ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS
|
|
|
- Bryan Ellis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Maple Grove Senior High School Jeff Rush rushsocialstudies.weebly.com, aplia.com Social Studies Department Required textbook Economics, McConnell and Brue, 17 th edition, Course description Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole or its basic parts or aggregates in an effort to obtain a general overview of the economy as a whole and how its parts relate to one another. As a result we will focus on economic measure such aggregates and the general price level to analyze economic problems. Students will be expected to be able to use critical thinking skills as they present their analysis along with appropriate graphical representations. Course grading Student work will be assessed in accordance with school, district, and classroom policies and expectations. Grades earned by students will be based on an evaluation of summative work (80%) and formative work (20%). Weekly quizzes and assigned readings It is expected that all assigned readings be completed by the beginning of the week for which they are assigned. Quizzes on assigned readings and classroom instruction are administered for formative purposes: students and the teacher should use these assessments as a means to determine the current level of understanding and areas where improvement is needed. As such, these quizzes will not always be announced. Unit exams Unit exams are designed to fulfill two general purposes. First, they serve as summative assessments of the information covered over multiple chapters. Second, they are meant to prepare students for taking the AP exam. Course mechanics Attendance: Attendance will be taken at the beginning of each class period. Please respect your classmates, your teacher, and your own learning by showing up on time. Classroom Behavior: All students are expected to behave with respect toward each other, their teacher, and the classroom. It is expected that students will bring all relevant course materials to class each day (pen/pencil, notebook/folder, & basic function calculator). Make-Up Procedures: It is the responsibility of absent students to check with a classmate or the teacher upon their return to school to receive any missed assignments or notes. Grades: Students will earn a grade based upon what they have learned, not simply what work has been attempted or completed. Final grades will include an evaluation of all assignments, quizzes, exams, and student learning. The following grading scale will be used: 1
2 A: 3.51 A-: 3.0 B+: 2.84 B: 2.67 B-: 2.5 C+ : 2.34 C: 2.17 C- : 2.0 D+: 1.84 D: 1.67 D-: 1.5 Formative Task Examples (20%) Summative Task Examples (80%) -Homework -Exam 1 -In-class assignments -Exam 2 -Reading quizzes -Exam 3 -APLIA practice -Comprehensive final Formative Tasks: o Students who are absent the day a formative assessment is assigned are expected to complete the task within five school days of their return. o Students who are absent the day a formative assessment is due are expected to turn in the task immediately upon their return. o Credit for formative work will only be granted if the work is completed prior to the initial summative assessment. Summative Tasks: o Students who are absent the day of a summative assessment are expected to complete the assessment within five school days of their return. Please make these arrangements with the instructor. o Reassessment assumptions: All original formative work is completed BEFORE INITIAL TEST and meets the standards. Additional assigned formative work is completed to standard. The format of the additional formative work is at the discretion of the instructor. The reassessment of the summative task will take place prior to the next summative assessment or within a reasonable timeframe established by the instructor. The format of the reassessment is at the discretion of the instructor. Students can boost their Maple Grove grade by scoring well on the AP exam as follows: Score on AP exam Course grade Standards-based grading (will be changed if students assessment score earned less than this during the trimester) District 279 Secondary Rubric Descriptors 5 A 4 Displays excellent quality and performs with high accuracy 4 A- 3 Displays high quality and performs with accuracy 3 B 2.67 Displays/performs with a mix of the criteria described above/below 0-2 No Impact 2 Displays basic, limited, or a lack of quality; performs with inconsistent, limited or lack of understanding 2
3 Course Outline Unit 1: Economic Fundamentals (5 Lessons) Topic I: Basic Economic Concepts Chapter 1 A. Scarcity: Define and illustrate. B. Opportunity Cost: Define and compute. 1. Marginal Analysis a. Costs and Benefits 2. Positive and Normative economics C. Society s Economizing Problem 1. Scarce resources 2. Resource Categories D. Production Possibilities Model: Draw and Describe. 1. Production Possibilities Table 2. Production Possibilities Graph 3. Law of Increasing Opportunity Cost a. Human Capital Formation b. Physical Capital Accumulation c. Research and Development, Technological Progress 4. Optimal Allocation a. Marginal Benefit equals Marginal Cost E. Unemployment, Growth, and the Future 1. A Growing Economy 2. Present Choices and Future Possibilities a. A Qualification: International Trade Topic II: The Market System and the Circular Flow Chapter 2 A. Economic Systems 1.Command and Market Systems Defined B. Characteristics of the Market System 1. Private Property 2. Freedom of Enterprise and Choice 3. Self-Interest 4. Competition 5. Markets and Prices 6. Technology and Capital Goods 7. Specialization 8. Use of Money 9. Active, but Limited Government C. Five Fundamental Questions 1. What Will Be Produced? 2. How Will It Be Produced? 3. Who Will Get What Is Produced? 4. How Will the System Accommodate Change? 5. How Will the System Promote Progress? D. The Invisible Hand E. The Demise of the Command System 1. The Coordination Problem 2. The Incentive Problem F. The Circular Flow Model 1. Resource/Factor Market 2. Product Market 3
4 Topic III: Demand, Supply, and Market Equilibrium Chapter 3 A.Demand: Define and illustrate demand through schedules and graphs. 1.Examine the inverse relationship existing between quantity demanded and price. Evaluate the Law of Demand. (Ceteris Paribus) 2.Distinguish between change(s) in quantity demanded and change(s) in demand. 3.Identify and explain the variables that cause a change in demand. 4.Illustrate graphically a change in demand versus a change in quantity demanded. B. Supply: Define and illustrate supply through schedules and graphs. 1.Examine the direct relationship existing between quantity supplied and price. Evaluate the Law of Supply. (Ceteris Paribus) 2. Distinguish between change(s) in quantity supplied and change(s) in supply. 3. Identify and explain the variables that cause a change in supply. 4.Illustrate graphically a change in supply versus a change in quantity supplied. C. Equilibrium Price and Quantity: Define and illustrate equilibrium through schedules and graphs. 1.Define and illustrate surpluses and shortages. 2.Define the effects of surpluses and shortages on prices and quantities. 3.Interpret the effects of a price floor and price ceiling on equilibrium price and quantity. 4.Market failures: lack of competition, externalities, and public goods. Topic IV: The United States Economy: Private and Public Sectors Chapter 4 A. Households 1. Income Receivers 2. Income Spenders B.Businesses Population 1. Plant; Firm; Industry Distinction C. The Public Sector: Government s Role 1. Providing the Legal Structure 2. Maintaining Competition 3. Redistributing Income 4. Reallocating Resources 5. Promoting Stability D. The Circular Flow Model Revisited E. Government Finance 1. Federal Level 2. State Level 4
