There are three methods for supplying funds under FILP: Fiscal Loan, Industrial Investment and Government Guarantee.
|
|
|
- Adelia Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
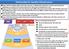
1 Outline of Fiscal Investment 4 FILP REPORT 2016Ⅰ2. Mechanism of FILP 3 FILP Methods There are three methods for supplying funds under FILP: Fiscal Loan, Industrial Investment and Government Guarantee. Fiscal Loan The Fiscal Loan utilizes the Fiscal Loan Fund consisting of funds procured through the issuance of FILP bonds and reserves or surplus funds deposited from government special accounts to provide long-term, fixed and low-interest loans to such entities as special government accounts, local governments, government-affiliated agencies, incorporated administrative agencies, The Fiscal Loan Fund is accounted for in the Fiscal Loan Fund Account of the FILP Special Account. Because Article 1 of the Fiscal Loan Fund Act requires Fiscal Loan Fund management to be secure and efficient, Article 10 of the Act limits Fiscal Loan Fund targets to national and local governments, government affiliated agencies, to secure the safety and publicity of the funds. Industrial Investment The Industrial Investment is the investment (mainly capital subscription) for industrial development and trade promotion, using such funds as national treasury payments by the Japan Bank for International Cooperation and dividends from NTT and JT shares which the Investment Account of the FILP Special Account hold. The Industrial Investment is accounted for in the Investment Account of the FILP Special Account. Fiscal Loan and Industrial Investment Market NTT, JT, FILP Bonds Interest bearing debt Redemption Dividends, Past investment returns, Fiscal Loan Fund FILP Special Account Fiscal Loan Account Industrial Investment FILP Special Account Investment Account In contrast to the Fiscal Loan, which entails fixed interest, the Industrial Investment provides funds for essential policy projects that have potential returns but cannot be funded sufficiently by the private sector alone because of their high risks. Government Guarantee The Government Guarantee is the guarantee provided by the government for bonds issued in financial markets by and loans to agencies (e.g. government-affiliated agencies, incorporated administrative agencies). With the Government Guarantee, FILP Agencies can procure funds necessary for business in a smooth and efficient way. Given that government-guaranteed bonds represent debt off the government s balance sheet and that the FILP reform has introduced loans from the Fiscal Loan Fund raised through FILP bonds (carrying lower interest than governmentguaranteed bonds), the government has been trying to reduce government-guaranteed bond issues as far as possible. Based on The FILP: its challenges and future perspective (see P18), the government recently continues to strictly screen individual Government Guarantee requests and implements them according to fund demand. Loan Collection Fixed interest loan Capital Subscription Capital Subscription including loans Return Secure & efficient (Fiscal Loan Fund Act, Article 1) Project with strong policy necessity, and redemption certainty Long-term funds, at fixed, low-interest rates Risk Money Project - with strong policy necessity - with promising return - not sufficient funds by the private sector alone due to high risks
2 COLUMN Utilizing Industrial Investment 1. Role of Industrial Investment In fields where there is high public interest but the private sector, even with expected long-term return, cannot provide sufficient funds because of high risks, FILP provides Industrial Investment as long-term risk money (equity or mezzanine finance) to induce private sector finance. This means that the government provides qualitative complements to private sector finance by taking risks the private sector cannot take, under an appropriate public-private risk sharing system. While private sector financial institutions provide primarily short- to medium-term (up-to-five-year) investment and are urged by their shareholders to secure short-term profits, Industrial Investment is available over a long time until the achievement of earnings. Therefore, Industrial Investment plays a key role in complementing the private sector investment market. In forming investment schemes and implementing investment, the government collaborates or cooperates with private enterprises and funds to make maximum use of private capitals. 2. Target Fields of Industrial Investment Industrial Investment has been provided to agencies (e.g. government-affiliated financial institutions, incorporated administrative agencies) to enhance their financial bases for providing capital funds and supporting projects required for policy objectives. In recent years, Industrial Investment has been made through public-private funds to provide longterm risk money as a catalyst to induce private capitals (public-private funds are described on P6). Particularly in fields such as research and development, and ventures, Industrial Investment must be utilized basically for private sector human resources and know-how to build new public-private partnerships led by the private Linking Interest Rates to Business Performances * Interest may be paid in full after a 10-year period. Interest on business may performance vary depending ( in the 10-year period ) 10 years Bullet repayment upon 10-year maturity Interest Principal sector. For this purpose, Innovation Network Corporation of Japan was created in FY2009. Later, in response to the government s growth strategy, Industrial Investment targets were broadened to cover collaboration among the primary, secondary and tertiary industries, the Cool Japan strategy and infrastructure development under the PFI (private finance initiative) and support for overseas development of infrastructure system. Meanwhile, investment in research and development corporations has been substantially reduced (to zero since FY 2014) as relevant projects at these corporations have been abolished with no adoption of new projects under the Basic Policy for Reforming Clerical Work and Projects at Incorporated Administrative Agencies (Cabinet Decision, December 7, 2010). 3. Role and Feature of Industrial Investment Capital Subscription and Loans Industrial Investment, unlike Fiscal Loan, provides mainly equity finance for high-risk projects. Recently, it has served as a source for mezzanine finance (loans with interest rates linked to borrowers performance), providing loans specially and limitedly in addition to equity finance. Industrial Investment loans can deal with long-term, bullet repayment loans with interest linked to business performance, which the Fiscal Loan cannot, and are used for Japan Finance Corporation and other organizations that handle mezzanine finance including subordinated loans. (Reference) Organizations subject to Industrial Investment loans (Initial FY2016 FILP Plan ) Japan Finance Corporation (Small and Medium Enterprise Unit): Subordinated capital loans (responding to earthquake disasters) Agriculture, forestry and fisheries Fund corporation for Innovation, Value-chain and Expansion Japan: Subordinated capital loans The Shoko Chukin Bank, Ltd. : Global niche top supply loan system, Effects of Subordinated Capital Loans Assets Resolving excessive debt [Assets>Debts] New loans are available Debts Subordinated capital loans Capital Treated as quasi-capital FILP REPORT ⅠOutline of Fiscal Investment
3 Outline of Fiscal Investment 6 FILP REPORT 2016ⅠCOLUMN Providing Risk Money through Public-Private Funds 1. What Are Public-Private Funds? While risk money provision from private sector funds has been insufficient in Japan, public-private funds, based on a principle of supplementing private business, induce private sector investment (pump-priming effect) by taking risks that are difficult for private sectors to take. Funds provision is Overview of Public-Private Funds (Targets of Industrial Investment) Institution Innovation Network Corporation of Japan (INCJ) Regional Economy Vitalization Corporation of Japan (REVIC) * Investment through Deposit Insurance Corporation of Japan Agriculture, forestry and fisheries Fund corporation for Innovation, Value-chain and Expansion Japan (A-FIVE) Private Finance Initiative Promotion Corporation of Japan Cool Japan Fund Inc. Fund for Japanese Industrial Competitiveness (Development Bank of Japan (DBJ)) Special Investment Operations (Development Bank of Japan (DBJ)) Japan Overseas Infrastructure Investment Corporation for Transport & Urban Development (JOIN) Fund Corporation for the Overseas Development of Japan's ICT and Postal Services Inc. (JICT) (Note) The figures are rounded. Public-Private Fund Scheme National government General account investment/ Industrial Investment Capital subscription ( ) Date of Establishment (Lifetime) July 2009 (15 years) March 2013 (10 years) January 2013 (20 years) October 2013 (15 years) November 2013 (20 years) March 2013 (About 10 years) June 2015 (10 years) October 2014 (-) November 2015 (20 years) Private sector Public-private fund Investment, Purpose of Establishment Invest in progressive projects in order to promote the creation of nextgeneration businesses through open innovation Support business turnaround for the selection, concentration and realignment of business operations, and back up new business startups, switches and local vitalization projects Support companies co-funded by one in agriculture, forestry, and fisheries and others in different industries, practicing collaboration among the primary, secondary and tertiary industries in order to develop aggressive agriculture, forestry and fisheries Industry Foster infrastructure investment markets by promoting the introduction of private sector funds for PFI projects that collect funds from usage charge income Invest and participate in Japan Mall and other projects for commercializing Japanese attractions to promote the overseas expansion of Cool Japan Promote creation of new businesses, from cooperation between different industries and by utilizing latent technology in corporations Investment, Pump-priming effect limited only for such policy objectives as the realization of the government s growth strategy, the revitalization of local economies, and the creation of new industries and markets. Those funds aim to realize economic growth led by the private sector. Promote financing by private financial institutions and support enterprises proactive growth initiatives in order to enhance their competitiveness and vitalize local economies Invest and participate in high-speed railway construction and other overseas projects in order to promote transportation and urban infrastructure exports Invest and participate in terrestrial digital broadcasting network development and other overseas projects in order to promote the overseas expansion of telecommunications, broadcasting and postal projects Investment, Sub-fund Private sector *Case for using sub-funds Pump-priming effect Investment, Investment, Industrial Investment (At the end of March 2016) 286 billion yen 13 billion yen * General account investment: 3 billion yen 30 billion yen 10 billion yen 41.6 billion yen 100 billion yen (loans) 65 billion yen 15.0 billion yen 1.9 billion yen Private sector Investment target companies Private sector investment (At the end of March 2016) 14 billion yen 10.1 billion yen 1.8 billion yen 10 billion yen 10.7 billion yen 50 billion yen *Proprietary DBJ funds 65 billion yen *Proprietary DBJ funds 5.9 billion yen 1.9 billion yen Investment,
