On the Economic Situation in Russia During Fourth Quarter of 2014 Third Quarter of 2015 and the Outlook for
|
|
|
- Mervin Norris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CENTER FOR MACROECONOMIC ANALYSIS AND SHORT-TERM FORECASTING Tel.: (749) , fax: (749) , D. Belousov, E. Abramova, A. Apokin, K. Mikhaylenko On the Economic Situation in Russia During Fourth Quarter of 2014 Third Quarter of 201 and the Outlook for Recent Trends General Overview of the Situation For over a year, a growing downturn has been the key trend defining the state of Russian economy. Year-end of 2014 demonstrated GDP growth of +0.6%. However, this growth was guaranteed only for the first six months, and also this was mostly due to increase in household consumption, against the background of the growing decline of fixed capital investments. This year the economy is projected to decline by. 4.0% (see Chart 1). Probabilities of shifting towards growth in the coming years are not yet clear. It is highly likely that in 2016 the Russian economy will face a mild downturn (stagnation is best case scenario), and in there will be an extremely sluggish growth Chart 1. GDP (Growth Rates, %) , estimate Chart 2. Contributions of the factors to GDP growth (% of GDP growth) , estimate household final consumption expenditure government final consumption expenditure gross fixed capital formation change in inventories export import other factors An essential feature of today's crisis is the contraction of almost every element of domestic final demand (see Chart 2). If participation of gross fixed capital formation went into the negative as far back as 201 (201: -2.0 of GDP percentage point; 2014: -1.2 of GDP percentage point; 201, estimate: -4.6 of percentage point), then the absolute decline in household consumption became a brand new and very powerful downturn factor only in the current year (201 estimate: -,0 of GDP percentage point). With this, the slowdown of household consumption is attributed to med-term factors: the need for companies to lower the pressure of labor expenses on their competitiveness; leaving the overheated consumer lending domain. Therefore, we have all the reasons to presume that a slowdown 1
2 in private demand will linger, which means a major restraint on the economic growth. The output is supported solely by expansion of net export, primarily due to major decrease in import, first of all owing to several waves of ruble devaluation. The export (even if we ignore the raw commodities and their dependency on the volatile market conditions) grows at low rates which is normal in the circumstances of the corporate lending collapse that occurred. How the Crisis Formed It should be noted that both the crisis itself and its pre-conditions formed two to three years prior to its official start. And they stem from the mechanism for recovering from the previous crisis wave by means of increased labor compensation growth (in the public sector and, due to activity of the competition on the labor market, in the economy overall 1 ), which encouraged a major expansion of households consumption. In the end, thanks to the increase of labor expenses, company profit margins have never recovered from the crisis, which initiated the reduction in private investment (201), forced bank lending to move from corporate into consumer sector, and resulted in depreciation pressure on the economy. In this circumstance, which basically still warranted correction in , the Russian economy moved towards the shock of the second half of During the past year (fourth quarter of 2014 third quarter of 201) Russia's economic development went through two phases, each approximately six months in length a deep recession at the turn of 2014 and 201 and stagnation in the second and third quarters of 201. Shock Recession Phase The crisis moved into the open in the latter half of 2014 and became full-blown in its fourth quarter. The end of 2014 was marked by a combination of three factors: the strengthening of the sanctions regime, the drop in oil prices, and the devaluation shock. On the one hand, the economic sanctions turned up an issue related to access of the Russian corporations to external lending which previously provided a basic resource for financing major longterm projects 2. On the other hand, global oil prices dropped by half (from USD 96 to 46 per barrel between September and January, see Chart ). This deprived the Russian companies and later the treasury of a major fraction of revenue; moreover, it inflicted a serious blow to the balance of payments stipulating strong devaluation pressure on the ruble. A drop in oil prices and general deterioration on the foreign and domestic markets led to an abrupt capital outflow (USD 76 billion in the fourth quarter). At the same time, the balance of payments crisis became a factor in major ruble devaluation: the rate of the ruble against the dualcurrency basket had dropped by more than time and a half. This, in turn, couldn't help but cause a spike in inflation, which in six month increased year-onyear from 7.% (August 2014) to 16.9% (March 201). 1 Economy-wide, the average monthly salary of a single employee per the exchange rate was around USD 1,000 by the start of 2014, moving close to the level of the Eastern European countries. 2 Here, a part was played often not even by the inflow of money to large projects, but by an anticipated through attraction of external financing international quality assessment of a project, risks, profitability, etc. The situation was worsened by the necessity for the companies to save up on currency in order to get through the peak of corporate debt repayment at the start of 201, and possibly, for speculative purposes; in any case, December 2014 marked a spike in currency demand on the stock exchange on behalf of only several major agents most likely serving the interests of some kind of heavy borrowers. 2
3 Graphic Chart. Urals Oil Prices (USD per barrel) Graphic Chart 4. Ratio of inflation and the interest rate of the Bank of Russia for shortterm REPO auctions (year-on-year, growth rate, %) minimum interest rates on REPO actions with maturity from 1 to 6 days, % (annual average) CPI (as compared with the same period last year, %) A unique crisis of the "stop-go regulation" became an additional factor: under the circumstances when a full-blown recession had already been underway in Russia, the Bank of Russia followed a strict interest-rate policy oriented towards suppression of the inflation and stabilization of the exchange rate. At the same time, up until the end of the year it was believed that in Russia utilization of the factors of production (low unemployment rate, high capacity utilization) remained on the high level, however, the signs of recession were practically ignored 4. Therefore, the rate (based on one-week direct REPO auctions) of the Bank of Russia was increased twofold, from 7.9% in the third quarter to 1.% in the first quarter of 201 (see Chart 4). However, this could not avert a spike in inflation, but the recession strengthened abruptly. In the fourth quarter fixed capital investments remained its primary focus. What turned out to be a deterrent was not even the drop in availability of the lending resources in itself (which definitely took place), but also demotivation of potential investors with the established level of rates and risks it is more profitable and safer to keep the existing resources in financial assets rather than engage in high-risk investment into real assets. With this, it seems that antiinflation efforts of the Bank of Russia worked "towards the opposite direction": a reduction in fixed capital investments led to the release of financial resources that in turn migrated to the foreign exchange market stipulating ruble devaluation and eventually increase of the inflation. In the fourth quarter of 2014 the output was somehow still supported by a rapid expansion of households consumption (in December, given the expected price growth in the new year, the consumer demand became abnormal and feverish). From the start of 201 consumer spending naturally began to decline (see Chart 7), and a fullscale economic downturn emerged. 4 Note that in accordance with the law, support of the output (prevention of recession, etc.) are not included in the objectives of the Bank of Russia. It goes without saying that in certain way the inflation was aided by the "anti-sanctions" introduced by Russia on the food market in the third quarter of 2014, the intention of which was to deprive the European countries and USA with allies of their motivation to extend the economic sanctions against Russia. The increase of the monopoly on regional food markets spurred up the inflation of course, but the consequences of the "anti-sanctions" were completely absorbed by the results of ruble devaluation (even more so that the specified restrictive measures one way or another helped to offset the balance of trade; without those measures the devaluation obviously would have been more profound).