5 Topic V: The United States in a Global Economy Chapter 5 A. Specialization and Comparative Advantage 1. Absolute v. Comparative Advantage 2. Comparative Advantage: Production Possibilities Analysis B. The Foreign Exchange Market 1. Dollar Yen Market 2. Changing Rates: Depreciation and Appreciation Essential Questions 1. What are the economic goals of any society? 2. How does the production possibilities model illustrate the economic problem of scarcity, choice, and cost? 3. How does the circular flow model explain the functioning of a market economy? 4. What are the guideposts to economic thinking? 5. Why do people trade? Key Teaching Concepts 1. Scarcity, Choice and Cost 2. Allocative, & Technical Efficiency 3. Rational Choice: MSC = MSB 4. Absolute vs. Comparative Advantage Graphical/Mathematical Analysis Graph a production possibility model Explain the shapes of the production possibilities curves. Explain how the production possibilities model shows scarcity, choice, and cost. Interpret selected points on the production possibilities model. Explain and show economic growth on the production possibility models Explain and show the effects of trade on a production possibility model. Draw and explain the components of a basic circular flow model. Calculate opportunity cost. Calculate comparative advantage. Calculate terms of trade and gains from trade. Unit 2: Measuring Economic Performance (16 Lessons) Part 1: Macroeconomic Measurement and Basic Concepts Topic I: Domestic Output and National Income Chapter 6 A. GDP: how is it defined? What is and is not included? Use of aggregates. B. Measuring GDP 1. Expenditure approach [GDP = C + I + G + Xn] where: C = Personal Consumption Expenditures I = Gross Private Investment G = Government Consumption Expenditures and Gross Investment Xn = Net Exports 2. Problems with calculating GDP: Non-market transactions, distribution, kind and quality of products. C. Other national accounts: net domestic product (NDP), national income (NI), personal income (PI), and disposable income (DI). 1. Circular Flow Model Revisited: understand its parts (product and factor markets) and how all economic activity is incorporated into its design. How can this be used to analyze intended and unintended impacts of policy or shocks? D. Nominal GDP verses Real GDP 1. Changing Nominal GDP (NGDP) to Real GDP (RGDP). How and why? a. Price Index 1. CPI 2. PPI 2. What RGDP doesn t adjust for: population, income distribution, externalities, types of production. 5
6 Topic II: Introduction to Economic Growth and Instability Chapter 7 A. Economic Growth 1. Growth as a goal 2. Main Sources of Growth B. The Business Cycle 1. The four phases of the business cycle 2. Causation of the Business Cycle 3. Impacts on: Durables and Nondurable s C. Unemployment: 1. How is Unemployment Measured? a. Full Employment 2. Types of Unemployment 3. Costs of Unemployment D. Inflation 1. The Meaning and Measurement of Inflation 2. Facts of Inflation 3. Types of Inflation 4. Complexities of Inflation E. Redistribution Effects of Inflation 1. Who is Hurt by Inflation? 2. Who is Unaffected or Helped by Inflation? F. Does Inflation Affect Output? Topic III: Basic Macroeconomic Relationships Chapter 8 A. The Income-Consumption and Income-Savings Relationships 1. Consumption and Savings schedules 2. Average and Marginal Propensities 3. Nonincome Determinants of Consumption and Savings B. The Interest-Rate - Investment Relationship 1. The Expected Rate of Return vs. Real Rate of Return 2. The Investment Demand Curve and Causes of Shifts C. The Multiplier Effect 1. Rationale 2. The Multiplier and the Marginal Propensities 3. How Large is the Actual Multiplier? Essential Questions 1. How do economist s measure inflation? 2. What causes (and does not cause) inflation? 3. What is the trade off between unemployment and inflation? 4. What is the role of expectations in accelerating (or decelerating) inflation? Key Teaching Concepts Business Cycle Circular Flow: Concept of Equilibrium MPS, MPC Multiplier Effect Graphical/Mathematical Draw and explain the components of a circular flow model; explain how the components are related to national income and GDP concepts. Draw and Label a Model of the Business Cycle and It s Four Phases Given a Price Index, Convert Nominal GDP to Real GDP. Compute the Multiplier, MPS and MPC Given data, Compute GDP by Both the Expenditures and Income Approaches 6
7 Part 2: Macroeconomic Models and Fiscal Policy Topic I: Aggregate Expenditures Model Chapter 9 A. Simplified Model/ Closed Economy 1. GDP = C + Ig 2. Assumptions: a. Savings b. Planned Investment c. Inventory Changes B. Adding International Trade 1. Net Exports and Aggregate Expenditures 2. Net Exports and Equilibrium GDP C. Adding the Public Sector 1. Government Purchases and Equilibrium GDP 2. Taxation and Equilibrium GDP D. Equilibrium Versus Full-Employment GDP 1. Expenditure gaps 2. Application to Inflation 1980s 3. Application to Full-Employment Output With Large Negative Net Exports E. Limitations of the Model Topic II: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Chapter 10 A. Aggregate Demand B. Changes in Aggregate Demand 1. How Changes in C, I, G or Xn shift the AD Curve C. Aggregate Supply D. Changes in Aggregate Supply 1. How Changes in Input Prices, Productivity or Legal-Institutional Environment Shift the AS Curve. E. Equilibrium and Changes in Equilibrium 1. Increase in AD: Demand-Pull Inflation 2. Decrease in AD: Recession and Cyclical Unemployment 3. Decrease in AS: Cost-Push Inflation 4. Increase in AS: Full Employment With Price-level Stability 7
8 Topic III: Fiscal Policy, Deficits and Debt Chapter 11 A. Fiscal Policy and the AD-AS Model 1. Expansionary Fiscal Policy 2. Concretionary Fiscal Policy 3. Policy Options: G or T? B. Built-in Stability 1. Types of Taxation a. Progressive b. Proportional c. Regressive C. Evaluating Fiscal Policy 1. Recent U.S. Fiscal Policy 2. Budget Deficits and Projections 3. Social Security Considerations D. Problems, Criticisms and Complications 1. Timing 2. Political Considerations 3. Crowding-out Effect E. The Public Debt 1. Ownership 2. Debt and GDP 3. Interest Charges F. Substantive Issues 1. Income Distribution 2. Incentives 3. Foreign-owned Debt Essential Questions 1. What are the various policies used to promote national output, employment and price stability? 2. What are the different models that explain the status of the national economy? 3. How does each of the models suggest a method and strategy for dealing with national economic problems? 4. How does the AS/AD model attempt to explain the national economy? Key Teaching Concepts Circular Flow: Concept of Equilibrium (AS=AD + Unplanned Inventories) AS/AD Model (Variable Price Model) Fiscal Policy Using AS/AD Model Graphical/Mathematical Draw and explain an AS/AD model at various levels of unemployment. Graph the changes in the AS/AD model given changes in SRAS, AD, and LRAS. Graph an income expenditure model (Keynesian cross) and its relationship to AS/AD model Graph the affects of fiscal policy decisions using the AE and AS-AD models. Given a multiplier effect, show changes in the AE and AS-AD models. 8
9 Unit 3: Monetary Policy and Policy Mixes (19 Lessons) Topic I: Money, Banking Chapter 12 A. Three Functions of Money B. Components of the Money Supply 1.M1: most narrowly defined money supply 2.M2: adding near monies to M 1 3.M3: adding large time deposits to M 2 C. What Backs the Money Supply? D. The Federal Reserve and the Banking System 1. Origins and organizational structure 2. FOMC 3. Fed Functions and the Money Supply Topic II: Money Creation Chapter 13 A. The Fractional Reserve System 1. Illustrating the Idea B. A Single Bank Model 1. Balance Sheet 2. Transactions and Their Effects C. Multiple Bank Model 1. Loans and Money Creation 2. The Money Multiplier 9