4 2. Public-Private Fund Guideline The government should, not only create public-private funds, but also assess and verify operations of the fund and take relevant measures to allow the fund to be managed for policy objectives regarding the growth of the Japanese economy. In September 2013, the government held a ministerial meeting on the promotion of the utilization of publicprivate funds (organized by the Chief Cabinet Secretary) to enhance cooperation between relevant administrative Organizational Requirements for Public-Private Funds (from Public-Private Fund Guideline) Function: Monitoring and checking key investment decisions Requirements: Independence, expertise Auditors, advisory boards, Function: Monitoring and checking conventional (see Note) investment decisions Requirements: Independence, expertise Auditors, outside directors, advisory boards, : Internal organization : Checking function : Auditors, advisory boards, put in orders and clarify auditing functions based on law and regulations, and outside experts and others advisory functions complementing auditing functions (advisory boards, ) and implement monitoring and checking according to their respective authorities and responsibilities. (Note) Including key decisions (such as judgments on conflict of interest), portfolio management and decisions to refer particularly important investment deals to higher-level decisions 3. Verifying Public-Private Funds T he Public-Private Fund Guideline calls on the government to assess and verify operations of a publicprivate sector fund and take relevant measures to allow the fund to be managed for policy objectives. An executive panel for a ministerial conference on the promotion of publicprivate sector funds has been set up for the verification in line with the Public-Private Fund Guideline, comprising officials from relevant government agencies and experts. The panel is scheduled to continue the periodic verification. Candidate investment deals agencies to verify the operations of public-private funds with a view to promoting their utilization. The government then decided and released a guideline for operations of publicprivate funds (hereinafter referred to as Public-Private Fund Guideline), which covered operations (policy objectives, complementing private business, ), investment setup and decision-making process, portfolio management, roles of private sector investors, and relations between the government, as supervisor and investor, and each fund. Function: Making key investment decisions Requirements: Expertise, independence, neutrality (full-time and outside directors (including those experienced in business administration), ) Key decisions (including judgments on conflict of interest), portfolio management, particularly important investment deals (see Note) Function: Making conventional investment decisions Requirements: full-time operations, short-cycle (weekly, ) meetings All investment deals Function: Exploring investment deals, implementing due diligence Requirements: Full-time operations, human resources development viewpoints Competent divisions, Based on September-end and March-end results, the panel compiled the first verification report in May 2014, the second in November 2014, the third in July 2015, the fourth in December 2015, and the fifth in June The report verifies how public-private funds are used, trends of the key performance indicator (KPI) set for each fund, collaboration between public-private funds, monitoring after investment decisions and portfolio management, FILP REPORT ⅠOutline of Fiscal Investment
5 Outline of Fiscal Investment 8 FILP REPORT 2016ⅠHistory of Fiscal Loan The history of the Fiscal Loan Fund dates back to the beginning of the Meiji Era. Since private financial institutions were not well developed in those days, various funds were amassed at the government. Initially, the government mainly took custody of funds, but later began accepting deposits (postal savings) and started investing the funds in government bonds. In accordance with the increase of postal savings, the government gradually began using the funds for investment in domestic industry and government-backed entities. Some of them, however, became irrecoverable. History of Fiscal Loan (Outline) Chronological table of Fiscal Loan Early Meiji Era Reserve Funds Handling Bylaws 1885 Deposit regulation Mid-late Meiji Era to Taisho Era 1925 Deposits Section Deposit Act Around WWII 1946 Under U.S. occupation Laws concerning Special Treatment of Losses incurred by Deposit Section of the Ministry of Finance, 1951 Trust Fund Bureau Fund Act Revision of Trust Fund Bureau Fund Act 2001 Fiscal Loan Fund Act Miscellaneous incomes other than tax incomes accumulated as savings and later as reserves. Deposits of funds to the Government Bond Bureau of the Ministry of Finance, which was also responsible for their management. Postal Savings deposited with the Government Bond Bureau for management. Depositing funds to Ministry of Finance was legalized and the Deposits Section was set up. Initially, the Ministry focused on custody business rather than investments. Investments by the Deposits Section shifted from government bonds to bonds issued by industrial banks and special-purpose banks. In the early Taisho Era, some loans became irrecoverable, like the Nishihara Loan (note). Improvement of the Deposits Section system became necessary in order to ensure proper custody and management of funds. Basic principles of management in secure and efficient ways and for the benefit of the state and public were clarified. Deposits Section Fund Management Committee was established. With the country placed on a war footing, investment of funds gradually shifted to state-backed entities and war industries, and focused on China. As a result, the investments resulted in a huge loss. Liquidation of assets and liabilities of the Deposits Section. GHQ ordered that recipient of the Deposits Section funds should basically be limited to the state and local governments. For post-war restoration, demand for long-term funds arose from industrial circles. Unified management of state funds Contribution to the promotion of public interest Investment of funds in secure and efficient ways The Act on Special Measures on the long-term management of the Trust Fund Bureau Fund and Postal Life Insurance Reserve was enforced. Development of interest deregulation and other changes in the economic and financial environment. The legal system for interest rates on deposits was amended and entrusted to government decree Foreign government bonds were added as targets for asset management of Trust Fund Bureau Fund Reflecting changes in environment, the focus of policies shifted from industry to living environment. Elimination of the requirement that all Postal Savings and Pension Reserves be deposited with the Trust Fund Bureau (FILP reform) Introduction of policy cost analysis Enhanced information disclosure Market-based fundraising (Note) Nishihara Loan is a series of loans extended to China in Some of the funds were financed from the Deposits Section but became irrecoverable. The state took over the irrecoverable principal and interest payments. In order to ensure that the Trust Fund Bureau Fund (predecessor of the Fiscal Loan Fund) is managed securely and efficiently, the recipients of FILP financing were limited by the law to the government (the General Account and Special Accounts), local governments, and their wholly owned corporations, Under the current Fiscal Loan Fund, a similar idea is followed.
6 FILP Reform A fundamental reform was undertaken of the FILP system was overhauled to eliminate mandatory deposits of postal (the FILP Reform) in FY2001. savings and pension reserves to the Trust Fund Bureau, Prior to this reform, it was mandatory to deposit the funds allowing for the independent investment (in the market in from postal savings and pension reserves to the Trust Fund principle) of the entire deposits. Funds required for FILP were Bureau Fund, which was the main means of raising capital converted to raise from the market through the issuance of for FILP. It can be addressed that FILP, using postal savings FILP bonds, enabling efficient fundraising to meet demand. and pension reserves, has contributed to the economic Moreover, FILP-target projects performed by FILP agencies development in Japan as a fiscal policy tool to use domestic were reviewed from the viewpoint of supplementing private savings efficiently to develop social capital. As the FILP business. FILP agencies were also allowed to issue FILP size grew enormously with financial resources collected agency bonds to independently raise funds required for their irrespective of actual demand for policy-requirement, however, projects. problems including the lack of efficient management were In addition, the policy cost analysis was introduced. The pointed out. analysis clarifies policy costs (including prospective subsidies, In response, the FILP Reform was undertaken to make opportunity costs of investments) to enrich information on the FILP more efficient and consistent with market principles. reasonability of FILP-target projects and the fiscal soundness Under the reform, firstly, the fundraising mechanism of FILP of FILP agencies from the viewpoint of FILP disclosure. Image of the FILP Reform Old FILP FILP Reform in FY2001 New FILP FILP agency bonds (self procurement) Postal savings Aggregate Scrutiny of FILP procurement required amount Trust FILP Financial FILP Fund agencies markets agencies Deposit ( ) Bureau Loan FILP FILP Loan interest rate Pension (government) reserves bonds Government bonds interest Postal savings Pension reserves Deposit abolition Independent management of all deposits Obligation to deposit all postal savings and pension reserves was eliminated. Instead, these funds are to be managed independently in the financial markets. Main Points of Reform Only the necessary amount of funds is to be raised through the issuance of FILP bonds in light of thorough scrutiny of the redemption certainty and the supplementary function to the private sector. Elimination of the mandatory deposit of Loan interest rates are based on market rates of Japanese government bonds according to loan period. all postal savings and pension reserves, and introduction of market-based fundraising Policy cost analysis is to be introduced and enhanced. Introduction of policy cost analysis and FILP agencies are to issue FILP agency bonds. rigorous expansion of information disclosure Information disclosure is to be substantially expanded to ensure the discipline of special public corporations, Outline of Fiscal Investment
7 Outline of Fiscal Investment 10 FILP REPORT 2016ⅠCOLUMN Funding and Loan Interest Rates for Fiscal Loan Fund The Fiscal Loan Fund s major financial resources are FILP bonds and deposits. As FILP bonds are a kind of government bonds, they are identical in product-designs with ordinary government bonds and are issued indistinctively. Therefore, the Fiscal Loan Fund s fundraising rates are equivalent to those of ordinary government bonds. Moreover, the Minister of Finance is authorized to determine the interest rate on deposits from national special accounts reserves or surpluses, based on government bonds rates and deposit periods (the minimum rate is set at 0.01%). The Fiscal Loan Fund s fundraising rates are thus basically equivalent to those of government bonds. On the other hand, the Minister of Finance establishes loan interest rates, based on loan periods and market yields on government bonds, reflecting different redemption methods (equal principal repayment, equal principal and interest repayment, and bullet repayment) and deferment periods (periods during which only interest is paid without principal Comparing Lending Rates (fixed rates with no deferment period) before and after FILP Reform (%) ( ) Reference: Virtual interest rate based on the August 2016 issue Pre-reform lending rate +0.2% (Coupon on 10-year interest-bearing JGB) repayment after lending). Basically, loan interest rates are equal to interest rates on government bonds. The abovementioned method for setting interest rates was introduced in the FILP reform. Until then, interest rate on deposits were fixed by cabinet orders based on government bonds and other market interest rates and the situations of depositors stipulated in the revision of Trust Fund Bureau Fund Act in Actually, just before the FILP reform, the interest rate on deposits for 7 years or more was set at a level that was 0.2% higher than the coupon rate on the 10-year interest-bearing government bonds issued every month. On the other hand, the loan interest rate was fixed at the same level as the rate on deposits for 7 years or more, regardless of loan periods. The FILP reform abolished the preferential regulations for depositors and enabled deposit and loan interest rates to be based on government bond yields, achieving FILP s consistency with market principles. Post-reform lending rate (Bullet repayment) Post-reform lending rate (Equal principal and interest repayment ) Post-reform lending rate (Equal principal repayment ) Loan period (years) (Notes) 1. The pre-reform lending rate is set at a level some 0.2% above a 10-year JGB coupon. 2. The post-reform lending rate is based on a JGB market interest rate (market yield), the loan period and the redemption method. 3. Based on a JGB market yield on August 3, 2016.
