UNIT 4 INDIAN STOCK MARKET : ORGANISATION AND FUNCTIONING
|
|
|
- Juniper Whitehead
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT 4 INDIAN STOCK MARKET : ORGANISATION AND FUNCTIONING Indian Stock Market : Organisation and Functioning Objectives The objectives of this unit are to: distinguish between primary market and secondary market highlight various types of traded securities, market players and trading arrangements which exist in India to discuss organization and functioning of primary and secondary markets for various types of securities in India Structure 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Primary Markets Principal Steps of a Public Issue Eligibility for an IPO Rights Issue Private Placement SEBI Guidelines for IPO's 4.3 Secondary Markets 4.4 Stock Market in India Origin and Growth Role and Functions Membership, Organization and Management Trading System Stock Market Information System 4.5 Summary 4.6 Self-assessment Questions/Exercises 4.7 Further Readings 4.1 INTRODUCTION Market is a place where buyers and sellers meet and exchange products. This definition is universal and applies to all markets. In this course, we will discuss more about the market called capital market. It is a place, where capital of different types is exchanged. Often individuals, like you, are the lenders or the suppliers of capital. Companies and various other institutions are the borrowers or the receivers of capital. The market is organized or divided into different ways. At a very broad level, the market is divided into (a) Short-term Capital Market (money market) and (b) Longterm capital market (also, called stock market). Another way of classifying the market is (a) Institutional Market and (b) Direct Market. As an investor you can deal with the market in different ways. Let us understand the market from individual's perspective. If the surplus money you have can be spared only for a short period, you have to look for savings of short-duration. Since the amount available is fairly small in such cases, you have to look for some institutional support for such savings. In other words, individuals don't directly deal with the money market, which specialize in short-term capital. Often, individuals approach an institution for this purpose. You can save your short-term surplus in a bank deposit or a mutual fund, which offer money market schemes. If the surplus money you have can be spared for a long-term, you have to look for investments of longer duration. Again, you can go to an institution, which offers long- 5
2 Securities Market in India term products or you can directly participate in the market. That is, you can deposit your money in a long-term fixed deposit or invest in a mutual funds scheme or directly buy securities in the market. When you intend to deal with the market on your own, you can deal with the market in two ways. The markets are accordingly classified into primary and secondary market. Primary market is the one in which the company approaches investors to raise capital. They can approach for debt capital or equity capital or combination of both. Dealing in primary market is fairly simple today. Like fixed deposit opening, you have to take up an application form of the issue and deposit the amount after filling up the form. Brokers and sub-brokers will normally help you to get forms and guide you to fill up the forms. What is important is you have to make sure that investments fit with your objective. Here too, financial dailies and magazines publish analytical report on primary market issues for the help of small investors. After your submission of application forms and if the company accepts the same, you will get a certificate or credit in your depository. In the event of too many people applying for the offer, the company may reject some applications. In such cases, you will get refund of the money that you have invested initially. Since the price is fixed in primary market, there will be competition for good issues. The uncertainty of getting allotment forces many investors, who are directly willing to deal with the market, to turn into secondary market. It is a place where an investor sells to another investor. Since there are large number of sellers and buyers, the market is dynamic. Securities prices change depending on the demand and supply of the securities. Secondary market exists for different types of securities like debt, equity and others. Investment in secondary market has also become easy, thanks to developments in Information and Computing Technologies. You have to open an account with the members of any stock exchanges of your choice. The procedure to open an account is fairly simple and it is somewhat similar to opening a Savings Bank Account with your banker. You can place your buying and selling orders over phone and often you get immediate confirmation of your purchase or sale. Today, it is also possible for you to buy and sell securities through internet. In this Unit, we will discuss more on how the stock market is organized and how investors can transact in buying and selling of securities in the market. 4.2 PRIMARY MARKETS Primary market is the segment in which new issues are made whereas secondary market is the segment in which outstanding issues are traded. It is for this reason that the Primary Market is also called New Issues Market and the Secondary Market is called Stock Market. In the primary market, new issues May be made in three ways, namely, public issue, rights issue, and private placement. Public Issues involves sale of securities to members of public. Rights issue involves sale of securities to the existing shareholders/debenture holders. Private placement involves selling securities privately to a selected group of investors. In the primary market, equity shares, fully convertible debentures (FCD), partially convertible debentures (PCD), and nonconvertible debentures(ncd) are the securities commonly issued by non-government public limited companies. Government companies issue equity shares and bonds. Primary market has become very active in India after the abolition of Controller of Capital Issue. You can refer Unit I (Tables 1.1 to 1.3) to find out the level of activities in primary market during the last few years. 6 In the primary market, issues are made either 'at par' or `at premium'. Pricing the new Issues is regulated under `Guidelines on Capital Issues' or what are also known as "Guidelines for Disclosure and Investors Protection" issued by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SERI). The SEBI guidelines on Disclosure and Investor Protection is now available in the SEBI website, These are detailed guidelines covering all issues relating to capital offerings. Prior to the promulgation of the ordinance no.9 of 1992 by which the Capital Issues (Control) Act has been repealed, the pricing of the new issues was regulated under the Controllers of Capital Issues' (CO) pricing formula. All Issues by a new company has to be made at par and for existing companies the issue price should be justified as per Malegam Committee recommendations by
3 The earnings per share (EPS) for the last three years and comparison of preissue price to earnings (P/E) ratio to the P/E ratio of the Industry. Latest Net Asset Value, Minimum return on increased networth to maintain pre-issue EPS. A company may also raise finance from the international markets by issuing GDR's and ADR's Principal steps of a Public Issue A draft prospectus is prepared giving out details of the Company, promoters background, Management, terms of the issue, project details, modes of financing, past financial performance, projected profitability and others. Additionally a Venture Capital Firm has to file the details of the terms subject to which funds are to be raised in the proposed issue in a document called the `placement memorandum'. Some of the steps involved in a public issue are a) b) c) d) e) h) i) j) k) Appointment of underwriters: The underwriters are appointed who commit to shoulder the liability and subscribe to the shortfall in case the issue is undersubscribed. For this commitment they are entitled to a commission upto maximum of 2.5 % on the amount underwritten. Appointment of Bankers: Bankers along with their branch network act as the collecting agencies and process the funds procured during the public issue. The Banks provide temporary loans for the period between the issue date and the date the issue proceeds becomes available after allotment, which is referred to as a `bridge loan'. Appointment of Registrars: Registrars process the application forms, tabulate the amounts collected during the Issue and initiate the allotment procedures. Appointment of the brokers to the Issue: Recognized members of the Stock exchanges are appointed as brokers to the Issue for marketing the Issue. They are eligible for a maximum brokerage of 1.5%. Filing of prospectus with the Registrar of Companies: The draft prospectus along with the copies of the agreements entered into with the Lead Manager, Underwriters, Bankers, Registrars and Brokers to the issue is filed with the Registrar of Companies of the state where the registered office of the company is located. f) Printing and dispatch of Application forms: The prospectus and application forms are printed and dispatched to all the merchant bankers, underwriters, brokers to the issue. g) Filing of the initial listing application: A letter is sent to the Stock exchanges where the issue is proposed to be listed giving the details and stating the intent of getting the shares listed on the Exchange. Statutory announcement: An abridged version of the prospectus and the Issue start and close dates are published in major English dailies and vernacular newspapers. Processing of applications: After the close of the Public Issue all the application forms are scrutinized, tabulated and then shares are allotted against these applications. Establishing the liability of the underwriter: In case the Issue is ;lot fully subscribed to, then the liability for the subscription falls on the underwriters who have to subscribe to the shortfall, in case they have not procured the amount committed by them as per the Underwriting agreement. Allotment of shares: after the Issue is subscribed to the minimum level, the allotment procedure as prescribed by SERI is initiated. l) Listing of the Issue: The shares after having been allotted have to be listed compulsorily in the regional stock exchange and optionally at the other stock exchanges. Indian Stock Market : Organisation and Functioning 7
4 Securities Market in India Eligibility for an IPO An Indian Company is allowed to make an IPO if: 1) 2) The company has a track record of dividend paying capability for 3 out of the immediately preceding 5 years; A public financial institution or scheduled commercial bank has appraised the project to be financed through the proposed offer and the appraising agency participates in the financing of the project to the extent of at least 10% of the Project cost. Typically a new company has to compulsorily issue shares at par, while the companies with a track record can issue shares at a premium Rights Issue The rights Issue involves selling of securities to the existing shareholders in proportion to their current holding. When a company issues additional equity capital, it has to be offered in the first instance to the existing shareholders on a pro-rata basis as per Section 81 of the Companies Act, The shareholders may by a special resolution forfeit this right, partially or fully by a special resolution to enable the company to issue additional capital to the public or alternatively by passing a simple resolution and taking the permission of the Central Government. There is no restriction on pricing of rights Issues Private Placement A private placement results from the sale of securities by the company to one or few investors. The issuers are normally the listed public limited companies or closely held public or private limited companies which cannot access the primary market. The securities are placed normally with the Institutional investors, Mutual funds or other Financial Institutions. In a number of cases, Indian companies have also offered shares to promoters under this route. SEBI has issued a separate guideline for pricing of such preferential offers SEBI Guidelines for IPO s For complete details of SEBI guidelines on IPO, you have to visit where you can download the complete guideline on Disclosure and Investor Protection) Guidelines, The salient features of these guidelines are given below: Promoters should contribute a minimum of 20% of the total issued capital, if the company is an unlisted one. Promoter's contribution is subject to a lock-in period of 3 years. Net Offer to the General Public has to be at least 25% of the Total Issue size for listing on a Stock Exchange. Minimum of 50% of the Net offer to the Public has to be reserved for Investors applying for 10 or less than 10 marketable lots of shares. In an Issue of more than Rs. 100 crores the issuer is allowed to place the whole issue by book-building. There should be at-least 5 investors for every 1 lakh of equity offered. 6 Allotment has to be made within 30 days of the closure of the Public Issue and 42 days in case of a Rights Issue All the listing formalities for a Public Issue has to be completed within 70 days from the date of closure of the subscription list. Indian Development Financial Institutions and Mutual Funds can be allotted securities upto 75% of the Issue Amount.