4 Jan-2010 Feb-2010 Mar-2010 Apr-2010 May-2010 Jun-2010 Jul-2010 Aug-2010 Sep-2010 Oct-2010 Nov-2010 Dec-2010 Jan-2011 Feb-2011 Mar-2011 Apr-2011 May-2011 Jun-2011 Jul-2011 Aug-2011 Sep-2011 Oct-2011 Nov-2011 Dec-2011 Jan-2012 Feb-2012 Mar-2012 Apr-2012 May-2012 Jun-2012 Jul-2012 Aug-2012 Sep-2012 Oct-2012 Nov-2012 Dec-2012 Jan-201 Feb-201 Mar-201 Apr-201 May-201 Jun-201 Jul-201 Aug-201 Sep-201 Oct-201 Nov-201 Dec-201 Jan-2014 Feb-2014 Mar-2014 Apr-2014 May-2014 Jun-2014 Jul-2014 Aug-2014 Sep-2014 Oct-2014 Nov-2014 Dec-2014 Jan-201 Feb-201 Mar-201 Apr-201 May-201 Jun-201 Jul-201 Aug-201 Stagnation Phase Starting from the second quarter of 201, the economic situation began to improve somewhat. Ruble devaluation allowed Russian companies (especially those oriented towards non-resource exports) to improve their financial state to a certain extent, although not as much as could have been expected judging by its depth 6. The Bank of Russia moved to a more stimulative policy by starting careful reduction of the interest rate. Under these circumstances Russia's economy began "searching for the bottom": long-term (2 months) periods of stabilization of real wages and consumption have been noted. Unemployment grows slowly (except that there is almost no growth in the skilled labor segment). Periods of investment stabilization have been noted (see Chart 8). This means that companies continue to hope for a speedy conclusion of the crisis and a shift to growth. By mid-year there even were hopes that signs of growth would appear already in the fourth quarter. At the present time these hopes have turned into an illusion. On the one hand, another drop in oil prices led to the new devaluation wave with its appropriate inflationary effect. On the other hand, this was also topped by a sharp increase of the regulated tariffs on the housing and utilities as well as transport services as of 1 July 201. Consequently, the inflation spike had practically "consumed" the potential of possible economic revival. It should not be left unmentioned that in itself the economic stabilization based on households consumption in our circumstances is a manifestation of the crisis: the increased risks of corporate lending push the banks to consumer lending. As a result, the economic growth is, of course, supported, however it is done at the expense of potential destabilization of the banking system. Therefore, consumer lending most likely and in the long view will start to die down. Graphic Chart. Nominal foreign currency to ruble exchange rates (rubles to a unit of foreign currency) real effictive ruble exchange rate (august 2008=%, left scale) bicurrency basket rate (0. USD+0.4 euro), rubles, end of the month (right scale) Graphic Chart 6. Dynamics of the investments into fixed capital and retail turnover (growth rates, %) fixed capital investments retail trade , estimate 6 Clearly, the "pendulous" strengthening of the ruble in the first and second quarter of 201 noticeably weakened the positive results of devaluation for competitiveness of the Russian companies. 4
5 01/12 0/12 0/12 07/12 09/12 11/12 01/1 0/1 0/1 07/1 09/1 11/1 01/14 0/14 0/14 07/14 09/14 11/14 01/1 0/1 0/1 07/1 01/12 0/12 0/12 07/12 09/12 11/12 01/1 0/1 0/1 07/1 09/1 11/1 01/14 0/14 0/14 07/14 09/14 11/14 01/1 0/1 0/1 07/1 Graphic Chart 7. Retail trade turnover (% to monthly average of 2012) Graphic Chart 8. Investments into fixed capital (% to monthly average of 2012) actual value seasonally adjusted actual value seasonally adjusted (right scale) Assumptions on National Policy and External Environment It is assumed in optimistic scenario that global oil prices will recover from an average of USD 0 per barrel in 2016 to USD in 2017, and USD 60 in In pessimistic scenario it is expected that the oil prices will drop further and will not gain back for the rest of the forecast period (about USD 40 per barrel in , and USD 4 in 2018). Russia's economic policy of the last year overall was designed to stabilize the situation (its nature was anti-crisis). The primary policy measures were focused on the following: - drop in inflation (a rather strict monetary policy of the Bank of Russia); - stabilization of the public sector (conducting random sequestration of state spending; in order to preserve budget stability, given the deficit of approximately,% GDP, federal budget reserve funds are being used as the primary source of funds instead of the sharply inflated borrowings on the foreign and domestic markets. - large-scale recapitalization of the banking system. At the same time, development objectives are resolved on a very limited scale a number of fairly large investment projects (in the field of transportation system reconstruction) as well as projects involving procurement of high-tech weapons, primarily aviation and space equipment, despite sequestration are carried out using funds from the federal budget (as well as a number of large regional budgets, in particular, Moscow's budget). The scope of support for science and technology activities remains fairly large (specifically, the National Technology Initiative has been launched mid-year).. Forecast Summary An Optimistic Scenario In the circumstances of recovery of global oil prices, the companies that obtained additional financial resources will resume their investment activities (2016: continued stagnation of %; 2017: %; 2018: %) after a three-year "innovative timeout" in At the same time, in order to sustain competitiveness, real wages will experience a much slower growth (2016: %; 2017: %; 2018: %). With this, there is going to be an almost inevitable in such situation soft correction of consumer lending, which will cause the trade turnover to fall behind personal income. In 2016 sales of consumer goods are going to decline by %; in 2017 they will begin to grow by %, and in 2018 by %. Therefore, gross domestic product will settle down in 2016 ( %); it will begin to grow in ( % and %, respectively).
6 Thanks to the expected strengthening of the ruble in the context of improved foreign economic conditions, it will be possible to keep the rate of inflation in 2016 in the range of %, followed by a rapid drop (2017:..7%, 2018: %; the target rate for the Bank of Russia is the inflation rate of 4.0%). A Pessimistic Scenario The further drop of oil prices is going to send a bad signal for the companies; the outflow of their resources into financial assets including foreign assets will remain. The treasury will have to conduct tough sequestration cuts of every major program according to most aggressive proposals of Russia's Ministry of Finance. Consequently, one can expect that the negative trend of investments into the fixed capital will continue (2016: downturn continues at %; 2017: stagnation at %; 2018: minor gain at %). Neither the companies, nor the budget system have enough resources to increase salaries (it is expected that regions will face a fairly harsh crisis). Consequently, it is expected that there will be an absolute reduction in real wages in 2016 ( %), and slow growth in ( % and %, respectfully). Given the inevitable in this scenario consumer lending crisis, sales will also be sluggish (2016: %; 2017: %; 2018: %). Under these circumstances one can expect that the full-scale crisis is going to continue in 2016 (GDP drop by %), followed by an extremely slow growth in the next years (2017: %, 2018: %). In 2016, yet another ruble devaluation can be expected (to % against the dualcurrency basket) followed by its stabilization. Consequently, the rate of inflation in this case will remain quite high (2016: %; 2017:..7%; 2018: 4.7.1%). 4. Policy Issues and Uncertainties The established economic policy is expected to remain in place as follows: - a moderately strict monetary policy (with the interest rate around the inflation rate); - a floating exchange rate for the ruble; - a moderately conservative budget policy (using budget reserve funds for partial financing of its deficit; saving budget resources including freezing of federal budget nominal expenditures in 2017 proposed by the Ministry of Finance of Russia in the event of unfavorable market conditions). Mid-term uncertainties are as follows: - commodity prices which largely depend on the regional situation of hydrocarbon producers (entry into market of carbohydrates from Iran, Iraq, and Libya; possibility of new agreements on production quotas between Iran and Saudi Arabia) and on the situation in demand regions, first of all in China's economy, to a large extend defining the growth scale for fuel demand; - behavior of companies. On the one hand, implementation of the opportunities for import substitution that emerged as a result of ruble devaluation and introduction of restrictive measures on the food markets anticipates that the issues associated with the level of quality and technology of Russian products will be resolved, which requires investment. On the other hand, investments, even those made at the expense of company own resources, are impeded by high risks (and an overall lack of understanding of mid-term market development), as well as disparity between investment returns into real assets and financial assets. This disparity to a large extent is stipulated by the high ruble interest rates. - risks of conflict zone expansion at Russia's south borders. 6
