for the selected food products over The prces for dary, grans, cookng ols and sugar have ncreased annually by 2.48, 2.38, 3.44 and 0.77% respectvely; however, there has been an nsgnfcant reducton of 0.18% n the meat prce durng the aforementoned years. The correspondng value for the food products, as a whole, has been 1.45%. Although there has been a general trend for all the tems, as Fgure 1 shows, some of them, such as sugar and cookng ols have ndcated a more fluctuatng trend. Fgure 1. Annual food prce ndces over The recent and expected growng surge n food prces has regnted concerns (Azzam & Rettab, 2012). The ncreasng prces of mported foods can affect the socal welfare of Iranan households snce a sgnfcant amount of ther everyday food s mported. For nstance, nearly 60% of ol crops and more than 40% of cereals suppled to the Iranans were mported n The aforementoned products accounted for more than 75% of Iranan food mports, of whch over 38% accounted for cereals, over the years 1961 to The
3 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, correspondng shares of cookng ols and meat were almost 17.5 and 5.3%, respectvely (FAO, 2009). 1.2 Lterature revew Durng the last two decades, many studes have been done on mports through usng economywde models, especally CGE models. These studes have focused specfcally on lberalzaton. For example, Farazadeh et al. (2017) have shown that removng mport barrers, ncludng tarff and nontarff barrers, n Iran can ncrease mports, especally mports of agrcultural commodtes snce agrcultural and agrcultural ndustres sectors are the most mportant sectors. Import s determned by a set of relatve prces and the degree of substtutablty n the emprcal models (Beghn et al., 2002). For nstance, the fndngs of studes done n Syra (Chemngu & Dessus, 2008), Norway (Fæhn & Holmøy, 2003), Malaysa and Indonesa (Arunanondcha, 2003), and Iran (Farazadeh et al., 2017) have showed that trade lberalzaton may lead to an ncrease n mports of agrcultural products. Karam et al. (2012) have also suggested that an ncrease n prce of food products after removng ther subsdes can lead to a decrease n ther mport. Esmael and Farazadeh (2016) have suggested relatve prce and tarff rate are among the drvng forces whch can affect mports of agrcultural products n Iran. Welfare has also been analyzed n trade lberalzaton context. The postve mpact of trade lberalzaton on welfare has been dentfed n developng countres (Acharya & Cohen, 2008; Hosoe, 2001; Jensen & Tarr, 2003) and n developed countres (Fæhn & Holmøy, 2003; Zhu & van Ierland, 2006; Adkns & Garbacco, 2007). As one of the sources, welfare gans mght be caused by a decrease n mport prces due to removal of trade barrers. Furthermore, welfare s expected to ncrease and mport prce s expected to decrease when producton occurs n a more effcent way (Zhu & van Ierland, 2006), or when t s produced by more productve frms (Olper et al., 2014). The possble welfare gans are avalable as far as mport prces are low; however, the expected condton turns out to be dfferent as the recent trend for an ncrease n food prces s expected to be renforced. As Azzam and Rettab (2012) have shown, n relaton to the UAE, ths may adversely affect the lowncome groups specfcally. Khosravnead et al. (2013) have also found that a rse n food prces may result n lower welfare of the urban households and, especally, have an adverse effect on lowncome groups. In addton to the possble mpact of mport prces on welfare, addressed by many demand analyss emprcal studes, there s a growng lterature on appled demand analyss n whch Translog or Almost Ideal Demand System (AIDS) functonal forms are used. These specfcatons have budgetshare equatons that are lnear functons of the logarthm of ncome; however, translog form s wdely used for factor demand. Koetse et al. (2008) and Ma et al. (2008) are two emprcal case studes n whch translog cost functon s used to estmate factor demand elastctes. Also, there s a great body of lterature whch has
4 192 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, nvestgated demand at households' level usng households' expendture survey data and AIDS model as the most conventonal approach. Some of the relevant studes nclude Deaton and Mulbaer (1980) for Great Brtan; Blancfort and Green (1983) for Unted States; Hayes et al. (1991) for Japan; Fulpon (1989) for France; Abdula et al. (1999) for Inda; Tefera (2010) for Ethopa; and Suharno (2010) for Indonesa. Farazadeh and Naaf (2004); Khosravnead et al. (2013); and Shahabad et al. (2016) are also examples of three other emprcal studes whch have beneftted from the AIDS approach to examne the household consumpton n Iran. Moreover, Falsafan and Ghahremanzadeh (2012) have examned meat demand n Iran through the applcaton of two systems of demand; namely a generalzed ordnary dfferental demand system and AIDS model. They have suggested that AIDS model s more consstent wth the behavor of Iranan households. However, the shortcomng of AIDS model stems from the assumpton of lnear Engel curve (Tefera, 2010). Banks et al. (1997) have proposed a generalzed Quadratc Almost Ideal Demand System model whch permts nonlnear Engel curves. Matsuda (2006) has appled a QAIDS model to estmate food demand n Japan. Caro et al. (2017) has also used a QAIDS model to examne purchases tax effect on food and beverage demand n Chle. The researchers have ponted to the flexblty and approprateness of the QAIDS model as compared to the LA/AIDS model. Hardng and Lovenhem (2017) have reported that the nonlnear nature of Engel curve needs to be consdered n the use of the QAIDS model. The researchers have examned tax on beverages n the US. The QAIDS model ncludes the desrable propertes of the LA/AIDS model. Addtonally, t s more compatble wth consumer expendture patterns (Arabatzs & Klonars, 2009). To the best of the present researchers' knowledge, there are only a few emprcal studes n whch AIDS model has been used to provde a model for mport demand 1. In the study done by Arabatzs and Klonars (2009), the QAIDS model was appled n relaton to wood product mported nto Greece. The current study that uses a QAIDS model to analyze the mport demand for foodstuffs can be consdered both as a contrbuton to the lterature and as a novelty. Another reason for why the present study s novel s that t takes nto consderaton the substtuton effect of prce changes n welfare analyss through the use of a second order Taylor expanson of the expendture functon. In addton, the present researchers have ndrectly provded some nsght nto the possble polcy opton of removng food subsdes as the food subsdy programs have been crtczed because of ther mproper targetng and mposton of an unnecessary burden on the publc budget (Karam et al., 2012). The removal of food subsdes s expected to ncrease food prces. 1Ths s manly due to emprcal studes' nterest n examnng mports as a whole or mport of an ndvdual commodty and closely related group of commodtes have not been consdered.
5 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, Gven the above mentoned condtons, the present study s to contrbute to the emprcal lterature of mport demand through the use of a QAIDS model and to explore the welfare mpacts of an ncrease n food prces through the use of the Compensated Varaton (CV). The remander of the present artcle has been organzed as follows: n the next secton the emprcal model s descrbed. The data are presented n the thrd secton. The emprcal results ncludng elastctes estmaton and welfare mplcatons are presented n the fourth secton and the paper ends wth our conclusons. The followng secton sheds lght on the emprcal model appled n the present study. 2. Methods The employed model s the lnear verson of the Quadratc Almost Ideal Demand System (QAIDS) model developed by Matsuda (2006) and Arabatzs and Klonars (2009). If p ( p 1,..., p n ) denotes the nomnal prce vector of n goods and y denotes the total expendture on the goods, the ndrect utlty functon of the QAIDS model can be determned through: [logv ( p, y)] 1 logylogf ( p) [ ] g( p) 1 h( p) where log s the natural logarthm and f ( p) g ( p) andare dstnct h ( p) prce aggregator functons defned as follows: log f ( p) logg( p) h( p) 1 0 logp logp logp (2) 2 log (3) 0 p 0 logp (4) f ( p) s homogeneous of degree one and g ( p) h( p ) are homogeneous of degree zero n p. Therefore, logv ( p, y) s homogenous of degree zero n p and y, as requred. Therefore, the parameters are assumed to meet the correspondng restrctons whch ontly ensure that the resultng demand system fulfls addngup, homogenety and Slutsky symmetry: , 1,2,..., n Applyng Roy s dentty, one can derve the expendture share equaton through the followng formula: (1) (5)
6 194 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, y y w logp log log 1,..., n f ( p) g( p) f( p) (6) where w stands for the expendture share of good for each ndvdual 2. To fnd the lnear approxmatons to the QAIDS model, both f(p) and g(p) need to be replaced wth composte varables. The most usual composte varable for the approxmaton to the translog aggregator functon f(p) n the AIDS s the Stone prce ndex, suggested by Deaton and Muellbauer (1980). However, Moschn (1995) has ndcated that the applcaton of Stone prce ndex nstead of f(p) can serously bas elastcty estmates as t can be affected by changes n unts of measurement. Therefore, the followng alternatve prce ndces have been suggested (Matsuda, 2006): 0 0 1/ 2w w log p / p 0 1 / 2 w logp / p T log P (7) S log P (8) C 0 log P 1/ 2w log p (9) T C where superscrpt 0 ndcates the base pont, P s the Tornqvst prce ndex, S P s the log lnear analogue of the Paasche prce ndex, and P s the log lnear analogue of the Laspeyres prce ndex. All the varables are for a lnearly homogeneous Cobb Douglas aggregator functon (Dewert, 1981). In order to Z 0 0 logp w w log p / p proposed by Matsuda approxmate g(p), the ndex Z (2006) was used. P may be vewed as a zero degree homogeneous analogue of T P and s also nvarant to changes n unts. Regardng the nonlnear approxmatons, the equatons for the expendture ( e LA ) and the uncompensated LA prce ( ) elastctes may also be modfed as follows: 2 e LA 2 y 1 log g f w w P P 1,..., n (10) f LA logp w w logp f g logp logp y y 2 log log g w P logp logp f ( p) f ( p) (11) 1,...,n 2It s worth notng that, as orgnally suggested by Deaton and Muellbauer (Alston et al., 2001); the ntercepts of the expendture share equatons are commonly expressed as the lnear functons of other explanatory varables.