8 COLUMN Taking Advantage of Low-Interest Rates for Proactive Utilization of FILP Government bond yields fell under the quantitative and qualitative easing with negative interest rates that the Bank of Japan adopted on January 29, In February 2016, the yield of the latest 10-year JGB became negative for the first time in the history. As government bond yields sank to negative, some argued for proactive utilization of Fiscal Loans, mainly financed by FILP bonds, in order to prompt private investment. Following such arguments, the Basic Policy on Economic and Fiscal Management and Reform 2016 (Cabinet Decision, June 2, 2016) and the Japan s Plan for Dynamic Engagement of All Citizens (Cabinet Decision, June 2, 2016) stated, We will also deliberate means regarding facilitation of necessary investments by taking advantage of the current super-low Under this situation, the Economic Measures for Realizing Investment for the Future (Cabinet Decision, August 2, 2016) stated, By taking advantage of the current lowinterest situation, the government will proactively utilize/ wield the fiscal investment and loan techniques funded by FILP bonds. The measures called for proactive use of FILP to provide long-term, low-interest loans, which private financial institutions cannot handle sufficiently, for infrastructure construction. Specific measures in this regard include accelerating the opening of the entire Superconductive Maglev (Linear Chuo Shinkansen) and other projected Shinkansen, promoting railway continuous grade separations, supporting overseas infrastructure development and revising the minimum loan interest rate for FILP. interest rates. Reference Cases for Utilization of FILP under Economic Measures for Realizing Investment for the Future (Cabinet Decision, August 2, 2016) Accelerating investment for the future by taking advantage of the current low-interest situation to provide superlong-term loans for infrastructure development and by reviewing the lower limits for FILP loan interest rates Bringing forward the opening of the entire Superconductive Maglev (Linear Chuo Shinkansen) (Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency): about 3 trillion yen in 2 years A low-interest FILP loan will be provided through Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency to Central Japan Railway Co. (JR CENTRAL) to allow the company to launch the construction of the Nagoya-Osaka portion of the planned Superconductive Maglev (Linear Chuo Shinkansen) just after opening the Tokyo-Nagoya portion to bring forward the opening of the entire by Supporting overseas infrastructure development (Japan Bank for International Cooperation): about 200 billion yen (about 500 billion yen in 5 years) Supporting Japanese companies overseas expansion in efficient fossil fuel power plants and other fields where Japanese companies have high technological capabilities, based on the High-quality Infrastructure Export Expansion Initiative. * In addition, measures will be taken to enhance financial resources of Japan Overseas Infrastructure Investment Corporation for Transport and Urban Development (JOIN), up to eight years. Image for accelerating the plan Promoting railway continuous grade separations, (Development Bank of Japan): about 500 billion yen Opening Shinagawa- Launching Nagoya- Opening the entire line ( Nagoya portion ) Osaka portion construction /initial plan ( /initial plan ) ( ) Supporting railway continuous grade separations, platform screen Shinagawa-Nagoya Business recovery Nagoya-Osaka door installation, barrier-free environment development, and utility pole portion construction period portion construction removal, Current plan * As for a railway continuous grade separations project, a FILP loan will (1) cover a railway operator s cost (about 10%) and (2) support the relevant enhancement of railway functions and the development of nearby lands. Long-term, fixed, low-interest Development Bank of Japan Loan loan Bringing forward Railway continuous grade Railway the opening FILP separations and other initiatives operator, Acceleration by up to 8 years Other financial institutions, FILP loan 2037 Reviewing the lower limits for FILP loan interest rates * No principal repayment for years. Equal principal and interest repayment over later 10 years (0.1% 0.01%) Reviewing the lower limits for FILP loan interest rates to spread benefits Accelerating projected Shinakansen development (Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency): about 800 billion yen of the current low-interest environment. [Example] Interest-bearing scholarship loans The revision will be reflected in interest rates on interest-bearing scholarship loans Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency will use a low-interest FILP loan for constructing the projected Shinkansen (with either fixed or variable interest rates) Long-term, Loans with interest rates fixed, low-interest loan equal to FILP loan rate* to reduce its interest payment burden and accelerate Shinkansen Japan Student developments. FILP Scholarship Services students (Note) Planned schedule for opening Shinkansen lines under construction Organization Shinhakodatehokuto-Sapporo (about 211 km) : FY2030-end Kanazawa-Tsuruga (about 125 km) : FY2022-end Takeoonsen-Nagasaki (about 66 km) : FY2022 Repayment Repayment * Interest rates on interest-bearing scholarship loans are fixed upon graduation. * In addition to the above, Japan Finance Corporation and others will support financing for small and medium-sized enterprises, and for restoration and reconstruction from the Kumamoto Earthquake. Outline of Fiscal Investment
9 Outline of Fiscal Investment 12 FILP REPORT 2016ⅠCOLUMN Trends of the FILP Plan Scale Trends of the FILP Plan Scale The FILP reform in FY2001 repealed the mandatory deposition of postal savings and pension reserves and introduced the mechanism of issuing FILP bonds to actively raise funds from the market in principle for Fiscal Loans, which account for the majority of the FILP, focusing on and improving the efficiency of projects. Since then, the scale of the FILP Plan has been slimmed down. The following measures have been implemented to review FILP target projects: The Reorganization and Rationalization Plan for Special Public Corporations (Cabinet Decision, December 2001) has been implemented to review projects and organizations of 163 special public corporations (including 38 FILP agencies). In 2004, the FILP Subcommittee of the Fiscal System Council checked whether the implementation of FILP reflected the aim of the FILP reform, confirmed the progress of FILP agency projects reform under the Reorganization and Rationalization Plan for Special Transition (flow) in FILP Plan (Unit: trillion yen) September 2008 The Lehman Shock Initial plan Revised plan ( ) Revision with supplementary budgets and follow-up funding by the flexible management clause March 2011 The Great East Japan Earthquake (Fiscal year) FILP Reform starts (Notes) 1. On an initial plan basis. Data in parentheses between FY2008 and FY2015 are those revised through supplementation and elasticity. 2. Based on general FILP prior to FY2000. Transition (stock) in FILP Plan Balance Public Corporations and examined the political necessity and financial soundness of FILP projects. (As a result, the subcommittee compiled the Comprehensive Review of the FILP Reform in December 2004.) In 2005, the subcommittee followed up on whether measures cited in the Comprehensive Review were steadily implemented. (In December 2005, it put together the Follow-up to the Comprehensive Review of the FILP Reform. ) In recent years, the scale of FILP flows temporarily increased in flow-base when FILP responded to Japan s social and economic situation including the economic and financial crisis after the Lehman Shock in September 2008 and the Great East Japan Earthquake in March But the FILP balance in stock-base has continued decreasing. Under the FY2016 FILP Plan, the FILP flow scale is about one-third of the peak (FY1996), the smallest since the FILP reform in FY2001, and the FILP stock scale slips far below half of the peak (FY2000). (Unit: trillion yen) (End of fiscal year) (estimate) FILP Reform starts (Note) The actual figures through FY2015. The FY2016 balance is the estimated figure in the FY2015 Financial Results and may change in the future.
