Bargaining in Standing Committees with an Endogenous Default
|
|
|
- Verity Sullivan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Barganng n Standng Commttees wt an Endogenous Default Vncent Anes Unversty of Nottngam Danel J. Sedmann Unversty of Nottngam August 15, 2013 Abstract Commttee votng as mostly been nvestgated from te perspectve of te standard Baron-Ferejon model of barganng over te dvson of a pe, n wc barganng ends as soon as te commttee reaces an agreement. In standng commttees, owever, exstng agreements can be amended. Ts paper studes an extenson of te Baron-Ferejon framework to a model wt an evolvng default tat reflects ts mportant feature of polcymakng n standng commttees: In eac of an nfnte number of perods, te ongong default can be amended to a new polcy wc s, n turn, te default for te next perod). Te model provdes a number of qute dfferent predctons. ) From a postve perspectve, te key dstncton turns on weter te quota s less tan unanmty. In tat case, patent enoug players waste substantal sares of te pe eac perod and te sze prncple fals n some pure strategy Markov perfect equlbra. By contrast, te unque Markov perfect equlbrum outcome n a unanmty commttee concdes wt tat n te correspondng Baron-Ferejon framework. ) If players ave eterogeneous dscounts ten a large class of subgame perfect equlbra ncludng all Markov perfect equlbra) are neffcent wt a nonunanmty quota, and all subgame perfect equlbra are neffcent wt a nonunanmty quota. JEL classfcaton: C73, C78, D71, D72. Keywords: Legslatve barganng, endogenous default, pork barrel, polcy persstence. Address: Scool of Economcs, Room B18, Te Sr Clve Granger Buldng, Unversty of Nottngam, Unversty Park, Nottngam NG7 2RD, Unted Kngdom. Emal: vncent.anes@nottngam.ac.uk. Address: Scool of Economcs, Room B34, Te Sr Clve Granger Buldng, Unversty of Nottngam, Unversty Park, Nottngam NG7 2RD, Unted Kngdom. Emal: danel.sedmann@nottngam.ac.uk. 1
2 1 Introducton Commttee votng as mostly been nvestgated from te perspectve of te standard Baron- Ferejon model of barganng n an ad oc commttee over te dvson of a sngle pe: players earn an exogenously fxed default payoff untl te commttee reaces an agreement, wen negotatons end. However, many commttees suc as legslatures) are dynamc n two senses: ) ter members reac a sequence of polcy agreements so te commttee s standng), and ) a new pe s dvded accordng to te same proportons as te last pe unless te last agreement s amended so te default s endogenous). In ts paper, we study a model wc captures tese dynamc aspects of polcy makng. Eac perod begns wt a default polcy.e. a dvson of te pe among players) nerted from te prevous perod; and a player s randomly drawn to make a proposal wc s ten voted up or down by te commttee; f voted up, te proposal s mplemented and becomes te new default; f voted down, te ongong default s mplemented and remans n place untl te next perod. Ts process contnues ad nfntum. Ts model naturally represents Congressonal legslaton on socal polcy and enttlements: te prevously agreed law remans n place untl Congress decdes to amend t. From a formal pont of vew, ts model of a standng commttee yelds a barganng game wt an endogenous default n wc a pe s avalable for dvson eac perod. In contrast to Baron and Ferejon 1989), we allow players to ave dfferent dscount factors, and any concave utlty functons; we consder any quota ncludng majorty and unanmty rules); and we allow players to be selected to propose wt dfferent probabltes. Analyss of ts game rases varous nterestng questons, suc as: 1) Wen do statonary Markov perfect equlbra SMPEs) exst and, wen tey do, are ter outcomes unque? 2) Must eac pe be dvded between a mnmal wnnng majorty as predcted by te sze prncple n every SMPE? 3) Is eac pe fully dvded tat s, s te dvson of te pe statcally effcent) n every SMPE? 4) Are equlbra Pareto effcent? 5) How does te endogenety of te evolvng default affect SMPE outcomes? And 6) How do te answers to tese questons depend on te quota? Te lterature on standng commttees as only posed te frst two questons. Our contrbuton s to bypass tecncal ssues wc ave stymed progress, and tereby to say muc more about eac of te sx questons. We provde te followng answers: 2
3 1) Equlbrum exstence and multplcty of equlbrum outcomes. We construct pure strategy SMPEs for any game wt a non-unanmty quota and patent enoug players, and also prove agan usng constructve arguments) tat unanmty games possess pure strategy SMPEs, rrespectve of patence. However, we ave radcally dfferent results on multplcty for games wt and wtout a unanmty quota. We start wt te latter case. Take any pont n te polcy space at wc at least a mnmal wnnng majorty ave a postve sare of te pe. If players are suffcently patent ten we can construct a pure strategy SMPE n wc tat polcy s mplemented n te frst perod and never amended a property wc we call no-delay). By contrast, any game wt a unanmty quota as a unque SMPE outcome. 1 Te prevous lterature wc we wll survey n te next secton) as focused on exstence of SMPEs n barganng games wt an evolvng default. Our results demonstrate tat exstence s not a problem wen players are patent enoug or f tere s a unanmty quota. 2) Te sze prncple. Te sze prncple as been central to te study of legslatures snce Rker 1962). Te class of solutons wc we construct for non-unanmty games contans SMPEs n wc te pe s sared amongst more tan a mnmal wnnng coalton. Our model terefore provdes a new explanaton for wy majortes n legslatures are typcally supramnmal. 3) Waste. Our results on te dvson of te pe agan dffer, dependng on te quota. We sow tat SMPE agreements n games wtout a unanmty quota typcally waste some of te pe wen all players are patent enoug. Specfcally, for every ε > 0, we can construct an SMPE n wc a polcy wc wastes proporton 1 ε of te pe s agreed to n te frst perod and never amended. By contrast, none of te pe s wasted n any subgame perfect equlbrum SPE), rrespectve of players patence, n games wt a unanmty quota. More strongly, players can waste any proporton of te pe n SMPEs of nonunanmty games wc also fal te sze prncple. Our model can terefore explan features wc are common n pork barrel poltcs cf. Evans 2004)). 1 Trougout we use te term outcome to refer to te vector of average dscounted) payoffs from te nfnte sequence of pe dvsons. 3
4 4) Pareto neffcency. If all players sare te same dscount factor ten Pareto effcency only turns on weter te entre pe s dstrbuted n every perod. Wt eterogenous dscount factors, owever, temporal patterns also matter. For nstance, our no-delay SMPEs ncludng tose wtout waste) support polcy sequences wc can be Pareto mproved by operatng transfers across perods. More generally, our analyss of SPEs reveals tat Pareto neffcency s not lmted to tose SMPEs. If preferences are lnear n sare of te current pe as n Baron and Ferejon 1989)) ten, n te generc case were all players ave dfferent dscount factors, an SPE can be effcent only f t reles on complex, story-dependent punsments. Dynamc equlbra.e. tose SPEs n wc beavor depends at most) on te lst of polces mplemented n all prevous perods are all Pareto neffcent. On te oter and, every SPE of a unanmty commttee s neffcent f two or more players ave dfferent dscount factors. Te ntuton s tat some player must eventually earn te entre pe n any effcent polcy sequence; 2 and no suc polcy sequence can be played n any equlbrum. 5) Te Effects of an Endogenous Default. Tese results stand n sarp contrast to te propertes of te Baron-Ferejon model of an ad oc commttee, n wc a sngle pe s dvded. In tat model, statonary equlbrum outcomes are unque, only mnmal wnnng coaltons form, and none of te pe s wasted Baron and Ferejon 1989)). 3 Tese propertes clearly carry over to a couple of dynamc varants wt exogenous defaults: n one varant, an ad oc commttee agrees once to te dvsons of a sequence of pes; n anoter varant, a standng commttee negotates dvson of a new pe once t as agreed on dvson of te exstng pe, earnng notng eac perod tll a wnnng coalton forms. Usng tose varants as bencmarks, our results mply tat default endogenety as profound mplcatons for standng commttees wt a nonunanmty quota: Default endogenety may cause statc neffcency waste), allow supramnmal coaltons to form, and create a large multplcty of equlbrum outcomes. None of tese propertes can old wt a unanmty quota. More strkngly, we sow tat tere s a unque SMPE outcome, wc concdes wt te unque statonary SPE outcome n te equvalent Baron-Ferejon model of an ad oc commttee. 2 More mpatent players must be served frst f at least two players eac earn a postve sare of some pe. 3 Eraslan 2002) sows tat tese results extend to games wt eterogeneous dscount factors and any quota. Specfcally: ex post effcency and te sze prncple old wen players ave strctly concave preferences, but unqueness and ex ante effcency mgt fal because of random proposers). 4
5 As for Pareto neffcency, te same argument as n our model also apples to te standng commttee model wt an exogenous default sketced above. By contrast, an ad oc commttee wc negotates over te sequence of pe dvsons must reac a Pareto effcent agreement n any equlbrum because any proposer s a resdual clamant). Ts suggests tat effcency may fal n our model because te commttee cannot commt not to renegotate agreements. 6) Effect of te quota. Our postve results above reveal tat dynamc aspects of standng commttees polcymakng only matter f te quota s less tan unanmty: Wt a unanmty quota, tere s a unque SMPE outcome n wc te statcally effcent polcy reaced by an ad oc commttee s mplemented mmedately and never amended; oterwse, f players are patent enoug ten tere s a multplcty of pure strategy no-delay SMPEs, some of wc are statcally neffcent. As for normatve results, owever, dynamc aspects matter even wt a unanmty quota: f dscount factors are eterogeneous ten all SPEs are Pareto neffcent. We relate our model and results to te lterature n te next secton. We present our model n Secton 3, and provde results on commttees wt a non-unanmty and a unanmty quota respectvely n Sectons 4 and 5. We consder te mplcatons of an endogenous default n Secton 6. Secton 7 concludes. Most of te proofs appear n te Appendx. 2 Related Lterature Baron and Ferejon 1989) as spawned an enormous lterature; we refer readers to Eraslan and McLennan 2011) for a recent lst of contrbutons, ncludng exstence and unqueness results for any quota. Te lterature on barganng n standng commttees wt an endogenous default s muc smaller, 4 most lkely for tecncal reasons: n equlbrum, te proposals wc would be accepted may vary dscontnuously wt te default polcy because of expectatons about future play. Te ensung dscontnuous transton probabltes preclude te use of conventonal fxed pont arguments to establs exstence of even mxed 4 Ts lterature started wt Baron 1996). Papers wc we do not survey nclude Gomes and Jeel 2005, Secton III.A), Bernem et al 2006), Anes 2010), Dermeer and Fong 2011, 2012), Zápal 2011a,b), Battagln et al 2012), Nunnar 2012), Bowen et al 2012), Bowen and Zaran 2012), and Anes and Sedmann fortcomng), to cte a few. 5
6 strategy equlbra. Moreover, most of ts lterature as focused on majorty rule games, and as terefore not consdered te effect of varyng te quota. By contrast, ts problem s central to our analyss. Kalandraks 2004) and Baron and Bowen 2013) study majorty rule games wt tree equally patent, rsk neutral players, equprobable proposers, and a statcally effcent ntal default; Kalandraks 2010) extends te model to games wt fve or more players wose preferences are concave. Kalandraks 2004) and 2010) sow tat tese games ave an SMPE n wc te default mmedately reaces an ergodc dstrbuton were eac proposer takes te entre pe; but players mx over extra-equlbrum proposals; Baron and Bowen construct a no-delay SMPE n wc te proposer mxes over er sngle) coalton partner. 5 By contrast, we follow Baron and Ferejon 1989) by supposng tat te ntal default s statcally neffcent, and allowng players to propose polces wc waste some of te pe. 6 In te SMPEs wc we construct, te default reaces a sngle polcy mmedately), and no player mxes, on or off te pat. Duggan and Kalandraks 2012) use a fxed pont argument to establs exstence of pure strategy SMPEs for games n wc preferences and te default are subject to stocastc socks. 7 constructve arguments. By contrast, we prove exstence n unperturbed games by and large) usng Kalandraks 2004) and 2010) equlbra volate te sze prncple, n te sense tat a submnmal wnnng coalton sares te pe. By contrast, Battagln and Palfrey s 2012) expermental results on contnuous allocaton problems suggest tat conventonal volatons of te sze prncple are emprcally relevant: 45% of agreed polces were close to te centrod of te smplex. Some of) our constructed equlbra volate te sze prncple n ts sense, as do te equlbra constructed by Bowen and Zaran 2012) and Rcter 2013): Bowen and Zaran requre preferences to be strctly concave and te ntal default to be statcally effcent, and sow tat te sze prncple s volated wen dscount factors take ntermedate values and te ntal default s not too nequtable. We also allow for but do 5 In Kalandraks 2004) [resp. Baron and Bowen 2012)], ndfferent voters always accept [resp. reject]. Indfferent voters respond dfferently to amendments of polces on and off te equlbrum pats we construct. 6 We sow tat ts s possble n non-unanmty games. On te oter and, t s easy to see tat tere would stll be multple no-delay equlbrum outcomes f waste were precluded by restrctng te polcy space. 7 Ter results apply to a class of stage games wc ncludes pe dvson. 6