7 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, where f f S w, f P P or P P f log P 0 f T (12) w w / 2f P P log P 0 f C w f P P log P log P g w w 0 f 0 P f g 1 P g P Z (13) where s the Kronecker delta and equal to unty f and zero otherwse. In order to calculate elastctes, the system of Eq. (6) was estmated usng the seemngly unrelated regresson (SUR). The estmated compensated elastctes were used to explore the welfare mpacts of real prce changes usng Compensated Varaton (CV) measure. CV has been defned as the maxmum Wllngness to Pay (WTP) for an ncrease n consumpton, wthout becomng worse off compared to the ntal level of utlty (Johansson, 1993). CV can be expressed usng the expendture functon e (p, u), as follows: CV e( p, u ) e( p, u ) (14) c c where u stands for utlty, and p c for the vector of prces for consumer goods. The subscrpts (0) and (1) refer to the ntal perod and the perod after prce change, respectvely. The compensated varaton for the frst order effect of prce changes, whch does not take nto account households behavoral response substtuton between commodtes, can be approxmated usng a frst order Taylor expanson of the mnmum expendture functon as follows (Fredman & Levnsohn, 2002): n lne w lnp 1 c (15) where w s the budget share of good n the ntal perod, and ln pc represents the proportonate consumer and producer prce changes of commodty. If households can substtute for the goods wth the largest ncrease n prce, then the ncome requred to mantan households level of utlty after prce changes wll be lower. Thus, one has to consder a second order Taylor expanson of expendture functon whch allows for substtuton behavor as follows (Fredman & Levnsonh, 2002): n n n 1 lne w lnpc w ln( pc) ln( pc) (16)
8 196 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, where stands for the compensated prce elastcty. Ths method was used to analyze the welfare mpacts of an ncrease n food prces by Fredman and Levnsohn (2002) and Mnot and Golett (2000) for households n Vetnam and by Tefera (2010) for households n Ethopa. 3. Data As one can see from Table 1, the selected products are grans, meat, cookng ols, tea, cheese, and sugar. These products account for more than 80% of total food mports over the years 1980 to 2012 and are consdered as some extremely mportant and senstve products as they play a sgnfcant role n food securty (Esmael & Farazadeh, 2016). Grans have accounted for more than 54% of the mport value over the aforementoned perod, followed by cookng ols and sugar, each wth a share 20.7% and 11.5%, respectvely. Moreover, meat products have comprsed 7.4% of the mport value of the selected products over the specfed years. Among all the products, wheat, wth a share of around 24% on average, has had the greatest contrbuton to the mport value over the specfed perod. The average mport value share for rce, soybean ol, sugar and maze have been between 10 and 16%. On average, an annual amount of mllon USD has been spent on the mport of the selected food products durng the specfed perod. The data on mport quanttes and values, durng the years 1980 to 2012, has been taken from FAO dataset. The prces for each dfferent commodty category have been determned by dvdng the relevant value nto the relevant quantty. Tarff data was also taken from varous ssues of the Statstcal Yearbook of Iran publshed by the Iranan Customs Organzaton. 4. Results It s dffcult to nterpret the demand system parameters drectly (Lewbel, 1995) 3. Therefore, appled data was used to estmate Eq. (6) and to compute correspondng elastctes through the use of Evews 9 Software. The four systems of equatons were estmated based on Eq. (6) usng Seemngly Unrelated Regresson (SUR) estmaton method, as appled by Azzam and Rettab (2012). Frst, the three man mported products, namely cereals, meat and cookng ols were consdered ndvdually. Then, cheese, tea and sugar were consdered whle cereals, meat and cookng ols were appled n terms of ther aggregate levels. To meet the theoretcal condtons, restrctons of homogenety and symmetry as well as the addtonal restrcton for Slutsky symmetry were mposed on the systems whle one of the budget shares was excluded n each system 4. The results have been presented n the followng sectons. The fndngs 3. The estmated results regardng demand system coeffcents have been presented n the Appendx, Tables A1 and A2. 4. The true elastctes can be calculated through these restrctons. In addton, the total number of free parameters of the QAIDS model exceeds those of AIDS by n 1, where n s the number of equatons (Matsuda, 2006). Havng lower degrees of freedom n QAIDS model, mposng the restrctons
9 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, on elastctes wll be presented frst. Then, the welfare analyss wll be dscussed. Table 1. The Average Import Quantty, Import Value and Expendture Share for the Selected Food Products Import quantty (1000 tones) Import value (mllon USD) Expendture Share (%) Grans Meat Wheat Maze Rce Barley Red meat Sheep meat Poultry Cookng ols Soybean ol Sunflower ol Butter Maze ol Tea Cheese Sugar Elastcty The fndngs regardng prce and expendture elastctes for the ndvdual products of grans, meat and cookng ols and the products' elastctes as aggregate commodtes have been depcted n Tables 2 and 3. It can be seen that the ownprce elastctes for grans and most of the meat groups have not been statstcally sgnfcant. However, ownprce elastcty of cookng ol groups has been statstcally sgnfcant. In general, a statstcally sgnfcant elastcty was observed n relaton to most of the cookng ols and poultry whch were assocated wth hgh prce senstvty. In case of poultry, a 1% rse n the ownprce was assocated wth an average decrease of 3.73% n mport. Smlarly, decreases n mport for soybean ol, sunflower ol and butter were revealed as 1.4%, 2.5% and 1.6%, respectvely. As far as the man groups were concerned, of the grans, meat and cookng ols, only the grans, wth the ownprce elastcty of nearly 1, showed a statstcally sgnfcant response. Therefore, as far as each category of grans s consdered separately, no sgnfcant ownprce response can be expected (Table 2); however, all categores of grans, when consdered as an aggregate commodty, are senstve to ther ownprce changes ncreases the degrees of freedom. It may mprove the relatve precson of the estmated parameters (Guarat & Porter, 2008).
10 198 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, (Table 3). One can arrve at a dfferent concluson regardng the cookng ols, as there were sgnfcant ownprce elastctes for most of the ndvdual products but no statstcally sgnfcant ownprce elastcty for the aggregate group. The response for these may have been caused by the relatonshp between ndvdual commodtes whch can be explaned by the cross prce effect. Regardng the cross prce elastctes, wheat may be consdered as more solated than other grans snce t has no statstcally sgnfcant cross prce effect. Mousav and Sadrolashraf (2007) reported populaton and domestc producton as the man determnants of wheat mports, leavng nsgnfcant role for other factors. Esmael and Farazadeh (2016) also proposed domestc producton as the maor drvng force for mport demand for wheat. The substtutonablty between maze and barley was observed whle the mazerce and rcebarley appeared as complements. Gven the elastctes' absolute values, the complementary relatonshp between maze and barley was more sgnfcant than the substtuton relatonshp between them. Regardng the statstcal sgnfcance and the absolute value of elastctes for grans, the negatve responses of the mport to prce changes was more than the postve responses. Therefore, consderng the grans as a whole, one may expect a sgnfcant response to the ownprce changes. In case of meat tems, sheep meat played a more mportant role than the two others as t showed a statstcally sgnfcant relatonshp wth others. In terms of absolute values, a hgher degree of substtuton was found between sheep meat and poultry whle sheep meat had a complementary relatonshp wth red meat. In general, the mport response of meat tems to prce changes s statstcally sgnfcant. However, the prce changes of meat products as a whole are not expected to affect ther mport (Table 3). In other words, ndvdual meat products mport changes n opposte drecton as ther prce changes, leavng no sgnfcant response for ther aggregate mport. The present fndng s consstent wth the fndngs of Esmael and Farazadeh (2016). In spte of the great senstvty of cookng ols products wth respect to ther ownprces, most cross elastctes were not consderable as they showed low absolute values or statstcally nsgnfcant coeffcents. Among all the cross prce effects, complementary relatonshps of buttersoybean ol and maze olsunflower ol were statstcally sgnfcant. In general, the responses of the mport of cookng ols were senstve to ther ownprce changes and most of the cross prce elastctes were statstcally nsgnfcant. Ths pattern of prce response for cookng ols products can lead to an nsgnfcant prce response when all cookng ols are regarded as an aggregate group. As shown n Table 1, for the most of cookng ols tems, expendture share was low. A lower budget share may nduce an nsgnfcant response to prce changes. As shown n Table 3, demands for tea and cheese were elastc, wth respect to ther own prce changes. For the other commodtes, however, there seems to be an nsgnfcant response n terms of elastcty magntude or statstcal
11 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, mportance. A 1% ncrease n tea and cheese prces can cause a fall n ther mport demands by more than 1.8% and 1.3%, respectvely. As far as the magntude of cross prce elastctes s concerned, the relatonshp between the aggregate groups and tea may be dfferent from those of the aggregate groups. However, when there s a focus on the statstcal sgnfcance, grans can also be consdered more mportant than others. Grans showed a complementary relatonshp wth most of the other tems. Consderng absolute values, however, the cross prce effects were not sgnfcant. In case of tea, substtuton effect can be better conceved than complementary mpact wth hgher elastcty coeffcents. The low budget share of tea may result n substtuton of tea as prces for other tems rse. Based on expendture elastcty, dfferent responses can be also observed as commodtes are aggregated. Among the gran tems, only maze showed statstcally nsgnfcant expendture elastcty; however, barley and rce showed statstcally sgnfcant expendture elastctes of 2.72% and 1.60%, respectvely, and thus they may be consdered as luxury goods. Smlarly, expendture elastcty of grans as a whole was also statstcally sgnfcant. Therefore, the group of grans, as a whole, mght also be consdered as luxury because a 1% ncrease n expendture share can lead to a 1.74% ncrease n demand. Rce s expected to have a sgnfcant contrbuton to ths response snce mported rce s mostly consumed by lowncome groups wth a hgher propensty to consumpton. Table 2. Prce and Expendture Elastctes of Indvdual Products Grans Meat Cookng ols Wheat Maze Rce Barley Uncompensated prce demand elastctes Red meat Sheep meat Poultry Soybean ol Sunflower Butter Maze ol ol wheat a Maze Rce Barley Red meat Sheep meat Poultry Soybean ol Sunflower ol Butter Maze ol Expendture elastctes a The levels of statstcal sgnfcance are denoted wth ***, ** and * whch stand for 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1 levels of sgnfcance, respectvely.
12 200 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, Among the cookng ols, maze ol, wth nsgnfcant expendture elastcty, showed a statstcally nsgnfcant response to expendture changes. Consderng senstvty to expendture changes, there was a consderable dfference among the ndvdual cookng ol tems. Whle a 1% rse n expendture can ncrease butter demand by 0.40%, t can ncrease demands for soybean and sunflower ols by 1.1% and 1.33%, respectvely. The cookng ols as an aggregate group also showed a sgnfcant expendture elastcty. However, t appears to be a necessty as a 1% ncrease n expendture s expected to ncrease demand for cookng ols by only 0.77%. Table 3. Prce and Expendture Elastctes of Aggregate Products Grans Meat Cookng ols Tea Cheese Sugar Uncompensated prce demand elastctes Grans 0.96 a Meat Cookng ols Tea Cheese Sugar Expendture elastctes a The levels of statstcal sgnfcance are denoted wth ***, ** and * whch stand for 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1 levels of sgnfcance, respectvely. 4.1 Welfare changes The welfare mpacts of the change n prce of selected food tems wll be examned n ths secton. Smulatons are based on the annual changes n real prces, presented by FAO (2012), durng the years 1990 to As llustrated n Fgure 1, the prce for the selected food tems mported nto Iran has rsen over the specfed perod. Azzam and Rettab (2012) have also enumerated the years as a perod durng whch ncrease n prces became more apparent for the global food products. There was an ncrease n annual prces for dary, grans, cookng ols and sugar, each wth 2.48, 2.38, 3.44 and 0.77%, respectvely but a 0.18% decrease n prce for meat over the same years. Welfare changes were determned through the use of Equatons (15) and (16), as the frst and second order Taylor expanson of the mnmum expendture functon. Three scenaros for prce changes have been consdered n welfare smulaton. Scenaro One ncluded prce changes for all the ndvdual commodtes over the years In other words, welfare changes for each food tem were calculated ndvdually. It s also worth mentonng that the annual prce change of the products was smlar to ther average growth rate durng the aforementoned perod. Scenaro Two ncluded ncreases n prce for all the selected commodtes, except meat, reported, n terms of ther annual average values, by FAO for the years 1990 to Although ths scenaro was smlar