10 Topic III: Interest Rates and Monetary Policy Chapter 14 A. Interest Rates 1. Demand for Money a. Transactions Demand v. Asset Demand b. Total Money Demand 2. The Equilibrium Interest Rate 3. Interest Rates and Bond Prices B. Tools of Monetary Policy 1. Open-Market Operations a. Buying Securities b. Selling Securities 2. The Reserve Ratio a. Raising the Ratio b. Lowering the Ratio 3. The Discount Rate 4. Relative Importance C. Targeting the Federal Funds Rate 1. Expansionary Monetary Policy 2. Restrictive Monetary Policy 3. The Taylor Rule D. Monetary Policy, Real GDP, and the Price Level 1. Cause-Effect Chain 2. Market for Money 3. Effects of Expansionary Monetary policy 4. Effects of Restrictive Monetary Policy 5. Present and Future Value of Money E. Monetary Policy: Evaluation and Issues 1. Recent U.S. Policy 2. Problems and Complications Essential Questions 1. How do banks operate? 2. How does the FED promote a fully employed economy? Key Teaching Concepts Basic bank operations of deposits, withdrawals Required and excess reserves. Deposit Multiplier (1/rr) FED operations Affects of monetary policy on AD and national output, employment and price stability. Monetary Policy using AS/AD Models Graphical/Mathematical Chart and explain what happens to excess reserves, required reserves, and lending ability when demand deposits are made by individuals Graphically illustrate the affects on money supply and interest rate with an increase/decrease in the money supply Given changes in the open market operations, graph the changes in Money Supply, Money Demand, and interest rates. Graphically, compare and contrast the use of monetary policy and fiscal policy on interest rates. Given changes in monetary policy (FED), use the AS/AD model to graph the Keynesian transmission effect. 10
11 Topic IV: Extending the Analysis Chapters 15 & 16 A. From Short Run to Long Run 1. SRAS and LRAS 2. Long-run Equilibrium in the AD-AS Model B. Applying the Extended AD-AS Model 1. Demand-pull Inflation 2. Cost-push Inflation 3. Recession C. The Inflation-Unemployment Relationship 1. The Phillips Curve 2. Aggregate Supply Shocks D. The Long-Run Phillips Curve 1. Short-run Phillips curve 2. Long-run Vertical Phillips Curve 3. Disinflation E. Taxation and Aggregate Supply 1. Taxes and Incentives to Work 2. Incentives to Save and Invest 3. The Laffer Curve F. Economic Growth 1. Supply Factors 2. Demand Factors 3. Efficiency Factor G. Production Possibilities Analysis 1. Growth and production Possibilities 2. Labor and Productivity 3. Growth in the AD-AS Model H. Accounting for Growth 1. Labor Inputs Versus Labor Productivity 2. Technological Advance 3. Quantity of Capital 4. Education and Training 5. Economies of Scale and Resource Allocation 6. Other Factors I. Productivity Acceleration: A New Economy? J. Is Growth Desirable and Sustainable? Essential Questions 1. What are the various policies used to promote national output, employment and price stability? 2. What are the different combinations of fiscal and monetary policy? 3. What are the affects of using monetary policy and/or fiscal policy on interest rates, price stability, and employment and national income? Key Teaching Concepts Assess the impact of the following on interest rates, employment, price stability and national output: Explain and illustrate easy money/tight fiscal policy. Explain and illustrate tight money and easy fiscal policy Explain and differentiate between deficits and national debt. Explain crowding out affect Debate the issues between activist and non-activist among fiscal and monetary policy makers Draw and explain how the Phillips Curve explains the relationship between unemployment and inflation rates. Explain and differentiate between a short run and long run Phillips Curve Show how the AS/AD model is similar to the Phillips Curve Graphical/Mathematical Graph the affects of a combined monetary and fiscal policy. Compare effects of monetary policy, fiscal policy given differing elasticity for investment demand and/or demand for money 11
12 Compare graphically the Keynesian and Monetarist controversies concerning the use of fiscal and monetary policy Graph the short run trade offs between inflation and unemployment (Phillips Curve) Use an AS/AD illustration with an increase in AD to explain the movements along a Phillips Curve. Using the Phillips Curve, graph how changes in the AS/AD model would appear on the Phillips Curve Model. Graphically illustrate, how expectations affect the Phillips Curve model. Unit 4: The International Economy (4Lessons) Topic I: International Trade and Finance Chapters 35 & 36 A. Why do Nations Trade? 1. Review Absolute and Comparative advantage B. Supply and Demand Analysis of Exports and Imports C. Trade Barriers 1. Economic Impact of Tariffs 2. Economic Impact of Quotas 3. Net Costs of Tariffs and Quotas D. The Case for Protectionism 1. Critical Review of Seven Major Arguments In Favor E. The Balance of Payments 1. Current account 2. Capital account 3. International debt of the United States F. Flexible Exchange Rates 1.Depreciation and Appreciation 2.Determinants of Exchange Rates 3.Flexible Rates and the Balance of Payments 4.Disadvantages of Flexible Rates Essential Questions 1. Why do nations engage in international trade? 2. Why do nations sometimes impose restrictions on international trade? 3. How do exchange rates affect international trade? 4. What is the affect of international markets on the US economy in terms of price stability, employment, and economic growth? 5. What is a trade deficit? Key Teaching Concepts Calculate terms of trade Advanced arguments for projectionist policies and those for free trade. Explain the affects of exports and imports on Aggregate demand and the international balance of trade Graphical/Mathematical Graph demand and supply for US currency AND demand and supply for foreign currency. Graph the impact of an increase/decrease in net exports on AS/AD models. Graph impact of an appreciated dollar/depreciated dollar on AS/AD Graph the impact of tariffs 12
Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics
 Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics Instructional Philosophy The Advanced Placement Macroeconomics curriculum is a full year program designed to provide both an overview of economics. Economics
Garden City High School Course: AP Macroeconomics Instructional Philosophy The Advanced Placement Macroeconomics curriculum is a full year program designed to provide both an overview of economics. Economics
AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016
 AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016 Ms. Huynh ( Win ), Room 126 Phone: (626) 441-5820 Ext 2126 Email: Thuynh@spusd.net Curricular Overview This semester long course will introduce students to the principles
AP Macroeconomics Fall Semester 2016 Ms. Huynh ( Win ), Room 126 Phone: (626) 441-5820 Ext 2126 Email: Thuynh@spusd.net Curricular Overview This semester long course will introduce students to the principles
Course Name: AP Macroeconomics and the Free Enterprise System. One Semester Course: 18 weeks, M-F, 7 period day, 51 minutes per class
 Course Name: AP Macroeconomics and the Free Enterprise System One Semester Course: 18 weeks, M-F, 7 period day, 51 minutes per class Bibliography of Texts: Main Text: McConnell, Campbell R. and Stanley
Course Name: AP Macroeconomics and the Free Enterprise System One Semester Course: 18 weeks, M-F, 7 period day, 51 minutes per class Bibliography of Texts: Main Text: McConnell, Campbell R. and Stanley
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics
 Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Introduction Welcome to AP Macroeconomics! This is a challenging course; taught at the college level, this course requires that you operate at a level higher than what
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Introduction Welcome to AP Macroeconomics! This is a challenging course; taught at the college level, this course requires that you operate at a level higher than what
AP Macroeconomics Trent Thornton Voice mail:
 AP Macroeconomics 2011-2012 Trent Thornton Voice mail: 480-224-2894 E-mail: Thornton.trent@chandler.k12.az.us Required Reading: N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 5 th ed. Ohio: South-Western
AP Macroeconomics 2011-2012 Trent Thornton Voice mail: 480-224-2894 E-mail: Thornton.trent@chandler.k12.az.us Required Reading: N. Gregory Mankiw, Principles of Economics, 5 th ed. Ohio: South-Western
Macroeconomics. Identify and apply relevant terminology and concepts to economic issues and problems.