7 not requre) strctly concave preferences; 8 but te sze prncple fals n our constructon wenever all players are patent enoug. Rcter 2013) constructs an egaltaran Markov perfect equlbrum by allowng offers to waste some of te pe. Tese offers are only made n order to deter devatons from equlbrum play, and are terefore never observed on te pat. We also follow Baron and Ferejon 1989) by allowng for suc statcally neffcent offers. However, n contrast to Rcter, tese offers are made on te equlbrum pat n some of) our constructons. In oter words, we explan waste. Baron 1991) argues tat Congress often bot wastes resources and splts te remander among a supramnmal majorty durng dstrbutve barganng. Baron sows tat closed and open rule models based on Baron and Ferejon 1989) can explan waste aka pork), but can only explan tese volatons of te sze prncple by appealng to a norm of unversalsm. 9 By contrast, equlbra n our model exbt bot features. Sedmann and Wnter 1998) and Okada 2000), nter ala, study barganng wt an endogenous default n superaddtve caracterstc functon games. 10 Hyndman and Ray 2007) prove tat all ncludng story-dependent) subgame perfect equlbra of caracterstc functon games are absorbng, and tat tey are asymptotcally statcally effcent f tere s a fnte number of feasble polces. Tey also sow by example tat tese results do not carry over to games n partton functon form. Now smple games are n caracterstc functon form f and only f te quota s unanmty. We explot ter frst result wen provng tat every equlbrum of a unanmty game s no-delay; ter second result also olds n our model wtout requrng fnteness). Furtermore, statcally neffcent equlbra exst bot n our model wt a non-unanmty quota and n Hyndman and Ray s model wt a partton functon form. However, Hyndman and Ray focus on asymptotc statc effcency, and assume a common dscount factor; we consder Pareto effcency and, crucally for assocated results, allow dscount factors to dffer. Fnally, we turn to te no-delay property. Polcy outcomes of our no-delay SMPEs can be nterpreted as a specal case of Acemoglu et al s 2012) dynamcally stable states, wc are defned as poltcal states reaced n a fnte number of perods and never canged) n 8 As Battagln and Palfrey 2012) note, ter expermental evdence on suc games suggests tat some subjects ave strctly concave preferences. 9 Te sze prncple olds n open rule games f tere are enoug players. 10 Sedmann and Wnter focus on equlbra n wc te grand coalton forms after a number of steps. Wle we cannot exclude delay wt a non-unanmty quota, our constructons all nvolve no-delay equlbra. 7
8 pure strategy SMPEs of barganng games wt an endogenous default and patent players. Hence, our results caracterze and prove exstence of a class of dynamcally stable states n votng stuatons were, n contrast to tose studed n Acemoglu et al 2012), te set of polces s nfnte and polcy preferences are not acyclc. No-delay equlbra are also specal cases of Baron and Bowen s 2013) noton of a coalton Markov perfect equlbrum; but te mxed strategy) equlbra wc tey construct for te comparable, basc model) are no-delay. By defnton, te default canges once n a no-delay equlbrum: polcy s persstent. Ts predcton s consstent wt a wdespread clam tat agences are never termnated. 11 A related lterature explans wy statcally neffcent polces may be persstent so te polcy sequence s neffcent). However, te mecansms n ts lterature rely on prvately ncurred adjustment costs Coate and Morrs 1999)), ncomplete nformaton e.g. Mtcell and Moro 2006)) or te growng power of ncumbent factons Persco et al 2011)). By contrast, no-delay equlbra are neffcent n our model because relatvely mpatent players cannot commt to decreasng sares of te pe. 3 Notaton and Defntons 3.1 Te Standng Commttee Game In eac of an nfnte number of dscrete perods, ndexed t = 1, 2,..., up to a unt of a dvsble resource te pe can be allocated among te members of a commttee N {1,..., n}, n 2. Tus, te set of feasble polces eac perod s { } n X x 1,..., x n ) [0, 1] n : x 1. We denote te polcy mplemented n perod t, and terefore te default at te begnnng of perod t + 1, by x t = x t 1,..., n) xt. At te start of eac perod t, player s selected wt probablty p 0, 1) to propose a polcy n X. We say tat a player wo proposes te exstng default passes. All players ten smultaneously vote to accept or to reject te cosen proposal. Te votng rule used n every perod t s a quota q wc satsfes n/2 < q n. Specfcally, f at least q players accept proposal y X ten t s mplemented as te commttee decson n perod t and becomes te default next perod.e. x t = y); and f y secures less tan q votes ten te prevous default, x t 1, s mplemented 11 See Kaufman 1976) for te conventonal clam, and Lews 2002) for a dssentng vew. =1 8
9 agan and becomes te default n perod t + 1.e. x t = x t 1 ). Te default n perod 1 s x 0 = 0,..., 0). Our man results do not depend on wc polcy n X s te exogenous) ntal default.) We wll refer to { x t} t=1 suc tat every xt s feasble as a polcy sequence. Once polcy x t as been mplemented, every player receves an nstantaneous payoff 1 δ ) u x t ), were u s a strctly ncreasng, contnuously dfferentable concave utlty functon, and δ 0, 1) s s dscount factor. Tus, player s payoff from a polcy sequence { x t } t=1 s 1 δ ) ) t=1 δt 1 u x t. We say tat dscount factors are eterogeneous f δ δ j for some par of players and j; and tat dscount factors are strctly eterogeneous f δ δ j for every par of players and j. Te assumptons above defne a dynamc game, wc we wll refer to as a standng commttee game. Our man purpose s to analyze te equlbra of ts game. 3.2 Equlbrum and Effcency Equlbrum concept. We follow te standard approac of concentratng trougout on stage-undomnated subgame perfect equlbra SPEs);.e., SPEs n wc, at any votng stage, no player uses a weakly domnated strategy. Ts excludes strategy combnatons n wc players all vote one way, and are ndfferent wen q < n because tey are nonpvotal. Hencefort, we leave t as understood tat any reference to equlbra s to equlbra tat satsfy ts property. For our postve analyss, we wll n addton concentrate as te prevous lterature) on te strcter crteron of statonary Markov perfect equlbra SMPEs),.e., SPEs n wc all players use strateges wc only depend on te current payoff-relevant relevant state: n proposal stages, players coces of probablty dstrbutons over X) only depend on te ongong default; n votng stages, players coces of probablty dstrbutons over {accept, reject}) only depend on te current default and te proposal just made. We wll be partcularly nterested n pure strategy SMPEs, were every player s coce s determnstc after every story. Absorbng ponts and no-delay strateges. A story at any stage of te game descrbes all tat as transpred n te prevous perods and stages te sequence of proposers, ter respectve proposals and te assocated pattern of votes). Of partcular nterest are mplementaton stores to use te language of Hyndman and Ray 2007)),.e., tose at wc a polcy s about to be mplemented. For eac x X, te set of mplementaton stores at wc polcy x s about to be mplemented s denoted by H x. Let H x X H x be te set of all possble mplementaton stores. 9
10 Every strategy profle σ n conjuncton wt recognton probabltes) generates a transton functon P σ on mplementaton stores, were P σ, H ) s te probablty gven σ) tat te next perod s mplementaton story s n H, gven tat te mplementaton story for te current perod s. Tus, for all N, all x X and all H x, player s contnuaton value at s gven by V σ ) = 1 δ ) u x ) + δ V σ ) P σ, d ). We say tat x X s an absorbng pont of σ f and only f P σ, H x ) = 1 for all H x, and denote by Aσ) {x X : P σ, H x ) = 1 for all H x } te set of absorbng ponts of σ. We wll say tat σ s no-delay f and only f: ) Aσ) ; and ) for all H, tere s x Aσ) suc tat H x. In words, a strategy profle s no-delay f te commttee mplements an absorbng pont at any mplementaton story ncludng tose off te equlbrum pat). In te case of statonary Markov strateges, we wll ndulge n a slgt abuse of notaton and replace mplementaton stores by polces n te defntons above. For nstance, P σ x, Y ) wll denote te probablty gven statonary Markov strategy σ) tat te commttee cooses a polcy n Y n te next perod gven tat polcy x s mplemented n te current perod so tat Aσ) {x X : P σ x, {x}) = 1}. In)effcency. It s nstructve to dstngus between two notons of neffcency. Frst, polcy x X s statcally neffcent f N x < 1; we wll refer to 1 N x as waste. 12 Second, σ s Pareto neffcent f te vector of payoffs t generates s Pareto domnated by te nfnte-orzon payoff arsng from some possbly stocastc) polcy sequence n X. Evdently, every equlbrum nducng a polcy sequence wc contans a statcally neffcent polcy s Pareto neffcent, but te converse s false. 4 Nonunanmty Commttees Let W be te collecton of wnnng coaltons: W {C N : S q}. Trougout ts secton, we assume tat q < n: agreement requres less tan unanmous consent. 12 Recall tat u.) s strctly ncreasng n x. 10
11 4.1 Smple Solutons We wll construct a class of pure strategy no-delay SMPEs, n wc eac player j N s only offered two dfferent sares of te pe a g offer x j > 0 and a low offer y j < x j after any story. In every perod and for any ongong default, eac proposer condtonal on beng recognzed to make an offer) mplctly selects a wnnng coalton C by makng g offers to te members of C and low offers to te members of N \C. If eac player receves a low offer from at least one proposer, ten we refer to te set of suc proposals one for eac player) as a smple soluton. Formally: Defnton 1. Let C {C } N W be a class of coaltons suc tat, for eac N, C and / C j for some j N \ {}. Let x = x 1,..., x n ) and y = y 1,..., y n ) be two vectors n [0, 1] n satsfyng x > y and x j + y j 1, j C j / C for all N. Te smple soluton nduced by C, x, y) s te set of polces S { x C } were for all, j N. x C j { xj f j C, y j f j / C, Before we turn our attenton to te constructon of equlbra temselves, a few remarks are n order about smple solutons: 1. A smple soluton exsts f and only f q < n: f q < n ten te man smple soluton, n wc te pe s dvded equally among every mnmal wnnng coalton, s a notable example of a smple soluton cf. Wlson 1971)); f q = n ten eac player must be ncluded n te unque wnnng coalton N and, terefore, tere s no smple soluton. 2. If q < n ten any polcy wc assgns a postve sare to at least q players s part of some smple soluton. N, To see ts, take an arbtrary polcy z X suc tat { : z > 0} q. For expostonal convenence, we order te players n N n suc a way tat z z +1 for eac = 1,..., n 1 tus ensurng tat z > 0 for all q). Consder te smple soluton nduced by C, x, y), were x = { z f q z + ε n q f > q, y = { z ε f q z 11 f > q, ε > 0 arbtrarly small,
12 and C s te coalton tat ncludes and te next q 1 players followng te order 1, 2,..., n 1, n, 1, 2,..., q 1. It s readly cecked tat C, x, y) satsfes all te condtons of Defnton 1 n partcular y 0 for all N), and tat x C 1 = z. 3. Te defnton of te class C of coaltons does not requre all of tem to be dstnct; but t s easy to confrm tat C must contan at least n/n q) dstnct coaltons. 4. Te polces n a smple soluton may all assgn a postve sare to a supramnmal coalton, and mgt all nvolve waste. 5. Polces wc assgn a postve sare to fewer tan a mnmal wnnng coalton cannot be ncluded n a smple soluton. Suc polces nclude te ntal default and te vertces of te smplex. 4.2 Prelmnary Intutons If all players are myopc ten tere s a unque SPE n wc eac proposer successfully clams te entre pe. More generally, t s easy to sow tat tere s no absorbng SPE wen players dscount factors are small. Indeed, owng to te emptness of te core, tere s always a wnnng coalton wc can make all ts sort-sgted) members strctly better off by amendng any potental absorbng pont to anoter polcy n X. For future reference, we record ts observaton as: 13 Observaton 1. Let q < n. If δ = 0 for eac N ten eac perod s proposer receves te entre pe n te unque SPE. Furtermore, tere exsts ˆδ 0, 1) suc tat tere s no absorbng SPE wenever max N δ < ˆδ. Neverteless, we wll sow tat t s possble to construct a no-delay and terefore absorbng) SMPE wen players dscount factors are suffcently large. Te followng example llustrates Defnton 1, and provdes an ntutve presentaton of some key mecansms bend our equlbrum constructon. Example 1. Let n = 3, q = 2, p = 1/3, δ = δ and u x ) = x for all N. 14 Take, for example, te smple soluton S = {1/3, 1/3, 1/6), 1/6, 1/3, 1/3), 1/3, 1/6, 1/3)} tat s, C 1 = {1, 2}, C 2 = {2, 3}, C 3 = {1, 3} and x j = 1/3, y j = 1/6 for every player 13 A formal proof s avalable upon request. 14 Tese are precsely te assumptons made by Kalandraks 2004). In contrast to tat paper, owever, we requre te ntal default to be 0,..., 0), and allow for polces wc do not exaust te pe. 12
