12 months commencing 1 st April of every day
|
|
|
- Lindsay Holt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 1: BASIC CONCEPTS Sr Particulars Explanation 1 Component of Income Tax law 1) Income tax Act, 1961, 2) Finance Act, 3) Income Tax Rules, 1961, 4) Circulars / Notification from CBDT, 5) Supreme Court and High Court Decisions. 2 India 1) The territory of India as per Article 1 of the constitution, 2) Its territorial waters, seabed and subsoil underlying such waters, 3) Continental Shelf, 4) Exclusive Economic Zone, or 5) Any other specified Maritime Zone, and 6) The air space above its Territory and Territorial waters. 3 Income Tax Rules CBDT is empowered to frame rules from time to time to carry out the purpose and proper administration of the Act. 4 Circulars/Notifications CBDT issues Circulars and Notifications from time to time 5 Types of Amendments Prospective / Immediate/Retrospective effect 6 Person Sec 2(31) Individual, HUF, Firm, Company, AOP, BOI, Local Authority, AJP. 7 Assessee Sec 2(7) 1) Assesse means any person who is liable to pay any tax or any other sum under the Income Tax Act, ) Every person in respect of whom any proceedings has been taken for the assessment of income, loss and refund. 3) Deemed Assessee : Legal representative 4) Assessee in default : Fail to deduct TDs 8 Assessment year [Sec.2(9)] 12 months commencing 1 st April of every day 9 Previous Year [Sec. 3] Financial year prior to Assessment Year. In case of newly established business or profession from the date of set up to the end of Financial year, 10 Exceptions to the general rule that income of a previous year is taxed in its assessment year Details Shipping Business of Non-Resident Persons leaving India AOP / BOI / AJP formed for a particular event or purpose Persons likely to transfer property to avoid tax Discontinued Business Assessment Mandatory Mandatory Mandatory Mandatory Assessment is discretionary 11 Cash Credits [Sec. 68] Taxable in the FY in which it is found credited in books of accounts if Assessee offers unsatisfactory explanation about its nature and source. 12 Unexplained Investments made by Assessee which are not recorded in books and he offers AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 1
2 Investments [Sec. 69] 13 Unexplained money, Bullion, Jewel or valuable article etc [Sec. 69A] 14 Investments, etc. not fully disclosed in books of account [Sec. 69B] 15 Unexplained Expenditure, etc. [Sec. 69C] 16 Amount borrowed / repaid on Hundi expected by A/c Payee Cheque [Sec. 69D] 17 Sec. 68, 69, 69A, 69B, 69C, 69D no explanation or offers unsatisfactory explanation about its nature and source, then the value of investment is deemed to be Income of the Assessee of such FY. Where in any FY the assessee is found to be the owner of Money, Bullion, jewellery, or any valuable article and those are not recorded in books and he offers no explanations of offers unsatisfactory explanation about its nature and source, then the value of those assets is deemed to be Income of the Assessee of such FY. Where in any FY the assessee has made investments or is found to be the owner of money, Bullion, Jewellery, etc the AO finds that amount expended exceeds the amount recorded in books and assessee offers no explanation or offers unsatisfactory explanation about excess amount, then such excess amount is deemed to be Income of the assessee of such FY. Where assessee incurred any expenditure and he offers no or unsatisfactory explanation about source of expenditure or part thereof, then such amount may be deemed to be income of the assessee of such FY. Such expenditure shall not be allowed as deduction under any head of income. Where any amount borrowed on Hundi or repaid the same otherwise than through and Account Payee Cheque drawn on Bank, then such amount shall be treated as income of the person for the PY in which the amount borrowed or repaid. If the amount is taxed at the time of borrowing the same cannot be taxed at the time of repayment. Amount repaid includes interest on borrowed amount. I o e is hargea le u der the head Other Sour es at 30%. No dedu tio i respect of any expenditure/ allowance or any set-off of any loss shall be allowed. (Sec. 115BBE). 18 Income [Sec. 2(24)] Includes 1) Income chargeable under various heads, 2) Voluntary contributions received, 3) E ployees o tri utio to Welfare Fu ds, 4) Amount received under Keyman Insurance Policy including Bonus, 5) Gift in kind, 6) Any sum of money or value of property as defined u/s 56(2)(vii)/ (viia), 7) Value of shares of a company (closely held company) received in any Previous Year, by a Firm or a Company (closed held company), from any person(s), 8) Any consideration received for issued of shares as exceeds the Fair market Value referred u/s 56(2)(viib), 9) Advance forfeited on failed negotiations for transfer of Capital Asset, 10) Subsidy, Duty Drawback, Grant (Whatever name called) received by the assessee from central Govt/ State Govt/ any Authority, other than the grants which considered as cost of Asset u/s.43(1). AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 2
3 19 Method of accounting Relevant only for Profits and Gains from business or and Income from other sources. Based on cash or mercantile system of accounting used regularly by Assessee, subject to specified exceptions. 20 Exemption Section 10 deals with income exempt from tax. 21 Deductions Sec 80C to 80U deals with deductions. Assessee need to claim. 22 Relief Exemptions & Deductions reduces income where as relief reduces income tax liability. 23 Heads of income & Source of Income 1) Salaries, 2) Income from house property, 3) profits and gains of business or profession, 4) capital gains, and 5) Income from other sources Source is part of head of income. 24 Tax, Surcharge & Cess 1) Tax and surcharge is general purpose revenue. 2) Tax is applied on income. 3) Surcharge is applied on income tax. 4) Cess is specific purpose revenue. It is to be applied on tax plus surcharge. 25 Rounding off of Total Income [Sec. 288A] 26 Rounding off of Tax, interest etc. [Sec. 288B] Rounded off to nearest Ten Rupees. Rounded off to nearest Ten Rupees. 27 Application of Income An obligation to apply income, which has accrued or has arisen or has been received amounts to merely the apportionment of Income. Essential are 1) Income accrues to the assessee, 2) Income reaches the assessee, and 3) Income is applied to discharge an obligation, whether self-imposed or gratuitous. 28 Diversion of Income An obligation to apply the income in a particular way before it is received by the assessee or before it has arisen or accrued to the assessee results in diversion of income. The source in charged with an overriding title, which diverts the i o e Esse tials of Diversio of I o e are 1) Income is diverted as source, 2) there is an overriding charge or title for such diversion, and 3) Charge / Obligation is on the source of Income & not on the receives. 29 Chargeability of Income Tax (Sec. 2(17)] Income Tax is charged for Any Assessment year at the rates prescribed in the Finance Act in respect of Total Income of the previous year of every person. AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 3
4 TAX RATES FOR AY Tax rate Resident Individual (Male & Female), HUF, AOP, BOI & AJP Resident Individual ( Age >= 60) Senior citizen (Male& Female) NIL 2,50,000 3,00,000 5,00,000 10% 2,50,001 to 5,00,000 3,00,001 to 5,00,000 NA Resident Individual (Age >=80) Super senior citizen( Male & Female) 20% 5,00,001 to 10,00,000 5,00,001 to 10,00,000 5,00,001 to 10,00,000 30% Above 10,00,000 Above 10,00,000 Above 10,00,000 Add Education cess Secondary and Higher secondary Education cess 15% ( Amendment Finance Act 2016) if Total Income exceeds Rs 1 crore 2% on Tax plus surcharge (If applicable) 1% on Tax plus surcharge (If applicable) REBATE U/ 87A A resident individual (whose net income does not exceed Rs. 5, 00,000) can avail rebate u/s. 87A. It is deductible from income tax before calculating education cess. Net income = GTI Deduction u/s 80C to 80U The amount of rebate is 100% of income tax or Rs. 5,000 whichever is less.[amendment Finance Act 2016] It is to be deducted before education cess. Rebate u/s 87A and surcharge cannot come at a time. NON RESIDENT ASSESSEE For Non-Resident individual exempted income shall be upto Rs. 2, 50,000 irrespective of Age Tax Rate for Non- Resident. 15% if income exceeds 1cr 3% on Tax + SC Rebate u/s 87A is not available. KEY NOTE Total Income does not include taxable Long Term Capital Gain (20%), Short Term Capital Gain (15%) on Securities subjected to STT, Lottery Winnings, Horse races, etc. (30%) and other Income chargeable at Special Rates. FOR OTHER ASSESSEES / PERSONS (W.e.f. AY 17-18) Assesse Rate of tax TI <Rs. 1 Crore TI > Rs.1 Crore, but TI Rs. Crores TI > Rs.10 crores Rate of EC + SHEC Domestic Companies 30% 7% 12% 3% Foreign Companies 40% 2% 5% 3% AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 4
5 Firms and LLP 30% 12% 12% 3% Local Authorities 30% 12% 12% 3% Co operative Societies For First Rs.10,000 For Next Rs.10,000 For the Balance 10% 20% 30% % % 3% 3% 3% FOR DOMESTIC COMPANIES TI = Total Income TT = Total Turnover GR = Gross Receipts Asst. Year Tax Rate SC Cess TT / GI < Rs. 5 Crores in FY TT / GI > Rs. 5 Crores in FY TI < Rs. 1 Crores 29% 30% - 3% TI > Rs. 1 Crore, but < Rs. 10 Crores 29% 30% 70% 3% TI > Rs. 10 Crores 29% 30% 12% 3% MARGINAL RELIEF Meaning Applicable to Condition Marginal relief Marginal relief in provided to insure that the additional income tax payable including surcharge on excess of income over Rs.1,00,00,000 is limited to the amount by which the income is more than Rs.1.00,00,000 All assessee Net income is slight more than Rs.1,00,00,000 [in case of corporate assessee slight more than 10 crore] [{(Income tax + surcharge) on actual income} Income tax on 1 crore] [actual income 1 crore] In case of corporate assessee: [{(Income tax + surcharge) on actual income) income tax on 10crore] [Actual Income 10 crore] Illustration 1 Compute the amount of marginal relief available if the income of Mr. Apple is Rs 1.02crores and tax Payable Solution Computation of Marginal Relief Particular Amount Total income Rs. 1 crore Rs.1.02 crore Rate tax Slab rate Slab rate AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 5
6 Tax liability before surcharge and cess Rs lakhs Rs lakhs Add: 15% NA Rs lakhs Tax liability after surcharge before Cess Rs lakhs Rs lakhs Marginal relief = (Income Tax + surcharge) on actual income] [(Income Tax on Rs. 1 crore) (Income Rs.1 crore)] =Rs. [( ) lakhs ( ) lacs] =Rs lakhs Rs.2 lakhs =Rs lakhs Computation of Tax payable Total income Rate of Tax Tax liability before surcharge and cess Add: Tax liability surcharge before cess Less: Marginal relief Tax liability before cess Add Education 3% Tax liability Rs crore Slab Rate Rs lakhs Rs lakhs Rs lakhs Rs lakhs lakhs lakhs lakhs AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 6
7 1. If total income of Mt. X, resident, age 50 years, is Rs. 3,80,000/-, his tax liability including surcharge and cess shall be (a) Rs. 8,240 (b) Rs. 10,000 (c) Rs. 10,300 (d) Rs. 8,300 Computation of tax liability Particulars Working Amount Tax liability before Rebate Rs. 2,50,000 Nil Nil Rs. 1,00,000 10% 13,000 Total 13,000 Less: Rebate u/s 87A 5,000 Liability before surcharge 8,000 Add: surcharge Nil Tax liability after surcharge 8,000 Add: Education cess 3% of above 240 Total 8, Calculate income tax payable by an individual (aged 30 years) for AY if his total income is Rs. 1,01,20,000 (a) Rs. 30,33,350 (b) Rs. 32,41,510 (c) Rs. 29,46,830 (d) Rs. 34,39,790 Computation of tax liability Particulars Working Amount Tax liability before rebate Rs. 2,50,000 Nil Nil Rs. 2,50,000 10% 25,000 Rs. 5,00,000 20% 1,00,000 Balance 30% 27,36,000 Total 28,61,000 Less: Rebate u/s 87A Nil Liability before surcharge 28,61,000 Add: Surcharge 84,000 Tax liability after surcharge 29,45,000 Add: Education cess 3% of above 88,350 Total 30,33,350 AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 7
