AN IN-DEPTH STUDY OF ORGANISATION AND WORKING OF DERIVATIVES WITH REFERENCE TO INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET
|
|
|
- Arleen Carson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AN IN-DEPTH STUDY OF ORGANISATION AND WORKING OF DERIVATIVES WITH REFERENCE TO INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET A thesis Submitted for the Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy IN Management Submitted to GANPAT UNIVERSITY Submitted by SHAH MAYUR DASHARATHLAL REGISTRATION NO. MM/02/03/07. Under the Guidance of PROF. D. M. PESTONJEE Ex-Professor IIM Ahmedabad February 2011
2 PREFACE Derivatives, today, have become an integral part of the financial system of a country as well as at international level. They have influenced almost every aspect of capital and money markets all over the world ranging from investing, raising of funds and managing the risk. Due to the globalization and liberalization process initiated by the states all over the world, the international trade and financial activities have grown in multifold resulting rising levels of all types of risks for market participants such as market risk, interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk, inflation risk and price risk. Managing all these risks is essential and significant to be successful in financial and trading activities. Financial derivatives like options, futures, forwards and swaps have emerged in the financial markets to handle and manage such risks. New products and strategies are being developed at the fast rate in order to cope with changing environment. Financial markets in India continue to evolve towards growth and efficiency resulting into a manifold rise in financial activities in depth and width. Market participants, financial institutions and investors are looking in a different way to play efficiently in the market. During the mid 1990s, Indian government initiated the process of liberalizing of the financial market in all sectors specifically opening the market for foreign investment. As a result, the infrastructure of the financial markets geared to international norms in all respects. The stock market s structure and trading in India have gone under a sea change. Institutionalization of broking activities, modernization, automation of stock exchanges and entry of foreign institutional investors have opened a multiple options to various participants in the financial markets. Options and futures in India commenced from 2000 on National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay stock exchange (BSE) in stock index futures, stock futures, stock index options and stock options. It was a welcome step on the part of the government since it was important in the present environment. This was significant development in the i
3 history of Indian stock markets. A lot of trading in futures and options segment in Indian stock market was seen and number of market participants increased phenomenal in a short period. As a result, awareness about the financial derivative instruments and their application has increased among the investing people at large. On the other side of this development was that element of risk and volatility in the stock market has risen. So the broad objective at the outset was to study derivatives traded in Indian capital market and acquire understanding about what the investors in India perceive regarding derivatives. The research present in forthcoming pages aims to capture an understanding regarding growth and development of capital market in India, major reforms in capital market, derivatives and their types, features, need for and evolution of derivatives in India. The thesis is an endeavor to understand the empirical profile of high net worth individual investors (HNIs) in Gujarat state and systematically investigate the usage, satisfaction level, factors considered by investors while investing into derivatives. The research is intended to assist corporate professional, brokers, policy makers, educationalists, researchers and all others who would like to understand further about Indian capital market and derivatives. ii
4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Derivatives is a newer area and the challenging task of conducting research in this area would have been difficult for me without the support of all those who helped me directly or indirectly in successfully completing it. I am indebted to Prof. (Dr.) D. M. Pestonjee for being a supportive guide. He motivated me to undertake this research work, guided through this process and helped me focus the study. His skills, as a researcher and guide helped me overcome all the hurdles. Without his constant support and encouragement I would not have been able to complete the research work successfully. I owe a debt of gratitude to Prof. Mahendra Sharma, Dean, FMS, Ganpat University for his moral support and motivation. I wish to thank the industry people, who supported me a lot for my primary research. A special thanks to Mr. Tejas Shah, India Infoline, Ahmedabad; Mr. Jagrut patel, Anagram Equity, Ahmedabad; Mr. B. V. Shah, Angel Broking., Rajkot; Mr. Satish Shah, Angel Broking., Surat; Mr. Suresh Patel, Rathi Broking ltd., Baroda. I am thankful to Dr. Akash Patel, Dr. Narayan Baser, Dr. Parag Sanghani for their continuous help during my research work. I am thankful to Dr. S. O.Junare, National Institute of Cooperative Management, Gandhingar for their continuous help during my research work. I would also like to thank my friend Mr. Amit A. Patel at V. M. Patel Institute of Management for providing valuable support to me during the course of research. I would like to thank all my family members, my father Dashrathlal B. Shah, my mother Smt. Pushpaben, and my wife Ankita for their love, blessings and moral support through out my research work. I give my special thanks to my wife without whose sacrifice and iii
5 constant support this thesis would not have seen the light of the day. Thank you all for being there when I needed someone to talk to and for your keen interest in my development. At last, I thank the one and all, for the divine blessings. Mayur Shah iv
6 DECLARATION BY CANDIDATE This thesis titled AN IN-DEPTH STUDY OF ORGANIZATION & WORKING OF DERIVATIVES WITH REFERENCE TO INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET is submitted in fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Management to Ganpat University, Mehsana. I declare that this thesis is based on my original work except for quotations and citations which have been duly acknowledged. I also declare that this thesis has not been previously or concurrently submitted either in whole or in part, for any other qualification to Ganpat University or other institutions. Date: Place: Ganpat University (Shah Mayur D.) v
7 CERTIFICATE OF GUIDE This is to certify that this thesis titled AN IN-DEPTH STUDY OF ORGANIZATION & WORKING OF DERIVATIVES WITH REFERENCE TO INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET submitted by Shah Mayur Dasharathlal, at Faculty of Management Studies, Ganpat University, Mehsana is the bonafide work completed under my supervision and guidance for the fulfillment of the requirement for the award of the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) in Management. Date: Place: Ganpat University (Prof. D. M. Pestonjee) vi
8 CONTENTS Preface Acknowledgement Declaration by Candidate Certificate of Guide List of Tables List of Figures I III V VI XI XII CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO THESIS Background and Justification to the Research Capital Market of India: Introduction and Overview Financial System in India Financial Intermediaries Financial Instruments Financial Services Financial Market Money Market Capital Market Functions of Capital Market Primary Market Secondary Market Developments and Major Reforms in Indian Capital Market Outline of the Thesis 25 CHAPTER 2 DERIVATIVES INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW An Introduction History of Derivatives Need for Derivatives in India Evolution of Derivatives in India Major Recommendations of Dr. L. C. Gupta Committee 36 vii
9 2.6 Factors Contributing To the Growth of Derivatives Benefits of Derivatives Definition of Financial Derivative Features of Financial Derivative Types and Classifications of Derivatives Uses of Derivatives Critique of Derivatives Myths about Derivatives Emerging Structure of Derivatives Markets in India Categories of Derivatives Traded in India Equity Derivatives Derivative Trading at NSE and BSE Futures and Options as Derivative Instruments & Its Application. 77 CHAPTER 3 DERIVATIVES LITERATURE REVIEW An Introduction Stabilization Arguments Destabilization Arguments Investors Perceptions about Derivatives 135 CHAPTER 4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY An Introduction Objective of the Study Hypothesis of the Study Scope of the Study Research Methodology 142 CHAPTER 5 DATA ANALYSIS AND RESEARCH FINDINGS Details of the Investors Surveyed Hypothesis Testing and Analysis of Variance Findings 163 viii
10 5.3 Factor Analysis An introduction Factor Analysis Process Conducting Factor analysis for Perceptions of Investors - A Detailed Explanation Findings Conducting Factor analysis on Factors to be considered while Investing into Derivatives Findings Linking Factor Analysis Findings with Demographic factor Cluster Analysis An introduction Cluster Analysis Process Conducting Cluster Analysis for Various Perception on Growth of Derivatives in India: A Detailed Explanation Findings Conducting Cluster Analysis on Various Perceptions about Derivatives: A Detailed Explanation Findings 225 CHAPTER 6 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS An Introduction Scope of the Study Data Collection and Research Methodology Emergence of Derivatives as an Important Segment in Indian Capital Market Conclusions related to Test of Differences Conclusions related to Factor Analysis Conclusions related to Cluster Analysis Limitations of the Study Directions for Further Research 240 ix
11 BIBLIOGRAPHY 242 ANNEXURE No ANNEXURE No ANNEXURE No x
12 LIST OF TABLES Table 1.1: Market Participants in Securities Market 12 Table 1.2: Mobilization of Resource from Primary Market 15 Table 1.3: Turnover on all Exchanges 18 Table 1.4: Stock Market Indicators 21 Table 2.1: Evolution of Derivatives 34 Table 2.2: Business Growth in Derivatives segment 68 Table 2.3: Buy Calls and Sell Puts 108 Table 2.4: Sell calls and Buy Puts 111 Table 2.5: Bull Spread 114 Table 2.6: Bear Spread 117 Table 5.1: City wise details 148 Table 5.2: Age wise details 148 Table 5.3: Gender wise details 149 Table 5.4: Marital Status 149 Table 5.5: Occupation wise details 149 Table 5.6: Income profile 149 Table 5.7: Occupation 150 Table 5.8: Proportion of Investment into Derivatives 150 Table 5.9: Percentage of Income available for derivative 151 Table 5.10: Purpose of investment 151 Table 5.11: Types of contracts 151 Table 5.12: Education profile of investors 152 Table 5.13: Contract period of trading 152 Table 5.14 Descriptives related to On-way ANOVA 154 Table 5.15 F test and Significance values in One-Way ANOVA 159 Table 5.16: Case Processing Summary and Reliability Statistics 177 Table 5.17: KMO and Bartlett's Test 177 Table 5.18: Communalities 180 Table 5.19: Total Variance Explained 182 xi
13 Table 5.20: Rotated Component Matrix(a) 183 Table 5.21: Final Rotated Component Matrix with variable name 184 Table 5.22 Reliability Statistics 186 Table 5.23: KMO and Bartlett's Test 187 Table 5.24: Communalities Principal Component Method 189 Table 5.25: Total Variance Explained and Eigenvalues 191 Table 5.26: Rotated Component Matrix 192 Table 5.27: Final rotated matrix with variable name 194 Table 5.28: Agglomeration Schedule 200 Table 5.29: Initial Cluster Centers 205 Table 5.30: Final Cluster Centers 206 Table 5.31 Number of Cases in each Cluster 206 Table 5.32: Cluster Membership 206 Table 5.33: Agglomeration Schedule Ward s Procedure 213 Table 5.34: Initial Cluster Centers Non Hierarchical Method 218 Table 5.35: Final Cluster Centers - Non Hierarchical Method 219 Table 5.36: Number of Cases in each Cluster 220 Table 5.37: Cluster Membership- Non Hierarchical Method 220 Table 6.1: List of Hypothesis 228 LIST OF FIGURES Figure 2.1: Types of Derivatives 51 Figure 2.2: Types of Derivatives 51 Figure 2.3: Payoff for buyer of futures 86 Figure 2.4: Payoff for seller of futures 87 Figure 2.5: Variation of basis over time 91 Figure 2.6: Payoff for investor who went Long Nifty at Figure 2.7: Payoff for buyer of call option 100 Figure 2.8: Payoff profile for writer of call options: Short call 101 Figure 2.9: Payoff for buyer of put option 102 xii
14 Figure 2.10: Payoff for writer of put option 103 Figure 2.11: Payoff for writer of put options at various strikes 109 Figure 2.12: Payoff for seller of call option at various strikes 112 Figure 2.13: Payoff for buyer of put options at various strikes 113 Figure 2.14: Payoff for a bull spread created using call options 114 Figure 2.15: Payoff for a bear spread created using call options 117 Figure 5.1: ANOVA Process 153 xiii
15 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE THESIS 1.1 Background and Justification to the Research 1.2 Capital Market of India: Introduction and Overview Financial System in India Financial Intermediaries Financial Instruments Financial Services Financial Market Money Market Capital Market Functions of Capital Market Primary Market Secondary Market 1.3 Developments and Major Reforms in Indian Capital Market 1.4 Outline of the Thesis 1
