Economics Today The Macro View Roger LeRoy Miller Seventeenth Edition
|
|
|
- Howard Gilbert
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Economics Today The Macro View Roger LeRoy Miller Seventeenth Edition
2 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: Pearson Education Limited 2014 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without either the prior written permission of the publisher or a licence permitting restricted copying in the United Kingdom issued by the Copyright Licensing Agency Ltd, Saffron House, 6 10 Kirby Street, London EC1N 8TS. All trademarks used herein are the property of their respective owners. The use of any trademark in this text does not vest in the author or publisher any trademark ownership rights in such trademarks, nor does the use of such trademarks imply any affiliation with or endorsement of this book by such owners. ISBN 10: ISBN 10: ISBN 13: ISBN 13: British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library Printed in the United States of America
3 The Macroeconomy: Unemployment, Inflation, and Deflation WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW Key Features of Business Fluctuations Business fluctuations are increases and decreases in business activity. A positive fluctuation is an expansion, which is an upward movement in business activity from a trough, or low point, to a peak, or high point. A negative fluctuation is a contraction, which is a drop in the pace of business activity from a previous peak to a new trough. MyEconLab continued business fluctuations expansion contraction recession depression leading indicators Key Figure Figure 6 WHERE TO GO TO PRACTICE MyEconLab Study Plan 7.6 Animated Figure 6 Log in to MyEconLab, take a chapter test, and get a personalized Study Plan that tells you which concepts you understand and which ones you need to review. From there, MyEconLab will give you further practice, tutorials, animations, videos, and guided solutions. For more information, visit PROBLEMS All problems are assignable in MyEconLab; exercises that update with real-time data are marked with. Answers to odd-numbered problems appear at the end of the chapter. 1. Suppose that you are given the following information: Total population Adult, noninstitutionalized, nonmilitary population Unemployment million million 7.5 million a. If the labor force participation rate is 70 percent, what is the labor force? b. How many workers are employed? c. What is the unemployment rate? 2. Suppose that you are given the following information: Labor force Adults in the military Nonadult population Employed adults Institutionalized adults Nonmilitary, noninstitutionalized adults not in labor force million 1.5 million 48.0 million million 3.5 million 40.8 million a. What is the total population? b. How many people are unemployed, and what is the unemployment rate? c. What is the labor force participation rate? 3. Suppose that the U.S. nonmilitary, noninstitutionalized adult population is 224 million, the number employed is 156 million, and the number unemployed is 8 million. a. What is the unemployment rate? b. Suppose that there is a difference of 60 million between the adult population and the combined total of people who are employed and unemployed. How do we classify these 60 million people? Based on these figures, what is the U.S. labor force participation rate? 4. During the course of a year, the labor force consists of the same 1,000 people. Employers have chosen not to hire 20 of these people in the face of government regulations making it too costly to employ them. Hence, they remain unemployed throughout the year. At the same time, every month during the year, 30 different people become unemployed, and 30 other different people who were unemployed find jobs. There is no seasonal employment. a. What is the frictional unemployment rate? b. What is the unemployment rate? c. Suppose that a system of unemployment compensation is established. Each month, 30 new people (not including the 20 that employers have chosen not to employ) continue to become unemployed, but each monthly group of newly unemployed now takes two months to find a job. After this change, what is the frictional unemployment rate?
4 The Macroeconomy: Unemployment, Inflation, and Deflation d. After the change discussed in part (c), what is the unemployment rate? 5. Suppose that a nation has a labor force of 100 people. In January, Amy, Barbara, Carine, and Denise are unemployed. In February, those four find jobs, but Evan, Francesco, George, and Horatio become unemployed. Suppose further that every month, the previous four who were unemployed find jobs and four different people become unemployed. Throughout the year, however, three people Ito, Jack, and Kelley continually remain unemployed because firms facing government regulations view them as too costly to employ. a. What is this nation s frictional unemployment rate? b. What is its structural unemployment rate? c. What is its unemployment rate? 6. In a country with a labor force of 200, a different group of 10 people becomes unemployed each month, but becomes employed once again a month later. No others outside these groups are unemployed. a. What is this country s unemployment rate? b. What is the average duration of unemployment? c. Suppose that establishment of a system of unemployment compensation increases to two months the interval that it takes each group of job losers to become employed each month. Nevertheless, a different group of 10 people still becomes unemployed each month. Now what is the average duration of unemployment? d. Following the change discussed in part (c), what is the country s unemployment rate? 7. A nation s frictional unemployment rate is 1 percent. Seasonal unemployment does not exist in this country. Its cyclical rate of unemployment is 3 percent, and its structural unemployment rate is 4 percent. What is this nation s overall rate of unemployment? 8. In 2012, the cost of a market basket of goods was $2,000. In 2014, the cost of the same market basket of goods was $2,100. Use the price index formula to calculate the price index for 2014 if 2012 is the base year. 9. Suppose that in 2013, a typical U.S. student attending a state-supported college bought 10 textbooks at a price of $100 per book and enrolled in 25 credit hours of coursework at a price of $360 per credit hour. In 2014, the typical student continued to purchase 10 textbooks and enroll in 25 credit hours, but the price of a textbook rose to $110 per book, and the tuition price increased to $400 per credit hour. The base year for computing a student price index using this information is What is the value of the student price index in 2013? In 2014? Show your work. 10. Between 2013 and 2014 in a particular nation, the value of the consumer price index for which the base year is 2010 rose by percent, to a value of 120 in What was the value of the price index in 2013? 11. Consider the following price indexes: 90 in 2013, 100 in 2014, 110 in 2015, 121 in 2016, and 150 in Answer the following questions. a. Which year is likely the base year? b. What is the inflation rate from 2014 to 2015? c. What is the inflation rate from 2015 to 2016? d. If the cost of a market basket in 2014 is $2,000, what is the cost of the same basket of goods and services in 2013? In 2017? 