8 3. What will be the amount of marginal relief available to an individual (52 years) whose total income is Rs. 1,00,10,000/- (a) Rs. 4,17,200 (b) Rs. 4,24,200 (c) Rs. 3,35,800 (d) Rs. 2,82,800 Particulars Working Case 1 Tax liability before Rebate Rs. 2,50,000 Nil Nil Rs. 2,50,000 10% 25,000 Rs. 5,00,000 20% 1,00,000 Balance Income 30% 27,03,000 Total 28,28,000 Less: Rebate u/s 87A As income exceeds Rs. 5,00,000 Nil Liability before surcharge [A] 28,28,000 Add: Surcharge B = [15% of (A)] 4,24,200 Marginal relief B 70%(Rs. 1,00,10,000 Rs. 1,00,10,000) 4,17, What will be the amount of tax (including surcharge and cess) of an individual (58 year) having total income of Rs. 1,05,00,000/- (a) Rs. 34,24,750 (b) Rs. 34,31,960 (c) Rs. 33,65,010 (d) Rs. 35,68,950 Particulars Working Case 2 Tax liability before Rebate Rs. 2,50,000 Nil Nil Rs. 2,50,000 10% 25,000 Rs. 5,00,000 20% 1,00,000 Balance income 30% 28,50,000 Total 29,75,000 Less: Rebate u/s 87A As income exceeds Rs. 5,00,000 Nil Lability before surcharge [A] 29,75,000 Add: Surcharge B = [15% of (A)] 4,46,250 Less marginal relief B 70%(Rs. 1,05,00,000 Rs. 1,00,00,000) 96,250 Effective surcharge [C] 3,50,000 Tax liability after surcharge [A + C] 33,25,000 Add: Education cess 3% of above 99,750 Total 34,24,750 Rounded of 34,24,750 AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 8
9 5. Income-tax (including surcharge and cess) payable by a resident individual (aged 80 years) having total income of Rs. 5,00,000 is. (a) Nil (b) Rs. 18,540 (c) Rs. 23,690 (d) Rs. 25,750 In Case of Resident Individual is exempt upto Rs. 5,00, Income-tax (including surcharge and cess) payable by a non-resident individual (aged 80 years) having total income of Rs. 5,00,000 is. (a) Nil (b) Rs. 18,540 (c) Rs. 23,690 (d) Rs. 25,750 Computation of tax liability Particulars Working Amount Tax liability Rs. 2,50,000 Nil Nil Rs. 2,50,000 10% 25,000 Total 25,000 Add: Education cess 3% of above 750 Total 25, Income-tax (including surcharge and cess) payable by a resident individual (aged 63 years) having total income of Rs. 4,30,000 is Rs. (a) Rs. 8,240 (b) Rs. 10,300 (c) Rs. 15,450 (d) Rs. 13,390 Computation of Tax Liability Particulars Working Amount Tax liability before Rebate Rs. 3,00,000*Nil Nil Rs. 1,30,000*10% 13,000 Total 13,000 Less: Rebate u/s 87A 5,000 Liability before surcharge 8,000 Add: Surcharge Nil Tax liability after surcharge 8,000 Add: Education cess 3% of the above 240 Total 8,240 AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 9
10 8. Income-tax (including surcharge and cess) payable by a company having total income of Rs. 4,00,000 is. (a) Rs. 1,23,600 (b) Rs. 46,350 (c) Rs. 30,900 (d) Rs. 1,35,960 Computation of tax liability Particulars Working Amount Tax liability Rs. 4,00,000 30% 1,20,000 Add: Education cess 3% of above 3,600 Total 1,23, Income-tax (including surcharge and cess) payable by a resident individual (aged 45 years) having total income of Rs. 8,40,000 is Rs. (a) Rs. 93,730 (b) Rs. 95,790 (c) Rs. 90,640 (d) Rs. 70,040 Computation of tax liability Particulars Working Amount Tax liability before Rebate Rs. 2,50,000 Nil Nil Rs. 2,50,000 10% 25,000 Rs. 3,40,000 20% 68,000 Total 93,000 Less: Rebate u/s 87A Nil Liability before surcharge 93,000 Add: Surcharge Tax liability after surcharge 93,000 Add: education cess 3% of above 2,790 Total 95, Income-tax (including surcharge and cess) payable by a resident HUF having total income of Rs. 2,60,000 is Rs. (a) 1,030 (b) Nil (c) Rs. 1,000 (d) Rs. 2,060 Nil AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 10
11 Computation of tax liability Particulars Working Amount Tax liability before Rebate Rs. 2,50,000 Nil Nil Rs. 10,000 10% 1,000 Total 1,000 Less: Rebate u/s 87A Nil Liability before surcharge 1,000 Add: Surcharge Tax liability after surcharge 1,000 Add: Education cess 3% of above 30 Total 1,030 Nil AGRAWAL CLASSES Page 11
12 CHAPTER 2: RESIDENTIAL STATUS Sr Particulars Explanation 1 Why Residential status? To decide where to pay tax in India or Outside India. 2 Criteria to decide Residential status 3 Hints for determination of Residential status Person Individual HUF Company Other assessee Criteria Period of stay in India Place of control and Management Place of effective management Place of control and Management 1) Citizenship of a country and residential status of that country are different concepts. 2) If person is resident in India in the P.Y. relevant to an A.Y. in respect of any source of income, he shall be deemed to be resident in India for his other source of income. 3) If an individual stays on a ship, which is in the territorial waters of India, then it shall be treated as his presence in India. 4) 24 hrs. Shall be treated as one day. 5) It is not essential that stay should be at same place. 6) Continuous stay is not required. Counting of number of days: If nothing is mentioned about the time of arrival and departure than the day of arrival and the day of departure both shall be include for determining residential status of an Individual RESIDENTIAL STATUS AT A GLANCE Assessee Condition to be a Resident Condition to be an Ordinary Resident Individual Sec 6(1) Assessee satisfies any one condition of sec. 6(1) i.e. 1. He is in India in the previous year for a period of 182 days or more; or 2. He is in India for a period of 60 days or more during the previous year and 365 days or during more during 4 previous years immediately preceding the relevant previous year. Exceptions: In the following cases, (b) is irrelevant. 1. An Indian citizen, who leaves India during the previous year for employment purpose. 2. An Indian citizen, who leaves India during the Assessee satisfies both the conditions of sec. 6(6). 1. He has been resident in India in at least 2 out of 10previous years immediately preceding the relevant previous year; and 2. He has resided in India for a period of 730 days or more during 7 previous years immediately proceeding the relevant previous year. Page 1
13 previous year as a member of crew of an Indian ship. 3. An Indian citizen or a person of Indian origin, who normally resides outside India, comes on a visit to India during the previous year. Note A person is said to be of Indian origin if he or either of his parents or any of his grandparents (maternal & paternal) was born in undivided India. AMENDMENT FINANCE ACT 2015 Determination of Residential Status of Crew Member of a Ship: W.e.f. 01/04/2016 In the case of an Individual, being an Indian Citizen and a member of the Crew of a Foreign-hound Ship leaving India, the period(s) of stay in India shall, in respect of such voyage, be determined in the manner and subject to such prescribed conditions. For determining the period of Stay in India, the following period shall not be included: Period beginning from Date entered into the Continuous Discharge Certificate in respect of joining the ship by the said individual for the eligible voyage Period ending to Date entered into Continuous Discharge Certificate in respect of the signing off by that individual from the ship in respect of such voyage. RULES FOR DETERMINING THE RESIDENTIAL STATUS OF HUF [SECTION 6[2]] Place of Control & Management Fully In India Partly in India Fully outside India Resident Resident Non-Resident Residential status ADDITIONAL CONDITIONS TO TEST AS TO WHEN A HUF IS ROR & RNOR Condition Particulars 1 Karta has been resident in India in at least 2 out of 10 previous years immediately preceding the relevant previous year. 2 Karta has been in India for a period of 730 days or more during 7 years immediately preceding the relevant previous year. INCIDENCE OF TAX [SEC. 5] For individual and HUF Nature of income Ordinarily resident Not ordinarily resident Non-resident Income received in India (no matter where it is earned) Taxable Taxable Taxable Income earned in India (no matter where it is received) Taxable Taxable Taxable Income earned and received outside India from a source Taxable Taxable Not Taxable controlled from India Income earned and received outside India from a source Taxable Not Taxable Not Taxable Page 2
14 not controlled from India Note: Past year untaxed income brought in India shall not be taxable in the current year; however, past year file shall be reassessed. RESIDENTIAL STATUS OF A COMPANY [Sec.6 (3)] Sr Place of Control Indian Company Foreign Company Place of Effective Management (POEM) 1 Wholly in India Resident Resident 2 Wholly outside India Resident Non-resident 3 Partly in India and partly outside India Resident Resident FOR DETERMINING THE RESIDENTIAL STATUS OF FIRM, AOP & BOI [SECTION 6(4)] Place of Control and Management situated Status Fully in India Resident in India Partly in India Resident in India Fully outside India Non-Resident RESIDENTIAL STATUS & INCIDENCE OF TAX Nature of income Resident Non resident Income received in India (no matter where it is earned) Taxable Taxable Income earned in India (no matter where it is received) Taxable Taxable Income earned and received outside India from a source controlled from India Income earned and received outside India from a source not controlled from India Taxable Taxable Not Taxable Not Taxable Note: Past year untaxed income brought in India shall not be taxable in the current year; however, past year file shall be reassessed. KEY NOTES Remittance v/s Receipt: Receipt is different from remittance. The receipt of income refers to the first occasion when the recipient gets the money under his control. Once amount is received as income any subsequent remittance of amount to India dose not result income in India. If income is accrued and received outside India in any year preceeding the previous year and later on remitted to India in current financial year is not taxable. Page 3
15 SECTION 7 AND 9 What is received in India? Received In India Accrued In India Sec. 7 Sec. 9 Received In India Deemed to be received in India Accrue in India Deemed to accrued in Any income received in India during PY, by any assessee chargeable to tax a) Contribution made by the employer to the recognised provident fund in excess of 12% of the salary of the employee. b) Interest credited to the RPF of the employee which is in excess of 9.5% p.a. c) Transfer balance from the unrecognised fund to a Recognised Provident fund (It has been discussed in the Chapter on Income from salaries). d) The contribution made, by the Central Government or any other employer in the previous year, to the account of an employee under a notified contributory pension scheme referred to in section 80CCD. a) Income from connection in India b) Salary earned in India c) Salary from Govt., by an Indian citizen for services rendered outside India d) Income from dividend paid by an Indian Company e) Income from interest payable by specified person f) Income from royalty g) Income from technical services h) Income from any property/assets or source of income in India i) Income on transfer of a capital asset situated in India. Meaning of business connection: Includes If the assessee (non-resident) has an authority in in India who can conclude contracts on his behalf and he and he habitually exercises such authority then it shall be treat as business connection in India. However, if the activities are limited to the purchase of goods or merchandise for the nonresident then it shall not be treated as business connection; or If the assessee (non-resident) has an authority who habitually maintains in India a stock of goods or merchandise from which he regularly deliver goods or merchandise on behalf of the assessee then it shall not be treated as business connection; or If the assessee (non-resident) Hs an authority who habitually secures orders in India for such assessee. Page 4