7 Table 1. Main macroeconomic indicators forecast (optimistic scenario) CPI (end of the year) GDP Industrial output Fixed capital investments Real wage Real disposable houshold income Retail trade turnover Paid services Export, bln. USD Import, bln. USD Trade balance, bln. USD Ruble exchange rate, annual average, rubles per USD Urals oil price, USD per barrell Table 2. Main macroeconomic indicators forecast (pessimistic scenario) CPI (end of the year) GDP Industrial output Fixed capital investments Real wage Real disposable houshold income Retail trade turnover Paid services Export, bln. USD Import, bln. USD Trade balance, bln. USD Ruble exchange rate, annual average, rubles per USD Urals oil price, USD per barrell
Anti-crisis State Policy in Russia
 1 Anti-crisis State Policy in Russia Vera Kononova Institute for Complex Strategic Studies 1 December 2016 Seminar Outline 1. Anti-crisis Policy Goals The main goals and targets adopted by the Government
1 Anti-crisis State Policy in Russia Vera Kononova Institute for Complex Strategic Studies 1 December 2016 Seminar Outline 1. Anti-crisis Policy Goals The main goals and targets adopted by the Government
Development of the Russian Economy in and Forecast for
 .....................6.6.6.6.7.7 CENTER FOR MACROECONOMIC ANALYSIS AND SHORT-TERM FORECASTING Tel.: (+799) 9-7-, fax: (+799) 9-9-, e-mail: mail@forecast.ru, http://www.forecast.ru Development of the Russian
.....................6.6.6.6.7.7 CENTER FOR MACROECONOMIC ANALYSIS AND SHORT-TERM FORECASTING Tel.: (+799) 9-7-, fax: (+799) 9-9-, e-mail: mail@forecast.ru, http://www.forecast.ru Development of the Russian
International economy in the first quarter of 2009
 The article is based on data with cutoff date as of June, 9. I volume, 8/9B International economy in the first quarter of 9 GLOBAL ECONOMY The GDP development in OECD countries recorded a further decrease
The article is based on data with cutoff date as of June, 9. I volume, 8/9B International economy in the first quarter of 9 GLOBAL ECONOMY The GDP development in OECD countries recorded a further decrease
RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY. RUSSIA S ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY December 2018
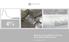 4% RUSSIA S ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND December 1 2 Consumer prices (1) At the end of 1, inflation is expected to be close to 4%, which corresponds to the Bank of Russia s target 2 Inflation indicators, % YoY
4% RUSSIA S ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND December 1 2 Consumer prices (1) At the end of 1, inflation is expected to be close to 4%, which corresponds to the Bank of Russia s target 2 Inflation indicators, % YoY
All the BRICs dampening world trade in 2015
 Aug Weekly Economic Briefing Emerging Markets All the BRICs dampening world trade in World trade in has been hit by an unexpectedly sharp drag from the very largest emerging economies. The weakness in
Aug Weekly Economic Briefing Emerging Markets All the BRICs dampening world trade in World trade in has been hit by an unexpectedly sharp drag from the very largest emerging economies. The weakness in
Russia: Macro Outlook for 2019
 October 2018 Russia: Macro Outlook for 2019 Natalia Orlova Head of Alfa Bank Macro Insights +7 495 795 36 77 norlova@alfabank.ru Egypt Saudi Arabia Brazil S. Africa UAE Iraq China Japan US Mexico UK Russia
October 2018 Russia: Macro Outlook for 2019 Natalia Orlova Head of Alfa Bank Macro Insights +7 495 795 36 77 norlova@alfabank.ru Egypt Saudi Arabia Brazil S. Africa UAE Iraq China Japan US Mexico UK Russia
Weekly Macroeconomic Review
 20/12/2011 Weekly Macroeconomic Review Expectations derived from the capital market Our forecast Inflation in the coming months Future cumulative inflation next 12 CPIs (through November 2012 CPI) Inflation
20/12/2011 Weekly Macroeconomic Review Expectations derived from the capital market Our forecast Inflation in the coming months Future cumulative inflation next 12 CPIs (through November 2012 CPI) Inflation
GAIDAR INSTITUTE FOR ECONOMIC POLICY RUSSIAN ECONOMY IN 2015 TRENDS AND OUTLOOKS (ISSUE 37)
 GAIDAR INSTITUTE FOR ECONOMIC POLICY RUSSIAN ECONOMY IN 2015 TRENDS AND OUTLOOKS (ISSUE 37) Gaidar Institute Publishers Moscow / 2016 171 UDC BBC 33(470+571)(066)"2015" 65.9(2Рос) R95 Russian Economy in
GAIDAR INSTITUTE FOR ECONOMIC POLICY RUSSIAN ECONOMY IN 2015 TRENDS AND OUTLOOKS (ISSUE 37) Gaidar Institute Publishers Moscow / 2016 171 UDC BBC 33(470+571)(066)"2015" 65.9(2Рос) R95 Russian Economy in
1. Macroeconomic Highlights
 1. Macroeconomic Highlights ht Macroeconomic Highlights Resilient growth over the last 2 years, despite the global economic slowdown Banking industry robust with high level of CAR and low NPLN. In 2008
1. Macroeconomic Highlights ht Macroeconomic Highlights Resilient growth over the last 2 years, despite the global economic slowdown Banking industry robust with high level of CAR and low NPLN. In 2008
Viet Nam GDP growth by sector Crude oil output Million metric tons 20
 Viet Nam This economy is weathering the global economic crisis relatively well due largely to swift and strong policy responses. The GDP growth forecast for 29 is revised up from that made in March and
Viet Nam This economy is weathering the global economic crisis relatively well due largely to swift and strong policy responses. The GDP growth forecast for 29 is revised up from that made in March and
О КЛЮЧЕВОЙ СТАВКЕ RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND CHALLENGES TO MONETARY POLICY. December Bank of Russia Presentation for Investors
 О КЛЮЧЕВОЙ СТАВКЕ RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND CHALLENGES TO MONETARY POLICY Bank of Russia Presentation for Investors December 16 USD per barrel RUB / USD 2 Oil Eхporters Production-cut Agreements Support
О КЛЮЧЕВОЙ СТАВКЕ RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND CHALLENGES TO MONETARY POLICY Bank of Russia Presentation for Investors December 16 USD per barrel RUB / USD 2 Oil Eхporters Production-cut Agreements Support
Valentyn Povroznyuk, Radu Mihai Balan, Edilberto L. Segura
 September 214 GDP grew by 1.2% yoy in Q2 214. Industrial output growth was equal to 1.4% yoy in June 214. The consolidated budget deficit narrowed to.2% of GDP in January-July 214. Consumer inflation slightly
September 214 GDP grew by 1.2% yoy in Q2 214. Industrial output growth was equal to 1.4% yoy in June 214. The consolidated budget deficit narrowed to.2% of GDP in January-July 214. Consumer inflation slightly
RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES. Bank of Russia.
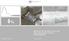 RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES Bank of Russia June 218 < -1% -9-8% -7-6% -5-4% -3-2% -1 % 1 2% 3 4% 5 6% 7 8% 9 1% 11 12% 13 14% 15 16% > 17% Share in the consulmer basket, % RUSSIAN
RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES Bank of Russia June 218 < -1% -9-8% -7-6% -5-4% -3-2% -1 % 1 2% 3 4% 5 6% 7 8% 9 1% 11 12% 13 14% 15 16% > 17% Share in the consulmer basket, % RUSSIAN
Managing Global Shocks: The Case of Indonesia
 Managing Global Shocks: The Case of Indonesia Dr. Hartadi A. Sarwono Deputy Governor IIF Asian Regional Economic Forum Singapore, March 5, 2009 Outline 2 1. Crisis highlights 2. Macroconomic Condition
Managing Global Shocks: The Case of Indonesia Dr. Hartadi A. Sarwono Deputy Governor IIF Asian Regional Economic Forum Singapore, March 5, 2009 Outline 2 1. Crisis highlights 2. Macroconomic Condition
RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY. RUSSIA S ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY February 2019
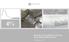 % RUSSIA S ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND February 19 Consumer prices In January 19, annual inflation held at the lower bound of the Bank of Russia expectations (.% YoY). Faster growth of food prices to.% (vs.7%
% RUSSIA S ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND February 19 Consumer prices In January 19, annual inflation held at the lower bound of the Bank of Russia expectations (.% YoY). Faster growth of food prices to.% (vs.7%
RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY. Bank of Russia.