12. The real interest rate is 4 percent, and the nominal interest rate is 6 percent. What is the anticipated rate of inflation? 13. Currently, the price index used to calculate the inflation rate is equal to 90. The general expectation throughout the economy is that next year its value will be 99. The current nominal interest rate is 12 percent. What is the real interest rate? 14. At present, the nominal interest rate is 7 percent, and the expected inflation rate is 5 percent. The current year is the base year for the price index used to calculate inflation. a. What is the real interest rate? b. What is the anticipated value of the price index next year? 15. Suppose that in 2017 there is a sudden, unanticipated burst of inflation. Consider the situations faced by the following individuals. Who gains and who loses? a. A homeowner whose wages will keep pace with inflation in 2017 but whose monthly mortgage payments to a savings bank will remain fixed b. An apartment landlord who has guaranteed to his tenants that their monthly rent payments during 2017 will be the same as they were during 2016 c. A banker who made an auto loan that the auto buyer will repay at a fixed rate of interest during 2017 d. A retired individual who earns a pension with fixed monthly payments from her past employer during 2017
5 The Macroeconomy: Unemployment, Inflation, and Deflation 16. Consider the diagram at the right. The line represents the economy s growth trend, and the curve represents the economy s actual course of business fluctuations. For each part below, provide the letter label from the portion of the curve that corresponds to the associated term. a. Contraction b. Peak c. Trough d. Expansion Level of National Business Activity S U Growth trend Time V X ECONOMICS ON THE NET Looking at the Unemployment and Inflation Data This chapter reviewed key concepts relating to unemployment and inflation. In this application, you get a chance to examine U.S. unemployment and inflation data on your own. Title: Bureau of Labor Statistics: Employment and Unemployment Navigation: Use the link at to visit the Employment page of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Click on Top Picks next to Labor Force Statistics (Current Population Survey CPS). Application Perform the indicated operations, and answer the following questions. 1. Retrieve data for Civilian Labor Force Level, Employment Level, and Unemployment Level. Can you identify periods of sharp cyclical swings? Do they show up in data for the labor force, employment, or unemployment? 2. Are cyclical factors important? For Group Study and Analysis Divide the class into groups, and assign a price index to each group. Ask each group to take a look at the index for All Years at the link to the BLS statistics on inflation at /chap07. Have each group identify periods during which their index accelerated or decelerated (or even fell). Do the indexes ever provide opposing implications about inflation and deflation?
6 Answers to Odd-Numbered Problems 1. a. Multiplying the fraction of people who participate in the labor force, 0.7, times the adult, noninstitutionalized, nonmilitary population of million yields a labor force of million. b. Subtracting the 7.5 million unemployed from the labor force of million yields million people who are employed. c. Dividing the 7.5 million unemployed by the million in the labor force and multiplying by 100 yields an unemployment rate of about 5.36 percent. 3. a. The labor force equals the number employed plus the number unemployed, or 156 million + 8 million = 164 million. In percentage terms, therefore, the unemployment rate is 100 times 8 million>164 million, or 4.9 percent. b. These 60 million people are not in the labor force. The labor force participation rate is, in percentage terms, 100 times 164 million>224 million, or 73.2 percent. 5. a. Four of the 100 people are always continuously unemployed because they are between jobs, so the frictional unemployment rate is (4>100) * 100 = 4 percent. b. Three of the 100 people are always unemployed as a result of government regulations, so the structural unemployment rate is (3>100) * 100 = 3 percent. c. The unemployment rate is the sum of the frictional and structural rates of unemployment, or 7 percent. 7. The overall unemployment rate is 8 percent, and the natural rate of unemployment is 5 percent. 9. In 2013, the value of the price index is $10,000> $10,000 * 100 = 100. In 2014, the value of the price index is $11,100>$10,000 * 100 = a b. 10 percent c. 10 percent d. $1,800 in 2013; $3,000 in The expected rate of inflation is equal to 100 * [(99-90)>90] = 10 percent. Hence, the real interest rate equals the difference between the 12 percent nominal interest rate and the 10 percent anticipated inflation rate, or 2 percent. 15. a. The homeowner gains; the savings bank loses. b. The tenants gain; the landlord loses. c. The auto buyer gains; the bank loses. d. The employer gains; the pensioner loses. ANSWERS TO QUICK QUIZZES Quick Quiz 1: (i) Unemployed... labor force; (ii) job losers... reentrants... job leavers... new entrants; (iii) increase; (iv) female Quick Quiz 2: (i) Frictional; (ii) Structural; (iii) natural Quick Quiz 3: (i) base; (ii) Consumer Price; (iii) GDP deflator; (iv) Personal Consumption Expenditure Quick Quiz 4: (i) greater... less; (ii) purchasing power; (iii) resource Quick Quiz 5: (i) business fluctuations; (ii) trough... peak; (iii) recession; (iv) external shocks
7
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Macroeconomics Principles, Applications, and Tools O'Sullivan Sheffrin Perez Eighth Edition
 Macroeconomics Principles, Applications, and Tools O'Sullivan Sheffrin Perez Eighth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the
Macroeconomics Principles, Applications, and Tools O'Sullivan Sheffrin Perez Eighth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the
Financial Management Principles and Applications Titman Keown Martin Twelfth Edition
 Financial Management Principles and Applications Titman Keown Martin Twelfth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
Financial Management Principles and Applications Titman Keown Martin Twelfth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Macroeconomics Robert J. Gordon Twelfth Edition
 Macroeconomics Robert J. Gordon Twelfth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk
Macroeconomics Robert J. Gordon Twelfth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk
Advanced Accounting Floyd A. Beams Joseph H. Anthony Bruce Bettinghaus Kenneth Smith Eleventh edition
 Advanced Accounting Floyd A. Beams Joseph H. Anthony Bruce Bettinghaus Kenneth Smith Eleventh edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout
Advanced Accounting Floyd A. Beams Joseph H. Anthony Bruce Bettinghaus Kenneth Smith Eleventh edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout
Cost-Benefit Analysis Concepts and Practice Boardman Greenberg Vining Weimer Fourth Edition