16 Does not In the case of a business, in respect of which all the operations are not carried out in India include [Explanation 1(a) to section 9(1) (i)]: In the case of a business of which all the operations are not carried out in India, the income of the business deemed to accrue or arise in India shall be only such part of income as is reasonably attributable to the operations carried out in India. Therefore, it follows that such part of income which cannot be reasonably attributed to the operations in India, is not deemed to accrue or arise in India. Purchase of goods in India for export [Explanation 1(b) to section 9(1)(i)]: In the case of non resident, no income shall be deemed to accrue or arise in India to him through or from operations which are confined to the purchase of goods in India for the purpose of export. Collection of news and views in India for transmission out of India [Explanation 1(c) to section 9(1) (i)]: in the case of a non resident, being a person engaged in the business of running a news agency or of publishing newspapers, magazines or journals, no income shall be deemed to accrue or arise in India to him through or from activities which are confined to the collection of news and views in India from transmission out of India. Shooting of cinematograph films in India [Explanation 1(d) to section 9(1)(i)]: In the case of a nonresident, no income shall be deemed to accrue or arise in India through or from operations which are confined to the shooting of any cinematograph film in India, if such non-resident is: a. An individual, who is not a citizen of India or b. A which does not have any partner who is a citizen of India or who is resident in India; or c. A company which does not have any shareholder who is a citizen of India or who is resident in India. Activities confined to display of rough diamonds in SNZs [Explanation 1(e) to section 9(1)(i): In order to facilitate the FMCs to undertake activity of display of uncut diamond (without any sorting or sale) in a Special Notified Zone (SNZ), clause (e) has been inserted in Explanation 1 to section 9(1)(i) to provide that in the case of a foreign company engaged in the business of mining of diamonds, no income shall be deemed to accrue or arise in India to it through or from the activities which are confined to display of uncut an unsorted diamonds in any special zone notified by the Central Government in the Official Gazette in this behalf. [Amendment Fin Act 2016] Explanation no 6 and 7 have been interested by Fin Act 2015 w-e-f 1/4/2016 as given below Explanation 6 provides that the share of interest in a company of entity registered or incorporated outside India, shall be deemed to derived its value substantially from the assets (whether tangible or intangible) in India, if on the specified date, the value of Indian assets, - (a) > Rs. 10 Crore; and (b) Represents at least 50% of the value of all the assets owned by the company or entity, as the case may be; Explanation 7: to section 9(1) (i) provides that no income shall be deemed to accrue or arise to a non-resident from transfer, outside India, of any share of, or interest in, a company or an entity, registered or incorporated outside India, in the following ceases: Page 5
17 (1) Foreign company or entity directly owns the assets situated in India (2) Foreign company or entity directly owns the assets situated in India AND AND The transferor (whether individually or along with its associated enterprises), at any time in the 12 months preceding the date of transfer, does not hold 1) The right of management or control in relation to foreign company or entity; or 2) The voting power or share capital or interest > 5% of the total voting power or total share capital or total interest, as the case may be, of the foreign company or entity; or The transferor (whether individually or long with its associated enterprises), at any time in the 12 months preceding the date of transfer, does not hold 1) The right of management or control in relation to foreign company or entity; or 2) Any right in, or in relation to, foreign company or entity which would entitle him to the right of management or control in the company or entity that directly owns the assets situated in India; or 3) Such percentage of voting power or share capital or interest in foreign company or entity which result in holding of (either individually or long with associated enterprises) a voting power or share capital or interest exceeding 5% of the total voting power or total share capital or total interest, as the case may be, of the company or entity that directly owns the assets situated in India; In effect, the exemption shall be available to the transferor of a share of, or interest in a foreign entity if he along with its associated enterprises, - 1) Neither held the right of control or management 2) Nor held voting power or share capital or interest exceeding 5% of the total voting power or total share capital. SALARY INCOME [SEC 9(1) (ii)] Salary income shall be deemed to be earned in India if services are rendered in India. Exception to the above rule If salary is payable to- 1) Government employee b) who is a citizen of India; c) for services rendered outside India -then such salary (even service rendered outside India) shall be deemed to be earned in India. Key Note: Any allowances or perquisites paid to above employee shall be exempted u/s 10(7). Pension received in India by abroad: If an assessee, residing in India, receives pension from abroad from past services rendered in foreign country, then such income shall be treated as income accruing abroad, and shall not be liable to tax in India. Page 6
18 DIVIDEND INCOME [SEC 9(1) (iii)] Any dividend Paid by an Indian company outside India shall be deemed to accrue to arise in India. Dividend income paid to a non- resident by Indian company is deemed to accrue or arise in India only on payment and not on declaration. KEY NOTE: Dividend from Indian company shall be exempted u/s 10(34). INTEREST, ROYALTY & FEES FOR TECH. SERVICE-WHEN DEEMED TO ACCRUE OR ARISE IN INDIA 1. Accrual of Interest 9(1)(v) in India: Payer Purpose of Payment Is the payment deemed to accrue or arise in India Taxability in the hands of receiver Government Any purpose Yes All Assessee Resident For carrying on Business or profession outside India or earning income outside India No ROR Taxable NOR Not Taxable NR Not Taxable [For NOR or NR assumed first receipt not in India] Resident For any other purpose Yes All Assessee Non-Resident For carrying on business or Yes All Assessee profession in India Non-Resident For any other Purpose No 2. Accrual of Royalty 9(1)(vi), and Fees for Technical Service 9(1)(vii) in India: Payer Purpose of payment Is the payment deemed to accrue or arise in India ROR Taxable NOR Not Taxable NR Not Taxable [for NOR or NR assumed first receipt not in India] Taxability in the hands of receiver Government Any purpose Yes All Assessee Resident For carrying on business or profession outside India or earning Income outside India No ROR Taxable NOR Not taxable NR Not taxable [For NOR or NR assumed first receipt not in India] Resident For any other purpose Yes All Assessee Non-resident Non-resident For carrying on business or profession in India or any other source in India Yes All Assessee For any other purpose No ROR Taxable NOR Not taxable NR Not taxable [For NOR or NR assumed first receipt not in India] Page 7
19 INCOME FROM PROPERTY IN INDIA 9(1) (i) Income arising through or from any property or any asset or source of income in India Ex: Mr. Mac Mohan residing in China leases out a building situated in Nagpur and receives rent in China. Such rental income shall be deemed to accrue or arise in India as the building (i.e. source of income) is situated in India. INCOME FROM TRANSFER OF PROPERTY IN INDIA Income arising through or from the transfer of a capital asset situated in India Ex: If Mr. Mohan sells the building situated in Nagpur to a person Outside India and receives consideration outside India, such income shall also be deemed to accrue or arise in India as the property transferred is situated in India. Page 8
20 PRACTICAL QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. X, a foreign citizen, resident in India during the previous year for 83 days. What will be his residential status for previous year His stay in India during the last few previous years are given in the table Year Days Year Days Year Days Year Days (a) Resident and Ordinary Resident in India (b) Resident but not Ordinary Resident in India (c) Non-resident (d) Resident Solution During the previous year , X was in India for 83 days & during 4 years immediately preceding the previous year, he was in India for 378 days as shown below: Year Total No. of days stayed in India Thus, he satisfies one of the conditions satisfied u/s 6(1) & consequently, he becomes resident in India in the PY Further, to determine whether X is an ordinarily resident or not, he needs to satisfy both conditions laid down u/s 6(6). Year Presence in India (In Days) Resident (R) or Non- Resident (NR) Condition satisfied to become a resident R 6(1)(c) NR None R 6(1)(c) R 6(1)(c) R Both R Both NR None R 6(1)(c) R 6(1)(c) R 6(1)(c) Condition (i): of sec. 6(6) requires that an individual should be resident in Indian for at least 2 out of 10 years preceding the relevant previous year. X was resident in India for 8 out of 10 years immediately preceding the previous year. Thus, he satisfies this condition. Page 9
21 Condition (ii): of sec. 6(6) requires that an individual should be present in India for at least 730 days during 7 years preceding to relevant previous year. X was in India for 1090 days during to Hence, the satisfies this condition also. X satisfies condition (ii) of sec. 6(1) as well as both the conditions of sec. 6(6). Thus, he is a resident and ordinarily resident in Indian for the previous year Miss pal, an Indian citizen, left India for first time on 1 st April, 2016 for joining job in Tokyo. She came to India on 11 th October, 2016 for any 190 days. What will be her residential status for PY ? (a) Non-resident (b) Resident (c) Resident and Ordinary Resident (d) Resident but not Ordinary Resident Solution Number of days Miss Pal stayed in India can be calculated as under: PY Apr May June July Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar Total Since she left India for employment purpose. Hence for becoming resident she has to stay in India for at least 182 days. However, she is in India for only 173 days during the previous year, thus she is a non-resident for the PY Andy, a British national, comes to India for the first time during During the financial year , , , , and , he was in India for 55 days, 60 days, 80 days, 160 days and 70 days respectively. Determine his residential status for the assessment year (a) Non-resident (b) Resident (c) Resident and Ordinary Resident (d) Resident but not Ordinary Resident Solution During the previous year , Andy was in India for 70 days & during 4 years immediately preceding the previous year, he was in India for 355 days as shown below. Year Total No. of days stayed in India Thus, he does not satisfy Sec. 6(1) & consequently, he is a non-resident in India for the previous year Sam came to India first time during the previous year During the previous year, he stayed in India for 50 days. What will be his residential status for PY ? Page 10
22 (a) Non-resident (b) Resident (c) Resident and Ordinary Resident (d) Resident but not Ordinary Resident Since Sam resides in India only for 50 days in the previous year , he does not satisfy any of the conditions satisfied in sec. 6(1). He is, therefore, a non-resident in India for the PY Mr. X age 19 years, left India for first time on May 31, Determine his residential status for the previous year if he left Indian for world tour. (a) Non-resident (b) Resident but not Ordinary Resident (c) Resident and Ordinary Resident (d) Resident Solution During the previous year , Mr. X was in India for 61 days as shown below PY Apr May June July Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar Total During the previous year , X stayed in India for 61 days. Further, he was in India for more than 365 days during 4 years immediately preceding the relevant previous year (as he left India for first time). 6. Mr. X aged 19 years, left India for first time on May 03, 2016 for a year. Determine his residential status for the previous year if he left India for world tour. (a) Non-resident (b) Resident but not Ordinary Resident (c) Resident and Ordinary Resident (d) Resident Solution During the previous year , X stayed in India for 33 days only. He does not satisfy any of the condition given u/s 6(1), hence he is a non-resident 7. X came India for first time on July 24, From July 24, 2012 to December 25, 2013 he was in India again, he came to India on August 5, 2016 for employment purpose & left India on November 25, 2016 permanently. Determine his status for the previous year assuming he is a Indian citizen. (a) Non-resident (b) Resident but not Ordinary Resident (c) Resident and Ordinary Resident (d) Resident Page 11