13 j = 1, 2, 3. If δ 12/13 ten te followng strategy profle forms a pure strategy, no-delay SMPE wose set of absorbng ponts s S: Player always offers 1/3 to te players n C and 1/6 to te player outsde C f te ongong default does not belong to S, and passes oterwse; Player accepts proposal z wen te ongong default s w f and only f one of te followng condtons olds: ) w S and w = 1/6; ) w / S, z S, and z 1 δ)w + 5δ/18); or ) w, z / S and z w. A formal proof of ts statement s obtaned as a specal case of Teorem 1. Te ntuton s as follows. It s readly cecked tat ts pure) strategy profle s no-delay and tat S s te set of absorbng ponts: eac polcy x C n S s proposed by player wt probablty 1/3, accepted by te two members of majorty coalton C, and never amended. To see wy ts s an SMPE, observe frst tat eac patent) player = 1, 2, 3 can only end up n two possble states n te long-run: a good state n wc se receves 1/3 n all perods, and a bad state n wc se receves 1/6 n all perods. Indeed, any ongong default w s eter an absorbng pont tself or wll lead mmedately to some absorbng pont x C j S, wt x C j {1/6, 1/3}. In te former case, player s expected payoff s w = 1/3 f C j, and w = 1/6 oterwse. In te latter case, receves w n te current perod and 2/3 1/3 + 1/3 1/6 = 5/18 n te next perod C j wt probablty 2/3). Her expected payoff s terefore 1 δ)w + 5δ/18), wc s less tan 1/3 for all w 0, 1) recall tat δ 12/13). Tus, every player seeks to maxmze resp. mnmze) te probablty of endng up n a good resp. bad) state. In votng stages, ts ncludes rejectng any proposal to cange a default polcy x C j wt C j to anoter polcy y even f y Pareto domnates x C ): beng n a good state, would not run te rsk of endng up n a bad state. It also ncludes acceptng any proposal x C j wt C j wen te ongong default s not already a good state for. As te C j s are wnnng coaltons, tese observatons mply tat any attempt to cange a default n S would be unsuccessful, and tat any proposal to cange a default outsde S to a polcy n S would be successful. In proposal stages, t s terefore optmal for player to propose x C oterwse. f te ongong default s not an absorbng pont, and to pass 13
14 Ts example llustrates wy our results are radcally dfferent from tose obtaned n te standard Baron-Ferejon model of an ad oc commttee. In partcular, t explans wy sares of te pe can be perpetually wasted n equlbrum: any devaton to proposng a Pareto-superor polcy would be rejected, as polcy would revert to one of te statcally neffcent absorbng ponts. It also sows tat te pe can be sared amongst more tan a mnmal wnnng coalton n equlbrum. 4.3 Postve Results Our frst result generalzes te argument above to any nonunanmty quota, any concave utlty functons, and any smple soluton. We descrbe a pure strategy no-delay SMPE n wc eac polcy n a smple soluton s proposed by some player, and no oter polcy s proposed as a smple equlbrum. Teorem 1. Suppose tat q < n, and let S be a smple soluton. Tere exsts δ 0, 1) suc tat te followng s true wenever mn N δ δ: Tere exsts a pure-strategy nodelay SMPE wose set of absorbng ponts s S. Te proof of ts teorem, lke tose of all oter teorems n te paper, s provded n te Appendx. Teorem 1 as several nterestng mplcatons: Multplcty of SMPE outcomes. We noted above tat any polcy say, z) wc assgns a postve sare to q or more players s part of a smple soluton. Teorem 1 terefore mples tat z s an absorbng pont of an SMPE of any game wt q < n and patent enoug players. In tat SMPE, player 1 proposes z wc s accepted by all members of coalton C 1 = {1,..., q} W, and never amended. Ts argument does not apply to polces wc assgn a postve sare to fewer tan q players ncludng te ntal default), and can terefore not be part of a smple soluton. Polces wc assgn a zero sare to some wnnng coalton cannot be absorbng ponts because every member of suc a coalton could proftably devate as a proposer. 15 Mnmal wnnng coaltons. Te Baron-Ferejon model predcts tat only mnmal wnnng coaltons sare te pe n any statonary SPE. Teorem 1 mmedately mples tat ts property, often referred to as te sze prncple, may fal n our model wt an 15 As Kalandraks 2004, 2010) demonstrates, suc polces could neverteless be part of an ergodc set. 14
15 evolvng default: As mentoned earler, polces n a smple soluton may all assgn a postve sare to a supramnmal coalton. Waste. Anoter mportant mplcaton of Teorem 1 s tat endogenety of te default may create substantal statc) neffcences n equlbrum. For any ε 0, 1), let X ε be te set of polces suc tat te commttee wastes more tan 1 ε: X ε { x X : N x < ε }. It s easy to fnd smple solutons tat are subsets of X ε. For nstance, take te smple soluton nduced by C, x, y) were, for eac N, x = ε/2q, y = 0, and C s te coalton tat ncludes and te next q 1 players followng te order 1, 2,..., n 1, n, 1, 2,..., q 1. Teorem 1 mples tat any non-unanmty game wt patent enoug players as a pure-strategy no-delay SMPE wose absorbng ponts all belong to X ε : te commttee wastes at least 1 ε n every perod along te equlbrum pat. Ts agan stands n sarp contrast to te statonary SPEs of te Baron-Ferejon model, n wc waste never occurs. Agreements may n fact be even worse relatve to te ntal default tan our presentaton as terto suggested. Specfcally, te proof of Teorem 1 does not rely on our supposton tat x 0 = 0,..., 0); so we can construct smple equlbra n wc every absorbng polcy s strctly Pareto-domnated by te ntal default by approprately selectng x 0 ). 16 Teorem 1 also mples tat tere are SMPEs n wc statcally neffcent polces are retaned ndefntely. Ts property s emprcally nterestng: for example, Branard and Verder 1997) descrbe persstent protecton as one of te central stylzed facts n trade p222). Teorem 1 terefore contrbutes to te lterature on polcy persstence, wtout requrng as n Coate and Morrs 1999) and Acemoglu and Robnson 2008)) tat players can unlaterally nvest n sustanng polces. Pork barrel poltcs. We ave noted tat SMPE agreements may waste some of te pe and tat te sze prncple may fal. Teorem 1 says tat bot propertes can old n te same equlbrum. Accordng to Scattscneder 1935), ts combnaton of propertes caracterzed US trade polcy before Indeed, Baron 1991) clams tat legslaton 16 Ts property s stronger tan a related result n Bernem et al s 2006) and Anes and Sedmann s fortcomng) models of barganng wt an evolvng default: tat te equlbrum agreement s worse tan x 0 for some wnnng coalton. 15
16 on dstrbutve ssues often exbts ts combnaton. 17 He also argues tat models of ad oc commttees can explan pork, but not volatons of te sze prncple. By contrast, Teorem 1 mples tat equlbrum agreements n a standng commttee may satsfy bot propertes wtout appealng to a norm of unversalsm. We record te observatons above as Corollary 1. Suppose tat q < n. For eac of te followng statements, tere exsts δ 0, 1) suc tat ts statement s true wenever mn N δ δ: ) Tere exst multple pure-strategy no-delay SMPEs; ) Any polcy wc assgns a postve sare to q or more players s an absorbng pont n some pure-strategy no-delay SMPE; ) Tere are SMPEs wc fal te sze prncple; v) For every ε 0, 1), tere s a pure-strategy SMPE σ suc tat P σ x, X ε ) = 1 for all x X; v) Tere are no-delay SMPEs n wc te agreement wastes some of te pe and fals te sze prncple. 4.4 Pareto Effcency Corollary 1) mples tat some smple equlbra are statcally effcent. If players ave a common dscount factor ten tese equlbra are also Pareto effcent; but wastng some of te pe s not te only possble knd of neffcency n dynamc models wen dscount factors are eterogeneous. Our am n ts subsecton s to demonstrate tat a large class of SPEs are Pareto neffcent n suc a case. To ts end, we wll consder a broader class of SPEs tan SMPEs, for te latter elmnate by defnton all Pareto effcent sequences tat are not Markovan. 18 It s possble to construct effcent SPEs. For nstance, Secton B n te appendx llustrates ow te Pareto effcent polcy sequence tat always assgns te entre pe to te same player can be sustaned as an SPE wenever all players are patent enoug. Suc equlbra, owever, are supported by complex, story-dependent punsments. Bernem and Slavov 2009), Vartanen 2011, fortcomng), and Anes and Sedmann fortcomng, 17 Evans 2004) documents te falure of te sze prncple, and argues tat Congress may often pass neffcent publc good projects. 18 Specfcally, polcy sequences n wc a player earns a postve sare for 1 < T < perods are not Markovan. 16
17 Secton 5.2) consder dynamc votng frameworks n wc beavor n every perod t only depends on te lst of polces mplemented n all prevous perods x 1,..., x t 1). We refer to SPEs tat satsfy ts property as dynamc equlbra. In suc equlbra, perod-t proposals only depend on x 1,..., x t 1), and perod-t votng decsons only depend on x 1,..., x t 1) and te proposal just made. In contrast to Markov perfecton, suc a form of story-dependence does not n prncple restrct te set of polcy sequences tat can be supported by a strategy profle. Neverteless, t turns out tat f all players ave lnear preferences u x ) = x ) and dscount factors are strctly eterogeneous ten all dynamc equlbra are Pareto neffcent. Players ave lnear preferences n Baron and Ferejon 1989), and muc of te ensung lterature.) Teorem 2. Let q < n. If u x ) = x for all N and δ δ j for all, j N ten all dynamc equlbra are Pareto neffcent. Te argument for Teorem 2 s easest to see wen te equlbra are no-delay lke smple equlbra). As dscount factors are strctly eterogeneous, effcency requres eter tat one player always earns te entre pe or front loadng te sares of less patent players, and eventually assgnng te entre pe to te most patent player. Neter s possble n equlbrum. In contrast to Teorem 1, te premse of Teorem 2 does not requre tat players be patent enoug. It only requres strct eterogenety. It s easy to confrm tat te argument works as long as enoug players ave dfferent dscount factors. It s easy to confrm tat Teorem 2 also olds wen every u s strctly concave and dfferentable. To see ts, note tat effcency ten requres tat te pat be determnstc and statcally effcent. Te most mpatent player to ever receve a postve sare say, ) must receve a strctly decreasng sare on any effcent pat. Ts follows from smple explotaton of te Kun-Tucker condtons assocated wt te Pareto optmalty problem.) No suc pat could be played n equlbrum because player could proftably devate qua proposer by passng, tereby delayng te decrease n ts sare. On te oter and, tere cannot be an equlbrum n wc te most patent receves te entre pe eac perod, as anoter player could proftably devate to proposng a polcy wc gves er a postve sare. 17
18 5 Unanmty Commttees Ts secton examnes equlbra of standng commttee games n wc agreement requres unanmous consent: tat s, q = n. 5.1 Prelmnary Example As n te prevous secton, we begn wt a smple example tat wll provde some ntuton for te general results tat follow. Example 1 Contnued. Consder a varant on Example 1 of Secton 4.2) n wc te default can only be canged f all tree players accept a proposal: tat s, q = n = 3. Te oter prmtves of te example reman te same: p = 1/3, δ = δ and u x) = x for all N. We wll construct a no-delay equlbrum σ n wc, at any default x X, te selected proposer say ) successfully offers te commttee a polcy x + s x) n 1. We can tnk of proposer offerng to sare te amount of pe not dstrbuted yet.e. 1 x 1 + x 2 + x 3 ) wt te oter players, wt s j x) beng te extra) sare offered by proposer to player j. 19 In suc a stuaton, proposer s optmal offer to player j, x j +s j x), must leave te latter ndfferent between acceptng and rejectng. If j rejected s offer, se would receve er payoff from te ongong default n te current perod, 1 δ)x j, and would ten receve offer x j + s k j x) from eac proposer k = 1, 2, 3 wt probablty 1/3 n te next perod. Te followng condton must terefore old: [ x j + s jx) = 1 δ)x j + δ x j + s1 j x) + s2 j x) + s3 j x) ] 3 or, equvalently s jx) = δ 3 [ s 1 j x) + s 2 jx) + s 3 jx) ] 1) for eac and j. Gven te sares of te pe offered to te oter commttee members, proposer receves te resdual: 3 x + s [ x) = 1 xj + s jx) ]. 2) j=1 19 Hence, all proposers pass wen te ongong default s already n te unt smplex: s x) = 0, 0, 0) for all = 1, 2, 3 wenever x 2. 18