13 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, to scenaro One; t dd not nclude the changes n meat prce because, despte the prces for the other products, the prce for meat tended to decrease over the specfed years. The value for the welfare change, as reported n Table 4, was the sum of the values for welfare changes determned for all the selected food products, through the use of Equatons (15) and (16). In ths scenaro, dary products prce ncrease whch s 2.48% was appled for cheese. A 1.15% ncrease n prce for tea, whch was the average prce ncrease for all the food tems, was also appled n welfare analyss. Scenaro Three ncluded prce changes n scenaro One; however, meat was also consdered, showng a 0.18% decrease n prce. The reported values for welfare changes (Table 4) were the sum of values for welfare changes n relaton to all the selected food tems. As shown n Table 4, there was an nsgnfcant dfference between the frst and the second order welfare mpacts. Ths can ndcate a low possblty for substtutng one commodty wth the other when there s a change n the relatve prces. Ths may reveal that a bundle of all commodtes are needed and ths can leave lttle room to substtute for the goods wth the largest ncrease n prce. An ncrease n prce for grans was assocated by the greatest welfare loss among the selected groups, as an ncrease n ther annual prce led to a 1.15% welfare reducton. An ncrease n the annual prce of cookng ols was also followed by a 0.83% welfare reducton. As shown n Table 1, more than half of mport expendtures of the selected products have belonged to grans. Ths has led to hgher welfare losses followed by an ncrease n prces. The correspondng welfare loss for changes n the ndvdual prce ndces of sugar was nearly 0.1%. Although the expendture share for sugar was sgnfcant (Table 1), the modest ncrease n prce for sugar durng the selected perod of tme resulted n a small welfare loss. The decrease n meat prce was also accompaned wth an nsgnfcant welfare ncrease, due to both nsgnfcant prce changes as well as lower expendture share. In general, prce changes of all the commodtes can ncrease mport expendtures by nearly 2.2%. Karam et al. (2012) has also reported the low welfare effects of ncrease n prces of food tems after removng ther subsdy. Table 4. Frst and Second Order Welfare Impacts (Expendture Changes) of Prce Changes (%) Indvdual prce changes by annual growth, (Scenaro1) Grans Meat Cookng ols Tea Cheese Sugar Changes n prces of all the selected commodtes except meat (Scenaro2) Changes n prces of all the selected commodtes (Scenaro3) Frst order Second order
14 202 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, Concluson Whle the man focus of the emprcal works n Iran has been on the effects of removal of food subsdes (Farazadeh & Naaf, 2005; Karam et al., 2012; Gharbnavaz & Waschk, 2015), a narrow focus has been on the ncreasng prces of mported food products. Azzam and Rettab (2012) have ndcated that the ncreasng prces of mported food can result n welfare losses, especally among lowncome groups. Domestc producers, however, can beneft from hgher prces as they wll produce more products and receve hgher prces. Ths study nvestgates the drvng forces behnd mport demand for the man mported food products through the use of a QAIDS model and by takng nto account the welfare mpact of an ncrease n prces of the selected tems. The QAIDS model has been wdely used for case studes based on household survey data. However, a few emprcal case studes are also avalable n relaton to mport demand. The fndngs of the present study ndcated that grans, meat and cookng ols as well as sugar were not ownprce elastc but cheese and tea showed sgnfcant responses to ther ownprces. Low response to ownprce changes was also found for the ndvdual products of grans and meat. However, all the ndvdual cookng ol products, except maze ol, showed an ownprce elastc behavor, unlke what was observed for ther aggregate response. As the cross prce elastctes ndcated, substtuton relatonshp was more lkely than complementary relatonshp for the cookng ols. Ths mght account for the ownprce nelastc behavor of cookng ols as a whole. Regardng the ownprce elastctes, ths mplcaton can be consdered for grans and meat products, as well. The Insgnfcant responses of these ndvdual tems to ther ownprce changes are the man reason behnd the ownprce nelastc response of aggregate grans and meat. Consderng the absolute values as well as statstcal sgnfcance, the mported food products showed an nsgnfcant response to prce changes and ths can offer polcy makers a low possblty of prcng polcy. Ths, to some extent, may stem from the food subsdy system n whch prce changes are not completely transferred to the domestc market and whch makes the government be responsble for provdng consumers wth ther basc needs. However, regardng the subsdes burden on the publc budget and neffcent dstrbuton system whch does not target the poor properly (Karam et al., 2012); food subsdy s expected to be removed. In other words, as long as the government plays the central role n markets of such food products as grans and meat, an nsgnfcant response to prce wll be expected. Low elastctes can also be responsble for a low welfare change of nearly 2.2%. Azzam and Rettab (2012) have estmated a correspondng welfare loss of approxmately 4.5% for the UAE. In case of Iran, the welfare losses need to be consdered n the context of severe poverty. For example, Mahmood (2013) has reported that for the most part of the years , around 40% of people n urban areas of Iran have been poor. Therefore, food subsdy system can be supported as much as food prces tend to ncrease and when a large number of
15 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, households are consdered as poor. Especally, the CV can be nterpreted as a supplementary ncome or as a compensaton for hgher food prces (Azzam & Rettab, 2012). Subsdzaton has also been consdered as a polcy, adopted by the Mexcan government, to stop the rse n food prces n Mexco (Attanaso et al., 2013). Regardng expendture elastctes, an nsgnfcant response can also be expected. The hgher response of grans can be attrbuted to rce because Iranan consumers care a lot about rce consumpton and ts qualty. Consderng Iran's per capta ncome, mport response to expendture can also be consdered as very mportant. Current GNI per capta, PPP n Iran (15,440 USD n 2014) s much lower than those of the developed economes (UNDP, 2015) and a sgnfcant ncrease n Iran's per capta ncome can nduce a sgnfcant mport, and thus must be taken nto account. As far as the techncal features and suggestons for future studes are concerned, t s worth notng that traderelated polcy analyss can beneft from the results obtaned from the QAIDS model, as suggested by Arabatzs and Klonars (2009). The results can be used n trade models as well as n measurements of costs and benefts assocated wth changes n trade polces concernng mport of food products. Furthermore, from a techncal pont of vew, the lnear approxmatons of the QAIDS model, when nonstatonary tme seres are used, can be especally useful (Matsuda, 2006). The QAIDS model ncludes desrable propertes of the popular AIDS model of Deaton and Muellbauer (1980). In addton, t s compatble wth the consumer expendture patterns. The QAIDS model, quadratc n the logarthm of total expendture, can turn a luxury nto a necessty through ncreasng expendtures (Arabatzs and Klonars, 2009). Future studes can nvestgate the welfare effects of rsng food prces for dfferent ncome groups, for whch groupspecfc elastctes are needed. Fnally, gven the hgh possblty for reducng food subsdes, the appled scenaros can also be examned through the food subsdy removal opton.
16 204 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, References Abdula, A., Jan, D. K., & Sharma, A. K. (1999). Household food demand n Inda. Journal of Agrcultural Economcs, 50(2), Acharya, S., & Cohen, S. (2008). Trade lberalzaton and household welfare n Nepal. Journal of Polcy Modelng, 30, Adkns, L. G., & Garbacco, R. F. (2007). Coordnatng global trade and envronmental polcy: The role of preexstng dstortons. Natonal Center for Envronmental Economcs, U.S. Envronmental Protecton Agency. Washngton, D. C., Unted States. Alston, J. M., Chalfant, J. A., & Pggott, N. E. (2001). Incorporatng demand shfters n the Almost Ideal demand system. Economcs Letters, 70, Arabatzs, G., & Klonars, S. (2009). An analyss of Greek wood and wood product mports: Evdence from the lnear quadratc ads. Forest Polcy and Economcs, 11, Arunanondcha, J. M. (2003). Appled general equlbrum analyss of trade lberalzaton on landbased sectors n Malaysa and Indonesa. Journal of Polcy Modelng, 25, Attanaso, O., D Maro, V., Lechene, V., & Phllps, D. (2013). Welfare consequences of food prces ncreases: Evdence from rural Mexco. Journal of Development Economcs, 104, Azzam, A. M., & Rettab, B. (2012). A welfare measure of consumer vulnerablty to rsng prces of food mports n the UAE. Food Polcy, 37, Banks, J., Blundell, R. W., & Lewbel, A. (1997). Quadratc Engel curves and consumer demand. Revew of Economcs and Statstcs, 79, Beghn, J., Dessus, S., RonaldHolst, D., &Van der Mensbrugghe, D. (2002). Emprcal modelng of trade and envronment, trade and envronment n general equlbrum: Evdence from developng economcs. Chapter 3, New York, the USA: Kluwer Academc Publshers. Blancfort, L., & Green, R. (1983). An almost deal demand system ncorporatng habts: An analyss of expendture on food and aggregate commodty groups. Revew of Economcs and Statstcs, 65, Borenszten, E., & Renhart, C. M. (1994). The macroeconomc determnants of commodty prces. IMF Staff Papers, 41, Caro, J. C., Ng, S. W., Talle, L. S., & Popkn, B. M. (2017). Desgnng a tax to dscourage unhealthy food and beverage purchases: The case of Chle. Food Polcy, 71, Chemngu, M. A., & Dessus, S. (2008). Assessng nontarff barrers n Syra. Journal of Polcy Modelng, 30, Deaton, A., & Muellbauer, J. (1980). An almost deal demand system. Amercan Economc Revew, 70(3), Dewert, W. E. (1981). The economc theory of ndex numbers: A survey, n Essays n the Theory and Measurement of Consumer Behavor: In Honor of
17 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, Sr Rchard Stone. Ed. by A. S. Deaton, Cambrdge, U.K., Cambrdge Unversty Press, Esmael, A., & Farazadeh, Z. (2016). Adustment and stablty n mport demand of the Iranan agrcultural senstve and crtcal products. Journal of Agrcultural Economcs and Development, 95, [n Persan]. Fæhn, T., & Holmøy, E. (2003). Trade lberalzaton and effects on pollutve emssons to ar and deposts of sold waste: A general equlbrum assessment for Norway. Economc Modelng, 20, Falsafan, A., & Ghahremanzadeh, M. (2012). Proper functonal form selecton to analyze meat demand n Iran. Food Research (Agrcultural Scence), 22(2), [n Persan]. FAO Statstcal Database. (2012). Farazadeh, Z., & Naaf, B. (2004). Study of consumer behavor: Case of subsdzed food tems. Journal of Agrcultural Economcs and Development, 47, [n Persan]. Farazadeh, Z., & Naaf, B. (2005). The effects of food subsdy reform n Iran. 5th Internatonal Conference of Asan Socety of Agrcultural Economsts. Zahedan, Iran. Farazadeh, Z., Zhu, X., & Bakhshoodeh, M. (2017). Trade reform n Iran for accesson to the World Trade Organzaton: Analyss of welfare and envronmental mpacts. Economc Modelng, 63, Fredman, J., & Levnsohn, J. (2002). The dstrbutonal mpacts of Indonesa s fnancal crss on household: A rapd response methodology. The World Bank Economc Revew, 16, Fulpon, L. (1989). The almost deal demand system: An applcaton to food and meat groups for France. Journal of Agrcultural Economcs, 40(1), Gharbnavaz, M. R., & Waschk, R. (2015). Food and energy subsdy reforms n Iran: A general equlbrum analyss. Journal of Polcy Modelng, 37, Guarat, D. N., & Porter, D. C. (2008). Basc Econometrcs (5 th ed.). New York, the USA: McGrawHll. Hardng, M., & Lovenhemc, M. (2017). The effect of prces on nutrton: Comparng the mpact of productand nutrentspecfc taxes. Journal of Health Economcs, 53, Hayes, D., Wahl, T., & Wllams, G. (1990). Testng restrctons on a model of Japanese meet demand. Amercan Journal of Agrcultural Economcs, 72(3), Hosoe, N. (2001). A general equlbrum analyss of Jordan s trade lberalzaton. Journal of Polcy Modelng, 23, Jensen, J., & Tarr, D. (2003). Trade, exchange rate, and energy prcng reform n Iran: Potentally large effcency effects and gans to the poor. Revew of Development Economc, 7, Johansson, P. O. (1993). Costbeneft analyss of envronmental changes, Cambrdge, the UK: Cambrdge Unversty Press.
18 206 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, Karam, A., Esmael, A., & Naaf, N. (2012). Assessng effects of alternatve food subsdy reform n Iran. Journal of Polcy Modelng, 34, Khosravnead, A., K., Khodadadkash, F., & Sohbat, Z. (2013). Evaluatng effect of ncrease n food prces on the Iranan urban households. Journal of Economc Strateges, 4(4), [n Persan]. Koetse, M. J., de Groot, H. F., & Florax, R. J. G. M. (2008). Captalenergy substtuton and shfts n factor demand: A metaanalyss. Energy Economcs, 30, Lewbel, A. (1995). Consstent nonparametrc hypothess test wth an applcaton to Slutesky symmetry. Journal of Econometrcs, 67, Ma, H., Oxley, L., Gbson, J., & Km, B. (2008). Chna's energy economy: Techncal change, factor demand and nterfactor/nterfuel substtuton. Energy Economcs, 30, Mahmood, A. (2013). Estmaton of relatve poverty n urban areas of Iran (Applcaton of panel data n Lnear Expendture System). Economc growth and Development Research, 13, [n Persan]. Matsuda, T. (2006). Lnear approxmatons to the quadratc almost deal demand system. Emprcal Economcs, 33, Mnot, N., & Golett, F. (2000). Rce Market Lberalzaton and Poverty n Vet Nam. Research Report 114. Washngton DC, the USA: Internatonal food Polcy Research Insttute. Moschn, G. (1995). Unts of Measurement and the Stone Index n Demand System Estmaton. Amercan Journal of Agrcultural Economcs, 77, Mousav, S. N., Sadrolashraf, M. (2007). Effects of globalzaton on supply, demand and mport of Iranan wheat. Journal of Agrcultural Economcs, 1(1), [In Persan]. Olper, A., Pacca, L., & Curz, D. (2014). Trade, mport competton and productvty growth n the food ndustry. Food Polcy, 49, Shahabad, A., Kamal, P., & Kabryan, M. (2016). Analyzng the behavor of consumer n urban areas n ChaharmahalBakhtar provnce. Journal of Regonal Plannng, 22, 114. [n Persan]. Suharno, V. V. (2010). An almost deal demand system for food based on cross secton data: Rural and urban East Java, Indonesa. Unpublshed doctoral dssertaton, Unversty of GeorgAugust. Göttngen, Germany. Tefera, N. (2010). Essays on Welfare, Demand and Reslence to Food Insecurty n Rural Ethopa. Unpublshed doctoral dssertaton, Unversty of Cattolca. Mlan, Italy. UNDP (Unted Natons Development Program)(2015). Human Development Report UN Plaza, New York, NY 10017, USA. Zhu, X., & van Ierland, E. C. (2006). The enlargement of the European Unon: Effects on trade and emssons of greenhouse gasses. Ecologcal Economcs, 57, 1 14.