23 Solution During the previous year , X was in India for 113 days as shown below PY Apr May June July Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar Total Further, he was in India for more than 365 days during 4 years immediately preceding the previous year as shown below: PY Apr May June July Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Jan Feb Mar Total As he satisfies condition given in sec. 6(1)(c), he is a resident in India. Further, he was resident during 2 out of 10 years immediately preceding the relevant previous year but he was in India only for 520 days in 7 years immediately preceding the relevant previous year. As he is not satisfying dual conditions of sec. 6(6), he is a resident but not ordinarily resident in India for the previous year Co i g i I dia for e plo e t purpose is ot overed e eptio to se Ram provides following details of income, calculate the income which is liable to be taxed in India for the AY assuming that he is a non-resident Particulars Amount Salary received in India from a former employer of UK 1,40,000 Income from tea business in Nepal being controlled from India 10,000 Interest on company deposit in Canada (1/3 rd received in India) 30,000 Profit from a business in Mumbai controlled from UK 1,00,000 Profit for the year from a business in Tokyo remitted to India 2,00,000 Income from a property in India but received in USA 45,000 Income from a property in London but received in Delhi 1,50,000 Income from a property in London but received in Canada 2,50,000 Income from a business in Jambia but controlled from Turkey 10,000 (a) Rs. 4,45,000 (b) Rs. 4,55,000 (c) Rs. 7,35,000 (d) None of these Solution Calculation of Income Liable to be taxed in India of Ram for the AY Page 12
24 Particulars Non-resident Salary received in India from a former employer of UK 1,40,000 Income from tea business in Nepal being controlled from India Interest on company deposit in Canada - - 1/3 rd received in India 10,000-2/3 rd received outside India Nil Profit from a business in Mumbai controlled from UK 1,00,000 Profit for year from a business in Tokyo remitted to India Nil Income from a property in India but received in USA 45,000 Income from a property in London but received in Delhi 1,50,000 I o e fro a propert i Lo do ut re eived i Ca ada Income from a business in Jambia but controlled from Turkey Income liable to tax in India 4,45,000 Nil Nil Nil 9. Teji, a citizen of India, is an export manager of Arjun Overseas Ltd., an Indian company since He has been regularly visiting USA for export promotion. He spent the following days in USA during the last five years; determine his residential status for AY assuming that prior to , he had never travelled abroad. Previous year ended Number of days spent in USA days days days days days (a) Resident or ordinary resident (b) Resident but not ordinary resident (c) Non-resident (d) Resident Solution During previous year , Teji was in India for 70 days (i.e., 366 days 295 days) & during four years immediately preceding be previous year, he was in India for 412 days as shown below: Year Total No. of days stayed in India 46 days 215 days 95 days 55 days 412 days ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Thus, he satisfies one of the conditions specified u/s 6(1) & consequently, he becomes resident for the PY Further, to determine whether Teji is an ordinary resident or not, he needs to satisfy both condition laid down in sec. 6(6). His days of stay in India in last few years are as follows: Page 13
25 S N Year Presence in India (in days) Resident (R) or nonresident (NR) Condition satisfied to become a resident NR None R Sec. 6(1)(c) R Both NR None R Both R Both R Both R Both R Both R Both Condition (i): of sec. 6(6) requires that an individual should be resident in India for at least 2 out of 10 years immediately preceding the relevant previous year. Teji was resident in India for 8 out of 10 years immediately preceding the previous year. Thus, he satisfied this condition. Condition (ii): of sec. 6(6) requires that an individual should be present in India for at least 730 days during 7 years immediately preceding the relevant previous year. Teji was in India for 1507 days during to Hence, he satisfies this condition also. Teji satisfies the condition for sec. 6(1)(c) as well as both the conditions of sec. 6(6). Thus, he is a resident and ordinarily resident in India for the previous year From the following information compute the taxable income of Shri Amiyo Roy Choudhury for the assessment year , assuming that Shri Roy Choudhury is a Resident but not ordinarily resident: Remuneration for consultancy services rendered in Italy Rs. 30,000 but received in India. Income from business in Ireland and received in Ireland Rs. 65,000. The business is, however, controlled from India Pension for services rendered in India but received in Israel Rs. 25,000 Interest on deposit in a local bank in Indonesia Rs. 20,000 (a) Rs. 1,20,000 (b) Rs. 55,000 (c) Rs. 1,40,000 (d) Rs. 1,10,000 Solution Computation of total income in India of Sri Amiyo Roy Chowdhury S N Particulars Resident but not ordinarily resident (a) Remuneration received in India 30,000 Page 14
26 (b) Income from business situated outside India but controlled from India 65,000 (c) Pension for services rendered in India received outside India 25,000 (d) Interest earned and received outside India Nil Total Income 1,20, During the financial year , Sri Avirup Acharya had the following incomes. Compute the income of Sri Acharya if he is Non-resident in India. Income from profession in India but received in USA Rs. 1,00,000 Agriculture income accrued and received in Australia Rs. 20,000 Income from business from Indonesia not brought into India Rs. 3,00,000. The business is controlled from India Property income accrued and received in London (out of which Rs. 40,000 was remitted to India) Rs. 1,30,000 Interest from deposits with an African company but received in India Rs. 75,000 (a) Rs. 1,75,000 (b) Rs. 4,75,000 (c) Rs. 6,05,000 (d) Rs. 1,00,000 Solution Calculation of Income Liable to be taxed in India of Sri Avirup Acharya Particulars Non-resident Income from profession in India but received in USA Rs. 1,00,000 Interest from deposits with an African company but received in India Rs. 75,000 Income liable to tax in India 1,75, Mr. Jeff, a citizen of USA came to India for 80 days, 90 days, 110 days and 130 days in the financial years , , and respectively. Determine his residential status for the Assessment year (a) Resident (b) Non-resident (c) Ordinary resident (d) Not ordinary resident Solution During the previous year , Mr. Jeff was in India for 130 days & during 4 years immediately preceding the previous year, he has in India for 280 days as shown below: Year Total No. of days stayed in India Page 15
27 Thus, he does not satisfy sec. 6(1) & consequently, he is a non-resident in India for the previous year Mr. A furnished the following particular of his income during the previous year : Gift of Rs. 52,000 received in foreign currency from a relative in India Income from agriculture in Bangladesh, received thereof Rs. 2,00,000 and subsequently remitted to India Arrears of salary Rs. 70,000 received in India from a former employer in England Income from property received abroad but later on remitted to India Rs. 3,20,000 (Rs. 1 lakh used in Bahrain for educational expenses and Rs. 2 lakhs remitted in India later.) Profit from business outside India managed from India Rs. 90,000 and received outside India. Find out the gross total income of Mr. A for the assessment year if Mr. A is Resident and ordinarily resident. (a) Rs. 6,80,000 (b) Rs. 1,60,000 (c) Rs. 70,000 (d) Rs. 6,28,000 Solution Computation of total income in India of Mr. A Particulars Income from agriculture in Bangladesh, received thereof and subsequently remitted to India Resident but not ordinarily resident Rs. 2,00,000 Arrears of salary received in India from a former employer in England Rs. 70,000 Income from property received abroad but later on remitted to India Rs. 3,20,000 Profit from business outside India managed from India and received outside India Rs. 90,000 Income liable to tax in India Rs. 6,80,000 Page 16
Basics of Income Tax
 CHAPTER : Basics of Income Tax CONCEPT 1: Short Title, Extent and Commencement [Section 1] a) Short title : Income Tax Act 1961 b) Extent : Whole of India c) Commencement : 1 st April, 1962 CONCEPT 2:
CHAPTER : Basics of Income Tax CONCEPT 1: Short Title, Extent and Commencement [Section 1] a) Short title : Income Tax Act 1961 b) Extent : Whole of India c) Commencement : 1 st April, 1962 CONCEPT 2:
1. Basic concepts of Income Tax
 Quick review of the chapter: Sections Particulars Sec. 2(7) Assessee Sec. 2(9) Assessment year Sec. 2(24) Income Sec. 2 (31) Person Sec. 2(34) & 3 "Previous Year" defined Sec. 80B(5) Gross total income
Quick review of the chapter: Sections Particulars Sec. 2(7) Assessee Sec. 2(9) Assessment year Sec. 2(24) Income Sec. 2 (31) Person Sec. 2(34) & 3 "Previous Year" defined Sec. 80B(5) Gross total income
RESIDENTIAL STATUS & SCOPE OF TOTAL INCOME
 Get More Updates From Caultimates.com Join with us : http://facebook.com/groups/caultimates Residential Status & Scope of Total Income 135 RESIDENTIAL STATUS & SCOPE OF TOTAL INCOME SECTION 5 TO 9 PARTICULARS
Get More Updates From Caultimates.com Join with us : http://facebook.com/groups/caultimates Residential Status & Scope of Total Income 135 RESIDENTIAL STATUS & SCOPE OF TOTAL INCOME SECTION 5 TO 9 PARTICULARS
Residence and Scope of Total Income
 2 Residence and Scope of Total Income 2.1 Residential Status [Section 6] The incidence of tax on any assessee depends upon his residential status under the Act. Therefore, after determining whether a particular
2 Residence and Scope of Total Income 2.1 Residential Status [Section 6] The incidence of tax on any assessee depends upon his residential status under the Act. Therefore, after determining whether a particular
1 Basics of Income Tax Law &
 1 Basics of Income Tax Law & Residential Status This Chapter Includes : Basics of Taxation; Direct Taxes & Indirect Taxes; Sources and Authority of Taxes in India; Seventh Schedule of the Constitution;
1 Basics of Income Tax Law & Residential Status This Chapter Includes : Basics of Taxation; Direct Taxes & Indirect Taxes; Sources and Authority of Taxes in India; Seventh Schedule of the Constitution;
On the Basis of Residential Status
 Scope of total income (Section 5) This section has divided the scope of total income into 3 different cases (a) Resident and ordinarily resident (ROR) (b) Resident but not ordinarily resident (RNOR) (c)
Scope of total income (Section 5) This section has divided the scope of total income into 3 different cases (a) Resident and ordinarily resident (ROR) (b) Resident but not ordinarily resident (RNOR) (c)
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO INCOME TAX ACT 1961
 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO INCOME TAX ACT 1961 Section Topics 2(7) Assessee 2(7A) Assessing Officer 2(9) Assessment year 2(25A) India 2(31) Person 2(34)/3 Previous Year or Uniform Previous Year 2(45) Total
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION TO INCOME TAX ACT 1961 Section Topics 2(7) Assessee 2(7A) Assessing Officer 2(9) Assessment year 2(25A) India 2(31) Person 2(34)/3 Previous Year or Uniform Previous Year 2(45) Total
Income Ta Income Tax (A.Y (A.Y )
 1 Income Tax (A.Y. 2011-12) 12) What is a Finance Bill? a) The Finance Bill incorporates all the financial proposals of the Government for the following year. b) It is ordinarily introduced in the Lok
1 Income Tax (A.Y. 2011-12) 12) What is a Finance Bill? a) The Finance Bill incorporates all the financial proposals of the Government for the following year. b) It is ordinarily introduced in the Lok