19 Combnng 1) and 2), we obtan te polcy x+s x) absorbng pont) successfully offered by eac player at any default x X: x + s x) = x + 3 2δ 1 3 x j + s jx) = x j + δ j=1 x j 3 j=1 x j,, j. In partcular, eac player expects to earn 1/3 n te game tself: V σ x 0 ) = 1/3. Its smplcty notwtstandng, tere are two noteworty features of ts example. Frst, te set of absorbng ponts of te no-delay SMPE σ concdes wt te unt smplex: x j + s j x) 2 for all x X and all, j N. Second, te SMPE outcome concdes wt tat of te analogous Baron-Ferejon model wt a unanmty quota. As te rest of ts secton wll demonstrate, tese propertes do not rely on our parametrc assumptons. 5.2 Postve Results Te man results of ts secton nge on te followng lemma, wc generalzes te propertes of Example 1 above to SPEs. Lemma 1. If q = n ten every SPE σ s a pure strategy no-delay SPE wt Aσ) = n 1. Tus, under unanmty rule, a standng commttee selects an absorbng pont n te smplex mmedately at any ongong default. In contrast to non-unanmty commttees, terefore, waste never occurs n an equlbrum of unanmty commttee games. In oter words, te unanmty game as and only as no-delay, statcally effcent SPEs. Te argument for Lemma 1 repeatedly explots a monotoncty property of SPE value functons wc depend on features of te story oter tan te state): players cannot be punsed for devatng wtout ter consent. Ts property does not rely on statonarty, and terefore apples to all SPEs. Ts monotoncty condton wll allow us to explot Hyndman and Ray 2007) Proposton 1, wc mples n our model) tat te equlbrum default converges almost surely. By contrast, even SMPE value functons need not be monotonc, absent unanmty; so SMPEs can be statcally neffcent wen q < n. Our next result asserts exstence of a pure strategy no-delay equlbrum n wc resources are never wasted. Te premse of Teorem 3 dffers from te premse of Teorem 19
20 1 our analogous result for q < n) n two mportant respects. Frst, we no longer requre tat players be patent enoug. Second, Teorem 3 asserts tat te polces reaced from any default ncludng te ntal default) are statcally effcent. Te latter property also old n te standard Baron-Ferejon model wt a unanmty quota Banks and Duggan 2000, 2006)). Te second part of te teorem strengtens te analog between equlbrum play n our game and n Baron and Ferejon 1989). Teorem 3. If q = n ten: ) a pure strategy no-delay SMPE exsts; and ) tere s a unque SMPE outcome, wc concdes wt te statonary SPE outcome of te Baron- Ferejon model. In contrast to nonunanmty games recall Observaton 1), a no-delay equlbrum exsts n unanmty games even wen dscount factors are small. We prove Teorem 3) usng a constructon wc generalzes tat employed n Example 1 above: A fxed pont argument s used to sow tat tere are proposals for eac player wc move te default nto te smplex and make every respondent ndfferent between acceptng and rejectng, gven tat defaults n te smplex would not be amended; and tat no player can proftably devate from proposng suc polces or acceptng suc an offer. Te proof of Teorem 3) establses tat pure-strategy statonary equlbrum outcomes n standng and ad oc commttee games concde. Te result ten follows from Merlo and Wlson 1995) Teorem 2, wc sows tat Baron and Ferejon s 1989) model of an ad oc commttee as a unque equlbrum outcome wen q = n. In te Introducton, we asked ow play n standng and ad oc commttees dffers. Our results n te last secton ental a sgnfcant contrast across statonary equlbrum outcomes n te two games wen q < n. Teorem 3) mples tat ts contrast does not carry over to games wt a unanmty quota. 5.3 Pareto effcency Teorem 2 states tat every dynamc equlbrum of a non-unanmty game wt lnear preferences s neffcent f dscount factors are strctly eterogeneous. Pareto effcency ten requres tat some player eventually gets te entre pe: wc s mpossble n equlbrum. In addton, Corollary 1) states tat tere are no-delay, statcally neffcent equlbra. If q = n ten waste s mpossble n any SPE by Lemma 1). However, te neffcency result carres over, ts tme to every SPE. 20
21 Teorem 4. If q = n and δ δ j, for some, j N, ten any SPE s Pareto neffcent. In contrast to Teorem 2, te premse of Teorem 4 does not requre lnear preferences, and weakens strct eterogenety to eterogenety. We obtan ts stronger result because te SPEs of a unanmty game are no-delay Lemma 1). Ts extra structure allows us to prove neffcency by constructng a Pareto-mprovng polcy sequence. 6 Te Effects of an Endogenous Default Te analyss n te prevous sectons as revealed mportant dfferences between our standng commttee game and Baron and Ferejon s 1989) statc game wt an ad oc commttee. Te comparson s drectly relevant to commttees lke te Supreme Court, wose applcaton of te stare decss rule determnes weter a decson can be amended. If te rule s strctly appled ten te frst decson establses a precedent: te Court can ten not revst a case t as already decded as n Baron-Ferejon). By contrast, prevous decsons only govern lower court rulngs untl amended f stare decss s noperatve. 20 In ts secton, we compare equlbrum outcomes n our dynamc model wt dynamc varants of te Baron-Ferejon model n wc a commttee decdes on ten polcy mplemented n an nfnte sequence of perods. We wll return to te Supreme Court example n te next secton.) We focus on two suc models: Ad oc commttee wt commtment ablty. In ts varant, te game ends once te commttee as agreed to a sngle polcy ; but n contrast to te standard Baron-Ferejon model, a polcy specfes te way n wc a sequence of pes wll be dvded. Standng commttee wt an exogenous default. In ts varant, te commttee negotates over dvson of a sngle pe eac perod. Once an agreement s reaced, players earn utlty from ter sare of te pe, and te commttee starts to negotate dvson of anoter pe. Te ntal default for te new negotatons s exogenously fxed as te n-vector 0,..., 0). Statonary equlbra of bot models clearly sare a couple of propertes wt Baron and Ferejon s 1989) statc model: Eac pe s sared by a mnmal wnnng coalton of players; and eac pe s fully sared tere s no waste. Te argument for standng commttees 20 Te two models naturally capture oter aspects of te Court: justces bargan before votng on eac case. Furtermore, lfe tenure stablzes membersp of te Court, wo may be partcularly patent. 21
22 wt an exogenous default corresponds to tat used to derve equlbra n te conventonal Baron-Ferejon model: for statonarty precludes condtonng te current dvson on te story up to te current perod. 21 Conventonal arguments also ental tese propertes for an ad oc commttee wt commtment ablty, were te same coalton sares te pe n every perod. However, te sequence of polces agreed by te two commttees n equlbrum dffer wen dscount factors are eterogeneous. In partcular, an ad oc commttee wt commtment ablty must agree to a Pareto-effcent sequence of polces, as any proposer s a resdual clamant of every pe. Tese observatons can serve as bencmarks wt wc to compare te results of te prevous sectons. Some notable dfferences can be observed: ) Substantal sares of te pe can be ndefntely wasted and te sze prncple may fal n nonunanmty standng commttees wt an endogenous default, wereas waste never occurs and only mnmal wnnng coaltons form n commttees wt an exogenous default. Tus, wle models wt an exogenous default can explan pork but not volatons of te sze prncple, agreements n a standng commttee wt an endogenous default may possess bot propertes. Interestngly, default endogenety does not generate waste wen te quota s unanmty. ) Equlbrum play n te standng commttee game s Pareto neffcent wen dscount factors are strctly eterogeneous and preferences are lnear. Teorem 2 also apples to standng commttees wt an exogenous default, as statonarty requres repetton of te same expected payoff. As mentoned above, owever, ad oc commttees wt commtment ablty reac Pareto-effcent agreements n every equlbrum. Te key dfference from our model s tat an ad oc commttee wt commtment ablty cannot renegotate an agreement. Vewed n ts lgt, our model demonstrates tat equlbrum play n a standng commttee wt an endogenous default s genercally neffcent because players cannot commt not to renegotate te exstng agreement. 7 Concludng Remarks Ts paper as dentfed a class of pure strategy statonary Markov perfect) equlbra for pe-dvson barganng games wt an endogenous default and patent enoug players, wc supplements exstng constructons. Ts as allowed us to provde a number of predctons about decson makng n standng commttees, and to dentfy mportant 21 Indeed, te equlbrum s no-delay and unque. 22
23 mplcatons of an endogenous default. In addton, te dentfed equlbra to te standng commttee game ave a no-delay property: te frst polcy proposal s accepted and remans n place n all future perods. Banks and Duggan 2000, 2006) ave generalzed te standard model of barganng n ad oc commttees to nclude any convex set of polces as well as purely dstrbutonal polces, and establsed exstence of a mxed-strategy) statonary SPE. Before concludng, a smlar extenson of our model of barganng n standng commttees to more general polcy spaces s wort dscussng. Our postve results for non-unanmty games reled on te exstence of smple solutons. Toug te defnton of a smple soluton needs to be extended to ts more general settng, te logc bend ts extenson remans te same as for Defnton 1. Eac player can be n two possble states: a good state, n wc se as a g utlty u, or a bad state, n wc se as a low utlty v. Eac proposer selects a polcy x C wc gves all members of wnnng coalton C ter g utlty, and gves te oter players ter low utlty. Put dfferently, eac proposer selects te coalton C of players wo wll be n a good state. Fgure 1: Smple Soluton n te Spatal Model Fgure 1 provdes an example n te standard spatal model: n = 3; q = 2; X s a 23
24 nonempty, compact and convex subset of R 2 ; and u x) = x ˆx for all x X and all N, were ˆx X stands for te deal polcy of player. Baron and Herron 2003) use computatonal metods to study ts settng n a fnte-orzon verson of our standng commttee game. Gven ter results, Baron and Herron conjecture tat proposals are always statcally effcent n te nfnte orzon case; and tat proposals are closer to te centrod of te saded trangle n Fgure 1, te more patent are players, and te longer s te orzon. Te example n Fgure 1 dsproves ter conjecture: Te set of polces S = { x C 1, x C 2, x C 3} n Fgure 1 consttutes a smple soluton and, terefore, te set of absorbng ponts of some pure-strategy no-delay SMPE wenever players are suffcently patent. Te arguments used to prove Teorem 1 stll apply.) Ts equlbrum s bot statcally and Pareto neffcent: all te polces n S le outsde te statc Pareto set te grey trangle n Fgure 1) and all players would be strctly better off f te expected polcy p x C were agreed mmedately and never amended. Ts s n accord wt our fndngs for te dstrbutve settng. Tese remarks suggest tat our results may be applcable to commttees lke te Supreme Court, wose polcy space s arguably) more naturally tougt of as spatal tan as dvsons of a pe. Te lterature on precedent n consttutonal law as consdered ow stare decss affects te trade-off between predctablty of te law and te rsk of error: 22 stare decss forces predctablty; and te lterature supposes tat a dvded Court would oterwse regularly overturn precedent. 23 We ave argued above tat a Court wc operates accordng to strct stare decss s equvalent to a Baron-Ferejon ad oc commttee, wereas our model represents a Court wc does not recognze precedent; and ave suggested tat te justces are typcally patent. Our results ten provde two contrbutons to te lterature. Frst, our constructon of no-delay SMPEs wen players are patent suggests tat te law may well be stable, even f precedent s not recognzed. 24 Second, our comparson of Baron-Ferejon wt our model suggests tat stare decss may prevent te Court from reacng statcally) neffcent decsons. Havng dscussed ow smple solutons may exst wt dfferent polcy spaces, we sould 22 Relevant papers nclude Scauer 1987), Stone 1988), Waldron 2012) and Kozel fortcomng). 23 Te lterature as typcally treated te Court as a untary body. However, Barrett 2013) consders ow stare decss affects play by ndvdual justces wt dfferent consttutonal vewponts or, equvalently, preferences). Se focuses on barganng once a precedent as been set; wereas we consder ow stare decss determnes wc precedent would be set. 24 Ts predcton s surely plausble: te Court rarely overturns precedent n areas lke consttutonal law) were stare decss as less force. See Gerardt 2008) C. 1 for a dscusson of te evdence. 24
Bargaining in Standing Committees with an Endogenous Default
 Barganng n Standng Commttees wt an Endogenous Default Vncent Anes Unversty of Nottngam Danel J. Sedmann Unversty of Nottngam July 7, 2014 Abstract Commttee votng as mostly been nvestgated from te perspectve
Barganng n Standng Commttees wt an Endogenous Default Vncent Anes Unversty of Nottngam Danel J. Sedmann Unversty of Nottngam July 7, 2014 Abstract Commttee votng as mostly been nvestgated from te perspectve
CeDEx Discussion Paper Series. Discussion Paper No Vincent Anesi and Daniel J. Seidmann July Bargaining in Standing Committees
 Dscusson Paper No. 2012-09 Vncent Anes and Danel J. Sedmann July 2012 Barganng n Standng Commttees CeDE Dscusson Paper Seres ISSN 1749-3293 The Centre for Decson Research and Epermental Economcs was founded
Dscusson Paper No. 2012-09 Vncent Anes and Danel J. Sedmann July 2012 Barganng n Standng Commttees CeDE Dscusson Paper Seres ISSN 1749-3293 The Centre for Decson Research and Epermental Economcs was founded
2. Equlibrium and Efficiency
 . Equlbrum and Effcency . Introducton competton and effcency Smt s nvsble and model of compettve economy combne ndependent decson-makng of consumers and frms nto a complete model of te economy exstence
. Equlbrum and Effcency . Introducton competton and effcency Smt s nvsble and model of compettve economy combne ndependent decson-makng of consumers and frms nto a complete model of te economy exstence
Lecture 7. We now use Brouwer s fixed point theorem to prove Nash s theorem.