10 Response to Economic and Financial Crisis and the Great East Japan Earthquake The FILP Plan features flexible fund provision responding been proactively used to meet fund demand arising from the to the social and economic changes as it represents a fiscal economic and financial crisis after the Lehman Shock and policy not dependent on tax revenues as well as includes after the Great East Japan Earthquake. built-in measures to increase the planned Fiscal Loan amount FILP projects in this respect, for example, include support and the ceiling on government guarantee within a certain (Safety-Net Loans and Crisis Response Operations) for range every fiscal year, responding promptly and flexibly to cash-strapped enterprises, post-disaster restoration and changes in the economic and other conditions. FILP has reconstruction, and disaster prevention and reduction. Response to Economic and Financial Crisis after Lehman Shock Support measures Financial support for enterprises, Local government projects Others Support measures Safety-Net Loans for SMEs and micro business operators Crisis Response Operations Emergency operations to support Japanese overseas business activities Details To stabilize business performances of SMEs and micro enterprises, Japan Finance Corporation created a special loan system for reconstruction from the Great East Japan Earthquake and a special capital enhancement system for supporting post-disaster reconstruction (a subordinated capital loan system for disaster-affected SMEs) in a bid to take all possible measures to support cash flow for enterprises. To stabilize business performances of disaster-affected business operators, the government expanded crisis response loans (two-step loans) through the designated financial institutions (Development Bank of Japan Inc. and The Shoko Chukin Bank, Ltd.) to provide funds to meet demand. FILP has provided funds for emergent and quick-impact disaster prevention/reduction measures (e.g. seismic retrofitting of public school facilities, antitsunami measures for rivers, ) based on lessons learned from the Great East Japan Earthquake. FILP has provided funds for the reconstruction of housing and healthcare/welfare facilities damaged by the Great East Japan Earthquake. Urban Renaissance Agency/Disaster Reconstruction Project/Disaster Public Housing /Ishinomaki City, Miyagi Details Loans were made to SMEs and other firms that suffered temporary sales and profit drops due to social and other factors and were expected to recover over the medium to long term. Such loans provided between FY2008 and FY2010 totaled 11 trillion yen. After the Lehman Shock, even large enterprises had difficulties in raising funds as it became difficult for them to issue bonds. To address cash flow deterioration for enterprises in response to the government s economic measures, Development Bank of Japan Inc. and The Shoko Chukin Bank, Ltd. designated by the government for lending to private enterprises, provided crisis response loans. Crisis response loans from Development Bank of Japan Inc. totaled about 3.7 trillion yen, while those from The Shoko Chukin Bank, Ltd. aggregated about 4.8 trillion yen. In order to support overseas operations of Japanese enterprises, Japan Bank for International Cooperation provided about 2.5 trillion yen loans. FILP Response to the Great East Japan Earthquake Urban Renaissance Agency/Disaster Reconstruction Project/Disaster Public Housing /Kesennuma City, Miyagi FILP REPORT ⅠOutline of Fiscal Investment
Recent FILP Initiatives
 Ⅱ Recent FILP Initiatives Japan Oil, Gas and Metals Corporation/Overseas Development Liability Guarantee/Sierra Gorda Copper Mine/Chile Region II (Photo provided by Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd.) 1.
Ⅱ Recent FILP Initiatives Japan Oil, Gas and Metals Corporation/Overseas Development Liability Guarantee/Sierra Gorda Copper Mine/Chile Region II (Photo provided by Sumitomo Metal Mining Co., Ltd.) 1.
3 Debt Management Systems
 3 Debt Management Systems (1) System All the bonds issued to fund a shortfall in General Account and Special Accounts of the national budget are repaid through the Government Debt Consolidation Fund (GDCF).
3 Debt Management Systems (1) System All the bonds issued to fund a shortfall in General Account and Special Accounts of the national budget are repaid through the Government Debt Consolidation Fund (GDCF).
JFC JFC Activities
 9 JFC Activities Response to the Earthquake 10 Provision of Policy-based Financing 11 Working towards Improved Customer Service that Reflects Comprehensive Capabilities 13 Overview of Operations in and
9 JFC Activities Response to the Earthquake 10 Provision of Policy-based Financing 11 Working towards Improved Customer Service that Reflects Comprehensive Capabilities 13 Overview of Operations in and
 Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency (Incorporated Administrative Agency) (Construction Account) 1. Summary of operations implemented using FILP funds 2. Amount of lending under
Japan Railway Construction, Transport and Technology Agency (Incorporated Administrative Agency) (Construction Account) 1. Summary of operations implemented using FILP funds 2. Amount of lending under
Improving China s PPP Fund System with Reference of Japan s. Experience
 Improving China s PPP Fund System with Reference of Japan s Experience HU Bin, XING Yan National Institute of Finance & Development (NIFD) Abstract: Over recent years, China has created a large number
Improving China s PPP Fund System with Reference of Japan s Experience HU Bin, XING Yan National Institute of Finance & Development (NIFD) Abstract: Over recent years, China has created a large number
Policy 1-1-1: Initiatives aimed at achieving greater efficiency in public finance, etc. through prioritized allocations of budget
 Policy Goal 1-1: Improve the efficiency and quality of public finance through prioritized allocations of budget General outline of the goal The government is conducting numerous activities in a broad range
Policy Goal 1-1: Improve the efficiency and quality of public finance through prioritized allocations of budget General outline of the goal The government is conducting numerous activities in a broad range
Japan Expressway Holding and Debt Repayment Agency (Incorporated Administrative Agency)
 Japan Expressway Holding and Debt Repayment Agency (Incorporated Administrative Agency) http://www.jehdra.go.jp 1. Summary of operations implemented using FILP funds Japan Expressway Holding and Debt Repayment
Japan Expressway Holding and Debt Repayment Agency (Incorporated Administrative Agency) http://www.jehdra.go.jp 1. Summary of operations implemented using FILP funds Japan Expressway Holding and Debt Repayment
Framework of Debt Management. This part explains the fundamental framework of debt management.
 Framework of Debt Management This part explains the fundamental framework of debt management. Chapter 1 Government Bonds (JGBs) 1 Primary Market for Government Bonds JGBs are issued in various types, depending
Framework of Debt Management This part explains the fundamental framework of debt management. Chapter 1 Government Bonds (JGBs) 1 Primary Market for Government Bonds JGBs are issued in various types, depending
3. Outlines of Special Reports to the Diet and the Cabinet and Special Reports on audit requested by the Diet
 3. Outlines of Special Reports to the Diet and the Cabinet and Special Reports on audit requested by the Diet (1) Special Report to the Diet and the Cabinet The following six matters (23 cases) were reported
3. Outlines of Special Reports to the Diet and the Cabinet and Special Reports on audit requested by the Diet (1) Special Report to the Diet and the Cabinet The following six matters (23 cases) were reported
Deposit Insurance Premium Rates from the Medium- to Long-Term Perspective
 Deposit Insurance Premium Rates from the Medium- to Long-Term Perspective January 30, 2015 The Study Group on Deposit Insurance Premium Rates 1 I. Introduction Under the deposit insurance system of Japan,
Deposit Insurance Premium Rates from the Medium- to Long-Term Perspective January 30, 2015 The Study Group on Deposit Insurance Premium Rates 1 I. Introduction Under the deposit insurance system of Japan,
ANNUAL REPORT THE SHOKO CHUKIN BANK
 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 ANNUAL REPORT 2002 2003 2004 THE SHOKO CHUKIN BANK 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 ANNUAL REPORT 2002 2003 2004 THE SHOKO CHUKIN BANK 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
CONTENTS FACT BOOK 2014 Overview Ⅰ Economy and Market Trends Ⅱ Securities Industry Overview Statistical Data
 FACT BOOK 2014 Ⅰ Economy and Market Trends Overview 01 1 Economic Overview In 2013, the Japanese economy steadily improved, supported by Abenomics fiscal and monetary initiatives and other factors. The
FACT BOOK 2014 Ⅰ Economy and Market Trends Overview 01 1 Economic Overview In 2013, the Japanese economy steadily improved, supported by Abenomics fiscal and monetary initiatives and other factors. The
Comprehensive Immediate Policy Package
 Comprehensive Immediate Policy Package Easing Public Anxiety (Summary by the Cabinet Office) August 29, 2008 Joint Meeting of the Government and the Ruling Parties Council on the Comprehensive Immediate
Comprehensive Immediate Policy Package Easing Public Anxiety (Summary by the Cabinet Office) August 29, 2008 Joint Meeting of the Government and the Ruling Parties Council on the Comprehensive Immediate
Debt Management Systems
 3 Debt Management Systems (1) System Fig.2-17 Mechanism of General Account Transfer Fixed-rate transfer Special transfer on tax reduction-related Special Deficit-financing Bonds Transfer of budgetary surplus
3 Debt Management Systems (1) System Fig.2-17 Mechanism of General Account Transfer Fixed-rate transfer Special transfer on tax reduction-related Special Deficit-financing Bonds Transfer of budgetary surplus
Ministry of Finance.