SURENDER KR. SINGHAL & CO
 PROPOSED TAX RATES FOR FINANCIAL YEAR 2016-17 A. Y. 2017-18 Income Tax Rates for Individuals, HUF Individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) and Artificial Jurisdictional Person: Net Income Range Income
PROPOSED TAX RATES FOR FINANCIAL YEAR 2016-17 A. Y. 2017-18 Income Tax Rates for Individuals, HUF Individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) and Artificial Jurisdictional Person: Net Income Range Income
CS EXECUTIVE TAX LAWS & PRACTICE CA SACHIN GUPTA
 CS EXECUTIVE TAX LAWS & PRACTICE CA SACHIN GUPTA INDEX S.NO. CHAPTER NAME PAGE NO. 1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF INCOME TAX 1 26 2. RESIDENTIAL STATUS 27 47 3. INCOME UNDER HEAD HOUSE PROPERTY 48 75 4. UNDER HEAD
CS EXECUTIVE TAX LAWS & PRACTICE CA SACHIN GUPTA INDEX S.NO. CHAPTER NAME PAGE NO. 1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF INCOME TAX 1 26 2. RESIDENTIAL STATUS 27 47 3. INCOME UNDER HEAD HOUSE PROPERTY 48 75 4. UNDER HEAD
Most Important Question of INCOME TAX
 Most Important Question of INCOME TAX Residential Status 1. In 2 nd additional condition, assessee should have stayed in India for: a) more than 730 days during 7 immediately preceding previous year b)
Most Important Question of INCOME TAX Residential Status 1. In 2 nd additional condition, assessee should have stayed in India for: a) more than 730 days during 7 immediately preceding previous year b)
Jagannath Institute of Management Sciences Lajpat Nagar. BBA Sem V Income Tax
 Jagannath Institute of Management Sciences Lajpat Nagar BBA Sem V Income Tax UNIT- 1 Introduction and Important Definitions Introduction Basic concepts of Income Tax Act Income [Section 2(24)] Capital
Jagannath Institute of Management Sciences Lajpat Nagar BBA Sem V Income Tax UNIT- 1 Introduction and Important Definitions Introduction Basic concepts of Income Tax Act Income [Section 2(24)] Capital
Income-tax and Death are the only two inevitable things in life In India, taxes were levied even in ancient times refer to Manu Smriti & Arthashastra
 Income-tax and Death are the only two inevitable things in life In India, taxes were levied even in ancient times refer to Manu Smriti & Arthashastra Why to Pay Tax? It was only for the good of his subjects
Income-tax and Death are the only two inevitable things in life In India, taxes were levied even in ancient times refer to Manu Smriti & Arthashastra Why to Pay Tax? It was only for the good of his subjects
The determination of the residential status of a person is very significant in order to find out his tax liability
 RESIDENTIAL STATUS The determination of the residential status of a person is very significant in order to find out his tax liability whether an income, accrued to an individual outside india, is taxable
RESIDENTIAL STATUS The determination of the residential status of a person is very significant in order to find out his tax liability whether an income, accrued to an individual outside india, is taxable
1 Introduction and Important Definitions
 Star Rating On the basis of Maximum marks from a chapter On the basis of Questions included every year from a chapter On the basis of Compulsory questions from a chapter Nil j Nil 1 Introduction and Important
Star Rating On the basis of Maximum marks from a chapter On the basis of Questions included every year from a chapter On the basis of Compulsory questions from a chapter Nil j Nil 1 Introduction and Important
UNDERSTANDING-- TAXATION SYSTEM
 UNDERSTANDING-- TAXATION SYSTEM TO UNDERSTAND TAXATION SYSTEM IN TOTALITY ONE HAS TO UNDERSTAND ALL OF THE FOLLOWING The Core 1 3 5 8 7 1. Act 2. Rules 3. Notifications 4. Circulars The outer effects affecting
UNDERSTANDING-- TAXATION SYSTEM TO UNDERSTAND TAXATION SYSTEM IN TOTALITY ONE HAS TO UNDERSTAND ALL OF THE FOLLOWING The Core 1 3 5 8 7 1. Act 2. Rules 3. Notifications 4. Circulars The outer effects affecting
Free of Cost ISBN: CS Executive Programme Module-I (Solution upto June & Questions of Dec Included)
 Free of Cost ISBN: 978-93-5034-584-9 Appendix CS Executive Programme Module-I (Solution upto June - 2013 & Questions of Dec - 2013 Included) Paper - 3: Tax Laws Chapter - 3: Basis of Charge and Scope of
Free of Cost ISBN: 978-93-5034-584-9 Appendix CS Executive Programme Module-I (Solution upto June - 2013 & Questions of Dec - 2013 Included) Paper - 3: Tax Laws Chapter - 3: Basis of Charge and Scope of
MOCK TEST SOLUTION A.Y Total No. of Question 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages 20 Time Allowed 3 Hours Maximum Marks 100 MKG
![MOCK TEST SOLUTION A.Y Total No. of Question 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages 20 Time Allowed 3 Hours Maximum Marks 100 MKG MOCK TEST SOLUTION A.Y Total No. of Question 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages 20 Time Allowed 3 Hours Maximum Marks 100 MKG](/thumbs/73/68647623.jpg) MOCK TEST SOLUTION IPC (Intermediate) (Computation of Total Income And Tax Liability, Taxability of Gift, Advance Payment of Tax, Residential Status & Scope of Total Income, House Property, Agricultural
MOCK TEST SOLUTION IPC (Intermediate) (Computation of Total Income And Tax Liability, Taxability of Gift, Advance Payment of Tax, Residential Status & Scope of Total Income, House Property, Agricultural
CMA VIPUL SHAH DIRECT TAX JUNE/DEC - 17 AMENDMENTS FIN. ACT 2016 INDEX
 INDEX SR NO CHAPTER NAME PAGE NO 1 Basic Concepts 2 2 Residential Status 4 3 Income Exempt From Tax 8 4 Income From Salary 12 5 Income From House Property 13 6 Income From Business Or Profession 14 7 Capital
INDEX SR NO CHAPTER NAME PAGE NO 1 Basic Concepts 2 2 Residential Status 4 3 Income Exempt From Tax 8 4 Income From Salary 12 5 Income From House Property 13 6 Income From Business Or Profession 14 7 Capital
Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate)
 Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate) By CA Mahavir Jain B.Com.; DISA; FCA Partner : JMT & Associates Email: jmtca301@gmail.com Issues in Taxation of Non-Corporate Income is a very vast subject.
Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate) By CA Mahavir Jain B.Com.; DISA; FCA Partner : JMT & Associates Email: jmtca301@gmail.com Issues in Taxation of Non-Corporate Income is a very vast subject.
DEDUCTION, COLLECTION AND RECOVERY OF TAX
 DEDUCTION, COLLECTION AND RECOVERY OF TAX Section Particulars 190 different modes of payment of tax: tds, tcs, advance tax, tax u/s 192(1A) 191 failure to deduct tax, and direct payment of tax 192 tds
DEDUCTION, COLLECTION AND RECOVERY OF TAX Section Particulars 190 different modes of payment of tax: tds, tcs, advance tax, tax u/s 192(1A) 191 failure to deduct tax, and direct payment of tax 192 tds
IGP-CS Basic Concept M.Test 1 CA Vivek Gaba
 IGP-CS Basic Concept M.Test 1 CA Vivek Gaba 1. Power to impose income tax on agriculture income is with a) Central government b) State government c) Partly with central government and partly with state
IGP-CS Basic Concept M.Test 1 CA Vivek Gaba 1. Power to impose income tax on agriculture income is with a) Central government b) State government c) Partly with central government and partly with state
UCM 54 INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE - I Unit-1 Introduction to Income Tax Act 1961 Type:20% Theory 80% Problem Question & Answers
 UCM 54 INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE - I Unit-1 Introduction to Income Tax Act 1961 Type:20% Theory 80% Problem Question & Answers PART A 1. What is assessment year? (April 2014, 2013, 2012) ASSESSMENT YEAR
UCM 54 INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE - I Unit-1 Introduction to Income Tax Act 1961 Type:20% Theory 80% Problem Question & Answers PART A 1. What is assessment year? (April 2014, 2013, 2012) ASSESSMENT YEAR
J.M.PATEL COLLEGE OF COMMERCE 1
 UNDERSTANDING-- TAXATION SYSTEM TO UNDERSTAND TAXATION SYSTEM IN TOTALITY ONE HAS TO UNDERSTAND ALL OF THE FOLLOWING The Core 1 Taxation 2 3 5 4 6 8 7 1. Act 2. Rules 3. Notifications 4. Circulars The
UNDERSTANDING-- TAXATION SYSTEM TO UNDERSTAND TAXATION SYSTEM IN TOTALITY ONE HAS TO UNDERSTAND ALL OF THE FOLLOWING The Core 1 Taxation 2 3 5 4 6 8 7 1. Act 2. Rules 3. Notifications 4. Circulars The
CHAPTER 8: RECOVERY OF TAX TAX DEDUCTED AT SOURCE
 CHAPTER 8: RECOVERY OF TAX TAX DEDUCTED AT SOURCE SECTIONS RATE PARTICULARS 192: Deduction of Tax on Slab Every Employer has a liability to deduct TDS on salary on monthly basis on tax from salary Rate
CHAPTER 8: RECOVERY OF TAX TAX DEDUCTED AT SOURCE SECTIONS RATE PARTICULARS 192: Deduction of Tax on Slab Every Employer has a liability to deduct TDS on salary on monthly basis on tax from salary Rate
(A) received from the Government in pursuance of an agreement made by the non-resident/ foreign company with the Government, or
 Section 115A - 10% on Royalty and FTS Where the total income of a foreign company or a non-resident includes any income by way of royalty or fees for technical services other than the income referred to
Section 115A - 10% on Royalty and FTS Where the total income of a foreign company or a non-resident includes any income by way of royalty or fees for technical services other than the income referred to
Chapter 1 : Income Tax Concept and Computation of Income Tax
 Chapter 1 : Income Tax Concept and Computation of Income Tax This Chapter includes : I. Taxation in India 1. Taxes and its levying authority 2. Tax Structure 3. Hierarchy of Taxes levied and collected
Chapter 1 : Income Tax Concept and Computation of Income Tax This Chapter includes : I. Taxation in India 1. Taxes and its levying authority 2. Tax Structure 3. Hierarchy of Taxes levied and collected
DEDUCTION OF TAX AT SOURCE
 DEDUCTION OF TAX AT SOURCE SECTION 190 TO 206AA Section 190 Deduction at source and advance payment Section 191 Direct payment Section 192 Deduction of tax from salary income Section 193 Deduction of tax
DEDUCTION OF TAX AT SOURCE SECTION 190 TO 206AA Section 190 Deduction at source and advance payment Section 191 Direct payment Section 192 Deduction of tax from salary income Section 193 Deduction of tax
SAMVIT ACADEMY IPCC MOCK EXAM
 Disclaimer (Read carefully) SUGGESTED ANSWERS - Group 1 Taxation (Code GST) The answers given below are prepared by the faculty of Samvit Academy as per their views and experience. The working notes, notes
Disclaimer (Read carefully) SUGGESTED ANSWERS - Group 1 Taxation (Code GST) The answers given below are prepared by the faculty of Samvit Academy as per their views and experience. The working notes, notes
Basic Concept. Rates of Income Tax for assessment year
 Page 1 Amendment CA.SAGAR REGMI Basic Concept Rates of Income Tax for assessment year 2016-17 A. Individual 1. In case of individual being resident of India of the age of 60 years or more but less than
Page 1 Amendment CA.SAGAR REGMI Basic Concept Rates of Income Tax for assessment year 2016-17 A. Individual 1. In case of individual being resident of India of the age of 60 years or more but less than
INTRODUCTION OF TAX PLANNING
 INTRODUCTION OF TAX PLANNING UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF THE CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Meaning of Planning 1.3 Meaning of Management 1.4 Meaning of Evasion 1.5 Meaning of Avoidance 1.6 Basics 1.7 Summary 1.8
INTRODUCTION OF TAX PLANNING UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF THE CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Meaning of Planning 1.3 Meaning of Management 1.4 Meaning of Evasion 1.5 Meaning of Avoidance 1.6 Basics 1.7 Summary 1.8
BATCH : GI 1 to GI 5
 (0.5 6=3M) MITTAL COMMERCE CLASSES BATCH : GI 1 to GI 5 DATE: 18.08.2017 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 TIMING: 3 Hours PAPER 4 : TAXATION Question No. 1 is Compulsory Answer any five questions from the remaining
(0.5 6=3M) MITTAL COMMERCE CLASSES BATCH : GI 1 to GI 5 DATE: 18.08.2017 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 TIMING: 3 Hours PAPER 4 : TAXATION Question No. 1 is Compulsory Answer any five questions from the remaining
A BUDGET FOR A Y From the desk of - B.L. Tulsian Advocate. R. Tulsian & Co LLP Chartered Accountants.