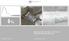 RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY Bank of Russia September 218 2 Annual inflation is returning to 4% faster than expected. Acceleration of food prices drove CPI to +3.1% YoY in August Contributions
RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY Bank of Russia September 218 2 Annual inflation is returning to 4% faster than expected. Acceleration of food prices drove CPI to +3.1% YoY in August Contributions
PRESENTATION BY PROF. E. TUMUSIIME-MUTEBILE, GOVERNOR, BANK OF UGANDA, TO THE NRM RETREAT, KYANKWANZI, JANUARY
 BANK OF UGANDA PRESENTATION BY PROF. E. TUMUSIIME-MUTEBILE, GOVERNOR, BANK OF UGANDA, TO THE NRM RETREAT, KYANKWANZI, JANUARY 19, 2012 MACROECONOMIC MANAGEMENT IN TURBULENT TIMES Introduction I want to
BANK OF UGANDA PRESENTATION BY PROF. E. TUMUSIIME-MUTEBILE, GOVERNOR, BANK OF UGANDA, TO THE NRM RETREAT, KYANKWANZI, JANUARY 19, 2012 MACROECONOMIC MANAGEMENT IN TURBULENT TIMES Introduction I want to
DEVELOPMENT TRENDS, INFLUENCE FACTORS, FORECAST MACROINDICATORS OF UKRAINE S ECONOMY FOR THE PERION UNTIL 1015
 UKRAINE COUNTRY REPORT: DEVELOPMENT TRENDS, INFLUENCE FACTORS, FORECAST MACROINDICATORS OF UKRAINE S ECONOMY FOR THE PERION UNTIL 1015 New York, October 22-24, 2012 Valeriy Heyets, Maria Skrypnychenko
UKRAINE COUNTRY REPORT: DEVELOPMENT TRENDS, INFLUENCE FACTORS, FORECAST MACROINDICATORS OF UKRAINE S ECONOMY FOR THE PERION UNTIL 1015 New York, October 22-24, 2012 Valeriy Heyets, Maria Skrypnychenko
Export Group Meeting on the Contribution and Effective Use of External Resources for Development, in Particular for Productive Capacity Building
 Export Group Meeting on the Contribution and Effective Use of External Resources for Development, in Particular for Productive Capacity Building 22-24 February 21 Debt Sustainability and the Implications
Export Group Meeting on the Contribution and Effective Use of External Resources for Development, in Particular for Productive Capacity Building 22-24 February 21 Debt Sustainability and the Implications
MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT JULY-DECEMBER 2004
 MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT JULY-DECEMBER 2004 Monetary Policy Statement (July-December 2004) Monetary Policy Statement July-December, 2004 Macroeconomic Outlook and Monetary Policy Stance Recent global
MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT JULY-DECEMBER 2004 Monetary Policy Statement (July-December 2004) Monetary Policy Statement July-December, 2004 Macroeconomic Outlook and Monetary Policy Stance Recent global
HKU Announced 2013 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast
 COMMUNICATIONS & PUBLIC AFFAIRS OFFICE THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Enquiry: 2859 1106 Website: http://www.hku.hk/cpao For Immediate Release HKU Announced 2013 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast Hong Kong Economic
COMMUNICATIONS & PUBLIC AFFAIRS OFFICE THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Enquiry: 2859 1106 Website: http://www.hku.hk/cpao For Immediate Release HKU Announced 2013 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast Hong Kong Economic
Development of Economy and Financial Markets of Kazakhstan
 Development of Economy and Financial Markets of Kazakhstan National Bank of Kazakhstan Macroeconomic development GDP, real growth, % 116 112 18 14 1 113,5 11,7 216,7223,8226,5 19,8 19,8 19,3 19,619,7 199,
Development of Economy and Financial Markets of Kazakhstan National Bank of Kazakhstan Macroeconomic development GDP, real growth, % 116 112 18 14 1 113,5 11,7 216,7223,8226,5 19,8 19,8 19,3 19,619,7 199,
Econometric modeling of Ukrainian macroeconomic tendencies
 Martynovych Daria Econometric modeling of Ukrainian macroeconomic tendencies Motivation. Most countries wish to have a significant influence in the world. After the collapse of the Soviet Union all the
Martynovych Daria Econometric modeling of Ukrainian macroeconomic tendencies Motivation. Most countries wish to have a significant influence in the world. After the collapse of the Soviet Union all the
Commercial Cards & Payments Leo Abruzzese October 2015 New York
 US, China and emerging markets: What s next for the global economy? Commercial Cards & Payments Leo Abruzzese October 2015 New York Overview Key points for 2015-16 Global economy struggling to gain traction
US, China and emerging markets: What s next for the global economy? Commercial Cards & Payments Leo Abruzzese October 2015 New York Overview Key points for 2015-16 Global economy struggling to gain traction
Russian Federation. Recent Economic Developments and Challenges. October 2015 IMF MOSCOW OFFICE
 Russian Federation Recent Economic Developments and Challenges IMF MOSCOW OFFICE October 215 1 Outline Shocks affecting Russia s economy Policy Reaction: Monetary and Fiscal Policy Responses Current economic
Russian Federation Recent Economic Developments and Challenges IMF MOSCOW OFFICE October 215 1 Outline Shocks affecting Russia s economy Policy Reaction: Monetary and Fiscal Policy Responses Current economic
2 Macroeconomic Scenario
 The macroeconomic scenario was conceived as realistic and conservative with an effort to balance out the positive and negative risks of economic development..1 The World Economy and Technical Assumptions
The macroeconomic scenario was conceived as realistic and conservative with an effort to balance out the positive and negative risks of economic development..1 The World Economy and Technical Assumptions
HKU Announced 2011 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast
 COMMUNICATIONS & PUBLIC AFFAIRS OFFICE THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Enquiry: 2859 1106 Website: http://www.hku.hk/cpao For Immediate Release HKU Announced 2011 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast Economic Outlook
COMMUNICATIONS & PUBLIC AFFAIRS OFFICE THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Enquiry: 2859 1106 Website: http://www.hku.hk/cpao For Immediate Release HKU Announced 2011 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast Economic Outlook
Other similar crisis: Euro, Emerging Markets
 Session 15. Understanding Macroeconomic Crises. Mexican Crisis 1994-95 Other similar crisis: Euro, Emerging Markets Global Scenarios 2017-2021 The Mexican Peso Crisis in 1994: Background An economy that
Session 15. Understanding Macroeconomic Crises. Mexican Crisis 1994-95 Other similar crisis: Euro, Emerging Markets Global Scenarios 2017-2021 The Mexican Peso Crisis in 1994: Background An economy that
China Economic Outlook 2013
 China Economic Outlook 2 Key Developments in Brief - Mild recovery of GDP growth: +8 8.5% - Construction and consumption as main drivers - Inflationary pressure to increase: +3% - Tight labor market and
China Economic Outlook 2 Key Developments in Brief - Mild recovery of GDP growth: +8 8.5% - Construction and consumption as main drivers - Inflationary pressure to increase: +3% - Tight labor market and
The Long Journey to Recovery. Russia Economic Report April 2016 Edition No. 35
 The Long Journey to Recovery Russia Economic Report April 216 Edition No. 35 1 2 3 The anticipated recovery was delayed and the economy adjusted through a sharp income drop. The government s policy response
The Long Journey to Recovery Russia Economic Report April 216 Edition No. 35 1 2 3 The anticipated recovery was delayed and the economy adjusted through a sharp income drop. The government s policy response
MID-TERM REVIEW OF MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT 2006
 MID-TERM REVIEW OF MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT 1. Introduction 1.1 There are three objectives to undertake a mid-term review of the Monetary Policy Statement (MPS). First, it is intended to review progress
MID-TERM REVIEW OF MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT 1. Introduction 1.1 There are three objectives to undertake a mid-term review of the Monetary Policy Statement (MPS). First, it is intended to review progress
RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES. Bank of Russia.
 RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES Bank of Russia July 218 < -1% -1-9% -9-8% -8-7% -7-6% -6-5% -5-4% -4-3% -3-2% -2-1% -1 % 1% 1 2% 2 3% 3 4% 4 5% 5 6% 6 7% 7 8% 8 9% 9 1% 1 11% 11
RUSSIAN ECONOMIC OUTLOOK AND MONETARY POLICY CHALLENGES Bank of Russia July 218 < -1% -1-9% -9-8% -8-7% -7-6% -6-5% -5-4% -4-3% -3-2% -2-1% -1 % 1% 1 2% 2 3% 3 4% 4 5% 5 6% 6 7% 7 8% 8 9% 9 1% 1 11% 11
Macroeconomic Outlook: Implications for Agriculture. It has been 26 years since we have experienced a significant recession
 Macroeconomic Outlook: Implications for Agriculture John B. Penson, Jr. Regents Professor and Stiles Professor of Agriculture Texas A&M University Our Recession History September 1902 August1904 23 May
Macroeconomic Outlook: Implications for Agriculture John B. Penson, Jr. Regents Professor and Stiles Professor of Agriculture Texas A&M University Our Recession History September 1902 August1904 23 May
FINANCIAL STABILITY IN THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS
 NATIONAL BANK OF 1 THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS FINANCIAL STABILITY IN THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS 2010 MINSK, 2011 2 This publication has been prepared by the Banking Supervision Directorate in concert with the
NATIONAL BANK OF 1 THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS FINANCIAL STABILITY IN THE REPUBLIC OF BELARUS 2010 MINSK, 2011 2 This publication has been prepared by the Banking Supervision Directorate in concert with the
Finland falling further behind euro area growth
 BANK OF FINLAND FORECAST Finland falling further behind euro area growth 30 JUN 2015 2:00 PM BANK OF FINLAND BULLETIN 3/2015 ECONOMIC OUTLOOK Economic growth in Finland has been slow for a prolonged period,
BANK OF FINLAND FORECAST Finland falling further behind euro area growth 30 JUN 2015 2:00 PM BANK OF FINLAND BULLETIN 3/2015 ECONOMIC OUTLOOK Economic growth in Finland has been slow for a prolonged period,
HKU announces 2015 Q2 HK Macroeconomic Forecast
 Press Release HKU announces 2015 Q2 HK Macroeconomic Forecast April 9, 2015 1 Overview The APEC Studies Programme of the Hong Kong Institute of Economics and Business Strategy at the University of Hong
Press Release HKU announces 2015 Q2 HK Macroeconomic Forecast April 9, 2015 1 Overview The APEC Studies Programme of the Hong Kong Institute of Economics and Business Strategy at the University of Hong
What is Monetary Policy?