 Japanese Public Finance Fact Sheet 2013 http://www.mof.go.jp/english/index.htm Ministry of Finance Table of Contents 1.General Account Budget for FY 2013 1 2.Highlight of the FY 2013 Budget 3 3.Comparison
Japanese Public Finance Fact Sheet 2013 http://www.mof.go.jp/english/index.htm Ministry of Finance Table of Contents 1.General Account Budget for FY 2013 1 2.Highlight of the FY 2013 Budget 3 3.Comparison
Rating Methodology for Local Public Bodies
 Last updated: June 1, 2017 Rating Methodology for Local Public Bodies In rating a local public body, JCR assesses each local public body s tax-bearing capacity, fiscal conditions, fiscal management, and
Last updated: June 1, 2017 Rating Methodology for Local Public Bodies In rating a local public body, JCR assesses each local public body s tax-bearing capacity, fiscal conditions, fiscal management, and
Continuation of Measures Against Large-Scale Purchases of Shares of the Company (Takeover Defense Measures)
 To Whom It May Concern [Translation] May 16, 2018 Hiroyuki Iwakuma, Representative Director and President Heiwa Real Estate Co., Ltd. 1-10, Nihonbashi Kabuto-cho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo (Code No. 8803) First Sections
To Whom It May Concern [Translation] May 16, 2018 Hiroyuki Iwakuma, Representative Director and President Heiwa Real Estate Co., Ltd. 1-10, Nihonbashi Kabuto-cho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo (Code No. 8803) First Sections
Summary of First-Quarter Business Results for the Financial Year Ending 31 March 2006 (Consolidated)
 Summary of First-Quarter Business Results for the Financial Year Ending 31 March 2006 (Consolidated) 28 July 2005 Listed company s name: Shinko Securities Co., Ltd. Listing stock exchanges: Tokyo, Osaka,
Summary of First-Quarter Business Results for the Financial Year Ending 31 March 2006 (Consolidated) 28 July 2005 Listed company s name: Shinko Securities Co., Ltd. Listing stock exchanges: Tokyo, Osaka,
25 January 2006 Summary of Third-Quarter Business Results for the Financial Year Ending 31 March 2006 (Consolidated)
 25 January 2006 Summary of Third-Quarter Business Results for the Financial Year Ending 31 March 2006 (Consolidated) Listed company s name: Shinko Securities Co., Ltd. Listing stock exchanges: Tokyo, Osaka,
25 January 2006 Summary of Third-Quarter Business Results for the Financial Year Ending 31 March 2006 (Consolidated) Listed company s name: Shinko Securities Co., Ltd. Listing stock exchanges: Tokyo, Osaka,
Highlights of the Budget for FY2011
 Provisional translation Highlights of the Budget for FY2011 December 2010 Ministry of Finance Outline of FY2011 Budget (General Account) 1) Steady implementation of the New Growth Strategy with focus on
Provisional translation Highlights of the Budget for FY2011 December 2010 Ministry of Finance Outline of FY2011 Budget (General Account) 1) Steady implementation of the New Growth Strategy with focus on
Policy Goal 1-1: Improve the efficiency and quality of public finance through prioritized allocations of budget.
 Goal 1-1: Improve the efficiency and quality of public finance through prioritized allocations of budget. Thinking behind the The government conducts many activities in a wide range of fields; these are
Goal 1-1: Improve the efficiency and quality of public finance through prioritized allocations of budget. Thinking behind the The government conducts many activities in a wide range of fields; these are
Program for Accelerating the Rebirth of Japan. - Promoting Recovery of Japan's economy and Reconstruction of the disaster-affected areas -
 Program for Accelerating the Rebirth of Japan - Promoting Recovery of Japan's economy and Reconstruction of the disaster-affected areas - Decided on by the Cabinet on November 30, 2012 I. Basic Concepts
Program for Accelerating the Rebirth of Japan - Promoting Recovery of Japan's economy and Reconstruction of the disaster-affected areas - Decided on by the Cabinet on November 30, 2012 I. Basic Concepts
Japan Securities Finance Co., Ltd.
 8511 Tokyo Stock Exchange First Section Analyst Nozomu Kunishige Index Summary----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8511 Tokyo Stock Exchange First Section Analyst Nozomu Kunishige Index Summary----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Basic Framework for Fiscal Consolidation: Medium-term Fiscal Plan
 Basic Framework for Fiscal Consolidation: Medium-term Fiscal Plan I. Basic Understanding August 8, 2013 Approved by the Cabinet A strong economy is a source of national strength. Without economic growth,
Basic Framework for Fiscal Consolidation: Medium-term Fiscal Plan I. Basic Understanding August 8, 2013 Approved by the Cabinet A strong economy is a source of national strength. Without economic growth,
ETIC decides to support Yamanishi Co., Ltd.
 ETIC decides to support Yamanishi Co., Ltd. February 9, 2012 Enterprise Turnaround Initiative Corporation of Japan The Enterprise Turnaround Initiative Corporation of Japan ( ETIC ) has decided to provide
ETIC decides to support Yamanishi Co., Ltd. February 9, 2012 Enterprise Turnaround Initiative Corporation of Japan The Enterprise Turnaround Initiative Corporation of Japan ( ETIC ) has decided to provide
Proposals for Post-Earthquake Reconstruction -- From the Standpoint of Financial Analysts --
 Proposals for Post-Earthquake Reconstruction -- From the Standpoint of Financial Analysts -- Summary Version 1 On June 17, 2011, the Securities Analysts Association of Japan (SAAJ) published proposals
Proposals for Post-Earthquake Reconstruction -- From the Standpoint of Financial Analysts -- Summary Version 1 On June 17, 2011, the Securities Analysts Association of Japan (SAAJ) published proposals
20,000,000,000 yen. Allotted by a third-party allotment method. Japan Industrial Solutions Fund I
 (Note) This document has been translated from the Japanese original for reference purposes only. In the event of any discrepancy between this translated document and the Japanese original, the original
(Note) This document has been translated from the Japanese original for reference purposes only. In the event of any discrepancy between this translated document and the Japanese original, the original
JFC Activities. 1 Responses to Economic Crisis 10 2 Efforts to Maximize Integration Effects. 3 Overview of Operations in FY2009,
 JFC Activities 2 JFC 21 1 Responses to Economic Crisis 1 2 Efforts to Maximize Integration Effects (Business-matching Service through Collaboration between Business Units) 13 3 Overview of Operations in
JFC Activities 2 JFC 21 1 Responses to Economic Crisis 1 2 Efforts to Maximize Integration Effects (Business-matching Service through Collaboration between Business Units) 13 3 Overview of Operations in
Partnership for Quality Infrastructure
 Partnership for Quality Infrastructure Japan will fully mobilize public and private resources, in collaboration with other countries and international organizations, to address the immense demand for infrastructure
Partnership for Quality Infrastructure Japan will fully mobilize public and private resources, in collaboration with other countries and international organizations, to address the immense demand for infrastructure
2. Deregulation and Liberalization of the Japanese Non-Life Insurance Market
 2. Deregulation and Liberalization of the Japanese Non-Life Insurance Market The Japanese non-life insurance market entered an epoch-making era with the new Insurance Business Law which took effect on
2. Deregulation and Liberalization of the Japanese Non-Life Insurance Market The Japanese non-life insurance market entered an epoch-making era with the new Insurance Business Law which took effect on
Japanese Public Finance Fact Sheet
 Japanese Public Finance Fact Sheet ー FY2010 Budget (Supplementary Data) ー 1. FY2010 General Account Budget 1 2. Highlights of the FY2010 Budget 3 3. Comparison of the Government Budget to a Household Budget
Japanese Public Finance Fact Sheet ー FY2010 Budget (Supplementary Data) ー 1. FY2010 General Account Budget 1 2. Highlights of the FY2010 Budget 3 3. Comparison of the Government Budget to a Household Budget
Lessons from Japan: How Abenomics Can Provide Solutions for Advanced Countries
 Lessons from Japan: How Abenomics Can Provide Solutions for Advanced Countries Yasushi Kinoshita Former Administrative Vice Minister, Ministry of Finance, Japan Visiting Fellow, Center on Japanese Economy
Lessons from Japan: How Abenomics Can Provide Solutions for Advanced Countries Yasushi Kinoshita Former Administrative Vice Minister, Ministry of Finance, Japan Visiting Fellow, Center on Japanese Economy
Financial and Corporate Information
 Financial and Corporate Information 32 Five-Year Summary (Consolidated) 33 Management s Discussion and Analysis 34 Asset Quality 36 Consolidated Balance Sheet 37 Consolidated Statement of Income 37 Consolidated
Financial and Corporate Information 32 Five-Year Summary (Consolidated) 33 Management s Discussion and Analysis 34 Asset Quality 36 Consolidated Balance Sheet 37 Consolidated Statement of Income 37 Consolidated
(Summary) 2. Necessity of Reorganizing J-REITs through Mergers and Other Measures