 Cost-Benefit Analysis Concepts and Practice Boardman Greenberg Vining Weimer Fourth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the
Cost-Benefit Analysis Concepts and Practice Boardman Greenberg Vining Weimer Fourth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the
Valuation: The Art and Science of Corporate Investment Decisions Sheridan Titman John Martin Second Edition
 Valuation: The Art and Science of Corporate Investment Decisions Sheridan Titman John Martin Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies
Valuation: The Art and Science of Corporate Investment Decisions Sheridan Titman John Martin Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies
Exploring Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Comprehensive Grauer Scheeren Mulbery Second Edition
 Exploring Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Comprehensive Grauer Scheeren Mulbery Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the
Exploring Microsoft Office Excel 2007 Comprehensive Grauer Scheeren Mulbery Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the
Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets John C. Hull Eighth Edition
 Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets John C. Hull Eighth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on
Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets John C. Hull Eighth Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on
Construction Accounting and Financial Management Steven Peterson Third Edition
 Construction Accounting and Financial Management Steven Peterson Third Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit
Construction Accounting and Financial Management Steven Peterson Third Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM0 JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 04 All
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM0 JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 04 All
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting Nobles Mattison Matsumura Fourth Edition
 Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting Nobles Mattison Matsumura Fourth Edition Pearson Education imited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
Horngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting Nobles Mattison Matsumura Fourth Edition Pearson Education imited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
CHAPTER 6: MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL
 Principles of Macroeconomics CHAPTER 6: MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL Learning Goals: A. A recession started in March 2001 and ended in November 2001. What defines a recession, who makes
Principles of Macroeconomics CHAPTER 6: MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL Learning Goals: A. A recession started in March 2001 and ended in November 2001. What defines a recession, who makes
Introduction. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Chapter 7. Explain how the U.S. government calculates the official unemployment rate
 Chapter 7 The Macroeconomy:, Inflation, and Deflation Introduction Why is it that the responsibility for announcing the start of economic contractions and expansions does not rest with elected officials?
Chapter 7 The Macroeconomy:, Inflation, and Deflation Introduction Why is it that the responsibility for announcing the start of economic contractions and expansions does not rest with elected officials?
Fundamentals of Futures and Options Markets
 GLOBAL EDITION Fundamentals of Futures and Markets EIGHTH EDITION John C. Hull Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Katie Rowland Editorial Project Manager: Emily Biberger Editorial Assistant:
GLOBAL EDITION Fundamentals of Futures and Markets EIGHTH EDITION John C. Hull Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Katie Rowland Editorial Project Manager: Emily Biberger Editorial Assistant:
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation
 Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
Chapter 6 GDP, Unemployment and Inflation - Microeconomics: study of how households and firms make choices & how they interact in markets. - Macroeconomics: study of the economy as a whole, including topics
British Library Cataloguing-in-Publication Data A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library
 Editorial Director: Sally Yagan Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Director Editorial Services: Ashley Santora Editorial Project Manager: Karen Kirincich Editorial Assistant: Jane Avery Editorial Assistant:
Editorial Director: Sally Yagan Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Director Editorial Services: Ashley Santora Editorial Project Manager: Karen Kirincich Editorial Assistant: Jane Avery Editorial Assistant:
Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle
 Name: Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle Directions Activity listen and view today s PowerPoint lesson. As you view each slide, write in any
Name: Date: Block # Economics Guided Notes Unit Four Day #2 CPI, Unemployment and the Business Cycle Directions Activity listen and view today s PowerPoint lesson. As you view each slide, write in any
To Joan, Scott, Mary, Susie, Cathy, Liz, Garth, Jens, Laura, Dawn, Jesse, and Duncan
 To Joan, Scott, Mary, Susie, Cathy, Liz, Garth, Jens, Laura, Dawn, Jesse, and Duncan VP/Editorial Director: Sally Yagan AVP/Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Julie Broich Senior International
To Joan, Scott, Mary, Susie, Cathy, Liz, Garth, Jens, Laura, Dawn, Jesse, and Duncan VP/Editorial Director: Sally Yagan AVP/Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Julie Broich Senior International
5 MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL* Chapter. Key Concepts
 Chapter 5 MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL* Key Concepts The Business Cycle The periodic but irregular up-and-down movement in production and jobs is the business cycle. Business cycles have
Chapter 5 MONITORING CYCLES, JOBS, AND THE PRICE LEVEL* Key Concepts The Business Cycle The periodic but irregular up-and-down movement in production and jobs is the business cycle. Business cycles have
Principles of Macroeconomics. Twelfth Edition. Chapter 13. The Labor Market in the Macroeconomy. Copyright 2017 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Principles of Macroeconomics Twelfth Edition Chapter 13 The Labor Market in the Macroeconomy Copyright 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 13-1 Copyright Copyright 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 13-2 Chapter Outline
Principles of Macroeconomics Twelfth Edition Chapter 13 The Labor Market in the Macroeconomy Copyright 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 13-1 Copyright Copyright 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 13-2 Chapter Outline
Chapter 9: Unemployment and Inflation
 Chapter 9: Unemployment and Inflation Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 28, 2013 Learning Objectives 1. Measuring the Unemployment Rate, the Labor Force Participation Rate, and the Employment Population Ratio.