16 1.1 BACKGROUND AND JUSTIFICATION TO THE RESEARCH Starting from a controlled economy, India has moved towards a world where prices fluctuate every day. The introduction of risk management instruments in India gained momentum in the last few years due to liberalisation process and Reserve Bank of India s (RBI) efforts in creating currency forward market. Derivatives are an integral part of liberalisation process to manage risk. NSE gauging the market requirements initiated the process of setting up derivative markets in India. In July 1999, derivatives trading commenced in India 1 In practice, some foreign investors also invest in Indian markets by issuing Participatory Notes to an off-shore investor. Among exchange-traded derivative markets in Asia, India was ranked second behind S. Korea for the first quarter of How about China, with who India is frequently compared in other respects? China is preparing to develop its derivatives markets rapidly. It has recently entered into joint ventures with the leading U.S. futures exchanges. It has taken steps to loosen currency controls, and the Central Bank has allowed domestic and foreign banks to trade yuan forward and swaps contracts on behalf of clients. However, unlike India, China has not fully implemented necessary reforms of its stock markets, which is likely to hamper growth of its derivatives markets. Indian market has equalled or exceeded many other regional markets. While the growth is being spearheaded mainly by retail investors, private sector institutions and large corporations, smaller companies and state-owned institutions are gradually getting into the act. Foreign brokers such as JP Morgan Chase are boosting their presence in India in reaction to the growth in derivatives. The variety of derivatives instruments available for trading is also expanding. There remain major areas of concern for Indian derivatives users. Large gaps exist in the range of derivatives products that are traded actively. In equity derivatives, NSE figures show that almost 90% of activity is due to stock futures or index futures, whereas trading in options is limited to a few stocks, partly because they are settled in cash and not the 1 Susan, Thomas (ed), Derivative Markets in India, (New Delhi, Tata McGraw-Hill 2003), p. 15 2
17 underlying stocks. Exchange-traded derivatives based on interest rates and currencies are virtually absent. The past decade has witnessed the multifold growth in the volume of international trade and business due to the wave of globalization and liberalization all over the world. As a result, the demand for the international money and financial instruments increased significantly at the global level. In this respect, changes in the interest rates, exchange rates, and stock market prices at the different financial markets have increased the financial risks to the corporate world. Adverse changes have even threatened very survival of the business world. It is, therefore, to manage such risks, the new financial instruments have been developed in the financial markets, which are also popularly known as financial derivatives. As Indian derivatives markets grow more sophisticated, greater investor awareness will become essential. NSE has programmes to inform and educate brokers, dealers, traders, and market personnel. In addition, institutions will need to devote more resources to develop the business processes and technology necessary for derivatives trading. A numbers of theoretical and empirical studies have been done on the impact of the introduction of derivatives in the stock markets on the stock return volatility. The studies are concerned with both the developed as well as developing countries. There are two sets of views according to the theoretical as well as empirical findings. One is of the view that introduction of derivatives has increased the volatility and market performance, through forwarding its speculative roles and the other view is that the introduction of derivatives has reduced the volatility in the stock market thus increasing the stability of the stock market. There is lot of things remain unexplored in India so far as derivatives are concerned, this research thesis focuses more on investor s perceptions about derivatives in India. This research can be justified due to its theoretical and practical contributions to the body of knowledge. The present research makes a significant contribution in terms of 3
18 understanding derivatives and perceptions of investors regarding derivatives across major cities of Gujarat. The value of this study will be justified by the empirical research that will attempt to make an important contribution to the body of knowledge and the literature in the area of derivatives and perceptions of investors with regard to satisfaction level, its features, uses, benefits, limitations, factors affecting to derivatives etc. Most of the previous studies have limited their investigations to impact of derivatives on cash market. This study is conducted in India capturing the experience of investors and their perceptions since the introduction of derivatives in India till date. This research employs the study of hypothesis using ANOVA testing, Factor Analysis, Cluster analysis to understand the investors perceptions in better way. Few studies have tried to to employ the same. The results and insights obtained concerning the investors views regarding derivatives will be used to infer conclusions which will make significant contributions to the existing body of literature. 1.2 CAPITAL MARKET OF INDIA: INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Financial System in India: Capital is one of the important factors of production in any economy. In economy, a well organized financial system provides adequate capital formation through savings, finance and investments 2. An investment depends upon Savings and in turn Savings depends upon earnings of an individual or profits of the organization. This system may be viewed as a set of sub-systems with so many elements which are interdependent and interlinking with each other to produce the purposeful result with in the boundary. Hence, the term 2 L. M. Bhole, Financial Institutions and Markets: Structure, Growth and Innovation. (New Delhi, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2007) pp
19 system in the context of finance means a set of complex and closely connected financial institutions, instruments, agents, markets and so on which are interdependent and interlinking with each other to produce the economic growth with in the country. Transfer process is effectively fulfilled by the financial system to facilitate economic growth through the channel of finance. In the recent past the Indian Financial System has undergone sea changes and invented many new channels of financial sub-systems through the process of financial reforms. This thesis is based on this recent past which will be dealt thoroughly later in coming chapters on derivatives. Let s have a brief look at the Indian financial system and its components to have background knowledge first. Indian financial system can be broadly grouped into main pillars like (1) financial market (2) financial intermediaries (3) financial instruments (4) financial services Financial Intermediaries: Financial Intermediaries also termed as Financial Institutions. We can classify the financial intermediaries into two groups one is organized financial intermediaries and other one is unorganized financial intermediaries. Organized financial intermediaries comes under the purview of regulating authorities namely Reserve Bank of India, Securities Exchange Board of India, Companies Act, Securities Contract (Regulation) Act and so on. Whereas unorganized financial institutions are not cover under the purview of these regulating authorities, such type of institutions are called local money lenders, pawn brokers etc. Our study is mainly focusing on formal or organized financial intermediaries only 3. Organised financial intermediaries can be classified as Banking Institutions, Non Banking Financial Institutions, Insurance Companies and Housing Finance Companies. 3 Ajit Singh, Financial Liberalization, Stock Markets and Economic Development. The Economic Journal, vol. 107 (May 1997), pp
20 These financial intermediaries plays vital role in the capital formation by means of mobilizing savings and facilitating the allocation of funds in an effective manner. These intermediaries provide the convenience to the small investors by mobilizing their savings in the form of divisibility and distribute the claims at the time of maturity or redemption Financial instruments: Financial instruments can be categorized into various parts namely equity shares, preference shares, debt instruments and various combinations of these, time deposits, Mutual Funds and insurance polices, futures, options etc. A financial asset/instrument/security is a claim against another economic unit and is held as a store of value and for the return that is expected 4. While the value of a tangible/physical asset depends on its physical properties such as buildings, machines, furniture's, vehicles and so on, a financial asset represents a claim to future cash flows in the form of interest, dividends and so on. They are a claim on a stream of income and/or particular assets.. The entity/economic unit that offer the future cash flows are the issuer of the financial instrument and the owner of the security is the investor. Depending upon the nature of claim/return, an instrument may be (i) debt (security) such as bonds, debentures, term loans, (ii) equity (security) shares and (iii) hybrid security such as preference shares and convertibles. Based on the type of issuer, the security may be (1) direct (2) indirect and (3) derivative. The securities issued by manufacturing companies are direct assets (e.g. shares/debentures). Indirect assets are claims against financial intermediaries (e.g. units of mutual funds). The derivative instruments include options and futures. The prevalence of a variety of securities to suit the investment requirements of heterogeneous investors offers differentiated investment choice to them and is an important element in the maturity and sophistication of the financial system. 4 Bimal, Jalan,, Finance and Development, RBI bulletin, (June 2000), pp
21 1.2.4 Financial Services: Financial services have been growing rapidly with the emergence of new investment flows in financial reconstitute a large and growing sector in almost all economies. Trade and investment flows in financial services have been growing rapidly with the emergence of new and growing markets in developing and transition economies, with modernization, rapid technological change, use of new financial instruments, and financial and trade liberalization 5. The financial services sector is also quite large and complex and covers a wide range of activities and instruments, including for instance, corporate banking, derivatives, factoring, foreign exchange trading, pensions and investment fund management, advisory and consultancy services, insurance broking and underwriting, project finance, securities trading, venture capital, and wholesale and retail banking services. Given the range of instruments and activities that fall under the purview of the financial services sector, there are also a large number of players Financial Market: The Indian Financial Market promotes the enormous savings of the economy, by providing an effective channel of returns to the investors from whom the savings are mobilized. Hence, the term Financial Markets can be defined as a market for the exchange of capital and credit including the money markets and the capital markets. Financial Markets are facilitating tools for procurement of funds and invest in to various assets. The main activities of Financial Markets can be viewed as sale or purchase of shares or stocks, bonds, bills of exchange, commodities, future and options, foreign currency etc. Financial market can be broadly classified into (i) Money market (ii) Capital market. 5 Bharati, Pathak, Indian Financial Systems, (Delhi, Pearson Education, 2006), pp
22 1.2.6 Money Market The Money Market refers to the market for short term debt instrument which has maturity less than one year. The Money Market provides the borrower to borrow the funds for shorter period with lowest cost of funds. At the same time it also facilitates to the investor a platform to invest his savings which can generate interest thereon. Money Markets does not have an organised trading market place such as the stock exchange for its primary issue and secondary market trades. The participants in the money market are banks, primary dealers, and financial institutions, mutual funds, non-bank financial companies, manufacturing companies, State Governments, provident funds, non-resident Indians, overseas corporate bodies, foreign institutional investors and trusts. The RBI and Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulate the participants and use of instruments in the money market depending upon their respective roles in the financial system 6. For instance, financial institutions and mutual funds are allowed only as lenders in the call money market but are permitted to buy and sell Commercial Paper Capital Market: Capital Market is the market for long term finance with the maturity period more than one year. The Capital Market deals with the stock markets which provide financing through the issuance of shares or common stock in the primary market, and enable the subsequent trading in the secondary market. Capital Markets also deals with Bond Market which provide financing through issuance of Bonds in the primary market and subsequent trading thereof in the secondary market 7. 6 Bharati, Pathak, Indian Financial Systems, (Delhi, Pearson Education, 2008), pp Bharti, Pathak,, Indian Financial Systems, (Delhi, Pearson Education, 2008), pp
