EVOLUTION OF INCOME TAX SYSTEM IN INDIA
|
|
|
- Bethanie Lamb
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 3 EVOLUTION OF INCOME TAX SYSTEM IN INDIA 3.1 Income Tax System in India from 1860 to 1939 Income Taxation from 1860 to 1886 In its modem form, the income-tax was introduced in India for the first time in 1860 as a temporary measure to overcome the financial difficulties created by the events of Thus the credit for introducing income-tax in its modem form in India goes to the British. It may be asserted that, like the introduction of the study of English language in Indian Education, the introduction of Income-tax in the Indian financial system is one of the few happy heritages of British rule in this country '. The period from 1860 to 1886 was a period of experiment in which 23 Acts were passed in the field of direct taxation. In the year 1860, tax was levied at 2 percent on income between Rs. 200 and Rs.500 and at 4 percent on incomes above Rs.500. It is significant to note that even at that time the authorities were very careful about exemptions. Persons earning income less than Rs.200 a year from all sources (Including agriculture income) were exempt from tax. All government property was also exempted. Exemption were also granted to cultivators of land, the rent value of which was less than Rs. 600 per annum and to religious and charitable institutions. Thereafter rates were changed from time to time. This Act of 1860 lapsed in Although the income-tax of 1860 was not operated successfully, the procedure concerning levy and collection of tax was continued under different nomenclature thereafter viz. licence tax (introduced in 1867 and abondoned the next year), Certificate tax (introduced in 1868 and abondoned the next year), General Income- Tax (introduced in 1869 and abolished in the year 1873) and a licence tax on trades and professions (introduced in 1878). Agriculture Income was excluded from the licence tax '(1867) and the Act VI of 1880, applicable to whole of India together with the local Acts, raised the exemption limit to Rs. 500 per annum, but the rate continued to be 2 percent, This Act together with the local Acts remained in force till Ultimately the Act took the final form in favour of income tax since the experience, convinced the Government that income taxation had cometo form a necessary compliment of its revenues and was the only means of compelling the official and professional classes to pay taxes who prospersed most at that time. Therefore, afresh legislation was undertaken in 1886 which was the first systematic legisation on income-tax. 1. Rao, V.K.R.V. : Taxation of Income in India. Longmans Green & C.n I -td, Rnmh.iv 1Q11
2 The 1886 Act 35 Act II of 1886 was the first important landmark in the history of income-tax in our country. This act was not only a great improvement on its predecessors but its basic scheme contained the germs of the subsequent Income tax Acts also. This Act excluded agricultural income from the ambit of the income-tax which has continued to be a feature of income tax since and introduced a definition of agricultural income in almost the form in which it stands today. Income was divided in to four heads Viz., income from salaries and pensions, profits of companies, interest on securities and other sources of income including income from house property. The tax was levied on individual s different sources of income separately and not on his total income. A flat rate of 5 pies in the rupee of 192 pies (about 2.6 percent) was applied on income over Rs. 2,000/- with a rate of 4 pies on salaries between Rs.500 and Rs. 2,000. Interest on securities was also taxed at the same rate. In the year 1903 the taxable minimum was raised to Rs. 1,000.Enhanced rates of taxation by gradation or graduation were introduced in 1916 when eight different rates of tax were prescribed for the different brackets of income. The first world war also caused increase in tax rates. An additional income tax was also introduced for the first time in 1917 in the name of super-tax. This super-tax was introduced mainly with a view to raise more revenue for the government. While income-tax was being levied at step basis for super-tax the slab system was used. Till 1916, there was no penally for failure to furnish a retum(except in the case of companies) but in 1917, it was made obligatory for an assessee, with an income of Rs. 2,000, to make a return. The Act of 1886 stood in force for 32 years till 1918 with a number of amendments. IM-m&Afi! In 1918, a new act was enacted - the Act VII of 1918, which was introduced to re-cast the entire tax law. The scheme of all income if it accrues or arises or is received in British India from whatever source it is derived [Sec.3 (l)],i.e. total income, was introduced for the first time to determine the rate. The tax levy was imposed in respect of the taxable income of the year of assessment, unlike on the income of the previous year, as obtained under the earlier Acts. Section 2 of the Act contained many definitions. The terms company and previous year were defined. The term assessee included a firm and Hindu undivided family. Section 3(2) contained a list of ten items of exemptions including agricultural income. Taxable income was divided in to six heads viz., income from salaries, interest on securities, income derived from house property, income derived from business, income from professional earnings and income derived from other sources. The rates varied from four pies in the rupee to twelve pies in the rupee. This Act remained in force up to 1922 when, on the recommendations of All-India
3 36 Income-tax Committee-appointed in 1921, The Indian Income-tax Act XI of 1922 came in to being. The 1922 Act This Act of 1922 marked an important change from the Act of 1918 by shifting the administration of the income tax from the hands of Provincial Government to the Central government. Another remarkable feature of this Act was that the rales were to be enunciated by the annual finance Acts instead of in the basic enactment. This Act, like the Act of 1918 applied to all incomes except capital gains, casual income and incomes in kind not convertible in to money (except rent free accommodation). Charge in the year of assessment was established on the basis of the income of the previous year, instead of using the income of the 'previous year to make adjustment when the actual income of the assessment year was ascertained (1918 Act). The levy of Super-tax was being incorporated in the provisions of this Act now which was being assessed as a separate-tax till then and the super-tax was defined as an additional duty of income tax. The assessable entities were individual, Hindu Undivided family, company, firm and other association of individual. This Act permitted an assessee to set off loss of profits or gains under one head of income against profit under any other head, both relating to the same assessment year. Further, this Act granted relief in respect of discontinuance of a business which had been assessed under the Act of The Act of 1922 was amended as many as twenty times between 1922 and 1939 as it was realised that there were loopholes in the administration of the Act which might lead to tax-avoidance and tax evasion, and the rates of tax were also being increased since from 1921 onwards, the increasing need for government s growing expenditure compelled the taxing authority to pay more emphasis on taxes on income Thus, by 1939, these taxes occupied the second important position among Central taxes, and they made a contribution of about 20 percent of the total tax revenue to the Govt, of India. With increased taxation, more deductions, allowances and reliefs were also allowed from time to time. The Indian Taxation Hnquiry Committee was also constituted in to consider different aspects of taxation. Act VII of 1939 was an Amendment Act which was based upon the Income-tax Committee also called Aiyer s Committee s Report(1936). This Committee was appointed to make an investigation of the Indian Income-tax system in all aspects and to report on both the
4 37 incidence and efficiency of administration of the tax. The recommendations made by this committee changed the basic structure of the 1922 Act and ushered in a new era, both in the matter of incidence of tax on income and its administration. This Act of 1939, marked a departure from the past, by bringing to charge the foreign income of residents in British India. An intermediate class of assessees between residents and non-residents called resident but ont ordinarily resident created2. This Amendment Act, 1939 gave a new definition of income which was an inclusive definition. A number of different types of receipts were included in income which were not otherwise taxable/salary which was taxable on receipt basis was to be taxed on due basis according to this Act. It granted to a business, for the first time, relief by way of carry forward of loss for a period of six years. Slab system was introduced in 1939 for income-tax also and since then it is an integral part of the Indian income-tax system. Slab system is no doubt, better than step system. Under the step system, a single average rate is charged on each taxpayer s entire (total) income, increasing with the size of that income, where as under the slab system, the total income is split into slabs and progressive higher rates are charged on successive slabs of income. Roughly, to effect, progression, whereas the step system prescribes average rates, (tax liability as a percentage of income), the slab system prescribes marginal rates (the rate on the last increment of income). Under step system, when the total income just exceeds one of the levels at which the rate increases, the whole income, not merely that excess, will be taxed at a higher rate. For example, the income is Rs.l 0,000 and it is being taxed at 5 percent. If the incbme exceeds by Rs.50, the whole income of Rs.l 0,050 will be taxed at the next higher rate, e.g., 10 percent. This increase of Rs.50 in the income will increase the tax payable from Rs.500 to Rs On the other hand, under slab system an increased rate is applied only to the increase in income above a slab, the tax as percentage of the total income rises gradually as the income rises. This Act also introduced many provisions to check tax avoidance. 3.2 Income Taxation from 1939 to 1961 The drastic changes of 1939 did not prove very effective as far as the income-tax reform was concerned. Therefore, the 1922 Act was amended nine times between 1940 and 1947 and not less than twenty nine times between 1939 and Each Amendment Act passed had been of immense importance. The scheme of payment of tax in advance was introduced in 1944 and the diffrentiation between earned and unearned income in 1945 was also introduced. The scheme of provisional assessment, was introduced in Meaningsof residents, non-residents and resident but not ordinarily resident are given in Ch.4 Present structure of Income Taxation in India.