5 Allotment to categories of FII's and NRI's/OCB's is upto a maximum of 24% which can be further extended to 30% by an application to the RBI - supported by a resolution passed in the General Meeting. 10% individual ceiling for each category a) Permanent employees b) Shareholding of the promoting companies Securities issued to the promoter, his group companies by way of firm allotment and reservation have a lock-in period of 3 years. However shares allotted to FII s and certain Indian and Multilateral Development Financial Institutions and Indian Mutual Funds are not subject to Lock-in periods. The minimum period for which a Public Issue has to be kept open is 3 working days and the maximum for which it can be kept open is 10 working days. The minimum period for a Rights Issue is 15 working days and the maximum is 60 working days. A public issue is effected if the issue is able to procure 90% of the Total issue size within 60 days from the date of earliest closure of the Public Issue. In case of over-subscription the company may have the right to retain the excess application money and allot shares more than the proposed Issue which is referred to as the `green-shoe' option. A Rights Issue has to procure 90% subscription in 60 days of the opening of the Issue. 4.3 SECONDARY MARKETS The secondary market is the segment in which outstanding issues are traded and thus provide liquidity. Investors, who seek both profitability and liquidity, need both primary and secondary markets. There is thus a direct and complementary interface between the primary and secondary markets. Secondary market exists both for shortterm (money market) securities and long-term securities. It exists for debt, equity and a variety of hybrid securities. While the secondary market activities in money market securities are conducted over phone or through market makers, the trading is more organized for long-term securities and conducted through stock exchanges. Buying and selling securities in secondary market is fairly simple. Investors have to open an account with a member of stock exchange and then place orders through the member. For an orderly functioning of market, a set of institutions is required. The role of institutions assumes importance in securities market because the market deals with high value financial assets. Institutions connected with securities markets are Stock Exchanges ( and Members of Stocks Exchanges (popularly called brokers), Clearing Corporation, Depository ( and Transfer Agents and Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) ( Technology has converted stock exchanges into a virtual institution. Earlier, there was an importance for the physical location of stock exchange because it was a place where brokers or their assistants negotiate the prices (outsiders can hear only some noise but brokers understand the meaning) and enter into transactions on behalf of their client-investors. Since the telecommunication was very poor in India, one or two stock exchanges have been opened up in every state to cater to the needs of the investors of the region. India is one of the few countries with a large number of stock exchanges. Thanks to development in telecommunication and information technology, the physical constraint was removed during the last few years. National Stock Exchange today has its presence everywhere in the country. Bombay Stock Exchange has also expanded its network. Many other stock exchanges are finding it difficult to compete with these two principal stock exchanges and trying to come together and create new business. This new development has improved transparency of operations and brought down the cost. Today, stockbrokers are operating from their office through computer network and investors can see the price at which the transactions are settled. Internet based stock braking ( or allows investors to enter into transactions by themselves without Indian Stock Market : Organisation and Functioning 9
6 Securities Market in India 10 contacting their brokers directly. Competition has brought down the brokerage from 2% to in India around 0.5% and today the brokerage rate in India is one of the lowest in the world. This transformation has taken place in a matter of few months. Members of stock exchanges, called stock brokers, are intermediary between buyers and sellers. Buying and selling securities through members of stock exchange is beneficial, legally and functionally. Entry of major institutions like ICICI, Kotak Mahindra, into brokerage services and development in technology including intenet based broking service have improved the quality of service. Many of these brokerage houses offer a number of facilities to the investors at no extra cost. Clearing corporation enables the members to settle the transactions entered among themselves on behalf of their client-investors. It operates something similar to cheque clearing service offered by RBI for the banks. Earlier when securities are traded in physical form, a large number of securities have to be exchanged between members and clearing corporation had a major work on this part. Today, after depository facility was introduced, the workload of the clearing corporations has come down significantly. Clearing corporation today facilitate the members to transfer (or receive) securities to (or from) depositories and also settle monetary part of the transactions. It is an institution exclusively serving the brokers. Depository service is another major development in the Indian stock market. It allows investors to hold securities in electronic form (like you are holding cash in your bank account) and transfers electronically when they sell the shares. The operation is fairly simple. Investors have to open a depository account with a member of depository service provider (we have two depository service providers in India - National Securities Depository Ltd and Central Depository Services (India) Limited). Investors can give physical securities that they are holding for cancellation (provided depository facility is available for the securities/company) and convert them in to electronic holding. A large number of companies have depository holding facility and SEBI has put it compulsory to trade certain stocks only under depository mode. When an investor apply new shares next time in the primary market, they can ask the issuer to credit the depository account in the event of successful allotment. Any new purchases in the secondary market can also be credited in the depository account. Investors will get periodical statement on their holding from the member with whom the depository account is maintained. Many depository participants allow the investors to see their account through Internet. There was some resistance from retail investors for this change but today everyone started seeing the benefit of this service. A significant part of volume traded today is settled through depository mode. Apart from holding the stocks electronically, there are other benefits from depository services.- There is no need to apply for transfer of shares after the purchase of shares. If an investor buys securities in physical form and desire to transfer the shares in her/his name, she/he has to fill-up the transfer deed, affix transfer fee (0.5% of market value of stock) and then send the same to transfer agent. There is a cost, time and uncertainty involved in the transfer. Under depository mode, the shares are transferred in a short period of time without any further action from your side. For more details about depository, visit one of the web sites ( or of depository service providers or the members of depository service providers. Transfer agents maintains the members register of the companies. On the instructions of the company, they transfer the shares from the existing members to new member. When an investor buys a share in a physical mode and intend to transfer the share in her/his name, she/he has to send the transfer deed along with share certificate to the Transfer Agent. There are many transfer agents like Karvy Consultants Ltd ( and MCS Ltd. After initial verification, they will place the shares received for transfer for the approval of company's Board. The shares are transferred in the name of investors after the approval of the Board and investor will receive communication to this effect along with share certificates from the Transfer Agent. Some companies perform this transfer of shares internally whereas many leading companies have outsourced this service by appointing one of these transfer agents. The process of verification and other formalities connected with transfer has been simplified after the introduction of depository services.
7 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates the Institutions and Intermediaries connected with the securities to protect the interest of investors, Particularly the small investors. SERI is a government sponsored but independent body. SEBI has prescribed detailed regulations and guidelines for various activities related to transactions of securities market (See Regulations are primarily intended to protect small investors. Despite strong resistance, SEBI is pushing several reforms connected with securities market. Some of the major achievements of SEBI so far are bringing transparency in the securities market operation, speeding up the technological progress and improving disclosure norms. SERI is struggling hard to prevent insider trading and price rigging. Since regulation is a complex task, it will take time to complete the process. Indian Stock Market : Organisation and Functioning Activity -1 i) Write brief note on a recent public issue of a company. The note may include the size of the issue, type of security offered, price, justification of premium, registrar, banker to issue, underwriter, etc.... ii) Visit any one or more of the web sites and describe your additional learning on the regulation of Primary and Secondary Markets STOCK MARKET IN INDIA From scattered and small beginnings in the 19 th Century, India ' s stock market has risen to great heights. By 1990, we had 19 Stock Exchanges in the country and by 2002 there were 23 Stock Exchanges as listed in the later sections of this unit. You might be interested in knowing more about the origin and the growth of stock market in India. What functions does it perform? What is the form of organization of stock exchanges in India? How are these administered? We shall, now, address to these and other questions Origin and Growth Organizations and institutions, whether they are economic, social or political, are products of historical events and exigencies. The events continually replace and/or reform the existing organizations, so as to make them relevant and operational in contemporary situations. It is, therefore, useful to briefly acquaint ourselves with the origin and growth of the stock market in India. Stock exchanges of India in a rudimentary form originated in 1800 and since that time have developed through six broad stages : The East India Company and few commercial banks floated shares sporadically, through a very small group of brokers. According to a newspaper in 1850, in Bombay during there were only half a dozen recognised brokers. The year 1850 marked a watershed. A wave of company flotations took over the market ; the number of brokers spurted to 60. The backbone of industrial growth and the resulting boom in share flotation was the legendary personality of the financial world, Premchand Roychand. 11
8 Securities Market in India 12 In 1860 the stock market created a unique history. The entire market was gripped by what is known as share mania. The American Civil War created cotton famine. Indian cotton manufacturers exploited this situation and exported large quantities of cotton. The resulting increase in export earnings opened opportunities for share investments. New companies started to come up. Excessive speculation and reckless buying became the order of the day. This mania lasted upto It marks the end of the first phase in the Indian stock exchange history because with the cessation of the Civil War, demand for Indian cotton slumped abruptly. The share became worthless pieces of paper. To be exact, on July 1, 1865 all shares ceased to exist because all time bargains which had matured could not be fulfilled : We find another distinct phase during The mania effect haunted the stock exchange of Bombay during these 25 years. Above everything else, it led to foundation of a regular market for securities. Since the market was established in Bombay, it soon became and still is the leading and the most organized stock exchange in India. A number of stock brokers who geared up themselves, set up a voluntary organization in 1887, called Native Share and Stockbrokers Association. The brokers drew up codes of conduct for brokerage business and mobilized private funds for industrial growth. It also mobilized funds for government securities (gilt edged securities), especially of the Bombay Port Trust and the Bombay Municipality. A similar organization was started at Ahmedabad in : Political developments gave a big fillip to share investment. The Swadeshi Movement led by Mahatma Gandhi encouraged the indigeneous trading and business class to start industrial enterprises. As a result, Calcutta became another major centre of share trading. The trading was prompted by the coal boom of Thus the third stock exchange was started by Calcutta stock brokers. During Inter-war years demand for industrial goods kept increasing due to British involvement in the World Wars. Existing enterprises in steel and cotton textiles, woolen textiles, tea and engineering goods expanded and new ventures were floated. Yet another stock exchange was started at Madras in The period can be considered as the period of development of the existing stock exchanges in India. In this period industrial development planning played the pivotal role of expanding the industrial and commercial base of the country. Two more stock exchanges were set up, at Hyderabad in 1943 and at Delhi in At the time of Independence seven stock exchanges were functioning located in the major cities of the country. Between 1946 and 1990, 12 more stock exchanges were set up trading the shares of 4843 additional listed companies. There are 23 stock exchanges in the country, 23 of them being regional ones with allocated areas. Three others set up in the reforms era, viz., National Stock Exchange (NSE), the Over the Counter Exchange of India Limited (OTCEI), and Interconnected Stock Exchange of India Limited (ISE) have mandate to nationwide trading network. The ISE is promoted by 15 regional stock exchanges in the country and has been set up at Mumbai. The ISE provides a member-broker of any of these stock exchanges an access into the national market segment, which would be in addition to the local trading segment available at present. The NSE and OCTEI, ISE and majority of the regional stock exchanges have adopted the Screen Based Trading System (SBTS) to provide automated and modern facilities for trading in a transparent, fair and open manner with access to investors across the country. 9,877 companies were listed on the stock exchanges as on 31 March 1999, and the market capitalization was 5,30,772 crore. The number of primary listed companies at various stock exchanges in India was 9,644 as on end of March, The market capitalisation at NSE was Rs. 6,36,861 crore by March The following are the names of the various stock exchanges in India The Bombay Stock Exchange The Ahmedabad Stock exchange Association Bangalore Stock Exchange The Calcutta Stock Exchange Association Cochin Stock Exchange