23 1.2.8 Functions of Capital Markets 8 : 1) The organised and regulated capital market motivates individual to save and invest funds. The availability of safe and profitable source of investment is an essential criterion to create propensity to save and invest on the part of the earning public. 2) It provides for the investors a safe and productive channels for investment of savings and secure the recurring benefit of return thereon, as long as the savings are retained. 3) It provides liquidity to the savings of the investors, by developing a secondary capital market, and thus makes even short term savings, consistently available for long-term users 4) It thus mobilizes savings of large number of individuals, families and associations and make the same available for meeting the large capital needs of organised industry, trade and business and for progress and development of the country as a whole and its economy. Financial markets are also classified as primary and secondary markets. The primary market deals in fresh capital / new securities therefore they are known as new issue Markets. Secondary markets deal in securities already issued or existing or outstanding. The primary markets mobilize savings and they supply fresh capital to business units. While secondary market helps in raising additional capital by providing liquidity to existing capital. The term capital market is coexistence not only with the stock market but also with the money market. However, in its popular usage, it refers to the stock market. It is not always possible to include a given participant (say a bank) only in either of the two (money and capital) markets. 8 B. M. Misra, Fifty Years of The Indian Capital Market RBI occasional papers, (June and September 1999), p.8. 9
24 In the ensuing pages, research is mainly concerned with capital market in its popular sense focusing upon organisation and working of its emerging derivative segment. Let s have a look at it. Organization of securities market The term securities market refers to the market provided by the different stock exchanges to securities which includes corporate securities such as shares, stocks, debentures, bonds, government securities such as dated securities and Treasury bill and right, titles or interest in such securities which includes derivatives in securities such as options and futures contract 9. Size and design of securities market Transfer of resources from those with idle resources to others who have a productive need for them is perhaps most efficiently achieved through the securities markets. Stated formally, securities markets provide channels for reallocation of savings to investments and entrepreneurship and thereby decouple these two activities. As a result, the savers and investors are not constrained by their individual abilities, but by the economy s abilities to invest and save respectively, which inevitably enhances savings and investment in the economy. Savings are linked to investments by a variety of intermediaries through a range of complex financial products called securities which is defined in the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 to include: (1) Shares, scrips, stocks, bonds, debentures, debenture stock or other marketable securities of a like nature in or of any incorporated company or body corporate; (a) Derivatives; (b) Units of any other instrument issued by any collective investment scheme to the investors in such schemes; (c) Security receipt as defined in clause (zg) of section 2 of the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest Act, 2002; 9 National Stock Exchange, Indian Securities Market: A Review, volume IV,
25 (d) Units or any other such instrument issued to the investors under any mutual fund scheme; (e) any certificate or instrument (by whatever name called), issued to an investor by any issuer being a special purpose distinct entity which possesses any debt or receivable, including mortgage debt, assigned to such entity, and acknowledging beneficial interest of such investor in such debt or receivable, including mortgage debt, as the case may be; (2) Government securities, (a) Such other instruments as may be declared by the Central Government to be securities; and (3) Rights or interest in securities. There are a set of economic units who demand securities in lieu of funds and others who supply securities for funds. These demand for and supply of securities and funds determine, under competitive market conditions in both goods and securities market, the prices of securities which reflect the present value of future prospects of the issuer, adjusted for risks and also prices of funds 10. It is not that the users and suppliers of funds meet each other and exchange funds for securities. It is difficult to accomplish such double coincidence of wants. The amount of funds supplied by the supplier may not be the amount needed by the user. Similarly, the risk, liquidity and maturity characteristics of the securities issued by the issuer may not match preference of the supplier. In such cases, they incur substantial search costs to find each other. Search costs are minimized by the intermediaries who match and bring the suppliers and users of funds together. These intermediaries may act as agents to match the needs of users and suppliers of funds for a commission, help suppliers and users in creation and sale of securities for a fee or buy the securities issued by users and in turn, sell their own securities to suppliers to book profit. It is, thus, a misnomer that securities market disintermediates by establishing a direct relationship between the savers and the users of funds. The market does not work in a vacuum; it requires services of a large variety of intermediaries. The 10 Ajay, Shah, Securities Markets Towards Greater Efficiency, in K. S. Parikh (ed.) India Development Report, (Delhi, Oxford University Press, 1997 ) 11
26 disintermediation in the securities market is in fact an intermediation with a difference; it is a risk-less intermediation, where the ultimate risks are borne by the savers and not the intermediaries. A large variety and number of intermediaries provide intermediation services in the Indian securities market as may be seen from Table The securities market, thus, has essentially three categories of participants, namely the issuers of securities, investors in securities and the intermediaries. The issuers and investors are the consumers of services rendered by the intermediaries while the investors are consumers (they subscribe for and trade in securities) of securities issued by issuers. In pursuit of providing a product to meet the needs of each investor and issuer, the intermediaries churn out more and more complicated products. They educate and guide them in their dealings and bring them together. Those who receive funds in exchange for securities and those who receive securities in exchange for funds often need the reassurance that it is safe to do so. This reassurance is provided by the law and by custom, often enforced by the regulator. The regulator develops fair market practices and regulates the conduct of issuers of securities and the intermediaries so as to protect the interests of suppliers of funds. The regulator ensures a high standard of service from intermediaries and supply of quality securities and non- manipulated demand for them in the market 11. Table 1.1 : Market Participants in Securities Market Number as on March Market Participants Securities Appellate Tribunal 1 1 Regulators* 4 4 Depositories 2 2 Stock Exchanges With Equities Trading With Debt Market Segment 2 2 With Derivative Trading Ajay, Shah, and Susan Thomas, Policy Issues In India s Capital Markets In 2000AD, in Surjit S. Bhalla (ed.), New Economic Policies For a new India, Indian Council of Social Science Research, (Haranand Publication Pvt. Ltd., 2000), pp
27 Brokers 9,443 9,487 Corporate Brokers 4,110 4,183 Sub-brokers 27,541 44,073 FIIs 996 1,319 Portfolio Managers Custodians Primary Dealers Merchant Bankers Bankers to an Issue Debenture Trustees Underwriters Venture Capital Funds Foreign Venture Capital Investors Mutual Funds Collective Investment Schemes 0 0 (Source: SEBI Handbook) The securities / capital market has two interdependent and inseparable segments: the primary and the secondary market Primary Market The primary market provides the channel for sale of new securities. Primary market provides opportunity to issuers of securities; Government as well as corporates, to raise resources to meet their requirements of investment and/or discharge some obligation. They may issue the securities at face value, or at a discount/premium and these securities may take a variety of forms such as equity, debt etc. They may issue the securities in domestic market and/or international market. The primary market issuance is done either through public issues or private placement. A public issue does not limit any entity in investing while in private placement, the issuance is done to select people. In terms of the Companies Act, 1956, an issue becomes public if it results in allotment to more than 50 persons. This means an issue resulting in allotment to less than 50 persons is private placement. There are two major types of issuers who issue securities. The corporate 13
28 entities issue mainly debt and equity instruments (shares, debentures, etc.), while the governments (central and state governments) issue debt securities (dated securities, treasury bills). The price signals, which subsume all information about the issuer and his business including associated risk, generated in the secondary market, help the primary market in allocation of funds Resources rose through public issues declined by 91.5 per cent to Rs. 2,031 crore during April-June 2008 over those in the corresponding period of last year. The number of issues declined from 24 in April-June 2007 to 15 in April-June The average size of public issues also declined to Rs.135 crore during April-June 2008 from Rs.994 crore during April-June All public issues during April-June 2008 were in the form of equity. Out of 15 issues during April-June 2008, 13 issues were initial public offerings (IPOs), accounting for 78.4 per cent of total resource mobilisation. Mobilisation of resources through private placement increased by 45.7 per cent to Rs.2,12,568 crore during over the previous year. Resources mobilised by private sector entities increased by 58.3 per cent during , while those by public sector entities increased by 29.7 per cent. Financial intermediaries (both from public sector and private sector) accounted for the bulk (67.9 per cent) of the total resource mobilization from the private placement market during (68.9 per cent during ). Resources raised through Euro issues American Depository Receipts (ADRs) and Global Depository Receipts (GDRs) by Indian corporate during April-June 2008 at Rs.4,056 crore were substantially higher than those during the corresponding period of previous year. During April-June 2008, net mobilisation of resources by mutual funds declined by 25.3 per cent to Rs.38,437 crore over the corresponding period of 2007 (Table 49). Scheme-wise, during April-June 2008, 90.0 per cent of net mobilisation of funds was under income/debt oriented schemes. Growth-oriented schemes accounted for 7.9 per cent of net resource mobilisation during April-June L. M. Bhole, Financial Institutions and Markets: Structure, Growth, and Innovation, (New Delhi, Tata McGraw-Hill, 2006) 13 SEBI, Hand Book of Statistics on Indian Securities Market 2008, pp
29 Table 1.2: Mobilization of Resource from Primary Market (Source: SEBI Handbook) Secondary Market Secondary market refers to a market where securities are traded after being initially offered to the public in the primary market and/or listed on the Stock Exchange. Majority of the trading is done in the secondary market. Secondary market comprises of equity markets and the debt markets. The secondary market enables participants who hold securities to adjust their holdings in response to changes in their assessment of risk and return. They also sell securities for cash to meet their liquidity needs. Once the new securities are issued in the primary market they are traded in the stock (secondary) 15
30 market. The backbone of the capital market is formed by the various securities exchanges that provide a forum for equity (equity market) and debt (debt market) transactions 14. The secondary market is operated through two mediums, namely, the Over-the Counter (OTC) market and the Exchange- Traded market. OTC markets are informal markets where trades are negotiated. Most of the trades in the government securities are in the OTC market. All the spot trades where securities are traded for immediate delivery and payment take place in the OTC market. The exchanges do not provide facility for spot trades in a strict sense. Closest to spot market is the cash market in exchanges where settlement takes place after some time. There are 19 exchanges (at the end of March 2008) in India and all of them follow a systematic settlement period. All the trades taking place over a trading cycle (day=t) are settled together after a certain time (T+2 day). Trades executed on NSE and BSE only are cleared and settled by a clearing corporation which provides novation and settlement guarantee. Nearly 100% of the trades in market are settled through demat delivery. For example, NSE also provides a formal trading platform for trading of a wide range of debt securities including government securities in both retail and wholesale mode. NSE also provides trading in derivatives of equities, interest rate as well indices. A variant of secondary market is the forward market, where securities are traded for future delivery and payment. Pure forward is out side the formal market. The versions of forward in formal market are futures and options. In futures market, standardized securities are traded for future delivery and settlement. These futures can be on a basket of securities like an index or an individual security. In case of options, securities are traded for conditional future delivery. There are two types of options a put option permits the owner to sell a security to the writer of options at a predetermined price while a call option permits the owner to purchase a security from the writer of the option at a predetermined price. These options can also be on individual stocks or basket of stocks 14 Bharti, Pathak,, Indian Financial Systems, (Delhi, Pearson Education, 2008 ), pp