5 38 A tax on capital gains was imposed for the first time in 1946, although the concept of capital gains has been amended many times by later amendments. In 1947, the Taxation of Income (Investigation Commission) Act, 1947, was passed. The India Income Tax (Amendment) Act, 1953 (XXV of 1953), effective from 1 April, 1952, gave effect to the recommendations of this Commission. In April 1953, the Government appointed another Commission, known as the Taxation Enquiry Commission under the chairmanship of Dr. John Mathai. Its terms of reference were very much wider than those of the 1935 Committee and 1947 Investigation Commission, The main task entrusted to this commission was to examine the tax system in relation to the incidence of the tax system regarding the distribution of the burden of taxation and inequalities of income and wealth, the suitability of the tax system with reference to the developmenmt programme of the country, the effects of income taxation on capital formation and development of productive enterprise, and the use of taxation in dealing with inflationary and deflationary situations. The Finance Act of 1955 incorporated many changes recommended by this Commission and this was the beginning when the recommendations of the commission were given the effect from time to time. In January 1956, the Indian Statistical Institute invited Mr. NicholasKaldorto investigate the Indian Tax System in the light of the revenue requirement of the second five-year plan. His report was concentrated on the question of personal and business taxation. He submitted an exhaustive report for a coordinated tax system and therefore,the result was the enactment of several Taxation Acts, viz., the wealth-tax Act 1957, the Expenditure-tax Act, 1957 and the Gift-tax Act, Income-tax was also revived on Capital Gains. In 1956, The Government also referred the Act to the Law Commission in order to recast the Act on logicallines and to make its provisions more intelligible and simple without affecting the basic tax structure. The report of the Law Commission was received by the1 Government on 26 Sept Meantime, the Direct Taxes Administration Enquiry Committee, under the Chairmanship of Shri Mahavir Tyagi was appointed by the government to consider measures designed to minimise the inconvenience to assessees and to prevent evasion of income-tax. This Committee submitted its Report on 30th Nov The recommendations made in the two reports took shape in the Income Tax Act The Incomcrlax Act, 1961 The Income-tax Bill, 1961 which was submitted to the Lok Sabhaon the 24th April, 1961 was the outcome of above recommendations. On 1st may, 1961, it was referred to a Select Committee and its report was presented to the Lok Sabha on 10th August, After passing through both the House of Parliament, the Bill received the assent of the President on 13th Sep.,
6 and the Act came in to force with effect from 1st April, 1962 by replacing the Indian Income Tax Act, 1922 which had remained in operation for 40 years. The present law of income tax is governed by the Income Tax Act, 1961, which has 298 sections and 4 schedules and is applicable to whole of India including the state of Jammu and Kashmir. The search for an effective tax system answering the developing needs of the nation has led to the appointment of various committees and commissions which have led to many changes in the Act, Changes have been brought in by almost every Finance Act, AmendingActs and Ordinances. About 70 laws have been passed between 1962 to 1989 to amend the Income-tax Act, Some of these amendments were made in pursuance of the recommendations made by (i) Bhootalingham s Report on Rationalisation and Simplification of Tax Structure submitted in two parts, one dated 5th April, 1967 and the other dated 26 Dec., 1967,(ii) the Report of the Working Group of Administrative Reforms Commission on Central Direct Taxes Administration, headed by Shri Mahavir Tyagi (1969), (iii) the Report of the Direct Taxes Enquiry Committee (1971), under the chairmanship of Justice K.N.Wanchoo, regarding unearthing black money, preventing evasion and avoidance of taxes, and reducing arears, (iv) the Committee on Taxation of Agricultural Wealth and Income (1972), (v) the Interim Report (1977) and final Report (1978) of the Direct Tax Laws Committee headed by Shri C.C Chokshi, (vi) the Report of the Enquiry Committee under the Chairmanship of Shri Bhoothaligam regarding changes in the concepts of the financial year and the previors year, (vii) Economic Administration Reforms Commission, called L.K.Jha Commission (1981), which submitted its report in 1983, (viii) a long term fiscal policy, announced by the government and laid before the Parliament on 19th Dec, 1985,(ix) a White paper enunciating government s policy published in 1986, and (xx) Direct Tax Laws (Amendment) Act, 1987 and A study on black money was published in March 1985 by the National Institute of Public Finance and Policy in India, with contributions by Dr. RJ.Chelliah. An expert Committee was also constituted in 1989 on revision of tax reforms, which submitted the interim report in The Tax Reforms Committee was also appointed in 1991 under the Chairmanship of Sh. Raja J.Chelliah which submitted its Final Report Part-I in Aug, 1992, and final Report Part- II in January Some of the recommendations of the Tax Reforms committee have already been implemented in subsequent budgets. This Committee is basically concerned with the question of administrative reforms with respect to both direct and indirect taxes. The Committee also presents detailed and specific recommendations for important changes in India s tax structure. The essence of these changes is to lower nominal rates and to broaden tax-base. This Committee is also in favour of progressive income taxes. Therefore, even the Income-tax Act of 1961, which was then considered to be very comprehensive, had to be amended from time to time.
7 40 The 1961, Act has enlarged the number of categories of assessable entities to seven as against six of the 1922 Act, including every.artificial juridical person, who has not been included in the six categories, i.e. residuary class3. A scheme of self-assessment was introduced which, in course of time, displaced the scheme of provisional assessment. Provisions regarding advance tax, interest and penalty were made more rigorous. Regarding reopening of back assessment for escaped income, the Act retained the limit of eight years where the assessee has failed to make a return or failed to disclose all meterial facts. The procedures for assessment were completely recast in April 1989, i.e., assessment year Income-tax revenue originates mainly from two taxpaying entities Viz., Companies and Individuals - Hindu Undividedfamily, Registered firms and others contribute very little. Since this study is concerned with Individuals - which account for more than 99 % of the 'Salaried- Class - 'Companies are not taken in to account Some Salient Feature of the Rate Structure of Income -Tax on Individual in India : The rates of income-tax as well as the slabs have undergone frequent changes from time to time. In pre-independence time, the tax system was designed with the single main objective of raising sufficient amount of revenue for expenditure of Government for administration and allied services. The position, however, has completely changed in post-independence period. In designing the tax system, Government took into consideration the objective of growth with social justice, which led to the frequent changes in the income-tax structure from time to time. Besides, the tax on income was levied in a variety of ways viz. income-tax; surcharge on income-tax; super-tax; surcharge on super-tax; surcharge on earned incomes; surcharge on unearned incomes; additional surcharge; special surcharge etc. The Finance Act,1963, imposed additional surcharge for the assessment year This levy of additional surcharge was closely connected with the Compulsory Deposit Scheme (1963), which gave place to Annual Deposit for the assessment year and onwards. Although the main objectives of the above mentioned ways adopted, were to withdraw the purchasing power on account of prevailing inflationary pressures on the economy and to make large funds available to the public sector, the system became complicated year by year. 3. Details are given in 4th Chapter, Present structure of Income Taxation.
8 41 To simplify the system, super-tax was subsequently integrated with income-tax by the Finance Act, 1965 that is, effective from the assessment year The distinction between earned and unearned incomes, introduced in 1945, was completely abolished from April 1,1968. Now there was only one type of surcharge and one kind of tax, that is, income-tax was levied at varying rates on different slabs of incomes and a surcharge was added at a prescribed rate upon the tax so computed to arrive at the total tax liability. An attempt has always been made by the Government to keep the incidence of tax at a relatively lower level for persons in the lower income groups. Therefore, a minimum exemption limit all individuals having prescribed income are not subject to tax has always been provided by the different Income-Tax Acts. Since 1947, exemption limit has been gradually raised. At the time of introduction of the Income-Tax Act, 1961, exemption limit was Rs.3,000 for individual and Rs. 6,000 for Hindu Undivided Family. From the assessment year , these exemption limits were subject to the provision of family allowance computed in accordance with the personal circumstances of an individual. More concession was given to married individual with two or more children compared to unmarried one or married having one child. Under the Finance Act 1965, every individual got relief on account of personal allowance in terms of amount of tax otherwise payable depending upon the marital status. This was in addition to a minimum exemption limit. This scheme of personal allowance was discontinued by the Finance Act, 1970 and first tax free slab was prescribed for the first time for the assessment year for individuals whose income up to Rs.5,000 was fully exempt from tax whatever their marital status may be. This step further simplified the system. Since, the Direct Taxes Enquiry Committee (1971), popularly known as Wanehoo Committee, recommended reduction in the rates of direct taxes which were mainly responsible for tax evasion because they made tax evasion more attractive, the maximum marginal rate of income-tax on individual was reduced from 97.7 per cent in the assessment year to 66.0 per cent in on income exceeding Rs.l Lac [ Government of India, Finance Acts (various years)]. The number of slabs was reduced to 7 from 8 in the budget of In the number of slabs became 4 and now it is 3, i.e., in the budget of This is also an important step towards the simplification of tax system.