Chapter 9: Unemployment and Inflation Yulei Luo SEF of HKU January 28, 2013 Learning Objectives 1. Measuring the Unemployment Rate, the Labor Force Participation Rate, and the Employment Population Ratio.
To our spouses and children, and to all our students, past and present.
 To our spouses and children, and to all our students, past and present. Editor-in-Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Ellen Geary Publisher, Global Edition: Laura Dent Director of Editorial Services:
To our spouses and children, and to all our students, past and present. Editor-in-Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Ellen Geary Publisher, Global Edition: Laura Dent Director of Editorial Services:
Inflation. Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives
 CHAPTER 9 Unemployment and Inflation Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives 9.1 Measuring the Unemployment Rate, the Labor Force Participation Rate, and the Employment-Population Ratio (pages 268 277)
CHAPTER 9 Unemployment and Inflation Chapter Summary and Learning Objectives 9.1 Measuring the Unemployment Rate, the Labor Force Participation Rate, and the Employment-Population Ratio (pages 268 277)
An Introduction to Programming Using Python. David I. Schneider
 Global edition An Introduction to Programming Using Python David I. Schneider Vice President and Editorial Director, ECS: Marcia J. Horton Executive Editor: Tracy Johnson Assistant Acquisitions Editor,
Global edition An Introduction to Programming Using Python David I. Schneider Vice President and Editorial Director, ECS: Marcia J. Horton Executive Editor: Tracy Johnson Assistant Acquisitions Editor,
Chapter 3. Productivity, Employment
 Chapter 3 Productivity, Output, and Employment Chapter Outline The Production Function The Demand for Labor The Supply of Labor Labor Market Equilibrium Unemployment Relating Output and Unemployment: Okun
Chapter 3 Productivity, Output, and Employment Chapter Outline The Production Function The Demand for Labor The Supply of Labor Labor Market Equilibrium Unemployment Relating Output and Unemployment: Okun
Economics Unit 3 Summary
 SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
3. The phase of the business cycle in which real GDP is at a minimum is called: A. the peak. B. a recession. C. the trough. D. the underside.
 1. Most economists agree that the immediate determinant of the volume of output and employment is the: A. composition of consumer spending. B. ratio of public goods to private goods production. C. level
1. Most economists agree that the immediate determinant of the volume of output and employment is the: A. composition of consumer spending. B. ratio of public goods to private goods production. C. level
Consequences of Business Fluctuations
 Aggregate Output Consequences of Business Fluctuations Parts of Chapter 14 + Other Issues Discussion Topics Fluctuations in business activity Consequences of business fluctuations Macroeconomic policy
Aggregate Output Consequences of Business Fluctuations Parts of Chapter 14 + Other Issues Discussion Topics Fluctuations in business activity Consequences of business fluctuations Macroeconomic policy
To Rebecca, Natasha, and Hannah, for the love and for being there J. B. To Kaui, Pono, Koa, and Kai, for all the love and laughter P. D.
 To Rebecca, Natasha, and Hannah, for the love and for being there J. B. To Kaui, Pono, Koa, and Kai, for all the love and laughter P. D. Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Katie Rowland
To Rebecca, Natasha, and Hannah, for the love and for being there J. B. To Kaui, Pono, Koa, and Kai, for all the love and laughter P. D. Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Katie Rowland
United Kingdom issued by the Copyright Licensing Agency Ltd, Saffron House, 6 10 Kirby Street, London EC 1N 8TS.
 Vice President, Business Publishing: Donna Battista Senior Acquisitions Editor: Lacey Vitetta Editorial Assistant: Christine Donovan Vice President, Product Marketing: Maggie Moylan Director of Marketing,
Vice President, Business Publishing: Donna Battista Senior Acquisitions Editor: Lacey Vitetta Editorial Assistant: Christine Donovan Vice President, Product Marketing: Maggie Moylan Director of Marketing,
2. In terms of dollar volume of exports and imports, the most important trading partner for the United States is:
 1. In the U.S. economy, all are generally accepted economic functions of government except: A) The provision of public goods B) The production and distribution of consumer goods C) Pursuing policies that
1. In the U.S. economy, all are generally accepted economic functions of government except: A) The provision of public goods B) The production and distribution of consumer goods C) Pursuing policies that
The diagram above illustrates the pattern of: A) Wage movements over time B) Price level movements C) Economic growth patterns D) Business cycles
 Problem Set Econ 2013: Chapter 9: Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Name ID: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 1) The
Problem Set Econ 2013: Chapter 9: Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Name ID: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 1) The
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices
 SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS. Macroeconomics
 GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS Macroeconomics GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Macroeconomic Concepts SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured.
GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS Macroeconomics GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARDS INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS Macroeconomic Concepts SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured.
MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1. 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because:
 MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because: A. Nominal GDP can increase simply because of price increases over time. B. Real
MACROECONOMICS REVIEW FOR EXAM #1 1. Real GDP is better than nominal GDP in making comparisons of GDP over time because: A. Nominal GDP can increase simply because of price increases over time. B. Real
Summer Examinations 2015
 Summer Examinations 2015 Module Title Level Time Allowed Introduction to Macroeconomics Four Two hours Instructions to students: Enter your student number not your name on all answer books. Section A:
Summer Examinations 2015 Module Title Level Time Allowed Introduction to Macroeconomics Four Two hours Instructions to students: Enter your student number not your name on all answer books. Section A:
Macroeconomic TOPIC Measurements, Part I: Prices and Unemployment
 1 Macroeconomic TOPIC Measurements, Part I: Prices and Unemployment Employment and Unemployment Population Survey In the U.S., the population is divided into two groups: The working-age population or civilian
1 Macroeconomic TOPIC Measurements, Part I: Prices and Unemployment Employment and Unemployment Population Survey In the U.S., the population is divided into two groups: The working-age population or civilian
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION
 ECO 183 (R) / Page 1 of 9 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION Section A : Answer ALL questions.