 Recommendations Towards the Revitalization of J-REITs and Japanese Real Estate Investment Market - The Final Report of the Forum for Building Up the Real Estate Investment Market that is Trusted by Investors
Recommendations Towards the Revitalization of J-REITs and Japanese Real Estate Investment Market - The Final Report of the Forum for Building Up the Real Estate Investment Market that is Trusted by Investors
Macroeconomy and Capital Markets Workshop Report
 Macroeconomy and Capital Markets Workshop Report - Toward Invigorating the Japanese Economy - March 27, 2012 Tokyo Stock Exchange Group, Inc. Introduction At the end of last year, the Tokyo stock market
Macroeconomy and Capital Markets Workshop Report - Toward Invigorating the Japanese Economy - March 27, 2012 Tokyo Stock Exchange Group, Inc. Introduction At the end of last year, the Tokyo stock market
Financial Statements
 Fiscal 2014 (1 April 2014 to 31 March 2015) Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Financial Statements Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities 1 Contents Balance Sheets 1 Statements of Income
Fiscal 2014 (1 April 2014 to 31 March 2015) Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Financial Statements Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities 1 Contents Balance Sheets 1 Statements of Income
Final Report of the Working Group. on Shortening Stock Settlement Cycle in the Japanese Market. June 30, 2016
 Final Report of the Working Group on Shortening Stock Settlement Cycle in the Japanese Market June 30, 2016 Working Group on Shortening Stock Settlement Cycle DISCLAIMER: This is the reference translation
Final Report of the Working Group on Shortening Stock Settlement Cycle in the Japanese Market June 30, 2016 Working Group on Shortening Stock Settlement Cycle DISCLAIMER: This is the reference translation
Local Government Bonds
 Last Updated: February 26, 2008 Local Government Bonds 1. The basics behind rating local government bonds JCR evaluates local government bonds in Japan by assessing local governments in conjunction with
Last Updated: February 26, 2008 Local Government Bonds 1. The basics behind rating local government bonds JCR evaluates local government bonds in Japan by assessing local governments in conjunction with
Working Group on Review of Investment Trust and Investment Corporation Regulation. Final Report
 PROVISIONAL TRANSLATION December 7, 2012 Working Group on Review of Investment Trust and Investment Corporation Regulation Final Report 1. Introduction (1) Historical background The Act on Investment Trusts
PROVISIONAL TRANSLATION December 7, 2012 Working Group on Review of Investment Trust and Investment Corporation Regulation Final Report 1. Introduction (1) Historical background The Act on Investment Trusts
Audit Report for FY2015: Outline of Selected Audit Findings
 Audit Report for FY2015: Outline of Selected Audit Findings The Audit Report for FY2015 covers a wide variety of cases in different categories. The following is an outline of the audit findings on matters
Audit Report for FY2015: Outline of Selected Audit Findings The Audit Report for FY2015 covers a wide variety of cases in different categories. The following is an outline of the audit findings on matters
OUTLINE OF AUDIT RESULTS-FY2007 AUDIT REPORT-
 OUTLINE OF AUDIT RESULTS-FY2007 AUDIT REPORT- CHAPTER Ⅰ OUTLINE OF AUDIT ACTIVITIES 42 Section 1. Audit Policies 42 Section 2. Audit Implementation 46 (Coverage of audit) 46 (In-office documentary audit
OUTLINE OF AUDIT RESULTS-FY2007 AUDIT REPORT- CHAPTER Ⅰ OUTLINE OF AUDIT ACTIVITIES 42 Section 1. Audit Policies 42 Section 2. Audit Implementation 46 (Coverage of audit) 46 (In-office documentary audit
Basic Policy for the Administration and Investment of Employees' Pension Insurance Benefit Association Reserve Fund
 Basic Policy for the Administration and Investment of Employees' Pension Insurance Benefit Association Reserve Fund (Established on October 1, 2015) (Revised on March 3, 2017) (Last revised on July 19,
Basic Policy for the Administration and Investment of Employees' Pension Insurance Benefit Association Reserve Fund (Established on October 1, 2015) (Revised on March 3, 2017) (Last revised on July 19,
Name of Representative:
 April 19, 2018 Company Name: FamilyMart UNY Holdings Co., Ltd. (Code No. 8028; First sections of Tokyo Stock Exchange and Nagoya Stock Exchange) Name of Representative: Koji Takayanagi, Representative
April 19, 2018 Company Name: FamilyMart UNY Holdings Co., Ltd. (Code No. 8028; First sections of Tokyo Stock Exchange and Nagoya Stock Exchange) Name of Representative: Koji Takayanagi, Representative
SME Financing in Japan. January 18, Osamu Tsukahara Senior Executive Director.
 REFERENCE 4 th International Conference Regional Finance in Recent Period and the Way Forward SME Financing in Japan January 18, 2008 Osamu Tsukahara Senior Executive Director E-mail : tsukahara.o@jasme.go.jp
REFERENCE 4 th International Conference Regional Finance in Recent Period and the Way Forward SME Financing in Japan January 18, 2008 Osamu Tsukahara Senior Executive Director E-mail : tsukahara.o@jasme.go.jp
[11] Pension Security
![[11] Pension Security [11] Pension Security](/thumbs/76/72984392.jpg) [11] Pension Security Outline of Pension System Overview Japanese Pension system In Japan, every people of working-age population shall be an insured person of National Pension and receive a Basic in their
[11] Pension Security Outline of Pension System Overview Japanese Pension system In Japan, every people of working-age population shall be an insured person of National Pension and receive a Basic in their
INDUSTRY OVERVIEW SOURCE OF INFORMATION
 3rd Sch3 The information presented in this section is, including certain facts, statistics and data, derived from the CIC Report, which was commissioned by us and from various official government publications
3rd Sch3 The information presented in this section is, including certain facts, statistics and data, derived from the CIC Report, which was commissioned by us and from various official government publications
As all of the measures were rated "s: Goal achieved," achievements in this area were rated "S: Goal achieved."
 Policy Goal 4-1: Ensure the smooth supply of Bank of Japan notes and coins, and suppress the counterfeit or altered currency Article 3 of the Act for Establishment of the Ministry of Finance states that
Policy Goal 4-1: Ensure the smooth supply of Bank of Japan notes and coins, and suppress the counterfeit or altered currency Article 3 of the Act for Establishment of the Ministry of Finance states that
Status of Risk Management
 Status of Upgrading Basic Stance In today s environment, characterized by ongoing liberalization and internationalization of financial services and development of financial and information technology,
Status of Upgrading Basic Stance In today s environment, characterized by ongoing liberalization and internationalization of financial services and development of financial and information technology,
Basic Policy for Employees Pension Insurance Benefit Adjustment Fund
 Basic Policy for Employees Pension Insurance Benefit Adjustment Fund (Established on October 1, 2015) (Last revised on July 1, 2017) In accordance with Article 112-4, Paragraph (1) of the Local Public
Basic Policy for Employees Pension Insurance Benefit Adjustment Fund (Established on October 1, 2015) (Last revised on July 1, 2017) In accordance with Article 112-4, Paragraph (1) of the Local Public
Current Japanese Fiscal Conditions and Issues to be Considered
 Current Japanese Fiscal Conditions and Issues to be Considered 2006 Ministry of Finance Table of Contents I Current Fiscal Situation 1 1. FY2006 General Account Budget 1 2. Trends in General Account Expenditures
Current Japanese Fiscal Conditions and Issues to be Considered 2006 Ministry of Finance Table of Contents I Current Fiscal Situation 1 1. FY2006 General Account Budget 1 2. Trends in General Account Expenditures
Provisional Translation Economic Outlook for FY2005 and Basic Economic and Fiscal Management Measures
 Provisional Translation Economic Outlook for FY2005 and Basic Economic and Fiscal Management Measures January 21, 2005 Cabinet Decision 1. Economic and Fiscal Management and the Japanese Economy in FY2004
Provisional Translation Economic Outlook for FY2005 and Basic Economic and Fiscal Management Measures January 21, 2005 Cabinet Decision 1. Economic and Fiscal Management and the Japanese Economy in FY2004
Financial Statements
 Fiscal 2013 (1 April 2013 to 31 March 2014) Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Financial Statements Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities 1 Financial Statements Balance Sheets 1 Statements
Fiscal 2013 (1 April 2013 to 31 March 2014) Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Financial Statements Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities 1 Financial Statements Balance Sheets 1 Statements
RISA Partners, Inc. Consolidated Interim Results. First half of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2010
 RISA Partners, Inc. Consolidated Interim Results First half of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2010 This document has been translated from the original Japanese as a guide for non-japanese investors.