 Topcs on the Border of Economcs and Computaton December 11, 2005 Lecturer: Noam Nsan Lecture 7 Scrbe: Yoram Bachrach 1 Nash s Theorem We begn by provng Nash s Theorem about the exstance of a mxed strategy
Topcs on the Border of Economcs and Computaton December 11, 2005 Lecturer: Noam Nsan Lecture 7 Scrbe: Yoram Bachrach 1 Nash s Theorem We begn by provng Nash s Theorem about the exstance of a mxed strategy
ECE 586GT: Problem Set 2: Problems and Solutions Uniqueness of Nash equilibria, zero sum games, evolutionary dynamics
 Unversty of Illnos Fall 08 ECE 586GT: Problem Set : Problems and Solutons Unqueness of Nash equlbra, zero sum games, evolutonary dynamcs Due: Tuesday, Sept. 5, at begnnng of class Readng: Course notes,
Unversty of Illnos Fall 08 ECE 586GT: Problem Set : Problems and Solutons Unqueness of Nash equlbra, zero sum games, evolutonary dynamcs Due: Tuesday, Sept. 5, at begnnng of class Readng: Course notes,
Equilibrium in Prediction Markets with Buyers and Sellers
 Equlbrum n Predcton Markets wth Buyers and Sellers Shpra Agrawal Nmrod Megddo Benamn Armbruster Abstract Predcton markets wth buyers and sellers of contracts on multple outcomes are shown to have unque
Equlbrum n Predcton Markets wth Buyers and Sellers Shpra Agrawal Nmrod Megddo Benamn Armbruster Abstract Predcton markets wth buyers and sellers of contracts on multple outcomes are shown to have unque
Spring 2018 Social Sciences 7418 University of Wisconsin-Madison. Transactions and Portfolio Crowding Out
 Economcs 44 Menze D. Cnn Sprng 8 Socal Scences 748 Unversty of Wsconsn-Madson. Standard IS-LM Transactons and Portfolo Crowdng Out Transactons crowdng out of nvestment s te reducton n nvestment attrbutable
Economcs 44 Menze D. Cnn Sprng 8 Socal Scences 748 Unversty of Wsconsn-Madson. Standard IS-LM Transactons and Portfolo Crowdng Out Transactons crowdng out of nvestment s te reducton n nvestment attrbutable
- contrast so-called first-best outcome of Lindahl equilibrium with case of private provision through voluntary contributions of households
 Prvate Provson - contrast so-called frst-best outcome of Lndahl equlbrum wth case of prvate provson through voluntary contrbutons of households - need to make an assumpton about how each household expects
Prvate Provson - contrast so-called frst-best outcome of Lndahl equlbrum wth case of prvate provson through voluntary contrbutons of households - need to make an assumpton about how each household expects
Introduction to game theory
 Introducton to game theory Lectures n game theory ECON5210, Sprng 2009, Part 1 17.12.2008 G.B. Ashem, ECON5210-1 1 Overvew over lectures 1. Introducton to game theory 2. Modelng nteractve knowledge; equlbrum
Introducton to game theory Lectures n game theory ECON5210, Sprng 2009, Part 1 17.12.2008 G.B. Ashem, ECON5210-1 1 Overvew over lectures 1. Introducton to game theory 2. Modelng nteractve knowledge; equlbrum
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture VI: Industry Supply
 Elements of Economc Analyss II Lecture VI: Industry Supply Ka Hao Yang 10/12/2017 In the prevous lecture, we analyzed the frm s supply decson usng a set of smple graphcal analyses. In fact, the dscusson
Elements of Economc Analyss II Lecture VI: Industry Supply Ka Hao Yang 10/12/2017 In the prevous lecture, we analyzed the frm s supply decson usng a set of smple graphcal analyses. In fact, the dscusson
A MODEL OF COMPETITION AMONG TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE PROVIDERS BASED ON REPEATED GAME
 A MODEL OF COMPETITION AMONG TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE PROVIDERS BASED ON REPEATED GAME Vesna Radonć Đogatovć, Valentna Radočć Unversty of Belgrade Faculty of Transport and Traffc Engneerng Belgrade, Serba
A MODEL OF COMPETITION AMONG TELECOMMUNICATION SERVICE PROVIDERS BASED ON REPEATED GAME Vesna Radonć Đogatovć, Valentna Radočć Unversty of Belgrade Faculty of Transport and Traffc Engneerng Belgrade, Serba
OPERATIONS RESEARCH. Game Theory
 OPERATIONS RESEARCH Chapter 2 Game Theory Prof. Bbhas C. Gr Department of Mathematcs Jadavpur Unversty Kolkata, Inda Emal: bcgr.umath@gmal.com 1.0 Introducton Game theory was developed for decson makng
OPERATIONS RESEARCH Chapter 2 Game Theory Prof. Bbhas C. Gr Department of Mathematcs Jadavpur Unversty Kolkata, Inda Emal: bcgr.umath@gmal.com 1.0 Introducton Game theory was developed for decson makng
Fall 2016 Social Sciences 7418 University of Wisconsin-Madison. Transactions and Portfolio Crowding Out
 Economcs 435 Menze D. Cnn Fall 6 Socal Scences 748 Unversty of Wsconsn-Madson. Standard IS-LM Transactons and ortfolo Crowdng Out Transactons crowdng out of nvestment s te reducton n nvestment attrbutable
Economcs 435 Menze D. Cnn Fall 6 Socal Scences 748 Unversty of Wsconsn-Madson. Standard IS-LM Transactons and ortfolo Crowdng Out Transactons crowdng out of nvestment s te reducton n nvestment attrbutable
PREFERENCE DOMAINS AND THE MONOTONICITY OF CONDORCET EXTENSIONS
 PREFERECE DOMAIS AD THE MOOTOICITY OF CODORCET EXTESIOS PAUL J. HEALY AD MICHAEL PERESS ABSTRACT. An alternatve s a Condorcet wnner f t beats all other alternatves n a parwse majorty vote. A socal choce
PREFERECE DOMAIS AD THE MOOTOICITY OF CODORCET EXTESIOS PAUL J. HEALY AD MICHAEL PERESS ABSTRACT. An alternatve s a Condorcet wnner f t beats all other alternatves n a parwse majorty vote. A socal choce
Applications of Myerson s Lemma
 Applcatons of Myerson s Lemma Professor Greenwald 28-2-7 We apply Myerson s lemma to solve the sngle-good aucton, and the generalzaton n whch there are k dentcal copes of the good. Our objectve s welfare
Applcatons of Myerson s Lemma Professor Greenwald 28-2-7 We apply Myerson s lemma to solve the sngle-good aucton, and the generalzaton n whch there are k dentcal copes of the good. Our objectve s welfare
UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM
 UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS DISCUSSION PAPER 99/28 Welfare Analyss n a Cournot Game wth a Publc Good by Indraneel Dasgupta School of Economcs, Unversty of Nottngham, Nottngham NG7 2RD,
UNIVERSITY OF NOTTINGHAM SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS DISCUSSION PAPER 99/28 Welfare Analyss n a Cournot Game wth a Publc Good by Indraneel Dasgupta School of Economcs, Unversty of Nottngham, Nottngham NG7 2RD,
CS 286r: Matching and Market Design Lecture 2 Combinatorial Markets, Walrasian Equilibrium, Tâtonnement
 CS 286r: Matchng and Market Desgn Lecture 2 Combnatoral Markets, Walrasan Equlbrum, Tâtonnement Matchng and Money Recall: Last tme we descrbed the Hungaran Method for computng a maxmumweght bpartte matchng.
CS 286r: Matchng and Market Desgn Lecture 2 Combnatoral Markets, Walrasan Equlbrum, Tâtonnement Matchng and Money Recall: Last tme we descrbed the Hungaran Method for computng a maxmumweght bpartte matchng.
Jeffrey Ely. October 7, This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License.
 October 7, 2012 Ths work s lcensed under the Creatve Commons Attrbuton-NonCommercal-ShareAlke 3.0 Lcense. Recap We saw last tme that any standard of socal welfare s problematc n a precse sense. If we want
October 7, 2012 Ths work s lcensed under the Creatve Commons Attrbuton-NonCommercal-ShareAlke 3.0 Lcense. Recap We saw last tme that any standard of socal welfare s problematc n a precse sense. If we want
references Chapters on game theory in Mas-Colell, Whinston and Green
 Syllabus. Prelmnares. Role of game theory n economcs. Normal and extensve form of a game. Game-tree. Informaton partton. Perfect recall. Perfect and mperfect nformaton. Strategy.. Statc games of complete
Syllabus. Prelmnares. Role of game theory n economcs. Normal and extensve form of a game. Game-tree. Informaton partton. Perfect recall. Perfect and mperfect nformaton. Strategy.. Statc games of complete
Games and Decisions. Part I: Basic Theorems. Contents. 1 Introduction. Jane Yuxin Wang. 1 Introduction 1. 2 Two-player Games 2
 Games and Decsons Part I: Basc Theorems Jane Yuxn Wang Contents 1 Introducton 1 2 Two-player Games 2 2.1 Zero-sum Games................................ 3 2.1.1 Pure Strateges.............................
Games and Decsons Part I: Basc Theorems Jane Yuxn Wang Contents 1 Introducton 1 2 Two-player Games 2 2.1 Zero-sum Games................................ 3 2.1.1 Pure Strateges.............................
CS 541 Algorithms and Programs. Exam 1 Solutions
 CS 5 Algortms and Programs Exam Solutons Jonatan Turner 9/5/0 Be neat and concse, ut complete.. (5 ponts) An ncomplete nstance of te wgrap data structure s sown elow. Fll n te mssng felds for te adjacency
CS 5 Algortms and Programs Exam Solutons Jonatan Turner 9/5/0 Be neat and concse, ut complete.. (5 ponts) An ncomplete nstance of te wgrap data structure s sown elow. Fll n te mssng felds for te adjacency
Bargaining over Strategies of Non-Cooperative Games
 Games 05, 6, 73-98; do:0.3390/g603073 Artcle OPEN ACCESS games ISSN 073-4336 www.mdp.com/ournal/games Barganng over Strateges of Non-Cooperatve Games Guseppe Attanas, *, Aurora García-Gallego, Nkolaos
Games 05, 6, 73-98; do:0.3390/g603073 Artcle OPEN ACCESS games ISSN 073-4336 www.mdp.com/ournal/games Barganng over Strateges of Non-Cooperatve Games Guseppe Attanas, *, Aurora García-Gallego, Nkolaos
Tests for Two Ordered Categorical Variables
 Chapter 253 Tests for Two Ordered Categorcal Varables Introducton Ths module computes power and sample sze for tests of ordered categorcal data such as Lkert scale data. Assumng proportonal odds, such
Chapter 253 Tests for Two Ordered Categorcal Varables Introducton Ths module computes power and sample sze for tests of ordered categorcal data such as Lkert scale data. Assumng proportonal odds, such
15-451/651: Design & Analysis of Algorithms January 22, 2019 Lecture #3: Amortized Analysis last changed: January 18, 2019
 5-45/65: Desgn & Analyss of Algorthms January, 09 Lecture #3: Amortzed Analyss last changed: January 8, 09 Introducton In ths lecture we dscuss a useful form of analyss, called amortzed analyss, for problems
5-45/65: Desgn & Analyss of Algorthms January, 09 Lecture #3: Amortzed Analyss last changed: January 8, 09 Introducton In ths lecture we dscuss a useful form of analyss, called amortzed analyss, for problems
Problems to be discussed at the 5 th seminar Suggested solutions
 ECON4260 Behavoral Economcs Problems to be dscussed at the 5 th semnar Suggested solutons Problem 1 a) Consder an ultmatum game n whch the proposer gets, ntally, 100 NOK. Assume that both the proposer
ECON4260 Behavoral Economcs Problems to be dscussed at the 5 th semnar Suggested solutons Problem 1 a) Consder an ultmatum game n whch the proposer gets, ntally, 100 NOK. Assume that both the proposer
Problem Set 6 Finance 1,
 Carnege Mellon Unversty Graduate School of Industral Admnstraton Chrs Telmer Wnter 2006 Problem Set 6 Fnance, 47-720. (representatve agent constructon) Consder the followng two-perod, two-agent economy.
Carnege Mellon Unversty Graduate School of Industral Admnstraton Chrs Telmer Wnter 2006 Problem Set 6 Fnance, 47-720. (representatve agent constructon) Consder the followng two-perod, two-agent economy.
Appendix - Normally Distributed Admissible Choices are Optimal
 Appendx - Normally Dstrbuted Admssble Choces are Optmal James N. Bodurtha, Jr. McDonough School of Busness Georgetown Unversty and Q Shen Stafford Partners Aprl 994 latest revson September 00 Abstract
Appendx - Normally Dstrbuted Admssble Choces are Optmal James N. Bodurtha, Jr. McDonough School of Busness Georgetown Unversty and Q Shen Stafford Partners Aprl 994 latest revson September 00 Abstract
II. Random Variables. Variable Types. Variables Map Outcomes to Numbers
 II. Random Varables Random varables operate n much the same way as the outcomes or events n some arbtrary sample space the dstncton s that random varables are smply outcomes that are represented numercally.