9 42 The exemption limit for individuals has been continuously enhanced from Rs. 5,000 for the assessment year to Rs.6,000 for the assessment year and to further Rs. 12,000 for the assessment year The following table 4 depicts the exemption limit provided under the law and the range of marginal tax rates applicable to individual tax payers in different assessment years from to
10 43 Table 4 Range of Marginal Tax Rates Applicable to Individual Taxpayers in the Assessment years to Assessment Years Exclusive of Surcharge (Percent) Surcharge On Income Tax(Percent) Inclusive of Surcharge (Percent) Exemption Limit (In Rs 000) ' and and Nil and and * Notes : 1. If income does not exceed Rs. 10,000, it is treatedas exempt. 2. If Income does not exceed Rs.12,000, it is treatedas exempt. 3. Applicable only if the taxable income exceeds Rs.50,000 and otherwise Nil. 4. Applicableonly if the taxable incomeexceedsrs. 75,000 and otherwise Nil. 5. Applicableonly if the taxableincomeexceedsrs. 75,000 and otherwise Nil. 6. Applicableonly ifthetaxableincomeexceeds Rs. 1,00,000 and otherwise Nil. *. No surcharge is leviable from A.Y and maximum marginal rate is applicable to income over Rs. 1,20,000 (which is over Rs. 1,00,000 for all the previous assessment years mentioned above). Source : Budget of Union Government of India, for different years. *
11 44 The maximum marginal tax rate (exclusive of surcharge) was 60 percent from the assessment year to and the rate inclusive of surcharge varied from 72 percent to 67,50 percent because of variation in the rate of surcharge. Subsequently, maximum marginal tax rate has been brought down to 40 percent. Marginal tax rates at low income levels continued to rise in early eighties and reached at 33 percent in the year and remained same till , Subsequently, marginal tax rates at low income levels also continued to decline like maximum marginal tax rates resulting in 20 per cent in the assessment year and further, 15 percent in the assessment year This decline in the rate of income tax on individuals in the first income slab, i.e., between Rs to Rs.60Q00 in the assessment year , as compared to the assessment year , has reduced the tax liability on different income levels. The table 5 reveals the impact of reduction of tax rate in the first income slab in the case of individuals. Table. 5 Tax Liability in the case of individuals at Different Income Levels in the Assessment Year and , and the Resultant Relief. in Rs. Total Tax Tax Relief Income Liability in Liability in Amount % the assessment the assessment year year
12 45 Five percent decline in the rate of income tax on individuals, as compared to previous year, in the first income slab caused 25 percent relief from income tax up to the income level of Rs (first income slab) in the assessment year With the increase in the level of income from Rs to Rs , tax relief declined from 11.8 percent to 1.9 percent respectively. The exemption limit for individual income tax payers has been substantially raised during the period to from Rs. 8,000 to Rs.40,000. While the range of marginal tax rates exclusive as well as inclusive of surcharge in the assessment years to is shown in table 4, the marginal tax rates by income brackets are presented for the same period in table 6.
13 46 Iabk-6 Marginal Tax Rates Applicable to Individual Taxpayers in the Assessment Years to (Percent) Taxable Income & Assessment Years to On the first Rs. 10,000 Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs. 2, Nil ' Nil Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs. 2, Nil Nil.Nil ' Nil Nil On the next Rs. 2, Nil On the next Rs Nil On the next Rs. 2, On the next Rs. 5, On the next Rs. 5, On the next Rs. 5, On the next Rs. 5, On the next Rs. 10, On the next Rs. 10, On the next Rs. 10, On the next Rs. 10, On the next Rs.5, On the next Rs. 15, On the next Rs.20, Over Rs. 1,20, ' Contd...
14 47 :- Tablfc.6 Taxable Assessment Years. Income & On the first Rs. 10,000 Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs.2,500 Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs.2,500 Nil Nil Nil NiL Nil NiL Nil On the next Rs.2,500 Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs.500 Nil Nil Nil Nil.Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs.2, Nil Nil Nil. Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs.5, Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs.3, Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs.2, Nil Nil Nil Nil On the next Rs.5, Nil ' Nil Nil On the next Rs.5, Nil Nil On the next Rs. 10, On the next Rs. 10, On the next Rs. 10, On the next Rs. 10, On the next Rs.5, On the next Rs. 15, On the next Rs.20, Over Rs. 1,20, Note: The marginal tax rates presented here do not include surcharge or special surcharge: if any. Source : Budget of Union Government of India, for different years. Both the tables (5 & 6) given above reveal the declining marginal rates of income-tax on individuals in India. But the general impression that India is a highly taxed nation is still true in regard to rate of income-tax on individuals. The following table 7 reveals the different income-tax rates on individual in OECD member countries.
15 48 Table? Rate Schedules of Central Government Income Tax on individual in different countries Country Lowest Rate of Income tax on Individuals, Highest Rate of Income Tax on Individuals Australia Austria Belgium Canada Denmark Finland 7.0 ^ 39.0 France 5.0. Germany 19.0 ti wana. p3.0 Greece 5.0 *fc #0.0 Iceland India Ireland Itlay Japan Luxemburg Mexico Netherlands Newzealand Norway Portugal Spain Sweeden Switzerland Turkey United Kingdom United States OECD Average * Notes : 1. * Unweighted 2. For comparison with India, member countries of OECD have been chosen for convenience as the data for these countries are readily available. 3. OECD stands for Organisation for Economic Co. operation and Development. Source: Revenue Statistics of OECD Member Countries, OECD, Paris, 1994.
16 49 A comparison of personal income tax rate in India with OECD member countries reveals that still India comes in the list of Highly Taxed Nations. Although rates of personal income tax (lowest as well as highest) in India are lower compared to some OECD member countries, because these rates have been declined in India compared to previous years, still the lowest as well as the highest rates are higher than the OECD average rates(lowest as well as highest). Which proves the comparatively heavy burden of income-tax on individual tax-payers in India. To reduce the burden of income - tax on individuals, besides raising the exemption limit, scope of deductions has also been widened and the ceilings have been raised from time to time. For Example, the ceiling on the amount of investment in specified assets that qualifies for a graded deduction up to assessment year (Sec.^Gp^WSs^sed from Rs. 10,000 in to Rs.40,000 with effect from The ceiling on allowable deduction of intereslsdiumbend received from some specified assets has been raised from Rs.5,000 in to Rs. 9,000 in to 13,000 with effect from the year and subsequently it has been enhanced to Rs. 15,000 with effect from the assessment year The list of specified assets have also been enlarged. With effect from the assessment year the system of itemised expense deduction with respect to expenditureincidental to earning salary income has been replaced by a standard deduction based on the salary income. The ceiling on the amount of standard deduction has been raised from Rs.3,500 in to Rs.5,000 in , Rs. 12,000 in and subsequently to Rs. 15, /3 % of gross salary, whichever is less,in case of salaried women Rs. 18,000 or 331/3 % of gross salary, whichever is less, having income upto Rs.75,000) with effect from theassessment year Standard deduction has been raised to Rs. 18,000 for persons drawing salary up to Rs.60,000 in the current budget for the assessment year , which will provide relief to the low -paid salaried employees. Thus, a salaried employee with an income of Rs per year, making the minimum contribution to his provident fund, will now pay no tax at all. If he has no savings, he will still pay only Rs After reviewing the evolution of income tax system and analysing the changes occurred from time to time in the structure of income tax, now we will discuss the present structure of income tax in India and its justification. 4. This section (80 C) was applicable up to the assessment yearl The same investments and contributions (specified under sec. 80 C) are now eligible for rebate from tax under section 88 from the assessment year Finance Minister s Budget Speech, Union Budget,
Burden of Taxation: International Comparisons
 Burden of Taxation: International Comparisons Standard Note: SN/EP/3235 Last updated: 15 October 2008 Author: Bryn Morgan Economic Policy & Statistics Section This note presents data comparing the national
Burden of Taxation: International Comparisons Standard Note: SN/EP/3235 Last updated: 15 October 2008 Author: Bryn Morgan Economic Policy & Statistics Section This note presents data comparing the national
Question 1. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 Question 1 PAPER 5 : TAXATION Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. Wherever necessary suitable assumptions may be made by the candidates. Answer the following with reasons
Question 1 PAPER 5 : TAXATION Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. Wherever necessary suitable assumptions may be made by the candidates. Answer the following with reasons
FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2014 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF SAID ACT AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE
 FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2014 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF SAID ACT Section/Schedule CIRCULAR NO.1/2015 [F.NO.142/13/2014 TPL], DATED 21 1 2015 AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE Finance (No.2) Act, 2014 First
FINANCE (NO.2) ACT, 2014 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF SAID ACT Section/Schedule CIRCULAR NO.1/2015 [F.NO.142/13/2014 TPL], DATED 21 1 2015 AMENDMENTS AT A GLANCE Finance (No.2) Act, 2014 First
EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE(No.2) ACT, 2014
 CIRCULAR NO. 01/2015 F. No. 142/13/2014-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) ******* Dated, the 21st January, 2015 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE
CIRCULAR NO. 01/2015 F. No. 142/13/2014-TPL Government of India Ministry of Finance Department of Revenue (Central Board of Direct Taxes) ******* Dated, the 21st January, 2015 EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE
8-Jun-06 Personal Income Top Marginal Tax Rate,
 8-Jun-06 Personal Income Top Marginal Tax Rate, 1975-2005 2005 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 Australia 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 48% 49% 49% Austria
8-Jun-06 Personal Income Top Marginal Tax Rate, 1975-2005 2005 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 Australia 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 47% 48% 49% 49% Austria
INCOME-TAX AND BASED ON FINANCE ACT, FINANCE ACT, 2007 WITH NOTES 49 I.T. NOTES 69 I.T. NOTES 97 I.T. NOTES I.T. NOTES 139 I.T.
 EHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR VG.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA
EHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR VG.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA S ITRR V.G.MEHTA
Tax is imposition financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or other the functional equivalent of the state.
 1. What is Tax What is Tax? Tax is imposition financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or other the functional equivalent of the state. How many Types of Taxes are there and what are they?
1. What is Tax What is Tax? Tax is imposition financial charge or other levy upon a taxpayer by a state or other the functional equivalent of the state. How many Types of Taxes are there and what are they?
A Study on Tax Planning Pattern of Salaried Assessee
 A Study on Tax Planning Pattern of Salaried Assessee Mrs.R.VASANTHI M.Com,M.Phil,(Ph.d) Assistant Professor Department of Commerce CA,PSGR Krishnammal college for women,coimbatore-641 004 E-Mail ID: thanuvasa@gmail.com
A Study on Tax Planning Pattern of Salaried Assessee Mrs.R.VASANTHI M.Com,M.Phil,(Ph.d) Assistant Professor Department of Commerce CA,PSGR Krishnammal college for women,coimbatore-641 004 E-Mail ID: thanuvasa@gmail.com
TAX POLICY: RECENT TRENDS AND REFORMS IN OECD COUNTRIES FOREWORD
 TAX POLICY: RECENT TRENDS AND REFORMS IN OECD COUNTRIES FOREWORD This publication provides an overview of recent trends in domestic taxation in OECD countries over the period 1999 to 2002, and a summary
TAX POLICY: RECENT TRENDS AND REFORMS IN OECD COUNTRIES FOREWORD This publication provides an overview of recent trends in domestic taxation in OECD countries over the period 1999 to 2002, and a summary
Legislative Brief The Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2010
 Legislative Brief The Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2010 The Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2010 was introduced in the Lok Sabha by the Minister for Finance on August 31, 2010. The Bill has been referred to the Standing
Legislative Brief The Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2010 The Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2010 was introduced in the Lok Sabha by the Minister for Finance on August 31, 2010. The Bill has been referred to the Standing
Significant changes in the proposed Direct Taxes Code, 2013
 Significant changes in the proposed Direct Taxes Code, 2013 The Income-tax Act was passed in 1961 and has been amended every year through the Finance Act. The Wealth-tax Act was passed in 1957 and has
Significant changes in the proposed Direct Taxes Code, 2013 The Income-tax Act was passed in 1961 and has been amended every year through the Finance Act. The Wealth-tax Act was passed in 1957 and has
STATISTICS. Taxing Wages DIS P O NIB LE E N SPECIAL FEATURE: PART-TIME WORK AND TAXING WAGES
 AVAILABLE ON LINE DIS P O NIB LE LIG NE www.sourceoecd.org E N STATISTICS Taxing Wages «SPECIAL FEATURE: PART-TIME WORK AND TAXING WAGES 2004-2005 2005 Taxing Wages SPECIAL FEATURE: PART-TIME WORK AND
AVAILABLE ON LINE DIS P O NIB LE LIG NE www.sourceoecd.org E N STATISTICS Taxing Wages «SPECIAL FEATURE: PART-TIME WORK AND TAXING WAGES 2004-2005 2005 Taxing Wages SPECIAL FEATURE: PART-TIME WORK AND
Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals
 RATES OF INCOME TAX Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals Basic exemption limit has been increased from Rs 2 lacs to Rs 2.50 lacs for resident individuals or HUF. Income slabs Income
RATES OF INCOME TAX Union Budget 2014 Analysis of Major Direct tax proposals Basic exemption limit has been increased from Rs 2 lacs to Rs 2.50 lacs for resident individuals or HUF. Income slabs Income
Legislative Brief. The Draft Direct Taxes Code Bill, Highlights of the Bill. Key Issues and Analysis
 Legislative Brief The Draft Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2009 The draft Bill was released for public discussion on August 12 th, 2009 by the Finance Minister Shri Pranab Mukherjee. Recent Briefs: The Legal
Legislative Brief The Draft Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2009 The draft Bill was released for public discussion on August 12 th, 2009 by the Finance Minister Shri Pranab Mukherjee. Recent Briefs: The Legal
Income Tax Changes made in Income Tax Provisions in the Union Budget which would affect Salaried Class
 Income Tax 2013-14 Changes made in Income Tax Provisions in the Union Budget 2013-14 which would affect Salaried Class A. RATES OF INCOME-TAX I. Rates of income-tax in respect of income liable to tax for
Income Tax 2013-14 Changes made in Income Tax Provisions in the Union Budget 2013-14 which would affect Salaried Class A. RATES OF INCOME-TAX I. Rates of income-tax in respect of income liable to tax for
Income Ta Income Tax (A.Y (A.Y )
 1 Income Tax (A.Y. 2011-12) 12) What is a Finance Bill? a) The Finance Bill incorporates all the financial proposals of the Government for the following year. b) It is ordinarily introduced in the Lok
1 Income Tax (A.Y. 2011-12) 12) What is a Finance Bill? a) The Finance Bill incorporates all the financial proposals of the Government for the following year. b) It is ordinarily introduced in the Lok
The Case for Fundamental Tax Reform: Overview of the Current Tax System
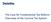 The Case for Fundamental Tax Reform: Overview of the Current Tax System Sources of Federal Receipts Projected for 2016 Excise Taxes 2.9% Estate & Gift Taxes 0.6% Corporate Income Taxes 9.8% Other Taxes
The Case for Fundamental Tax Reform: Overview of the Current Tax System Sources of Federal Receipts Projected for 2016 Excise Taxes 2.9% Estate & Gift Taxes 0.6% Corporate Income Taxes 9.8% Other Taxes
OECD Report Shows Tax Burdens Falling in Many OECD Countries
 OECD Centres Germany Berlin (49-30) 288 8353 Japan Tokyo (81-3) 5532-0021 Mexico Mexico (52-55) 5281 3810 United States Washington (1-202) 785 6323 AUSTRALIA AUSTRIA BELGIUM CANADA CZECH REPUBLIC DENMARK
OECD Centres Germany Berlin (49-30) 288 8353 Japan Tokyo (81-3) 5532-0021 Mexico Mexico (52-55) 5281 3810 United States Washington (1-202) 785 6323 AUSTRALIA AUSTRIA BELGIUM CANADA CZECH REPUBLIC DENMARK
Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011
 Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011 RATES OF INCOME-TAX FOR THE ASSESSMENT YEAR 2012-13 o Tax slab rates have been changed for individuals and HUF, which is given by way of a
Salient features of Direct Tax Proposals of Union Budget 2011 RATES OF INCOME-TAX FOR THE ASSESSMENT YEAR 2012-13 o Tax slab rates have been changed for individuals and HUF, which is given by way of a
Basics of Income Tax
 CHAPTER : Basics of Income Tax CONCEPT 1: Short Title, Extent and Commencement [Section 1] a) Short title : Income Tax Act 1961 b) Extent : Whole of India c) Commencement : 1 st April, 1962 CONCEPT 2:
CHAPTER : Basics of Income Tax CONCEPT 1: Short Title, Extent and Commencement [Section 1] a) Short title : Income Tax Act 1961 b) Extent : Whole of India c) Commencement : 1 st April, 1962 CONCEPT 2:
Finance (No. 2) Bill 2014
 Finance (No. 2) Bill 2014 Proposed Income Tax Amendments Mr. R.N. LAKHOTIA Leading Income Tax Consultant & Author The Finance Minister presented the Finance (No.2) Bill 2014 along with the Union Budget
Finance (No. 2) Bill 2014 Proposed Income Tax Amendments Mr. R.N. LAKHOTIA Leading Income Tax Consultant & Author The Finance Minister presented the Finance (No.2) Bill 2014 along with the Union Budget
Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate)
 Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate) By CA Mahavir Jain B.Com.; DISA; FCA Partner : JMT & Associates Email: jmtca301@gmail.com Issues in Taxation of Non-Corporate Income is a very vast subject.
Issues in Taxation of Income (Non-Corporate) By CA Mahavir Jain B.Com.; DISA; FCA Partner : JMT & Associates Email: jmtca301@gmail.com Issues in Taxation of Non-Corporate Income is a very vast subject.