31 like index. Two exchanges, namely NSE and the Bombay Stock Exchange, (BSE) provide trading of derivatives of securities. Today the market participants have the flexibility of choosing from a basket of products like: Equities, Bonds issued by both Government and Companies, Futures on benchmark indices as well as stocks, Options on benchmark indices as well as stocks, Futures on interest rate products like Notional 91-day T-Bills, 10 year notional zero coupon bond and 6% notional 10 year bond. The stock exchanges are the exclusive centers for trading of securities. Listing of companies on a Stock Exchange is mandatory to provide an opportunity to investors to invest in the securities of local companies. The trading volumes on exchanges have been witnessing phenomenal growth for last few years. Since the advent of screen based trading system in , it has been growing by leaps and bounds and reported a total turnover of Rs.51, 30,816 crore during The growth of turnover has, however, not been uniform across exchanges. The increase in turnover took place mostly at big exchanges (NSE and BSE) and it was partly at the cost of small exchanges that failed to keep pace with the changes. The business moved away from small exchanges to big exchanges, which adopted technologically superior trading and settlement systems. The huge liquidity and order depth of big exchanges further diverted liquidity of other stock exchanges. The 19 small exchanges put together reported less than 0.02% of total turnover during , while 2 big exchanges accounted for over % of turnover. For most of the exchanges, the raison d être for their existence, i.e. turnover, has disappeared. NSE and BSE are the major exchanges having nationwide operations. NSE operated through 2,956 VSATs in 245 cities at the end of March SEBI Annual Report , Various issues. 17
32 Table 1.3: Turnover on all Exchanges (In Rs. crore) Exchange NSE 19,45,287 35,51,038 BSE 9,56,185 15,78,857 Uttar Pradesh Ahmedabad 0 0 Calcutta Madras 1 0 OTCEI 0 0 Delhi 0 0 Hyderabad 92 0 Bangalore 0 0 Magadh 0 0 Bhubaneshwar 1 0 Cochin 0 0 Coimbatore 0 0 Gauhati 0 0 Jaipur 0 0 Ludhiana 0 0 Madhya Pradesh 0 0 Mangalore 0 0 Pune 0 0 SKSE 0 0 Vadodara 0 0 Total 29,03,058 5,130,816 NSE+BSE 29,01,472 5,129,895 Total (Except NSE + BSE) 1, (Source: SEBI Handbook) 18
33 The past decade in many ways has been remarkable for securities market in India. It has grown exponentially as measured in terms of amount raised from the market, number of stock exchanges and other intermediaries, the number of listed stocks, market capitalisation, trading volumes and turnover on stock exchanges, and investor population. Along with this growth, the profiles of the investors, issuers and intermediaries have changed significantly. The market has witnessed several institutional changes resulting in drastic reduction in transaction costs and significant improvements in efficiency, transparency, liquidity and safety. In a short span of time, Indian derivatives market has got a place in list of top global exchanges. The market capitalization has grown over the period indicating more companies using the trading platform of the stock exchange. As of March 2008, the market capitalization of NSE was Rs. 48,581,217 million 16. The market capitalization ratio is defined as market capitalization of stocks divided by GDP. It is used as a measure of stock market size. It is of economic significance since market is positively correlated with the ability to mobilize capital and diversify risk. The trading volumes on exchanges have been witnessing phenomenal growth over the past few years. During , the capital market segment of NSE itself only reported a trading volume of Rs. 35,510,382 million. The turnover ratio, which reflects the volume of trading in relation to the size of the market, stood at 73.09% in the year The turnover ratio is defined as the total value of shares traded on a country s stock exchange divided by market capitalization. It is used as a measure of trading activity or liquidity in the stock markets. The top 2 stock exchanges accounted for nearly 99% of turnover, while the rest of the exchanges had negligible volumes during The movement of the NIFTY50, the most widely used indicator of the market, has been responding to changes in the government s economic policies, the increase in FIIs inflows, etc. Domestic stock markets, which remained generally firm up to first week of January 2008, witnessed severe bouts of volatility thereafter due to heightened concerns over the severity of sub-prime lending crisis in the US and its spillover to other market segments 16 Capital Market, 3-16 May
34 and in other countries. The domestic stock markets recovered somewhat during April- May On May 21, 2008, the BSE Sensex registered gains of 10.2 per cent over end- March The upward trend was attributed to better than expected fourth quarter results of declared by IT majors, net purchases by FIIs in the Indian equity market, and some easing of international crude oil prices. The market sentiment, however, turned cautious thereafter mainly on account of hike in domestic retail fuel prices, rise in domestic inflation rate, net sales by FIIs in the Indian equity market, concerns over rising trade deficit and depreciation of the rupee, downward trend in major international equity markets, increase in international crude oil prices and other sector and stock specific news. As a result, both the BSE Sensex and the S&P CNX Nifty closed lower at and , respectively, on July 23, 2008, registering losses of 4.5 per cent and 5.4 per cent, respectively, over their end-march 2008 level. Between end- March 2008 to July 23, 2008, the BSE Sensex moved in a range of According to the data released by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), FIIs made net sales of Rs.16,279 crore (US $ 4.0 billion) in the Indian equity market during so far (up to July 17, 2008) as against net purchases of Rs.30,777 crore (US $ 7.4 billion) during the corresponding period of the previous year 17. Mutual funds, on the other hand, made net purchases of Rs.3,654 crore during so far (up to July 17, 2008) as compared with net purchases of Rs.2,604 crore during the corresponding period of last year. The sectoral indices witnessed a mixed trend during the current financial year so far (up to July 18, 2008). The losers among the sectoral indices were capital goods, auto, banking, public sector undertakings, metal, fast moving consumer goods, consumer durables and oil and gas, while the gainers were information technology and healthcare sector stocks. NSE in the cash segment during April-June 2008 was higher by 38.2 per cent than the corresponding period of SEBI, Hand Book of Statistics on Indian Securities Market
35 Table 1.4: STOCK MARKET INDICATORS Source: BSE and NSE Fact book published. (Based on Sensex 30 scrips and nifty 50 scrips) Reforms in the securities market, particularly the establishment and empowerment of SEBI, market determined allocation of resources, screen based nation-wide trading, dematerialization and electronic transfer of securities, rolling settlement and ban on deferral products, sophisticated risk management and derivatives trading, have greatly improved the regulatory framework and efficiency of trading and settlement. Indian market is now comparable to many developed markets in terms of a number of qualitative parameters. Let s have a look at each major developments and reforms taken place for the last 20 years briefly. 21
CHAPTER 10 Financial Market
 CHAPTER 10 Financial Market A financial market refers to a market where the creation and exchange of financial assets (such as shares and debentures) takes place. Allocative Function of Financial Market
CHAPTER 10 Financial Market A financial market refers to a market where the creation and exchange of financial assets (such as shares and debentures) takes place. Allocative Function of Financial Market
PUBLIC AWARENESS TOWARDS CAPITAL MARKET INVESTMENT WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO JRF SECURITIES LIMITED, HYDERABAD
 Research Communication ISSN 2394-2762(Print) e-issn 2394-2770(Online) PUBLIC AWARENESS TOWARDS CAPITAL MARKET INVESTMENT WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO JRF SECURITIES LIMITED, HYDERABAD *Dr. R. Ganapathi *Corresponding
Research Communication ISSN 2394-2762(Print) e-issn 2394-2770(Online) PUBLIC AWARENESS TOWARDS CAPITAL MARKET INVESTMENT WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO JRF SECURITIES LIMITED, HYDERABAD *Dr. R. Ganapathi *Corresponding
REFORMS IN INDIAN PRIMARY MARKET A VIEW
 REFORMS IN INDIAN PRIMARY MARKET A VIEW Dr.A.Sathish Kumar Professor Sree Chaitanya Institute of Management and Computer Science Karimnagar, A.P., India B.Anusha Assistant Professor Sree Chaitanya PG College
REFORMS IN INDIAN PRIMARY MARKET A VIEW Dr.A.Sathish Kumar Professor Sree Chaitanya Institute of Management and Computer Science Karimnagar, A.P., India B.Anusha Assistant Professor Sree Chaitanya PG College
The Secondary Market. The secondary market for equity 4.5 The trading intensity of Indian stock exchanges is impressive by world standards.
 The Secondary Market The secondary market for equity 4.5 The trading intensity of Indian stock exchanges is impressive by world standards. Table 4.2 : Biggest exchanges by number of transactions in 2005
The Secondary Market The secondary market for equity 4.5 The trading intensity of Indian stock exchanges is impressive by world standards. Table 4.2 : Biggest exchanges by number of transactions in 2005
Impact of General Elections 2014 on Indian Stock Market with Special References to the Stock of Select Companies in BSE
 DOI : 10.18843/ijms/v5i3(1)/15 DOIURL :http://dx.doi.org/10.18843/ijms/v5i3(1)/15 Impact of General Elections 2014 on Indian Stock Market with Special References to the Stock of Select Companies in BSE
DOI : 10.18843/ijms/v5i3(1)/15 DOIURL :http://dx.doi.org/10.18843/ijms/v5i3(1)/15 Impact of General Elections 2014 on Indian Stock Market with Special References to the Stock of Select Companies in BSE
Chapter V Findings, Conclusion & Recommendations
 Chapter V Findings, Conclusion & Recommendations The Indian Stock Market has come a long way from the earlier days of out-cry system to the present day screen based and net based paperless trading system.
Chapter V Findings, Conclusion & Recommendations The Indian Stock Market has come a long way from the earlier days of out-cry system to the present day screen based and net based paperless trading system.
Trends of Capital Market in India
 Trends of Capital Market in India Jency S M. Phil Scholar, St. Berchmans College, Changanassery, Kottayam, Kerala, India Abstract Capital markets help to channelize surplus funds into productive use. Generally,
Trends of Capital Market in India Jency S M. Phil Scholar, St. Berchmans College, Changanassery, Kottayam, Kerala, India Abstract Capital markets help to channelize surplus funds into productive use. Generally,
Financial Derivatives Market: An analysis for the decade
 By: T. MUTHUKUMARAN Dr V.K. SOMASUNDARAM Financial Derivatives Market: An analysis for the decade Derivatives trading commenced in India in June 2000 after the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
By: T. MUTHUKUMARAN Dr V.K. SOMASUNDARAM Financial Derivatives Market: An analysis for the decade Derivatives trading commenced in India in June 2000 after the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks
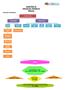 CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks Key Concepts in nutshell: CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL MARKET: It refers to the market which creates and exchanges financial assets. FUNCTIONS OF FINANICIAL
CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks Key Concepts in nutshell: CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL MARKET: It refers to the market which creates and exchanges financial assets. FUNCTIONS OF FINANICIAL
A study on investor perception towards investment in capital market with special reference to Coimbatore City
 2017; 3(3): 150-154 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(3): 150-154 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 09-01-2017 Accepted: 10-02-2017 PSG College of Arts and
2017; 3(3): 150-154 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2017; 3(3): 150-154 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 09-01-2017 Accepted: 10-02-2017 PSG College of Arts and
A STUDY ON THE BUSINESS GROWTH OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE FROM TO
 A STUDY ON THE BUSINESS GROWTH OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE FROM 2001-02 TO 2014-15 DR.G.AMUDHA* & DR.V.KANNAN* *ASSISTANT PROFESSORS OF ST.JOSEPH S INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT, TRICHIRAPPALLI-02. ABSTRACT:
A STUDY ON THE BUSINESS GROWTH OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE FROM 2001-02 TO 2014-15 DR.G.AMUDHA* & DR.V.KANNAN* *ASSISTANT PROFESSORS OF ST.JOSEPH S INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT, TRICHIRAPPALLI-02. ABSTRACT:
UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS
 UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS Introduction : Financial Market is a market for creation and exchange of financial assets like share, bonds etc. It helps in mobilising savings and channelising them into the
UNIT 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS Introduction : Financial Market is a market for creation and exchange of financial assets like share, bonds etc. It helps in mobilising savings and channelising them into the
Solved questions on Indian capital market
 Solved questions on Indian capital market 1. In private placement, issuance is done to. (2 marks) (a) more than 50 persons (b) less than 100 persons (c) less than 50 persons (d) less than 10 persons 2.