RISA Partners, Inc. Consolidated Interim Results First half of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2010 This document has been translated from the original Japanese as a guide for non-japanese investors.
Treasury Funds and Japanese Government Securities Services
 Chapter IX Treasury Funds and Japanese Government Securities Services The Bank of Japan provides services related to the receipt and payment of funds of the government (treasury funds), the government
Chapter IX Treasury Funds and Japanese Government Securities Services The Bank of Japan provides services related to the receipt and payment of funds of the government (treasury funds), the government
Financial Results for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2012
 May 25, 2012 Financial Results for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2012 Nippon Life Insurance Company (the Company or the Parent Company ; President: Yoshinobu Tsutsui) announces financial results for
May 25, 2012 Financial Results for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2012 Nippon Life Insurance Company (the Company or the Parent Company ; President: Yoshinobu Tsutsui) announces financial results for
Formulation of Super Regional Strategy
 February 12, 2003 Resona Holdings, Inc. Formulation of Super Regional Strategy Resona Holdings, Inc. ("Resona HD") formulated "Super Regional Strategy" ("the Plan") as a new medium-term management plan
February 12, 2003 Resona Holdings, Inc. Formulation of Super Regional Strategy Resona Holdings, Inc. ("Resona HD") formulated "Super Regional Strategy" ("the Plan") as a new medium-term management plan
Tokyo Metropolitan Government
 Tokyo Metropolitan Government Bureau of Finance, November 06 Highlights Tokyo is one of the largest cities in the world in terms of GDP. Tokyo at a Glance Tokyo (A) Japan (B) A/B(%) Population 3.5mn 7.mn
Tokyo Metropolitan Government Bureau of Finance, November 06 Highlights Tokyo is one of the largest cities in the world in terms of GDP. Tokyo at a Glance Tokyo (A) Japan (B) A/B(%) Population 3.5mn 7.mn
Footnotes [page 1] The Basic Discount Rates and Basic Loan Rates [page 6] <Memo> Amount and Number of Banknotes Issued
![Footnotes [page 1] The Basic Discount Rates and Basic Loan Rates [page 6] <Memo> Amount and Number of Banknotes Issued Footnotes [page 1] The Basic Discount Rates and Basic Loan Rates [page 6] <Memo> Amount and Number of Banknotes Issued](/thumbs/89/99424947.jpg) Footnotes [page 1] The Basic Discount Rates and Basic Loan Rates (a) Extension of discounts of export advance bills and that of export usance bills in yen were abolished on October 1, 1972. (b) Extension
Footnotes [page 1] The Basic Discount Rates and Basic Loan Rates (a) Extension of discounts of export advance bills and that of export usance bills in yen were abolished on October 1, 1972. (b) Extension
Development of Institutional Frameworks Pertaining to Financial and Capital Markets
 Development of Institutional Frameworks Pertaining to Financial and Capital Markets (Provisional Translation) January 21, 2010 Financial Services Agency Introduction In response to the recent global financial
Development of Institutional Frameworks Pertaining to Financial and Capital Markets (Provisional Translation) January 21, 2010 Financial Services Agency Introduction In response to the recent global financial
Announcement in Relation to Planned Commencement of Tender Offer for Shares in FamilyMart UNY Holdings Co., Ltd. (Code No. 8028)
 April 19, 2018 This document is an English translation of a statement written initially in Japanese. The Japanese original should be considered as the primary version. ITOCHU Corporation (Code No. 8001,
April 19, 2018 This document is an English translation of a statement written initially in Japanese. The Japanese original should be considered as the primary version. ITOCHU Corporation (Code No. 8001,
Sales Representatives Manual. Volume 1
 Sales Representatives Manual Volume 1 2017 Sales Representatives Manual Volume 1 2017 Foreword Financial instruments business operators and registered financial institutions play very important roles as
Sales Representatives Manual Volume 1 2017 Sales Representatives Manual Volume 1 2017 Foreword Financial instruments business operators and registered financial institutions play very important roles as
Financial Statements. 1 General Account. Balance Sheet (as of March 31, 2011) Assets. Ⅰ Current assets
 Financial Statements 1 General Account Balance Sheet (as of March 31, 2011) Assets Ⅰ Current assets Cash and bank deposits 121,419,899,271 Inventories Stored goods 448,220,780 448,220,780 Advance payments
Financial Statements 1 General Account Balance Sheet (as of March 31, 2011) Assets Ⅰ Current assets Cash and bank deposits 121,419,899,271 Inventories Stored goods 448,220,780 448,220,780 Advance payments
Recent Local Financial System Reform (Trinity Reform)
 COSLOG Up-to-date Documents on Local Autonomy in Japan No.2 Recent Local Financial System Reform (Trinity Reform) Hiroshi IKAWA Professor, National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies Council of Local
COSLOG Up-to-date Documents on Local Autonomy in Japan No.2 Recent Local Financial System Reform (Trinity Reform) Hiroshi IKAWA Professor, National Graduate Institute for Policy Studies Council of Local
Recent Economic Developments
 Recent Economic Developments September 26, 218 Cabinet Office Government of Japan Contact for inquiries: Directorate General for Economic Research +81-3-6257-1567
Recent Economic Developments September 26, 218 Cabinet Office Government of Japan Contact for inquiries: Directorate General for Economic Research +81-3-6257-1567
1 Economic Overview. Securities Market in 2009
 1 1 Economic Overview Securities Market in 29 In retrospect, the Japanese economy in 29 experienced a severe recession in the wake of the global economic stagnation and financial uncertainty caused by
1 1 Economic Overview Securities Market in 29 In retrospect, the Japanese economy in 29 experienced a severe recession in the wake of the global economic stagnation and financial uncertainty caused by
Partnership for Quality Infrastructure
 Partnership for Quality Infrastructure Japan will fully mobilize public and private resources, in collaboration with other countries and international organizations, to address the immense demand for infrastructure
Partnership for Quality Infrastructure Japan will fully mobilize public and private resources, in collaboration with other countries and international organizations, to address the immense demand for infrastructure
Semiannual Financial Statements
 For the six months ended 30 September 2016 Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Semiannual Financial Statements Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Contents Semiannual Balance Sheets
For the six months ended 30 September 2016 Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Semiannual Financial Statements Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Contents Semiannual Balance Sheets
RISA Partners, Inc. Consolidated Third-Quarter Results. First nine months of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2010
 RISA Partners, Inc. Consolidated Third-Quarter Results First nine months of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2010 This document has been translated from the original Japanese as a guide for non-japanese
RISA Partners, Inc. Consolidated Third-Quarter Results First nine months of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2010 This document has been translated from the original Japanese as a guide for non-japanese
We will begin with an overview of the financial situation of all public pension plans as a whole.
 Chapter 2: Financial situation This chapter will examine current situations and recent trends pertaining to fiscal revenue and expenditure, insured persons and mutual aid association members, beneficiaries,
Chapter 2: Financial situation This chapter will examine current situations and recent trends pertaining to fiscal revenue and expenditure, insured persons and mutual aid association members, beneficiaries,
Ordinary income. change (%) ( million) Net assets per share ( ) Net income share ( million) (%) ( million) (%) ( million) (%) ( million) (%) ( )
 Consolidated Financial Statements for the First Quarter of Fiscal Year 2012 ending March 31, 2013 31-Jul-12 These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principals generally
Consolidated Financial Statements for the First Quarter of Fiscal Year 2012 ending March 31, 2013 31-Jul-12 These financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principals generally
Japan Securities Finance Co., Ltd.