 What is Monetary Policy? Monetary stability means stable prices and confidence in the currency. Stable prices are defined by the Government's inflation target, which the Bank seeks to meet through the
What is Monetary Policy? Monetary stability means stable prices and confidence in the currency. Stable prices are defined by the Government's inflation target, which the Bank seeks to meet through the
MPC MARKET PERCEPTIONS SURVEY - MARCH
 MPC MARKET PERCEPTIONS SURVEY - MARCH 2018 1 CONTENTS BACKGROUND......4 SURVEY METHODOLOGY......4 HIGHLIGHTS OF THE SURVEY.........4 INFLATION EXPECTATIONS....5 EXCHANGE RATE EXPECTATIONS...6 PRIVATE SECTOR
MPC MARKET PERCEPTIONS SURVEY - MARCH 2018 1 CONTENTS BACKGROUND......4 SURVEY METHODOLOGY......4 HIGHLIGHTS OF THE SURVEY.........4 INFLATION EXPECTATIONS....5 EXCHANGE RATE EXPECTATIONS...6 PRIVATE SECTOR
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF MONTHLY REPORTS ON THE OIL MARKET
 COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF MONTHLY REPORTS ON THE OIL MARKET AN INTERNATIONAL ENERGY FORUM PUBLICATION JUNE 2018 RIYADH, SAUDI ARABIA JUNE 2018 SUMMARY FINDINGS FROM A COMPARISON OF DATA AND FORECASTS ON
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF MONTHLY REPORTS ON THE OIL MARKET AN INTERNATIONAL ENERGY FORUM PUBLICATION JUNE 2018 RIYADH, SAUDI ARABIA JUNE 2018 SUMMARY FINDINGS FROM A COMPARISON OF DATA AND FORECASTS ON
State of Palestine Ministry of Finance. Fiscal Developments & Macroeconomic Performance: Fourth Quarter and Full year 2013 Report
 State of Palestine Ministry of Finance Fiscal Developments & Macroeconomic Performance: Fourth Quarter and Full year 2013 Report Macro Macro Fiscal Fiscal Unit Unit Oct February,, 2013 2014 Section 1:
State of Palestine Ministry of Finance Fiscal Developments & Macroeconomic Performance: Fourth Quarter and Full year 2013 Report Macro Macro Fiscal Fiscal Unit Unit Oct February,, 2013 2014 Section 1:
Emerging Markets Weekly Economic Briefing
 Emerging Markets Weekly Economic Briefing The risks of renewed capital flight from emerging markets Recent episodes of capital flight from emerging markets have highlighted the vulnerability of a number
Emerging Markets Weekly Economic Briefing The risks of renewed capital flight from emerging markets Recent episodes of capital flight from emerging markets have highlighted the vulnerability of a number
SUMMARY OF MACROECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS
 SUMMARY OF MACROECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS NOVEMBER 2018 2 Summary of macroeconomic developments, November 2018 Indicators of global economic activity suggest a continuation of solid growth in the final quarter
SUMMARY OF MACROECONOMIC DEVELOPMENTS NOVEMBER 2018 2 Summary of macroeconomic developments, November 2018 Indicators of global economic activity suggest a continuation of solid growth in the final quarter
Recent Economic Developments
 REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA Recent Economic Developments January, 2010 Published by Investors Relations Unit Republic of Indonesia Address Bank Indonesia International Directorate Investor Relations Unit Sjafruddin
REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA Recent Economic Developments January, 2010 Published by Investors Relations Unit Republic of Indonesia Address Bank Indonesia International Directorate Investor Relations Unit Sjafruddin
Mexican Q1 economic data: a reality shock, or there is still a brighter outlook?
 Mexican Q1 economic data: a reality shock, or there is still a brighter outlook? Rafael Amiel, Director Latin America Economics IHS Global Insight Julio 2013 Mexico becomes fashionable again Mexico Makes
Mexican Q1 economic data: a reality shock, or there is still a brighter outlook? Rafael Amiel, Director Latin America Economics IHS Global Insight Julio 2013 Mexico becomes fashionable again Mexico Makes
Global Financial Crisis: Impact on India
 Global Financial Crisis: Impact on India Mathew Joseph Pankaj Vashisht ICRIER-INVENT Workshop Current Developments in Indian Financial System New Delhi 20 March 2009 1 Roots of Global Crisis Global macroeconomic
Global Financial Crisis: Impact on India Mathew Joseph Pankaj Vashisht ICRIER-INVENT Workshop Current Developments in Indian Financial System New Delhi 20 March 2009 1 Roots of Global Crisis Global macroeconomic
INDONESIA. The Real Economy
 INDONESIA Macroeconomic stability is strengthening in Indonesia. The external environment is likely to be supportive for the economy. This positive trend is reflected in the recent upgrade of Indonesia
INDONESIA Macroeconomic stability is strengthening in Indonesia. The external environment is likely to be supportive for the economy. This positive trend is reflected in the recent upgrade of Indonesia
The Future of Mexican Monetary Policy
 The Future of Mexican Monetary Policy Mr. Javier Guzmán Calafell, Deputy Governor, Banco de México* XP Securities Mexico Summit Mexico City, 2 March 2017 */ The views expressed herein are strictly personal.
The Future of Mexican Monetary Policy Mr. Javier Guzmán Calafell, Deputy Governor, Banco de México* XP Securities Mexico Summit Mexico City, 2 March 2017 */ The views expressed herein are strictly personal.
Erdem Başçi: Recent economic and financial developments in Turkey
 Erdem Başçi: Recent economic and financial developments in Turkey Speech by Mr Erdem Başçi, Governor of the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, at the press conference for the presentation of the April
Erdem Başçi: Recent economic and financial developments in Turkey Speech by Mr Erdem Başçi, Governor of the Central Bank of the Republic of Turkey, at the press conference for the presentation of the April
Jul-Sep st Preliminary GDP Estimate
 Japan's Economy 16 November 2015 (No. of pages: 5) Japanese report: 16 Nov 2015 Jul-Sep 2015 1 st Preliminary GDP Estimate Second consecutive quarter of negative growth due mainly to inventory adjustment
Japan's Economy 16 November 2015 (No. of pages: 5) Japanese report: 16 Nov 2015 Jul-Sep 2015 1 st Preliminary GDP Estimate Second consecutive quarter of negative growth due mainly to inventory adjustment
Global Economic Prospects: Navigating strong currents
 Global Economic Prospects: Navigating strong currents Andrew Burns World Bank January 18, 2011 http://www.worldbank.org/globaloutlook Main messages Most developing countries have passed with flying colors
Global Economic Prospects: Navigating strong currents Andrew Burns World Bank January 18, 2011 http://www.worldbank.org/globaloutlook Main messages Most developing countries have passed with flying colors
5. Prices and the Exchange Rate
 3 5. Prices and the Exchange Rate 5. Prices and the Exchange Rate Since the beginning of the year, inflation in Serbia has been extremely low, the cumulative growth rate in the first seven months is %.