Gross to net salary of a local executive and total cost to employer comparison for selected countries
 Gross to net salary of a local executive and total cost to employer comparison for selected countries Married, two dependant children All the numbers are in EURO Country Gross Salary Employee Income Net
Gross to net salary of a local executive and total cost to employer comparison for selected countries Married, two dependant children All the numbers are in EURO Country Gross Salary Employee Income Net
A Comparison of the Tax Burden on Labor in the OECD, 2017
 FISCAL FACT No. 557 Aug. 2017 A Comparison of the Tax Burden on Labor in the OECD, 2017 Jose Trejos Research Assistant Kyle Pomerleau Economist, Director of Federal Projects Key Findings: Average wage
FISCAL FACT No. 557 Aug. 2017 A Comparison of the Tax Burden on Labor in the OECD, 2017 Jose Trejos Research Assistant Kyle Pomerleau Economist, Director of Federal Projects Key Findings: Average wage
Income-tax and Death are the only two inevitable things in life In India, taxes were levied even in ancient times refer to Manu Smriti & Arthashastra
 Income-tax and Death are the only two inevitable things in life In India, taxes were levied even in ancient times refer to Manu Smriti & Arthashastra Why to Pay Tax? It was only for the good of his subjects
Income-tax and Death are the only two inevitable things in life In India, taxes were levied even in ancient times refer to Manu Smriti & Arthashastra Why to Pay Tax? It was only for the good of his subjects
AN APPRAISAL OF CORPORATE TAX IN INDIA: A SELF ASSESSMENT
 Volume 5, Issue 1 (January, 2016) Online ISSN-2320-0073 Published by: Abhinav Publication Abhinav International Monthly Refereed Journal of Research in AN APPRAISAL OF CORPORATE TAX IN INDIA: A SELF ASSESSMENT
Volume 5, Issue 1 (January, 2016) Online ISSN-2320-0073 Published by: Abhinav Publication Abhinav International Monthly Refereed Journal of Research in AN APPRAISAL OF CORPORATE TAX IN INDIA: A SELF ASSESSMENT
III BCOM (CA) [ ] Semester V Core:INCOME TAX LAW AND PRACTICE 503B Multiple Choice Questions.
![III BCOM (CA) [ ] Semester V Core:INCOME TAX LAW AND PRACTICE 503B Multiple Choice Questions. III BCOM (CA) [ ] Semester V Core:INCOME TAX LAW AND PRACTICE 503B Multiple Choice Questions.](/thumbs/71/65799137.jpg) 1 of 23 8/12/17, 2:57 PM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
1 of 23 8/12/17, 2:57 PM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2016
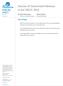 FISCAL FACT No. 517 July, 2016 Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2016 By Kyle Pomerleau Director of Federal Projects Kevin Adams Research Assistant Key Findings OECD countries rely heavily on
FISCAL FACT No. 517 July, 2016 Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2016 By Kyle Pomerleau Director of Federal Projects Kevin Adams Research Assistant Key Findings OECD countries rely heavily on
INTRODUCTION OF TAX PLANNING
 INTRODUCTION OF TAX PLANNING UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF THE CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Meaning of Planning 1.3 Meaning of Management 1.4 Meaning of Evasion 1.5 Meaning of Avoidance 1.6 Basics 1.7 Summary 1.8
INTRODUCTION OF TAX PLANNING UNIT 1 STRUCTURE OF THE CHAPTER 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Meaning of Planning 1.3 Meaning of Management 1.4 Meaning of Evasion 1.5 Meaning of Avoidance 1.6 Basics 1.7 Summary 1.8
Approach to Employment Injury (EI) compensation benefits in the EU and OECD
 Approach to (EI) compensation benefits in the EU and OECD The benefits of protection can be divided in three main groups. The cash benefits include disability pensions, survivor's pensions and other short-
Approach to (EI) compensation benefits in the EU and OECD The benefits of protection can be divided in three main groups. The cash benefits include disability pensions, survivor's pensions and other short-
As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2017 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 1 st February, 2017.
 Budget 2017-18 Highlights for Non-Residents As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2017 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 1 st February, 2017. The Indian Budget has provisions affecting the taxability
Budget 2017-18 Highlights for Non-Residents As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2017 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 1 st February, 2017. The Indian Budget has provisions affecting the taxability
Registration of Foreign Limited Partnerships in the Cayman Islands
 Registration of Foreign Limited Partnerships in the Cayman Islands Preface This publication has been prepared for the assistance of those who are considering registration of a foreign limited partnership
Registration of Foreign Limited Partnerships in the Cayman Islands Preface This publication has been prepared for the assistance of those who are considering registration of a foreign limited partnership
FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE
 FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE COMPILED BY: CA.ARUN GUPTA ca.arungupta77@gmail.com A. Rates of Taxes: 1. It is proposed to make the following changes in tax rates: In case of Resident
FINANCE BILL 2017-DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS AT GLANCE COMPILED BY: CA.ARUN GUPTA ca.arungupta77@gmail.com A. Rates of Taxes: 1. It is proposed to make the following changes in tax rates: In case of Resident
Chapter 1 : Income Tax Concept and Computation of Income Tax
 Chapter 1 : Income Tax Concept and Computation of Income Tax This Chapter includes : I. Taxation in India 1. Taxes and its levying authority 2. Tax Structure 3. Hierarchy of Taxes levied and collected
Chapter 1 : Income Tax Concept and Computation of Income Tax This Chapter includes : I. Taxation in India 1. Taxes and its levying authority 2. Tax Structure 3. Hierarchy of Taxes levied and collected
CHAPTER 5 Growth and Pattern of Revenue of the Central Government
 CHAPTER 5 Growth and Pattern of Revenue of the Central Government In order to perform it s functions-social, economic and general-government needs funds which have to be garnered from a variety of sources
CHAPTER 5 Growth and Pattern of Revenue of the Central Government In order to perform it s functions-social, economic and general-government needs funds which have to be garnered from a variety of sources
Corporate Tax Issues in the Baltics
 Corporate Tax Issues in the Baltics In the last twenty years the Baltic States has gone through many historical changes. The changes have affected the political system, society, economics, capital market
Corporate Tax Issues in the Baltics In the last twenty years the Baltic States has gone through many historical changes. The changes have affected the political system, society, economics, capital market
CA. Divakar Vijayasarathy
 CA. Divakar Vijayasarathy Introduction Tax and Regulatory Regime in India Global Estate Tax Regime Possible Estate Planning Structures Practical Perspective to Estate Tax Planning 1 Death leads to movement
CA. Divakar Vijayasarathy Introduction Tax and Regulatory Regime in India Global Estate Tax Regime Possible Estate Planning Structures Practical Perspective to Estate Tax Planning 1 Death leads to movement
SURENDER KR. SINGHAL & CO
 PROPOSED TAX RATES FOR FINANCIAL YEAR 2016-17 A. Y. 2017-18 Income Tax Rates for Individuals, HUF Individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) and Artificial Jurisdictional Person: Net Income Range Income
PROPOSED TAX RATES FOR FINANCIAL YEAR 2016-17 A. Y. 2017-18 Income Tax Rates for Individuals, HUF Individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) and Artificial Jurisdictional Person: Net Income Range Income
the taxation of families
 CARE RESEARCH PAPER the taxation of families international comparisons 2017 By Leonard Beighton, Don Draper and Alistair Pearson Fiscal Policy Consultants Contents Preface Acknowledgements Executive Summary
CARE RESEARCH PAPER the taxation of families international comparisons 2017 By Leonard Beighton, Don Draper and Alistair Pearson Fiscal Policy Consultants Contents Preface Acknowledgements Executive Summary
How budgetary policy has shaped the Irish income tax system
 Administration, vol. 62, no. 4 (215), pp. 17 118 How budgetary policy has shaped the Irish income tax system David Cronin Central Bank of Ireland Ronan Hickey Central Bank of Ireland Gerard Kennedy Central
Administration, vol. 62, no. 4 (215), pp. 17 118 How budgetary policy has shaped the Irish income tax system David Cronin Central Bank of Ireland Ronan Hickey Central Bank of Ireland Gerard Kennedy Central
Paper 7 Applied Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 hours Full Marks: 100
 Paper 7 Applied Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 hours Full Marks: 100 All the questions relate to the assessment year 2014-15, unless stated otherwise. Working notes should form part of the answers. Answer
Paper 7 Applied Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 hours Full Marks: 100 All the questions relate to the assessment year 2014-15, unless stated otherwise. Working notes should form part of the answers. Answer