9 The Delhi Stock Exchange Association The Guwahati Stock Exchange The Hyderabad Stock Exchange Jaipur Stock Exchange Kanara Stock Exchange The Ludhiana Stock Exchange Association Madras stock Exchange Madhya Pradesh Stock Exchange The Magadh Stock Exchange Mangalore Stock Exchange Pune Stock Exchange Saurashtra Kutch Stock Exchange The Uttar Pradesh Stock Exchange Association Vadodara Stock Exchange Coimbatore Stock Exchange Over The Counter Exchange of India The National Stock Exchange of India inter-connected Stock Exchange of India Limited Role and Functions The history of stock exchanges in foreign countries as well as in India shows that the development of joint stock enterprise would never have reached its present stage but for the facilities which the stock exchanges provided for dealing in securities. Stock exchanges have a very important function to fulfil in the country's economy. In Union of India vs. Allied International Products Ltd (1971) 41 Comp Cas 127 (SC) : (1970) 3 SCC 5941], the Supreme Court of India has enunciated the role of the stock exchanges in these words: Indian Stock Market : Organisation and Functioning A Stock Exchange fulfils a vital function in the economic development of a nation: its main function is to `qualify' capital by enabling a person who has invested money in, say a factory or a railway, to convert it into cash by disposing off his shares in the enterprise to someone else. Investment in joint stock companies is attractive to the public, because the value of the shares is announced day after day in the stock exchanges, and shares quoted on the exchanges are capable of almost immediate conversion into money. In modern days a company stands little chance of inducing the public to subscribe to its capital, unless its shares are quoted in an approved stock exchange. All public companies are anxious to inform the investing public that the shares of the company will be quoted on the stock exchange. The stock exchange is really an essential pillar of the private sector corporate economy. It discharges three essential functions in the process of capital formation and in raising resources for the corporate sector. They are : First, the stock exchange provides a market place for purchase and sale of securities viz., shares, bonds, debentures, etc. It, therefore, ensures the free transferability of securities which is the essential basis for the joint stock enterprise system. The private sector economy cannot function without the assurance provided by the stock exchange to the owners of shares and bonds that they can be sold in the market at any time. At the same time those who wish to invest their surplus funds in securities for long-term capital appreciation or for speculative gain can also buy stocks of their choice in the market. 13
10 Securities Market in India 14 Secondly, the stock exchange provides the linkage between the savings in the household sector and the investment in corporate economy. It mobilizes savings, channelises them as securities into those enterprises which are favoured by the investors on the basis of such criteria as future growth prospects, good returns and appreciation of prevalence on the Indian scene of such interventionist factors as industrial licensing, provision of credit to private sector by public sector development banks, price controls and foreign exchange regulations. The stock exchanges discharge this function by laying down a number of regulations which have to be complied with while making public issues e.g. offering at least the prescribed percentage of capital of the public, keeping the subscription list open for a minimum period of three days, making provisions for receiving applications at least at the centres where there are recognised stock exchanges and allotting the shares against applications on a fair and unconditional basis with the weightage being given to the applications in lower categories, particularly those applying for shares worth Rs.500 or Rs.1,000, etc. Members of stock exchanges also assist in the floatation of new issues by acting as managing brokers/official broker of new issue. In that capacity, they, inter alia, try to sell these issues to investors spread all over the country. They also act as under-writers to new issues. In this way, the broker community provides an organic linkage between the primary and the secondary markets. Thirdly, by providing a market quotation of the prices of shares and bonds, a sort of collective judgement simultaneously reached by many buyers and sellers in the market-the stock exchanges serves the role of a barometer, not only of the state of health of individual companies, but also of the nation's economy as a whole. It is often not realised that changes in share prices are brought about by a complex set of factors, all operating on the markets simultaneously. Share values as a whole are subject to secular trends set by the economic progress of the nation, and governed by factors like general economic situation, financial and monetary policies, tax changes, political environment, international economic and financial developments, etc. These trends are influenced to some extent by periodical cycles of booms and depressions in the free market economies. As against these long-term trends, the day-to-day prices are influenced by another variety of factors notably, the buying or selling of major operators, the buying and selling of shares by the investment financial institutions such as the U.T.I. or L.I.C. which have in recent years emerged as the largest holders of corporate securities, speeches and pronouncements by ministers and other government spokesmen, statements by company chairmen at annual general meetings and reports of bonus issues or good dividends by companies, etc., while these factors, both long-term and short-term, act as macro influences on the corporate sector and the level of stock prices as a whole, there is also a set of micro influences relating to prospects of individual companies such as the reputation of the management, the state of industrial relations in the enterprises, the volume of retained earnings and the related prospects of capitalization of reserves, etc., which have a bearing on the level of prices. In the complex interplay of all these forces, which leads to day-to-day quotation of prices of all listed securities, speculation plays a crucial role. In the absence of speculative operations, every purchase by an investor has to be matched by a sale of the same security by an investor-seller, and this may lead to sharp fluctuation in prices. With speculative sale and purchases taking place continuously, actual sale and purchase by investors on a large scale are absorbed by the market with small changes in prices. There are always some professional operators who are hoping that the prices would rise. There are others predicting that prices will fall. Both these groups acting on their respective assumption buy or sell continuously in the market. Their operation helps to bring about an orderly adjustment of prices. Without these speculative operations, a stock exchange can become a very mechanical thing. However, excessive speculation endangers market equilibrium and must be discouraged through appropriate safeguards. The regulatory authorities should always take necessary precautionary measures to prevent and penalize excessive speculation and to discipline trading. A fact which needs to be emphasized is that the stock exchanges in India also serve the joint sector units as also to some extent public sector enterprises. There is substantial private participation in the share capital of a number of government companies such as Balmer Lawrie, Andrew Yule, Gujarat State Fertilizers
11 Corporation, Gujarat Narmada Fertilizers Corporation, State Bank of India, ICICI, etc. In recent times some of the Central public sector companies have gone in for public debentures through the stock exchanges. Also, there are some public sector companies like VSNL which have made their share capital open for public subscription. Another important function that the stock exchanges in India discharge is of providing a market for gilt-edged securities i.e. securities issued by the Central Government, State government, Municipalities, Improvement Trusts and other public bodies. These securities are automatically listed on the stock exchanges when they are issued and transactions in these take place regularly on the stock exchanges Membership, Organisation and Management By virtue of the century-old tradition, stock exchanges is a highly organized and smooth functioning network in the world. The membership of stock exchanges initially comprised of individuals and partnership firms. Later on companies were also allowed to become members. A number of financial institutions are now members of Indian stock exchanges. Over the years, stock exchanges have been organized in various forms. For example, while the Bombay Stock Exchange, Ahmedabad Stock Exchange and M.P. (Indore) Stock Exchange were organised as voluntary non-profit making association of persons, the Calcutta Stock Exchange, Delhi Stock Exchange, U.P. (Kanpur) Stock Exchange, Ludhiana Stock Exchange, Cochin Stock Exchange, Gauhati Stock Exchange, Jaipur Stock Exchange, and Kanara (Mangalore) Stock Exchange were organised as public limited companies. Quite a few others have been organised as companies limited by guarantee. The internal governance of every stock exchange rests in a Governing Board Comprising Members of the Board and Executive Director/President. Members of the Governing Board include brokers and non-brokers. Governing Bodies of stock exchanges also have government nominees. The Executive Director/President is expected to ensure strict compliance by all members of the exchange of rules/by laws, margin regulations and trading restriction, etc. Subject to the previous approval of SEBI, under the law, Governing Bodies of stock exchanges have wide powers to make bye-laws. Governing Bodies can admit, punish, censure and also expel any member, any partner, any remisier, and authorised clerk and employee. It has the power to adjudicate disputes. Above all, it has the power to make, amend, suspend and enforce rules, by-laws, regulations and supervise the entire functioning of a stock exchange Trading System Trading system differ from exchange to exchange. In the next few pages, the trading system followed by the National stock Exchange is described. Students desire to know more about the trading system of other exchanges in India as well as outside India can visit respective web sites of stock exchanges. NSE operates on the 'National Exchange for Automated Trading' (NEAT) system, a fully automated screen based trading system, which adopts the principle of an order driven market. NSE consciously opted in favour of an order driven system as opposed to a quote driven system. This has helped reduce jobbing spreads not only on NSE but in other exchanges as well, thus reducing transaction costs. Till the advent of NSE, an investor wanting to transact in a security not traded on the nearest exchange had to route orders through a series of correspondent brokers to the appropriate exchange. This resulted in a great deal of uncertainty and high transaction costs. NSE has made it possible for an investor to access the same market and order book, irrespective of location, at the same price and at the same cost. Market Types The NEAT system has four types of market. They are : Normal : All orders which are of regular lot size or multiples thereof are traded in the Normal Market. For shares which are traded in the compulsory dematerialised mode, the market lot is one share. Normal market consists of various book types wherein orders are segregated as Regular lot orders, Special Term orders, Negotiated Traded orders and Stop Loss orders depending on their order attributes. Indian Stock Market : Organisation and Functioning 15
12 Securities Market in India 16 Odd Lot Market : All orders whose order size is less than the regular lot size are traded in the odd-lot market. An order is called an odd lot order if the order size is less than regular lot size. These orders do not have any special terms attributes attached to them. In an odd-lot market, both the price and quantity of both the orders (buy and sell) should exactly match for the trade to take place. Currently the odd lot market facility is used for the Limited Physical Market as per the SEBI directives. Spot Market : Spot orders are similar to the normal market orders except that spot orders have different settlement periods vis-à-vis normal market. These orders do not have any special terms attributes attached to them. Currently the Spot Market is being used for the Automated Lending & Borrowing Mechanism (ALBM) session. Auction Market : In the Auction Market, auctions are initiated by the Exchange on behalf of trading members for settlement related reasons. There are 3 participants in this market : Initiator : The party who initiates the auction process is called an initiator. Competitor : The party who enters orders on the same side as of the initiator is called a Competitor. Solicitor : The party who enters orders on the opposite side as of the initiator is called a Solicitor. Order Books The NSE trading system provides complete flexibility to members in the kinds of orders that can be placed by them. Orders are first numbered and time-stamped on receipt and then immediately processed for potential match. Every order has a distinctive order number and a unique time stamp on it. If a match is not found, then the orders are stored in different `books'. Orders are stored in price-time priority in various books in the following sequence: - Best Price - Within Price, by time priority. Price priority means that if two orders are entered into the system, the order having the best price gets the higher priority. Time priority means if two orders having the same price are entered, the order that is entered first gets the higher priority. The Capital Market segment has following types of books: Regular Lot Book : The Regular Lot Book contains all regular lot orders that have none of the following attributes attached to them. - All or None (AON) - Minimum Fill (MF) - Stop Loss (SL) Special Terms Book : The Special Terms book contains all orders that have either of the following terms attached: - All or None (AON) - Minimum Fill (MF) (Note : Currently, special term orders i.e. AON and MF are not available on the system as per the SEBI directives. ) Negotiated Trade Book : The Negotiated. Trade book contains all negotiated order entries captured by the system before they have been matched against their counterparty trade entries. These entries are matched with identical counterparty entries only. It is to be noted that these entries contain a counterparty code in addition to other order details. Stop-Loss Book : Stop Loss orders are stored in this book till the trigger price specified in the order is reached or surpassed. When the trigger price is reached or surpassed, the order is released in the Regular lot book. The stop loss condition is met under the following circumstances:
13 SELL ORDER - A sell order in the Stop loss book gets triggered when the last traded price in the normal market reaches or falls below the trigger price of the order. BUY ORDER - A buy order in the Stop Loss book gets triggered when the last traded price in the normal market reaches or exceeds the trigger price of the order. Odd Lot Book : The Odd lot book contains all odd lot orders (orders with quantity less than marketable lot) in the system. The system attempts to match an active odd lot order against passive orders in the book. Cur r ently, pursuant to a SEBI directive, the Odd Lot Market is being used for orders which have a quantity less than or equal to 500 (Qty more than the market lot) for trading. This is referred as the Limited Physical Market (LPM). Spot Book : The Spot lot book contains all spot orders (orders having only the settlement period different) in the system. The system attempts to match an active spot lot order against the passive orders in the book. Currently the Spot Market book type is being used for conducting the Automated Lending & Borrowing Mechanism (ALBM) session. Auction Book : This book contains orders that are entered for all auctions. The matching process for auction orders in this book is initiated only at the end of the solicitor period. Order Matching Rules The best buy order is matched with the best sell order. An order may match partially with another order resulting in multiple trades. For order matching, the best buy order is the one with the highest price and the best sell order is the one with the lowest price. This is because the system views all buy orders available from the point of view of a seller and all sell orders from the point of view of the buyers in the market. So, of all buy orders available in the market at any point of time, a seller would obviously like to sell at the highest possible buy price that is offered. Hence, the best buy order is the order with the highest price and the best sell order is the order with the lowest price. Members can proactively enter orders in the system which will be displayed in the system till the full quantity is matched by one or more of counter-orders and result into trade(s) or is cancelled by the member. Alternatively, members may be reactive and put in orders that match with existing orders in the system. Orders lying unmatched in the system are `passive' orders and orders that come in to match the existing orders are called `active' orders. Orders are always matched at the passive order price. This ensures that the earlier orders get priority over the orders that come in later. Order Conditions A Trading Member can enter various types of orders depending upon his/her requirements. These conditions are broadly classified into three categories: time related conditions, price-related conditions and quantity related conditions. Time Conditions DAY - A Day order, as the name suggests, is an order which is valid for the day on which it is entered. If the order is not matched during the day, the order gets cancelled automatically at the end of the trading day. GTC - A Good Till Cancelled (GTC) order is an order that remains in the system until it is cancelled by the Trading Member. It will therefore be able to span trading days if it does not get matched. The maximum number of days a GTC order can remain in the system is notified by the Exchange from time to time. GTD - A Good Till Days/Date (GTD) order allows the Trading Member to specify the days/date up to which the order should stay in the system. At the end of this period the order will get flushed from the system. Each day/date counted is a calendar day and inclusive of holidays. The days/date counted are inclusive Indian Stock Market : Organisation and Functioning 17
14 Securities Market in India 18 of the day/date on which the order is placed. The maximum number of days a GTD order can remain in the system is notified by the Exchange from time to time. IOC - An Immediate or Cancel (IOC) order allows a Trading Member to buy or sell a security as soon as the order is released into the market, failing which the order will be removed from the market. Partial match is possible for the order, and the unmatched portion of the order is cancelled immediately. Price Conditions Limit Price/Order - An order which allows the price to be specified while entering the order into the system. Market Price/Order - An order to buy or sell securities at the best price obtainable at the time of entering the order. Stop Loss (SL) Price/Order - The one which allows the Trading Member to place an order which gets activated only when the market price of the relevant security reaches or crosses a threshold price. Until then the order does not enter the market. SELL ORDER A sell order in the Stop Loss book gets triggered when the last traded price in the normal market reaches or falls below the trigger price of the order. BUY ORDER A buy order in the Stop Loss book gets triggered when the last traded price in the normal market reaches or exceeds the trigger price of the order. e.g. If for stop loss buy order, the trigger is Rs , the limit price is Rs and the market (last traded) price is Rs , then this order is released into the system once the market price reaches or exceeds Rs This order is added to the regular lot book with time of triggering as the time stamp, as a limit order of Rs Quantity Conditions Disclosed Quantity (DQ)- An order with a DQ condition allows the Trading Member to disclose only a part of the order quantity to the market. For example, an order of 1000 with a disclosed quantity condition of 200 will mean that 200 is displayed to the market at a time. After this is traded, another 200 is automatically released and so on till the full order is executed. The Exchange may set a minimum disclosed quantity criteria from time to time. MF - Minimum Fill (MF) orders allow the Trading Member to specify the minimum quantity by which an order should be filled. For example, an order of 1000 units with minimum fill 200 will require that each trade be for at least 200 units. In other words, there will be a maximum of 5 trades of200 each or a single trade of The Exchange may lay down norms of MF from time to time. AON - All or None orders allow a Trading Member to impose the condition that only the full order should be matched against. This may be by way of multiple trades. If the full order is not matched it will stay in the books till matched or cancelled Stock Market Information System Stock exchange quotations and indices published in daily newspapers are the main source of information on stock exchange trades and turnover. Dailies like Economic Times, Financial Express, Business Standard, Business Line, Times of India and Hindustan Times publish daily quotations and indices. As for Bombay Stock Exchange quotations published in Economic Times, information on equity shares, starting from the first column, is presented in the following order: Company's name; previous day's closing price in brackets; all the daily traded prices as published by the BSE ; key financial parameters such as earnings per share (EPS), cash earnings per share (CPS), cash P/E (price to earnings ratio), return on net worth (RN W) and gross profit margin (GPM) etc. on different days; P/E ; and the high and low prices in the preceding 52 weeks.
CHAPTER 10 Financial Market
 CHAPTER 10 Financial Market A financial market refers to a market where the creation and exchange of financial assets (such as shares and debentures) takes place. Allocative Function of Financial Market
CHAPTER 10 Financial Market A financial market refers to a market where the creation and exchange of financial assets (such as shares and debentures) takes place. Allocative Function of Financial Market
UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS
 UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS Introduction : Financial Market is a market for creation and exchange of financial assets like share, bonds etc. It helps in mobilising savings and channelising them into the
UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS Introduction : Financial Market is a market for creation and exchange of financial assets like share, bonds etc. It helps in mobilising savings and channelising them into the
(a) Bonus/capitalisation issues which represent only book keeping entries.
 What are the Chief Functions of the New Issue Market? The main function of the New Issue Market is to facilitate the transfer of resources from savers to users. Conceptually, however, the New Issue Market
What are the Chief Functions of the New Issue Market? The main function of the New Issue Market is to facilitate the transfer of resources from savers to users. Conceptually, however, the New Issue Market
CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks
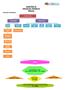 CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks Key Concepts in nutshell: CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL MARKET: It refers to the market which creates and exchanges financial assets. FUNCTIONS OF FINANICIAL
CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks Key Concepts in nutshell: CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL MARKET: It refers to the market which creates and exchanges financial assets. FUNCTIONS OF FINANICIAL
Chapter V Findings, Conclusion & Recommendations
 Chapter V Findings, Conclusion & Recommendations The Indian Stock Market has come a long way from the earlier days of out-cry system to the present day screen based and net based paperless trading system.
Chapter V Findings, Conclusion & Recommendations The Indian Stock Market has come a long way from the earlier days of out-cry system to the present day screen based and net based paperless trading system.
Terms and conditions
 Terms and conditions The cash segment A] Introduction This document contains important information regarding the terms and conditions, which apply to your E-Trading Account with R. Wadiwala Securities
Terms and conditions The cash segment A] Introduction This document contains important information regarding the terms and conditions, which apply to your E-Trading Account with R. Wadiwala Securities
REGULATORY FRAMEWORK GOVERNING INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS IN INDIA
 CHAPTER 4 REGULATORY FRAMEWORK GOVERNING INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS IN INDIA This chapter presents the regulatory framework governing the issuance of IPOs through public offer, book building and online route.
CHAPTER 4 REGULATORY FRAMEWORK GOVERNING INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS IN INDIA This chapter presents the regulatory framework governing the issuance of IPOs through public offer, book building and online route.
SEBI (ISSUE OF CAPITAL AND DISCLOSURE REQUIREMENTS) REGULATIONS, 2009 [Previously SEBI (Disclosure and Investors Protection) Guidelines 2000]
![SEBI (ISSUE OF CAPITAL AND DISCLOSURE REQUIREMENTS) REGULATIONS, 2009 [Previously SEBI (Disclosure and Investors Protection) Guidelines 2000] SEBI (ISSUE OF CAPITAL AND DISCLOSURE REQUIREMENTS) REGULATIONS, 2009 [Previously SEBI (Disclosure and Investors Protection) Guidelines 2000]](/thumbs/75/71507226.jpg) SEBI (ISSUE OF CAPITAL AND DISCLOSURE REQUIREMENTS) REGULATIONS, 2009 [Previously SEBI (Disclosure and Investors Protection) Guidelines 2000] Payel Jain Academy of Financial Services Pvt. Ltd PUBLIC OFFER-
SEBI (ISSUE OF CAPITAL AND DISCLOSURE REQUIREMENTS) REGULATIONS, 2009 [Previously SEBI (Disclosure and Investors Protection) Guidelines 2000] Payel Jain Academy of Financial Services Pvt. Ltd PUBLIC OFFER-
5. Enumerate the various penalties which can be imposed under SEBI Act, 1992 for various
 SL&C Page 1 STUDY I - GENESIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF REGULATORY FRAMEWORK 1. Briefly discuss the evolution, growth and functions of financial system in India. 2. Explain the role of securities market in economic
SL&C Page 1 STUDY I - GENESIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF REGULATORY FRAMEWORK 1. Briefly discuss the evolution, growth and functions of financial system in India. 2. Explain the role of securities market in economic
Section A (Short Answer Type Questions)
 B.Com. (Hons.) V Semester Paper Title: Paper Code: AS-2640 *(Prepared by Mr. Amit Manglani, Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce, GGV) Note: These model answers are a depiction of important points
B.Com. (Hons.) V Semester Paper Title: Paper Code: AS-2640 *(Prepared by Mr. Amit Manglani, Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce, GGV) Note: These model answers are a depiction of important points
Bonanza Portfolio Ltd
 Public Issue of Tax Free Secured Redeemable Non-Convertible Bonds issued by HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS In exercise of the powers conferred by item (h) of sub-clause (iv) of clause (15) of Section 10 of
Public Issue of Tax Free Secured Redeemable Non-Convertible Bonds issued by HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS In exercise of the powers conferred by item (h) of sub-clause (iv) of clause (15) of Section 10 of
FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) STOCK MARKET (PART-2)
 FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) STOCK MARKET (PART-2) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers! Welcome to the lecture series of financial market operations. Today we shall take up part 2 of the unit 3 rd. We
FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) STOCK MARKET (PART-2) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers! Welcome to the lecture series of financial market operations. Today we shall take up part 2 of the unit 3 rd. We
BSE SME Exchange - Presentation
 Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd. Bombay Stock Exchange Limited BSE SME Exchange - Presentation 6 th Feb 2012 About SME Industry About SME Industry Classification of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises 3 About
Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd. Bombay Stock Exchange Limited BSE SME Exchange - Presentation 6 th Feb 2012 About SME Industry About SME Industry Classification of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises 3 About
ISSUE STRUCTURE. The key common terms and conditions of the Bonds are as follows: COMMON TERMS FOR ALL SERIES OF THE BONDS
 ISSUE STRUCTURE The CBDT has, by the CBDT Notification, authorised our Company to raise the Bonds aggregating to ` 10,00,000 lakhs. Pursuant to the CBDT Notification and the Prospectus Tranche-1, our Company
ISSUE STRUCTURE The CBDT has, by the CBDT Notification, authorised our Company to raise the Bonds aggregating to ` 10,00,000 lakhs. Pursuant to the CBDT Notification and the Prospectus Tranche-1, our Company
Further, the Dividend income is tax free, if the company is liable to dividend distribution tax.
 FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) on RGESS Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme (RGESS) 1. What is RGESS? Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme (RGESS), is a tax saving scheme announced in the Union Budget
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) on RGESS Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme (RGESS) 1. What is RGESS? Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme (RGESS), is a tax saving scheme announced in the Union Budget
Trading Rules of Shenzhen Stock Exchange
 Disclaimer: This English translation of Trading Rules (2016) is for information purpose only. The SZSE does not guarantee its accuracy and reliability and accepts no liability resulting from any error
Disclaimer: This English translation of Trading Rules (2016) is for information purpose only. The SZSE does not guarantee its accuracy and reliability and accepts no liability resulting from any error
CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD
 CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD PART I: ELIGIBILITY REQUIREMENTS Reference date 4. Unless otherwise provided in this Chapter, an issuer making an initial public offer of specified securities
CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD PART I: ELIGIBILITY REQUIREMENTS Reference date 4. Unless otherwise provided in this Chapter, an issuer making an initial public offer of specified securities
A STUDY ON THE BUSINESS GROWTH OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE FROM TO
 A STUDY ON THE BUSINESS GROWTH OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE FROM 2001-02 TO 2014-15 DR.G.AMUDHA* & DR.V.KANNAN* *ASSISTANT PROFESSORS OF ST.JOSEPH S INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT, TRICHIRAPPALLI-02. ABSTRACT:
A STUDY ON THE BUSINESS GROWTH OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE FROM 2001-02 TO 2014-15 DR.G.AMUDHA* & DR.V.KANNAN* *ASSISTANT PROFESSORS OF ST.JOSEPH S INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT, TRICHIRAPPALLI-02. ABSTRACT:
SEBI Board Meeting. The SEBI Board met in Mumbai today and took the following decisions:
 SEBI Board Meeting PR No.20/2018 The SEBI Board met in Mumbai today and took the following decisions: I. Review of SEBI (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeovers) Regulations, 2011 The Board has
SEBI Board Meeting PR No.20/2018 The SEBI Board met in Mumbai today and took the following decisions: I. Review of SEBI (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeovers) Regulations, 2011 The Board has
International Capital Market
 J B GUPTA CLASSES 98184931932, drjaibhagwan@gmail.com, www.jbguptaclasses.com Copyright: Dr JB Gupta 16 International Capital Market Global Depository Receipts American Depository Receipts External Commercial
J B GUPTA CLASSES 98184931932, drjaibhagwan@gmail.com, www.jbguptaclasses.com Copyright: Dr JB Gupta 16 International Capital Market Global Depository Receipts American Depository Receipts External Commercial
Financial Market in India. Samir K Mahajan
 Financial Market in India Financial Market Financial Market is a mechanism which enables participants to deal in financial claims. It s a platform to in which lender and borrower of funds interact to determine
Financial Market in India Financial Market Financial Market is a mechanism which enables participants to deal in financial claims. It s a platform to in which lender and borrower of funds interact to determine
SYNOPSIS PAPERLESS TRADING IN INDIAN STOCK MARKETS
 SYNOPSIS PAPERLESS TRADING IN INDIAN STOCK MARKETS Research Scholar: Joseph George Supervisor: Dr M Thomas John Branch: Commerce INTRODUCTION: The stock exchange is an organized market for the purchase
SYNOPSIS PAPERLESS TRADING IN INDIAN STOCK MARKETS Research Scholar: Joseph George Supervisor: Dr M Thomas John Branch: Commerce INTRODUCTION: The stock exchange is an organized market for the purchase
CIRCULAR CIR/IMD/DF/55/2016
 CIRCULAR CIR/IMD/DF/55/2016 May 11, 2016 To All Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs) All Parties to InvITs All Stock Exchanges All Merchant Bankers Dear Sir / Madam, Sub: Guidelines for public issue
CIRCULAR CIR/IMD/DF/55/2016 May 11, 2016 To All Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs) All Parties to InvITs All Stock Exchanges All Merchant Bankers Dear Sir / Madam, Sub: Guidelines for public issue
New Platform for SMEs in India to Provide a Tax Efficient Exit for Investors
 Real Estate Laws Foreign entities cannot engage in real estate business in India. The only permissible transaction involving real estate is where the non-resident party carries out development of a minimum
Real Estate Laws Foreign entities cannot engage in real estate business in India. The only permissible transaction involving real estate is where the non-resident party carries out development of a minimum
Public Issue of India Infoline Finance Ltd. NCD
 P a g e 1 Q1. What is the nature and size of issue? Issue Related FAQs Ans: Public Issue of Non-convertible Debentures (NCDs) in the nature of Sub-ordinated debt of face value of Rs. 1,000/- per bond with
P a g e 1 Q1. What is the nature and size of issue? Issue Related FAQs Ans: Public Issue of Non-convertible Debentures (NCDs) in the nature of Sub-ordinated debt of face value of Rs. 1,000/- per bond with
FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) CAPITAL MARKET (PART-1)
 FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) CAPITAL MARKET (PART-1) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers, Welcome to the lecture series on Financial Market Operations. Today we are going to take up Unit -3 and we are
FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) CAPITAL MARKET (PART-1) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers, Welcome to the lecture series on Financial Market Operations. Today we are going to take up Unit -3 and we are
General Information Document for Investing in Public Issues
 Last updated on, 2014 AMSONS APPARELS LIMITED (CIN: U74899DL2003PLC122266) Our Company was originally incorporated at New Delhi as Amsons Apparels Private Limited on 16 th September, 2003 under the provisions
Last updated on, 2014 AMSONS APPARELS LIMITED (CIN: U74899DL2003PLC122266) Our Company was originally incorporated at New Delhi as Amsons Apparels Private Limited on 16 th September, 2003 under the provisions
The SEBI ICDR and Listing Regulations checklists
 The SEBI ICDR and Listing Regulations checklists February 2018 KPMG.com/in Foreword Introduction Planning for an IPO is like conducting a symphony it has several facets, each intrinsically linked to the
The SEBI ICDR and Listing Regulations checklists February 2018 KPMG.com/in Foreword Introduction Planning for an IPO is like conducting a symphony it has several facets, each intrinsically linked to the
Indian Depository Receipts
 Historical Background Indian Depository Receipts The world has became global village due to the technology advancement and as a result the Securities Market have become international. Companies that previously
Historical Background Indian Depository Receipts The world has became global village due to the technology advancement and as a result the Securities Market have become international. Companies that previously
A monthly publication from South Indian Bank. To kindle interest in economic affairs... To empower the student community...
 To kindle interest in economic affairs... To empower the student community... Open YAccess www.sib.co.in ho2099@sib.co.in A monthly publication from South Indian Bank SIB STUDENTS ECONOMIC FORUM Experience
To kindle interest in economic affairs... To empower the student community... Open YAccess www.sib.co.in ho2099@sib.co.in A monthly publication from South Indian Bank SIB STUDENTS ECONOMIC FORUM Experience
CONTENTS. Procedure and Conditions for listing of securities on WDM 7. Criteria for listing on the WDM segment 8
 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1 2. Exchange Operations 3 Capital Market Segment 3 Futures & Options Segment 3 Wholesale Debt Market Segment 4 3. Listing Of Securities on WDM Segment 7 Procedure and Conditions
CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1 2. Exchange Operations 3 Capital Market Segment 3 Futures & Options Segment 3 Wholesale Debt Market Segment 4 3. Listing Of Securities on WDM Segment 7 Procedure and Conditions
SEBI in its recent board meeting introduced some dynamic proposals in the
 2015] SEBI S NEW INITIATIVES : TIMELINE REDUCTION OF PUBLIC-ISSUE 31 [2015] 131 SCL 31 (Mag.) SEBI S NEW INITIATIVES : TIMELINE REDUCTION OF PUBLIC-ISSUE, START-UP LISTING, RECLASSIFICATION OF PROMOTERS
2015] SEBI S NEW INITIATIVES : TIMELINE REDUCTION OF PUBLIC-ISSUE 31 [2015] 131 SCL 31 (Mag.) SEBI S NEW INITIATIVES : TIMELINE REDUCTION OF PUBLIC-ISSUE, START-UP LISTING, RECLASSIFICATION OF PROMOTERS
RURAL ELECTRIFICATION CORPORATION LIMITED (A Government of India Undertaking)
 RURAL ELECTRIFICATION CORPORATION LIMITED (A Government of India Undertaking) HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS Interest from these Bonds shall not be included in total income of any person as per provisions
RURAL ELECTRIFICATION CORPORATION LIMITED (A Government of India Undertaking) HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS Interest from these Bonds shall not be included in total income of any person as per provisions
CAIIB Risk Management Module C TREASURY MANAGEMENT
 CAIIB Risk Management Module C TREASURY MANAGEMENT It is necessary to understand and appreciate the three distinct roles Treasury is expected to play: a. Liquidity Management: Treasury is responsible for
CAIIB Risk Management Module C TREASURY MANAGEMENT It is necessary to understand and appreciate the three distinct roles Treasury is expected to play: a. Liquidity Management: Treasury is responsible for
Order Execution Policy financial instruments
 Order Execution Policy financial instruments Applicable from 3 January 2018 DB0172UK 2017.09 This policy sets out the principles that we follow when executing orders for our retail and professional clients
Order Execution Policy financial instruments Applicable from 3 January 2018 DB0172UK 2017.09 This policy sets out the principles that we follow when executing orders for our retail and professional clients
 7 FORMATION OF JOINT STOCK COMPANY You have learnt that formation of a sole proprietorship organisation or a partnership firm does not involve much formalities so much so that even the registration is
7 FORMATION OF JOINT STOCK COMPANY You have learnt that formation of a sole proprietorship organisation or a partnership firm does not involve much formalities so much so that even the registration is
HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LIMITED
 HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LIMITED CIN No: L27020MH1958PLC011238 Registered Office: Century Bhavan, 3rd Floor, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, Mumbai- 400 030 Email: hil.investors@adityabirla.com website:www.hindalco.com
HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LIMITED CIN No: L27020MH1958PLC011238 Registered Office: Century Bhavan, 3rd Floor, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, Mumbai- 400 030 Email: hil.investors@adityabirla.com website:www.hindalco.com
Business Proposal SKUNG GROUP
 Business Proposal SKUNG GROUP This Proposal is a brief write up of our Areas of expertise, Working model, Revenue sharing model, Trading platform, Marketing support, compliances etc. Dear Sir/Madam, We
Business Proposal SKUNG GROUP This Proposal is a brief write up of our Areas of expertise, Working model, Revenue sharing model, Trading platform, Marketing support, compliances etc. Dear Sir/Madam, We
Shriram City Union Finance Limited. Issue Related FAQs
 Shriram City Union Finance Limited Issue Related FAQs Q1. What is the Nature & Size of the Issue? Ans: Public Issue by Shriram City Union Finance Limited, ( Company or Issuer ) of Secured Non- Convertible
Shriram City Union Finance Limited Issue Related FAQs Q1. What is the Nature & Size of the Issue? Ans: Public Issue by Shriram City Union Finance Limited, ( Company or Issuer ) of Secured Non- Convertible
New Issue Market-An Overview
 Chapter-Ill New Issue Market-An Overview Chapter-m New Issue Market-An Overview In this chapter, an attempt has been made to discuss the functions of new issue market, the instruments of issue, functionaries
Chapter-Ill New Issue Market-An Overview Chapter-m New Issue Market-An Overview In this chapter, an attempt has been made to discuss the functions of new issue market, the instruments of issue, functionaries
Standard Chartered Indian Depository Receipts Frequently Asked Questions: Table of Contents
 Standard Chartered Indian Depository Receipts Frequently Asked Questions: Table of Contents The IDR Facility... 1 Rights of IDR Holders... 2 Ownership and Trading of IDRs... 3 IDR Fees... 4 Other Questions
Standard Chartered Indian Depository Receipts Frequently Asked Questions: Table of Contents The IDR Facility... 1 Rights of IDR Holders... 2 Ownership and Trading of IDRs... 3 IDR Fees... 4 Other Questions
I N M A R K E T T E R M S
 I N M A R K E T T E R M S After hours Means before the opening auction call period and after the end of the closing auction call period and any extensions thereto and any other time that the equities market
I N M A R K E T T E R M S After hours Means before the opening auction call period and after the end of the closing auction call period and any extensions thereto and any other time that the equities market
Mutual Fund MUTUAL FUND MEANING
 MUTUAL FUND MEANING means a fund established in the form of a trust to raise monies through the sale of units to the public or a section of the public under one or more schemes for investing in securities
MUTUAL FUND MEANING means a fund established in the form of a trust to raise monies through the sale of units to the public or a section of the public under one or more schemes for investing in securities
An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market. Manendra Singh*
 Article 222 KNOWLEDGE RESOURCE [Vol. 38 An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market Manendra Singh* The growth of financial sector in India at present is
Article 222 KNOWLEDGE RESOURCE [Vol. 38 An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market Manendra Singh* The growth of financial sector in India at present is
Disclosure of Interests under the Securities and Futures Ordinance
 Disclosure of Interests under the Securities and Futures Ordinance Hong Kong Shanghai Beijing Yangon www.charltonslaw.com TABLE OF CONTENTS A. DISCLOSURE BY SUBSTANTIAL SHAREHOLDERS... 1 1. SUBSTANTIAL
Disclosure of Interests under the Securities and Futures Ordinance Hong Kong Shanghai Beijing Yangon www.charltonslaw.com TABLE OF CONTENTS A. DISCLOSURE BY SUBSTANTIAL SHAREHOLDERS... 1 1. SUBSTANTIAL
Negotiated Dealing System (NDS)
 Negotiated Dealing System (NDS) Till 2002, the Government securities market was mainly a telephone market. Buyers and sellers traded over telephone and submitted physical Subsidiary General Ledger (SGL)
Negotiated Dealing System (NDS) Till 2002, the Government securities market was mainly a telephone market. Buyers and sellers traded over telephone and submitted physical Subsidiary General Ledger (SGL)
A Wholly Owned Government Company
 PUBLIC ISSUE OF TAX FREE SECURED REDEEMABLE NON CONVERTIBLE DEBENTURES of face value of ` 1,000 each having tax benefits under section 10(15) (iv) (h) Income Tax Act, 1961, as amended for an amount aggregating
PUBLIC ISSUE OF TAX FREE SECURED REDEEMABLE NON CONVERTIBLE DEBENTURES of face value of ` 1,000 each having tax benefits under section 10(15) (iv) (h) Income Tax Act, 1961, as amended for an amount aggregating
PART V - MINIMUM OFFER TO PUBLIC, RESERVATIONS, ETC.
 PART V - MINIMUM OFFER TO PUBLIC, RESERVATIONS, ETC. Minimum offer to public. 41. 84 [ The minimum net offer to the public shall be subject to the provisions of clause (b) of sub-rule (2) of rule 19 of
PART V - MINIMUM OFFER TO PUBLIC, RESERVATIONS, ETC. Minimum offer to public. 41. 84 [ The minimum net offer to the public shall be subject to the provisions of clause (b) of sub-rule (2) of rule 19 of
The DFSA Rulebook. General Module (GEN) GEN/VER40/08-17
 The DFSA Rulebook General Module (GEN) GEN/VER40/08-17 Contents The contents of this module are divided into the following chapters, sections and appendices: 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 Application... 1 2
The DFSA Rulebook General Module (GEN) GEN/VER40/08-17 Contents The contents of this module are divided into the following chapters, sections and appendices: 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 Application... 1 2
ARTICLES OF ASSOCIATION OF SPECIAL CLOSED-END TYPE REAL ESTATE INVESTMENT COMPANY INVL BALTIC REAL ESTATE
 ARTICLES OF ASSOCIATION OF SPECIAL CLOSED-END TYPE REAL ESTATE INVESTMENT COMPANY INVL BALTIC REAL ESTATE The Articles of Association were signed in Vilnius on [ ] [ ] [ ] Authorised person: [ ] [ ] 1
ARTICLES OF ASSOCIATION OF SPECIAL CLOSED-END TYPE REAL ESTATE INVESTMENT COMPANY INVL BALTIC REAL ESTATE The Articles of Association were signed in Vilnius on [ ] [ ] [ ] Authorised person: [ ] [ ] 1
1. What are the various types of financial markets? 2. What is meant by the Secondary Market?
 MARKET BASIC 1. What are the various types of financial markets? The financial markets can broadly be divided into money and capital market. Money Market: Money market is a market for debt securities that
MARKET BASIC 1. What are the various types of financial markets? The financial markets can broadly be divided into money and capital market. Money Market: Money market is a market for debt securities that
RURAL ELECTRIFICATION CORPORATION LIMITED (A Government of India Undertaking) HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS
 RURAL ELECTRIFICATION CORPORATION LIMITED (A Government of India Undertaking) HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS Interest from these Bonds shall not be included in total income of any person as per provisions
RURAL ELECTRIFICATION CORPORATION LIMITED (A Government of India Undertaking) HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS Interest from these Bonds shall not be included in total income of any person as per provisions
Central Depository Services (India) Limited
 Central Depository Services (India) Limited Convenient Dependable Secure COMMUNIQUÉ TO DEPOSITORY PARTICIPANTS CDSL/OPS/DP/POLCY/4232 February 06, 2014 RAJIV GANDHI EQUITY SAVINGS SCHEME (RGESS), 2013
Central Depository Services (India) Limited Convenient Dependable Secure COMMUNIQUÉ TO DEPOSITORY PARTICIPANTS CDSL/OPS/DP/POLCY/4232 February 06, 2014 RAJIV GANDHI EQUITY SAVINGS SCHEME (RGESS), 2013
Dematerialization of Shares & Retail Investors in India - A Study
 Volume-5, Issue-3, June-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 393-400 Dematerialization of Shares & Retail Investors in India - A Study Dr. Surendar G Assistant
Volume-5, Issue-3, June-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 393-400 Dematerialization of Shares & Retail Investors in India - A Study Dr. Surendar G Assistant
JM Financial Credit Solutions Limite d
 JM FINANCIAL CREDIT SOLUTIONS LIMITED INVESTMENT RATIONALE The issue offers yields ranging from 9.24% to 9.74% depending up on the Category of Investor and the option applied for. The NCDs have been rated
JM FINANCIAL CREDIT SOLUTIONS LIMITED INVESTMENT RATIONALE The issue offers yields ranging from 9.24% to 9.74% depending up on the Category of Investor and the option applied for. The NCDs have been rated
Financial Framework in India
 Financial Framework in India For Finance related courses and CSE Main Optional Paper on Finance 10x10 Learning TM 1 10x10 Learning TM 2 Laws applicable to the Financial Sector : Act = 15. Rules = 10. Regulations
Financial Framework in India For Finance related courses and CSE Main Optional Paper on Finance 10x10 Learning TM 1 10x10 Learning TM 2 Laws applicable to the Financial Sector : Act = 15. Rules = 10. Regulations
Rolling Settlement in Stock Exchange
 Rolling Settlement in Stock Exchange INTRODUCTION This article aims to understand the concept of rolling settlement in stock exchanges in some depth. It aims to focus on the following aspects- Meaning,
Rolling Settlement in Stock Exchange INTRODUCTION This article aims to understand the concept of rolling settlement in stock exchanges in some depth. It aims to focus on the following aspects- Meaning,
A Primer Quick Reference User Manual
 A Primer Quick Reference User Manual [December 2010] INDEX Sr. No. Details Page No. 1 About BSE 3 2 3 4 5 6 Genesis of the StAR MF platform 4 Benefits for the stakeholders 4 StAR MF platform 5 Application
A Primer Quick Reference User Manual [December 2010] INDEX Sr. No. Details Page No. 1 About BSE 3 2 3 4 5 6 Genesis of the StAR MF platform 4 Benefits for the stakeholders 4 StAR MF platform 5 Application
: ` per share. IPO opens during : Sept 28 Oct 04, 2011 Book Running Lead Manager : Atherstone Capital Markets Ltd.
 I P O N O T E Onelife Capital Advisors Ltd. September 27, 2011 Price Band : `100-110 per share Minimum Bid Lot Size : 50 Equity Shares Maximum Bid Lot Size : 1800 Equity Shares IPO opens during : Sept
I P O N O T E Onelife Capital Advisors Ltd. September 27, 2011 Price Band : `100-110 per share Minimum Bid Lot Size : 50 Equity Shares Maximum Bid Lot Size : 1800 Equity Shares IPO opens during : Sept
Appendix 2. In this appendix underlining indicates new text and striking through indicates deleted text.
 Appendix 2 In this appendix underlining indicates new text and striking through indicates deleted text. This text includes the amendments resulting from CP 103 on Insurance Activities which come in to
Appendix 2 In this appendix underlining indicates new text and striking through indicates deleted text. This text includes the amendments resulting from CP 103 on Insurance Activities which come in to
LUXEMBOURG STOCK EXCHANGE MARKETS TRADING MANUAL
 LUXEMBOURG STOCK EXCHANGE MARKETS TRADING MANUAL Published 2017 Entry into force 03 January 2018 Terms beginning with a capital letter shall have the same meaning as those defined in Part 0 of the Rules
LUXEMBOURG STOCK EXCHANGE MARKETS TRADING MANUAL Published 2017 Entry into force 03 January 2018 Terms beginning with a capital letter shall have the same meaning as those defined in Part 0 of the Rules
Synopsis. Introduction. IPO Unlisted Companies. PIPEs & QIPs Listed Companies. Issues - Insider Trading and Takeover Regulations.
 Public offering of securities India Synopsis Introduction IPO Unlisted Companies General conditions for doing an IPO in India IPO Process Issues PIPEs & QIPs Listed Companies Overview of Investments &
Public offering of securities India Synopsis Introduction IPO Unlisted Companies General conditions for doing an IPO in India IPO Process Issues PIPEs & QIPs Listed Companies Overview of Investments &
Research Analyst With Sebi
 How To Get Registered As A Research Analyst With Sebi A Definitive Guide by CS Kruti Gogri www.cskruti.com Disclaimer I have made every effort to ensure that the information provided in this guide is obtained
How To Get Registered As A Research Analyst With Sebi A Definitive Guide by CS Kruti Gogri www.cskruti.com Disclaimer I have made every effort to ensure that the information provided in this guide is obtained
Y V Reddy: Developing debt markets in India review and prospects
 Y V Reddy: Developing debt markets in India review and prospects Remarks by Dr Y V Reddy, Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, at a meeting of Central Bank Governors of Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean,
Y V Reddy: Developing debt markets in India review and prospects Remarks by Dr Y V Reddy, Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, at a meeting of Central Bank Governors of Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean,
Listing Requirements Secondary Listing- Exclusively Listed on Regional Stock Exchange
 Listing Requirements Secondary Listing- Exclusively Listed on Regional Stock Exchange Criteria for Secondary Listing The applicant Company whose securities that are proposed for secondary listing shall
Listing Requirements Secondary Listing- Exclusively Listed on Regional Stock Exchange Criteria for Secondary Listing The applicant Company whose securities that are proposed for secondary listing shall
CHAPTER: 5 SOURCES OF DOMESTIC EQUITY FUND, VARIOUS ROUTES OF CAPITAL ISSUES FOR INDIAN COMPANIES AND CHANGE IN THEIR REGULATIONS
 CHAPTER: 5 SOURCES OF DOMESTIC EQUITY FUND, VARIOUS ROUTES OF CAPITAL ISSUES FOR INDIAN COMPANIES AND CHANGE IN THEIR REGULATIONS 5,1 SOURCES OF DOMESTIC EQUITY CAPITAL 5.1.1 Equity shares 5.1.1.1 Equity
CHAPTER: 5 SOURCES OF DOMESTIC EQUITY FUND, VARIOUS ROUTES OF CAPITAL ISSUES FOR INDIAN COMPANIES AND CHANGE IN THEIR REGULATIONS 5,1 SOURCES OF DOMESTIC EQUITY CAPITAL 5.1.1 Equity shares 5.1.1.1 Equity
ISTANBUL STOCK EXCHANGE STOCK MARKET REGULATION
 Official Journal No: 559 From Capital Markets Board: Purpose ISTANBUL STOCK EXCHANGE STOCK MARKET REGULATION Article - The purpose of this Regulation is to set forth the rules and operation principles
Official Journal No: 559 From Capital Markets Board: Purpose ISTANBUL STOCK EXCHANGE STOCK MARKET REGULATION Article - The purpose of this Regulation is to set forth the rules and operation principles
INDIA INFRASTRUCTURE FINANCE COMPANY LIMITED A wholly owned Government of India Undertaking
 HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS INDIA INFRASTRUCTURE FINANCE COMPANY LIMITED A wholly owned Government of India Undertaking Interest from these Bonds do not form part of total income as per provisions of Section
HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS INDIA INFRASTRUCTURE FINANCE COMPANY LIMITED A wholly owned Government of India Undertaking Interest from these Bonds do not form part of total income as per provisions of Section
Home >> FAQs - Display Date: 17/10/2014
 http://www.rbi.org.in/commonman/english/scripts/faqs.aspx?id=711#23 Home >> FAQs - Display Date: 17/10/2014 Government Securities Market in India A Primer 1. What is a Government Security? 1.1 A Government
http://www.rbi.org.in/commonman/english/scripts/faqs.aspx?id=711#23 Home >> FAQs - Display Date: 17/10/2014 Government Securities Market in India A Primer 1. What is a Government Security? 1.1 A Government
Visit us at 2/7/17
 1 Margin collected by the Stock Exchange from the members having unduly large outstanding position or the margin levied on volatile scrips based on adhoc basis keeping in view the risk perspective. Adjustable
1 Margin collected by the Stock Exchange from the members having unduly large outstanding position or the margin levied on volatile scrips based on adhoc basis keeping in view the risk perspective. Adjustable
CHAPTER- III AN OVERVIEW OF INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET
 CHAPTER- III AN OVERVIEW OF INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET 3.1 Introduction Capital Market is one of the significant aspects of every financial market. Hence, it is necessary to study its correct meaning. Broadly
CHAPTER- III AN OVERVIEW OF INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET 3.1 Introduction Capital Market is one of the significant aspects of every financial market. Hence, it is necessary to study its correct meaning. Broadly
Listings, registration, dealings and settlement
 1. Listings The Company currently has a primary listing of Shares on the SGX-ST, which it intends to maintain alongside its proposed dual primary listing of Shares on the Stock Exchange. Application has
1. Listings The Company currently has a primary listing of Shares on the SGX-ST, which it intends to maintain alongside its proposed dual primary listing of Shares on the Stock Exchange. Application has
THE GAZETTE OF INDIA EXTRAORDINARY. PART II - SECTION 3 - SUB-SECTION (ii) PUBLISHED BY AUTHORITY NOTIFICATION. MUMBAI, THE 16th DAY OF MAY, 1996
 THE GAZETTE OF INDIA EXTRAORDINARY PART II - SECTION 3 - SUB-SECTION (ii) PUBLISHED BY AUTHORITY NOTIFICATION MUMBAI, THE 16th DAY OF MAY, 1996 SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA (DEPOSITORIES AND
THE GAZETTE OF INDIA EXTRAORDINARY PART II - SECTION 3 - SUB-SECTION (ii) PUBLISHED BY AUTHORITY NOTIFICATION MUMBAI, THE 16th DAY OF MAY, 1996 SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA (DEPOSITORIES AND
`IREDA Public Issue of Tax Free Bonds
 HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS INDIAN RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT AGENCY LIMITED (A GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ENTERPRISE) Interest from these Bonds do not form part of total income as per provisions of Section
HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS INDIAN RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT AGENCY LIMITED (A GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ENTERPRISE) Interest from these Bonds do not form part of total income as per provisions of Section
E T E R N I T Y : L AW A P P R I S E
 E T E R N I T Y : L AW A P P R I S E * P r i v a t e C i r c u l a t i o n O n l y RBI: Foreign Exchange Management (Remittance of Assets) Regulations RBI: Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations
E T E R N I T Y : L AW A P P R I S E * P r i v a t e C i r c u l a t i o n O n l y RBI: Foreign Exchange Management (Remittance of Assets) Regulations RBI: Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations
BSE Trading Rules July 2012 TRADING RULES FOR EQUITY SECURITIES JULY 2012
 TRADING RULES FOR EQUITY SECURITIES JULY 2012 i TABLE OF CONTENTS Page No: CHAPTER 1... 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 TRADING BOARDS... 1 1.2 TRADING AND SYSTEM OPERATION SESSIONS... 2 1.2.1 Pre-trading Session...
TRADING RULES FOR EQUITY SECURITIES JULY 2012 i TABLE OF CONTENTS Page No: CHAPTER 1... 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 TRADING BOARDS... 1 1.2 TRADING AND SYSTEM OPERATION SESSIONS... 2 1.2.1 Pre-trading Session...
Witnesseth. Page 1 of 24
 Model Listing Agreement for listing of Indian Depository Receipts issued by the issuing companies whose securities market regulator is signatory to the Multilateral Memorandum of Understanding (MMOU) of
Model Listing Agreement for listing of Indian Depository Receipts issued by the issuing companies whose securities market regulator is signatory to the Multilateral Memorandum of Understanding (MMOU) of
Chapter-10 Financial Markets
 Chapter-10 Financial Markets Contents:- 1. MeaningofFinancialMarkets. 2. ParticipantsofFinancialMarkets. 3. FunctionsofFinancialMarkets. 4. ClassificationofFinancialMarkets. i) MoneyMarket a) Meaning b)
Chapter-10 Financial Markets Contents:- 1. MeaningofFinancialMarkets. 2. ParticipantsofFinancialMarkets. 3. FunctionsofFinancialMarkets. 4. ClassificationofFinancialMarkets. i) MoneyMarket a) Meaning b)
Qualified Foreign Investors entry in the Indian Capital Markets
 Qualified Foreign Investors entry in the Indian Capital Markets "The Indian Government has recently permitted Foreign Investors termed as Qualified Foreign Investors ( QFIs ) who meet prescribed Know Your
Qualified Foreign Investors entry in the Indian Capital Markets "The Indian Government has recently permitted Foreign Investors termed as Qualified Foreign Investors ( QFIs ) who meet prescribed Know Your
IFLR India Awards "Team of the Year" in the Indian Investment Banks category. Primary and Secondary Issuance Process
 IFLR India Awards 2011 - "Team of the Year" in the Indian Investment Banks category Primary and Secondary Issuance Process May 2012 Table of Contents Section 1 Section 2 Capital Markets Overview Trends
IFLR India Awards 2011 - "Team of the Year" in the Indian Investment Banks category Primary and Secondary Issuance Process May 2012 Table of Contents Section 1 Section 2 Capital Markets Overview Trends
Securities and Exchange Board of India (Delisting of Equity Shares) Regulations, 2009
 Ministry : Securities and Exchange Board of India Notification No : LAD-NRO/GN/2008-2009/09/165992 Date : 10.06.2009 Securities and Exchange Board of India (Delisting of Equity Shares) Regulations, 2009
Ministry : Securities and Exchange Board of India Notification No : LAD-NRO/GN/2008-2009/09/165992 Date : 10.06.2009 Securities and Exchange Board of India (Delisting of Equity Shares) Regulations, 2009
CIRCULAR. CFD/DIL3/CIR/2017/21 March 10, All Listed Entities who have listed their equity and convertibles All the Recognized Stock Exchanges
 CIRCULAR CFD/DIL3/CIR/2017/21 March 10, 2017 All Listed Entities who have listed their equity and convertibles All the Recognized Stock Exchanges Dear Sir/Madam, Sub: Schemes of Arrangement by Listed Entities
CIRCULAR CFD/DIL3/CIR/2017/21 March 10, 2017 All Listed Entities who have listed their equity and convertibles All the Recognized Stock Exchanges Dear Sir/Madam, Sub: Schemes of Arrangement by Listed Entities
CIRCULAR. CIR/DDHS/P/ 121/2018 Date: August 16, 2018
 CIRCULAR CIR/DDHS/P/ 121/2018 Date: August 16, 2018 To Recognized Stock Exchanges (other than commodity stock exchanges) Self-Certified Syndicate Banks, Depositories Merchant Bankers, Stock Brokers Registrars
CIRCULAR CIR/DDHS/P/ 121/2018 Date: August 16, 2018 To Recognized Stock Exchanges (other than commodity stock exchanges) Self-Certified Syndicate Banks, Depositories Merchant Bankers, Stock Brokers Registrars
INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS (IPOs) REGULATIONS & PROCESS
 INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS (IPOs) REGULATIONS & PROCESS Options for Raising Funds Fund Raising Options Debt Equity Hybrid In India From Banks & FIs Public issue of Bonds/Debentures IPO FPO Rights Issue Various
INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS (IPOs) REGULATIONS & PROCESS Options for Raising Funds Fund Raising Options Debt Equity Hybrid In India From Banks & FIs Public issue of Bonds/Debentures IPO FPO Rights Issue Various
Notice pursuant to Section 110 of the Companies Act, 2013
 Notice pursuant to Section 110 of the Companies Act, 2013 1 Reliance Home Finance Limited CIN: L67190MH2008PLC183216 Registered Office: Reliance Centre, 6 th Floor, South Wing, Off Western Express Highway
Notice pursuant to Section 110 of the Companies Act, 2013 1 Reliance Home Finance Limited CIN: L67190MH2008PLC183216 Registered Office: Reliance Centre, 6 th Floor, South Wing, Off Western Express Highway
CHAPTER V FOREIGN INVESTMENT AND EXTERNAL COMMERCIAL BORROWING
 CHAPTER V FOREIGN INVESTMENT AND EXTERNAL COMMERCIAL BORROWING Chapter V is conveniently divided into four sections. Section A deals with foreign investment. Foreign investment comprises of two components
CHAPTER V FOREIGN INVESTMENT AND EXTERNAL COMMERCIAL BORROWING Chapter V is conveniently divided into four sections. Section A deals with foreign investment. Foreign investment comprises of two components
SEBI & ITS FUNCTIONS
 SEBI & ITS FUNCTIONS Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was set up in 1988 to regulate the functions of securities market. SEBI promotes orderly and healthy development in the stock market but initially
SEBI & ITS FUNCTIONS Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was set up in 1988 to regulate the functions of securities market. SEBI promotes orderly and healthy development in the stock market but initially
2. Alteration of Capital Clause in the
 HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LIMITED CIN No: L27020MH1958PLC011238 Registered Office: Century Bhavan, 3 rd Floor, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli Mumbai 400 030 E Mail : hil.investors@adityabirla.com website : www.hindalco.com
HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LIMITED CIN No: L27020MH1958PLC011238 Registered Office: Century Bhavan, 3 rd Floor, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli Mumbai 400 030 E Mail : hil.investors@adityabirla.com website : www.hindalco.com
Exposure Draft SECRETARIAL STANDARD DIVIDEND
 Exposure Draft SECRETARIAL STANDARD ON DIVIDEND The following is the text of the Secretarial Standard-3 (SS-3) on Dividend, issued by the Council of the Institute of Company Secretaries of India. Adherence
Exposure Draft SECRETARIAL STANDARD ON DIVIDEND The following is the text of the Secretarial Standard-3 (SS-3) on Dividend, issued by the Council of the Institute of Company Secretaries of India. Adherence
CHAPTER-V FINANCIAL MARKETS IN INDIA
 CHAPTER-V FINANCIAL MARKETS IN INDIA Financial markets in India comprise the money market Government securities market, capital market, insurance market, and the foreign exchange market. Recently, the
CHAPTER-V FINANCIAL MARKETS IN INDIA Financial markets in India comprise the money market Government securities market, capital market, insurance market, and the foreign exchange market. Recently, the
MAHINDRA ASSET MANAGEMENT COMPANY PVT. LTD. (INVESTMENT MANAGER TO MAHINDRA MUTUAL FUND) INVESTMENT VALUATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES
 MAHINDRA ASSET MANAGEMENT COMPANY PVT. LTD. (INVESTMENT MANAGER TO MAHINDRA MUTUAL FUND) INVESTMENT VALUATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES 1 INDEX Sr. No: Particular Page No(s) I Introduction 3 II Purpose 3 III
MAHINDRA ASSET MANAGEMENT COMPANY PVT. LTD. (INVESTMENT MANAGER TO MAHINDRA MUTUAL FUND) INVESTMENT VALUATION POLICY AND PROCEDURES 1 INDEX Sr. No: Particular Page No(s) I Introduction 3 II Purpose 3 III
SHARES 101. Differences Between Stocks And Shares. What Is A Stock? Five Things To Know About Shares. What Is A Stock Market?
 SHARES 101 Differences Between Stocks And Shares None. There are always questions being asked about the differences between stocks and shares. The bottom line is that stocks and shares are the same thing,
SHARES 101 Differences Between Stocks And Shares None. There are always questions being asked about the differences between stocks and shares. The bottom line is that stocks and shares are the same thing,
SME Access to Market Based Finance
 SME Access to Market Based Finance BSE- Exchange with Maximum Listed Companies Worldwide Historic brand and an iconic listing franchise Key highlights n Oldest stock exchange in Asia, established in 1875
SME Access to Market Based Finance BSE- Exchange with Maximum Listed Companies Worldwide Historic brand and an iconic listing franchise Key highlights n Oldest stock exchange in Asia, established in 1875
SALIENT FEATURES OF SEBI (FOREIGN PORTFOLIO INVESTORS) REGULATIONS, 2014
 SALIENT FEATURES OF SEBI (FOREIGN PORTFOLIO INVESTORS) REGULATIONS, 2014 The Securities and Exchange Board of India has made regulations to put in place a framework for registration and procedures with
SALIENT FEATURES OF SEBI (FOREIGN PORTFOLIO INVESTORS) REGULATIONS, 2014 The Securities and Exchange Board of India has made regulations to put in place a framework for registration and procedures with
NISM Series IX: Merchant Banking Certification Examination. Test Objectives
 NISM Series IX: Merchant Banking Certification Examination Test Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to the Capital Market 1.1 Introduction to the Indian Capital Market 1.1.1 Explain the Capital market structure
NISM Series IX: Merchant Banking Certification Examination Test Objectives Chapter 1: Introduction to the Capital Market 1.1 Introduction to the Indian Capital Market 1.1.1 Explain the Capital market structure
Company Highlights. Strengths. Strategies. Financials Performance
 PUBLIC ISSUE OF TAX FREE, SECURED, REDEEMABLE, NON CONVERTIBLE BONDS of face value of ` 1,000 each, having tax benefits under section 10(15) (iv) (h) Income Tax Act, 1961, as amended for an amount aggregating
PUBLIC ISSUE OF TAX FREE, SECURED, REDEEMABLE, NON CONVERTIBLE BONDS of face value of ` 1,000 each, having tax benefits under section 10(15) (iv) (h) Income Tax Act, 1961, as amended for an amount aggregating
OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR PURCHASE AND SALE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
 Securities Department October 2014 OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR PURCHASE AND SALE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS Str 1 / 16 The Management Board of OTP Banka d.d. Hrvatska, at Domovinskog rata 3, 23 000 Zadar, www.otpbanka.hr
Securities Department October 2014 OPERATING PROCEDURE FOR PURCHASE AND SALE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS Str 1 / 16 The Management Board of OTP Banka d.d. Hrvatska, at Domovinskog rata 3, 23 000 Zadar, www.otpbanka.hr
UNIT 2 : ISSUE, FORFEITURE AND RE-ISSUE OF SHARES
 COMPANY ACCOUNTS 10.17 UNIT 2 : ISSUE, FORFEITURE AND RE-ISSUE OF SHARES LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this unit, you will be able to: Appreciate various types of shares and share capital. Learn the
COMPANY ACCOUNTS 10.17 UNIT 2 : ISSUE, FORFEITURE AND RE-ISSUE OF SHARES LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this unit, you will be able to: Appreciate various types of shares and share capital. Learn the
1 ANNA UNIVERSITY, CHENNAI REGULATION 2013 BA7022 MERCHANT BANKING AND FINANCIAL SERVICES PROF. I. ARUL EDISON ANTHONY RAJ,
 Page 1 QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWER KEY Page 1 TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWER KEY UNIT-I 1. What do you mean by financial system? A financial system or financial sector functions as an intermediary and facilitates
Page 1 QUESTION BANK WITH ANSWER KEY Page 1 TWO MARK QUESTIONS WITH ANSWER KEY UNIT-I 1. What do you mean by financial system? A financial system or financial sector functions as an intermediary and facilitates
Gilt inter dealer brokers and wholesale dealer brokers [ ]
![Gilt inter dealer brokers and wholesale dealer brokers [ ] Gilt inter dealer brokers and wholesale dealer brokers [ ]](/thumbs/73/68958557.jpg) Attachment 2 to Stock Exchange Notice N13/11 Member firm services Gilt inter dealer brokers and wholesale dealer brokers [1120-1128] List of users 1124 A member firm which operates a service that is available
Attachment 2 to Stock Exchange Notice N13/11 Member firm services Gilt inter dealer brokers and wholesale dealer brokers [1120-1128] List of users 1124 A member firm which operates a service that is available