 Macroeconomics Course Text and Study Guide Text: McConnell, Campbell R. and Stanley L. Brue. Macroeconomics: Principles, Problems, and Policies, 17th edition. McGraw-Hill, 2008. ISBN 0-07-327308-2. Study
Macroeconomics Course Text and Study Guide Text: McConnell, Campbell R. and Stanley L. Brue. Macroeconomics: Principles, Problems, and Policies, 17th edition. McGraw-Hill, 2008. ISBN 0-07-327308-2. Study
ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS
 ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Instructor: James J. Sostack Jr. Department: Social Studies Length of Course: Full Year (A/B Block format) Weight 1.20 Grade Level
ELIZABETHTOWN AREA HIGH SCHOOL SYLLABUS ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Instructor: James J. Sostack Jr. Department: Social Studies Length of Course: Full Year (A/B Block format) Weight 1.20 Grade Level
CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE
 CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE Course Name(s): Grade(s): 11-12 Department: Course Length: Pre-requisite: Macroeconomics Social Studies 1 Semester Microeconomics Textbook/Key Resource: McConnell and Brue. Macroeconomics
CURRICULUM COURSE OUTLINE Course Name(s): Grade(s): 11-12 Department: Course Length: Pre-requisite: Macroeconomics Social Studies 1 Semester Microeconomics Textbook/Key Resource: McConnell and Brue. Macroeconomics
INDIAN HILL EXEMPTED VILLAGE SCHOOL DISTRICT Social Studies Curriculum - May 2009 AP Economics
 Course Description: This full-year college-level course begins with basic economic concepts and proceeds to examine both microeconomics and macroeconomics in greater detail. There are five units which
Course Description: This full-year college-level course begins with basic economic concepts and proceeds to examine both microeconomics and macroeconomics in greater detail. There are five units which
AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition
 AP Macroeconomics Mrs. Cook 1 st Period Room 210 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition Unit One: Basic Economic
AP Macroeconomics Mrs. Cook 1 st Period Room 210 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Course Outline Required text: Economics: Principles, Problems, and Policies McConnel and Brue 15 th edition Unit One: Basic Economic
AP Economics Pacing Guide
 AP Economics Pacing Guide Course Description: The purpose of AP Macroeconomics is to understand the principles of economics that apply to an economic system as a whole. The course will explore the study
AP Economics Pacing Guide Course Description: The purpose of AP Macroeconomics is to understand the principles of economics that apply to an economic system as a whole. The course will explore the study
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Mr. Jonker Room 212
 Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Mr. Jonker Room 212 Phone Number/Voice Mail: 231-348-2144 Conference Period: 1 st Hour Website: http://www.petoskeyschools.org/jonker.zp.t/ Twitter: http://twitter.com/ap_economics
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Mr. Jonker Room 212 Phone Number/Voice Mail: 231-348-2144 Conference Period: 1 st Hour Website: http://www.petoskeyschools.org/jonker.zp.t/ Twitter: http://twitter.com/ap_economics
A. Regular attendance is crucial to success in this class. Poor attendance will harm your participation grade. Grade categories are as follows:
 AP Macroeconomics JOHNSON Spring 11 AP Macroeconomics is a one-semester, college-level course. Each student is expected to take the AP Macroeconomics Exam that is administered in May. Successful achievement
AP Macroeconomics JOHNSON Spring 11 AP Macroeconomics is a one-semester, college-level course. Each student is expected to take the AP Macroeconomics Exam that is administered in May. Successful achievement
Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline June 2013
 Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline June 2013 Department: Course Title: Social Science Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Grade Level: 12 Course Number: 1705 Prerequisite:
Murrieta Valley Unified School District High School Course Outline June 2013 Department: Course Title: Social Science Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Grade Level: 12 Course Number: 1705 Prerequisite:
AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview
 AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve requirement).
AP Macroeconomics Graphical Overview 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve requirement).
AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers
 AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve
AP Macroeconomics - Mega Macro Review Sheet Answers 1. The business cycle. 2. Aggregate supply curve (with breakdown of sections). 3. Expansionary ( easy ) monetary policy (Buy bonds, discount rate, reserve
Advanced Placement Macro Economics
 Advanced Placement Macro Economics Economics is a study of mankind in the ordinary business of life. Alfred Marshall Through the AP Macroeconomics course, students will have a better understanding of the
Advanced Placement Macro Economics Economics is a study of mankind in the ordinary business of life. Alfred Marshall Through the AP Macroeconomics course, students will have a better understanding of the
Buchholz, Todd. New Ideas From Dead Economists. New York: Plame, 1999
 AP MACROECONOMICS COURSE SYLLABUS AP Macroeconomics is a one semester college level course. The AP Macroeconomics course is designed as an initial college level course in macroeconomics and as a foundation
AP MACROECONOMICS COURSE SYLLABUS AP Macroeconomics is a one semester college level course. The AP Macroeconomics course is designed as an initial college level course in macroeconomics and as a foundation
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP MACROECONOMICS-2018 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/21 st (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/20 th (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP MACROECONOMICS-2018 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/21 st (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/20 th (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
Georgia Standards of Excellence Economics 2016
 A Correlation of 2016 To the Georgia Standards of Excellence Economics 2016 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE GEORGIA STANDARDS OF EXCELLENCE (GSE) GRADES K-12 SOCIAL STUDIES AND SCIENCE Subject Area: Economics
A Correlation of 2016 To the Georgia Standards of Excellence Economics 2016 FORMAT FOR CORRELATION TO THE GEORGIA STANDARDS OF EXCELLENCE (GSE) GRADES K-12 SOCIAL STUDIES AND SCIENCE Subject Area: Economics
FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP MACROECONOMICS-2017 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/22 nd (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/21 st (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
AP MACROECONOMICS-2017 Name: FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Instructions: DUE: Day of FINAL EXAM => Friday 12/22 nd (1 st & 2 nd Periods) Thursday 12/21 st (4 th period) Section 1: PRODUCTION POSSIBLITIES FRONTIER
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.
![Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I.](/thumbs/77/76534172.jpg) Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
Dunbar s Big Review Sheet AP Macroeconomics Exam Content Area [Hubbard Textbook pages] (percentage coverage on AP Macroeconomics Exam) I. Basic Economic Concepts (8-12%) Three Fundamental Questions [8]:
PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS MACROECONOMICS ECON Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0
 PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS MACROECONOMICS ECON 2010 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0 Laboratory Hours: 0 Date Revised: Fall 2012 Catalog Course Description: A presentation of
PELLISSIPPI STATE COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS MACROECONOMICS ECON 2010 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 3.0 Laboratory Hours: 0 Date Revised: Fall 2012 Catalog Course Description: A presentation of
Principles of Macroeconomics ECO 2251-THWA Fall 2011 MW 2:00 3:15 pm Bibb Graves 221
 TROY UNIVERSITY SORRELL COLLEGE OF BUSINESS Principles of Macroeconomics ECO 2251-THWA Fall 2011 MW 2:00 3:15 pm Bibb Graves 221 Instructor: Dr. George R. Crowley Office Location: Bibb Graves 137C Office
TROY UNIVERSITY SORRELL COLLEGE OF BUSINESS Principles of Macroeconomics ECO 2251-THWA Fall 2011 MW 2:00 3:15 pm Bibb Graves 221 Instructor: Dr. George R. Crowley Office Location: Bibb Graves 137C Office
VHS AP Economics Syllabus Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Syllabus 33 week course
 VHS AP Economics Syllabus Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Syllabus 33 week course Textbook: Krugman, P., & Wells, R., (2006). Economics. NY: Worth Publishers Recommended Reading: Buccholz,, Todd, New
VHS AP Economics Syllabus Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Syllabus 33 week course Textbook: Krugman, P., & Wells, R., (2006). Economics. NY: Worth Publishers Recommended Reading: Buccholz,, Todd, New
Macroeconomics
 Macroeconomics 978-1-63545-006-4 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Senior Contributing Authors: Steve
Macroeconomics 978-1-63545-006-4 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewtonalta.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Senior Contributing Authors: Steve
Fluctuations of Investment Durability Irregularity of Innovation Variability of Profits Variability of Expectations
 Shifts in the Invest Demand Curve Acquisition, Maintenance and Operating Costs Business Taxes Technological Change Stock of Capital Goods on Hand Expectations Fluctuations of Investment Durability Irregularity
Shifts in the Invest Demand Curve Acquisition, Maintenance and Operating Costs Business Taxes Technological Change Stock of Capital Goods on Hand Expectations Fluctuations of Investment Durability Irregularity
Expansionary Fiscal Policy 2. If the economy is experiencing a recession what type of fiscal policy would be in order?