 A BUDGET A N A L Y S I S FOR A Y 2020-21 From the desk of - B.L. Tulsian Advocate R. Tulsian & Co LLP Chartered Accountants www.rtulsian.com Page2 Contents Amendment of Section 16... 3 Amendment to Section
A BUDGET A N A L Y S I S FOR A Y 2020-21 From the desk of - B.L. Tulsian Advocate R. Tulsian & Co LLP Chartered Accountants www.rtulsian.com Page2 Contents Amendment of Section 16... 3 Amendment to Section
2 (a) Municipal taxes paid by Mr. Hari `4,200 per annum (b) House insurance `1,000 (iii) He earned `1,00,000 in share speculation business and lost `1
 NEW COURSE INCOME TAX PAPER SECTION-A Marks: 60 Question No. 1 is compulsory. Candidates are also required to answer any Five questions from the remaining Six questions. In case, any candidate answers
NEW COURSE INCOME TAX PAPER SECTION-A Marks: 60 Question No. 1 is compulsory. Candidates are also required to answer any Five questions from the remaining Six questions. In case, any candidate answers
Paper 7 Direct Taxation
 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 Hours Full Marks: 100
Paper 7 Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 Hours Full Marks: 100
Income from Other Sources
 Income from Other Sources SECTION 56: INCOME FROM OTHER SOURCES CHARGING SECTION Income from other sources is a residuary head of income i.e. income not chargeable under any other head, and which is not
Income from Other Sources SECTION 56: INCOME FROM OTHER SOURCES CHARGING SECTION Income from other sources is a residuary head of income i.e. income not chargeable under any other head, and which is not
Marking Scheme. Session TAXATION (782) CLASS XII. Total marks: 100 Theory: 60 Marks Practical: 40 Marks. 1 Deduction From Gross Total Income
 Marking Scheme Session 2018-19 TAXATION (782) CLASS XII Total marks: 100 Theory: 60 Marks Practical: 40 Marks UNITS UNIT NAME TOTAL 1 Deduction From Gross Total Income 2 Computation Of Ta x Liability Of
Marking Scheme Session 2018-19 TAXATION (782) CLASS XII Total marks: 100 Theory: 60 Marks Practical: 40 Marks UNITS UNIT NAME TOTAL 1 Deduction From Gross Total Income 2 Computation Of Ta x Liability Of
Residential Status, Scope Of Total Income Under Income Tax, and Foreign Tax Credit
 1 KARTHIK RANGANATHAN ASSOCIATES Residential Status, Scope Of Total Income Under Income Tax, and Foreign Tax Credit Seminar on NRI Taxation ICAI SIRC, Chennai April 29, 2017 Karthik Ranganathan Tax and
1 KARTHIK RANGANATHAN ASSOCIATES Residential Status, Scope Of Total Income Under Income Tax, and Foreign Tax Credit Seminar on NRI Taxation ICAI SIRC, Chennai April 29, 2017 Karthik Ranganathan Tax and
IPCC DIRECT TAX AMEDNMENTS FOR MAY/JUNE 2017
 AY 17-18 IPCC DIRECT TAX AMEDNMENTS FOR MAY/JUNE 2017 www.vipulshah.org By CMA Vipul V. Shah AY 17-18 CHAPTER 1 BASIC CONCEPTS EXEMPTION OF CENTRAL GOVERNMENT SUBSIDY OR GRANT OR CASH ASSISTANCE, ETC.
AY 17-18 IPCC DIRECT TAX AMEDNMENTS FOR MAY/JUNE 2017 www.vipulshah.org By CMA Vipul V. Shah AY 17-18 CHAPTER 1 BASIC CONCEPTS EXEMPTION OF CENTRAL GOVERNMENT SUBSIDY OR GRANT OR CASH ASSISTANCE, ETC.
Foreign Collaboration
 CHAPTER 17 Foreign Collaboration Some Key Points (a) The tax liability of a foreign collaborator and the Indian counter part is dependent on their residential status and the applicable provisions of DTAA,
CHAPTER 17 Foreign Collaboration Some Key Points (a) The tax liability of a foreign collaborator and the Indian counter part is dependent on their residential status and the applicable provisions of DTAA,
Incomes Which Do Not Form Part of Total Income
 3 Incomes Which Do Not Form Part of Total Income Section Key Points Particulars 10(1) Agricultural income is exempt under section 10(1). However, agricultural income has to be aggregated with non-agricultural
3 Incomes Which Do Not Form Part of Total Income Section Key Points Particulars 10(1) Agricultural income is exempt under section 10(1). However, agricultural income has to be aggregated with non-agricultural
Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX
 Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX HOW TO COMPUTE TAX PAYABLE Once the net taxable income is computed, the next step is to compute the final tax payable. The final tax payable is computed as follows: (1) Taxable
Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX HOW TO COMPUTE TAX PAYABLE Once the net taxable income is computed, the next step is to compute the final tax payable. The final tax payable is computed as follows: (1) Taxable
1.1 Overview of income-tax law in India
 1 Basic Concepts 1.1 Overview of income-tax law in India Income-tax is a tax levied on the total income of the previous year of every person. A person includes an individual, Hindu Undivided Family (HUF),
1 Basic Concepts 1.1 Overview of income-tax law in India Income-tax is a tax levied on the total income of the previous year of every person. A person includes an individual, Hindu Undivided Family (HUF),
Budget 2017 Synopsis Part II Analysis of Rupiya
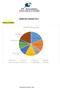 Budget 2017 Synopsis Part II Analysis of Rupiya Facts & Findings: Out of 125 crore Indians only 15% ie 19 crore pay income tax % of Taxpayers (Out of 19 Crore) % Contribution To Tax Revenue 01% 26% 1%
Budget 2017 Synopsis Part II Analysis of Rupiya Facts & Findings: Out of 125 crore Indians only 15% ie 19 crore pay income tax % of Taxpayers (Out of 19 Crore) % Contribution To Tax Revenue 01% 26% 1%
Rates of Taxes. Rates for deduction of Income
 CA Mohan S. Phadke Rates of Taxes I. Rates of Income Tax in respect of income liable to tax for the assessment year 2013-14 a) In respect of income of all categories of assessees liable to tax for the
CA Mohan S. Phadke Rates of Taxes I. Rates of Income Tax in respect of income liable to tax for the assessment year 2013-14 a) In respect of income of all categories of assessees liable to tax for the
Question 1. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 Question 1 PAPER 5 : TAXATION Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. Wherever necessary suitable assumptions may be made by the candidates. Answer the following with reasons
Question 1 PAPER 5 : TAXATION Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. Wherever necessary suitable assumptions may be made by the candidates. Answer the following with reasons
Budget Presented For: Klaus Vogel Group Presented By: Mr. Kuntal Dave Date: March 8, 2013
 Budget 2013 Presented For: Klaus Vogel Group Presented By: Mr. Kuntal Dave Date: March 8, 2013 Index Direct Tax Proposals Implications of amendments proposed in the Finance Bill, 2013 2 Direct Tax Proposals
Budget 2013 Presented For: Klaus Vogel Group Presented By: Mr. Kuntal Dave Date: March 8, 2013 Index Direct Tax Proposals Implications of amendments proposed in the Finance Bill, 2013 2 Direct Tax Proposals
INCOME-TAX AND BASED ON FINANCE ACT, FINANCE ACT, 2007 WITH NOTES 49 I.T. NOTES 69 I.T. NOTES 97 I.T. NOTES I.T. NOTES 139 I.T.
 EHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR VG.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA
EHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR VG.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA
Assessment Year
 Assessment Year 2016-2017 Income Income Income Income Income From Salaries from Capital Gains from Business and Profession from House Property from Other Sources Individual/HUF Firm Company Trust AOP/BOI/Co-op
Assessment Year 2016-2017 Income Income Income Income Income From Salaries from Capital Gains from Business and Profession from House Property from Other Sources Individual/HUF Firm Company Trust AOP/BOI/Co-op
TDS under section 195 of the Income-tax Act. CA Vishal Palwe 16 December 2017 Seminar on International Taxation at WIRC
 TDS under section 195 of the Income-tax Act CA Vishal Palwe 16 December 2017 Seminar on International Taxation at WIRC Overview of section 195 Overview of section 195 195(1) Any person paying to non-resident
TDS under section 195 of the Income-tax Act CA Vishal Palwe 16 December 2017 Seminar on International Taxation at WIRC Overview of section 195 Overview of section 195 195(1) Any person paying to non-resident
Tax is imposition financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or other the functional equivalent of the state.
 1. What is Tax What is Tax? Tax is imposition financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or other the functional equivalent of the state. How many Types of Taxes are there and what are they?
1. What is Tax What is Tax? Tax is imposition financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or other the functional equivalent of the state. How many Types of Taxes are there and what are they?