ECO 183 (R) / Page 1 of 9 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UNIVERSITY FOUNDATION PROGRAMME ECO 183 : FOUNDATION ECONOMICS (MACROECONOMICS) RESIT EXAMINATION : AUGUST 2002 SESSION Section A : Answer ALL questions.
Chapter 3: Productivity, Output, and Employment
 Chapter 3: Productivity, Output, and Employment Yulei Luo SEF of HKU September 12, 2013 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON2220: Macro Theory September 12, 2013 1 / 29 Chapter Outline The Production Function The
Chapter 3: Productivity, Output, and Employment Yulei Luo SEF of HKU September 12, 2013 Luo, Y. (SEF of HKU) ECON2220: Macro Theory September 12, 2013 1 / 29 Chapter Outline The Production Function The
Instructor s Manual. Fundamentals of Financial Management. Thirteenth edition. James C. Van Horne John M. Wachowicz, Jr.
 Instructor s Manual Fundamentals of Financial Management Thirteenth edition James C. Van Horne John M. Wachowicz, Jr. For further instructor material please visit: www.pearsoned.co.uk/wachowicz ISBN: 978-0-273-71364-7
Instructor s Manual Fundamentals of Financial Management Thirteenth edition James C. Van Horne John M. Wachowicz, Jr. For further instructor material please visit: www.pearsoned.co.uk/wachowicz ISBN: 978-0-273-71364-7
3. Suppose the following data represent the market demand for college education: a. If tuition is set at $5,000, how many students will enroll?
 PS 4: 38 points Government Intervention: Chapter 9 problems 3. Suppose the following data represent the market demand for college education: a. If tuition is set at $5,000, how many students will enroll?
PS 4: 38 points Government Intervention: Chapter 9 problems 3. Suppose the following data represent the market demand for college education: a. If tuition is set at $5,000, how many students will enroll?
ECON 201. The Business Cycle. Business Cycle 4 phases 10/1/2009. Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation
 ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
ECON 201 Chapter 6 Business Cycles, Unemployment, & Inflation The Business Cycle The U.S. has experienced economic instability associated with business cycles. Business Cycles alternating rises and declines
1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
McGraw-Hill/Irwin 2002 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
 The Business Cycle Macroeconomics The Great Depression was the springboard for modern macroeconomics. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of aggregate economic behavior, of the economy as a whole.
The Business Cycle Macroeconomics The Great Depression was the springboard for modern macroeconomics. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of aggregate economic behavior, of the economy as a whole.
THE EMPLOYMENT SITUATION: SEPTEMBER 2000
 Internet address: http://stats.bls.gov/newsrels.htm Technical information: USDL 00-284 Household data: (202) 691-6378 Transmission of material in this release is Establishment data: 691-6555 embargoed
Internet address: http://stats.bls.gov/newsrels.htm Technical information: USDL 00-284 Household data: (202) 691-6378 Transmission of material in this release is Establishment data: 691-6555 embargoed
Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation
 CHAPTER 24 Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Remember that there is nothing stable in human affairs; therefore avoid undue elation in prosperity, or undue depression in adversity.
CHAPTER 24 Economic Growth, Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation Remember that there is nothing stable in human affairs; therefore avoid undue elation in prosperity, or undue depression in adversity.
Unemployment Rate = 1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
A. unchanged decrease B. surplus decrease C. unchanged no change D. surplus increase E. unchanged increase A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E.
 AP Macroeconomics Test (Answers on last Page) 1. Which of the following correctly describes the components of Aggregate Demand? A. Consumption expenditures + Investment expenditures + Government expenditures
AP Macroeconomics Test (Answers on last Page) 1. Which of the following correctly describes the components of Aggregate Demand? A. Consumption expenditures + Investment expenditures + Government expenditures
Chapter Outline. Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression
 Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression Chapter Outline Measuring the Economy Real Gross Domestic Product and Why
Chapter 6 Every Macroeconomic Word You Have Ever Heard: Gross Domestic Product, Inflation, Unemployment, Recession and Depression Chapter Outline Measuring the Economy Real Gross Domestic Product and Why
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7 th Edition
 Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7 th Edition Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7e Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Chap 7-1 Learning Objectives
Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7 th Edition Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions Statistics for Managers Using Microsoft Excel 7e Copyright 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Chap 7-1 Learning Objectives
Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle
 Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle Multiple Choice Questions Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The sources of
Chapter 11 Macroeconomic Issues: Economic Growth and the Business Cycle Multiple Choice Questions Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The sources of
CHAPTER 8 FISCAL POLICY: COPING WITH INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT
 CHAPTER 8 FISCAL POLICY: COPING WITH INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT Chapter in a Nutshell To say that an economy is in equilibrium tells us very little about the general state of the economy. The model showing
CHAPTER 8 FISCAL POLICY: COPING WITH INFLATION AND UNEMPLOYMENT Chapter in a Nutshell To say that an economy is in equilibrium tells us very little about the general state of the economy. The model showing
Unemployment Rate = 1. A large number of economic statistics are released regularly. These include the following:
 CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