3 5. Prices and the Exchange Rate 5. Prices and the Exchange Rate Since the beginning of the year, inflation in Serbia has been extremely low, the cumulative growth rate in the first seven months is %.
Russian Overview. August 27-September 2
 FX September 2, 2005 Russian Overview. August 27-September 2 FX USD/RUB continued to reflect USD moves against the euro, being stable against CBR s USD-euro basket Rubble appreciation against the trade-weighted
FX September 2, 2005 Russian Overview. August 27-September 2 FX USD/RUB continued to reflect USD moves against the euro, being stable against CBR s USD-euro basket Rubble appreciation against the trade-weighted
QUESTION 2. QUESTION 3 Which one of the following is most indicative of a flexible short-term financial policy?
 QUESTION 1 Compute the cash cycle based on the following information: Average Collection Period = 47 Accounts Payable Period = 40 Average Age of Inventory = 55 QUESTION 2 Jan 41,700 July 39,182 Feb 18,921
QUESTION 1 Compute the cash cycle based on the following information: Average Collection Period = 47 Accounts Payable Period = 40 Average Age of Inventory = 55 QUESTION 2 Jan 41,700 July 39,182 Feb 18,921
Poland s Economic Prospects
 Poland s Economic Prospects Unicredit Conference Warsaw, June 8, 11 Mark Allen Senior IMF Resident Representative for Central and Eastern Europe Recovery is driven by domestic demand Contributions to Real
Poland s Economic Prospects Unicredit Conference Warsaw, June 8, 11 Mark Allen Senior IMF Resident Representative for Central and Eastern Europe Recovery is driven by domestic demand Contributions to Real
1 RED June/July 2018 JUNE/JULY 2018
 1 RED June/July 20 JUNE/JULY 20 2 RED June/July 20 MAJOR HIGHLIGHTS Headline consumer inflation grew by 4.9 per cent in June 20 compared to 4.8 per cent recorded in May 20 Inflation rate (% y/y) 4.9 (June)
1 RED June/July 20 JUNE/JULY 20 2 RED June/July 20 MAJOR HIGHLIGHTS Headline consumer inflation grew by 4.9 per cent in June 20 compared to 4.8 per cent recorded in May 20 Inflation rate (% y/y) 4.9 (June)
Presentation to Chief Executive Officers of Commercial and Microfinance Banks Dr. Patrick Njoroge Governor, Central Bank of Kenya
 Presentation to Chief Executive Officers of Commercial and Microfinance Banks Dr. Patrick Njoroge Governor, Central Bank of Kenya August 6, 2015 Outline 1. The Information basis for the MPC meeting 2.
Presentation to Chief Executive Officers of Commercial and Microfinance Banks Dr. Patrick Njoroge Governor, Central Bank of Kenya August 6, 2015 Outline 1. The Information basis for the MPC meeting 2.
Dynamic Change, Economic Fluctuations, and the AD-AS Model
 Dynamic Change, Economic Fluctuations, and the AD-AS Model Full Length Text Part: Macro Only Text Part: 3 Chapter: 10 3 Chapter: 10 To Accompany Economics: Private and Public Choice 13th ed. James Gwartney,
Dynamic Change, Economic Fluctuations, and the AD-AS Model Full Length Text Part: Macro Only Text Part: 3 Chapter: 10 3 Chapter: 10 To Accompany Economics: Private and Public Choice 13th ed. James Gwartney,
BELARUSIAN MACROECONOMIC FORECAST No. 2(13), November 2016
 BELARUSIAN MACROECONOMIC FORECAST No. 2(13), November 2016 Macroeconomic adjustment leads to a prolonged recession Executive summary GDP: We expect the recession to continue in 2016 and 2017; real output
BELARUSIAN MACROECONOMIC FORECAST No. 2(13), November 2016 Macroeconomic adjustment leads to a prolonged recession Executive summary GDP: We expect the recession to continue in 2016 and 2017; real output
Equity Market Outlook. May, 2016
 Equity Market Outlook May, 2016 Global Economy Update Jan-15 Feb-15 Mar-15 Apr-15 May-15 Jun-15 Jul-15 Aug-15 Sep-15 Oct-15 Nov-15 Dec-15 Jan-16 Feb-16 Mar-16 Apr-16 Global Central Bank Monetary Policies
Equity Market Outlook May, 2016 Global Economy Update Jan-15 Feb-15 Mar-15 Apr-15 May-15 Jun-15 Jul-15 Aug-15 Sep-15 Oct-15 Nov-15 Dec-15 Jan-16 Feb-16 Mar-16 Apr-16 Global Central Bank Monetary Policies
The real change in private inventories added 0.15 percentage points to the second quarter GDP growth, after subtracting 0.65% in the first quarter.
 QIRGRETA Monthly Macroeconomic Commentary United States The U.S. economy rebounded in the second quarter of 2007, growing at an annual rate of 3.4% Q/Q (+1.8% Y/Y), according to the GDP advance estimates
QIRGRETA Monthly Macroeconomic Commentary United States The U.S. economy rebounded in the second quarter of 2007, growing at an annual rate of 3.4% Q/Q (+1.8% Y/Y), according to the GDP advance estimates
7. Monetary Trends and Policy
 Quarterly Monitor No. 36 January March 214 47 7. Monetary and Policy Inflation has been stable for the past two quarters at about the lower level of the target corridor but the National Bank of Serbia
Quarterly Monitor No. 36 January March 214 47 7. Monetary and Policy Inflation has been stable for the past two quarters at about the lower level of the target corridor but the National Bank of Serbia
RESEARCH & KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT. Russia and Central Asia Macroeconomic Outlook 2017
 RESEARCH & KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Russia and Central Asia Macroeconomic Outlook 217 4 July 217 Russia and Central Asia Macroeconomic Outlook 217 Contents: 1. Introduction 5 2. Kazakhstan 7 3. Russia 12 4.
RESEARCH & KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT Russia and Central Asia Macroeconomic Outlook 217 4 July 217 Russia and Central Asia Macroeconomic Outlook 217 Contents: 1. Introduction 5 2. Kazakhstan 7 3. Russia 12 4.