8 Income from other Sources
 8 Income from other Sources 8.1 Introduction Any income, profits or gains includible in the total income of an assessee, which cannot be included under any of the preceding heads of income, is chargeable
8 Income from other Sources 8.1 Introduction Any income, profits or gains includible in the total income of an assessee, which cannot be included under any of the preceding heads of income, is chargeable
2.f List of benefits available to Small Businessmen [AY ] S.N. Particulars Section Benefits/Deductions allowed
![2.f List of benefits available to Small Businessmen [AY ] S.N. Particulars Section Benefits/Deductions allowed 2.f List of benefits available to Small Businessmen [AY ] S.N. Particulars Section Benefits/Deductions allowed](/thumbs/84/90875315.jpg) 2.f List of benefits available to Small Businessmen [AY 2017 18] S.N. Particulars Section Benefits/Deductions allowed A. Presumptive Taxation Scheme 1. Computation of income from eligible business on presumptive
2.f List of benefits available to Small Businessmen [AY 2017 18] S.N. Particulars Section Benefits/Deductions allowed A. Presumptive Taxation Scheme 1. Computation of income from eligible business on presumptive
FOREIGN COLLABORATION AND DOUBLE TAXATION RELIEF
 FOREIGN COLLABORATION AND DOUBLE TAXATION RELIEF STRUCTURE OF THE CHAPTER UNIT 7 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Agreement with foreign countries or specified territories [Sec. 90] 7.3 Adoption by Central Government
FOREIGN COLLABORATION AND DOUBLE TAXATION RELIEF STRUCTURE OF THE CHAPTER UNIT 7 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Agreement with foreign countries or specified territories [Sec. 90] 7.3 Adoption by Central Government
Paper 7- Direct Taxation
 Paper 7- Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7- Direct Taxation Full Marks: 100 Time Allowed: 3 hours
Paper 7- Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7- Direct Taxation Full Marks: 100 Time Allowed: 3 hours
SYLLABUS. B.Com V SEM (Tax) Subject Income Tax Law And Practice
 SYLLABUS B.Com V SEM (Tax) Subject Income Tax Law And Practice UNIT-I Unit-II Unit-III Unit-IV Unit-V General introduction of Indian income tax act, 1961. Basic concepts: income, agriculture income, casual
SYLLABUS B.Com V SEM (Tax) Subject Income Tax Law And Practice UNIT-I Unit-II Unit-III Unit-IV Unit-V General introduction of Indian income tax act, 1961. Basic concepts: income, agriculture income, casual
Income Tax Slabs & Rates for Assessment Year
 Individual resident aged below 60 years (i.e. born on or after 1st April 1956) or any NRI/ HUF/ AOP/ BOI/ AJP* Income Tax i. Where the taxable income does not exceed Rs. 2,50,000/-. NIL ii. Where the taxable
Individual resident aged below 60 years (i.e. born on or after 1st April 1956) or any NRI/ HUF/ AOP/ BOI/ AJP* Income Tax i. Where the taxable income does not exceed Rs. 2,50,000/-. NIL ii. Where the taxable
6. PROFITS AND GAINS OF BUSINESS OR PROFESSION 2
 Ph: 98851 25025/26 www.mastermindsindia.com 6. PROFITS AND GAINS OF BUSINESS OR PROFESSION 2 SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS Problem No. 1 Computing business income for A.Y.2015-16 is as follows Amount
Ph: 98851 25025/26 www.mastermindsindia.com 6. PROFITS AND GAINS OF BUSINESS OR PROFESSION 2 SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS Problem No. 1 Computing business income for A.Y.2015-16 is as follows Amount
For J B Nagar Study Circle Meeting
 For J B Nagar Study Circle Meeting Nature of income Individual and HUF ITR 1* (Sahaj) ITR 2 ITR 3 ITR 4 Income from salary/pension (for ordinarily resident person) Income from salary/pension (for not ordinarily
For J B Nagar Study Circle Meeting Nature of income Individual and HUF ITR 1* (Sahaj) ITR 2 ITR 3 ITR 4 Income from salary/pension (for ordinarily resident person) Income from salary/pension (for not ordinarily
Amendment of Direct Tax Dhruv Coaching Classes Pvt. Ltd. CMA Akshay Sen Direct Tax
 1 Direct Tax (AMENDMENTS) Finance Act, 2017 For CMA Inter & Final (June-18 & Dec-18 Exam.) By CMA AKSHAY SEN Dhruv Coaching Classes Pvt. Ltd. A1-A2,opposite Saras Dairy,Janta Store, Jaipur E-mail-dhruvcoachingclasses@gmail.com
1 Direct Tax (AMENDMENTS) Finance Act, 2017 For CMA Inter & Final (June-18 & Dec-18 Exam.) By CMA AKSHAY SEN Dhruv Coaching Classes Pvt. Ltd. A1-A2,opposite Saras Dairy,Janta Store, Jaipur E-mail-dhruvcoachingclasses@gmail.com
SUGGESTED SOLUTION CA FINAL MAY 2017 EXAM
 SUGGESTED SOLUTION CA FINAL MAY 2017 EXAM DIRECT TAX LAWS Test Code - F M J 4 0 1 3 Head Office : Shraddha, 3 rd Floor, Near Chinai College, Andheri (E), Mumbai 69. Tel : (022) 26836666 1 P a g e Answer-1
SUGGESTED SOLUTION CA FINAL MAY 2017 EXAM DIRECT TAX LAWS Test Code - F M J 4 0 1 3 Head Office : Shraddha, 3 rd Floor, Near Chinai College, Andheri (E), Mumbai 69. Tel : (022) 26836666 1 P a g e Answer-1
APPLICABILITY OF SERVICE TAX:
 SERVICE TAX It is an indirect tax. Service tax is a tax on services provided.the provisions of service tax are contained in chapter V of the Finance Act, 1994 and administered by the Central Excise Department.
SERVICE TAX It is an indirect tax. Service tax is a tax on services provided.the provisions of service tax are contained in chapter V of the Finance Act, 1994 and administered by the Central Excise Department.
DIRECT TAX Every bit and piece of my work is dedicated to every sleepless night my mother has spent for me
 Part A DIRECT TAX Every bit and piece of my work is dedicated to every sleepless night my mother has spent for me INDEX of Income Tax Amendments by FA, 2016 Chapter 1: Basic Concepts Particulars Rates
Part A DIRECT TAX Every bit and piece of my work is dedicated to every sleepless night my mother has spent for me INDEX of Income Tax Amendments by FA, 2016 Chapter 1: Basic Concepts Particulars Rates
Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011
 Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011 RATES OF INCOME-TAX FOR THE ASSESSMENT YEAR 2012-13 o Tax slab rates have been changed for individuals and HUF, which is given by way of a
Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011 RATES OF INCOME-TAX FOR THE ASSESSMENT YEAR 2012-13 o Tax slab rates have been changed for individuals and HUF, which is given by way of a
Bombay Chartered Accountants Society
 Bombay Chartered Accountants Society Filing of Income Tax Returns for the Assessment Year -09 09 by C.A. Contractor, Nayak & Kishnadwala Return of Income What is Return of Income? Return of Income now
Bombay Chartered Accountants Society Filing of Income Tax Returns for the Assessment Year -09 09 by C.A. Contractor, Nayak & Kishnadwala Return of Income What is Return of Income? Return of Income now
FINAL CA May 2018 DIRECT TAXATION
 FINAL CA May 2018 DIRECT TAXATION Test Code F 90 Branch: MULTIPLE Date: (50 Marks) compulsory. Note: All questions are Question 1 (10 marks) Computation of Book Profit for levy of MAT under section 115JB
FINAL CA May 2018 DIRECT TAXATION Test Code F 90 Branch: MULTIPLE Date: (50 Marks) compulsory. Note: All questions are Question 1 (10 marks) Computation of Book Profit for levy of MAT under section 115JB
Circular The Schedule of dates for filing income-tax returns is given below:
 Circular-2012 To, July 14, 2012 Dear Sir(s)/Madam, Sub: Income-tax, Wealth-tax, Service-tax and TDS returns for Assessment Year 2012-13 and payment of advance-tax for Assessment Year 2013-14 -------------------------------------------------------
Circular-2012 To, July 14, 2012 Dear Sir(s)/Madam, Sub: Income-tax, Wealth-tax, Service-tax and TDS returns for Assessment Year 2012-13 and payment of advance-tax for Assessment Year 2013-14 -------------------------------------------------------
R-2. Amendments at a glance
 R-2 Amendments at a glance Effected by the Finance ACT, 2018 $ Tax rates 0.11 Tax rates for the assessment years 2018-19 and 2019-20 are given in Referencer 1. 0.11-1 Income-tax - The following are the
R-2 Amendments at a glance Effected by the Finance ACT, 2018 $ Tax rates 0.11 Tax rates for the assessment years 2018-19 and 2019-20 are given in Referencer 1. 0.11-1 Income-tax - The following are the
(ALL BATCHES) DATE: MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 TIMING: 3¼Hours. PAPER 2 : Taxation
 (ALL BATCHES) DATE: 02.08.2018 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 TIMING: 3¼Hours PAPER 2 : Taxation SECTION - A Answer:1 (a) Computation of total income and tax liability of Dr. Niranjana for A.Y. 2018-19 I Income from
(ALL BATCHES) DATE: 02.08.2018 MAXIMUM MARKS: 100 TIMING: 3¼Hours PAPER 2 : Taxation SECTION - A Answer:1 (a) Computation of total income and tax liability of Dr. Niranjana for A.Y. 2018-19 I Income from
Lesson 1 DEFINITIONS. Previous Year [Section 3]
![Lesson 1 DEFINITIONS. Previous Year [Section 3] Lesson 1 DEFINITIONS. Previous Year [Section 3]](/thumbs/90/102179790.jpg) Lesson 1 DEFINITIONS Assessment Year [Section 2(9)] 1. Assessment year means the period of twelve months commencing on the first day of April every year and ending on 31 st March of next year. (For June
Lesson 1 DEFINITIONS Assessment Year [Section 2(9)] 1. Assessment year means the period of twelve months commencing on the first day of April every year and ending on 31 st March of next year. (For June
Interim Union Budget 2019 & Important changes for AY CA. PRAMOD JAIN B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA, IP
 Interim Union Budget 2019 & Important changes for AY 2019-20 CA. PRAMOD JAIN B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA, IP Shared at Nehru Place CPE Study Circle of NIRC of ICAI 7 th February 2019 INCOME
Interim Union Budget 2019 & Important changes for AY 2019-20 CA. PRAMOD JAIN B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA, IP Shared at Nehru Place CPE Study Circle of NIRC of ICAI 7 th February 2019 INCOME
Income Tax Reckoner AY:
 1. Rates of Income Tax Individuals having income > 5 Lacs* Individuals & Charitable Trust Senior Citizen (60 to 79) Very Senior citizen (80 and above) Rates Up to ` 2.00 Lacs Up to ` 2.50 Lacs Up to `
1. Rates of Income Tax Individuals having income > 5 Lacs* Individuals & Charitable Trust Senior Citizen (60 to 79) Very Senior citizen (80 and above) Rates Up to ` 2.00 Lacs Up to ` 2.50 Lacs Up to `
Budget Highlights
 Budget Highlights 2018-19 DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS Chartered Accountants 1 st Floor, Sapphire Business Centre, Above SBI Vadaj Branch, Usmanpura, Ashram Road, Ahmedabad-380013 Email: apcca@apcca.com Website:
Budget Highlights 2018-19 DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS Chartered Accountants 1 st Floor, Sapphire Business Centre, Above SBI Vadaj Branch, Usmanpura, Ashram Road, Ahmedabad-380013 Email: apcca@apcca.com Website:
Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals
 RATES OF INCOME TAX Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals Basic exemption limit has been increased from Rs 2 lacs to Rs 2.50 lacs for resident individuals or HUF. Income slabs Income
RATES OF INCOME TAX Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals Basic exemption limit has been increased from Rs 2 lacs to Rs 2.50 lacs for resident individuals or HUF. Income slabs Income
Contents. Finance Act, Increase in standard deduction of salaried taxpayers
 Contents Amendments made by Finance Act, 2019 at a Glance I-13 1 Finance Act, 2019 1.1 Highlights of amendments made to income-tax provisions 1 1.2 Relief to small taxpayers 1 1.3 Standard deductions raised
Contents Amendments made by Finance Act, 2019 at a Glance I-13 1 Finance Act, 2019 1.1 Highlights of amendments made to income-tax provisions 1 1.2 Relief to small taxpayers 1 1.3 Standard deductions raised
CA Final Paper 7 Direct Tax Laws Ch13 Unit1 CA Sudhindra Kumar Jain
 CA Final Paper 7 Direct Tax Laws Ch13 Unit1 CA Sudhindra Kumar Jain 2 Definition Section 2(17) In Which Public Are Substantially Interested Section 2(18) Indian Company Section 2(26) Domestic Company Section