Rates of Taxes. Rates for deduction of Income
 CA Mohan S. Phadke Rates of Taxes I. Rates of Income Tax in respect of income liable to tax for the assessment year 2013-14 a) In respect of income of all categories of assessees liable to tax for the
CA Mohan S. Phadke Rates of Taxes I. Rates of Income Tax in respect of income liable to tax for the assessment year 2013-14 a) In respect of income of all categories of assessees liable to tax for the
FB.COM/SUPERWHIZZ4U Income Tax Amendment for the Assessment
 FB.COM/SUPERWHIZZ4U Income Tax Amendment for the Assessment Year 2014-15 - SIPOY SATISH Highlights of Change in Direct Taxes in the Union Budget 2013 1. Rate of Income Tax for Individual a) Slab Rate Assessment
FB.COM/SUPERWHIZZ4U Income Tax Amendment for the Assessment Year 2014-15 - SIPOY SATISH Highlights of Change in Direct Taxes in the Union Budget 2013 1. Rate of Income Tax for Individual a) Slab Rate Assessment
Effective Tax Rates on Employee Stock Options in the European Union and the USA
 Brussels, May 23 Ref. Ares(214)75853-15/1/214 Effective Tax Rates on Employee Stock Options in the European Union and the USA Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...2 RESULTS...3 Normal taxation (no special
Brussels, May 23 Ref. Ares(214)75853-15/1/214 Effective Tax Rates on Employee Stock Options in the European Union and the USA Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...2 RESULTS...3 Normal taxation (no special
Circular The Schedule of dates for filing income-tax returns is given below:
 Circular-2012 To, July 14, 2012 Dear Sir(s)/Madam, Sub: Income-tax, Wealth-tax, Service-tax and TDS returns for Assessment Year 2012-13 and payment of advance-tax for Assessment Year 2013-14 -------------------------------------------------------
Circular-2012 To, July 14, 2012 Dear Sir(s)/Madam, Sub: Income-tax, Wealth-tax, Service-tax and TDS returns for Assessment Year 2012-13 and payment of advance-tax for Assessment Year 2013-14 -------------------------------------------------------
Overview of Transfer Pricing Regulations. CA Akshay Kenkre
 Overview of Transfer Pricing Regulations CA Akshay Kenkre 1 What is Transfer Pricing What is Transfer Price? A Price at which one person transfers physical goods, services, tangible or/ and intangibles
Overview of Transfer Pricing Regulations CA Akshay Kenkre 1 What is Transfer Pricing What is Transfer Price? A Price at which one person transfers physical goods, services, tangible or/ and intangibles
MTP_ Inter _Syllabus 2016_ June 2017_Set 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation
 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 Hours Full Marks: 100
Paper 7 Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 Hours Full Marks: 100
Statistical annex. Sources and definitions
 Statistical annex Sources and definitions Most of the statistics shown in these tables can be found as well in several other (paper or electronic) publications or references, as follows: the annual edition
Statistical annex Sources and definitions Most of the statistics shown in these tables can be found as well in several other (paper or electronic) publications or references, as follows: the annual edition
THE BUDGET Dhiren Shah & Co. Chartered Accountants Ahmedabad
 THE BUDGET 2019-20 Dhiren Shah & Co. Chartered Accountants Ahmedabad Address : 2nd & 3rd Floor, Swastik Avenue, Swastik society, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad- 380009. Contents Particulars Page No About Us 1
THE BUDGET 2019-20 Dhiren Shah & Co. Chartered Accountants Ahmedabad Address : 2nd & 3rd Floor, Swastik Avenue, Swastik society, Navrangpura, Ahmedabad- 380009. Contents Particulars Page No About Us 1
FOREIGN COLLABORATION AND DOUBLE TAXATION RELIEF
 FOREIGN COLLABORATION AND DOUBLE TAXATION RELIEF STRUCTURE OF THE CHAPTER UNIT 7 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Agreement with foreign countries or specified territories [Sec. 90] 7.3 Adoption by Central Government
FOREIGN COLLABORATION AND DOUBLE TAXATION RELIEF STRUCTURE OF THE CHAPTER UNIT 7 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Agreement with foreign countries or specified territories [Sec. 90] 7.3 Adoption by Central Government
Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2017
 FISCAL FACT No. 558 Aug. 2017 Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2017 Amir El-Sibaie Analyst Key Findings: OECD countries rely heavily on consumption taxes, such as the value-added tax, and social
FISCAL FACT No. 558 Aug. 2017 Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2017 Amir El-Sibaie Analyst Key Findings: OECD countries rely heavily on consumption taxes, such as the value-added tax, and social
THE FINANCE BILL, 2015
 BILL No. 26 OF THE FINANCE BILL, (AS INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA) THE FINANCE BILL, ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES CHAPTER I PRELIMINARY CLAUSES 1. Short title and commencement. CHAPTER II RATES OF INCOME-TAX 2. Income-tax.
BILL No. 26 OF THE FINANCE BILL, (AS INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA) THE FINANCE BILL, ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES CHAPTER I PRELIMINARY CLAUSES 1. Short title and commencement. CHAPTER II RATES OF INCOME-TAX 2. Income-tax.
GOVERNMENT PAPER. There are some signs that these views are changing with new generations.
 Older people on the labour market in Iceland Public policy and measures within continuing education Gissur Pétursson Directorate of Labour 1. Conditions on the labour market Employment participation among
Older people on the labour market in Iceland Public policy and measures within continuing education Gissur Pétursson Directorate of Labour 1. Conditions on the labour market Employment participation among
Board of the Centre Turin, 2-3 November 2006
 INTERNATIONAL TRAINING CENTRE OF THE ILO CC 68/7/b 68th Session Board of the Centre Turin, 2-3 November 2006 SEVENTH ITEM ON THE AGENDA STAFF QUESTIONS Proposed amendments to the Staff Regulations Report
INTERNATIONAL TRAINING CENTRE OF THE ILO CC 68/7/b 68th Session Board of the Centre Turin, 2-3 November 2006 SEVENTH ITEM ON THE AGENDA STAFF QUESTIONS Proposed amendments to the Staff Regulations Report
FINANCE ACT, EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE ACT, Explanatory notes to the provisions of the Finance Act, 2011
 FINANCE ACT, 2011 - EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE ACT, 2011 CIRCULAR NO. 02/2012 [F. NO.142/01/2012-SO(TPL)], DATED 22-5-2012 Explanatory notes to the provisions of the Finance Act,
FINANCE ACT, 2011 - EXPLANATORY NOTES TO THE PROVISIONS OF THE FINANCE ACT, 2011 CIRCULAR NO. 02/2012 [F. NO.142/01/2012-SO(TPL)], DATED 22-5-2012 Explanatory notes to the provisions of the Finance Act,
The Finance Act, the finer aspects
 The Finance Act, 2018 - the finer aspects P a g e 1 The Finance Act, 2018 has been enacted and is operative from April 1, 2018. From live screening to the Finance Bill, 2018 till its enactment and thereafter,
The Finance Act, 2018 - the finer aspects P a g e 1 The Finance Act, 2018 has been enacted and is operative from April 1, 2018. From live screening to the Finance Bill, 2018 till its enactment and thereafter,
As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2016 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 29th February, 2016.
 1 Budget 2016-2017 Highlights for Non-Residents As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2016 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 29th February, 2016. The Indian Budget presented by the Finance Minister
1 Budget 2016-2017 Highlights for Non-Residents As proposed in The Finance Bill, 2016 introduced by Finance Minister of India on 29th February, 2016. The Indian Budget presented by the Finance Minister
13 Assessment of Various Entities
 13 Assessment of Various Entities 13.1 Assessment of Companies 13.1.1 Meaning of Company for purposes of income-tax: Under the Income-tax Act, 1961, the term company has a much wider meaning than what
13 Assessment of Various Entities 13.1 Assessment of Companies 13.1.1 Meaning of Company for purposes of income-tax: Under the Income-tax Act, 1961, the term company has a much wider meaning than what
MOCK TEST SOLUTION A.Y Total No. of Question 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages 20 Time Allowed 3 Hours Maximum Marks 100 MKG
![MOCK TEST SOLUTION A.Y Total No. of Question 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages 20 Time Allowed 3 Hours Maximum Marks 100 MKG MOCK TEST SOLUTION A.Y Total No. of Question 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages 20 Time Allowed 3 Hours Maximum Marks 100 MKG](/thumbs/73/68647623.jpg) MOCK TEST SOLUTION IPC (Intermediate) (Computation of Total Income And Tax Liability, Taxability of Gift, Advance Payment of Tax, Residential Status & Scope of Total Income, House Property, Agricultural
MOCK TEST SOLUTION IPC (Intermediate) (Computation of Total Income And Tax Liability, Taxability of Gift, Advance Payment of Tax, Residential Status & Scope of Total Income, House Property, Agricultural
2018 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MUNICIPAL FISCAL HEALTH U.S. Tax Reform and Its Impact on State and Local Government Finance Presented by Jane L.