China Economic Outlook 2018 Feb 13, 2018
 Feb 13, Key Developments in Brief Economic Development Drivers of Growth Risks Predicted GDP growth of 6.5% in In 2017 growth exceeded the official target Service and modern production grow faster than
Feb 13, Key Developments in Brief Economic Development Drivers of Growth Risks Predicted GDP growth of 6.5% in In 2017 growth exceeded the official target Service and modern production grow faster than
Russian Economy: Macroeconomic
 RUSSIA Economy Russian Economy: Macroeconomic Trends and Medium-Term Forecast By Alexander Apokin, Dmitry Belousov, Vladimir Salnikov leading experts; Elena Penukhina, Anna Pestova experts, Center for
RUSSIA Economy Russian Economy: Macroeconomic Trends and Medium-Term Forecast By Alexander Apokin, Dmitry Belousov, Vladimir Salnikov leading experts; Elena Penukhina, Anna Pestova experts, Center for
Shanghai Market Turning the Corner
 Shanghai Market Turning the Corner C. H. Kwan Senior Fellow, Nomura Institute of Capital Markets Research When the Lehman Shock hit major global stock markets in mid-september 2008, the Shanghai Composite
Shanghai Market Turning the Corner C. H. Kwan Senior Fellow, Nomura Institute of Capital Markets Research When the Lehman Shock hit major global stock markets in mid-september 2008, the Shanghai Composite
2012 As the Fundamentals Improve Stateside, They Deteriorate Abroad
 N O R T H E R N T R U S T G L O B A L E C O N O M I C R E S E A R C H 212 As the Fundamentals Improve Stateside, They Deteriorate Abroad December 211 Paul L. Kasriel, Chief Economist PH: 312..15 plk1@ntrs.com
N O R T H E R N T R U S T G L O B A L E C O N O M I C R E S E A R C H 212 As the Fundamentals Improve Stateside, They Deteriorate Abroad December 211 Paul L. Kasriel, Chief Economist PH: 312..15 plk1@ntrs.com
CENTRAL BANK OF OMAN. Mid-Year Review of the Omani Economy 2010
 CENTRAL BANK OF OMAN Mid-Year Review of the Omani Economy 2010 December 2010 CENTRAL BANK OF OMAN Mid-Year Review of the Omani Economy 2010 Economic Research and Statistics Department CONTENTS Page Foreword
CENTRAL BANK OF OMAN Mid-Year Review of the Omani Economy 2010 December 2010 CENTRAL BANK OF OMAN Mid-Year Review of the Omani Economy 2010 Economic Research and Statistics Department CONTENTS Page Foreword
Oct-Dec st Preliminary GDP Estimate
 Japan's Economy 15 February 2016 (No. of pages: 5) Japanese report: 15 Feb 2016 Oct-Dec 2015 1 st Preliminary GDP Estimate GDP experiences negative growth for first time in two quarters hinting at risk
Japan's Economy 15 February 2016 (No. of pages: 5) Japanese report: 15 Feb 2016 Oct-Dec 2015 1 st Preliminary GDP Estimate GDP experiences negative growth for first time in two quarters hinting at risk
SURVEY OF PRIMARY DEALERS
 SURVEY OF PRIMARY DEALERS This survey is formulated by the Trading Desk at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York to enhance policymakers' understanding of market expectations on a variety of topics related
SURVEY OF PRIMARY DEALERS This survey is formulated by the Trading Desk at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York to enhance policymakers' understanding of market expectations on a variety of topics related
The Asian Face of the Global Recession
 The Asian Face of the Global Recession C.P. Chandrasekhar & Jayati Ghosh Delegates to the World Economic Forum at Davos this year came despondent and left in despair. Both the discussions and the new evidence
The Asian Face of the Global Recession C.P. Chandrasekhar & Jayati Ghosh Delegates to the World Economic Forum at Davos this year came despondent and left in despair. Both the discussions and the new evidence
Spanish economic outlook. June 2017
 Spanish economic outlook June 2017 1 2 3 Spanish economy a pleasant surprise Growth drivers Forecasts once again bright One of the most dynamic economies in Europe Spain growing at a faster rate than EMU
Spanish economic outlook June 2017 1 2 3 Spanish economy a pleasant surprise Growth drivers Forecasts once again bright One of the most dynamic economies in Europe Spain growing at a faster rate than EMU
HKU announces 2015 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast
 Press Release HKU announces 2015 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast July 7, 2015 1 Overview The APEC Studies Programme of the Hong Kong Institute of Economics and Business Strategy at the University of Hong
Press Release HKU announces 2015 Q3 HK Macroeconomic Forecast July 7, 2015 1 Overview The APEC Studies Programme of the Hong Kong Institute of Economics and Business Strategy at the University of Hong
Snapshot of SA Economy
 Snapshot of SA Economy Kgotso Radira 1 September 29 Economic Outlook Global share indices 2 Indices 18 16 14 12 1 8 6 4 25 26 27 28 29 S&P 5 FTSE 1 DAX Nikkei 3 Global interest rates 7 % 6 5 4 3 2 1 1999
Snapshot of SA Economy Kgotso Radira 1 September 29 Economic Outlook Global share indices 2 Indices 18 16 14 12 1 8 6 4 25 26 27 28 29 S&P 5 FTSE 1 DAX Nikkei 3 Global interest rates 7 % 6 5 4 3 2 1 1999
HKU announces 2015 Q4 HK Macroeconomic Forecast
 Press Release HKU announces 2015 Q4 HK Macroeconomic Forecast October 6, 2015 1 Overview The APEC Studies Programme of the Hong Kong Institute of Economics and Business Strategy at the University of Hong
Press Release HKU announces 2015 Q4 HK Macroeconomic Forecast October 6, 2015 1 Overview The APEC Studies Programme of the Hong Kong Institute of Economics and Business Strategy at the University of Hong
Monetary Policy Report. MONETARY POLICY REPORT (under paragraph 3 of article 18 of the Organic Law)
 MONETARY POLICY REPORT (under paragraph 3 of article 18 of the Organic Law) Banco de Cabo Verde May 2012 Banco de Cabo Verde / Maio 2012 BANCO DE CABO VERDE Department of Economic Studies and Statistics
MONETARY POLICY REPORT (under paragraph 3 of article 18 of the Organic Law) Banco de Cabo Verde May 2012 Banco de Cabo Verde / Maio 2012 BANCO DE CABO VERDE Department of Economic Studies and Statistics
SURVEY OF PRIMARY DEALERS
 SURVEY OF PRIMARY DEALERS This survey is formulated by the Trading Desk at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York to enhance policymakers' understanding of market expectations on a variety of topics related
SURVEY OF PRIMARY DEALERS This survey is formulated by the Trading Desk at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York to enhance policymakers' understanding of market expectations on a variety of topics related
Jan-Mar nd Preliminary GDP Estimate
 Japan's Economy 8 June 2016 (No. of pages: 5) Japanese report: 08 Jun 2016 Jan-Mar 2016 2 nd Preliminary GDP Estimate Real GDP growth rate revised upwards slightly from 1 st preliminary; results in accordance
Japan's Economy 8 June 2016 (No. of pages: 5) Japanese report: 08 Jun 2016 Jan-Mar 2016 2 nd Preliminary GDP Estimate Real GDP growth rate revised upwards slightly from 1 st preliminary; results in accordance
Maneuvering Past Stagflation: Prospects for the U.S. Economy In
 Maneuvering Past Stagflation: Prospects for the U.S. Economy In 2007-2008 By Michael Mussa Senior Fellow The Peter G. Peterson Institute for International Economics Washington, DC Presented at the annual
Maneuvering Past Stagflation: Prospects for the U.S. Economy In 2007-2008 By Michael Mussa Senior Fellow The Peter G. Peterson Institute for International Economics Washington, DC Presented at the annual
UKRAINE Market Monitor Review January-June 2018
 Picture: FSLC Ukraine UKRAINE Market Monitor Review January-June 218 HIGHLIGHTS Ukrainian economy continued its gradual growth for the third year in a row with 3.1 percent GDP increase in the first quarter
Picture: FSLC Ukraine UKRAINE Market Monitor Review January-June 218 HIGHLIGHTS Ukrainian economy continued its gradual growth for the third year in a row with 3.1 percent GDP increase in the first quarter
Recent Economic Developments and Monetary Policy in Mexico
 Recent Economic Developments and Monetary Policy in Mexico Javier Guzmán Calafell, Deputy Governor, Banco de México* United States-Mexico Chamber of Commerce, Northeast Chapter New York City, 2 June 2017
Recent Economic Developments and Monetary Policy in Mexico Javier Guzmán Calafell, Deputy Governor, Banco de México* United States-Mexico Chamber of Commerce, Northeast Chapter New York City, 2 June 2017
Inflation projection of Narodowy Bank Polski based on the NECMOD model
 Economic Institute Inflation projection of Narodowy Bank Polski based on the NECMOD model Warsaw / 9 March Inflation projection of the NBP based on the NECMOD model Outline: Introduction Changes between
Economic Institute Inflation projection of Narodowy Bank Polski based on the NECMOD model Warsaw / 9 March Inflation projection of the NBP based on the NECMOD model Outline: Introduction Changes between