 Stabilization Policies Reading Guide Chapters 12, 16, and 18 Chapter 12: Fiscal Policy 1. Assess the effect of fiscal policy on real output, price level, and the level of employment in the long run and
Stabilization Policies Reading Guide Chapters 12, 16, and 18 Chapter 12: Fiscal Policy 1. Assess the effect of fiscal policy on real output, price level, and the level of employment in the long run and
Principles of Macroeconomics
 Principles of Macroeconomics 978-1-63545-094-1 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Senior Contributing Authors:
Principles of Macroeconomics 978-1-63545-094-1 To learn more about all our offerings Visit Knewton.com Source Author(s) (Text or Video) Title(s) Link (where applicable) OpenStax Senior Contributing Authors:
Module 4: Applications of Supply and Demand
 The following list shows a summary of the topics covered in the macroeconomics course. Module 1: Economic Thinking Understanding Economics and Scarcity The Concept of Opportunity Cost Labor, Markets, and
The following list shows a summary of the topics covered in the macroeconomics course. Module 1: Economic Thinking Understanding Economics and Scarcity The Concept of Opportunity Cost Labor, Markets, and
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 2
 Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 2 Concept / Topic To Teach: Specific Objectives: Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Unit 3 Module 16 INCOME AND EXPENDITURES Comprehend the nature
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 2 Concept / Topic To Teach: Specific Objectives: Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Unit 3 Module 16 INCOME AND EXPENDITURES Comprehend the nature
Course Map Economics
 Course Title: Economics Course Map Text: Thinking Economics (National Council on Economic Education) Duration: one semester Frequency: one class period daily Year: 2013-2014 Other materials: Areas to be
Course Title: Economics Course Map Text: Thinking Economics (National Council on Economic Education) Duration: one semester Frequency: one class period daily Year: 2013-2014 Other materials: Areas to be
A. unchanged decrease B. surplus decrease C. unchanged no change D. surplus increase E. unchanged increase A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E.
 AP Macroeconomics Test (Answers on last Page) 1. Which of the following correctly describes the components of Aggregate Demand? A. Consumption expenditures + Investment expenditures + Government expenditures
AP Macroeconomics Test (Answers on last Page) 1. Which of the following correctly describes the components of Aggregate Demand? A. Consumption expenditures + Investment expenditures + Government expenditures
EIGHTEENTH EDITION. Macroeconomics. Principles, Problems, and Policies. Campbell R. McConnell. University ofnebraska. Stanley L.
 EIGHTEENTH EDITION Macroeconomics Principles, Problems, and Policies Campbell R. McConnell University ofnebraska Stanley L. Brue Pacific Lutheran University Sean M. Flynn Vassar College McGraw-Hill Irwin
EIGHTEENTH EDITION Macroeconomics Principles, Problems, and Policies Campbell R. McConnell University ofnebraska Stanley L. Brue Pacific Lutheran University Sean M. Flynn Vassar College McGraw-Hill Irwin
Dominican International School. AP MACROECONOMICS 1 Year, 1 Credit GRADE LEVEL: 11 and /19 TEACHER: Dr Mercia de Souza
 1 Dominican International School AP MACROECONOMICS 1 Year, 1 Credit GRADE LEVEL: 11 and 12 2018/19 TEACHER: Dr Mercia de Souza Course Description An AP course in Macroeconomics is designed to give students
1 Dominican International School AP MACROECONOMICS 1 Year, 1 Credit GRADE LEVEL: 11 and 12 2018/19 TEACHER: Dr Mercia de Souza Course Description An AP course in Macroeconomics is designed to give students
Chapter 1: Economics: The Core Issues - WHAT IS THIS CHAPTER ALL ABOUT?
 Principles of Economics ECON 2301/2302 Schiller, 14th Edition Chapter Learning Objectives Chapter 1: Economics: The Core Issues - The chapter introduces students to the basic building blocks of economics
Principles of Economics ECON 2301/2302 Schiller, 14th Edition Chapter Learning Objectives Chapter 1: Economics: The Core Issues - The chapter introduces students to the basic building blocks of economics
ABOUT THE EXAM. Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: Free Response Questions one third of total score:
 ABOUT THE EXAM Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: 60 questions, 70 minutes to complete 1 point each; no penalty for wrong answer Many of the questions are similar to the frqs; for questions
ABOUT THE EXAM Multiple Choice Questions two thirds of total score: 60 questions, 70 minutes to complete 1 point each; no penalty for wrong answer Many of the questions are similar to the frqs; for questions
Exam #3 Section # 11, 12 or 13 December 2012
 Economics 211 Macroeconomic Principles Exam #3 Section # 11, 12 or 13 December 2012 Name The value of this exam is 102 points plus 10 points for the Bonus Question. Instructor: Brian B. Young Please show
Economics 211 Macroeconomic Principles Exam #3 Section # 11, 12 or 13 December 2012 Name The value of this exam is 102 points plus 10 points for the Bonus Question. Instructor: Brian B. Young Please show
!&Z -** -. oremacroeconorracs. Gerald W. Stone Metropolitan State College of Denver. Worth Publishers
 V -** -.!&Z oremacroeconorracs 1 Gerald W. Stone Metropolitan State College of Denver Worth Publishers BRIEF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 Exploring Economics 1 CHAPTEFL2 j Production, Economic Growth, and Trade
V -** -.!&Z oremacroeconorracs 1 Gerald W. Stone Metropolitan State College of Denver Worth Publishers BRIEF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 Exploring Economics 1 CHAPTEFL2 j Production, Economic Growth, and Trade
Foundations of Economics 5 th Edition, AP Edition 2011
 A Correlation of 5 th Edition, AP Edition 2011 Advanced Placement Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Topics AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not involved in the
A Correlation of 5 th Edition, AP Edition 2011 Advanced Placement Microeconomics and Macroeconomics Topics AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which was not involved in the
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS ECO101 MACROECONOMICS. 3 Credit Hours. Prepared by: James Watson. Revised Date: February 2007 by James Watson
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS ECO101 MACROECONOMICS 3 Credit Hours Prepared by: James Watson Revised Date: February 2007 by James Watson Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean ECO101 MACROECONOMICS
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS ECO101 MACROECONOMICS 3 Credit Hours Prepared by: James Watson Revised Date: February 2007 by James Watson Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean ECO101 MACROECONOMICS
Everyone Loves Econ Notes
 Unit 1: Economic Fundamentals Everyone Loves Econ Notes Scarcity - the lack of resources for our unlimited wants. Ceteris Paribus Economists hold factors constant, except for what s being considered Goods
Unit 1: Economic Fundamentals Everyone Loves Econ Notes Scarcity - the lack of resources for our unlimited wants. Ceteris Paribus Economists hold factors constant, except for what s being considered Goods
ECON 1120: Macroeconomics
 ECON 1120: Macroeconomics General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office hours: TBA Class Sessions Per Week: 5 Total Weeks: 5 Total