19 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, Appendx Table A1: Estmated Parameters of the QUAIDS model for the Indvdual Products Dependen t varable (expendt ure share) Grans Meat Cookng ols Red meat Sheep meat Wheat Maze Rce Barley Intercept Wheat prce a Maze prce Rce prce Barley prce Expendt ure Squared expendtu re Adusted R Q(1) c 0.81( ( (0.1 6) 1) 5) Q(2) 0.87( ( (0.2 4) 9) 8) Jarque 0.82( ( (0.2 Berra 6) 1) 9) Intercept Red meat prce Sheep meat prce Poultry prce Expendt ure Squared expendtu re Adusted 2 R Poultry Soybean ol Sunflower ol Q(1) c 0.29( (0.1 8) 0) Q(2) 0.45( (0.2 9) 0) Jarque 0.35( (0.6 Berra 3) 3) Intercept Soybean ol prce Sunflower ol prce Butter Maze ol
20 208 Farazadeh & Esmael, Iranan Journal of Economc Studes, 5(2) 2016, Dependen t varable (expendt ure share) Grans Meat Cookng ols Wheat Maze Rce Barley Red Sheep Soybean Sunflower Maze Poultry meat meat ol ol Butter ol Butter prce Maze ol prce Expendture Squared expendture Adusted R Q(1) b 0.01( ( (0.4 3) 5) 4) Q(2) 0.36( ( (0.6 3) ) 3) Jarque Berra 1.84( ( (0.5 9) 1) 2) a The levels of statstcal sgnfcance are denoted wth ***, ** and * whch stand for 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1 levels of sgnfcance, respectvely. b Q( p ) s the sgnfcance level of the Lung Box statstc n whch the frst p of the resdual autocorrelatons s ontly equal to zero. Table A2: Estmated Parameters of the QUAIDS for the Aggregate Products Dependent varable (expendture share) Grans Cookng ols Meat Sugar Tea Cheese Intercept a Grans prce Cookng ols prce Meat prce Sugar prce Tea prce Cheese prce Expendture Squared expendture Adusted R Q(1) b 1.70(0.19) 2.37(0.12) 2.96(0.09) 0.07(0.78) 14.3(0.11) Q(2) 2.18(0.33) 2.54(0.28) 3.20(0.20) 10.99(0.14) 14.4(0.15) Jarque Berra 2.85(0.21) 0.50(0.77) 3.76(0.15) 1.82(0.40) 1.69(0.42) a The levels of statstcal sgnfcance are denoted wth ***, ** and * whch stand for 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1 levels of sgnfcance, respectvely. b Q( p ) s the sgnfcance level of the Lung Box statstc n whch the frst p of the resdual autocorrelatons s ontly equal to zero.
Raising Food Prices and Welfare Change: A Simple Calibration. Xiaohua Yu
 Rasng Food Prces and Welfare Change: A Smple Calbraton Xaohua Yu Professor of Agrcultural Economcs Courant Research Centre Poverty, Equty and Growth Unversty of Göttngen CRC-PEG, Wlhelm-weber-Str. 2 3773
Rasng Food Prces and Welfare Change: A Smple Calbraton Xaohua Yu Professor of Agrcultural Economcs Courant Research Centre Poverty, Equty and Growth Unversty of Göttngen CRC-PEG, Wlhelm-weber-Str. 2 3773
MgtOp 215 Chapter 13 Dr. Ahn
 MgtOp 5 Chapter 3 Dr Ahn Consder two random varables X and Y wth,,, In order to study the relatonshp between the two random varables, we need a numercal measure that descrbes the relatonshp The covarance
MgtOp 5 Chapter 3 Dr Ahn Consder two random varables X and Y wth,,, In order to study the relatonshp between the two random varables, we need a numercal measure that descrbes the relatonshp The covarance
CHAPTER 9 FUNCTIONAL FORMS OF REGRESSION MODELS
 CHAPTER 9 FUNCTIONAL FORMS OF REGRESSION MODELS QUESTIONS 9.1. (a) In a log-log model the dependent and all explanatory varables are n the logarthmc form. (b) In the log-ln model the dependent varable
CHAPTER 9 FUNCTIONAL FORMS OF REGRESSION MODELS QUESTIONS 9.1. (a) In a log-log model the dependent and all explanatory varables are n the logarthmc form. (b) In the log-ln model the dependent varable
ECONOMETRICS - FINAL EXAM, 3rd YEAR (GECO & GADE)
 ECONOMETRICS - FINAL EXAM, 3rd YEAR (GECO & GADE) May 17, 2016 15:30 Frst famly name: Name: DNI/ID: Moble: Second famly Name: GECO/GADE: Instructor: E-mal: Queston 1 A B C Blank Queston 2 A B C Blank Queston
ECONOMETRICS - FINAL EXAM, 3rd YEAR (GECO & GADE) May 17, 2016 15:30 Frst famly name: Name: DNI/ID: Moble: Second famly Name: GECO/GADE: Instructor: E-mal: Queston 1 A B C Blank Queston 2 A B C Blank Queston
Real Exchange Rate Fluctuations, Wage Stickiness and Markup Adjustments
 Real Exchange Rate Fluctuatons, Wage Stckness and Markup Adjustments Yothn Jnjarak and Kanda Nakno Nanyang Technologcal Unversty and Purdue Unversty January 2009 Abstract Motvated by emprcal evdence on
Real Exchange Rate Fluctuatons, Wage Stckness and Markup Adjustments Yothn Jnjarak and Kanda Nakno Nanyang Technologcal Unversty and Purdue Unversty January 2009 Abstract Motvated by emprcal evdence on
Evaluating Performance
 5 Chapter Evaluatng Performance In Ths Chapter Dollar-Weghted Rate of Return Tme-Weghted Rate of Return Income Rate of Return Prncpal Rate of Return Daly Returns MPT Statstcs 5- Measurng Rates of Return
5 Chapter Evaluatng Performance In Ths Chapter Dollar-Weghted Rate of Return Tme-Weghted Rate of Return Income Rate of Return Prncpal Rate of Return Daly Returns MPT Statstcs 5- Measurng Rates of Return
THE VOLATILITY OF EQUITY MUTUAL FUND RETURNS
 North Amercan Journal of Fnance and Bankng Research Vol. 4. No. 4. 010. THE VOLATILITY OF EQUITY MUTUAL FUND RETURNS Central Connectcut State Unversty, USA. E-mal: BelloZ@mal.ccsu.edu ABSTRACT I nvestgated
North Amercan Journal of Fnance and Bankng Research Vol. 4. No. 4. 010. THE VOLATILITY OF EQUITY MUTUAL FUND RETURNS Central Connectcut State Unversty, USA. E-mal: BelloZ@mal.ccsu.edu ABSTRACT I nvestgated
Economic Design of Short-Run CSP-1 Plan Under Linear Inspection Cost
 Tamkang Journal of Scence and Engneerng, Vol. 9, No 1, pp. 19 23 (2006) 19 Economc Desgn of Short-Run CSP-1 Plan Under Lnear Inspecton Cost Chung-Ho Chen 1 * and Chao-Yu Chou 2 1 Department of Industral
Tamkang Journal of Scence and Engneerng, Vol. 9, No 1, pp. 19 23 (2006) 19 Economc Desgn of Short-Run CSP-1 Plan Under Lnear Inspecton Cost Chung-Ho Chen 1 * and Chao-Yu Chou 2 1 Department of Industral
Effects of Model Specification and Demographic Variables on Food. Consumption: Microdata Evidence from Jiangsu, China. The Area of Focus:
 Effects of Model Specfcaton and Demographc Varables on Food Consumpton: Mcrodata Evdence from Jangsu, Chna Kang Ernest Lu lu.320@osu.edu and Wen S. Chern chern.1@osu.edu Department of Agrcultural, Envronmental,
Effects of Model Specfcaton and Demographc Varables on Food Consumpton: Mcrodata Evdence from Jangsu, Chna Kang Ernest Lu lu.320@osu.edu and Wen S. Chern chern.1@osu.edu Department of Agrcultural, Envronmental,
Spatial Variations in Covariates on Marriage and Marital Fertility: Geographically Weighted Regression Analyses in Japan
 Spatal Varatons n Covarates on Marrage and Martal Fertlty: Geographcally Weghted Regresson Analyses n Japan Kenj Kamata (Natonal Insttute of Populaton and Socal Securty Research) Abstract (134) To understand
Spatal Varatons n Covarates on Marrage and Martal Fertlty: Geographcally Weghted Regresson Analyses n Japan Kenj Kamata (Natonal Insttute of Populaton and Socal Securty Research) Abstract (134) To understand
Welfare Aspects in the Realignment of Commercial Framework. between Japan and China
 Prepared for the 13 th INFORUM World Conference n Huangshan, Chna, July 3 9, 2005 Welfare Aspects n the Realgnment of Commercal Framework between Japan and Chna Toshak Hasegawa Chuo Unversty, Japan Introducton
Prepared for the 13 th INFORUM World Conference n Huangshan, Chna, July 3 9, 2005 Welfare Aspects n the Realgnment of Commercal Framework between Japan and Chna Toshak Hasegawa Chuo Unversty, Japan Introducton
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture VI: Industry Supply
 Elements of Economc Analyss II Lecture VI: Industry Supply Ka Hao Yang 10/12/2017 In the prevous lecture, we analyzed the frm s supply decson usng a set of smple graphcal analyses. In fact, the dscusson
Elements of Economc Analyss II Lecture VI: Industry Supply Ka Hao Yang 10/12/2017 In the prevous lecture, we analyzed the frm s supply decson usng a set of smple graphcal analyses. In fact, the dscusson
A Utilitarian Approach of the Rawls s Difference Principle
 1 A Utltaran Approach of the Rawls s Dfference Prncple Hyeok Yong Kwon a,1, Hang Keun Ryu b,2 a Department of Poltcal Scence, Korea Unversty, Seoul, Korea, 136-701 b Department of Economcs, Chung Ang Unversty,
1 A Utltaran Approach of the Rawls s Dfference Prncple Hyeok Yong Kwon a,1, Hang Keun Ryu b,2 a Department of Poltcal Scence, Korea Unversty, Seoul, Korea, 136-701 b Department of Economcs, Chung Ang Unversty,
>1 indicates country i has a comparative advantage in production of j; the greater the index, the stronger the advantage. RCA 1 ij
 69 APPENDIX 1 RCA Indces In the followng we present some maor RCA ndces reported n the lterature. For addtonal varants and other RCA ndces, Memedovc (1994) and Vollrath (1991) provde more thorough revews.
69 APPENDIX 1 RCA Indces In the followng we present some maor RCA ndces reported n the lterature. For addtonal varants and other RCA ndces, Memedovc (1994) and Vollrath (1991) provde more thorough revews.
UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM
 UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS DISCUSSION PAPER 99/28 Welfare Analyss n a Cournot Game wth a Publc Good by Indraneel Dasgupta School of Economcs, Unversty of Nottngham, Nottngham NG7 2RD,
UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS DISCUSSION PAPER 99/28 Welfare Analyss n a Cournot Game wth a Publc Good by Indraneel Dasgupta School of Economcs, Unversty of Nottngham, Nottngham NG7 2RD,
Consumption Based Asset Pricing
 Consumpton Based Asset Prcng Mchael Bar Aprl 25, 208 Contents Introducton 2 Model 2. Prcng rsk-free asset............................... 3 2.2 Prcng rsky assets................................ 4 2.3 Bubbles......................................
Consumpton Based Asset Prcng Mchael Bar Aprl 25, 208 Contents Introducton 2 Model 2. Prcng rsk-free asset............................... 3 2.2 Prcng rsky assets................................ 4 2.3 Bubbles......................................
Microeconomics: BSc Year One Extending Choice Theory
 mcroeconomcs notes from http://www.economc-truth.co.uk by Tm Mller Mcroeconomcs: BSc Year One Extendng Choce Theory Consumers, obvously, mostly have a choce of more than two goods; and to fnd the favourable
mcroeconomcs notes from http://www.economc-truth.co.uk by Tm Mller Mcroeconomcs: BSc Year One Extendng Choce Theory Consumers, obvously, mostly have a choce of more than two goods; and to fnd the favourable
Domestic Savings and International Capital Flows
 Domestc Savngs and Internatonal Captal Flows Martn Feldsten and Charles Horoka The Economc Journal, June 1980 Presented by Mchael Mbate and Chrstoph Schnke Introducton The 2 Vews of Internatonal Captal
Domestc Savngs and Internatonal Captal Flows Martn Feldsten and Charles Horoka The Economc Journal, June 1980 Presented by Mchael Mbate and Chrstoph Schnke Introducton The 2 Vews of Internatonal Captal
Bilateral Trade Flows and Nontraded Goods
 Blateral Trade Flos and Nontraded Goods Yh-mng Ln Department of Appled Economcs, Natonal Chay Unversty, Taan, R.O.C. Emal: yxl173@mal.ncyu.edu.t Abstract Ths paper develops a monopolstc competton model
Blateral Trade Flos and Nontraded Goods Yh-mng Ln Department of Appled Economcs, Natonal Chay Unversty, Taan, R.O.C. Emal: yxl173@mal.ncyu.edu.t Abstract Ths paper develops a monopolstc competton model
International ejournals
 Avalable onlne at www.nternatonalejournals.com ISSN 0976 1411 Internatonal ejournals Internatonal ejournal of Mathematcs and Engneerng 7 (010) 86-95 MODELING AND PREDICTING URBAN MALE POPULATION OF BANGLADESH:
Avalable onlne at www.nternatonalejournals.com ISSN 0976 1411 Internatonal ejournals Internatonal ejournal of Mathematcs and Engneerng 7 (010) 86-95 MODELING AND PREDICTING URBAN MALE POPULATION OF BANGLADESH:
- contrast so-called first-best outcome of Lindahl equilibrium with case of private provision through voluntary contributions of households
 Prvate Provson - contrast so-called frst-best outcome of Lndahl equlbrum wth case of prvate provson through voluntary contrbutons of households - need to make an assumpton about how each household expects
Prvate Provson - contrast so-called frst-best outcome of Lndahl equlbrum wth case of prvate provson through voluntary contrbutons of households - need to make an assumpton about how each household expects
Utilizing an Almost Ideal Demand System
 792 Bulgaran Journal of Agrcultural Scence, 19 (No 4) 2013, 792-800 Agrcultural Academy Analyzng UAE s Imports of Fresh Fruts Utlzng an Almost Ideal Demand System M. S. Gheblaw 1, M. K. Alashry 2, S. Sherf
792 Bulgaran Journal of Agrcultural Scence, 19 (No 4) 2013, 792-800 Agrcultural Academy Analyzng UAE s Imports of Fresh Fruts Utlzng an Almost Ideal Demand System M. S. Gheblaw 1, M. K. Alashry 2, S. Sherf
5. Market Structure and International Trade. Consider the role of economies of scale and market structure in generating intra-industry trade.
 Rose-Hulman Insttute of Technology GL458, Internatonal Trade & Globalzaton / K. Chrst 5. Market Structure and Internatonal Trade Learnng Objectves 5. Market Structure and Internatonal Trade Consder the
Rose-Hulman Insttute of Technology GL458, Internatonal Trade & Globalzaton / K. Chrst 5. Market Structure and Internatonal Trade Learnng Objectves 5. Market Structure and Internatonal Trade Consder the
Taxation and Externalities. - Much recent discussion of policy towards externalities, e.g., global warming debate/kyoto
 Taxaton and Externaltes - Much recent dscusson of polcy towards externaltes, e.g., global warmng debate/kyoto - Increasng share of tax revenue from envronmental taxaton 6 percent n OECD - Envronmental
Taxaton and Externaltes - Much recent dscusson of polcy towards externaltes, e.g., global warmng debate/kyoto - Increasng share of tax revenue from envronmental taxaton 6 percent n OECD - Envronmental
Tradable Emissions Permits in the Presence of Trade Distortions
 85 Tradable Emssons Permts n the Presence of Trade Dstortons Shnya Kawahara Abstract Ths paper nvestgates how trade lberalzaton affects domestc emssons tradng scheme n a poltcal economy framework. Developng
85 Tradable Emssons Permts n the Presence of Trade Dstortons Shnya Kawahara Abstract Ths paper nvestgates how trade lberalzaton affects domestc emssons tradng scheme n a poltcal economy framework. Developng
The Effects of Industrial Structure Change on Economic Growth in China Based on LMDI Decomposition Approach
 216 Internatonal Conference on Mathematcal, Computatonal and Statstcal Scences and Engneerng (MCSSE 216) ISBN: 978-1-6595-96- he Effects of Industral Structure Change on Economc Growth n Chna Based on
216 Internatonal Conference on Mathematcal, Computatonal and Statstcal Scences and Engneerng (MCSSE 216) ISBN: 978-1-6595-96- he Effects of Industral Structure Change on Economc Growth n Chna Based on
Competition of Imported Wooden Bedroom Furniture in the United States
 Competton of Imported Wooden Bedroom Furnture n the Unted States Yang Wan 1, Changyou Sun 2, and Donald L. Grebner 3 1 Graduate Research Assstant, Department of Forestry, Msssspp State Unversty, Box 9681,
Competton of Imported Wooden Bedroom Furnture n the Unted States Yang Wan 1, Changyou Sun 2, and Donald L. Grebner 3 1 Graduate Research Assstant, Department of Forestry, Msssspp State Unversty, Box 9681,
Consumer Demand System Estimation and Value Added Tax Reforms in the Czech Republic *
 JEL classfcaton: D1; H0; H31 Keywords: consumer behavor, demand system, QUAIDS, tax reforms, value added tax Consumer Demand System Estmaton and Value Added Tax Reforms n the Czech Republc * Petr JANSKÝ
JEL classfcaton: D1; H0; H31 Keywords: consumer behavor, demand system, QUAIDS, tax reforms, value added tax Consumer Demand System Estmaton and Value Added Tax Reforms n the Czech Republc * Petr JANSKÝ
Political Economy and Trade Policy
 Poltcal Economy and Trade Polcy Motvaton When asked why no free trade?, most nternatonal economsts respond t must be poltcs In representatve democraces, trade polcy shaped not only by general electorate,
Poltcal Economy and Trade Polcy Motvaton When asked why no free trade?, most nternatonal economsts respond t must be poltcs In representatve democraces, trade polcy shaped not only by general electorate,
University of Toronto November 9, 2006 ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY. Term Test #1 L0101 L0201 L0401 L5101 MW MW 1-2 MW 2-3 W 6-8
 Department of Economcs Prof. Gustavo Indart Unversty of Toronto November 9, 2006 SOLUTION ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY Term Test #1 A LAST NAME FIRST NAME STUDENT NUMBER Crcle your secton of the course:
Department of Economcs Prof. Gustavo Indart Unversty of Toronto November 9, 2006 SOLUTION ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY Term Test #1 A LAST NAME FIRST NAME STUDENT NUMBER Crcle your secton of the course:
University of Toronto November 9, 2006 ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY. Term Test #1 L0101 L0201 L0401 L5101 MW MW 1-2 MW 2-3 W 6-8
 Department of Economcs Prof. Gustavo Indart Unversty of Toronto November 9, 2006 SOLUTION ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY Term Test #1 C LAST NAME FIRST NAME STUDENT NUMBER Crcle your secton of the course:
Department of Economcs Prof. Gustavo Indart Unversty of Toronto November 9, 2006 SOLUTION ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY Term Test #1 C LAST NAME FIRST NAME STUDENT NUMBER Crcle your secton of the course:
Impact of U.S. Cotton Subsidies: A Computable General Equilibrium Model Houtian Ge 1,a, Cristina Echevarria 2,b,James Nolan 1,c, Richard Gray 1,d
 0 Internatonal Conference on Socal Scences and Socety Impact of U.S. Cotton Subsdes: A Computable General Equlbrum Model Houtan Ge,a, Crstna Echevarra,b,James Nolan,c, Rchard Gray,d Department of BPBE,
0 Internatonal Conference on Socal Scences and Socety Impact of U.S. Cotton Subsdes: A Computable General Equlbrum Model Houtan Ge,a, Crstna Echevarra,b,James Nolan,c, Rchard Gray,d Department of BPBE,
Spurious Seasonal Patterns and Excess Smoothness in the BLS Local Area Unemployment Statistics
 Spurous Seasonal Patterns and Excess Smoothness n the BLS Local Area Unemployment Statstcs Keth R. Phllps and Janguo Wang Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas Research Department Workng Paper 1305 September
Spurous Seasonal Patterns and Excess Smoothness n the BLS Local Area Unemployment Statstcs Keth R. Phllps and Janguo Wang Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas Research Department Workng Paper 1305 September
Privatization and government preference in an international Cournot triopoly
 Fernanda A Ferrera Flávo Ferrera Prvatzaton and government preference n an nternatonal Cournot tropoly FERNANDA A FERREIRA and FLÁVIO FERREIRA Appled Management Research Unt (UNIAG School of Hosptalty
Fernanda A Ferrera Flávo Ferrera Prvatzaton and government preference n an nternatonal Cournot tropoly FERNANDA A FERREIRA and FLÁVIO FERREIRA Appled Management Research Unt (UNIAG School of Hosptalty
2) In the medium-run/long-run, a decrease in the budget deficit will produce:
 4.02 Quz 2 Solutons Fall 2004 Multple-Choce Questons ) Consder the wage-settng and prce-settng equatons we studed n class. Suppose the markup, µ, equals 0.25, and F(u,z) = -u. What s the natural rate of
4.02 Quz 2 Solutons Fall 2004 Multple-Choce Questons ) Consder the wage-settng and prce-settng equatons we studed n class. Suppose the markup, µ, equals 0.25, and F(u,z) = -u. What s the natural rate of
In the 1990s, Japanese economy has experienced a surge in the unemployment rate,
 Productvty Growth and the female labor supply n Japan Yoko Furukawa * Tomohko Inu Abstract: In the 990s, Japanese economy has experenced a surge n the unemployment rate, and ths s due partly to the recent
Productvty Growth and the female labor supply n Japan Yoko Furukawa * Tomohko Inu Abstract: In the 990s, Japanese economy has experenced a surge n the unemployment rate, and ths s due partly to the recent
An Application of Alternative Weighting Matrix Collapsing Approaches for Improving Sample Estimates
 Secton on Survey Research Methods An Applcaton of Alternatve Weghtng Matrx Collapsng Approaches for Improvng Sample Estmates Lnda Tompkns 1, Jay J. Km 2 1 Centers for Dsease Control and Preventon, atonal
Secton on Survey Research Methods An Applcaton of Alternatve Weghtng Matrx Collapsng Approaches for Improvng Sample Estmates Lnda Tompkns 1, Jay J. Km 2 1 Centers for Dsease Control and Preventon, atonal
A MODEL OF COMPETITION AMONG TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE PROVIDERS BASED ON REPEATED GAME
 A MODEL OF COMPETITION AMONG TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE PROVIDERS BASED ON REPEATED GAME Vesna Radonć Đogatovć, Valentna Radočć Unversty of Belgrade Faculty of Transport and Traffc Engneerng Belgrade, Serba
A MODEL OF COMPETITION AMONG TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE PROVIDERS BASED ON REPEATED GAME Vesna Radonć Đogatovć, Valentna Radočć Unversty of Belgrade Faculty of Transport and Traffc Engneerng Belgrade, Serba
Volume 30, Issue 1. Partial privatization in price-setting mixed duopoly. Kazuhiro Ohnishi Institute for Basic Economic Science, Japan
 Volume 3, Issue 1 Partal prvatzaton n prce-settng mxed duopoly Kazuhro Ohnsh Insttute for Basc Economc Scence, Japan Abstract Ths paper nvestgates a prce-settng mxed model nvolvng a prvate frm and a publc
Volume 3, Issue 1 Partal prvatzaton n prce-settng mxed duopoly Kazuhro Ohnsh Insttute for Basc Economc Scence, Japan Abstract Ths paper nvestgates a prce-settng mxed model nvolvng a prvate frm and a publc
Uniform Output Subsidies in Economic Unions versus Profit-shifting Export Subsidies
 nform Output Subsdes n Economc nons versus Proft-shftng Export Subsdes Bernardo Moreno nversty of Málaga and José L. Torres nversty of Málaga Abstract Ths paper focuses on the effect of output subsdes
nform Output Subsdes n Economc nons versus Proft-shftng Export Subsdes Bernardo Moreno nversty of Málaga and José L. Torres nversty of Málaga Abstract Ths paper focuses on the effect of output subsdes
The Analysis of Net Position Development and the Comparison with GDP Development for Selected Countries of European Union
 The Analyss of Net Poston Development and the Comparson wth GDP Development for Selected Countres of European Unon JAROSLAV KOVÁRNÍK Faculty of Informatcs and Management, Department of Economcs Unversty
The Analyss of Net Poston Development and the Comparson wth GDP Development for Selected Countres of European Unon JAROSLAV KOVÁRNÍK Faculty of Informatcs and Management, Department of Economcs Unversty
Flight Delays, Capacity Investment and Welfare under Air Transport Supply-demand Equilibrium
 Flght Delays, Capacty Investment and Welfare under Ar Transport Supply-demand Equlbrum Bo Zou 1, Mark Hansen 2 1 Unversty of Illnos at Chcago 2 Unversty of Calforna at Berkeley 2 Total economc mpact of
Flght Delays, Capacty Investment and Welfare under Ar Transport Supply-demand Equlbrum Bo Zou 1, Mark Hansen 2 1 Unversty of Illnos at Chcago 2 Unversty of Calforna at Berkeley 2 Total economc mpact of
Tests for Two Correlations
 PASS Sample Sze Software Chapter 805 Tests for Two Correlatons Introducton The correlaton coeffcent (or correlaton), ρ, s a popular parameter for descrbng the strength of the assocaton between two varables.