Jan F Qvigstad: Outlook for the Norwegian economy
 Jan F Qvigstad: Outlook for the Norwegian economy Address by Mr Jan F Qvigstad, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at Sparebank 1 Fredrikstad, 4 November 2009. The text below may
Jan F Qvigstad: Outlook for the Norwegian economy Address by Mr Jan F Qvigstad, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at Sparebank 1 Fredrikstad, 4 November 2009. The text below may
Using Comparative Inventory to Bet Against the Oil Market
 Using Comparative Inventory to Bet Against the Oil Market Art Berman MacroVoices Live Vancouver January 19, 2019 Slide 1 Oil-Price Collapse and Previous Collapses $220 Oil-Price Collapse Appears to be
Using Comparative Inventory to Bet Against the Oil Market Art Berman MacroVoices Live Vancouver January 19, 2019 Slide 1 Oil-Price Collapse and Previous Collapses $220 Oil-Price Collapse Appears to be
National Economic Conditions. Cheyenne AIA Meeting February 25th, 2011 Rob Godby
 National Economic Conditions Cheyenne AIA Meeting February 25th, 2011 Rob Godby Percent Change Recovery is Technically Underway 8 Quarter-Quarter Growth in Real GDP 6 4 2 0-2 -4-6 -8 I II III IV I II III
National Economic Conditions Cheyenne AIA Meeting February 25th, 2011 Rob Godby Percent Change Recovery is Technically Underway 8 Quarter-Quarter Growth in Real GDP 6 4 2 0-2 -4-6 -8 I II III IV I II III
The next recession will not be. The Great Recession. Damon Runberg, Economist Oregon Employment Department
 The next recession will not be The Great Recession Damon Runberg, Economist Oregon Employment Department Why the fears? Simplified Business Cycle Peak 2 consecutive quarters of GDP declines Wages Rise
The next recession will not be The Great Recession Damon Runberg, Economist Oregon Employment Department Why the fears? Simplified Business Cycle Peak 2 consecutive quarters of GDP declines Wages Rise
Zambia s Economic Outlook
 Zambia s Economic Outlook F R A N C I S C H I P I M O D I R E C T O R E C O N O M I C S B A N K O F Z A M B I A Z A M B I A I N V E S T M E N T C O N F E R E N C E N O V E M B E R 4, 2 0 1 5 L O N D O
Zambia s Economic Outlook F R A N C I S C H I P I M O D I R E C T O R E C O N O M I C S B A N K O F Z A M B I A Z A M B I A I N V E S T M E N T C O N F E R E N C E N O V E M B E R 4, 2 0 1 5 L O N D O
ASF Hong Kong Market Report
 HONG KONG ECONOMY ASF 2016 - Hong Kong Market Report Background As everyone knows, Hong Kong has a very good geographic location, it is surround by sea and backup by a huge China market. HK has taken a
HONG KONG ECONOMY ASF 2016 - Hong Kong Market Report Background As everyone knows, Hong Kong has a very good geographic location, it is surround by sea and backup by a huge China market. HK has taken a
RBI's Annual Monetary Policy
 Amol Agrawal amol@stcipd.com +91-22-66202234 RBI's Annual Monetary Policy 2012-13 In Annual Monetary Policy 2012-13, RBI surprised markets by easing Repo rate by 50 bps to 8%. The consensus market expectations
Amol Agrawal amol@stcipd.com +91-22-66202234 RBI's Annual Monetary Policy 2012-13 In Annual Monetary Policy 2012-13, RBI surprised markets by easing Repo rate by 50 bps to 8%. The consensus market expectations
SECTOR OUTLOOK INDICATORS AND UP TO DATE FIGURES
 SECTOR OUTLOOK INDICATORS AND UP TO DATE FIGURES October 2017 STILL ONGOING GROWTH DURING FOURTH QUARTER Exports already suffer the impact of the strong euro; Russia is slowly coming back Positive outlook
SECTOR OUTLOOK INDICATORS AND UP TO DATE FIGURES October 2017 STILL ONGOING GROWTH DURING FOURTH QUARTER Exports already suffer the impact of the strong euro; Russia is slowly coming back Positive outlook
Quarterly Report. April June 2015
 April June August 12, 1 1 Outline 1 2 Monetary Policy External Conditions 3 Economic Activity in Mexico Inflation Determinants Forecasts and Balance of Risks April-June 2 Monetary Policy Conduction in
April June August 12, 1 1 Outline 1 2 Monetary Policy External Conditions 3 Economic Activity in Mexico Inflation Determinants Forecasts and Balance of Risks April-June 2 Monetary Policy Conduction in
Leading Economic Indicator Nebraska
 Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: September 20, 2017 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident
Nebraska Monthly Economic Indicators: September 20, 2017 Prepared by the UNL College of Business Administration, Bureau of Business Research Author: Dr. Eric Thompson Leading Economic Indicator...1 Coincident
MPC MARKET PERCEPTIONS SURVEY - JULY
 MPC MARKET PERCEPTIONS SURVEY - JULY 2018 1 CONTENTS BACKGROUND......4 SURVEY METHODOLOGY......4 HIGHLIGHTS OF THE SURVEY.........4 INFLATION EXPECTATIONS....5 EXCHANGE RATE EXPECTATIONS...6 PRIVATE SECTOR
MPC MARKET PERCEPTIONS SURVEY - JULY 2018 1 CONTENTS BACKGROUND......4 SURVEY METHODOLOGY......4 HIGHLIGHTS OF THE SURVEY.........4 INFLATION EXPECTATIONS....5 EXCHANGE RATE EXPECTATIONS...6 PRIVATE SECTOR
Monetary and Exchange Rate Policy Responses to the Global Financial Crisis: The Case of Colombia
 Monetary and Exchange Rate Policy Responses to the Global Financial Crisis: The Case of Colombia Hernando Vargas Banco de la República Colombia March, 2009 Contents I. The state of the Colombian economy
Monetary and Exchange Rate Policy Responses to the Global Financial Crisis: The Case of Colombia Hernando Vargas Banco de la República Colombia March, 2009 Contents I. The state of the Colombian economy
MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE STATEMENT FOR FIRST QUARTER Governor s Presentation to the Media. 16 th May, 2018
 1 MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE STATEMENT FOR FIRST QUARTER 2018 Governor s Presentation to the Media 16 th May, 2018 INTRODUCTION 2 The presentation is structured as follows: 1. Decision of the Monetary Policy
1 MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE STATEMENT FOR FIRST QUARTER 2018 Governor s Presentation to the Media 16 th May, 2018 INTRODUCTION 2 The presentation is structured as follows: 1. Decision of the Monetary Policy
C H A P T E R 1 T H E I L L I N O I S R E P O R T
 C H A P T E R 1 8 T H E I L L I N O I S R E P O R T 2 0 1 3 C H A P T E R 1 Giertz After the Great Recession, Where is the Great Recovery? By J. Fred Giertz This chapter provides a broad overview of trends
C H A P T E R 1 8 T H E I L L I N O I S R E P O R T 2 0 1 3 C H A P T E R 1 Giertz After the Great Recession, Where is the Great Recovery? By J. Fred Giertz This chapter provides a broad overview of trends
MACRO-BRIEF: ANGOLA. August I. Angola s Economy: A Mid-Year Review
 MACRO-BRIEF: ANGOLA August 2009 I. Angola s Economy: A Mid-Year Review The global financial-economic crisis hit hard the economy of Angola as price of oil started a free fall trend in the second half of
MACRO-BRIEF: ANGOLA August 2009 I. Angola s Economy: A Mid-Year Review The global financial-economic crisis hit hard the economy of Angola as price of oil started a free fall trend in the second half of
Ukraine s Financial and Political Crisis. Anders Åslund Senior Fellow Peterson Institute for International Economics, Washington, DC
 Ukraine s Financial and Political Crisis Anders Åslund Senior Fellow Peterson Institute for International Economics, Washington, DC May, 2009 Theses 1. Democracy, but constitutional reform needed 2. Hard
Ukraine s Financial and Political Crisis Anders Åslund Senior Fellow Peterson Institute for International Economics, Washington, DC May, 2009 Theses 1. Democracy, but constitutional reform needed 2. Hard
Regional Economic Outlook
 Regional Economic Outlook Caucasus and Central Asia Azim Sadikov International Monetary Fund Resident Representative November 6, 2013 Outline Global Outlook CCA: Recent Developments, Outlook, and Risks
Regional Economic Outlook Caucasus and Central Asia Azim Sadikov International Monetary Fund Resident Representative November 6, 2013 Outline Global Outlook CCA: Recent Developments, Outlook, and Risks
BOFIT Forecast for Russia
 BOFIT Forecast for Russia 27 March 2018 BOFIT Russia Team BOFIT Forecast for Russia 2018 2020 Bank of Finland BOFIT Institute for Economies in Transition Bank of Finland BOFIT Institute for Economies in
BOFIT Forecast for Russia 27 March 2018 BOFIT Russia Team BOFIT Forecast for Russia 2018 2020 Bank of Finland BOFIT Institute for Economies in Transition Bank of Finland BOFIT Institute for Economies in
RECOVERY CONTINUES FOR LOGISTICS REAL ESTATE
 RECOVERY CONTINUES FOR LOGISTICS REAL ESTATE World events trigger soft patch The global economic soft patch in the first half of 2011 was primarily caused by the cost of oil reaching $114 per barrel, rising
RECOVERY CONTINUES FOR LOGISTICS REAL ESTATE World events trigger soft patch The global economic soft patch in the first half of 2011 was primarily caused by the cost of oil reaching $114 per barrel, rising