Solved questions on Indian capital market 1. In private placement, issuance is done to. (2 marks) (a) more than 50 persons (b) less than 100 persons (c) less than 50 persons (d) less than 10 persons 2.
CHAPTER-4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER-4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY The research methodology of the selected topic falls in the following dimensions: 4.1. TITLE: The title of the thesis is A Study on Investors' General and Legal Awareness
CHAPTER-4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY The research methodology of the selected topic falls in the following dimensions: 4.1. TITLE: The title of the thesis is A Study on Investors' General and Legal Awareness
: ` per share. IPO opens during : Sept 28 Oct 04, 2011 Book Running Lead Manager : Atherstone Capital Markets Ltd.
 I P O N O T E Onelife Capital Advisors Ltd. September 27, 2011 Price Band : `100-110 per share Minimum Bid Lot Size : 50 Equity Shares Maximum Bid Lot Size : 1800 Equity Shares IPO opens during : Sept
I P O N O T E Onelife Capital Advisors Ltd. September 27, 2011 Price Band : `100-110 per share Minimum Bid Lot Size : 50 Equity Shares Maximum Bid Lot Size : 1800 Equity Shares IPO opens during : Sept
SYNOPSIS PAPERLESS TRADING IN INDIAN STOCK MARKETS
 SYNOPSIS PAPERLESS TRADING IN INDIAN STOCK MARKETS Research Scholar: Joseph George Supervisor: Dr M Thomas John Branch: Commerce INTRODUCTION: The stock exchange is an organized market for the purchase
SYNOPSIS PAPERLESS TRADING IN INDIAN STOCK MARKETS Research Scholar: Joseph George Supervisor: Dr M Thomas John Branch: Commerce INTRODUCTION: The stock exchange is an organized market for the purchase
FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) STOCK MARKET (PART-2)
 FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) STOCK MARKET (PART-2) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers! Welcome to the lecture series of financial market operations. Today we shall take up part 2 of the unit 3 rd. We
FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) STOCK MARKET (PART-2) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers! Welcome to the lecture series of financial market operations. Today we shall take up part 2 of the unit 3 rd. We
CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction 1.2 The concept of Derivatives 1.3 Importance of Derivatives 1.4 History of Derivatives 1.5 Growth of Indian Derivatives and Global Derivatives 1.6 Derivative Market
CHAPTER-1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction 1.2 The concept of Derivatives 1.3 Importance of Derivatives 1.4 History of Derivatives 1.5 Growth of Indian Derivatives and Global Derivatives 1.6 Derivative Market
International Capital Market
 J B GUPTA CLASSES 98184931932, drjaibhagwan@gmail.com, www.jbguptaclasses.com Copyright: Dr JB Gupta 16 International Capital Market Global Depository Receipts American Depository Receipts External Commercial
J B GUPTA CLASSES 98184931932, drjaibhagwan@gmail.com, www.jbguptaclasses.com Copyright: Dr JB Gupta 16 International Capital Market Global Depository Receipts American Depository Receipts External Commercial
BSE SME Exchange - Presentation
 Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd. Bombay Stock Exchange Limited BSE SME Exchange - Presentation 6 th Feb 2012 About SME Industry About SME Industry Classification of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises 3 About
Bombay Stock Exchange Ltd. Bombay Stock Exchange Limited BSE SME Exchange - Presentation 6 th Feb 2012 About SME Industry About SME Industry Classification of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises 3 About
5. Enumerate the various penalties which can be imposed under SEBI Act, 1992 for various
 SL&C Page 1 STUDY I - GENESIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF REGULATORY FRAMEWORK 1. Briefly discuss the evolution, growth and functions of financial system in India. 2. Explain the role of securities market in economic
SL&C Page 1 STUDY I - GENESIS AND DEVELOPMENT OF REGULATORY FRAMEWORK 1. Briefly discuss the evolution, growth and functions of financial system in India. 2. Explain the role of securities market in economic
BFF1001 Week 1 Topic 1: What is finance
 BFF1001 Week 1 Topic 1: What is finance Definitions Deficit A deficit unit saves less money than it invests A deficit unit needs funds If saving is less than investment, a deficit occurs Surplus A surplus
BFF1001 Week 1 Topic 1: What is finance Definitions Deficit A deficit unit saves less money than it invests A deficit unit needs funds If saving is less than investment, a deficit occurs Surplus A surplus
CHAPTER - IV INVESTMENT PREFERENCE AND DECISION INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER - IV INVESTMENT PREFERENCE AND DECISION INTRODUCTION This Chapter examines the investment pattern of the retail equity investors in general and investment preferences, risk-return perceptions and
CHAPTER - IV INVESTMENT PREFERENCE AND DECISION INTRODUCTION This Chapter examines the investment pattern of the retail equity investors in general and investment preferences, risk-return perceptions and
Y V Reddy: Developing debt markets in India review and prospects
 Y V Reddy: Developing debt markets in India review and prospects Remarks by Dr Y V Reddy, Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, at a meeting of Central Bank Governors of Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean,
Y V Reddy: Developing debt markets in India review and prospects Remarks by Dr Y V Reddy, Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, at a meeting of Central Bank Governors of Asia, Latin America and the Caribbean,
A STUDY ON BEHAVIOR OF MUTUAL FUND INVESTORS IN INDIA
 www.arseam.com Impact Factor: 0.98 A STUDY ON BEHAVIOR OF MUTUAL FUND INVESTORS IN INDIA *Godala. Satya Narayana Reddy *Associate Professor, ST.MARY S ENGINEERING COLLEGE ABSTRACT Today a lot of investment
www.arseam.com Impact Factor: 0.98 A STUDY ON BEHAVIOR OF MUTUAL FUND INVESTORS IN INDIA *Godala. Satya Narayana Reddy *Associate Professor, ST.MARY S ENGINEERING COLLEGE ABSTRACT Today a lot of investment
CHAPTER I THE ISSUES, METHODOLOGY AND OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
 CHAPTER I THE ISSUES, METHODOLOGY AND OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY 1.1 INTRODUCTION Investment means parking of savings in some avenue that would yield considerable returns in the future. Savings could be kept
CHAPTER I THE ISSUES, METHODOLOGY AND OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY 1.1 INTRODUCTION Investment means parking of savings in some avenue that would yield considerable returns in the future. Savings could be kept
IMPACT OF NON-BANKING FINANCIAL COMPANIES (NBFCS) IN INDIAN ECONOMY GROWTH
 EPRA International Journal of Economic and Business Review Inno Space (SJIF) Impact Factor : 5.509(Morocco) e-issn : 2347-9671, p- ISSN : 2349-0187 Vol - 4, Issue- 3, March 2016 ISI Impact Factor : 1.259
EPRA International Journal of Economic and Business Review Inno Space (SJIF) Impact Factor : 5.509(Morocco) e-issn : 2347-9671, p- ISSN : 2349-0187 Vol - 4, Issue- 3, March 2016 ISI Impact Factor : 1.259
Acknowledgement. I am extremely thankful to Mr.D.Shyjan, Lecturer in the Department, for his timely help at various stages of the study.
 Acknowledgement I express my heartfelt thanks to my supervisor Dr.C.Krishnan, Selection Grade Lecturer, Government College, Kodencherry, Calicut, for invaluable advice, kind help, and constant and whole-hearted
Acknowledgement I express my heartfelt thanks to my supervisor Dr.C.Krishnan, Selection Grade Lecturer, Government College, Kodencherry, Calicut, for invaluable advice, kind help, and constant and whole-hearted
Constituent Deals in the Government Securities Market
 Constituent Deals in the Government Securities Market Dr. Golaka C. Nath & Ms. Sahana Rajaram The Indian government securities market has witnessed reasonable growth during the past two decades after the
Constituent Deals in the Government Securities Market Dr. Golaka C. Nath & Ms. Sahana Rajaram The Indian government securities market has witnessed reasonable growth during the past two decades after the
CHAPTER-4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER-4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 4.1 Introduction to Problem Statement 4.2 Approaches to the Problem 4.3 Research Questions 4.4 Research Design 4.5 Sample Design 4.6 Period of Study 4.7 Data Analysis 4.8
CHAPTER-4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 4.1 Introduction to Problem Statement 4.2 Approaches to the Problem 4.3 Research Questions 4.4 Research Design 4.5 Sample Design 4.6 Period of Study 4.7 Data Analysis 4.8
A STUDY ON INITIAL PERFORMANCE OF IPO S IN SINDIA DURING COMPARISON OF BOOK BUILDING AND FIXED PRICE MECHANISM
 A STUDY ON INITIAL PERFORMANCE OF IPO S IN SINDIA DURING 2015-16 - COMPARISON OF BOOK BUILDING AND FIXED PRICE MECHANISM Dr. P. Roopa Assistant Professor, Sree Vidyanikethan Institute of Management, Tirupati
A STUDY ON INITIAL PERFORMANCE OF IPO S IN SINDIA DURING 2015-16 - COMPARISON OF BOOK BUILDING AND FIXED PRICE MECHANISM Dr. P. Roopa Assistant Professor, Sree Vidyanikethan Institute of Management, Tirupati
Meaning. In a broad sense the term Financial Services means Mobilising and allocating savings. It can also be called Financial Intermediation
 Financial Services Meaning Classification of Fin. Service Industry Scope of Financial Services Sources of Revenue Causes for Financial Innovation New Financial Products & Services Innovative Financial
Financial Services Meaning Classification of Fin. Service Industry Scope of Financial Services Sources of Revenue Causes for Financial Innovation New Financial Products & Services Innovative Financial
FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT IN INDIA: TRENDS, IMPACT, DETERMINANTS AND INVESTORS EXPERIENCES
 FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT IN INDIA: TRENDS, IMPACT, DETERMINANTS AND INVESTORS EXPERIENCES by: MANPREET KAUR Department of Management Studies Submitted in fulfillment of the requirements of the degree
FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT IN INDIA: TRENDS, IMPACT, DETERMINANTS AND INVESTORS EXPERIENCES by: MANPREET KAUR Department of Management Studies Submitted in fulfillment of the requirements of the degree
OVERVIEW OF CAPITAL MARKET
 Contents About the author I-5 Preface to second edition I-7 Chapter-heads I-9 1 OVERVIEW OF CAPITAL MARKET 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Financial System in India 2 1.3 Financial Markets 4 1.4 Role of securities
Contents About the author I-5 Preface to second edition I-7 Chapter-heads I-9 1 OVERVIEW OF CAPITAL MARKET 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Financial System in India 2 1.3 Financial Markets 4 1.4 Role of securities
STOCK MARKET TERMINOLOGIES