II. Random Varables Random varables operate n much the same way as the outcomes or events n some arbtrary sample space the dstncton s that random varables are smply outcomes that are represented numercally.
Lecture Note 1: Foundations 1
 Economcs 703 Advanced Mcroeconomcs Prof. Peter Cramton ecture Note : Foundatons Outlne A. Introducton and Examples B. Formal Treatment. Exstence of Nash Equlbrum. Exstence wthout uas-concavty 3. Perfect
Economcs 703 Advanced Mcroeconomcs Prof. Peter Cramton ecture Note : Foundatons Outlne A. Introducton and Examples B. Formal Treatment. Exstence of Nash Equlbrum. Exstence wthout uas-concavty 3. Perfect
MgtOp 215 Chapter 13 Dr. Ahn
 MgtOp 5 Chapter 3 Dr Ahn Consder two random varables X and Y wth,,, In order to study the relatonshp between the two random varables, we need a numercal measure that descrbes the relatonshp The covarance
MgtOp 5 Chapter 3 Dr Ahn Consder two random varables X and Y wth,,, In order to study the relatonshp between the two random varables, we need a numercal measure that descrbes the relatonshp The covarance
SUPPLEMENT TO BOOTSTRAPPING REALIZED VOLATILITY (Econometrica, Vol. 77, No. 1, January, 2009, )
 Econometrca Supplementary Materal SUPPLEMENT TO BOOTSTRAPPING REALIZED VOLATILITY Econometrca, Vol. 77, No. 1, January, 009, 83 306 BY SÍLVIA GONÇALVES AND NOUR MEDDAHI THIS SUPPLEMENT IS ORGANIZED asfollows.frst,wentroducesomenotaton.
Econometrca Supplementary Materal SUPPLEMENT TO BOOTSTRAPPING REALIZED VOLATILITY Econometrca, Vol. 77, No. 1, January, 009, 83 306 BY SÍLVIA GONÇALVES AND NOUR MEDDAHI THIS SUPPLEMENT IS ORGANIZED asfollows.frst,wentroducesomenotaton.
Lecture Note 2 Time Value of Money
 Seg250 Management Prncples for Engneerng Managers Lecture ote 2 Tme Value of Money Department of Systems Engneerng and Engneerng Management The Chnese Unversty of Hong Kong Interest: The Cost of Money
Seg250 Management Prncples for Engneerng Managers Lecture ote 2 Tme Value of Money Department of Systems Engneerng and Engneerng Management The Chnese Unversty of Hong Kong Interest: The Cost of Money
Meaningful cheap talk must improve equilibrium payoffs
 Mathematcal Socal Scences 37 (1999) 97 106 Meanngful cheap talk must mprove equlbrum payoffs Lanny Arvan, Luıs Cabral *, Vasco Santos a b, c a Unversty of Illnos at Urbana-Champagn, Department of Economcs,
Mathematcal Socal Scences 37 (1999) 97 106 Meanngful cheap talk must mprove equlbrum payoffs Lanny Arvan, Luıs Cabral *, Vasco Santos a b, c a Unversty of Illnos at Urbana-Champagn, Department of Economcs,
Supplementary Material for Borrowing Information across Populations in Estimating Positive and Negative Predictive Values
 Supplementary Materal for Borrong Informaton across Populatons n Estmatng Postve and Negatve Predctve Values Yng Huang, Youy Fong, Jon We $, and Zdng Feng Fred Hutcnson Cancer Researc Center, Vaccne &
Supplementary Materal for Borrong Informaton across Populatons n Estmatng Postve and Negatve Predctve Values Yng Huang, Youy Fong, Jon We $, and Zdng Feng Fred Hutcnson Cancer Researc Center, Vaccne &
Random Variables. b 2.
 Random Varables Generally the object of an nvestgators nterest s not necessarly the acton n the sample space but rather some functon of t. Techncally a real valued functon or mappng whose doman s the sample
Random Varables Generally the object of an nvestgators nterest s not necessarly the acton n the sample space but rather some functon of t. Techncally a real valued functon or mappng whose doman s the sample
Quiz on Deterministic part of course October 22, 2002
 Engneerng ystems Analyss for Desgn Quz on Determnstc part of course October 22, 2002 Ths s a closed book exercse. You may use calculators Grade Tables There are 90 ponts possble for the regular test, or
Engneerng ystems Analyss for Desgn Quz on Determnstc part of course October 22, 2002 Ths s a closed book exercse. You may use calculators Grade Tables There are 90 ponts possble for the regular test, or
Financial mathematics
 Fnancal mathematcs Jean-Luc Bouchot jean-luc.bouchot@drexel.edu February 19, 2013 Warnng Ths s a work n progress. I can not ensure t to be mstake free at the moment. It s also lackng some nformaton. But
Fnancal mathematcs Jean-Luc Bouchot jean-luc.bouchot@drexel.edu February 19, 2013 Warnng Ths s a work n progress. I can not ensure t to be mstake free at the moment. It s also lackng some nformaton. But
Price and Quantity Competition Revisited. Abstract
 rce and uantty Competton Revsted X. Henry Wang Unversty of Mssour - Columba Abstract By enlargng the parameter space orgnally consdered by Sngh and Vves (984 to allow for a wder range of cost asymmetry,
rce and uantty Competton Revsted X. Henry Wang Unversty of Mssour - Columba Abstract By enlargng the parameter space orgnally consdered by Sngh and Vves (984 to allow for a wder range of cost asymmetry,
Static (or Simultaneous- Move) Games of Complete Information
 Statc (or Smultaneous- Move) Games of Complete Informaton Nash Equlbrum Best Response Functon F. Valognes - Game Theory - Chp 3 Outlne of Statc Games of Complete Informaton Introducton to games Normal-form
Statc (or Smultaneous- Move) Games of Complete Informaton Nash Equlbrum Best Response Functon F. Valognes - Game Theory - Chp 3 Outlne of Statc Games of Complete Informaton Introducton to games Normal-form
Mathematical Thinking Exam 1 09 October 2017
 Mathematcal Thnkng Exam 1 09 October 2017 Name: Instructons: Be sure to read each problem s drectons. Wrte clearly durng the exam and fully erase or mark out anythng you do not want graded. You may use
Mathematcal Thnkng Exam 1 09 October 2017 Name: Instructons: Be sure to read each problem s drectons. Wrte clearly durng the exam and fully erase or mark out anythng you do not want graded. You may use
Stochastic ALM models - General Methodology
 Stochastc ALM models - General Methodology Stochastc ALM models are generally mplemented wthn separate modules: A stochastc scenaros generator (ESG) A cash-flow projecton tool (or ALM projecton) For projectng
Stochastc ALM models - General Methodology Stochastc ALM models are generally mplemented wthn separate modules: A stochastc scenaros generator (ESG) A cash-flow projecton tool (or ALM projecton) For projectng
Special Interest Politics: Contribution Schedules versus Nash Bargaining
 Specal Interest Poltcs: Contrbuton Schedules versus Nash Barganng Achm Voss School of Economcs and Socal Scences, Unversty of Hamburg, Von-Melle-Park 5, 20146 Hamburg, Germany. Tel.: +49 40 42838 4529.
Specal Interest Poltcs: Contrbuton Schedules versus Nash Barganng Achm Voss School of Economcs and Socal Scences, Unversty of Hamburg, Von-Melle-Park 5, 20146 Hamburg, Germany. Tel.: +49 40 42838 4529.
Osaka University of Economics Working Paper Series No Hart Mas-Colell Implementation of the Discounted Shapley Value
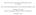 Osaka Unversty of Economcs Workng Paper Seres No 2014-2 Hart Mas-Colell Implementaton of the Dscounted Shapley Value Tomohko Kawamor Faculty of Economcs, Osaka Unversty of Economcs November, 2014 Hart
Osaka Unversty of Economcs Workng Paper Seres No 2014-2 Hart Mas-Colell Implementaton of the Dscounted Shapley Value Tomohko Kawamor Faculty of Economcs, Osaka Unversty of Economcs November, 2014 Hart
A Correction to: The Structure of General Equilibrium Shadow Pricing Rules for a Tax-Distorted Economy
 A Correcton to: Te Structure of General Equlbrum Sadow Prcng Rules for a Tax-Dstorted Economy Crs Jones Department of Economcs Faculty of Economcs and Commerce Te Australan Natonal Unversty Worng Paper
A Correcton to: Te Structure of General Equlbrum Sadow Prcng Rules for a Tax-Dstorted Economy Crs Jones Department of Economcs Faculty of Economcs and Commerce Te Australan Natonal Unversty Worng Paper
ME 310 Numerical Methods. Differentiation
 M 0 Numercal Metods fferentaton Tese presentatons are prepared by r. Cuneyt Sert Mecancal ngneerng epartment Mddle ast Tecncal Unversty Ankara, Turkey csert@metu.edu.tr Tey can not be used wtout te permsson
M 0 Numercal Metods fferentaton Tese presentatons are prepared by r. Cuneyt Sert Mecancal ngneerng epartment Mddle ast Tecncal Unversty Ankara, Turkey csert@metu.edu.tr Tey can not be used wtout te permsson
Global Optimization in Multi-Agent Models
 Global Optmzaton n Mult-Agent Models John R. Brge R.R. McCormck School of Engneerng and Appled Scence Northwestern Unversty Jont work wth Chonawee Supatgat, Enron, and Rachel Zhang, Cornell 11/19/2004
Global Optmzaton n Mult-Agent Models John R. Brge R.R. McCormck School of Engneerng and Appled Scence Northwestern Unversty Jont work wth Chonawee Supatgat, Enron, and Rachel Zhang, Cornell 11/19/2004
occurrence of a larger storm than our culvert or bridge is barely capable of handling? (what is The main question is: What is the possibility of
 Module 8: Probablty and Statstcal Methods n Water Resources Engneerng Bob Ptt Unversty of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Flow data are avalable from numerous USGS operated flow recordng statons. Data s usually
Module 8: Probablty and Statstcal Methods n Water Resources Engneerng Bob Ptt Unversty of Alabama Tuscaloosa, AL Flow data are avalable from numerous USGS operated flow recordng statons. Data s usually
Problem Set #4 Solutions
 4.0 Sprng 00 Page Problem Set #4 Solutons Problem : a) The extensve form of the game s as follows: (,) Inc. (-,-) Entrant (0,0) Inc (5,0) Usng backwards nducton, the ncumbent wll always set hgh prces,
4.0 Sprng 00 Page Problem Set #4 Solutons Problem : a) The extensve form of the game s as follows: (,) Inc. (-,-) Entrant (0,0) Inc (5,0) Usng backwards nducton, the ncumbent wll always set hgh prces,
Single-Item Auctions. CS 234r: Markets for Networks and Crowds Lecture 4 Auctions, Mechanisms, and Welfare Maximization
 CS 234r: Markets for Networks and Crowds Lecture 4 Auctons, Mechansms, and Welfare Maxmzaton Sngle-Item Auctons Suppose we have one or more tems to sell and a pool of potental buyers. How should we decde
CS 234r: Markets for Networks and Crowds Lecture 4 Auctons, Mechansms, and Welfare Maxmzaton Sngle-Item Auctons Suppose we have one or more tems to sell and a pool of potental buyers. How should we decde
Cyclic Scheduling in a Job shop with Multiple Assembly Firms
 Proceedngs of the 0 Internatonal Conference on Industral Engneerng and Operatons Management Kuala Lumpur, Malaysa, January 4, 0 Cyclc Schedulng n a Job shop wth Multple Assembly Frms Tetsuya Kana and Koch
Proceedngs of the 0 Internatonal Conference on Industral Engneerng and Operatons Management Kuala Lumpur, Malaysa, January 4, 0 Cyclc Schedulng n a Job shop wth Multple Assembly Frms Tetsuya Kana and Koch
Finance 402: Problem Set 1 Solutions
 Fnance 402: Problem Set 1 Solutons Note: Where approprate, the fnal answer for each problem s gven n bold talcs for those not nterested n the dscusson of the soluton. 1. The annual coupon rate s 6%. A
Fnance 402: Problem Set 1 Solutons Note: Where approprate, the fnal answer for each problem s gven n bold talcs for those not nterested n the dscusson of the soluton. 1. The annual coupon rate s 6%. A
Wages as Anti-Corruption Strategy: A Note
 DISCUSSION PAPER November 200 No. 46 Wages as Ant-Corrupton Strategy: A Note by dek SAO Faculty of Economcs, Kyushu-Sangyo Unversty Wages as ant-corrupton strategy: A Note dek Sato Kyushu-Sangyo Unversty
DISCUSSION PAPER November 200 No. 46 Wages as Ant-Corrupton Strategy: A Note by dek SAO Faculty of Economcs, Kyushu-Sangyo Unversty Wages as ant-corrupton strategy: A Note dek Sato Kyushu-Sangyo Unversty
Formation of Coalition Structures as a Non-Cooperative Game
 Formaton of Coalton Structures as a Non-Cooperatve Game Dmtry Levando Natonal Research Unversty Hgher School of Economcs, Moscow, Russa dlevando@hse.ru Abstract. The paper proposes a lst of requrements
Formaton of Coalton Structures as a Non-Cooperatve Game Dmtry Levando Natonal Research Unversty Hgher School of Economcs, Moscow, Russa dlevando@hse.ru Abstract. The paper proposes a lst of requrements
Market Competition, Institutions, and Contracting. Draft: Not for Citation or Circulation
 Market Competton, Insttutons, and Contractng Prelmnary Draft Prepared for Presentaton, Department of Agrcultural and Appled Economcs, Unversty of Wsconsn September 18, 009 Draft: Not for Ctaton or Crculaton
Market Competton, Insttutons, and Contractng Prelmnary Draft Prepared for Presentaton, Department of Agrcultural and Appled Economcs, Unversty of Wsconsn September 18, 009 Draft: Not for Ctaton or Crculaton
On the uniqueness of stable marriage matchings
 Economcs Letters 69 (2000) 1 8 www.elsever.com/ locate/ econbase On te unqueness of stable marrage matcngs Jan Eeckout* Unversty of Pennsylvana, Dept. of Economcs, 3718 Locust Walk, Pladelpa, PA 19104-6297,
Economcs Letters 69 (2000) 1 8 www.elsever.com/ locate/ econbase On te unqueness of stable marrage matcngs Jan Eeckout* Unversty of Pennsylvana, Dept. of Economcs, 3718 Locust Walk, Pladelpa, PA 19104-6297,
Real Exchange Rate Fluctuations, Wage Stickiness and Markup Adjustments
 Real Exchange Rate Fluctuatons, Wage Stckness and Markup Adjustments Yothn Jnjarak and Kanda Nakno Nanyang Technologcal Unversty and Purdue Unversty January 2009 Abstract Motvated by emprcal evdence on
Real Exchange Rate Fluctuatons, Wage Stckness and Markup Adjustments Yothn Jnjarak and Kanda Nakno Nanyang Technologcal Unversty and Purdue Unversty January 2009 Abstract Motvated by emprcal evdence on
Principles of Finance
 Prncples of Fnance Grzegorz Trojanowsk Lecture 6: Captal Asset Prcng Model Prncples of Fnance - Lecture 6 1 Lecture 6 materal Requred readng: Elton et al., Chapters 13, 14, and 15 Supplementary readng:
Prncples of Fnance Grzegorz Trojanowsk Lecture 6: Captal Asset Prcng Model Prncples of Fnance - Lecture 6 1 Lecture 6 materal Requred readng: Elton et al., Chapters 13, 14, and 15 Supplementary readng:
/ Computational Genomics. Normalization
 0-80 /02-70 Computatonal Genomcs Normalzaton Gene Expresson Analyss Model Computatonal nformaton fuson Bologcal regulatory networks Pattern Recognton Data Analyss clusterng, classfcaton normalzaton, mss.