CHAPTER The Data of Macroeconomics Questions for Review 1. GDP measures the total income earned from the production of the new final goods and services in the economy, and it measures the total expenditures
Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out. Robert Collier Test Yourself - Business Cycles and Unemployment
 Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out. Robert Collier Test Yourself - Business Cycles and Unemployment What is a business cycle? A business cycle is alternating periods of economic
Success is the sum of small efforts, repeated day in and day out. Robert Collier Test Yourself - Business Cycles and Unemployment What is a business cycle? A business cycle is alternating periods of economic
MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET
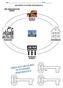 Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Name: Period THE CIRCULAR FLOW MODEL MEASURING ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE PRODUCT MARKET BUSINESSES HOUSEHOLDS RESOURCE MARKET 1. AKA: 2. 3. Additional Notes on Previous Page/Practice Workspace Quick Write Space
Macroeconomics, Spring 2007, Final Exam, several versions, Early May
 Name: _ Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date: Macroeconomics, Spring 2007, Final Exam, several versions, Early May Read these Instructions carefully! You must follow them exactly! I) On your Scantron card
Name: _ Days/Times Class Meets: Today s Date: Macroeconomics, Spring 2007, Final Exam, several versions, Early May Read these Instructions carefully! You must follow them exactly! I) On your Scantron card
Economics 207: Introduction to Macroeconomics Final Exam Instructions:
 Economics 207: Introduction to Macroeconomics Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete the following exam. Be sure to write your anme and student id ON YOUR SCANTRON and BELOW. Failure
Economics 207: Introduction to Macroeconomics Final Exam Instructions: You have 120 minutes to complete the following exam. Be sure to write your anme and student id ON YOUR SCANTRON and BELOW. Failure
Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004
 ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Ryerson University Fall 2005 Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004 Part A Multiple-Choice Questions [30 marks]
ECN 204 Introductory Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Ryerson University Fall 2005 Assignment 1 Deadline: September 23, 2004 Part A Multiple-Choice Questions [30 marks]
MACROECONOMICS - CLUTCH CH UNEMPLOYMENT AND INFLATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: LABOR FORCE AND UNEMPLOYMENT Tracking levels of employment within an economy gives meaningful data regarding the nation s productivity Labor Force the total number of workers,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: LABOR FORCE AND UNEMPLOYMENT Tracking levels of employment within an economy gives meaningful data regarding the nation s productivity Labor Force the total number of workers,
CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY
 CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY Business Cycles Economic growth is something that is beneficial to almost everyone Sometimes though, economic growth is interrupted by business cycles largely systematic
CHAPTER 14 ECONOMIC INSTABILITY Business Cycles Economic growth is something that is beneficial to almost everyone Sometimes though, economic growth is interrupted by business cycles largely systematic
Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards
 Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards Macroeconomic Concepts: SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Identify and describe the macroeconomic goals of
Name Economics: Unit Three Study Guide Unit One Standards Macroeconomic Concepts: SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Identify and describe the macroeconomic goals of
Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403
 Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403 http//vustudents.ning.com Actual budget The amount spent by the Federal government (to purchase goods and services and for transfer payments) less the amount of tax
Objectives of Macroeconomics ECO403 http//vustudents.ning.com Actual budget The amount spent by the Federal government (to purchase goods and services and for transfer payments) less the amount of tax
Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth. Unemployment. Unemployment. Measuring Unemployment
 Chapter 7, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth Measuring Components of the Rate The Costs of Inflation The Consumer Price Index The Costs of Inflation Long-Run Growth Output and Productivity Growth Measuring
Chapter 7, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth Measuring Components of the Rate The Costs of Inflation The Consumer Price Index The Costs of Inflation Long-Run Growth Output and Productivity Growth Measuring
Dominican International School. AP MACROECONOMICS 1 Year, 1 Credit GRADE LEVEL: 11 and /19 TEACHER: Dr Mercia de Souza
 1 Dominican International School AP MACROECONOMICS 1 Year, 1 Credit GRADE LEVEL: 11 and 12 2018/19 TEACHER: Dr Mercia de Souza Course Description An AP course in Macroeconomics is designed to give students
1 Dominican International School AP MACROECONOMICS 1 Year, 1 Credit GRADE LEVEL: 11 and 12 2018/19 TEACHER: Dr Mercia de Souza Course Description An AP course in Macroeconomics is designed to give students
How the Government Measures Unemployment
 What Does the Unemployment Rate Tell Us About an Economy s Health? (EA) At any one time, millions of Americans may be out of work. For many of them, the experience is devastating. They struggle to pay
What Does the Unemployment Rate Tell Us About an Economy s Health? (EA) At any one time, millions of Americans may be out of work. For many of them, the experience is devastating. They struggle to pay
Macro Economic questions Part I
 Macro Economic questions Part I Question Budget Rental Car buys new automobiles for its business from a U.S. company. The value of transaction would be included in which category of the GDP? a. consumer
Macro Economic questions Part I Question Budget Rental Car buys new automobiles for its business from a U.S. company. The value of transaction would be included in which category of the GDP? a. consumer
Print Your Name:. ID Number:.