 STOCK MARKET TERMINOLOGIES Annual Report A publication, including financial statements and a report on operations, issued by a company to its shareholders at the company's fiscal year-end. A fiscal year
STOCK MARKET TERMINOLOGIES Annual Report A publication, including financial statements and a report on operations, issued by a company to its shareholders at the company's fiscal year-end. A fiscal year
FOREIGN INSTITUTIONAL INVESTMENTS (FIIs) IN INDIA
 FOREIGN INSTITUTIONAL INVESTMENTS (FIIs) IN INDIA N.NOOKA RAJU* Prof. M. UMA DEVI** *Research Scholar, Dept. of Commerce and Mgt. Studies, Andhra University Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India **Department
FOREIGN INSTITUTIONAL INVESTMENTS (FIIs) IN INDIA N.NOOKA RAJU* Prof. M. UMA DEVI** *Research Scholar, Dept. of Commerce and Mgt. Studies, Andhra University Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, India **Department
MUTUAL FUNDS AN AVENUE TO INVESTORS
 MUTUAL FUNDS AN AVENUE TO INVESTORS. M.Sudha Madhavi I/C Principal & Associate Professor Saanvi P.G. College for Women Hyderabad-500058 Email : smakella@gmail.com ABSTRACT Mutual funds have become one
MUTUAL FUNDS AN AVENUE TO INVESTORS. M.Sudha Madhavi I/C Principal & Associate Professor Saanvi P.G. College for Women Hyderabad-500058 Email : smakella@gmail.com ABSTRACT Mutual funds have become one
A Study on Opinion of Working People towards Share Market Investment with Reference to Tiruchirapalli District
 Int. Journal of Management and Development Studies 5(2): 50-59 (2016) ISSN (Online): 2320-0685. ISSN (Print): 2321-1423 Impact Factor: 0.715 A Study on Opinion of Working People towards Share Market Investment
Int. Journal of Management and Development Studies 5(2): 50-59 (2016) ISSN (Online): 2320-0685. ISSN (Print): 2321-1423 Impact Factor: 0.715 A Study on Opinion of Working People towards Share Market Investment
INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET- BY ANMI (India)
 INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET- BY ANMI (India) 1) ANMI is a pan India association comprising of the trading members across India like National Stock Exchange (NSE), Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and other exchanges
INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET- BY ANMI (India) 1) ANMI is a pan India association comprising of the trading members across India like National Stock Exchange (NSE), Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and other exchanges
DETERMINATION OF WORKING CAPITAL
 E- Module 1 DETERMINATION OF WORKING CAPITAL Operating Cycle Approach The operating cycle can be said to be at the heart of the need for working capital 1. Taking the time lag into account for determining
E- Module 1 DETERMINATION OF WORKING CAPITAL Operating Cycle Approach The operating cycle can be said to be at the heart of the need for working capital 1. Taking the time lag into account for determining
Dematerialization of Shares & Retail Investors in India - A Study
 Volume-5, Issue-3, June-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 393-400 Dematerialization of Shares & Retail Investors in India - A Study Dr. Surendar G Assistant
Volume-5, Issue-3, June-2015 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 393-400 Dematerialization of Shares & Retail Investors in India - A Study Dr. Surendar G Assistant
SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS
 CHAPTER-7 SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS This chapter is divided into three sections. The first section enumerates the objectives and methodology of the study, the second section puts
CHAPTER-7 SUMMARY OF FINDINGS, CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS This chapter is divided into three sections. The first section enumerates the objectives and methodology of the study, the second section puts
Section A (Short Answer Type Questions)
 B.Com. (Hons.) V Semester Paper Title: Paper Code: AS-2640 *(Prepared by Mr. Amit Manglani, Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce, GGV) Note: These model answers are a depiction of important points
B.Com. (Hons.) V Semester Paper Title: Paper Code: AS-2640 *(Prepared by Mr. Amit Manglani, Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce, GGV) Note: These model answers are a depiction of important points
CHAPTER - I INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER - I INTRODUCTION Introduction Chapter deals with a brief note about importance of capital market, Statement of the problem, Objectives of the study, Hypothesis, scope of the study, Geographical
CHAPTER - I INTRODUCTION Introduction Chapter deals with a brief note about importance of capital market, Statement of the problem, Objectives of the study, Hypothesis, scope of the study, Geographical
IMPACT OF QUARTERLY FINANCIAL RESULTS ON MARKET PRICE OF SHARE: AN ANALYTICAL STUDY OF SELECTED INDIAN COMPANIES ABSTRACT
 IMPACT OF QUARTERLY FINANCIAL RESULTS ON MARKET PRICE OF SHARE: AN ANALYTICAL STUDY OF SELECTED INDIAN COMPANIES I. Introduction: ABSTRACT There are various corporate actions or events such as Mergers
IMPACT OF QUARTERLY FINANCIAL RESULTS ON MARKET PRICE OF SHARE: AN ANALYTICAL STUDY OF SELECTED INDIAN COMPANIES I. Introduction: ABSTRACT There are various corporate actions or events such as Mergers
Associate Professor and Head-Dual Programs, Jain University- Center for Management studies Corresponding Author: Dr. Raghu G Anand
 IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-issn: 78-487X, p-issn: 39-7668. Volume 9, Issue. Ver. III. (October. 7), PP 6-73 www.iosrjournals.org Modeling of the short-term returns pattern of
IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-issn: 78-487X, p-issn: 39-7668. Volume 9, Issue. Ver. III. (October. 7), PP 6-73 www.iosrjournals.org Modeling of the short-term returns pattern of
Financial Market in India. Samir K Mahajan
 Financial Market in India Financial Market Financial Market is a mechanism which enables participants to deal in financial claims. It s a platform to in which lender and borrower of funds interact to determine
Financial Market in India Financial Market Financial Market is a mechanism which enables participants to deal in financial claims. It s a platform to in which lender and borrower of funds interact to determine
BSE Ltd (BSE) -New Initiatives to drive growth
 BSE Ltd (BSE) -New Initiatives to drive growth BSE Ltd (BSE) 18-06-2018 Recommendation : Buy Strong brand recognition CMP : Rs 862 Target : NA % Allocation : 5% Sector : MISC Sensex : 35634 NSE code :
BSE Ltd (BSE) -New Initiatives to drive growth BSE Ltd (BSE) 18-06-2018 Recommendation : Buy Strong brand recognition CMP : Rs 862 Target : NA % Allocation : 5% Sector : MISC Sensex : 35634 NSE code :
International Journal of Current Research and Modern Education (IJCRME) ISSN (Online): ( Volume I, Issue I, 2016 A
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON NON PERFORMING ASSET MANAGEMENT OF SELECTED PUBLIC SECTOR BANK AND PRIVATE SECTOR BANK Harish Shetty* & S. N. Sandesha** Assistant professor, SDM College, Ujire, Karnataka Abstract:
A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON NON PERFORMING ASSET MANAGEMENT OF SELECTED PUBLIC SECTOR BANK AND PRIVATE SECTOR BANK Harish Shetty* & S. N. Sandesha** Assistant professor, SDM College, Ujire, Karnataka Abstract:
CHAPTER VI RISK TOLERANCE AMONG MUTUAL FUND INVESTORS
 CHAPTER VI RISK TOLERANCE AMONG MUTUAL FUND INVESTORS 6.1. Introduction Risk and return are inseparable twins 1. In generic sense, risk means the possibility of financial loss. In the investment world,
CHAPTER VI RISK TOLERANCE AMONG MUTUAL FUND INVESTORS 6.1. Introduction Risk and return are inseparable twins 1. In generic sense, risk means the possibility of financial loss. In the investment world,
PERFORMANCE OF LARGE CAP SHARE AND SMALL CAP SHARE: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF SELECTED COMPANIES SHARES
 PERFORMANCE OF LARGE CAP SHARE AND SMALL CAP SHARE: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF SELECTED COMPANIES SHARES Dr. Yagnesh M Dalvadi Faculty, PG Department of Business Studies, Sardar Patel University, Vallabh Vidyanagar,
PERFORMANCE OF LARGE CAP SHARE AND SMALL CAP SHARE: A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF SELECTED COMPANIES SHARES Dr. Yagnesh M Dalvadi Faculty, PG Department of Business Studies, Sardar Patel University, Vallabh Vidyanagar,
IMPACT AND EFFECTIVENESS OF CIRCUIT BREAKER IN STOCK MARKETS. Mohinder Singh ABSTRACT
 IMPACT AND EFFECTIVENESS OF CIRCUIT BREAKER IN STOCK MARKETS Mohinder Singh Assistant Professor, Department Of Commerce Govt. College SarkaghatDistt. Mandi (Himachal Pradesh) E-mail: mohinder_hira@ymail.com
IMPACT AND EFFECTIVENESS OF CIRCUIT BREAKER IN STOCK MARKETS Mohinder Singh Assistant Professor, Department Of Commerce Govt. College SarkaghatDistt. Mandi (Himachal Pradesh) E-mail: mohinder_hira@ymail.com
CAPITAL MARKET SCENARIO
 CAPITAL MARKET SCENARIO CHAPTER 3 THE INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET SCENARIO The capital market constitutes a vital segment of the Indian economy, along with the financial institutions that finance the economic
CAPITAL MARKET SCENARIO CHAPTER 3 THE INDIAN CAPITAL MARKET SCENARIO The capital market constitutes a vital segment of the Indian economy, along with the financial institutions that finance the economic
International Journal of Recent Scientific Research
 ISSN: 0976-3031 International Journal of Recent Scientific Research Impact factor: 5.114 A STUDY ON STRATEGIC GROWTH IN INDIAN FINANCIAL DERIVATIVES MARKET Prakash Yalavatti Volume: 6 Issue: 10 THE PUBLICATION
ISSN: 0976-3031 International Journal of Recent Scientific Research Impact factor: 5.114 A STUDY ON STRATEGIC GROWTH IN INDIAN FINANCIAL DERIVATIVES MARKET Prakash Yalavatti Volume: 6 Issue: 10 THE PUBLICATION
Received: 4 September Revised: 9 September Accepted: 19 September. Foreign Institutional Investment on Indian Capital Market: An Empirical Analysis
 Foreign Institutional Investment on Indian Capital Market: An Empirical Analysis Tom Jacob 1 & Thomas Paul Kattookaran 2 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, Christ College, Irinjalakuda, Kerala,
Foreign Institutional Investment on Indian Capital Market: An Empirical Analysis Tom Jacob 1 & Thomas Paul Kattookaran 2 1 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Commerce, Christ College, Irinjalakuda, Kerala,
Bonanza Portfolio Ltd
 Public Issue of Tax Free Secured Redeemable Non-Convertible Bonds issued by HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS In exercise of the powers conferred by item (h) of sub-clause (iv) of clause (15) of Section 10 of
Public Issue of Tax Free Secured Redeemable Non-Convertible Bonds issued by HIGHLIGHTS OF TAX BENEFITS In exercise of the powers conferred by item (h) of sub-clause (iv) of clause (15) of Section 10 of
Doctoral Thesis submitted In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the award of the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY MANAGEMENT. K.