0-80 /02-70 Computatonal Genomcs Normalzaton Gene Expresson Analyss Model Computatonal nformaton fuson Bologcal regulatory networks Pattern Recognton Data Analyss clusterng, classfcaton normalzaton, mss.
Production and Supply Chain Management Logistics. Paolo Detti Department of Information Engeneering and Mathematical Sciences University of Siena
 Producton and Supply Chan Management Logstcs Paolo Dett Department of Informaton Engeneerng and Mathematcal Scences Unversty of Sena Convergence and complexty of the algorthm Convergence of the algorthm
Producton and Supply Chan Management Logstcs Paolo Dett Department of Informaton Engeneerng and Mathematcal Scences Unversty of Sena Convergence and complexty of the algorthm Convergence of the algorthm
Tests for Two Correlations
 PASS Sample Sze Software Chapter 805 Tests for Two Correlatons Introducton The correlaton coeffcent (or correlaton), ρ, s a popular parameter for descrbng the strength of the assocaton between two varables.
PASS Sample Sze Software Chapter 805 Tests for Two Correlatons Introducton The correlaton coeffcent (or correlaton), ρ, s a popular parameter for descrbng the strength of the assocaton between two varables.
Understanding Annuities. Some Algebraic Terminology.
 Understandng Annutes Ma 162 Sprng 2010 Ma 162 Sprng 2010 March 22, 2010 Some Algebrac Termnology We recall some terms and calculatons from elementary algebra A fnte sequence of numbers s a functon of natural
Understandng Annutes Ma 162 Sprng 2010 Ma 162 Sprng 2010 March 22, 2010 Some Algebrac Termnology We recall some terms and calculatons from elementary algebra A fnte sequence of numbers s a functon of natural
Raising Food Prices and Welfare Change: A Simple Calibration. Xiaohua Yu
 Rasng Food Prces and Welfare Change: A Smple Calbraton Xaohua Yu Professor of Agrcultural Economcs Courant Research Centre Poverty, Equty and Growth Unversty of Göttngen CRC-PEG, Wlhelm-weber-Str. 2 3773
Rasng Food Prces and Welfare Change: A Smple Calbraton Xaohua Yu Professor of Agrcultural Economcs Courant Research Centre Poverty, Equty and Growth Unversty of Göttngen CRC-PEG, Wlhelm-weber-Str. 2 3773
Creating a zero coupon curve by bootstrapping with cubic splines.
 MMA 708 Analytcal Fnance II Creatng a zero coupon curve by bootstrappng wth cubc splnes. erg Gryshkevych Professor: Jan R. M. Röman 0.2.200 Dvson of Appled Mathematcs chool of Educaton, Culture and Communcaton
MMA 708 Analytcal Fnance II Creatng a zero coupon curve by bootstrappng wth cubc splnes. erg Gryshkevych Professor: Jan R. M. Röman 0.2.200 Dvson of Appled Mathematcs chool of Educaton, Culture and Communcaton
The Vickrey-Target Strategy and the Core in Ascending Combinatorial Auctions
 The Vckrey-Target Strategy and the Core n Ascendng Combnatoral Auctons Ryuj Sano ISER, Osaka Unversty Prelmnary Verson December 26, 2011 Abstract Ths paper consders a general class of combnatoral auctons
The Vckrey-Target Strategy and the Core n Ascendng Combnatoral Auctons Ryuj Sano ISER, Osaka Unversty Prelmnary Verson December 26, 2011 Abstract Ths paper consders a general class of combnatoral auctons
Dynamic Analysis of Knowledge Sharing of Agents with. Heterogeneous Knowledge
 Dynamc Analyss of Sharng of Agents wth Heterogeneous Kazuyo Sato Akra Namatame Dept. of Computer Scence Natonal Defense Academy Yokosuka 39-8686 JAPAN E-mal {g40045 nama} @nda.ac.jp Abstract In ths paper
Dynamc Analyss of Sharng of Agents wth Heterogeneous Kazuyo Sato Akra Namatame Dept. of Computer Scence Natonal Defense Academy Yokosuka 39-8686 JAPAN E-mal {g40045 nama} @nda.ac.jp Abstract In ths paper
General Examination in Microeconomic Theory. Fall You have FOUR hours. 2. Answer all questions
 HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examnaton n Mcroeconomc Theory Fall 2010 1. You have FOUR hours. 2. Answer all questons PLEASE USE A SEPARATE BLUE BOOK FOR EACH QUESTION AND WRITE THE
HARVARD UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS General Examnaton n Mcroeconomc Theory Fall 2010 1. You have FOUR hours. 2. Answer all questons PLEASE USE A SEPARATE BLUE BOOK FOR EACH QUESTION AND WRITE THE
A non-cooperative approach to the ordinal Shapley-Shubik rule
 A non-cooperatve approach to the ordnal Shapley-Shubk rule Juan Vdal-Puga vdalpuga@uvgo.es July 0, 05 Abstract In barganng problems, a rule satsfes ordnal nvarance f t does not depend on order-preservng
A non-cooperatve approach to the ordnal Shapley-Shubk rule Juan Vdal-Puga vdalpuga@uvgo.es July 0, 05 Abstract In barganng problems, a rule satsfes ordnal nvarance f t does not depend on order-preservng
Taxation and Externalities. - Much recent discussion of policy towards externalities, e.g., global warming debate/kyoto
 Taxaton and Externaltes - Much recent dscusson of polcy towards externaltes, e.g., global warmng debate/kyoto - Increasng share of tax revenue from envronmental taxaton 6 percent n OECD - Envronmental
Taxaton and Externaltes - Much recent dscusson of polcy towards externaltes, e.g., global warmng debate/kyoto - Increasng share of tax revenue from envronmental taxaton 6 percent n OECD - Envronmental
Quadratic Games. First version: February 24, 2017 This version: August 3, Abstract
 Quadratc Games Ncolas S. Lambert Gorgo Martn Mchael Ostrovsky Frst verson: February 24, 2017 Ths verson: August 3, 2018 Abstract We study general quadratc games wth multdmensonal actons, stochastc payoff
Quadratc Games Ncolas S. Lambert Gorgo Martn Mchael Ostrovsky Frst verson: February 24, 2017 Ths verson: August 3, 2018 Abstract We study general quadratc games wth multdmensonal actons, stochastc payoff
Finite Math - Fall Section Future Value of an Annuity; Sinking Funds
 Fnte Math - Fall 2016 Lecture Notes - 9/19/2016 Secton 3.3 - Future Value of an Annuty; Snkng Funds Snkng Funds. We can turn the annutes pcture around and ask how much we would need to depost nto an account
Fnte Math - Fall 2016 Lecture Notes - 9/19/2016 Secton 3.3 - Future Value of an Annuty; Snkng Funds Snkng Funds. We can turn the annutes pcture around and ask how much we would need to depost nto an account
Measures of Spread IQR and Deviation. For exam X, calculate the mean, median and mode. For exam Y, calculate the mean, median and mode.
 Part 4 Measures of Spread IQR and Devaton In Part we learned how the three measures of center offer dfferent ways of provdng us wth a sngle representatve value for a data set. However, consder the followng
Part 4 Measures of Spread IQR and Devaton In Part we learned how the three measures of center offer dfferent ways of provdng us wth a sngle representatve value for a data set. However, consder the followng
Utilitarianism. Jeffrey Ely. June 7, This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License.