ECON 1120: Macroeconomics General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office hours: TBA Class Sessions Per Week: 5 Total Weeks: 5 Total
Foundations of Economics 5 th Edition, AP*Edition 2011
 A Correlation of 5 th Edition, AP*Edition 2011 To the Advanced Placement Topics Microeconomics and Macroeconomics *Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, and Pre-AP are registered trademarks
A Correlation of 5 th Edition, AP*Edition 2011 To the Advanced Placement Topics Microeconomics and Macroeconomics *Advanced Placement, Advanced Placement Program, AP, and Pre-AP are registered trademarks
ECON 012: Macroeconomics
 General Information ECON 012: Macroeconomics Term: 2018 Summer Session Class Sessions Per Week: 5 Instructor: Staff Total Weeks: 6 Language of Instruction: English Total Class Sessions: 30 Classroom: TBA
General Information ECON 012: Macroeconomics Term: 2018 Summer Session Class Sessions Per Week: 5 Instructor: Staff Total Weeks: 6 Language of Instruction: English Total Class Sessions: 30 Classroom: TBA
AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus
 Contact Information AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus Teacher: Edmund Ned Maino Email: emaino@teh.k12.ca.us (I check email until 5pm, Monday-Friday) Phone: 661-822-2130 ext. 1701 (Please call between
Contact Information AP Macroeconomics (APE) Course Syllabus Teacher: Edmund Ned Maino Email: emaino@teh.k12.ca.us (I check email until 5pm, Monday-Friday) Phone: 661-822-2130 ext. 1701 (Please call between
HONG KONG SHUE YAN UNIVERSITY Department of Economics and Finance (Fall 2009 / Winter 2010)
 HONG KONG SHUE YAN UNIVERSITY Department of Economics and Finance (Fall 2009 / Winter 2010) Course Title : Principles of Economics Course Code : ECON 101 2 Year of Study : 1 Number of Credits : 3 Duration
HONG KONG SHUE YAN UNIVERSITY Department of Economics and Finance (Fall 2009 / Winter 2010) Course Title : Principles of Economics Course Code : ECON 101 2 Year of Study : 1 Number of Credits : 3 Duration
Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Syllabus
 Mr. Eric Krause Coral Reef Senior High School ekrause1@dadeschools.net 2018-2019 Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Syllabus All who have meditated on the art of governing mankind have been convinced that
Mr. Eric Krause Coral Reef Senior High School ekrause1@dadeschools.net 2018-2019 Advanced Placement Macroeconomics Syllabus All who have meditated on the art of governing mankind have been convinced that
EXAMINATION : MACROECONOMICS (MAC) ECONOMICS 1 (ECO101)
 Page 1 of 7 EXAMINATION : MACROECONOMICS (MAC) ECONOMICS 1 (ECO101) DATE : 23 OCTOBER 2013 TIME ALLOWED : 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS : 100 MATERIAL SUPPLIED : ANSWER BOOK INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. Please
Page 1 of 7 EXAMINATION : MACROECONOMICS (MAC) ECONOMICS 1 (ECO101) DATE : 23 OCTOBER 2013 TIME ALLOWED : 3 HOURS TOTAL MARKS : 100 MATERIAL SUPPLIED : ANSWER BOOK INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. Please
a. What is your interpretation of the slope of the consumption function?
 Economics 102 Spring 2017 Homework #5 Due May 4, 2017 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework (legibly).
Economics 102 Spring 2017 Homework #5 Due May 4, 2017 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework (legibly).
ECON 012: Macroeconomics
 ECON 012: Macroeconomics General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions Per Week: 5 Total Weeks: 6 Total
ECON 012: Macroeconomics General Information: Term: 2018 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions Per Week: 5 Total Weeks: 6 Total
ECON 012: Macroeconomics
 ECON 012: Macroeconomics General Information: Term: 2019 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions Per Week: 5 Total Weeks: 5 Total
ECON 012: Macroeconomics General Information: Term: 2019 Summer Session Instructor: Staff Language of Instruction: English Classroom: TBA Office Hours: TBA Class Sessions Per Week: 5 Total Weeks: 5 Total
Mater Academy Charter High School School Year AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Ms. De la Torre's Class Room 137
 Mater Academy Charter High School School Year 2011-2012 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Ms. De la Torre's Class Room 137 AP Macroeconomics emphasizes economics principles as applied to the economy as a whole.
Mater Academy Charter High School School Year 2011-2012 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Ms. De la Torre's Class Room 137 AP Macroeconomics emphasizes economics principles as applied to the economy as a whole.
MACROECONOMICS. Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions
 MACROECONOMICS Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best
MACROECONOMICS Section I Time 70 minutes 60 Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best
Basic Concepts. MICROECONOMICS: deals with specific economic units and a detailed consideration of these individual units.
 Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
Basic Concepts ECONOMICS: The study of how limited productive resources are efficiently allocated in a world of unlimited wants. SCARCITY: WANTS EXCEED RESOURCES We want more than we are capable of getting.
To Assess Mastery - Common Assessments/Unit tests, District Assessments, Major projects, Major papers
 AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Introduction: Economics presents new learning with a specific set of terms and concepts to be addressed. Developing an economic way of thinking is vital to understanding Economics
AP Macroeconomics Syllabus Introduction: Economics presents new learning with a specific set of terms and concepts to be addressed. Developing an economic way of thinking is vital to understanding Economics
Textbook Media Press. CH 27 Taylor: Principles of Economics 3e 1
 CH 27 Taylor: Principles of Economics 3e 1 The Building Blocks of Keynesian Analysis Keynesian economics is based on two main ideas: a) aggregate demand is more likely than aggregate supply to be the primary
CH 27 Taylor: Principles of Economics 3e 1 The Building Blocks of Keynesian Analysis Keynesian economics is based on two main ideas: a) aggregate demand is more likely than aggregate supply to be the primary
Pre-Test Chapter 9 ed17
 Pre-Test Chapter 9 ed17 Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect? A. Given the economy's MPS, a $15 billion reduction in government spending will reduce the equilibrium
Pre-Test Chapter 9 ed17 Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements is incorrect? A. Given the economy's MPS, a $15 billion reduction in government spending will reduce the equilibrium
GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE. -8- Unauthorized copying or reuse of any part of this page is illegal.
 30. Which of the following is most likely to be caused by an adverse supply shock? (A) Structural unemployment (B) Frictional unemployment (C) Demand-pull inflation (D) Cost-push inflation (E) Deflation
30. Which of the following is most likely to be caused by an adverse supply shock? (A) Structural unemployment (B) Frictional unemployment (C) Demand-pull inflation (D) Cost-push inflation (E) Deflation
Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points)
 EC132.02 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
EC132.02 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 17th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