 Econ2105, Professor Laury EXAM 1, FORM A (9/19/02) Print Your Name:. ID Number:. Multiple Choice (32 questions, 2.5 points each, 80 points total). Clearly indicate (by circling) the ONE BEST response to
Econ2105, Professor Laury EXAM 1, FORM A (9/19/02) Print Your Name:. ID Number:. Multiple Choice (32 questions, 2.5 points each, 80 points total). Clearly indicate (by circling) the ONE BEST response to
MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION
 21 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain why unemployment is a problem and define the unemployment rate and other labour market indicators Explain why
21 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION After studying this chapter, you will be able to: Explain why unemployment is a problem and define the unemployment rate and other labour market indicators Explain why
Unit 5 Notes. National Economic Performance
 Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics
Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics
Foundations of Finance
 GLOBAL EDITION Foundations of Finance The Logic and Practice of Financial Management EIGHTH EDITION Keown Martin Petty Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Katie Rowland Publisher, Global
GLOBAL EDITION Foundations of Finance The Logic and Practice of Financial Management EIGHTH EDITION Keown Martin Petty Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Acquisitions Editor: Katie Rowland Publisher, Global
Economics Spring Benchmark 2
 Directions: Read and answer each question carefully. Mark your answers on your bubble sheet. Do NOT write on exam. 1. What does the GDP, gross domestic product, measure? A) the amount of goods bought and
Directions: Read and answer each question carefully. Mark your answers on your bubble sheet. Do NOT write on exam. 1. What does the GDP, gross domestic product, measure? A) the amount of goods bought and
MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION*
 Chapt er 5 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* Key Concepts Employment and Unemployment Unemployment is a problem for both the unemployed worker and for society. Unemployed workers lose income and, if prolonged,
Chapt er 5 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* Key Concepts Employment and Unemployment Unemployment is a problem for both the unemployed worker and for society. Unemployed workers lose income and, if prolonged,
MONEY. Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout
 MONEY Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout Barter Economy A barter economy is an economy with no money. The only way you can get what you want in a barter economy is to trade something
MONEY Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout Barter Economy A barter economy is an economy with no money. The only way you can get what you want in a barter economy is to trade something
Problem Set #4 ANSWERS. Due Tuesday, April 1, 2008
 Name: SID: Discussion Section: Problem Set #4 ANSWERS Due Tuesday, April 1, 2008 Problem Sets MUST be word-processed except for graphs and equations. When drawing diagrams, the following rules apply: 1.
Name: SID: Discussion Section: Problem Set #4 ANSWERS Due Tuesday, April 1, 2008 Problem Sets MUST be word-processed except for graphs and equations. When drawing diagrams, the following rules apply: 1.
Economics Unit Four. Macroeconomics
 Economics Unit Four Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the whole economy together the aggregated spending, saving, and investing decisions of all consumers and businesses describes
Economics Unit Four Macroeconomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of the whole economy together the aggregated spending, saving, and investing decisions of all consumers and businesses describes
SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
 26 SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There are no substantial changes to this chapter. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
26 SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM WHAT S NEW IN THE FOURTH EDITION: There are no substantial changes to this chapter. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: By the end of this chapter, students should understand:
Unemployment and Inflation. 1 of of 29
 1 of 29 2 of 29 In early June 2008, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) announced that the unemployment rate for May 2008 was 5.5 percent. P R E P A R E D B Y FERNANDO QUIJANO, YVONN QUIJANO, AND XIAO
1 of 29 2 of 29 In early June 2008, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) announced that the unemployment rate for May 2008 was 5.5 percent. P R E P A R E D B Y FERNANDO QUIJANO, YVONN QUIJANO, AND XIAO
Measuring a Nation s Production and Income
 Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
Chapter Summary 5 Measuring a Nation s Production and Income In this chapter, we learned how economists and government statisticians measure the income and production for an entire country and what those
The problem with gross domestic product is the gross bit. There are no deductions involved: all economic activity is accounted as if it were of
 The problem with gross domestic product is the gross bit. There are no deductions involved: all economic activity is accounted as if it were of positive value. Social harm is added to, not subtracted from,
The problem with gross domestic product is the gross bit. There are no deductions involved: all economic activity is accounted as if it were of positive value. Social harm is added to, not subtracted from,
EXAM 3. There are 110 possible points on this exam. The test is out of 100.
 Name: KEY ECON 201 Montgomery College David Youngberg EXAM 3 There are 110 possible points on this exam. The test is out of 100. You have one class session to complete this exam, but you should be able
Name: KEY ECON 201 Montgomery College David Youngberg EXAM 3 There are 110 possible points on this exam. The test is out of 100. You have one class session to complete this exam, but you should be able
Business insights. Employment and unemployment. Sharp rise in employment since early 1975
 Business insights Employment and unemployment Early each month, usually the first Friday, the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) issues its report, "The Employment Situation." This publication
Business insights Employment and unemployment Early each month, usually the first Friday, the United States Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) issues its report, "The Employment Situation." This publication
Fiscal Sustainability and Competitiveness in Europe and Asia
 Fiscal Sustainability and Competitiveness in Europe and Asia This page Intentionally left blank Fiscal Sustainability and Competitiveness in Europe and Asia Ramkishen S. Rajan Adjunct Senior Research Fellow,
Fiscal Sustainability and Competitiveness in Europe and Asia This page Intentionally left blank Fiscal Sustainability and Competitiveness in Europe and Asia Ramkishen S. Rajan Adjunct Senior Research Fellow,
Business Statistics Norean D. Sharpe Richard D. De Veaux Paul Velleman Second Edition
 Business Statistics Norean D. Sharpe Richard D. De Veaux Paul Velleman Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
Business Statistics Norean D. Sharpe Richard D. De Veaux Paul Velleman Second Edition Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
Principles of Macroeconomics December 15th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points)
 EC132.01 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 15th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
EC132.01 Serge Kasyanenko Principles of Macroeconomics December 15th, 2005 name: Final Exam (100 points) This is a closed-book exam - you may not use your notes and textbooks. Calculators are not allowed.
Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010
 Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010 Dr. Stuart Allen 334-3166 Office Hours: Before Class Department Office 462 Bryan E-mail: stuart_allen@uncg.edu PURPOSE This course uses market analysis
Principles of Macroeconomics Economics 202 Spring 2010 Dr. Stuart Allen 334-3166 Office Hours: Before Class Department Office 462 Bryan E-mail: stuart_allen@uncg.edu PURPOSE This course uses market analysis
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England. and Associated Companies throughout the world
 AVP/Executive Editor: Stephanie Wall Editorial Director: Sally Yagan Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Director of Editorial Services: Ashley Santora Editorial Project Manager: Christina Rumbaugh Editorial
AVP/Executive Editor: Stephanie Wall Editorial Director: Sally Yagan Editor in Chief: Donna Battista Director of Editorial Services: Ashley Santora Editorial Project Manager: Christina Rumbaugh Editorial
Figure Sarver
 I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. About the business cycle and its primary phases. B. How unemployment and inflation are measured. C. About the types of unemployment and inflation
I. Learning Objectives In this chapter students will learn: A. About the business cycle and its primary phases. B. How unemployment and inflation are measured. C. About the types of unemployment and inflation
Macroeconomics. Based on the textbook by Karlin and Soskice: Macroeconomics: Institutions, Instability, and the Financial System
 Based on the textbook by Karlin and Soskice: : Institutions, Instability, and the Financial System Robert M Kunst robertkunst@univieacat University of Vienna and Institute for Advanced Studies Vienna October
Based on the textbook by Karlin and Soskice: : Institutions, Instability, and the Financial System Robert M Kunst robertkunst@univieacat University of Vienna and Institute for Advanced Studies Vienna October
A FIRST LOOK AT* MACROECONOMICS*
 C h a p t e r 4 A FIRST LOOK AT* MACROECONOMICS* Chapter Key Ideas Outline What Will Your World Be Like? A. What will happen to economic growth, unemployment, inflation, the government budget deficit,
C h a p t e r 4 A FIRST LOOK AT* MACROECONOMICS* Chapter Key Ideas Outline What Will Your World Be Like? A. What will happen to economic growth, unemployment, inflation, the government budget deficit,
MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH
 21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
21 MEASURING GDP AND ECONOMIC GROWTH GDP Defined GDP or gross domestic product is the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country in a given time period. This definition has four
Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth
 Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth 7.1 Unemployment 1 Multiple Choice 1) We can safely say that total output can increase if there is a(n) A) increase in the size of the labor force
Chapter 7 Unemployment, Inflation, and Long-Run Growth 7.1 Unemployment 1 Multiple Choice 1) We can safely say that total output can increase if there is a(n) A) increase in the size of the labor force
3. Investment in human capital shifts the aggregate production function: A) leftward. B) upward. C) rightward. D) downward.
 Econ 102 Exam 1 Name ID Section Number 1. Which of the following equations describes the calculation of the natural unemployment rate? A) Natural unemployment = frictional unemployment + cyclical unemployment.
Econ 102 Exam 1 Name ID Section Number 1. Which of the following equations describes the calculation of the natural unemployment rate? A) Natural unemployment = frictional unemployment + cyclical unemployment.
Midterm #2, version A, given Spring 2002 Note question #50 is from Chapter 11, which students are not responsible for on Exam 2 - Summer 02.
 Midterm #2, version A, given Spring 2002 Note question #50 is from Chapter 11, which students are not responsible for on Exam 2 - Summer 02. Answers (if you think you see an error, please contact me ASAP.
Midterm #2, version A, given Spring 2002 Note question #50 is from Chapter 11, which students are not responsible for on Exam 2 - Summer 02. Answers (if you think you see an error, please contact me ASAP.
ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM SPRING 2014 Prof. Bill Even FORM 3. Directions
 ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM SPRING 2014 Prof. Bill Even FORM 3 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique id and form number. Doing this properly is worth the equivalent
ECO202: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS FIRST MIDTERM EXAM SPRING 2014 Prof. Bill Even FORM 3 Directions 1. Fill in your scantron with your unique id and form number. Doing this properly is worth the equivalent
MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* *
 C h a p t e r 22 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* * Answers to the Review Quizzes Page 112 (page 518 in Economics) 1. What determines if a person is in the labor force? Workers who have a job and workers
C h a p t e r 22 MONITORING JOBS AND INFLATION* * Answers to the Review Quizzes Page 112 (page 518 in Economics) 1. What determines if a person is in the labor force? Workers who have a job and workers
EXAM PREP WORKSHOP # 2 > ECONOMIC MEASUREMENTS
 LIGHTHOUSE CPA SOCIAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT AP ECONOMICS EXAM PREP WORKSHOP # 2 > ECONOMIC MEASUREMENTS NAME : DATE : True or false, and explain why? 1. If a country could maintain a high economic growth
LIGHTHOUSE CPA SOCIAL SCIENCES DEPARTMENT AP ECONOMICS EXAM PREP WORKSHOP # 2 > ECONOMIC MEASUREMENTS NAME : DATE : True or false, and explain why? 1. If a country could maintain a high economic growth
We use GDP to compare different economies or to track the same economy over time.
 Lecture Notes ECON 1A: Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 5 - Introduction to Macroeconomics Introduction Macroeconomics looks at the big picture: Demand for: Average price of: Consumption by: Investment
Lecture Notes ECON 1A: Principles of Macroeconomics Chapter 5 - Introduction to Macroeconomics Introduction Macroeconomics looks at the big picture: Demand for: Average price of: Consumption by: Investment
Real Estate Expenses. Example 1. Example 2. To calculate the initial expenses of buying a home
 Real Estate Expenses To calculate the initial expenses of buying a home One of the largest investments most people ever make is the purchase of a home. The major initial expense in that purchase is the
Real Estate Expenses To calculate the initial expenses of buying a home One of the largest investments most people ever make is the purchase of a home. The major initial expense in that purchase is the