PASS Sample Sze Software Chapter 805 Tests for Two Correlatons Introducton The correlaton coeffcent (or correlaton), ρ, s a popular parameter for descrbng the strength of the assocaton between two varables.
Monetary Tightening Cycles and the Predictability of Economic Activity. by Tobias Adrian and Arturo Estrella * October 2006.
 Monetary Tghtenng Cycles and the Predctablty of Economc Actvty by Tobas Adran and Arturo Estrella * October 2006 Abstract Ten out of thrteen monetary tghtenng cycles snce 1955 were followed by ncreases
Monetary Tghtenng Cycles and the Predctablty of Economc Actvty by Tobas Adran and Arturo Estrella * October 2006 Abstract Ten out of thrteen monetary tghtenng cycles snce 1955 were followed by ncreases
R Square Measure of Stock Synchronicity
 Internatonal Revew of Busness Research Papers Vol. 7. No. 1. January 2011. Pp. 165 175 R Square Measure of Stock Synchroncty Sarod Khandaker* Stock market synchroncty s a new area of research for fnance
Internatonal Revew of Busness Research Papers Vol. 7. No. 1. January 2011. Pp. 165 175 R Square Measure of Stock Synchroncty Sarod Khandaker* Stock market synchroncty s a new area of research for fnance
Analysis of Household Demand for Food in South Africa: Model Selection, Expenditure Endogeneity, and the Influence of Socio- Demographic Effects
 Analyss of Household Demand for Food n South Afrca: Model Selecton, Expendture Endogenety, and the Influence of Soco- Demographc Effects Lesba Bopape and Robert Myers Abstract Ths study analyzes food expendture
Analyss of Household Demand for Food n South Afrca: Model Selecton, Expendture Endogenety, and the Influence of Soco- Demographc Effects Lesba Bopape and Robert Myers Abstract Ths study analyzes food expendture
Price and Quantity Competition Revisited. Abstract
 rce and uantty Competton Revsted X. Henry Wang Unversty of Mssour - Columba Abstract By enlargng the parameter space orgnally consdered by Sngh and Vves (984 to allow for a wder range of cost asymmetry,
rce and uantty Competton Revsted X. Henry Wang Unversty of Mssour - Columba Abstract By enlargng the parameter space orgnally consdered by Sngh and Vves (984 to allow for a wder range of cost asymmetry,
Forecasts in Times of Crises
 Forecasts n Tmes of Crses Aprl 2017 Chars Chrstofdes IMF Davd J. Kuenzel Wesleyan Unversty Theo S. Echer Unversty of Washngton Chrs Papageorgou IMF 1 Macroeconomc forecasts suffer from three sources of
Forecasts n Tmes of Crses Aprl 2017 Chars Chrstofdes IMF Davd J. Kuenzel Wesleyan Unversty Theo S. Echer Unversty of Washngton Chrs Papageorgou IMF 1 Macroeconomc forecasts suffer from three sources of
Household Energy Demand and the Equity and Efficiency Aspects of. Subsidy Reform in Indonesia
 Household Energy Demand and the Equty and Effcency Aspects of Subsdy Reform n Indonesa Susan Olva Department of Agrcultural and Resource Economcs Unversty of Calforna, Davs olva@prmal.ucdavs.edu John bson
Household Energy Demand and the Equty and Effcency Aspects of Subsdy Reform n Indonesa Susan Olva Department of Agrcultural and Resource Economcs Unversty of Calforna, Davs olva@prmal.ucdavs.edu John bson
EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY
 EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY HIGHER CERTIFICATE IN STATISTICS, 2013 MODULE 7 : Tme seres and ndex numbers Tme allowed: One and a half hours Canddates should answer THREE questons.
EXAMINATIONS OF THE HONG KONG STATISTICAL SOCIETY HIGHER CERTIFICATE IN STATISTICS, 2013 MODULE 7 : Tme seres and ndex numbers Tme allowed: One and a half hours Canddates should answer THREE questons.
DETERMINING THE EFFECT OF NAFTA ON THE NORTH AMERICAN SWEET POTATO MARKET
 DETERMINING THE EFFECT OF NAFTA ON THE NORTH AMERICAN SWEET POTATO MARKET YOUNGJAE LEE Department of Agrcultural Economcs and Agrbusness Lousana State Unversty AgCenter 242A Martn D. Woodn Hall Baton Rouge,
DETERMINING THE EFFECT OF NAFTA ON THE NORTH AMERICAN SWEET POTATO MARKET YOUNGJAE LEE Department of Agrcultural Economcs and Agrbusness Lousana State Unversty AgCenter 242A Martn D. Woodn Hall Baton Rouge,
Analysis of the Influence of Expenditure Policies of Government on Macroeconomic behavior of an Agent- Based Artificial Economic System
 Analyss of the Influence of Expendture olces of Government on Macroeconomc behavor of an Agent- Based Artfcal Economc System Shgeak Ogbayash 1 and Kouse Takashma 1 1 School of Socal Systems Scence Chba
Analyss of the Influence of Expendture olces of Government on Macroeconomc behavor of an Agent- Based Artfcal Economc System Shgeak Ogbayash 1 and Kouse Takashma 1 1 School of Socal Systems Scence Chba
Notes are not permitted in this examination. Do not turn over until you are told to do so by the Invigilator.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Economcs Man Seres PG Examnaton 2016-17 BANKING ECONOMETRICS ECO-7014A Tme allowed: 2 HOURS Answer ALL FOUR questons. Queston 1 carres a weght of 30%; queston 2 carres
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Economcs Man Seres PG Examnaton 2016-17 BANKING ECONOMETRICS ECO-7014A Tme allowed: 2 HOURS Answer ALL FOUR questons. Queston 1 carres a weght of 30%; queston 2 carres
Welfare Aspects of FDI to Source Country: An Example of Increasing FDI in China
 Welfare Aspects of FDI to Source Country: An Example of Increasng FDI n Chna Shh-Hsun Hsu, Yungho Weng Kung-Chung Hsu, Chng-Cheng Chang, Fang-Chu Tu * Abstract Ths paper takes FDI n Chna as an example
Welfare Aspects of FDI to Source Country: An Example of Increasng FDI n Chna Shh-Hsun Hsu, Yungho Weng Kung-Chung Hsu, Chng-Cheng Chang, Fang-Chu Tu * Abstract Ths paper takes FDI n Chna as an example
3/3/2014. CDS M Phil Econometrics. Vijayamohanan Pillai N. Truncated standard normal distribution for a = 0.5, 0, and 0.5. CDS Mphil Econometrics
 Lmted Dependent Varable Models: Tobt an Plla N 1 CDS Mphl Econometrcs Introducton Lmted Dependent Varable Models: Truncaton and Censorng Maddala, G. 1983. Lmted Dependent and Qualtatve Varables n Econometrcs.
Lmted Dependent Varable Models: Tobt an Plla N 1 CDS Mphl Econometrcs Introducton Lmted Dependent Varable Models: Truncaton and Censorng Maddala, G. 1983. Lmted Dependent and Qualtatve Varables n Econometrcs.
Quiz 2 Answers PART I
 Quz 2 nswers PRT I 1) False, captal ccumulaton alone wll not sustan growth n output per worker n the long run due to dmnshng margnal returns to captal as more and more captal s added to a gven number of
Quz 2 nswers PRT I 1) False, captal ccumulaton alone wll not sustan growth n output per worker n the long run due to dmnshng margnal returns to captal as more and more captal s added to a gven number of
Macroeconomic Theory and Policy
 ECO 209 Macroeconomc Theory and Polcy Lecture 7: The Open Economy wth Fxed Exchange Rates Gustavo Indart Slde 1 Open Economy under Fxed Exchange Rates Let s consder an open economy wth no captal moblty
ECO 209 Macroeconomc Theory and Polcy Lecture 7: The Open Economy wth Fxed Exchange Rates Gustavo Indart Slde 1 Open Economy under Fxed Exchange Rates Let s consder an open economy wth no captal moblty
UNIVERSITY OF WAIKATO. Hamilton New Zealand. Household Energy Demand and the Equity and Efficiency Aspects of Subsidy Reform in Indonesia
 UNIVERSITY OF WAIKATO Hamlton New Zealand Household Energy Demand and the Equty and Effcency Aspects of Subsdy Reform n Indonesa Susan Olva Unversty of Calforna, Davs John Gbson Unversty of Wakato Department
UNIVERSITY OF WAIKATO Hamlton New Zealand Household Energy Demand and the Equty and Effcency Aspects of Subsdy Reform n Indonesa Susan Olva Unversty of Calforna, Davs John Gbson Unversty of Wakato Department
Interregional Trade, Industrial Location and. Import Infrastructure*
 Interregonal Trade, Industral Locaton and Import Infrastructure* Toru Kkuch (Kobe Unversty) and Kazumch Iwasa (Kyoto Unversty)** Abstract The purpose of ths study s to llustrate, wth a smple two-regon,
Interregonal Trade, Industral Locaton and Import Infrastructure* Toru Kkuch (Kobe Unversty) and Kazumch Iwasa (Kyoto Unversty)** Abstract The purpose of ths study s to llustrate, wth a smple two-regon,
Highlights of the Macroprudential Report for June 2018
 Hghlghts of the Macroprudental Report for June 2018 October 2018 FINANCIAL STABILITY DEPARTMENT Preface Bank of Jamaca frequently conducts assessments of the reslence and strength of the fnancal system.