 2018 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MUNICIPAL FISCAL HEALTH U.S. Tax Reform and Its Impact on State and Local Government Finance Presented by Jane L. Campbell ; Director NDC Washington Office National Development
2018 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON MUNICIPAL FISCAL HEALTH U.S. Tax Reform and Its Impact on State and Local Government Finance Presented by Jane L. Campbell ; Director NDC Washington Office National Development
FINANCE BILL He has proposed to revise the tax slabs upwards as under:
 FINANCE BILL - 2010 The 2 nd budget of the 2 nd UPA Government for the year 2010 2011 was presented by the finance minister on 26 th February 2010. The finance minister has attempted to balance his direct
FINANCE BILL - 2010 The 2 nd budget of the 2 nd UPA Government for the year 2010 2011 was presented by the finance minister on 26 th February 2010. The finance minister has attempted to balance his direct
Setting up in Denmark
 Setting up in Denmark 6. Taxation The Danish tax system for individuals rests on the global taxation principle. The principle holds that the income of individuals and companies with full tax liability
Setting up in Denmark 6. Taxation The Danish tax system for individuals rests on the global taxation principle. The principle holds that the income of individuals and companies with full tax liability
IGP-CS Basic Concept M.Test 1 CA Vivek Gaba
 IGP-CS Basic Concept M.Test 1 CA Vivek Gaba 1. Power to impose income tax on agriculture income is with a) Central government b) State government c) Partly with central government and partly with state
IGP-CS Basic Concept M.Test 1 CA Vivek Gaba 1. Power to impose income tax on agriculture income is with a) Central government b) State government c) Partly with central government and partly with state
Paper 7 Direct Taxation
 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 Hours Full Marks: 100
Paper 7 Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7 Direct Taxation Time Allowed: 3 Hours Full Marks: 100
SUNIL CHOPRA & CO. Chartered Accountants
 1 SUNIL CHOPRA & CO. Chartered Accountants 3, 1 st Floor, Mandar, 193, Turner Road, Bandra (W), Mumbai 400050 Tel: 022-26515394 / 95, Fax: 26515438 Email: sccoca@gmail.com INTERIM UNION BUDGET 2019-20
1 SUNIL CHOPRA & CO. Chartered Accountants 3, 1 st Floor, Mandar, 193, Turner Road, Bandra (W), Mumbai 400050 Tel: 022-26515394 / 95, Fax: 26515438 Email: sccoca@gmail.com INTERIM UNION BUDGET 2019-20
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES
 COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 26.01.2006 COM(2006) 22 final REPORT FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 26.01.2006 COM(2006) 22 final REPORT FROM THE COMMISSION TO THE COUNCIL, THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT, THE EUROPEAN ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COMMITTEE AND THE COMMITTEE
UNDERSTANDING-- TAXATION SYSTEM
 UNDERSTANDING-- TAXATION SYSTEM TO UNDERSTAND TAXATION SYSTEM IN TOTALITY ONE HAS TO UNDERSTAND ALL OF THE FOLLOWING The Core 1 3 5 8 7 1. Act 2. Rules 3. Notifications 4. Circulars The outer effects affecting
UNDERSTANDING-- TAXATION SYSTEM TO UNDERSTAND TAXATION SYSTEM IN TOTALITY ONE HAS TO UNDERSTAND ALL OF THE FOLLOWING The Core 1 3 5 8 7 1. Act 2. Rules 3. Notifications 4. Circulars The outer effects affecting
Dr. BashirAhmad Joo. Human Resource Development Center University of Kashmir. The Business School University Of Kashmir.
 Management of Tax Liability for Salaried Individuals Presentation By Dr. BashirAhmad Joo Professor The Business School University Of Kashmir 0n 11 th March, 2017 Human Resource Development Center University
Management of Tax Liability for Salaried Individuals Presentation By Dr. BashirAhmad Joo Professor The Business School University Of Kashmir 0n 11 th March, 2017 Human Resource Development Center University
FOREWORD. Jersey. Services provided by member firms include:
 2016/17 FOREWORD A country's tax regime is always a key factor for any business considering moving into new markets. What is the corporate tax rate? Are there any incentives for overseas businesses? Are
2016/17 FOREWORD A country's tax regime is always a key factor for any business considering moving into new markets. What is the corporate tax rate? Are there any incentives for overseas businesses? Are
CHAPTER 7 PERCEPTION OF TAX PROFESSIONALS REGARDING INCOME TAX SYSTEM IN INDIA
 CHAPTER 7 PERCEPTION OF TAX PROFESSIONALS REGARDING INCOME TAX SYSTEM IN INDIA Tax professionals play an important role in the implementation of income tax law of the country. They help the taxpayers in
CHAPTER 7 PERCEPTION OF TAX PROFESSIONALS REGARDING INCOME TAX SYSTEM IN INDIA Tax professionals play an important role in the implementation of income tax law of the country. They help the taxpayers in
Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2018
 FISCAL FACT No. 581 Mar. 2018 Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2018 Amir El-Sibaie Analyst Key Findings In 2015, OECD countries relied heavily on consumption taxes, such as the value-added tax,
FISCAL FACT No. 581 Mar. 2018 Sources of Government Revenue in the OECD, 2018 Amir El-Sibaie Analyst Key Findings In 2015, OECD countries relied heavily on consumption taxes, such as the value-added tax,
FOREWORD. There is a dearth of job opportunities in India. In order to augment the job opportunities a national multi-skill
 FOREWORD The much anticipated Budget 2014 has been delivered amid an environment of price rise and huge expectations from the government. The people of India have decisively voted for a change. Slow decision
FOREWORD The much anticipated Budget 2014 has been delivered amid an environment of price rise and huge expectations from the government. The people of India have decisively voted for a change. Slow decision
FOREWORD. Isle of Man
 FOREWORD A country's tax regime is always a key factor for any business considering moving into new markets. What is the corporate tax rate? Are there any incentives for overseas businesses? Are there
FOREWORD A country's tax regime is always a key factor for any business considering moving into new markets. What is the corporate tax rate? Are there any incentives for overseas businesses? Are there
UCM 54 INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE - I Unit-1 Introduction to Income Tax Act 1961 Type:20% Theory 80% Problem Question & Answers
 UCM 54 INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE - I Unit-1 Introduction to Income Tax Act 1961 Type:20% Theory 80% Problem Question & Answers PART A 1. What is assessment year? (April 2014, 2013, 2012) ASSESSMENT YEAR
UCM 54 INCOME TAX LAW & PRACTICE - I Unit-1 Introduction to Income Tax Act 1961 Type:20% Theory 80% Problem Question & Answers PART A 1. What is assessment year? (April 2014, 2013, 2012) ASSESSMENT YEAR
Salary Income Tax Slab Rates In Pakistan
 Salary Income Tax Slab Rates 2012-13 In Pakistan In this article we will discuss only about AOP and BOI income tax slab rates. Sponsored Links THAT TIME I EARNED INCOME FROM SALARIES. THAN AFTER I AM (2)
Salary Income Tax Slab Rates 2012-13 In Pakistan In this article we will discuss only about AOP and BOI income tax slab rates. Sponsored Links THAT TIME I EARNED INCOME FROM SALARIES. THAN AFTER I AM (2)
1
 TAX & LEGAL & GENERAL INFORMATION A. Taxation on investing in Mutual Funds As per the taxation laws in force as at the date of this Scheme Information Document and the enactment of Finance Bill 2008,,the
TAX & LEGAL & GENERAL INFORMATION A. Taxation on investing in Mutual Funds As per the taxation laws in force as at the date of this Scheme Information Document and the enactment of Finance Bill 2008,,the
CHANGES IN INCOME TAX BY UNION BUDGET 2017
 CHANGES IN INCOME TAX BY UNION BUDGET 2017 CA SOHRABH JINDAL The Hon ble Finance Minister has announced the Union Budget 2017 on 1-2-2017. There are various changes in Law related to Income Tax. I have
CHANGES IN INCOME TAX BY UNION BUDGET 2017 CA SOHRABH JINDAL The Hon ble Finance Minister has announced the Union Budget 2017 on 1-2-2017. There are various changes in Law related to Income Tax. I have
LESSON 4 INCOME UNDER THE HEAD SALARIES - I
 LESSON 4 INCOME UNDER THE HEAD SALARIES - I Dr. Gurminder Kaur STRUCTURE 4.0 Introduction 4.1 Objectives 4.2 Heads of Income 4.3 Meaning of salary 4.4 Incomes forming part of Salary - I 4.4.1. Basic Salary
LESSON 4 INCOME UNDER THE HEAD SALARIES - I Dr. Gurminder Kaur STRUCTURE 4.0 Introduction 4.1 Objectives 4.2 Heads of Income 4.3 Meaning of salary 4.4 Incomes forming part of Salary - I 4.4.1. Basic Salary
The Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition of Tax Act, 2015
 The Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition of Tax Act, 2015 - An Overview National Tax Convention 2015 Western India Regional Council Hitesh D. Gajaria 4 July 2015 0 Contents
The Black Money (Undisclosed Foreign Income and Assets) and Imposition of Tax Act, 2015 - An Overview National Tax Convention 2015 Western India Regional Council Hitesh D. Gajaria 4 July 2015 0 Contents
VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH]
![VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH] VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH]](/thumbs/72/67119637.jpg) VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH] 1 BACK GROUND In his Budget Speech on 29 th February, 2016, the Finance Minister has listed 9 objectives for his tax proposals. One of the objectives relates to
VOLUNTARY DISCLOSURE SCHEME [CA P N SHAH] 1 BACK GROUND In his Budget Speech on 29 th February, 2016, the Finance Minister has listed 9 objectives for his tax proposals. One of the objectives relates to
Tax background paper. National Reform Summit John Daley, Grattan Institute August 2015
 Tax background paper National Reform Summit John Daley, Grattan Institute August 215 Summary Budget repair should include some tax increases Australia has small government by international standards Using
Tax background paper National Reform Summit John Daley, Grattan Institute August 215 Summary Budget repair should include some tax increases Australia has small government by international standards Using
Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX
 Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX HOW TO COMPUTE TAX PAYABLE Once the net taxable income is computed, the next step is to compute the final tax payable. The final tax payable is computed as follows: (1) Taxable
Unit 11: COMPUTATION OF TAX HOW TO COMPUTE TAX PAYABLE Once the net taxable income is computed, the next step is to compute the final tax payable. The final tax payable is computed as follows: (1) Taxable
Indian Taxation System for Banking & SSC - GK Notes in PDF
 Indian Taxation System for Banking & SSC - GK Notes in PDF Appearing for Government Exams? If yes then you must be aware that the General Knowledge Section is an integral part of all the govt. exams. If
Indian Taxation System for Banking & SSC - GK Notes in PDF Appearing for Government Exams? If yes then you must be aware that the General Knowledge Section is an integral part of all the govt. exams. If
Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights
 Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights Bansi S. Mehta & Co. All the following amendment are made effective from Assessment Years 2016-17, unless specifically mentioned otherwise. I - Residential Status,
Finance Bill, 2015 Direct Tax Highlights Bansi S. Mehta & Co. All the following amendment are made effective from Assessment Years 2016-17, unless specifically mentioned otherwise. I - Residential Status,
THE FINANCE BILL, 2011
 Bill No. 8-F of 2011 THE FINANCE BILL, 2011 (AS PASSED BY THE HOUSES OF PARLIAMENT LOK SABHA ON 22ND MARCH, 2011 RAJYA SABHA ON 24TH MARCH, 2011) ASSENTED TO ON 8TH APRIL, 2011 ACT NO. 8 OF 2011 Bill No.