 Utltaransm June 7, 2009 Ths work s lcensed under the Creatve Commons Attrbuton-NonCommercal-ShareAlke 3.0 Lcense. Utltaransm Why Utltaransm? We saw last tme that any standard of socal welfare s problematc
Utltaransm June 7, 2009 Ths work s lcensed under the Creatve Commons Attrbuton-NonCommercal-ShareAlke 3.0 Lcense. Utltaransm Why Utltaransm? We saw last tme that any standard of socal welfare s problematc
2) In the medium-run/long-run, a decrease in the budget deficit will produce:
 4.02 Quz 2 Solutons Fall 2004 Multple-Choce Questons ) Consder the wage-settng and prce-settng equatons we studed n class. Suppose the markup, µ, equals 0.25, and F(u,z) = -u. What s the natural rate of
4.02 Quz 2 Solutons Fall 2004 Multple-Choce Questons ) Consder the wage-settng and prce-settng equatons we studed n class. Suppose the markup, µ, equals 0.25, and F(u,z) = -u. What s the natural rate of
On the use of menus in sequential common agency
 Games and Economc Behavor 6 (2008) 329 33 www.elsever.com/locate/geb Note On the use of menus n sequental common agency Gacomo Calzolar a, Alessandro Pavan b, a Department of Economcs, Unversty of Bologna,
Games and Economc Behavor 6 (2008) 329 33 www.elsever.com/locate/geb Note On the use of menus n sequental common agency Gacomo Calzolar a, Alessandro Pavan b, a Department of Economcs, Unversty of Bologna,
Quadratic Games. First version: February 24, 2017 This version: December 12, Abstract
 Quadratc Games Ncolas S. Lambert Gorgo Martn Mchael Ostrovsky Frst verson: February 24, 2017 Ths verson: December 12, 2017 Abstract We study general quadratc games wth mult-dmensonal actons, stochastc
Quadratc Games Ncolas S. Lambert Gorgo Martn Mchael Ostrovsky Frst verson: February 24, 2017 Ths verson: December 12, 2017 Abstract We study general quadratc games wth mult-dmensonal actons, stochastc
Analysis of Variance and Design of Experiments-II
 Analyss of Varance and Desgn of Experments-II MODULE VI LECTURE - 4 SPLIT-PLOT AND STRIP-PLOT DESIGNS Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematcs & Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanpur An example to motvate
Analyss of Varance and Desgn of Experments-II MODULE VI LECTURE - 4 SPLIT-PLOT AND STRIP-PLOT DESIGNS Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematcs & Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanpur An example to motvate
Difference-Form Persuasion Contests
 Dfference-Form Persuason Contests Stergos Skaperdas a Amad Toukan b Samart Vadya c June 6, 03 ABSTACT: We explore te equlbrum propertes of dfference-form contest functons derved n Skaperdas and Vadya 0
Dfference-Form Persuason Contests Stergos Skaperdas a Amad Toukan b Samart Vadya c June 6, 03 ABSTACT: We explore te equlbrum propertes of dfference-form contest functons derved n Skaperdas and Vadya 0
Sequential equilibria of asymmetric ascending auctions: the case of log-normal distributions 3
 Sequental equlbra of asymmetrc ascendng auctons: the case of log-normal dstrbutons 3 Robert Wlson Busness School, Stanford Unversty, Stanford, CA 94305-505, USA Receved: ; revsed verson. Summary: The sequental
Sequental equlbra of asymmetrc ascendng auctons: the case of log-normal dstrbutons 3 Robert Wlson Busness School, Stanford Unversty, Stanford, CA 94305-505, USA Receved: ; revsed verson. Summary: The sequental
Prospect Theory and Asset Prices
 Fnance 400 A. Penat - G. Pennacch Prospect Theory and Asset Prces These notes consder the asset prcng mplcatons of nvestor behavor that ncorporates Prospect Theory. It summarzes an artcle by N. Barbers,
Fnance 400 A. Penat - G. Pennacch Prospect Theory and Asset Prces These notes consder the asset prcng mplcatons of nvestor behavor that ncorporates Prospect Theory. It summarzes an artcle by N. Barbers,
Intensive vs Extensive Margin Tradeo s in a Simple Monetary Search Model
 Intensve vs Extensve Margn Tradeo s n a Smple Monetary Search Model Sébasten Lotz y Unversty of Pars 2 Andre Shevchenko z Mchgan State Unversty Aprl 2006 hrstopher Waller x Unversty of Notre Dame Abstract
Intensve vs Extensve Margn Tradeo s n a Smple Monetary Search Model Sébasten Lotz y Unversty of Pars 2 Andre Shevchenko z Mchgan State Unversty Aprl 2006 hrstopher Waller x Unversty of Notre Dame Abstract
Linear Combinations of Random Variables and Sampling (100 points)
 Economcs 30330: Statstcs for Economcs Problem Set 6 Unversty of Notre Dame Instructor: Julo Garín Sprng 2012 Lnear Combnatons of Random Varables and Samplng 100 ponts 1. Four-part problem. Go get some
Economcs 30330: Statstcs for Economcs Problem Set 6 Unversty of Notre Dame Instructor: Julo Garín Sprng 2012 Lnear Combnatons of Random Varables and Samplng 100 ponts 1. Four-part problem. Go get some
Online Appendix for Merger Review for Markets with Buyer Power
 Onlne Appendx for Merger Revew for Markets wth Buyer Power Smon Loertscher Lesle M. Marx July 23, 2018 Introducton In ths appendx we extend the framework of Loertscher and Marx (forthcomng) to allow two
Onlne Appendx for Merger Revew for Markets wth Buyer Power Smon Loertscher Lesle M. Marx July 23, 2018 Introducton In ths appendx we extend the framework of Loertscher and Marx (forthcomng) to allow two
Optimal Service-Based Procurement with Heterogeneous Suppliers
 Optmal Servce-Based Procurement wth Heterogeneous Supplers Ehsan Elah 1 Saf Benjaafar 2 Karen L. Donohue 3 1 College of Management, Unversty of Massachusetts, Boston, MA 02125 2 Industral & Systems Engneerng,
Optmal Servce-Based Procurement wth Heterogeneous Supplers Ehsan Elah 1 Saf Benjaafar 2 Karen L. Donohue 3 1 College of Management, Unversty of Massachusetts, Boston, MA 02125 2 Industral & Systems Engneerng,
COST ALLOCATION IN PUBLIC ENTERPRISES: THE CORE AND ISSUES OF CROSS-SUBSIDIZATION. Haralambos D Sourbis*
 COST ALLOCATION IN PUBLIC ENTERPRISES: THE CORE AND ISSUES OF CROSS-SUBSIDIZATION By Haralambos D Sourbs* Abstract Ths paper examnes the mplcatons of core allocatons on the provson of a servce to a communty
COST ALLOCATION IN PUBLIC ENTERPRISES: THE CORE AND ISSUES OF CROSS-SUBSIDIZATION By Haralambos D Sourbs* Abstract Ths paper examnes the mplcatons of core allocatons on the provson of a servce to a communty
Optimal Information Disclosure in Auctions: The Handicap Auction
 Optmal Informaton Dsclosure n Auctons: Te Handcap Aucton Péter Eső Nortwestern Unversty, Kellogg MEDS Balázs Szentes Unversty of Ccago, Department of Economcs December 2002 Abstract We analyze te stuaton
Optmal Informaton Dsclosure n Auctons: Te Handcap Aucton Péter Eső Nortwestern Unversty, Kellogg MEDS Balázs Szentes Unversty of Ccago, Department of Economcs December 2002 Abstract We analyze te stuaton
The Vickrey-Target Strategy and the Core in Ascending Combinatorial Auctions
 The Vckrey-Target Strategy and the Core n Ascendng Combnatoral Auctons Ryuj Sano Insttute of Socal and Economc Research, Osaka Unversty Aprl 10, 2012 Abstract Ths paper consders a class of combnatoral
The Vckrey-Target Strategy and the Core n Ascendng Combnatoral Auctons Ryuj Sano Insttute of Socal and Economc Research, Osaka Unversty Aprl 10, 2012 Abstract Ths paper consders a class of combnatoral
Economic Design of Short-Run CSP-1 Plan Under Linear Inspection Cost
 Tamkang Journal of Scence and Engneerng, Vol. 9, No 1, pp. 19 23 (2006) 19 Economc Desgn of Short-Run CSP-1 Plan Under Lnear Inspecton Cost Chung-Ho Chen 1 * and Chao-Yu Chou 2 1 Department of Industral
Tamkang Journal of Scence and Engneerng, Vol. 9, No 1, pp. 19 23 (2006) 19 Economc Desgn of Short-Run CSP-1 Plan Under Lnear Inspecton Cost Chung-Ho Chen 1 * and Chao-Yu Chou 2 1 Department of Industral
A Comparison of Statistical Methods in Interrupted Time Series Analysis to Estimate an Intervention Effect
 Transport and Road Safety (TARS) Research Joanna Wang A Comparson of Statstcal Methods n Interrupted Tme Seres Analyss to Estmate an Interventon Effect Research Fellow at Transport & Road Safety (TARS)
Transport and Road Safety (TARS) Research Joanna Wang A Comparson of Statstcal Methods n Interrupted Tme Seres Analyss to Estmate an Interventon Effect Research Fellow at Transport & Road Safety (TARS)
Maturity Effect on Risk Measure in a Ratings-Based Default-Mode Model
 TU Braunschweg - Insttut für Wrtschaftswssenschaften Lehrstuhl Fnanzwrtschaft Maturty Effect on Rsk Measure n a Ratngs-Based Default-Mode Model Marc Gürtler and Drk Hethecker Fnancal Modellng Workshop
TU Braunschweg - Insttut für Wrtschaftswssenschaften Lehrstuhl Fnanzwrtschaft Maturty Effect on Rsk Measure n a Ratngs-Based Default-Mode Model Marc Gürtler and Drk Hethecker Fnancal Modellng Workshop
Discrete Dynamic Shortest Path Problems in Transportation Applications
 17 Paper No. 98-115 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1645 Dscrete Dynamc Shortest Path Problems n Transportaton Applcatons Complexty and Algorthms wth Optmal Run Tme ISMAIL CHABINI A soluton s provded for
17 Paper No. 98-115 TRANSPORTATION RESEARCH RECORD 1645 Dscrete Dynamc Shortest Path Problems n Transportaton Applcatons Complexty and Algorthms wth Optmal Run Tme ISMAIL CHABINI A soluton s provded for
Mechanisms for Efficient Allocation in Divisible Capacity Networks
 Mechansms for Effcent Allocaton n Dvsble Capacty Networks Antons Dmaks, Rahul Jan and Jean Walrand EECS Department Unversty of Calforna, Berkeley {dmaks,ran,wlr}@eecs.berkeley.edu Abstract We propose a
Mechansms for Effcent Allocaton n Dvsble Capacty Networks Antons Dmaks, Rahul Jan and Jean Walrand EECS Department Unversty of Calforna, Berkeley {dmaks,ran,wlr}@eecs.berkeley.edu Abstract We propose a
Solution of periodic review inventory model with general constrains
 Soluton of perodc revew nventory model wth general constrans Soluton of perodc revew nventory model wth general constrans Prof Dr J Benkő SZIU Gödöllő Summary Reasons for presence of nventory (stock of
Soluton of perodc revew nventory model wth general constrans Soluton of perodc revew nventory model wth general constrans Prof Dr J Benkő SZIU Gödöllő Summary Reasons for presence of nventory (stock of
Provision of public goods in a large economy
 Economcs Letters 61 (1998) 229 234 Provson of publc goods n a large economy Mark Gradsten* Ben-Guron Unversty and the Unversty of Pennsylvana, Pennsylvana, USA Receved 13 Aprl 1998; accepted 25 June 1998
Economcs Letters 61 (1998) 229 234 Provson of publc goods n a large economy Mark Gradsten* Ben-Guron Unversty and the Unversty of Pennsylvana, Pennsylvana, USA Receved 13 Aprl 1998; accepted 25 June 1998
High frequency repeated games with costly monitoring
 Theoretcal Economcs 13 (2018), 87 113 1555-7561/20180087 Hgh frequency repeated games wth costly montorng Ehud Lehrer School of Mathematcal Scences, Tel Avv Unversty and INSEAD Elon Solan School of Mathematcal
Theoretcal Economcs 13 (2018), 87 113 1555-7561/20180087 Hgh frequency repeated games wth costly montorng Ehud Lehrer School of Mathematcal Scences, Tel Avv Unversty and INSEAD Elon Solan School of Mathematcal
AC : THE DIAGRAMMATIC AND MATHEMATICAL APPROACH OF PROJECT TIME-COST TRADEOFFS
 AC 2008-1635: THE DIAGRAMMATIC AND MATHEMATICAL APPROACH OF PROJECT TIME-COST TRADEOFFS Kun-jung Hsu, Leader Unversty Amercan Socety for Engneerng Educaton, 2008 Page 13.1217.1 Ttle of the Paper: The Dagrammatc
AC 2008-1635: THE DIAGRAMMATIC AND MATHEMATICAL APPROACH OF PROJECT TIME-COST TRADEOFFS Kun-jung Hsu, Leader Unversty Amercan Socety for Engneerng Educaton, 2008 Page 13.1217.1 Ttle of the Paper: The Dagrammatc
FORD MOTOR CREDIT COMPANY SUGGESTED ANSWERS. Richard M. Levich. New York University Stern School of Business. Revised, February 1999
 FORD MOTOR CREDIT COMPANY SUGGESTED ANSWERS by Rchard M. Levch New York Unversty Stern School of Busness Revsed, February 1999 1 SETTING UP THE PROBLEM The bond s beng sold to Swss nvestors for a prce
FORD MOTOR CREDIT COMPANY SUGGESTED ANSWERS by Rchard M. Levch New York Unversty Stern School of Busness Revsed, February 1999 1 SETTING UP THE PROBLEM The bond s beng sold to Swss nvestors for a prce
Clearing Notice SIX x-clear Ltd
 Clearng Notce SIX x-clear Ltd 1.0 Overvew Changes to margn and default fund model arrangements SIX x-clear ( x-clear ) s closely montorng the CCP envronment n Europe as well as the needs of ts Members.
Clearng Notce SIX x-clear Ltd 1.0 Overvew Changes to margn and default fund model arrangements SIX x-clear ( x-clear ) s closely montorng the CCP envronment n Europe as well as the needs of ts Members.
Benefit-Cost Analysis
 Chapter 12 Beneft-Cost Analyss Utlty Possbltes and Potental Pareto Improvement Wthout explct nstructons about how to compare one person s benefts wth the losses of another, we can not expect beneft-cost
Chapter 12 Beneft-Cost Analyss Utlty Possbltes and Potental Pareto Improvement Wthout explct nstructons about how to compare one person s benefts wth the losses of another, we can not expect beneft-cost
Wage-rise contract and endogenous timing in international mixed duopoly
 Wage-rse contract and endogenous tmng n nternatonal med duopoly Kazuhro Ohnsh Osaka Unversty, Ph. D. July 007 Abstract The study of Matsumura (003) nvestgates a med duopoly model, where a domestc publc
Wage-rse contract and endogenous tmng n nternatonal med duopoly Kazuhro Ohnsh Osaka Unversty, Ph. D. July 007 Abstract The study of Matsumura (003) nvestgates a med duopoly model, where a domestc publc
Robust Stochastic Lot-Sizing by Means of Histograms
 Robust Stochastc Lot-Szng by Means of Hstograms Abstract Tradtonal approaches n nventory control frst estmate the demand dstrbuton among a predefned famly of dstrbutons based on data fttng of hstorcal
Robust Stochastc Lot-Szng by Means of Hstograms Abstract Tradtonal approaches n nventory control frst estmate the demand dstrbuton among a predefned famly of dstrbutons based on data fttng of hstorcal