 Evaluation of Investment Performance and Perception of Investors in Bengaluru and its Sub-Urban Area with respect to Equity Linked Savings Scheme Plans of Indian Mutual Funds Doctoral Thesis submitted
Evaluation of Investment Performance and Perception of Investors in Bengaluru and its Sub-Urban Area with respect to Equity Linked Savings Scheme Plans of Indian Mutual Funds Doctoral Thesis submitted
Financial market interdependence
 Financial market CHAPTER interdependence 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Section No. TITLE OF THE SECTION Page No. 1.1 Theme, Background and Applications of This Study 1 1.2 Need for the Study 5 1.3 Statement of the
Financial market CHAPTER interdependence 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Section No. TITLE OF THE SECTION Page No. 1.1 Theme, Background and Applications of This Study 1 1.2 Need for the Study 5 1.3 Statement of the
Consolidated FDI Policy (The article was published in the journal of Bombay Chartered Accountants Society in June 2010)
 Consolidated FDI Policy 2010 Bombay Chartered Accountants Society Naresh Ajwani (The article was published in the journal of Bombay Chartered Accountants Society in June 2010) 1. Ministry of Commerce and
Consolidated FDI Policy 2010 Bombay Chartered Accountants Society Naresh Ajwani (The article was published in the journal of Bombay Chartered Accountants Society in June 2010) 1. Ministry of Commerce and
Rakesh Mohan: Ownership and governance in private sector banks in India
 Rakesh Mohan: Ownership and governance in private sector banks in India Address by Dr Rakesh Mohan, Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, at the Conference on Ownership and Governance in Private
Rakesh Mohan: Ownership and governance in private sector banks in India Address by Dr Rakesh Mohan, Deputy Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, at the Conference on Ownership and Governance in Private
PERFORMANCE EVALUATION OF LIQUID DEBT MUTUAL FUND SCHEMES IN INDIA
 International Journal of Management, IT & Engineering Vol. 8 Issue 6, June 2018, ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
International Journal of Management, IT & Engineering Vol. 8 Issue 6, June 2018, ISSN: 2249-0558 Impact Factor: 7.119 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) CAPITAL MARKET (PART-1)
 FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) CAPITAL MARKET (PART-1) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers, Welcome to the lecture series on Financial Market Operations. Today we are going to take up Unit -3 and we are
FINANCIAL MARKET OPERATIONS (UNIT-3) CAPITAL MARKET (PART-1) 1. INTRODUCTION Hello viewers, Welcome to the lecture series on Financial Market Operations. Today we are going to take up Unit -3 and we are
Is foreign portfolio Investment beneficial to India s balance of Payments? : An Exploratory analysis
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Is foreign portfolio Investment beneficial to India s balance of Payments? : An Exploratory analysis Justine George Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, St Paul
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Is foreign portfolio Investment beneficial to India s balance of Payments? : An Exploratory analysis Justine George Assistant Professor, Department of Economics, St Paul
A Study of Relationship Between Cash and Derivative Segment in Indian Stock Market
 A Study of Relationship Between Cash and Derivative Segment in Indian Stock Market During the recent global recession Derivative instruments were largely criticised on account of their speculative nature.
A Study of Relationship Between Cash and Derivative Segment in Indian Stock Market During the recent global recession Derivative instruments were largely criticised on account of their speculative nature.
International Journal of Business and Administration Research Review, Vol.1, Issue.7, Oct - Dec, Page 41
 REFORMS IN INDIAN SECURITIES MARKET Bhoopal.M Doctoral Research Scholar, Part Time, External Category C, Dept. of Business Administration, Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Tirunelveli. Dr.G.Prabakaran
REFORMS IN INDIAN SECURITIES MARKET Bhoopal.M Doctoral Research Scholar, Part Time, External Category C, Dept. of Business Administration, Manonmaniam Sundaranar University, Tirunelveli. Dr.G.Prabakaran
CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD
 CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD PART I: ELIGIBILITY REQUIREMENTS Reference date 4. Unless otherwise provided in this Chapter, an issuer making an initial public offer of specified securities
CHAPTER II - INITIAL PUBLIC OFFER ON MAIN BOARD PART I: ELIGIBILITY REQUIREMENTS Reference date 4. Unless otherwise provided in this Chapter, an issuer making an initial public offer of specified securities
Securities Markets. Primary Market. The Secondary Market
 4 Securities Markets Securities markets performance in terms of information-processing, risk management and liquidity-provision functions improved further in 2005. In December 2005, there were 2,540 companies,
4 Securities Markets Securities markets performance in terms of information-processing, risk management and liquidity-provision functions improved further in 2005. In December 2005, there were 2,540 companies,
Gotham Absolute Return Fund. Institutional Class GARIX. Gotham Enhanced Return Fund. Institutional Class GENIX. Gotham Neutral Fund
 Gotham Absolute Return Fund Institutional Class GARIX Gotham Enhanced Return Fund Institutional Class GENIX Gotham Neutral Fund Institutional Class GONIX Gotham Index Plus Fund Institutional Class GINDX
Gotham Absolute Return Fund Institutional Class GARIX Gotham Enhanced Return Fund Institutional Class GENIX Gotham Neutral Fund Institutional Class GONIX Gotham Index Plus Fund Institutional Class GINDX
An Evaluation of Investors Grievances and Redressal Mechanism in Indian Capital Market
 An Evaluation of Investors Grievances and Redressal Mechanism in Indian Capital Market 1 Ch. Balaji, 2 Dr. Praveen Kumar 1,2 Rayalaseema University, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India Abstract This paper explains
An Evaluation of Investors Grievances and Redressal Mechanism in Indian Capital Market 1 Ch. Balaji, 2 Dr. Praveen Kumar 1,2 Rayalaseema University, Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, India Abstract This paper explains
Ch. 2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM
 Ch. 2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM To "finance" something means to pay for it. Since money (or credit) is the means of payment, "financial" basically means "pertaining to money or credit." Financial
Ch. 2 AN OVERVIEW OF THE FINANCIAL SYSTEM To "finance" something means to pay for it. Since money (or credit) is the means of payment, "financial" basically means "pertaining to money or credit." Financial
GIAN JYOTI E-JOURNAL, Volume 2, Issue 3 (Jul Sep 2012) ISSN X FOREIGN INSTITUTIONAL INVESTORS AND INDIAN STOCK MARKET
 FOREIGN INSTITUTIONAL INVESTORS AND INDIAN STOCK MARKET Dr Renuka Sharma 1 & Dr. Kiran Mehta 2 Abstract The investment made by FIIs in any capital market has grabbed the attention of researchers to identify
FOREIGN INSTITUTIONAL INVESTORS AND INDIAN STOCK MARKET Dr Renuka Sharma 1 & Dr. Kiran Mehta 2 Abstract The investment made by FIIs in any capital market has grabbed the attention of researchers to identify
SERVICES OFFERED BY PUBLIC AND PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS - CUSTOMERS AWARENESS IN TIRUPUR DISTRICT
 SERVICES OFFERED BY PUBLIC AND PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS - CUSTOMERS AWARENESS IN TIRUPUR DISTRICT V.Dhavamani, Research Scholar, PG and Research Department of commerce, Government Arts College, Udumalpet.
SERVICES OFFERED BY PUBLIC AND PRIVATE SECTOR BANKS - CUSTOMERS AWARENESS IN TIRUPUR DISTRICT V.Dhavamani, Research Scholar, PG and Research Department of commerce, Government Arts College, Udumalpet.
The impact of exchange rate fluctuation on NIFTY 50 with special reference to Dollar, Euro and British Pound
 DOI : 10.18843/ijms/v5i4(6)/17 DOIURL :http://dx.doi.org/10.18843/ijms/v5i4(6)/17 The impact of exchange rate fluctuation on NIFTY 50 with special reference to Dollar, Euro and British Pound Mr. Jibumon
DOI : 10.18843/ijms/v5i4(6)/17 DOIURL :http://dx.doi.org/10.18843/ijms/v5i4(6)/17 The impact of exchange rate fluctuation on NIFTY 50 with special reference to Dollar, Euro and British Pound Mr. Jibumon
Financial Framework in India
 Financial Framework in India For Finance related courses and CSE Main Optional Paper on Finance 10x10 Learning TM 1 10x10 Learning TM 2 Laws applicable to the Financial Sector : Act = 15. Rules = 10. Regulations
Financial Framework in India For Finance related courses and CSE Main Optional Paper on Finance 10x10 Learning TM 1 10x10 Learning TM 2 Laws applicable to the Financial Sector : Act = 15. Rules = 10. Regulations
Investing in Equities (BASIC GUIDE)
 Investing in Equities (BASIC GUIDE) Q. What is meant by Investing and how is it different from Savings? Ans. 'Investing' means building up to meet future consumption demand with the intention of making
Investing in Equities (BASIC GUIDE) Q. What is meant by Investing and how is it different from Savings? Ans. 'Investing' means building up to meet future consumption demand with the intention of making
Patterns in Trading Volume of Different Derivative Instruments in Indian Stock Market A Study with Reference to NSE & BSE
 International Journal of Accounting & Business Management Vol. 2 (No.1), April, 2014 Page: 103-111 ISSN: 2289-4519 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
International Journal of Accounting & Business Management Vol. 2 (No.1), April, 2014 Page: 103-111 ISSN: 2289-4519 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market. Manendra Singh*
 Article 222 KNOWLEDGE RESOURCE [Vol. 38 An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market Manendra Singh* The growth of financial sector in India at present is
Article 222 KNOWLEDGE RESOURCE [Vol. 38 An Overview of Financial Services Sector in India: A Huge Untapped Potential in the Market Manendra Singh* The growth of financial sector in India at present is
Rolling Settlement in Stock Exchange
 Rolling Settlement in Stock Exchange INTRODUCTION This article aims to understand the concept of rolling settlement in stock exchanges in some depth. It aims to focus on the following aspects- Meaning,
Rolling Settlement in Stock Exchange INTRODUCTION This article aims to understand the concept of rolling settlement in stock exchanges in some depth. It aims to focus on the following aspects- Meaning,
CONTENTS. Procedure and Conditions for listing of securities on WDM 7. Criteria for listing on the WDM segment 8
 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1 2. Exchange Operations 3 Capital Market Segment 3 Futures & Options Segment 3 Wholesale Debt Market Segment 4 3. Listing Of Securities on WDM Segment 7 Procedure and Conditions
CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1 2. Exchange Operations 3 Capital Market Segment 3 Futures & Options Segment 3 Wholesale Debt Market Segment 4 3. Listing Of Securities on WDM Segment 7 Procedure and Conditions
International Journal of Management (IJM), ISSN (Print), ISSN (Online) Volume 1, Number 2, July - Aug (2010), IAEME
 International Journal of Management (IJM), ISSN 0976 6502(Print), ISSN 0976 6510(Online) Volume 1, Number 2, July - Aug (2010), pp. 98-105 IAEME, http://www.iaeme.com/ijm.html IJM International Journal
International Journal of Management (IJM), ISSN 0976 6502(Print), ISSN 0976 6510(Online) Volume 1, Number 2, July - Aug (2010), pp. 98-105 IAEME, http://www.iaeme.com/ijm.html IJM International Journal
SKYBRIDGE DIVIDEND VALUE FUND OF FUNDVANTAGE TRUST STATEMENT OF ADDITIONAL INFORMATION. September 1, 2014
 SKYBRIDGE DIVIDEND VALUE FUND Class A Class C Class I SKYAX SKYCX SKYIX OF FUNDVANTAGE TRUST STATEMENT OF ADDITIONAL INFORMATION September 1, 2014 This Statement of Additional Information ( SAI ) provides
SKYBRIDGE DIVIDEND VALUE FUND Class A Class C Class I SKYAX SKYCX SKYIX OF FUNDVANTAGE TRUST STATEMENT OF ADDITIONAL INFORMATION September 1, 2014 This Statement of Additional Information ( SAI ) provides
Impact of Foreign Institutional Investors on Economic Growth
 Volume-6, Issue-3, May-June 2016 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 418-427 Impact of Foreign Institutional Investors on Economic Growth 1,2 Dr. Satendra Kumar Yadav
Volume-6, Issue-3, May-June 2016 International Journal of Engineering and Management Research Page Number: 418-427 Impact of Foreign Institutional Investors on Economic Growth 1,2 Dr. Satendra Kumar Yadav
Question 1. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 Question 1 PAPER 2 : STRATEGIC FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. Wherever appropriate, suitable assumption should be made by the candidates. (a) XY
Question 1 PAPER 2 : STRATEGIC FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Answer all questions. Working notes should form part of the answer. Wherever appropriate, suitable assumption should be made by the candidates. (a) XY
The Analysis of the Initial and Post Issue Performance of Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) in Indian Stock Market
 The Analysis of the Initial and Post Issue Performance of Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) in Indian Stock Market ar nh,ukfyfll vkwiq nh bfuf'k;y,.m ikslv b';q ijiqksjesal vkwiq bfuf'k;y ifcyd vkwiqfjaxl
The Analysis of the Initial and Post Issue Performance of Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) in Indian Stock Market ar nh,ukfyfll vkwiq nh bfuf'k;y,.m ikslv b';q ijiqksjesal vkwiq bfuf'k;y ifcyd vkwiqfjaxl
AN EVALUATING STUDY OF INDIAN STOCK MARKET SCENARIO WITH REFERENCE TO ITS GROWTH AND INCEPTION TREND ATTEMPTED BY INDIAN INVESTORS: RELATION WITH LPG
 AN EVALUATING STUDY OF INDIAN STOCK MARKET SCENARIO WITH REFERENCE TO ITS GROWTH AND INCEPTION TREND ATTEMPTED BY INDIAN INVESTORS: RELATION WITH LPG MADHVI ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, S.D INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT
AN EVALUATING STUDY OF INDIAN STOCK MARKET SCENARIO WITH REFERENCE TO ITS GROWTH AND INCEPTION TREND ATTEMPTED BY INDIAN INVESTORS: RELATION WITH LPG MADHVI ASSISTANT PROFESSOR, S.D INSTITUTE OF MANAGEMENT
ANSWER KEY C F.Y.B. Com. (FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT) (CHOICE BASE) SEMESTER - I / C Indian Financial System
 ANSWER KEY-00135 C0921 - F.Y.B. Com. (FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT) (CHOICE BASE) SEMESTER - I / C0584 - Indian Financial System Q1) a) Answer whether the below statements are True or False: (Attempt any 8) (8
ANSWER KEY-00135 C0921 - F.Y.B. Com. (FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT) (CHOICE BASE) SEMESTER - I / C0584 - Indian Financial System Q1) a) Answer whether the below statements are True or False: (Attempt any 8) (8
A monthly publication from South Indian Bank. To kindle interest in economic affairs... To empower the student community...
 To kindle interest in economic affairs... To empower the student community... Open YAccess www.sib.co.in ho2099@sib.co.in A monthly publication from South Indian Bank SIB STUDENTS ECONOMIC FORUM Experience
To kindle interest in economic affairs... To empower the student community... Open YAccess www.sib.co.in ho2099@sib.co.in A monthly publication from South Indian Bank SIB STUDENTS ECONOMIC FORUM Experience
INVESTORS AWARENESS ON MUTUAL FUNDS SERVICES IN COIMBATORE DISTRICT
 Journal of INVESTORS Asian Business AWARENESS Management ON MUTUAL FUNDS SERVICES IN COIMBATORE DISTRICT / 1 Vol. 3, No. 1, January-June 2011: 1-12 INVESTORS AWARENESS ON MUTUAL FUNDS SERVICES IN COIMBATORE
Journal of INVESTORS Asian Business AWARENESS Management ON MUTUAL FUNDS SERVICES IN COIMBATORE DISTRICT / 1 Vol. 3, No. 1, January-June 2011: 1-12 INVESTORS AWARENESS ON MUTUAL FUNDS SERVICES IN COIMBATORE
A Study on Trend Performance of Foreign Banks operating in India
 A Study on Trend Performance of Foreign Banks operating in India M.Kirthika Assistant Professor PSGR Krishnammal for Women Coimbatore Tamil Nadu South India S.Nirmala Associate Professor PSGR Krishnammal
A Study on Trend Performance of Foreign Banks operating in India M.Kirthika Assistant Professor PSGR Krishnammal for Women Coimbatore Tamil Nadu South India S.Nirmala Associate Professor PSGR Krishnammal
GOLD PRICE MOVEMENTS IN INDIA AND GLOBAL MARKET
 53 GOLD PRICE MOVEMENTS IN INDIA AND GLOBAL MARKET Shaik Saleem, Research Scholar, Department of Management Studies, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India. Dr. M. Srinivasa Reddy,
53 GOLD PRICE MOVEMENTS IN INDIA AND GLOBAL MARKET Shaik Saleem, Research Scholar, Department of Management Studies, Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India. Dr. M. Srinivasa Reddy,
Progress of Dematerialization of Securites in Depository System
 Progress of Dematerialization of Securites in Depository System Dr. Rajnikant Kumar Lutabarh, Ramnagar, Nainital, Uttarakhand. rajnikant201@gmail.com Abstract - Dematerialization is the process by which
Progress of Dematerialization of Securites in Depository System Dr. Rajnikant Kumar Lutabarh, Ramnagar, Nainital, Uttarakhand. rajnikant201@gmail.com Abstract - Dematerialization is the process by which
Indian Stock Exchanges & Foreign Institutional Investor, healthy Indicators for Indian economy
 Indian Stock Exchanges & Foreign Institutional Investor, healthy Indicators for Indian economy Dr. Kamlesh S. Dave Associate Professor : Commerce Shri J. H. Bhalodia Women s College, Saurashtra University
Indian Stock Exchanges & Foreign Institutional Investor, healthy Indicators for Indian economy Dr. Kamlesh S. Dave Associate Professor : Commerce Shri J. H. Bhalodia Women s College, Saurashtra University
SALIENT FEATURES OF SEBI (FOREIGN PORTFOLIO INVESTORS) REGULATIONS, 2014
 SALIENT FEATURES OF SEBI (FOREIGN PORTFOLIO INVESTORS) REGULATIONS, 2014 The Securities and Exchange Board of India has made regulations to put in place a framework for registration and procedures with
SALIENT FEATURES OF SEBI (FOREIGN PORTFOLIO INVESTORS) REGULATIONS, 2014 The Securities and Exchange Board of India has made regulations to put in place a framework for registration and procedures with
A STUDY OF MUTUAL FUNDS
 International Journal of Management (IJM) Volume 8, Issue 3, May June 2017, pp.213 219, Article ID: IJM_08_03_024 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?jtype=ijm&vtype=8&itype=3 Journal
International Journal of Management (IJM) Volume 8, Issue 3, May June 2017, pp.213 219, Article ID: IJM_08_03_024 Available online at http://www.iaeme.com/ijm/issues.asp?jtype=ijm&vtype=8&itype=3 Journal
A STUDY OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE: A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF STATE BANK OF INDIA AND ICICI BANK
 A STUDY OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE: A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF STATE BANK OF INDIA AND BANK Chahat Gupta, Assistant Professor, G.G.S. College for Women, Chandigarh, India Amandeep Kaur, Assistant Professor,
A STUDY OF FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE: A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF STATE BANK OF INDIA AND BANK Chahat Gupta, Assistant Professor, G.G.S. College for Women, Chandigarh, India Amandeep Kaur, Assistant Professor,
SME Access to Market Based Finance
 SME Access to Market Based Finance BSE- Exchange with Maximum Listed Companies Worldwide Historic brand and an iconic listing franchise Key highlights n Oldest stock exchange in Asia, established in 1875
SME Access to Market Based Finance BSE- Exchange with Maximum Listed Companies Worldwide Historic brand and an iconic listing franchise Key highlights n Oldest stock exchange in Asia, established in 1875
CHAPTER V FOREIGN INVESTMENT AND EXTERNAL COMMERCIAL BORROWING
 CHAPTER V FOREIGN INVESTMENT AND EXTERNAL COMMERCIAL BORROWING Chapter V is conveniently divided into four sections. Section A deals with foreign investment. Foreign investment comprises of two components
CHAPTER V FOREIGN INVESTMENT AND EXTERNAL COMMERCIAL BORROWING Chapter V is conveniently divided into four sections. Section A deals with foreign investment. Foreign investment comprises of two components
PERFORMANCE OF IDBI BANK WITH REFERENCE TO NON PERFORMING ASSETS
 PERFORMANCE OF IDBI BANK WITH REFERENCE TO NON PERFORMING ASSETS R.Navaneethakrishnasamy & M.Sharmila devi Ph.D. Research Scholar (Part-time), P.G and Research Department of Commerce, Sri S.R.N.M. College,
PERFORMANCE OF IDBI BANK WITH REFERENCE TO NON PERFORMING ASSETS R.Navaneethakrishnasamy & M.Sharmila devi Ph.D. Research Scholar (Part-time), P.G and Research Department of Commerce, Sri S.R.N.M. College,
Chapter 5. Conclusions, Findings and Suggestions
 Chapter 5 Conclusions, Findings and Suggestions 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Findings 5.3 Suggestions 5.4 Scope for Further Research 5.1 Introduction This chapter brings out major findings including problems and
Chapter 5 Conclusions, Findings and Suggestions 5.1 Introduction 5.2 Findings 5.3 Suggestions 5.4 Scope for Further Research 5.1 Introduction This chapter brings out major findings including problems and
A STUDY ON CO-INTEGRATION BETWEEN CNX NIFTY AND SECTROAL INDICES OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE
 Available online at: http://euroasiapub.org/current.php?title=ijrfm ISSN(o): 2231-5985 Impact Factor: 6.397 A STUDY ON CO-INTEGRATION BETWEEN CNX NIFTY AND SECTROAL INDICES OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE K.
Available online at: http://euroasiapub.org/current.php?title=ijrfm ISSN(o): 2231-5985 Impact Factor: 6.397 A STUDY ON CO-INTEGRATION BETWEEN CNX NIFTY AND SECTROAL INDICES OF NATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE K.