CA Final Paper 7 Direct Tax Laws Ch13 Unit1 CA Sudhindra Kumar Jain 2 Definition Section 2(17) In Which Public Are Substantially Interested Section 2(18) Indian Company Section 2(26) Domestic Company Section
MAJOR Income Tax Proposals in UNION BUDGET 2017
 MAJOR Income Tax Proposals in UNION BUDGET 2017 LUNAWAT & CO. Chartered Accountants 3 rd February 2017, Nehru Place CA. PRAMOD JAIN FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA THE CRUX TIMELY FILING OF RETURNS No
MAJOR Income Tax Proposals in UNION BUDGET 2017 LUNAWAT & CO. Chartered Accountants 3 rd February 2017, Nehru Place CA. PRAMOD JAIN FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA THE CRUX TIMELY FILING OF RETURNS No
AMENDMENTS MADE BY FINANCE ACT, RELEVANT FOR MAY 2015/NOV 2015 EXAM
 AMENDMENTS MADE BY FINANCE ACT, 2014- RELEVANT FOR MAY 2015/NOV 2015 EXAM FEW AMENDMENTS RELATING TO CAPITAL GAINS 1. SECTION 2(14)-EFFECTIVE FROM A.Y. 2015-16 Income arising from transfer of security
AMENDMENTS MADE BY FINANCE ACT, 2014- RELEVANT FOR MAY 2015/NOV 2015 EXAM FEW AMENDMENTS RELATING TO CAPITAL GAINS 1. SECTION 2(14)-EFFECTIVE FROM A.Y. 2015-16 Income arising from transfer of security
Taxation of Expatriates Issues which can be considered for taxation of Expatriates: - Residential Status. - Taxation of salary, perquisites, amenities
 SIRC of ICAI Tirupur Branch Taxation of Expatriates 9 th February, 2008 Naresh Ajwani Partner Rashmin Sanghvi & Associates Chartered Accountants Taxation of Expatriates Issues which can be considered for
SIRC of ICAI Tirupur Branch Taxation of Expatriates 9 th February, 2008 Naresh Ajwani Partner Rashmin Sanghvi & Associates Chartered Accountants Taxation of Expatriates Issues which can be considered for
Chapter 8 Income under the Head "Income from Other Sources"
 Chapter 8 Income under the Head "Income from Other Sources" 1. Basis of Charge Section 56(1) Income of every kind which is not exempt shall be chargeable to income-tax under the head "Income from Other
Chapter 8 Income under the Head "Income from Other Sources" 1. Basis of Charge Section 56(1) Income of every kind which is not exempt shall be chargeable to income-tax under the head "Income from Other
ARTICLE. On Finance Bill (Budget) Proposals 2013 Income Tax Act, 1961 By CA. SATISH AGARWAL
 ARTICLE On Finance Bill (Budget) Proposals 0 Income Tax Act, 96 By CA. SATISH AGARWAL Mobile : +99808957 Phone : +95769 Office : 9/4, East Patel Nagar, (Near Jaypee Sidharthe Hotel) New Delhi - 0008 :
ARTICLE On Finance Bill (Budget) Proposals 0 Income Tax Act, 96 By CA. SATISH AGARWAL Mobile : +99808957 Phone : +95769 Office : 9/4, East Patel Nagar, (Near Jaypee Sidharthe Hotel) New Delhi - 0008 :
T.D.S/T.C.S AT GLANCE FOR A.Y
 T.D.S/T.C.S AT GLANCE FOR A.Y. 2012-2013 Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) was introduced to facilitate the payment of Tax while receiving the income and it follows the concept Pay as you Earn. The tax deducted
T.D.S/T.C.S AT GLANCE FOR A.Y. 2012-2013 Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) was introduced to facilitate the payment of Tax while receiving the income and it follows the concept Pay as you Earn. The tax deducted
Elective Course in Commerce ECO-11 Elements of Income Tax APPENDIX 2014 Assessment Year
 Elective Course in Commerce ECO-11 Elements of Income Tax APPENDIX 2014 Assessment Year 2013-2014 School of Management Studies Indira Gandhi National Open University New Delhi 110068 Dear Student, As you
Elective Course in Commerce ECO-11 Elements of Income Tax APPENDIX 2014 Assessment Year 2013-2014 School of Management Studies Indira Gandhi National Open University New Delhi 110068 Dear Student, As you
The Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition Tax Act, 2015
 Introductory presentation on The Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition Tax Act, 2015 By CA. Abhishek Nagori abhishek.nagori@jlnus.com +91-94260-75397 Backdrop to the Act Long-standing
Introductory presentation on The Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition Tax Act, 2015 By CA. Abhishek Nagori abhishek.nagori@jlnus.com +91-94260-75397 Backdrop to the Act Long-standing
FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE
 FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE COMPILED BY: CA.ARUN GUPTA ca.arungupta77@gmail.com A. Rates of Taxes: 1. It is proposed to make the following changes in tax rates: In case of Resident
FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE COMPILED BY: CA.ARUN GUPTA ca.arungupta77@gmail.com A. Rates of Taxes: 1. It is proposed to make the following changes in tax rates: In case of Resident
MTP_ Inter _Syllabus 2016_ June 2018_Set 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation (DTX)
 Paper 7 Direct Taxation (DTX) Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 Hours Full Marks:
Paper 7 Direct Taxation (DTX) Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 Hours Full Marks:
IMPORTANT AMENDMENTS OF THE FINANCE ACT, /6/2011 Lecture Meeting of BCAS - C.A.Vipul Gandhi
 IMPORTANT AMENDMENTS OF THE FINANCE ACT,2010 22/6/2011 Lecture Meeting of BCAS - C.A.Vipul Gandhi 1 TAX RATES AND SLABS OF INCOME TAX RATES FOR INDIVIDUAL,HUF,AOP & BOI, ARTIFICIAL JUDICIAL PERSON U/S
IMPORTANT AMENDMENTS OF THE FINANCE ACT,2010 22/6/2011 Lecture Meeting of BCAS - C.A.Vipul Gandhi 1 TAX RATES AND SLABS OF INCOME TAX RATES FOR INDIVIDUAL,HUF,AOP & BOI, ARTIFICIAL JUDICIAL PERSON U/S
Total turnover/ Gross receipts 30% 30% of FY > Rs 50 Cr No change in rate of Surcharge
 1. Income Tax Rates: Category of Income New rate of tax Old rate Taxpayer for FY 2017-18 of tax Individuals/ Upto Rs 2.5 L Nil Nil HUF/ BOI/ Rs 2.5 to 5 L 5% 10% AOP/ Rs 5 to 10 L 20% 20% Artificial Above
1. Income Tax Rates: Category of Income New rate of tax Old rate Taxpayer for FY 2017-18 of tax Individuals/ Upto Rs 2.5 L Nil Nil HUF/ BOI/ Rs 2.5 to 5 L 5% 10% AOP/ Rs 5 to 10 L 20% 20% Artificial Above
BVZ5A/BPF5C/BVC5A/ BPG5C INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE I. Unit : I - V. BVZ5A/BPG5C/CYA5C - Income Tax Law & Practice - I
 BVZ5A/BPF5C/BVC5A/ BPG5C INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE I Unit : I - V BVZ5A/BPG5C/CYA5C - Income Tax Law & Practice - I UNIT 1 Meaning & Features of Income Important definitions under Income Tax Act Tax rate
BVZ5A/BPF5C/BVC5A/ BPG5C INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE I Unit : I - V BVZ5A/BPG5C/CYA5C - Income Tax Law & Practice - I UNIT 1 Meaning & Features of Income Important definitions under Income Tax Act Tax rate
Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX
 Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX HOW TO COMPUTE TAX PAYABLE Once the net taxable income is computed, the next step is to compute the final tax payable. The final tax payable is computed as follows: (1) Taxable
Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX HOW TO COMPUTE TAX PAYABLE Once the net taxable income is computed, the next step is to compute the final tax payable. The final tax payable is computed as follows: (1) Taxable
III BCOM (CA) [ ] Semester V Core:INCOME TAX LAW AND PRACTICE 503B Multiple Choice Questions.
![III BCOM (CA) [ ] Semester V Core:INCOME TAX LAW AND PRACTICE 503B Multiple Choice Questions. III BCOM (CA) [ ] Semester V Core:INCOME TAX LAW AND PRACTICE 503B Multiple Choice Questions.](/thumbs/71/65799137.jpg) 1 of 23 8/12/17, 2:57 PM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
1 of 23 8/12/17, 2:57 PM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS. Problem No. 1. Self study. Problem No. 2
 7. CAPITAL GAINS SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS Problem No. 1 Self study Problem No. 2 We know that capital gains arise only when we transfer a capital asset. The liability of capital gains tax in the
7. CAPITAL GAINS SOLUTIONS TO ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS Problem No. 1 Self study Problem No. 2 We know that capital gains arise only when we transfer a capital asset. The liability of capital gains tax in the
FINANCE BILL He has proposed to revise the tax slabs upwards as under:
 FINANCE BILL - 2010 The 2 nd budget of the 2 nd UPA Government for the year 2010 2011 was presented by the finance minister on 26 th February 2010. The finance minister has attempted to balance his direct
FINANCE BILL - 2010 The 2 nd budget of the 2 nd UPA Government for the year 2010 2011 was presented by the finance minister on 26 th February 2010. The finance minister has attempted to balance his direct
3. INCOME FROM SALARIES
 SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS FOR CLASSROOM DISCUSSION PROBLEM NO: 1 3. INCOME FROM SALARIES a) Value of the rent free unfurnished accommodation = 15% of salary for the relevant period = 15% of [( 6000 5) + (
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS FOR CLASSROOM DISCUSSION PROBLEM NO: 1 3. INCOME FROM SALARIES a) Value of the rent free unfurnished accommodation = 15% of salary for the relevant period = 15% of [( 6000 5) + (
CA. PRAMOD JAIN. B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA Shared at Laxmi Nagar CPE Study Circle of NIRC of ICAI 16 th February 2018
 Union Budget 2018 CA. PRAMOD JAIN B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA Shared at Laxmi Nagar CPE Study Circle of NIRC of ICAI 16 th February 2018 INCOME TAX PROPOSALS TAX RATES No change in tax
Union Budget 2018 CA. PRAMOD JAIN B. COM (H), FCA, FCS, FCMA, LL.B, MIMA, DISA Shared at Laxmi Nagar CPE Study Circle of NIRC of ICAI 16 th February 2018 INCOME TAX PROPOSALS TAX RATES No change in tax
INCOMES WHICH DO NOT FORM PART OF TOTAL INCOME
 3 INCOMES WHICH DO NOT FORM PART OF TOTAL INCOME Question 1 Choose the correct answer with reference to the provisions of the Income-tax Act, 1961. (i) For an employee in receipt of hostel expenditure
3 INCOMES WHICH DO NOT FORM PART OF TOTAL INCOME Question 1 Choose the correct answer with reference to the provisions of the Income-tax Act, 1961. (i) For an employee in receipt of hostel expenditure
Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights
 Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights Bansi S. Mehta & Co. All the following amendment are made effective from Assessment Years 2016-17, unless specifically mentioned otherwise. I - Residential Status,
Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights Bansi S. Mehta & Co. All the following amendment are made effective from Assessment Years 2016-17, unless specifically mentioned otherwise. I - Residential Status,
Tax Deduction at Source FY (AY )
 Tax Deduction at Source FY 2017-18 (AY 2018-19) CA Pranjal Joshi M.com, F.C.A., DipIFR (ACCA-UK), Cert. Business Valuation (ICAI) M/s Pranjal Joshi & Co Chartered Accountants TDS introduction - Income
Tax Deduction at Source FY 2017-18 (AY 2018-19) CA Pranjal Joshi M.com, F.C.A., DipIFR (ACCA-UK), Cert. Business Valuation (ICAI) M/s Pranjal Joshi & Co Chartered Accountants TDS introduction - Income
Paper 7 Applied Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 hours Full Marks: 100
 Paper 7 Applied Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 hours Full Marks: 100 All the questions relate to the assessment year 2014-15, unless stated otherwise. Working notes should form part of the answers. Answer
Paper 7 Applied Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 hours Full Marks: 100 All the questions relate to the assessment year 2014-15, unless stated otherwise. Working notes should form part of the answers. Answer
Vinodh & Muthu Chartered Accountants. Newsletter MAY 2016
 Vinodh & Muthu Chartered Accountants Newsletter MAY 2016 2 Dear Readers, Welcome to our newsletter. VMCA brings you the significant developments in taxation during the month of May 2016. We hope this edition
Vinodh & Muthu Chartered Accountants Newsletter MAY 2016 2 Dear Readers, Welcome to our newsletter. VMCA brings you the significant developments in taxation during the month of May 2016. We hope this edition