Hghlghts of the Macroprudental Report for June 2018 October 2018 FINANCIAL STABILITY DEPARTMENT Preface Bank of Jamaca frequently conducts assessments of the reslence and strength of the fnancal system.
Macroeconomic equilibrium in the short run: the Money market
 Macroeconomc equlbrum n the short run: the Money market 2013 1. The bg pcture Overvew Prevous lecture How can we explan short run fluctuatons n GDP? Key assumpton: stcky prces Equlbrum of the goods market
Macroeconomc equlbrum n the short run: the Money market 2013 1. The bg pcture Overvew Prevous lecture How can we explan short run fluctuatons n GDP? Key assumpton: stcky prces Equlbrum of the goods market
Money, Banking, and Financial Markets (Econ 353) Midterm Examination I June 27, Name Univ. Id #
 Money, Bankng, and Fnancal Markets (Econ 353) Mdterm Examnaton I June 27, 2005 Name Unv. Id # Note: Each multple-choce queston s worth 4 ponts. Problems 20, 21, and 22 carry 10, 8, and 10 ponts, respectvely.
Money, Bankng, and Fnancal Markets (Econ 353) Mdterm Examnaton I June 27, 2005 Name Unv. Id # Note: Each multple-choce queston s worth 4 ponts. Problems 20, 21, and 22 carry 10, 8, and 10 ponts, respectvely.
Tests for Two Ordered Categorical Variables
 Chapter 253 Tests for Two Ordered Categorcal Varables Introducton Ths module computes power and sample sze for tests of ordered categorcal data such as Lkert scale data. Assumng proportonal odds, such
Chapter 253 Tests for Two Ordered Categorcal Varables Introducton Ths module computes power and sample sze for tests of ordered categorcal data such as Lkert scale data. Assumng proportonal odds, such
Quiz on Deterministic part of course October 22, 2002
 Engneerng ystems Analyss for Desgn Quz on Determnstc part of course October 22, 2002 Ths s a closed book exercse. You may use calculators Grade Tables There are 90 ponts possble for the regular test, or
Engneerng ystems Analyss for Desgn Quz on Determnstc part of course October 22, 2002 Ths s a closed book exercse. You may use calculators Grade Tables There are 90 ponts possble for the regular test, or
Predicting the Effects of NAFTA: Now We Can Do It Better!
 Shkher, Journal of Internatonal and Global Economc Studes, 5(2), December 2012, 32-59 32 Predctng the Effects of NAFTA: Now We Can Do It Better! Serge Shkher * Suffolk Unversty Abstract The North Amercan
Shkher, Journal of Internatonal and Global Economc Studes, 5(2), December 2012, 32-59 32 Predctng the Effects of NAFTA: Now We Can Do It Better! Serge Shkher * Suffolk Unversty Abstract The North Amercan
U.S. Imports Demand for Cocoa Products by Country of Origin
 U.S. Imports Demand for Cocoa Products by Country of Orgn Luce Abena Kado Graduate Research Assstant Department of Food and Resource Economcs Unversty of Florda lucekado@gmal.com James L. Seale, Jr. Professor
U.S. Imports Demand for Cocoa Products by Country of Orgn Luce Abena Kado Graduate Research Assstant Department of Food and Resource Economcs Unversty of Florda lucekado@gmal.com James L. Seale, Jr. Professor
An Empirical Study on Stock Price Responses to the Release of the Environmental Management Ranking in Japan. Abstract
 An Emprcal Study on Stock Prce esponses to the elease of the Envronmental Management ankng n Japan Fumko Takeda Unversy of Tokyo Takanor Tomozawa Unversy of Tokyo Abstract Ths paper nvestgates how stock
An Emprcal Study on Stock Prce esponses to the elease of the Envronmental Management ankng n Japan Fumko Takeda Unversy of Tokyo Takanor Tomozawa Unversy of Tokyo Abstract Ths paper nvestgates how stock
Market Opening and Stock Market Behavior: Taiwan s Experience
 Internatonal Journal of Busness and Economcs, 00, Vol., No., 9-5 Maret Openng and Stoc Maret Behavor: Tawan s Experence Q L * Department of Economcs, Texas A&M Unversty, U.S.A. and Department of Economcs,
Internatonal Journal of Busness and Economcs, 00, Vol., No., 9-5 Maret Openng and Stoc Maret Behavor: Tawan s Experence Q L * Department of Economcs, Texas A&M Unversty, U.S.A. and Department of Economcs,
Impacts of Population Aging on Economic Growth and Structure Change in China
 Impacts of Populaton Agng on Economc Growth and Structure Change n Chna The feature of Chnese demographc structure s changng from a hgh fertlty rate, hgh death rate and low lfe expectancy to low fertlty
Impacts of Populaton Agng on Economc Growth and Structure Change n Chna The feature of Chnese demographc structure s changng from a hgh fertlty rate, hgh death rate and low lfe expectancy to low fertlty
The well-known analyses of Balassa (1964) and Samuelson (1964) provide an
 IMF Staff Papers Vol. 52, Number 3 2005 Internatonal Monetary Fund Real Exchange Rates n Developng Countres: Are Balassa-Samuelson Effects Present? EHSAN U. CHOUDHRI AND MOHSIN S. KHAN* There s surprsngly
IMF Staff Papers Vol. 52, Number 3 2005 Internatonal Monetary Fund Real Exchange Rates n Developng Countres: Are Balassa-Samuelson Effects Present? EHSAN U. CHOUDHRI AND MOHSIN S. KHAN* There s surprsngly
Staff Paper P13-5 November Staff Paper Series. On Price Endogeneity in the Analysis of Food Demand in China
 Staff Paper P13-5 November 2013 Staff Paper Seres On Prce Endogenety n the Analyss of Food Demand n Chna By Vardges Hovhannsyan and Marn Bozc Staff Paper P13-5 November 2013 On Prce Endogenety n the Analyss
Staff Paper P13-5 November 2013 Staff Paper Seres On Prce Endogenety n the Analyss of Food Demand n Chna By Vardges Hovhannsyan and Marn Bozc Staff Paper P13-5 November 2013 On Prce Endogenety n the Analyss
PRESS RELEASE. The evolution of the Consumer Price Index (CPI) of March 2017 (reference year 2009=100.0) is depicted as follows:
 HELLENIC EPUBLIC HELLENIC STATISTICAL AUTHOITY Praeus, Aprl 27 PESS ELEASE CONSUME PICE INDEX: March 27, annual nflaton.7% The evoluton of the Consumer Prce Index (CPI) of March 27 (reference year 29=.)
HELLENIC EPUBLIC HELLENIC STATISTICAL AUTHOITY Praeus, Aprl 27 PESS ELEASE CONSUME PICE INDEX: March 27, annual nflaton.7% The evoluton of the Consumer Prce Index (CPI) of March 27 (reference year 29=.)
A Bootstrap Confidence Limit for Process Capability Indices
 A ootstrap Confdence Lmt for Process Capablty Indces YANG Janfeng School of usness, Zhengzhou Unversty, P.R.Chna, 450001 Abstract The process capablty ndces are wdely used by qualty professonals as an
A ootstrap Confdence Lmt for Process Capablty Indces YANG Janfeng School of usness, Zhengzhou Unversty, P.R.Chna, 450001 Abstract The process capablty ndces are wdely used by qualty professonals as an
INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS FOR THE SHORT RUN (CHAPTER 1) WHY STUDY BUSINESS CYCLES? The intellectual challenge: Why is economic growth irregular?
 INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS FOR THE SHORT RUN (CHATER 1) WHY STUDY BUSINESS CYCLES? The ntellectual challenge: Why s economc groth rregular? The socal challenge: Recessons and depressons cause elfare
INTRODUCTION TO MACROECONOMICS FOR THE SHORT RUN (CHATER 1) WHY STUDY BUSINESS CYCLES? The ntellectual challenge: Why s economc groth rregular? The socal challenge: Recessons and depressons cause elfare
Homework 4 Answer Key
 Economcs 141 UCSC Professor Kletzer Sprng 2017 Homework 4 Answer Key 1. Use producton functon and MPK dagrams to examne Turkey and the EU. Assume that Turkey and the EU have dfferent producton functons
Economcs 141 UCSC Professor Kletzer Sprng 2017 Homework 4 Answer Key 1. Use producton functon and MPK dagrams to examne Turkey and the EU. Assume that Turkey and the EU have dfferent producton functons
ECO 209Y MACROECONOMIC THEORY AND POLICY LECTURE 8: THE OPEN ECONOMY WITH FIXED EXCHANGE RATES
 ECO 209 MACROECONOMIC THEOR AND POLIC LECTURE 8: THE OPEN ECONOM WITH FIXED EXCHANGE RATES Gustavo Indart Slde 1 OPEN ECONOM UNDER FIXED EXCHANGE RATES Let s consder an open economy wth no captal moblty
ECO 209 MACROECONOMIC THEOR AND POLIC LECTURE 8: THE OPEN ECONOM WITH FIXED EXCHANGE RATES Gustavo Indart Slde 1 OPEN ECONOM UNDER FIXED EXCHANGE RATES Let s consder an open economy wth no captal moblty
Which of the following provides the most reasonable approximation to the least squares regression line? (a) y=50+10x (b) Y=50+x (d) Y=1+50x
 Whch of the followng provdes the most reasonable approxmaton to the least squares regresson lne? (a) y=50+10x (b) Y=50+x (c) Y=10+50x (d) Y=1+50x (e) Y=10+x In smple lnear regresson the model that s begn
Whch of the followng provdes the most reasonable approxmaton to the least squares regresson lne? (a) y=50+10x (b) Y=50+x (c) Y=10+50x (d) Y=1+50x (e) Y=10+x In smple lnear regresson the model that s begn
Wages as Anti-Corruption Strategy: A Note
 DISCUSSION PAPER November 200 No. 46 Wages as Ant-Corrupton Strategy: A Note by dek SAO Faculty of Economcs, Kyushu-Sangyo Unversty Wages as ant-corrupton strategy: A Note dek Sato Kyushu-Sangyo Unversty
DISCUSSION PAPER November 200 No. 46 Wages as Ant-Corrupton Strategy: A Note by dek SAO Faculty of Economcs, Kyushu-Sangyo Unversty Wages as ant-corrupton strategy: A Note dek Sato Kyushu-Sangyo Unversty
EDC Introduction
 .0 Introducton EDC3 In the last set of notes (EDC), we saw how to use penalty factors n solvng the EDC problem wth losses. In ths set of notes, we want to address two closely related ssues. What are, exactly,
.0 Introducton EDC3 In the last set of notes (EDC), we saw how to use penalty factors n solvng the EDC problem wth losses. In ths set of notes, we want to address two closely related ssues. What are, exactly,
Does a Threshold Inflation Rate Exist? Quantile Inferences for Inflation and Its Variability
 Does a Threshold Inflaton Rate Exst? Inferences for Inflaton and Its Varablty WenShwo Fang Department of Economcs Feng Cha Unversty Tachung, TAIWAN Stephen M. Mller* Department of Economcs Unversty of
Does a Threshold Inflaton Rate Exst? Inferences for Inflaton and Its Varablty WenShwo Fang Department of Economcs Feng Cha Unversty Tachung, TAIWAN Stephen M. Mller* Department of Economcs Unversty of
Economics 1410 Fall Section 7 Notes 1. Define the tax in a flexible way using T (z), where z is the income reported by the agent.