3. Explain what the APS tells us about people s spending and saving habits.
 National Income and Price Determination Reading Guide Chapters 9, 10 and 11 Chapter 9: Building the Aggregate Expenditures Model Objective... 1. Explain how the consumption schedule helps us find equilibrium
National Income and Price Determination Reading Guide Chapters 9, 10 and 11 Chapter 9: Building the Aggregate Expenditures Model Objective... 1. Explain how the consumption schedule helps us find equilibrium
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Economics Today Twelfth Edition. Chapter 12 Consumption, Income, and the Multiplier
 Roger LeRoy Miller Economics Today Twelfth Edition Chapter 12 Consumption, Income, and the Multiplier Introduction Consumption spending by households is the largest component of U.S. GDP. To the extent
Roger LeRoy Miller Economics Today Twelfth Edition Chapter 12 Consumption, Income, and the Multiplier Introduction Consumption spending by households is the largest component of U.S. GDP. To the extent
2.2 Aggregate demand and aggregate supply
 The business cycle Short-term fluctuations and long-term trend Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the
The business cycle Short-term fluctuations and long-term trend Explain, using a business cycle diagram, that economies typically tend to go through a cyclical pattern characterized by the phases of the
5 Macroeconomics SAMPLE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE-CHOICE UNIT E09 Macroeconomics Summative Exam Sample Multiple-Choice Questions Circle the letter of each correct answer. 1. Which of the following monetary and fiscal policy combinations would
MULTIPLE-CHOICE UNIT E09 Macroeconomics Summative Exam Sample Multiple-Choice Questions Circle the letter of each correct answer. 1. Which of the following monetary and fiscal policy combinations would
7. Refer to the above graph. It depicts an economy in the: A. Immediate short run B. Short run C. Immediate long run D. Long run
 CHAPTER 29 1. When the price level decreases: A. The demand for money falls and the interest rate falls B. Holders of financial assets with fixed money values decrease their spending C. Holders of financial
CHAPTER 29 1. When the price level decreases: A. The demand for money falls and the interest rate falls B. Holders of financial assets with fixed money values decrease their spending C. Holders of financial
Principles of Macroeconomics: ECO201
 Principles of Macroeconomics: ECO201 Gogebic Community College E4946 Jackson Road Ironwood, MI 49938 (906)932-4231 or 1-800-682-5910 www.gogebic.edu Instructor: Dennis Mackey mackeyd@gogebic.edu Office:
Principles of Macroeconomics: ECO201 Gogebic Community College E4946 Jackson Road Ironwood, MI 49938 (906)932-4231 or 1-800-682-5910 www.gogebic.edu Instructor: Dennis Mackey mackeyd@gogebic.edu Office:
AP Macroeconomics review. By: Maria Villasmil. Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity.
 AP Macroeconomics review By: Maria Villasmil Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity. Factors of Production: 1)Land: natural resources 2) Labor:
AP Macroeconomics review By: Maria Villasmil Economis: The study of how people, firms, and government make decisions when faced with scarcity. Factors of Production: 1)Land: natural resources 2) Labor:
Eco202 Review, April 2013, Prof. Bill Even. I. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth
 Eco202 Review, April 2013, Prof. Bill Even I. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth A. Definition of GDP B. Measuring GDP 1. Expenditure side a) C+I+G+NX b) Definition of each component 2. Income
Eco202 Review, April 2013, Prof. Bill Even I. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth A. Definition of GDP B. Measuring GDP 1. Expenditure side a) C+I+G+NX b) Definition of each component 2. Income
Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010
 Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010 Dr. Stuart Allen 334-3166 Office Hours: Before Class Department Office 462 Bryan E-mail: stuart_allen@uncg.edu PURPOSE This course uses market analysis
Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010 Dr. Stuart Allen 334-3166 Office Hours: Before Class Department Office 462 Bryan E-mail: stuart_allen@uncg.edu PURPOSE This course uses market analysis
The Aggregate Expenditures Model. A continuing look at Macroeconomics
 The Aggregate Expenditures Model A continuing look at Macroeconomics The first macroeconomic model The Aggregate Expenditures Model What determines the demand for real domestic output (GDP) and how an
The Aggregate Expenditures Model A continuing look at Macroeconomics The first macroeconomic model The Aggregate Expenditures Model What determines the demand for real domestic output (GDP) and how an
ECO 2013: Macroeconomics Valencia Community College
 ECO 2013: Macroeconomics Valencia Community College Exam 3 Fall 2008 1. The most important determinant of consumer spending is: A. the level of household debt. B. consumer expectations. C. the stock of
ECO 2013: Macroeconomics Valencia Community College Exam 3 Fall 2008 1. The most important determinant of consumer spending is: A. the level of household debt. B. consumer expectations. C. the stock of
IM Syllabus ( ): Economics IM SYLLABUS ( ) ECONOMICS IM 08 SYLLABUS
 IM SYLLABUS (2011-2014) ECONOMICS IM 08 SYLLABUS 1 Economics IM 08 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I: Written exam (3 hrs) Aim As a general guideline, the emphasis in the teaching and examination
IM SYLLABUS (2011-2014) ECONOMICS IM 08 SYLLABUS 1 Economics IM 08 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I: Written exam (3 hrs) Aim As a general guideline, the emphasis in the teaching and examination
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to Exam #3. Section A: Multiple Choice Questions. (30 points; 2 pts each)
 ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to Exam #3 Section A: Multiple Choice Questions. (30 points; 2 pts each) #1. In an open economy where government spending was $30 billion, consumption was
ECON 1010 Principles of Macroeconomics Solutions to Exam #3 Section A: Multiple Choice Questions. (30 points; 2 pts each) #1. In an open economy where government spending was $30 billion, consumption was
1. The most basic premise of the aggregate expenditures model is that:
 1. The most basic premise of the aggregate expenditures model is that: A. The total output produced in the economy depends directly on the level of total spending B. The level of employment in the economy
1. The most basic premise of the aggregate expenditures model is that: A. The total output produced in the economy depends directly on the level of total spending B. The level of employment in the economy
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro
 Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro Concept / Topic To Teach: Unit 4 MODULE 22: SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL Specific Objectives: ELD Standards SYSTEM Week
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro Concept / Topic To Teach: Unit 4 MODULE 22: SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL Specific Objectives: ELD Standards SYSTEM Week
Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION
 Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION Ch 26: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply Purpose of aggregate supply: aggregate demand model is to explain
Disclaimer: This resource package is for studying purposes only EDUCATION Ch 26: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply Purpose of aggregate supply: aggregate demand model is to explain
Archimedean Upper Conservatory Economics, October 2016
 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to: A. the proportion of consumer spending as a function of
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The marginal propensity to consume is equal to: A. the proportion of consumer spending as a function of
ECNS Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity
 ECNS 202 -- Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity Mark the answer on the provided scantron sheet using a #2 lead pencil. Erase completely. I am not responsible for poorly marked or poorly erased asnwers.
ECNS 202 -- Fall 2009 Practice Examination Opportunity Mark the answer on the provided scantron sheet using a #2 lead pencil. Erase completely. I am not responsible for poorly marked or poorly erased asnwers.
Economics 102 Summer 2014 Answers to Homework #5 Due June 21, 2017
 Economics 102 Summer 2014 Answers to Homework #5 Due June 21, 2017 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the
Economics 102 Summer 2014 Answers to Homework #5 Due June 21, 2017 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture. Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Chapter 12. Consumption, Real GDP, and the Multiplier
 Chapter 12 Consumption, Real GDP, and the Multiplier Introduction Investment spending by businesses is a key component of economic growth. Expenditures on information technology were once expected to provide
Chapter 12 Consumption, Real GDP, and the Multiplier Introduction Investment spending by businesses is a key component of economic growth. Expenditures on information technology were once expected to provide
3 Macroeconomics SAMPLE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE-CHOICE UNIT E07 Unit Summative Assessment Sample Multiple-Choice Questions Circle the letter of each correct answer. 1. Which of the following best describes aggregate supply? (A) The amount buyers
MULTIPLE-CHOICE UNIT E07 Unit Summative Assessment Sample Multiple-Choice Questions Circle the letter of each correct answer. 1. Which of the following best describes aggregate supply? (A) The amount buyers
Hill College 112 Lamar Dr. Hillsboro, Texas 76645
 Hill College 112 Lamar Dr. Hillsboro, Texas 76645 COURSE SYLLABUS Course Prefix and Number ECON 2301 Course Title PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS Prepared by: T. SMITH Date: April 2010 Approved by: Susan
Hill College 112 Lamar Dr. Hillsboro, Texas 76645 COURSE SYLLABUS Course Prefix and Number ECON 2301 Course Title PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS Prepared by: T. SMITH Date: April 2010 Approved by: Susan
Answers and Explanations
 Answers and Explanations 1. The correct answer is (E). A change in the composition of output causes a movement along the production possibilities curve. A shift in the curve is caused by changes in technology,
Answers and Explanations 1. The correct answer is (E). A change in the composition of output causes a movement along the production possibilities curve. A shift in the curve is caused by changes in technology,
AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas
 AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas 1. Rule of 70: Used to determine how many years it takes for a value to double, given a particular annual growth rate. For example, if you put $20,000
AP Macroeconomics Formulas and Definitions: Key Formulas 1. Rule of 70: Used to determine how many years it takes for a value to double, given a particular annual growth rate. For example, if you put $20,000
AS Economics: ECON2 Economics: The National Economy 2009/10
 2 weeks 1 st Sep - 11 th Sep Term 1 Introduction to the objectives and instruments of government This is an introduction to 3.2.3, 3.2.1 macroeconomic policy the Unit and most of the content Candidates
2 weeks 1 st Sep - 11 th Sep Term 1 Introduction to the objectives and instruments of government This is an introduction to 3.2.3, 3.2.1 macroeconomic policy the Unit and most of the content Candidates
Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
 Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand ECO 301: Money and Banking 1 1.1 Goals Goals Specific Goals Be able to explain GDP fluctuations when the price level is also flexible. Explain how real GDP and the
Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand ECO 301: Money and Banking 1 1.1 Goals Goals Specific Goals Be able to explain GDP fluctuations when the price level is also flexible. Explain how real GDP and the
Webnote 228. Aggregate demand (AD) U-tube. Item hl sl Must Know Must know very well! Here are the details of what you need to know.
 Webnote 228 2.2 Aggregate demand and Big Questions: 1. What factors cause changes (shifts + movements) in AS and AD? 2. What can the AS/AD model show in the macro economy?. Draw + explain the 2 schools
Webnote 228 2.2 Aggregate demand and Big Questions: 1. What factors cause changes (shifts + movements) in AS and AD? 2. What can the AS/AD model show in the macro economy?. Draw + explain the 2 schools
AP Macro: Economic Models and Graphs Study Guide. Economic Conditions. Price Level. LRAS SRAS Price Level. Y F Y 1 Real GDP
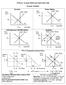 AP Macro: Economic Models and Graphs Study Guide Economic Conditions Recession LRAS SRAS Serious Inflation LRAS SRAS AD AD Y 1 Y F Real GDP Y F Y 1 Real GDP Full Employment with Mild Inflation LRAS SRAS
AP Macro: Economic Models and Graphs Study Guide Economic Conditions Recession LRAS SRAS Serious Inflation LRAS SRAS AD AD Y 1 Y F Real GDP Y F Y 1 Real GDP Full Employment with Mild Inflation LRAS SRAS
Disposable income (in billions)
 Section 4 version 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An increase in the MPC: A. increases the multiplier. B. shifts the autonomous investment
Section 4 version 2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An increase in the MPC: A. increases the multiplier. B. shifts the autonomous investment
Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403
 Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403 http//vustudents.ning.com Actual budget The amount spent by the Federal government (to purchase goods and services and for transfer payments) less the amount of tax
Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403 http//vustudents.ning.com Actual budget The amount spent by the Federal government (to purchase goods and services and for transfer payments) less the amount of tax
Economics 102 Homework #7 Due: December 7 th at the beginning of class
 Economics 102 Homework #7 Due: December 7 th at the beginning of class Complete all of the problems. Please do not write your answers on this sheet. Show all of your work. 1. The economy starts in long
Economics 102 Homework #7 Due: December 7 th at the beginning of class Complete all of the problems. Please do not write your answers on this sheet. Show all of your work. 1. The economy starts in long
1 of 15 12/1/2013 1:28 PM
 1 of 15 12/1/2013 1:28 PM Policy tools include Population growth, spending behavior, and invention. Wars, natural disasters, and trade disruptions. Tax policy, government spending, and the availability
1 of 15 12/1/2013 1:28 PM Policy tools include Population growth, spending behavior, and invention. Wars, natural disasters, and trade disruptions. Tax policy, government spending, and the availability
I. Learning Objectives II. The Income-Consumption and Income-Saving Relationships
 I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. How changes in income affect consumption (and saving). B. About factors other than income that can affect consumption. C. How changes in real
I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. How changes in income affect consumption (and saving). B. About factors other than income that can affect consumption. C. How changes in real
Learning Outcomes Assessment. Instructor: James C. McBrearty Academic year Economics 330
 Learning Outcomes Assessment Economics 330 Instructor: James C. McBrearty Academic year 2012-13 Overview Within the context of the Department of Economics learning objectives, the purpose of Economics
Learning Outcomes Assessment Economics 330 Instructor: James C. McBrearty Academic year 2012-13 Overview Within the context of the Department of Economics learning objectives, the purpose of Economics
Principle of Macroeconomics, Summer B Practice Exam
 Principle of Macroeconomics, Summer B 2017 Practice Exam 1) If real GDP in a small country in 2015 is $8 billion and real GDP in the same country in 2016 is $8.3 billion, the growth rate of real GDP between
Principle of Macroeconomics, Summer B 2017 Practice Exam 1) If real GDP in a small country in 2015 is $8 billion and real GDP in the same country in 2016 is $8.3 billion, the growth rate of real GDP between
Government Budget and Fiscal Policy CHAPTER
 Government Budget and Fiscal Policy 11 CHAPTER The National Budget The national budget is the annual statement of the government s expenditures and tax revenues. Fiscal policy is the use of the national
Government Budget and Fiscal Policy 11 CHAPTER The National Budget The national budget is the annual statement of the government s expenditures and tax revenues. Fiscal policy is the use of the national
Revision Sheets. AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context. Revision Sheets
 2018 http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/150000/velka/uk-map.jpg AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context Macroeconomic Objectives Low unemployment Improve external performance Objectives
2018 http://www.publicdomainpictures.net/pictures/150000/velka/uk-map.jpg AS Economics National Economy in a Global Context Macroeconomic Objectives Low unemployment Improve external performance Objectives
Consumption expenditure The five most important variables that determine the level of consumption are:
 The aggregate expenditure model: A macroeconomic model that focuses on the relationship between total spending and real GDP, assuming the price level is constant. Macroeconomic equilibrium: AE = GDP Consumption
The aggregate expenditure model: A macroeconomic model that focuses on the relationship between total spending and real GDP, assuming the price level is constant. Macroeconomic equilibrium: AE = GDP Consumption
Name: Student # : Section: RYERSON UNIVERSITY Department of Economics
 Name: Student # : Section: RYERSON UNIVERSITY Department of Economics ECN 204 (Section-7) TERM TEST 2 November, 2004 Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Time Limit: 50 minutes Total Pages Including the Cover Sheet:
Name: Student # : Section: RYERSON UNIVERSITY Department of Economics ECN 204 (Section-7) TERM TEST 2 November, 2004 Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Time Limit: 50 minutes Total Pages Including the Cover Sheet:
Economics Online Instructional Materials Correlation to the 2009 Economics and Personal Finance Standards of Learning and Curriculum Framework
 and Curriculum Framework Provider York County School Division Course Syllabus URL http://yorkcountyschools.org/virtuallearning/coursecatalog.aspx Course Title Economics & Personal Finace Last Updated 2010-11
and Curriculum Framework Provider York County School Division Course Syllabus URL http://yorkcountyschools.org/virtuallearning/coursecatalog.aspx Course Title Economics & Personal Finace Last Updated 2010-11