Bill No. 8-F of 2011 THE FINANCE BILL, 2011 (AS PASSED BY THE HOUSES OF PARLIAMENT LOK SABHA ON 22ND MARCH, 2011 RAJYA SABHA ON 24TH MARCH, 2011) ASSENTED TO ON 8TH APRIL, 2011 ACT NO. 8 OF 2011 Bill No.
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia takes part in some of the work of the OECD (agreement of 28th October 1961).
 I 1 Pursuant to article 1 of the Convention signed in Paris on 14th December 1960, and which came into force on 30th September 1961, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) shall
I 1 Pursuant to article 1 of the Convention signed in Paris on 14th December 1960, and which came into force on 30th September 1961, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) shall
TAX POLICY CENTER BRIEFING BOOK. Background. Q. What are the sources of revenue for the federal government?
 What are the sources of revenue for the federal government? FEDERAL BUDGET 1/4 Q. What are the sources of revenue for the federal government? A. About 48 percent of federal revenue comes from individual
What are the sources of revenue for the federal government? FEDERAL BUDGET 1/4 Q. What are the sources of revenue for the federal government? A. About 48 percent of federal revenue comes from individual
Indicator B3 How much public and private investment in education is there?
 Education at a Glance 2014 OECD indicators 2014 Education at a Glance 2014: OECD Indicators For more information on Education at a Glance 2014 and to access the full set of Indicators, visit www.oecd.org/edu/eag.htm.
Education at a Glance 2014 OECD indicators 2014 Education at a Glance 2014: OECD Indicators For more information on Education at a Glance 2014 and to access the full set of Indicators, visit www.oecd.org/edu/eag.htm.
FOREWORD. Cayman Islands
 2015/16 FOREWORD A country's tax regime is always a key factor for any business considering moving into new markets. What is the corporate tax rate? Are there any incentives for overseas businesses? Are
2015/16 FOREWORD A country's tax regime is always a key factor for any business considering moving into new markets. What is the corporate tax rate? Are there any incentives for overseas businesses? Are
The regional analyses
 The regional analyses EU & EFTA On average, in the EU & EFTA region, the case study company has a Total Tax Rate of 41.1%, made 13.1 tax payments and took 179 hours to comply with its tax obligations in
The regional analyses EU & EFTA On average, in the EU & EFTA region, the case study company has a Total Tax Rate of 41.1%, made 13.1 tax payments and took 179 hours to comply with its tax obligations in
FIN623 Online Quiz#2..Lecture# 1 to 15 Solved By. BY sadia ali
 FIN623 Online Quiz#2..Lecture# 1 to 15 Solved By Question # 2 of 15 ( Start time: 12:33:31 AM ) Total Marks: 1 Senior citizen-age 60 years & above where taxable income not exceeding tax liability reduced
FIN623 Online Quiz#2..Lecture# 1 to 15 Solved By Question # 2 of 15 ( Start time: 12:33:31 AM ) Total Marks: 1 Senior citizen-age 60 years & above where taxable income not exceeding tax liability reduced
MTP_ Intermediate _Syllabus 2012_Dec2016_Set 1 Paper 7- Direct Taxation
 Paper 7- Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7- Direct Taxation Full Marks : 100 Time allowed: 3 hours
Paper 7- Direct Taxation Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 7- Direct Taxation Full Marks : 100 Time allowed: 3 hours
Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2009 NPOs, Unincorporated Bodies, Financial Intermediaries, Rates of Taxes & TDS
 Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2009 NPOs, Unincorporated Bodies, Financial Intermediaries, Rates of Taxes & TDS Gautam Nayak Chartered Accountant BCAS Seminar 29 th August 2009 Rates of Taxes Substantial increase
Direct Taxes Code Bill, 2009 NPOs, Unincorporated Bodies, Financial Intermediaries, Rates of Taxes & TDS Gautam Nayak Chartered Accountant BCAS Seminar 29 th August 2009 Rates of Taxes Substantial increase
A BUDGET FOR A Y From the desk of - B.L. Tulsian Advocate. R. Tulsian & Co LLP Chartered Accountants.
 A BUDGET A N A L Y S I S FOR A Y 2020-21 From the desk of - B.L. Tulsian Advocate R. Tulsian & Co LLP Chartered Accountants www.rtulsian.com Page2 Contents Amendment of Section 16... 3 Amendment to Section
A BUDGET A N A L Y S I S FOR A Y 2020-21 From the desk of - B.L. Tulsian Advocate R. Tulsian & Co LLP Chartered Accountants www.rtulsian.com Page2 Contents Amendment of Section 16... 3 Amendment to Section
Lowest implicit tax rates on labour in Malta, on consumption in Spain and on capital in Lithuania
 STAT/13/68 29 April 2013 Taxation trends in the European Union The overall tax-to-gdp ratio in the EU27 up to 38.8% of GDP in 2011 Labour taxes remain major source of tax revenue The overall tax-to-gdp
STAT/13/68 29 April 2013 Taxation trends in the European Union The overall tax-to-gdp ratio in the EU27 up to 38.8% of GDP in 2011 Labour taxes remain major source of tax revenue The overall tax-to-gdp
Vinodh & Muthu. Tax Alert. Insight. Chartered Accountants. Country by Country Reporting & Master File
 Vinodh & Muthu Chartered Accountants Tax Alert Country by Country Reporting & Master File Insight The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development ( OECD ) report on Action 13 of Base Erosion
Vinodh & Muthu Chartered Accountants Tax Alert Country by Country Reporting & Master File Insight The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development ( OECD ) report on Action 13 of Base Erosion
2 (a) Municipal taxes paid by Mr. Hari `4,200 per annum (b) House insurance `1,000 (iii) He earned `1,00,000 in share speculation business and lost `1
 NEW COURSE INCOME TAX PAPER SECTION-A Marks: 60 Question No. 1 is compulsory. Candidates are also required to answer any Five questions from the remaining Six questions. In case, any candidate answers
NEW COURSE INCOME TAX PAPER SECTION-A Marks: 60 Question No. 1 is compulsory. Candidates are also required to answer any Five questions from the remaining Six questions. In case, any candidate answers
Romania. Structure and development of tax revenues. Romania. Table RO.1: Revenue (% of GDP)
 Structure and development of tax revenues Table RO.1: Revenue (% of GDP) 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 I. Indirect taxes 11.7 12.8 12.7 12.5 11.8 10.8 11.9 13.0 13.2 12.8 VAT 6.6 8.0
Structure and development of tax revenues Table RO.1: Revenue (% of GDP) 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 I. Indirect taxes 11.7 12.8 12.7 12.5 11.8 10.8 11.9 13.0 13.2 12.8 VAT 6.6 8.0
Major direct tax proposals in Finance Bill, 2017
 Major direct tax proposals in Finance Bill, 2017 Member firm Individual, HUF, BOI, AOP, AJP Tax Rates There is no change in the basic exemption limit for individuals/hufs. It is proposed to reduce the
Major direct tax proposals in Finance Bill, 2017 Member firm Individual, HUF, BOI, AOP, AJP Tax Rates There is no change in the basic exemption limit for individuals/hufs. It is proposed to reduce the
Budget Highlights
 Budget Highlights 2018-19 DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS Chartered Accountants 1 st Floor, Sapphire Business Centre, Above SBI Vadaj Branch, Usmanpura, Ashram Road, Ahmedabad-380013 Email: apcca@apcca.com Website:
Budget Highlights 2018-19 DIRECT TAX PROPOSALS Chartered Accountants 1 st Floor, Sapphire Business Centre, Above SBI Vadaj Branch, Usmanpura, Ashram Road, Ahmedabad-380013 Email: apcca@apcca.com Website:
