ECONOMIC GROWTH. Objectives. Transforming People s Lives. Transforming People s Lives. Transforming People s Lives CHAPTER
|
|
|
- Opal McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECONOMIC 30 GROWTH CHAPTER Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Describe the long-term growth trends in Canada and other countries and regions Identify the main sources of long-term real GDP growth Explain the productivity growth slowdown in Canada during the 1970s and the speedup during the 1990s Explain the rapid economic growth rates being achieved in Asia Explain the theories of economic growth Transforming People s Lives In Canada, real GDP per person doubled between 1961 and What causes the growth in production, income, and living standards? Elsewhere, notably in China and other parts of Asia, growth is even faster; technology 2,000 years old coexists with the most modern. Why is Asian growth so fast? Transforming People s Lives Lucas Wedge Here is the Lucas wedge for Canada. If the productivity growth slowdown of the 1970s hadn t happened, in 2001, real GDP per hour of labour would have been $67 rather than the $38 that we actually produced. Transforming People s Lives Actual, percent faster 0.5 percent faster 1.0 percent faster 2.0 percent faster Real GDP (billions of dollars) 1,028 1,131 1,246 1,508 2,206 Real GDP per hour of work (dollars) Real GDP per person 33,146 36,497 40,178 48,657 71,168 1
2 Long-Term Growth Trends Long-Term Growth Trends Growth in the Canadian Economy From 1926 to 2001, growth in real GDP per person in Canada averaged 2.2 percent per year. Real GDP per person fell precipitously during the Great Depression and rose rapidly during World War II. Figure 30.1 on the next slide illustrates. Long-Term Growth Trends Long-Term Growth Trends Country Australia Canada France Germany Japan Sweden United Kingdom United States Levels of Real GDP per Capita (1995 U.S. dollars, PPP basis) ,123 4,523 5,931 15,076 1,347 3,560 6,113 17,453 1,571 2,734 4,149 14,631 1,300 2,606 3,339 15, ,114 1,563 17,346 1,316 2,450 5,331 14,912 2,610 4,024 5,651 14,440 2,247 4,854 8,611 19,638 Annual Growth Rate Real GDP Growth in the World Economy Some developed nations have grown more rapidly than Canada. Until the 1990s, Japan grew fastest of the rich economies. Figure 30.2(a) illustrates. Long-Term Growth Trends Many developing countries in Africa, Central America, and South America stagnated during the 1980s, and have grown slowly since. They have fallen farther behind Canada. Figure 30.2(b) illustrates. 2
3 Long-Term Growth Trends Other formerly low-income economies Hong Kong, Korea, Singapore, and Taiwan are examples have grown very rapidly and have caught up or are catching up with Canada. Many other Asian nations have faster growth than Canada. Figure 30.3 illustrates. The Causes of Economic Growth: A First Look Preconditions for Economic Growth The basic precondition for economic growth is an appropriate incentive system. Three institutions are crucial to creation of the proper incentives Markets Property rights Monetary exchange The Causes of Economic Growth: A First Look For economic growth to persist, people must face incentives that encourage them to pursue three activities Saving and investment in new capital Investment in human capital Discovery of new technologies The Causes of Economic Growth: A First Look Saving and Investment in New Capital The accumulation of capital has dramatically increased output and productivity. Investment in Human Capital Human capital acquired through education, on-the-job training, and learning-by-doing has also dramatically increased output and productivity. Discovery of New Technologies Technological advances have contributed immensely to increasing productivity. 3
4 The quantity of real GDP supplied, Y, depends on the quantity of labour, L, the quantity of capital, K, and the state of technology, T. The purpose of growth accounting is to calculate how much real GDP growth results from the growth of labour and capital and how much is attributable to technological change. The key tool of growth accounting is the aggregate production function, Y = F(L, K, T ). Labour Productivity Labour productivity is real GDP per hour of labour; it equals real GDP divided by aggregate hours. Canadian productivity growth slowed after 1973 but then speeded up in the new economy of the late 1990s. Figure 30.4 shows Canadian productivity over the 1961 to 2001 period. Growth accounting divides growth in productivity into two components Growth in capital per hour of labour Technological change. Any productivity growth not accounted for by growth in capital is allocated to technological change, so this category is a broad catchall concept. The Productivity Curve The productivity curve is the relationship between real GDP per hour of labour and the amount of capital per hour of labour, with technology held constant. 4
5 Figure 30.5 illustrates the productivity curve. An increase in capital per hour brings a movement along productivity curve. Technological change shifts the productivity curve. The shape of the productivity curve reflects the law of diminishing returns. The law of diminishing returns states that, as the quantity of one input increases with the quantities of all other inputs remaining the same, output increases but ever smaller increments. Robert Solow discovered that diminishing returns are well described by the one-third rule: with no change in technology, on the average, a 1 percent increase in capital per hour of work brings a one-third of 1 percent increase in output per hour of labour. Accounting for the Productivity Growth Slowdown and Speedup The productivity function and one-third rule can be used to study productivity growth in Canada. Figure 30.6 on the next slides illustrates. Between 1961 and 1973 labour productivity increased by 47 percent a rate of 3.3 percent a year. Growth of capital per worker accounted for productivity growth of 1 percent a year. Technological change and other factors accounted for productivity growth of 2.3 percent a year. 5
6 Between 1973 and 1996 labour productivity increased by 25 percent a rate of 1 percent a year. Growth of capital per worker accounted for productivity growth of 0.6 percent a year. Technological change and other factors accounted for productivity growth of 0.4 percent a year. Between 1996 and 2001 labour productivity increased by 8.5 percent a rate of 1.6 percent a year. Growth of capital per worker accounted for productivity growth of 0.3 percent a year. Technological change and other factors accounted for productivity growth of 1.3 percent a year. Technological Change During the Production Growth Slowdown Technological change did not contribute much to advancing productivity during the 1970s for two reasons: Energy price hikes directed technological innovation to saving energy rather than to increasing productivity. Environmental protection laws were passed. Pollution abating investment raised the quality of life but did not increase measured GDP, so measured productivity did not increase. Achieving Faster Growth Growth accounting tell us that to achieve faster economic growth we must either increase the growth rate of capital per hour of labour or increasing the pace of technological advance. The main suggestions for achieving these objectives are Stimulate saving Higher saving rates may increase the growth rate of capital. Tax incentives might be provided to boost saving. 6
7 Stimulate research and development Because new discoveries can be used by everyone, not all the benefit of a discovery falls to the initial discoverer. So there is a tendency to under invest in research and development activity. Government subsidies might offset some of the underinvestment. Target high-technology firms The suggestion is that by subsidizing high-technology industries, a nation can enjoy a temporary advantage over its competitors. This is a very risky strategy, because it is unclear that government is better at picking winners than the profitseeking entrepreneurs. Encourage international trade Free international trade stimulates growth by extracting all the available gains from specialization and exchange The fastest growing nations are the ones with the fastest growing exports and imports. Improve the quality of education The benefits from education spread beyond the person being educated so there is a tendency to under invest in education. Classical Growth Theory Classical growth theory is the view that real GDP growth is temporary and that when real GDP per person rises above the subsistence level, a population explosion brings real GDP per person back to the subsistence level. The basic Classical idea There is a subsistence real wage rate, which is the minimum real wage rate needed to maintain life. Advances in technology lead to investment in new capital. Labour productivity increases and the real wage rate rises above the subsistence level. When the real wage rate is above the subsistence level, the population grows. Population growth increases the supply of labour, which lowers the real wage rate. The population continues to increase until the real wage rate has been driven back to the subsistence real wage rate. At this real wage rate, both population growth and economic growth stop. Contrary to the assumption of the classical theory, the historical evidence is that population growth rate is not tightly linked to income per person, and population growth does not drive incomes back down to subsistence levels. 7
8 Figure 30.7 illustrates the Classical growth theory. The neoclassical economics of population growth Neoclassical Growth Theory Neoclassical growth theory is the proposition that real GDP per person grows because technological change induces a level of saving and investment that makes capital per hour of labour grow. Growth ends only if technological change stops. The neoclassical view is that the population growth rate is independent of real GDP and the real GDP growth rate. The population growth rate equals the birth rate minus the death rate. The birth rate is determined by the opportunity cost of a woman s time. As women s wage rates have increased, the opportunity cost of having children has also increased and the birth rate has fallen. The death rate is determined by the quality and availability of health care. As the quality and availability of health care has improved, the death rate has fallen. The fall in both the birth rate and the death rate have offset each other and made the population growth rate independent of the level of income. The basic neoclassical idea Technology begins to advance more rapidly. New profit opportunities arise. Investment and saving increase. As technology advances and the capital stock grows, real GDP per person rises. Diminishing returns to capital per hour of labour lower the real interest rate and eventually growth stops unless technology keeps on advancing. 8
9 Figure 30.8 illustrates neoclassical growth theory. New Growth Theory New growth theory holds that real GDP per person grows because of choices that people make in the pursuit of profit and that growth can persist indefinitely. The theory emphasizes that In a market economy, discoveries result from choices Discoveries bring profit and competition destroys profit Discoveries are a public capital good Knowledge is not subject to diminishing returns Figure 30.9 illustrates new growth theory. Figure summarizes the ideas of new growth theory as a perpetual motion machine. 9
10 ECONOMIC 30 GROWTH CHAPTER THE END 10
The Basics of Economic Growth. Real GDP per person in Canada tripled in the 50 years between 1958 and 2008.
 Real GDP per person in Canada tripled in the 50 years between 1958 and 2008. What has brought about this growth in production, incomes, and living standards? We see even greater economic growth in modern
Real GDP per person in Canada tripled in the 50 years between 1958 and 2008. What has brought about this growth in production, incomes, and living standards? We see even greater economic growth in modern
ECONOMIC GROWTH CHAPTER
 ECONOMIC GROWTH 17 CHAPTER The Basics of Economic Growth U.S. real GDP per person and the standard of living tripled between 1960 and 2010. We see even more dramatic change in China, where incomes have
ECONOMIC GROWTH 17 CHAPTER The Basics of Economic Growth U.S. real GDP per person and the standard of living tripled between 1960 and 2010. We see even more dramatic change in China, where incomes have
Economic Growth C H A P T E R C H E C K L I S T. When you have completed your study of this chapter, you will be able to
 Economic Growth CHAPTER25 C H A P T E R C H E C K L I S T When you have completed your study of this chapter, you will be able to 1 Define and calculate the economic growth rate, and explain the implications
Economic Growth CHAPTER25 C H A P T E R C H E C K L I S T When you have completed your study of this chapter, you will be able to 1 Define and calculate the economic growth rate, and explain the implications
Chapter 6 ECONOMIC GROWTH. World Economic Growth. In this chapter-
 Chapter 6 ECONOMIC GROWTH In this chapter- Define and calculate the growth rate and explain the implications of sustained growth in economic activity Briefly describe the economic growth trends in the
Chapter 6 ECONOMIC GROWTH In this chapter- Define and calculate the growth rate and explain the implications of sustained growth in economic activity Briefly describe the economic growth trends in the
Macroeconomics (Code: E214) - Lecturer: Dr. Amira Akl Ahmed. Faculty of Commerce Department of Economics English Section Academic year 2013/2014
 Faculty of Commerce Department of Economics English Section Academic year 2013/2014 Questions for Chapter 6 of Macroeconomics, 10e (Parkin) First: Multiple choice questions The Basics of Economic Growth
Faculty of Commerce Department of Economics English Section Academic year 2013/2014 Questions for Chapter 6 of Macroeconomics, 10e (Parkin) First: Multiple choice questions The Basics of Economic Growth
Global Aging and Financial Markets
 Global Aging and Financial Markets Overview Presentation by Richard Jackson CSIS Global Aging Initiative MA s 16th Annual Washington Policy Seminar Cosponsored by Macroeconomic Advisers, LLC Council on
Global Aging and Financial Markets Overview Presentation by Richard Jackson CSIS Global Aging Initiative MA s 16th Annual Washington Policy Seminar Cosponsored by Macroeconomic Advisers, LLC Council on
FIRST LOOK AT MACROECONOMICS*
 Chapter 4 A FIRST LOOK AT MACROECONOMICS* Key Concepts Origins and Issues of Macroeconomics Modern macroeconomics began during the Great Depression, 1929 1939. The Great Depression was a decade of high
Chapter 4 A FIRST LOOK AT MACROECONOMICS* Key Concepts Origins and Issues of Macroeconomics Modern macroeconomics began during the Great Depression, 1929 1939. The Great Depression was a decade of high
Economic growth: Interesting Facts and Examples. 2Topic
 Economic growth: Interesting Facts and Examples 2Topic The Basics of Economic Growth U.S. real GDP per person and the standard of living tripled between 1960 and 2010. We see even more dramatic change
Economic growth: Interesting Facts and Examples 2Topic The Basics of Economic Growth U.S. real GDP per person and the standard of living tripled between 1960 and 2010. We see even more dramatic change
Long-term economic growth Growth and factors of production
 Understanding the World Economy Master in Economics and Business Long-term economic growth Growth and factors of production Lecture 2 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Output per capita
Understanding the World Economy Master in Economics and Business Long-term economic growth Growth and factors of production Lecture 2 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Output per capita
Macroeconomics II. Growth. Recent phenomenon Great diversity of growth experiences across countries. Why do some countries grow and others not?
 Macroeconomics II Growth Growth Theory Facts about growth Recent phenomenon Great diversity of growth experiences across countries What drives growth? Inputs Technology Why do some countries grow and others
Macroeconomics II Growth Growth Theory Facts about growth Recent phenomenon Great diversity of growth experiences across countries What drives growth? Inputs Technology Why do some countries grow and others
The Theory of Economic Growth
 The Theory of The Importance of Growth of real GDP per capita A measure of standards of living Small changes make large differences over long periods of time The causes and consequences of sustained increases
The Theory of The Importance of Growth of real GDP per capita A measure of standards of living Small changes make large differences over long periods of time The causes and consequences of sustained increases
Long-term economic growth Growth and factors of production
 Understanding the World Economy Master in Economics and Business Long-term economic growth Growth and factors of production Lecture 2 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Lecture 2 : Long-term
Understanding the World Economy Master in Economics and Business Long-term economic growth Growth and factors of production Lecture 2 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Lecture 2 : Long-term
Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics
 Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics Principles of Macroeconomics I. Economics as a Social Science A. Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments,
Chapter 4: A First Look at Macroeconomics Principles of Macroeconomics I. Economics as a Social Science A. Economics is the social science that studies the choices that individuals, businesses, governments,
The Theory of Economic Growth
 The Theory of 1 The Importance of Growth of real GDP per capita A measure of standards of living Small changes make large differences over long periods of time The causes and consequences of sustained
The Theory of 1 The Importance of Growth of real GDP per capita A measure of standards of living Small changes make large differences over long periods of time The causes and consequences of sustained
Growth, Capital Accumulation, and the Economics of Ideas
 Chapter 8 MODERN PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS Third Edition Growth, Capital Accumulation, and the Economics of Ideas Outline The Solow Model and Catching-Up Growth The Investment Rate and Conditional Convergence
Chapter 8 MODERN PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS Third Edition Growth, Capital Accumulation, and the Economics of Ideas Outline The Solow Model and Catching-Up Growth The Investment Rate and Conditional Convergence
ECON MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Instructor: Dr. Juergen Jung Towson University. J.Jung Chapter 8 - Economic Growth Towson University 1 / 64
 ECON 202 - MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Instructor: Dr. Juergen Jung Towson University J.Jung Chapter 8 - Economic Growth Towson University 1 / 64 Disclaimer These lecture notes are customized for the Macroeconomics
ECON 202 - MACROECONOMIC PRINCIPLES Instructor: Dr. Juergen Jung Towson University J.Jung Chapter 8 - Economic Growth Towson University 1 / 64 Disclaimer These lecture notes are customized for the Macroeconomics
Lab #7. Chapter 7 Growth, Productivity, and Wealth in the Long Run
 University of Lethbridge - Department of Economics ECON 1012 Introduction to Macroeconomics LAB Instructor: Michael G. Lanyi Lab #7 Chapter 7 Growth, Productivity, and Wealth in the Long Run Answer Sheet
University of Lethbridge - Department of Economics ECON 1012 Introduction to Macroeconomics LAB Instructor: Michael G. Lanyi Lab #7 Chapter 7 Growth, Productivity, and Wealth in the Long Run Answer Sheet
In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions
 In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What are the facts about living standards and growth rates around the world? Why does productivity matter for living standards? What determines
In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions What are the facts about living standards and growth rates around the world? Why does productivity matter for living standards? What determines
Macroeconomics CHAPTER 8. Long-Run Economic Growth
 Macroeconomics CHAPTER 8 Long-Run Economic Growth PowerPoint Slides by Can Erbil 2006 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved What you will learn in this chapter: How long-run growth can be measured by the
Macroeconomics CHAPTER 8 Long-Run Economic Growth PowerPoint Slides by Can Erbil 2006 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved What you will learn in this chapter: How long-run growth can be measured by the
Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth
 Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth Cheng Chen FBE of HKU October 12, 2017 Chen, C. (FBE of HKU) ECON2102/2220: Intermediate Macroeconomics October 12, 2017 1 / 59 Chapter Outline Discuss the sources of
Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth Cheng Chen FBE of HKU October 12, 2017 Chen, C. (FBE of HKU) ECON2102/2220: Intermediate Macroeconomics October 12, 2017 1 / 59 Chapter Outline Discuss the sources of
How Rich Will China Become? A simple calculation based on South Korea and Japan s experience
 ECONOMIC POLICY PAPER 15-5 MAY 2015 How Rich Will China Become? A simple calculation based on South Korea and Japan s experience EXECUTIVE SUMMARY China s impressive economic growth since the 1980s raises
ECONOMIC POLICY PAPER 15-5 MAY 2015 How Rich Will China Become? A simple calculation based on South Korea and Japan s experience EXECUTIVE SUMMARY China s impressive economic growth since the 1980s raises
POST-CRISIS GLOBAL REBALANCING CONFERENCE ON GLOBALIZATION AND THE LAW OF THE SEA WASHINGTON DC, DEC 1-3, Barry Bosworth
 POST-CRISIS GLOBAL REBALANCING CONFERENCE ON GLOBALIZATION AND THE LAW OF THE SEA WASHINGTON DC, DEC 1-3, 2010 Barry Bosworth I. Economic Rise of Asia Emerging economies of Asia have performed extremely
POST-CRISIS GLOBAL REBALANCING CONFERENCE ON GLOBALIZATION AND THE LAW OF THE SEA WASHINGTON DC, DEC 1-3, 2010 Barry Bosworth I. Economic Rise of Asia Emerging economies of Asia have performed extremely
Chapter 8. Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics and Policy 10/6/2010. Introduction. Technological progress in the Solow model
 Chapter 8 : Technology, Empirics and Policy Introduction In the Solow of Chapter 7, the production technology is held constant. income per capita is constant in the steady state. Neither point is true
Chapter 8 : Technology, Empirics and Policy Introduction In the Solow of Chapter 7, the production technology is held constant. income per capita is constant in the steady state. Neither point is true
Global Research and Development Expenditures: Fact Sheet
 Global Research and Development Expenditures: Fact Sheet John F. Sargent Jr. Specialist in Science and Technology Policy June 16, 2017 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov R44283 R esearch
Global Research and Development Expenditures: Fact Sheet John F. Sargent Jr. Specialist in Science and Technology Policy June 16, 2017 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov R44283 R esearch
About 80% of the countries have GDP per capita below the average income per head
 ECON 7010: Economics of Development Introduction to Economics Development Why poor countries consume less? Because they produce less Lack of physical capital (no tools and machinery) Lack of necessary
ECON 7010: Economics of Development Introduction to Economics Development Why poor countries consume less? Because they produce less Lack of physical capital (no tools and machinery) Lack of necessary
Objectives AGGREGATE DEMAND AND AGGREGATE SUPPLY
 AGGREGATE DEMAND 7 AND CHAPTER AGGREGATE SUPPLY Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Explain what determines aggregate supply Explain what determines aggregate demand Explain macroeconomic
AGGREGATE DEMAND 7 AND CHAPTER AGGREGATE SUPPLY Objectives After studying this chapter, you will able to Explain what determines aggregate supply Explain what determines aggregate demand Explain macroeconomic
CRS Report for Congress
 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21118 Updated April 26, 2006 U.S. Direct Investment Abroad: Trends and Current Issues Summary James K. Jackson Specialist in International
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21118 Updated April 26, 2006 U.S. Direct Investment Abroad: Trends and Current Issues Summary James K. Jackson Specialist in International
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMIC GROWTH. Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University
 INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMIC GROWTH Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University ROADMAP INCOME EXPENDITURE LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE IS CURVE LM CURVE SHORT-RUN IS-LM MODEL AGGREGATE DEMAND AGGREGATE
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMIC GROWTH Dongpeng Liu Department of Economics Nanjing University ROADMAP INCOME EXPENDITURE LIQUIDITY PREFERENCE IS CURVE LM CURVE SHORT-RUN IS-LM MODEL AGGREGATE DEMAND AGGREGATE
Commentary: The Search for Growth
 Commentary: The Search for Growth N. Gregory Mankiw For evaluating economic well-being, the single most important statistic about an economy is its income per capita. Income per capita measures how much
Commentary: The Search for Growth N. Gregory Mankiw For evaluating economic well-being, the single most important statistic about an economy is its income per capita. Income per capita measures how much
MACROECONOMICS. Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics, and Policy MANKIW. In this chapter, you will learn. Introduction
 C H A P T E R 8 Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics, and Policy MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2007 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this
C H A P T E R 8 Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics, and Policy MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2007 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this
Economic Growth II. macroeconomics. fifth edition. N. Gregory Mankiw. PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich Worth Publishers, all rights reserved
 CHAPTER EIGHT Economic Growth II macroeconomics fifth edition N. Gregory Mankiw PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2002 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved Learning objectives Technological progress
CHAPTER EIGHT Economic Growth II macroeconomics fifth edition N. Gregory Mankiw PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2002 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved Learning objectives Technological progress
LO AGENDA Mon 2/1. QOD #9: New Zombie GDP Review HW (CH 25 Q# 1-4 P #1) Economic Growth HW: Read pp Q #9-10
 LO1 25-1 AGENDA Mon 2/1 QOD #9: New Zombie GDP Review HW (CH 25 Q# 1-4 P #1) Economic Growth HW: Read pp 512-523 Q #9-10 LO1 25-2 QOD #9: New Zombie GDP Suppose that work hours in New Zombie are 200 in
LO1 25-1 AGENDA Mon 2/1 QOD #9: New Zombie GDP Review HW (CH 25 Q# 1-4 P #1) Economic Growth HW: Read pp 512-523 Q #9-10 LO1 25-2 QOD #9: New Zombie GDP Suppose that work hours in New Zombie are 200 in
Macroeconomics, Cdn. 4e (Williamson) Chapter 1 Introduction
 Macroeconomics, Cdn. 4e (Williamson) Chapter 1 Introduction 1) Which of the following topics is a primary concern of macro economists? A) standards of living of individuals B) choices of individual consumers
Macroeconomics, Cdn. 4e (Williamson) Chapter 1 Introduction 1) Which of the following topics is a primary concern of macro economists? A) standards of living of individuals B) choices of individual consumers
Chapter 10. Preview. Introduction. Trade Policy in Developing Countries
 Chapter 10 Trade Policy in Developing Countries Slides prepared by Thomas Bishop Copyright 2009 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Preview Import substituting industrialization Trade liberalization
Chapter 10 Trade Policy in Developing Countries Slides prepared by Thomas Bishop Copyright 2009 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Preview Import substituting industrialization Trade liberalization
MACROECONOMICS. Economic Growth II: Technology, Empirics, and Policy. N. Gregory Mankiw. PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich
 9 : Technology, Empirics, and Policy MACROECONOMICS N. Gregory Mankiw Modified for EC 204 by Bob Murphy PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2013 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU
9 : Technology, Empirics, and Policy MACROECONOMICS N. Gregory Mankiw Modified for EC 204 by Bob Murphy PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2013 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved IN THIS CHAPTER, YOU
LEC 2: Exogenous (Neoclassical) growth model
 LEC 2: Exogenous (Neoclassical) growth model Development of the model The Neo-classical model was an extension to the Harrod-Domar model that included a new term productivity growth The most important
LEC 2: Exogenous (Neoclassical) growth model Development of the model The Neo-classical model was an extension to the Harrod-Domar model that included a new term productivity growth The most important
Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth
 Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth Yulei Luo SEF of HKU October 10, 2013 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON2220: Macro Theory October 10, 2013 1 / 34 Chapter Outline Discuss the sources of economic growth and
Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth Yulei Luo SEF of HKU October 10, 2013 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON2220: Macro Theory October 10, 2013 1 / 34 Chapter Outline Discuss the sources of economic growth and
Economy in the LONG RUN
 Economy in the LONG RUN I. The Aggregate Production Function II. Classical Growth Model (not in textbook) III. Neo-classical Growth Model - without long term growth - with population and technology growth
Economy in the LONG RUN I. The Aggregate Production Function II. Classical Growth Model (not in textbook) III. Neo-classical Growth Model - without long term growth - with population and technology growth
3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Growth over the Very Long Run. 3.1 Introduction. Part 2: The Long Run. An Overview of Long-Run Economic Growth
 Part 2: The Long Run Media Slides Created By Dave Brown Penn State University 3.1 Introduction In this chapter, we learn: Some tools used to study economic growth, including how to calculate growth rates.
Part 2: The Long Run Media Slides Created By Dave Brown Penn State University 3.1 Introduction In this chapter, we learn: Some tools used to study economic growth, including how to calculate growth rates.
A FIRST LOOK AT* MACROECONOMICS*
 C h a p t e r 4 A FIRST LOOK AT* MACROECONOMICS* Chapter Key Ideas Outline What Will Your World Be Like? A. What will happen to economic growth, unemployment, inflation, the government budget deficit,
C h a p t e r 4 A FIRST LOOK AT* MACROECONOMICS* Chapter Key Ideas Outline What Will Your World Be Like? A. What will happen to economic growth, unemployment, inflation, the government budget deficit,
Hamid Rashid, Ph.D. Chief Global Economic Monitoring Unit Development Policy Analysis Division UNDESA, New York
 Hamid Rashid, Ph.D. Chief Global Economic Monitoring Unit Development Policy Analysis Division UNDESA, New York 1 Global macroeconomic trends Major headwinds Risks and uncertainties Policy questions and
Hamid Rashid, Ph.D. Chief Global Economic Monitoring Unit Development Policy Analysis Division UNDESA, New York 1 Global macroeconomic trends Major headwinds Risks and uncertainties Policy questions and
Economics. Production and Growth. In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: N. Gregory Mankiw. Incomes and Growth Around the World
 C H A P T E R 25 Production and Growth P R I N C I P L E S O F Economics N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
C H A P T E R 25 Production and Growth P R I N C I P L E S O F Economics N. Gregory Mankiw Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2009 South-Western, a part of Cengage Learning, all rights reserved
PART II OF THE COURSE: AGGREGATE SUPPLY AND LONG RUN GROWTH
 PART II OF THE COURSE: AGGREGATE SUPPLY AND LONG RUN GROWTH What causes real GDP per capita to rise by 2% per year in the long run? Why does real GDP growth not converge to zero? Why do some countries
PART II OF THE COURSE: AGGREGATE SUPPLY AND LONG RUN GROWTH What causes real GDP per capita to rise by 2% per year in the long run? Why does real GDP growth not converge to zero? Why do some countries
Why are some countries richer than others? Part 1
 Understanding the World Economy Why are some countries richer than others? Part 1 Lecture 1 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Practical matters Course website http://econ.sciences-po.fr/staff/nicolas-coeurdacier
Understanding the World Economy Why are some countries richer than others? Part 1 Lecture 1 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Practical matters Course website http://econ.sciences-po.fr/staff/nicolas-coeurdacier
Macroeconomics Sixth Edition
 N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics Sixth Edition 12 Production and Growth Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: What are the facts
N. Gregory Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics Sixth Edition 12 Production and Growth Premium PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich In this chapter, look for the answers to these questions: What are the facts
ISA RESEARCH BRIEFING
 ISA RESEARCH BRIEFING The Leading Growth Markets for Exporters July 31, 2018 Without a doubt, these are worrying days for exporters. Whether it is a business that is counting on export markets for much
ISA RESEARCH BRIEFING The Leading Growth Markets for Exporters July 31, 2018 Without a doubt, these are worrying days for exporters. Whether it is a business that is counting on export markets for much
Economic Growth: Extensions
 Economic Growth: Extensions 1 Road Map to this Lecture 1. Extensions to the Solow Growth Model 1. Population Growth 2. Technological growth 3. The Golden Rule 2. Endogenous Growth Theory 1. Human capital
Economic Growth: Extensions 1 Road Map to this Lecture 1. Extensions to the Solow Growth Model 1. Population Growth 2. Technological growth 3. The Golden Rule 2. Endogenous Growth Theory 1. Human capital
Managing Healthcare Expenditures: Fiscal Projections and Effects of Reforms
 Managing Healthcare Expenditures: Fiscal Projections and Effects of Reforms SANJEEV GUPTA DEPUTY DIRECTOR, FISCAL AFFAIRS DEPARTMENT TOKYO, JUNE 6, 2016 Outlook of Public Health Spending Percent of GDP
Managing Healthcare Expenditures: Fiscal Projections and Effects of Reforms SANJEEV GUPTA DEPUTY DIRECTOR, FISCAL AFFAIRS DEPARTMENT TOKYO, JUNE 6, 2016 Outlook of Public Health Spending Percent of GDP
Canadian Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycle
 28 Canadian Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycle Learning Objectives Explain how demand-pull and cost-push forces bring cycles in inflation and output Explain the short-run and long-run tradeoff
28 Canadian Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycle Learning Objectives Explain how demand-pull and cost-push forces bring cycles in inflation and output Explain the short-run and long-run tradeoff
Preview. Chapter 10. Introduction. Introduction
 Chapter 10 Trade Policy in Developing Countries Preview Import substituting industrialization Trade liberalization since 1985 Export oriented industrialization Slides prepared by Thomas Bishop Copyright
Chapter 10 Trade Policy in Developing Countries Preview Import substituting industrialization Trade liberalization since 1985 Export oriented industrialization Slides prepared by Thomas Bishop Copyright
Econ 340. Announcements. Overview of the World Economy. Lecture 1 Outline. Overview of the World Economy. Lecture 1 Overview of the World Economy
 Announcements Econ 340 Lecture 1 We will start discussing news next week, on Monday Jan 15. You should be watching for international economic news. Lecture 2: Institutions 2 Lecture 1 Outline Elements
Announcements Econ 340 Lecture 1 We will start discussing news next week, on Monday Jan 15. You should be watching for international economic news. Lecture 2: Institutions 2 Lecture 1 Outline Elements
Edexcel (B) Economics A-level
 Edexcel (B) Economics A-level Theme 3: The Global Economy 3.1 Globalisation 3.1.1 Growing economies Notes Growing economic power of: o Asia (China and India) Since WW2, global trade has increased significantly.
Edexcel (B) Economics A-level Theme 3: The Global Economy 3.1 Globalisation 3.1.1 Growing economies Notes Growing economic power of: o Asia (China and India) Since WW2, global trade has increased significantly.
Demographic Transition in Asia: Risk of Growing Old Before Becoming Rich
 Demographic Transition in Asia: Risk of Growing Old Before Becoming Rich Minsuk Kim International Monetary Fund Asia and Pacific Department 2017 Asia and Pacific Regional Economic Outlook May 12, 2017
Demographic Transition in Asia: Risk of Growing Old Before Becoming Rich Minsuk Kim International Monetary Fund Asia and Pacific Department 2017 Asia and Pacific Regional Economic Outlook May 12, 2017
Introduction to economic growth (1)
 Introduction to economic growth (1) EKN 325 Manoel Bittencourt University of Pretoria M Bittencourt (University of Pretoria) EKN 325 1 / 32 Introduction In the last century the USA has experienced a tenfold
Introduction to economic growth (1) EKN 325 Manoel Bittencourt University of Pretoria M Bittencourt (University of Pretoria) EKN 325 1 / 32 Introduction In the last century the USA has experienced a tenfold
Kazumasa Iwata: Japan s economy under demographic changes
 Kazumasa Iwata: Japan s economy under demographic changes Summary of a speech by Mr Kazumasa Iwata, Deputy Governor of the Bank of Japan, at the Australia- Japan Economic Outlook Conference, Sydney, 7
Kazumasa Iwata: Japan s economy under demographic changes Summary of a speech by Mr Kazumasa Iwata, Deputy Governor of the Bank of Japan, at the Australia- Japan Economic Outlook Conference, Sydney, 7
What we ve learned so far. The Solow Growth Model. Our objectives today 2/11/2009 ECON 206 MACROECONOMIC ANALYSIS. Chapter 5 (2 of 2)
 ECON 206 MACROECONOMIC ANALYSIS What we ve learned so far Roumen Vesselinov Class # 7 The key equations of the Solow Model are these: The production function And the capital accumulation equation How do
ECON 206 MACROECONOMIC ANALYSIS What we ve learned so far Roumen Vesselinov Class # 7 The key equations of the Solow Model are these: The production function And the capital accumulation equation How do
WTO lowers forecast after sub-par trade growth in first half of 2014
 PRESS RELEASE PRESS/722 26 September 214 (-) WTO lowers forecast after sub-par trade growth in first half of 214 TRADE STATISTICS WTO economists have reduced their forecast for world trade growth in 214
PRESS RELEASE PRESS/722 26 September 214 (-) WTO lowers forecast after sub-par trade growth in first half of 214 TRADE STATISTICS WTO economists have reduced their forecast for world trade growth in 214
CHAPTER 1 INDIA, G20 AND THE WORLD
 CHAPTER 1 INDIA, G20 AND THE WORLD INDIA IN WORLD POPULATION 1.1. The United Nations Population Division estimates the global population in 2010 at 6908.7 million. Compared to this, the population of India
CHAPTER 1 INDIA, G20 AND THE WORLD INDIA IN WORLD POPULATION 1.1. The United Nations Population Division estimates the global population in 2010 at 6908.7 million. Compared to this, the population of India
Econ 340. The Issues. The Washington Consensus. Outline: International Policies for Economic Development: Trade
 Econ 340 Lecture 19 International Policies for 2 3 The Issues The Two Main Issues: Should developing countries be open to international trade? Should developing countries be open to international capital
Econ 340 Lecture 19 International Policies for 2 3 The Issues The Two Main Issues: Should developing countries be open to international trade? Should developing countries be open to international capital
Economic and Investment Review. Kelvin Blacklock and Nick Scott Prudential Corporation Asia November 2004
 Economic and Investment Review Kelvin Blacklock and Nick Scott Prudential Corporation Asia November 24 24 Key messages Asia saves enormous amounts of capital and is fast becoming the world s provider of
Economic and Investment Review Kelvin Blacklock and Nick Scott Prudential Corporation Asia November 24 24 Key messages Asia saves enormous amounts of capital and is fast becoming the world s provider of
Trade and Development
 Trade and Development Table of Contents 2.2 Growth theory revisited a) Post Keynesian Growth Theory the Harrod Domar Growth Model b) Structural Change Models the Lewis Model c) Neoclassical Growth Theory
Trade and Development Table of Contents 2.2 Growth theory revisited a) Post Keynesian Growth Theory the Harrod Domar Growth Model b) Structural Change Models the Lewis Model c) Neoclassical Growth Theory
The Canada-U.S. Income Gap
 The Canada-U.S. Income Gap In the 1990s, the gap between and Canadian and American income levels widened significantly. Real personal income per capita in Canada fell 9 percentage points from 87.2 per
The Canada-U.S. Income Gap In the 1990s, the gap between and Canadian and American income levels widened significantly. Real personal income per capita in Canada fell 9 percentage points from 87.2 per
An Overview of World Goods and Services Trade
 Appendix IV An Overview of World Goods and Services Trade An overview of the size and composition of U.S. and world trade is useful to provide perspective for the large U.S. trade and current account deficits
Appendix IV An Overview of World Goods and Services Trade An overview of the size and composition of U.S. and world trade is useful to provide perspective for the large U.S. trade and current account deficits
TOPIC 4 Economi G c rowth
 TOPIC 4 Economic Growth Growth Accounting Growth Accounting Equation Y = A F(K,N) (production function). GDP Growth Rate =!Y/Y Growth accounting equation:!y/y =!A/A +! K!K/K +! N!N/N Output, in a country
TOPIC 4 Economic Growth Growth Accounting Growth Accounting Equation Y = A F(K,N) (production function). GDP Growth Rate =!Y/Y Growth accounting equation:!y/y =!A/A +! K!K/K +! N!N/N Output, in a country
How Global Aging Will Transform the Economy, Society, and Geopolitical Order of the 21 st Century
 How Global Aging Will Transform the Economy, Society, and Geopolitical Order of the 21 st Century Richard Jackson President Global Aging Institute LONGEVITY 13 Taipei September 21, 2017 The world stands
How Global Aging Will Transform the Economy, Society, and Geopolitical Order of the 21 st Century Richard Jackson President Global Aging Institute LONGEVITY 13 Taipei September 21, 2017 The world stands
ECONOMICS. ATAR course examination Marking Key
 ECONOMICS ATAR course examination 08 Marking Key Marking keys are an explicit statement about what the examining panel expect of candidates when they respond to particular examination items. They help
ECONOMICS ATAR course examination 08 Marking Key Marking keys are an explicit statement about what the examining panel expect of candidates when they respond to particular examination items. They help
Canadian Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycle
 28 Canadian Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycle After studying this chapter you will be able to! Explain how demand-pull and cost-push forces bring cycles in inflation and output! Explain the short-run
28 Canadian Inflation, Unemployment, and Business Cycle After studying this chapter you will be able to! Explain how demand-pull and cost-push forces bring cycles in inflation and output! Explain the short-run
American Productivity
 American Productivity Growth: Perspectives on the Slowdown Productivity growth in the United States has slowed dramatically in the past decade. Since the late 1960's productivity in the private economy
American Productivity Growth: Perspectives on the Slowdown Productivity growth in the United States has slowed dramatically in the past decade. Since the late 1960's productivity in the private economy
Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth
 Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth Yulei Luo Economics, HKU October 19, 2017 Luo, Y. (Economics, HKU) ECON2220: Intermediate Macro October 19, 2017 1 / 32 Chapter Outline Discuss the sources of economic
Chapter 6: Long-Run Economic Growth Yulei Luo Economics, HKU October 19, 2017 Luo, Y. (Economics, HKU) ECON2220: Intermediate Macro October 19, 2017 1 / 32 Chapter Outline Discuss the sources of economic
JAPANESE ECONOMY Private consumption may prove to be resilient US ECONOMY The economy remains buoyant despite some soft patches.
 JAPANESE ECONOMY Private consumption may prove to be resilient.... US ECONOMY The economy remains buoyant despite some soft patches. EUROPEAN ECONOMY U.K. economy is slowing mildly.... CHINESE ECONOMY
JAPANESE ECONOMY Private consumption may prove to be resilient.... US ECONOMY The economy remains buoyant despite some soft patches. EUROPEAN ECONOMY U.K. economy is slowing mildly.... CHINESE ECONOMY
THE SWISS AND WORLD WATCHMAKING INDUSTRIES IN % +9.1% -4.4% Hong Kong USA China Japan United Kingdom
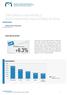 THE SWISS AND WORLD WATCHMAKING INDUSTRIES IN 2018 SWISS WATCH EXPORTS 21.2 billion francs +6.3% The outturn for watch industry exports in 2018 was in line with forecasts. The steady pace of growth early
THE SWISS AND WORLD WATCHMAKING INDUSTRIES IN 2018 SWISS WATCH EXPORTS 21.2 billion francs +6.3% The outturn for watch industry exports in 2018 was in line with forecasts. The steady pace of growth early
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Chapter 33. Comparative Advantage and the Open Economy
 Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 33 Comparative Advantage and the Open Economy All rights reserved. Introduction In the midst of the Great Recession of the late 2000s, the governments
Copyright 2011 by Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 33 Comparative Advantage and the Open Economy All rights reserved. Introduction In the midst of the Great Recession of the late 2000s, the governments
assumption. Use these two equations and your earlier result to derive an expression for consumption per worker in steady state.
 Tutorial sheet 2 for UBC Macroeconomics Martin Ellison, 2018 Exercise on consumption in the Solow growth model The Solow growth model is in steady-state when investment ss YY tt is exactly offset by depreciation
Tutorial sheet 2 for UBC Macroeconomics Martin Ellison, 2018 Exercise on consumption in the Solow growth model The Solow growth model is in steady-state when investment ss YY tt is exactly offset by depreciation
Answer key to the Multiple choice questions for Problem Set 1 February 19, 2007
 1 Answer key to the Multiple choice questions for Problem Set 1 February 19, 2007 Name: Instructions: Clearly mark what you believe is the best answer to each one of the following problems Question 1 Multiple
1 Answer key to the Multiple choice questions for Problem Set 1 February 19, 2007 Name: Instructions: Clearly mark what you believe is the best answer to each one of the following problems Question 1 Multiple
22/03/2012. Inflation Cycles. The 1920s were years of unprecedented prosperity.
 The 1920s were years of unprecedented prosperity. Then, in October 1929, the stock market crashed. Overnight, stock prices fell by 30 percent. The Great Depression began and by 1933, real GDP had fallen
The 1920s were years of unprecedented prosperity. Then, in October 1929, the stock market crashed. Overnight, stock prices fell by 30 percent. The Great Depression began and by 1933, real GDP had fallen
Chapter 4. Economic Growth
 Chapter 4 Economic Growth When you have completed your study of this chapter, you will be able to 1. Understand what are the determinants of economic growth. 2. Understand the Neoclassical Solow growth
Chapter 4 Economic Growth When you have completed your study of this chapter, you will be able to 1. Understand what are the determinants of economic growth. 2. Understand the Neoclassical Solow growth
Foundations of Macroeconomics
 GloBAl EdiTioN Foundations of Macroeconomics SEVENTH EdiTioN Robin Bade Michael Parkin MyEconLab Provides the Power of Practice optimize your study time with MyEconLab, the online assessment and tutorial
GloBAl EdiTioN Foundations of Macroeconomics SEVENTH EdiTioN Robin Bade Michael Parkin MyEconLab Provides the Power of Practice optimize your study time with MyEconLab, the online assessment and tutorial
Econ 20B Spr 2008 Sample Final Exam
 Econ 20B Spr 2008 Sample Final Exam Prof. Min Ouyang Please Do this sample final exam before looking at the answer key!!! Time limit: 120 minutes Instructions: 1) The exam is closed book. 2) Final exam
Econ 20B Spr 2008 Sample Final Exam Prof. Min Ouyang Please Do this sample final exam before looking at the answer key!!! Time limit: 120 minutes Instructions: 1) The exam is closed book. 2) Final exam
What is Macroeconomics?
 Lecture 1-1 What is Macroeconomics? 1. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics: the study of the major economic totals (aggregates). Issues involving the overall economic performance of the nation: do people find
Lecture 1-1 What is Macroeconomics? 1. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics: the study of the major economic totals (aggregates). Issues involving the overall economic performance of the nation: do people find
1 World Economy. Value of Finnish Forest Industry Exports Fell by Almost a Quarter in 2009
 1 World Economy The recovery in the world economy that began during 2009 has started to slow since spring 2010 as stocks are replenished and government stimulus packages are gradually brought to an end.
1 World Economy The recovery in the world economy that began during 2009 has started to slow since spring 2010 as stocks are replenished and government stimulus packages are gradually brought to an end.
The international environment
 The international environment This article (1) discusses developments in the global economy since the August 1999 Quarterly Bulletin. Domestic demand growth remained strong in the United States, and with
The international environment This article (1) discusses developments in the global economy since the August 1999 Quarterly Bulletin. Domestic demand growth remained strong in the United States, and with
Economic growth (Burda & Wyplosz, Macroeconomics. A European text, third edition. Oxford University Press, 2001: Part VI ch.18)
 Economic growth (Burda & Wyplosz, Macroeconomics. A European text, third edition. Oxford University Press, 2001: Part VI ch.18) Economic growth Increase in the value of goods and services produced by the
Economic growth (Burda & Wyplosz, Macroeconomics. A European text, third edition. Oxford University Press, 2001: Part VI ch.18) Economic growth Increase in the value of goods and services produced by the
IN THIS LECTURE, YOU WILL LEARN:
 IN THIS LECTURE, YOU WILL LEARN: the closed economy Solow model how a country s standard of living depends on its saving and population growth rates how to use the Golden Rule to find the optimal saving
IN THIS LECTURE, YOU WILL LEARN: the closed economy Solow model how a country s standard of living depends on its saving and population growth rates how to use the Golden Rule to find the optimal saving
Multiple Choice Questions (3 points each) Please answer the questions on the green scantron.
 ECON 203-200, Fall 2006 EXAM #2 Multiple Choice Questions (3 points each) Please answer the questions on the green scantron. 1) If the short run aggregate supply curve is vertical, a decrease in money
ECON 203-200, Fall 2006 EXAM #2 Multiple Choice Questions (3 points each) Please answer the questions on the green scantron. 1) If the short run aggregate supply curve is vertical, a decrease in money
1. a. The accompanying table shows each nation s real GDP per capita in terms of its. per capita per capita. Percentage of 1960 real GDP per capita
 AP Krugman Section 7 Problem Solutions 1. a. The accompanying table shows each nation s in terms of its 1960 and 2000 levels. Year Real GDP (2000 Argentina of 1960 of 2000 Real GDP per capita (2000 Ghana
AP Krugman Section 7 Problem Solutions 1. a. The accompanying table shows each nation s in terms of its 1960 and 2000 levels. Year Real GDP (2000 Argentina of 1960 of 2000 Real GDP per capita (2000 Ghana
Why are some countries richer than others? Part 2
 Understanding the World Economy Why are some countries richer than others? Part 2 Lecture 2 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Lecture 2 : Why are some countries richer than others?
Understanding the World Economy Why are some countries richer than others? Part 2 Lecture 2 Nicolas Coeurdacier nicolas.coeurdacier@sciencespo.fr Lecture 2 : Why are some countries richer than others?
Session 16. Review Session
 Session 16. Review Session The long run [Fundamentals] Output, saving, and investment Money and inflation Economic growth Labor markets The short run [Business cycles] What are the causes business cycles?
Session 16. Review Session The long run [Fundamentals] Output, saving, and investment Money and inflation Economic growth Labor markets The short run [Business cycles] What are the causes business cycles?
ECO 4933 Topics in Theory
 ECO 4933 Topics in Theory Introduction to Economic Growth Fall 2015 Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2 The Solow Growth Model Chapter 2 2 Assumptions: 1. The world consists of countries that produce and consume only
ECO 4933 Topics in Theory Introduction to Economic Growth Fall 2015 Chapter 2 1 Chapter 2 The Solow Growth Model Chapter 2 2 Assumptions: 1. The world consists of countries that produce and consume only
Commentary: Macroeconomic Policy and Long-Run Growth
 Symposium Sponsored by the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City August 27-29, 1992 "Policies for Long-Run Economic Growth Commentary: Macroeconomic Policy and Long-Run Growth Allan H. Meitzer DeLong and
Symposium Sponsored by the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City August 27-29, 1992 "Policies for Long-Run Economic Growth Commentary: Macroeconomic Policy and Long-Run Growth Allan H. Meitzer DeLong and
World Economic Trend, Spring 2006, No. 9
 World Economic Trend, Spring, No. 9 Published on June 8 by the Cabinet Office Key Points of Chapter 1 (summary) 1. Global price stability: Global economy continues to show price stability and recovery
World Economic Trend, Spring, No. 9 Published on June 8 by the Cabinet Office Key Points of Chapter 1 (summary) 1. Global price stability: Global economy continues to show price stability and recovery
Economic Development. Business Plan to restated. Accountability Statement
 Economic Development Business Plan 1999-2000 to 2001-02 - restated Accountability Statement As a result of government re-organization announced on May 25, 1999, the Ministry Business Plans included in
Economic Development Business Plan 1999-2000 to 2001-02 - restated Accountability Statement As a result of government re-organization announced on May 25, 1999, the Ministry Business Plans included in
Antonio Fazio: Overview of global economic and financial developments in first half 2004
 Antonio Fazio: Overview of global economic and financial developments in first half 2004 Address by Mr Antonio Fazio, Governor of the Bank of Italy, to the ACRI (Association of Italian Savings Banks),
Antonio Fazio: Overview of global economic and financial developments in first half 2004 Address by Mr Antonio Fazio, Governor of the Bank of Italy, to the ACRI (Association of Italian Savings Banks),
Measuring Unemployment Economic Growth and Productivity. unemployed. News
 Economic Growth and Productivity News Unemployment Redux Nations Have Experienced a Substantial Rise in Living Standards Over the Last 150 Years. Labor Productivity Accounts for a Great Deal of the Observed
Economic Growth and Productivity News Unemployment Redux Nations Have Experienced a Substantial Rise in Living Standards Over the Last 150 Years. Labor Productivity Accounts for a Great Deal of the Observed
Challenges For the Future of Chinese Economic Growth. Jane Haltmaier* Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. August 2011.
 Challenges For the Future of Chinese Economic Growth Jane Haltmaier* Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System August 2011 Preliminary *Senior Advisor in the Division of International Finance. Mailing
Challenges For the Future of Chinese Economic Growth Jane Haltmaier* Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System August 2011 Preliminary *Senior Advisor in the Division of International Finance. Mailing
WikiLeaks Document Release
 WikiLeaks Document Release February 2, 2009 Congressional Research Service Report RL34073 Productivity and National Standards of Living Brian W. Cashell, Government and Finance Division July 5, 2007 Abstract.
WikiLeaks Document Release February 2, 2009 Congressional Research Service Report RL34073 Productivity and National Standards of Living Brian W. Cashell, Government and Finance Division July 5, 2007 Abstract.
Click to edit Master title style. Presented by Sylvia Solf Private and Financial Sector Vice-presidency World Bank Group
 Doing Business 2009 Presented by Sylvia Solf Private and Financial Sector Vice-presidency World Bank Group 2007 Starting a business Dealing with construction permits Employing workers Registering property
Doing Business 2009 Presented by Sylvia Solf Private and Financial Sector Vice-presidency World Bank Group 2007 Starting a business Dealing with construction permits Employing workers Registering property
Markit economic overview
 Markit Economics Markit economic overview Global growth held back by emerging market stagnation August 11 2015 Developed world leads global growth higher for first time in four months Global economic growth
Markit Economics Markit economic overview Global growth held back by emerging market stagnation August 11 2015 Developed world leads global growth higher for first time in four months Global economic growth
FRBSF ECONOMIC LETTER
 FRBSF ECONOMIC LETTER 15- August, 15 Pacific Basin Note Is China s Growth Miracle Over? BY ZHENG LIU The recent slowdown in China s growth has caused concern about its long-term growth prospects. Evidence
FRBSF ECONOMIC LETTER 15- August, 15 Pacific Basin Note Is China s Growth Miracle Over? BY ZHENG LIU The recent slowdown in China s growth has caused concern about its long-term growth prospects. Evidence
Economic Growth. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Economic Growth 1 / 29
 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Growth 1 / 29 There are tremendous variations in the standard of living around the world. The large differences in income are reflected in large differences in
Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Economic Growth 1 / 29 There are tremendous variations in the standard of living around the world. The large differences in income are reflected in large differences in
China Economic Update Q April 27, 2018
 il 27, 2018 Key Developments in Brief Economic Development Drivers of Growth Risks Predicted GDP growth of 6.5% in Service and modern production Corporate debt, esp. stateowned 2018 grow fast enterprises
il 27, 2018 Key Developments in Brief Economic Development Drivers of Growth Risks Predicted GDP growth of 6.5% in Service and modern production Corporate debt, esp. stateowned 2018 grow fast enterprises