 Economcs 1410 Fall 2017 Harvard Unversty Yaan Al-Karableh Secton 7 Notes 1 I. The ncome taxaton problem Defne the tax n a flexble way usng T (), where s the ncome reported by the agent. Retenton functon:
Economcs 1410 Fall 2017 Harvard Unversty Yaan Al-Karableh Secton 7 Notes 1 I. The ncome taxaton problem Defne the tax n a flexble way usng T (), where s the ncome reported by the agent. Retenton functon:
Protecting India s Trade Liberalization? Tariff Reform, Antidumping and Safeguards
 Protectng Inda s Trade Lberalzaton? Tarff Reform, Antdumpng and Safeguards Chad P. Bown Brandes Unversty Patrca Tovar Brandes Unversty 30 October 2007 Prelmnary and ncomplete: please do not quote, cte
Protectng Inda s Trade Lberalzaton? Tarff Reform, Antdumpng and Safeguards Chad P. Bown Brandes Unversty Patrca Tovar Brandes Unversty 30 October 2007 Prelmnary and ncomplete: please do not quote, cte
TRADE IMPLICATIONS OF EXTENDING THE TURKEY-EU CUSTOMS UNION TO AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTS *
 Prelmnary draft please, do not quote TRADE IMPLICATIONS OF EXTENDING THE TURKEY-EU CUSTOMS UNION TO AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTS * H. Ozan ERUYGUR Mddle East Techncal Unversty, Department of Economcs, Ankara
Prelmnary draft please, do not quote TRADE IMPLICATIONS OF EXTENDING THE TURKEY-EU CUSTOMS UNION TO AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTS * H. Ozan ERUYGUR Mddle East Techncal Unversty, Department of Economcs, Ankara
COMPETITION BETWEEN DOMESTIC AND IMPORTED FARMED FISH A DEMAND SYSTEM ANALYSIS
 COMPETITION BETWEEN DOMESTIC AND IMPORTED FARMED FISH A DEMAND SYSTEM ANALYSIS Except where reference s made to the work of others, the work descrbed n ths thess s my own or was done n collaboraton wth
COMPETITION BETWEEN DOMESTIC AND IMPORTED FARMED FISH A DEMAND SYSTEM ANALYSIS Except where reference s made to the work of others, the work descrbed n ths thess s my own or was done n collaboraton wth
WPS4077 THE COMPOSITION OF GROWTH MATTERS FOR POVERTY ALLEVIATION * Abstract
 Publc Dsclosure Authorzed Publc Dsclosure Authorzed Publc Dsclosure Authorzed Publc Dsclosure Authorzed THE COMPOSITION OF GROWTH MATTERS FOR POVERTY ALLEVIATION * Norman Loayza The World Bank Abstract
Publc Dsclosure Authorzed Publc Dsclosure Authorzed Publc Dsclosure Authorzed Publc Dsclosure Authorzed THE COMPOSITION OF GROWTH MATTERS FOR POVERTY ALLEVIATION * Norman Loayza The World Bank Abstract
CANADA I. BASIC "T3ICAT0RS
 Trade Development Summary September 1953 CANADA I. BASIC "T3ICAT0RS (a) Producton The rate of ncrease n ndustral producton s not losng any of ts momentum, and output durng the frst four months of the year
Trade Development Summary September 1953 CANADA I. BASIC "T3ICAT0RS (a) Producton The rate of ncrease n ndustral producton s not losng any of ts momentum, and output durng the frst four months of the year
FORD MOTOR CREDIT COMPANY SUGGESTED ANSWERS. Richard M. Levich. New York University Stern School of Business. Revised, February 1999
 FORD MOTOR CREDIT COMPANY SUGGESTED ANSWERS by Rchard M. Levch New York Unversty Stern School of Busness Revsed, February 1999 1 SETTING UP THE PROBLEM The bond s beng sold to Swss nvestors for a prce
FORD MOTOR CREDIT COMPANY SUGGESTED ANSWERS by Rchard M. Levch New York Unversty Stern School of Busness Revsed, February 1999 1 SETTING UP THE PROBLEM The bond s beng sold to Swss nvestors for a prce
Module Contact: Dr P Moffatt, ECO Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 2
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Economcs Man Seres PG Examnaton 2012-13 FINANCIAL ECONOMETRICS ECO-M017 Tme allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL FOUR questons. Queston 1 carres a weght of 25%; Queston 2 carres
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Economcs Man Seres PG Examnaton 2012-13 FINANCIAL ECONOMETRICS ECO-M017 Tme allowed: 2 hours Answer ALL FOUR questons. Queston 1 carres a weght of 25%; Queston 2 carres
Conditional beta capital asset pricing model (CAPM) and duration dependence tests
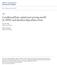 Edth Cowan Unversty Research Onlne ECU Publcatons Pre. 2011 2009 Condtonal beta captal asset prcng model (CAPM) and duraton dependence tests Davd E. Allen Edth Cowan Unversty Imbarne Bujang Edth Cowan
Edth Cowan Unversty Research Onlne ECU Publcatons Pre. 2011 2009 Condtonal beta captal asset prcng model (CAPM) and duraton dependence tests Davd E. Allen Edth Cowan Unversty Imbarne Bujang Edth Cowan
Was the Barrier to Labor Mobility an Important Factor for the Prewar Japanese Stagnation?
 MPRA Munch Personal RePEc Archve Was the Barrer to Laor Molty an Important Factor for the Prewar Japanese Stagnaton? Shuhe Aok Graduate School of Economcs, Unversty of Tokyo 9. Aprl 2008 Onlne at http://mpra.u.un-muenchen.de/878/
MPRA Munch Personal RePEc Archve Was the Barrer to Laor Molty an Important Factor for the Prewar Japanese Stagnaton? Shuhe Aok Graduate School of Economcs, Unversty of Tokyo 9. Aprl 2008 Onlne at http://mpra.u.un-muenchen.de/878/
THE ECONOMICS OF TAXATION
 THE ECONOMICS OF TAXATION Statc Ramsey Tax School of Economcs, Xamen Unversty Fall 2015 Overvew of Optmal Taxaton Combne lessons on ncdence and effcency costs to analyze optmal desgn of commodty taxes.
THE ECONOMICS OF TAXATION Statc Ramsey Tax School of Economcs, Xamen Unversty Fall 2015 Overvew of Optmal Taxaton Combne lessons on ncdence and effcency costs to analyze optmal desgn of commodty taxes.
Conditional Beta Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and Duration Dependence Tests
 Condtonal Beta Captal Asset Prcng Model (CAPM) and Duraton Dependence Tests By Davd E. Allen 1 and Imbarne Bujang 1 1 School of Accountng, Fnance and Economcs, Edth Cowan Unversty School of Accountng,
Condtonal Beta Captal Asset Prcng Model (CAPM) and Duraton Dependence Tests By Davd E. Allen 1 and Imbarne Bujang 1 1 School of Accountng, Fnance and Economcs, Edth Cowan Unversty School of Accountng,
Demand for food in Ondo state, Nigeria: Using quadratic almost ideal demand system
 E3 Journal of Busness Management and Economcs Vol. 4(1). pp.001-019, January, 2013 Avalable onlne http://www.e3ournals.org ISSN 2141-7482 E3 Journals 2013 Full length research paper Demand for food n Ondo
E3 Journal of Busness Management and Economcs Vol. 4(1). pp.001-019, January, 2013 Avalable onlne http://www.e3ournals.org ISSN 2141-7482 E3 Journals 2013 Full length research paper Demand for food n Ondo
Explaining and Comparing
 ACES EU CENTERS OF EXCELLENCE GRANT AY2011-12 DELIVERABLE GWU Explanng and Comparng AY 2011-12 Practcal Modfed Gn Index Amr Shoham (wth M Malul, Danel Shapra) Practcal Modfed Gn Index M Malul, Danel Shapra
ACES EU CENTERS OF EXCELLENCE GRANT AY2011-12 DELIVERABLE GWU Explanng and Comparng AY 2011-12 Practcal Modfed Gn Index Amr Shoham (wth M Malul, Danel Shapra) Practcal Modfed Gn Index M Malul, Danel Shapra
Financial crisis and exchange rates in emerging economies: An empirical analysis using PPP- UIP-Framework
 Fnancal crss and exchange rates n emergng economes BEH: www.beh.pradec.eu Peer-revewed and Open access journal ISSN: 1804-5006 www.academcpublshngplatforms.com The prmary verson of the journal s the on-lne
Fnancal crss and exchange rates n emergng economes BEH: www.beh.pradec.eu Peer-revewed and Open access journal ISSN: 1804-5006 www.academcpublshngplatforms.com The prmary verson of the journal s the on-lne
The Role of Global Economic Growth in Pakistani Agri-Food Exports
 The Pakstan Development Revew 50:3 (Autumn 2011) pp. 245 256 The Role of Global Economc Growth n Pakstan Agr-Food Exports ZAHOOR UL HAQ, MOHAMED GHEBLAWI, and SAFDAR MUHAMMAD * Ths analyss uses least squares
The Pakstan Development Revew 50:3 (Autumn 2011) pp. 245 256 The Role of Global Economc Growth n Pakstan Agr-Food Exports ZAHOOR UL HAQ, MOHAMED GHEBLAWI, and SAFDAR MUHAMMAD * Ths analyss uses least squares
PRESS RELEASE. CONSUMER PRICE INDEX: December 2016, annual inflation 0.0% HELLENIC REPUBLIC HELLENIC STATISTICAL AUTHORITY Piraeus, 11 January 2017
 HELLENIC EPUBLIC HELLENIC STATISTICAL AUTHOITY Praeus, 11 January 2017 PESS ELEASE CONSUME PICE INDE: December 2016, annual nflaton % The Consumer Prce Index (CPI), wth reference year 2009=10, n December
HELLENIC EPUBLIC HELLENIC STATISTICAL AUTHOITY Praeus, 11 January 2017 PESS ELEASE CONSUME PICE INDE: December 2016, annual nflaton % The Consumer Prce Index (CPI), wth reference year 2009=10, n December
Chapter 5 Bonds, Bond Prices and the Determination of Interest Rates
 Chapter 5 Bonds, Bond Prces and the Determnaton of Interest Rates Problems and Solutons 1. Consder a U.S. Treasury Bll wth 270 days to maturty. If the annual yeld s 3.8 percent, what s the prce? $100 P
Chapter 5 Bonds, Bond Prces and the Determnaton of Interest Rates Problems and Solutons 1. Consder a U.S. Treasury Bll wth 270 days to maturty. If the annual yeld s 3.8 percent, what s the prce? $100 P
ASYMMETRIC TRADE FLOWS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR COMPETITIVENESS, EFFICIENCY AND TRADE
 ASYMMETRIC TRADE FLOWS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR COMPETITIVENESS, EFFICIENCY AND TRADE YOUNGJAE LEE Department of Agrcultural Economcs and Agrbusness Lousana State Unversty AgCenter 242A Martn D. Woodn
ASYMMETRIC TRADE FLOWS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR COMPETITIVENESS, EFFICIENCY AND TRADE YOUNGJAE LEE Department of Agrcultural Economcs and Agrbusness Lousana State Unversty AgCenter 242A Martn D. Woodn
FRAGMENTATION, PRODUCTIVITY AND RELATIVE WAGES IN THE UK: A GENERAL EQUILIBRIUM APPROACH * Alexander Hijzen. University of Nottingham
 FRAGMENTATION, PRODUCTIVITY AND RELATIVE WAGES IN THE UK: A GENERAL EQUILIBRIUM APPROACH Alexander Hjzen Unversty of Nottngham Abstract Feenstra and Hanson (1999) propose a two-stop method to analyse the
FRAGMENTATION, PRODUCTIVITY AND RELATIVE WAGES IN THE UK: A GENERAL EQUILIBRIUM APPROACH Alexander Hjzen Unversty of Nottngham Abstract Feenstra and Hanson (1999) propose a two-stop method to analyse the