 8511 Tokyo Stock Exchange First Section Analyst Nozomu Kunishige Index Summary----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
8511 Tokyo Stock Exchange First Section Analyst Nozomu Kunishige Index Summary----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Japanese ODA Loan. Ex-Ante Evaluation
 Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation 1. Name of the Project Country: The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka Project: Development Policy Loan (Private Sector Development, Governance Improvement,
Japanese ODA Loan Ex-Ante Evaluation 1. Name of the Project Country: The Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka Project: Development Policy Loan (Private Sector Development, Governance Improvement,
Research notes Basic Information on Recent Elderly Employment Trends in Japan
 Research notes Basic Information on Recent Elderly Employment Trends in Japan Yutaka Asao The aim of this paper is to provide basic information on the employment of older people in Japan over the last
Research notes Basic Information on Recent Elderly Employment Trends in Japan Yutaka Asao The aim of this paper is to provide basic information on the employment of older people in Japan over the last
Detailed Recommendations 2: Develop Green Funds
 Detailed Recommendations 2: Develop Green Funds 2 This is a background paper to the report: Establishing China s Green Financial System published by the Research Bureau of the People s Bank of China and
Detailed Recommendations 2: Develop Green Funds 2 This is a background paper to the report: Establishing China s Green Financial System published by the Research Bureau of the People s Bank of China and
Consolidated Financial Results for the Second Quarter Ended September 30, 2012
 Consolidated Financial Results for the Second Quarter Ended September 30, 2012 SHARP CORPORATION Stock exchange listings: Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka Code number: 6753 URL: http://www.sharp.co.jp/
Consolidated Financial Results for the Second Quarter Ended September 30, 2012 SHARP CORPORATION Stock exchange listings: Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka Code number: 6753 URL: http://www.sharp.co.jp/
Information Disclosure Based on the Principles for Financial Market Infrastructures: The BOJ-NET Funds Transfer System
 Information Disclosure Based on the Principles for Financial Market Infrastructures: The BOJ-NET Funds Transfer System Bank of Japan June 2017 Table of Contents 1. Executive Summary...2 2. Summary of Major
Information Disclosure Based on the Principles for Financial Market Infrastructures: The BOJ-NET Funds Transfer System Bank of Japan June 2017 Table of Contents 1. Executive Summary...2 2. Summary of Major
The Bank of Japan s Eligible Collateral Framework and Recently Accepted Collateral
 The s Eligible Collateral Framework and Recently Accepted Collateral 1 The s Eligible Collateral Framework and Recently Accepted Collateral I. Summary 1 The completely revised its eligible collateral framework
The s Eligible Collateral Framework and Recently Accepted Collateral 1 The s Eligible Collateral Framework and Recently Accepted Collateral I. Summary 1 The completely revised its eligible collateral framework
1. Main Results Data (1) Operational Indicators (2) Investment Indicators (3) Accounting Indicators
 1. Main Results Data... 104 (1) Operational Indicators... 104 (2) Investment Indicators... 108 (3) Accounting Indicators... 114 2. Financial Data... 115 Outline of Japan Post s Accounts System and Restructuring
1. Main Results Data... 104 (1) Operational Indicators... 104 (2) Investment Indicators... 108 (3) Accounting Indicators... 114 2. Financial Data... 115 Outline of Japan Post s Accounts System and Restructuring
Fiscal 2006 Economic Outlook and Basic Stance for Economic and Fiscal Management. 1. Economic and Fiscal Management and the Japanese Economy in FY2005
 Provisional Translation Fiscal 2006 Economic Outlook and Basic Stance for Economic and Fiscal Management January 20, 2006 Cabinet Decision 1. Economic and Fiscal Management and the Japanese Economy in
Provisional Translation Fiscal 2006 Economic Outlook and Basic Stance for Economic and Fiscal Management January 20, 2006 Cabinet Decision 1. Economic and Fiscal Management and the Japanese Economy in
Fiscal 2003 Economic Outlook and Basic Stance for Economic and Fiscal Management
 Provisional Translation Fiscal 2003 Economic Outlook and Basic Stance for Economic and Fiscal Management Cabinet approval Dec. 19, 2002 1. Fiscal 2002 economic and fiscal managements and the Japanese economy
Provisional Translation Fiscal 2003 Economic Outlook and Basic Stance for Economic and Fiscal Management Cabinet approval Dec. 19, 2002 1. Fiscal 2002 economic and fiscal managements and the Japanese economy
For the six months ended 30 September Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Semiannual Financial Statements
 For the six months ended 30 September 2018 Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Semiannual Financial Statements Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Contents Semiannual Balance Sheets
For the six months ended 30 September 2018 Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Semiannual Financial Statements Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Contents Semiannual Balance Sheets
Recent Economic Developments
 Recent Economic Developments June 28, 218 Cabinet Office Government of Japan Contact for inquiries: Directorate General for Economic Research +81-3-6257-1567
Recent Economic Developments June 28, 218 Cabinet Office Government of Japan Contact for inquiries: Directorate General for Economic Research +81-3-6257-1567
Profile. Establishment
 Profile Establishment On February 24, 1995 the Japanese government set a policy to merge the Mutual Aid association of Private School Personnel and the Japan Private School Promotion Foundation in order
Profile Establishment On February 24, 1995 the Japanese government set a policy to merge the Mutual Aid association of Private School Personnel and the Japan Private School Promotion Foundation in order
December 17, To Whom it may concern:
 To Whom it may concern: December 17, 2018 NTT URBAN DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION Rep: Hiroshi Nakagawa President and Chief Executive Officer (Tokyo Stock Exchange (First Section) Code No.8933) Attn: Hideyuki
To Whom it may concern: December 17, 2018 NTT URBAN DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION Rep: Hiroshi Nakagawa President and Chief Executive Officer (Tokyo Stock Exchange (First Section) Code No.8933) Attn: Hideyuki
Survey on Fund Provision for Socially Beneficial Business. Outline
 Survey Commissioned by the Cabinet Office Survey on Fund Provision for Socially Beneficial Business Outline March 30, 2018 INTAGE RESEARCH Inc. Premise and Points to Note We conducted a questionnaire survey
Survey Commissioned by the Cabinet Office Survey on Fund Provision for Socially Beneficial Business Outline March 30, 2018 INTAGE RESEARCH Inc. Premise and Points to Note We conducted a questionnaire survey
Highlights of the Draft FY2018 Budget
 Highlights of the Draft FY2018 Budget FY2018 Budget: Highlights FY2018 budget, the budget for final year of the intensive reform period set in the Fiscal Consolidation Plan, continues to pursue both economic
Highlights of the Draft FY2018 Budget FY2018 Budget: Highlights FY2018 budget, the budget for final year of the intensive reform period set in the Fiscal Consolidation Plan, continues to pursue both economic
Nippon Commercial Development Co., Ltd.
 For the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2017 Annual Select 2017 Nippon Commercial Development Co., Ltd. 4-1-1, Imabashi, Chuo Ward, Osaka City (Securities Code: 3252) +81-6-4706-7501 Buy land Lease land Sell
For the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2017 Annual Select 2017 Nippon Commercial Development Co., Ltd. 4-1-1, Imabashi, Chuo Ward, Osaka City (Securities Code: 3252) +81-6-4706-7501 Buy land Lease land Sell
Total amount of loans to be disbursed. Number of borrowers
 February 7, 019 Bank of Japan Overview of New Loans Loan Disbursement under the Fund-Provisioning Measure to Support Strengthening the Foundations for Economic Growth billion yen, number of institutions
February 7, 019 Bank of Japan Overview of New Loans Loan Disbursement under the Fund-Provisioning Measure to Support Strengthening the Foundations for Economic Growth billion yen, number of institutions
Total amount of loans to be disbursed. Number of borrowers
 August 30, 018 Bank of Japan Overview of New Loans Loan Disbursement under the Fund-Provisioning Measure to Support Strengthening the Foundations for Economic Growth billion yen, number of institutions
August 30, 018 Bank of Japan Overview of New Loans Loan Disbursement under the Fund-Provisioning Measure to Support Strengthening the Foundations for Economic Growth billion yen, number of institutions
Summary of Opinions at the Monetary Policy Meeting 1,2 on December 17 and 18, 2015
 Not to be released until 8:50 a.m. Japan Standard Time on Friday, January 8, 2016. January 8, 2016 Bank of Japan Summary of Opinions at the Monetary Policy Meeting 1,2 on December 17 and 18, 2015 I. Opinions
Not to be released until 8:50 a.m. Japan Standard Time on Friday, January 8, 2016. January 8, 2016 Bank of Japan Summary of Opinions at the Monetary Policy Meeting 1,2 on December 17 and 18, 2015 I. Opinions
Total amount of loans to be disbursed. Number of borrowers
 Overview of New Loans Loan Disbursement under the Fund-Provisioning Measure to Support Strengthening the Foundations for Economic Growth billion yen, number of institutions Total amount of loans to be
Overview of New Loans Loan Disbursement under the Fund-Provisioning Measure to Support Strengthening the Foundations for Economic Growth billion yen, number of institutions Total amount of loans to be
REVIC to Provide Support to Nakayama Steel Works, Ltd.
 REVIC to Provide Support to Nakayama Steel Works, Ltd. March 28 th, 2013 Regional Economy Vitalization Corporation of Japan The Regional Economy Vitalization Corporation of Japan ( REVIC ), has decided
REVIC to Provide Support to Nakayama Steel Works, Ltd. March 28 th, 2013 Regional Economy Vitalization Corporation of Japan The Regional Economy Vitalization Corporation of Japan ( REVIC ), has decided
I. Settlement of Accounts for Fiscal 2009 II. Settlement of Accounts for Expenses for Fiscal 2009
 The Bank's Accounts I. Settlement of Accounts for Fiscal 2009 A. Assets and Liabilities, Profits and Losses, and Capital Adequacy Ratio B. Financial Statements C. Schedule for the Financial Statements
The Bank's Accounts I. Settlement of Accounts for Fiscal 2009 A. Assets and Liabilities, Profits and Losses, and Capital Adequacy Ratio B. Financial Statements C. Schedule for the Financial Statements
[11] Pension Security
![[11] Pension Security [11] Pension Security](/thumbs/82/86224541.jpg) [11] Pension Security Outline of Pension System Overview Japanese Pension system In Japan, every people of working-age population shall be an insured person of National Pension and receive a Basic pension
[11] Pension Security Outline of Pension System Overview Japanese Pension system In Japan, every people of working-age population shall be an insured person of National Pension and receive a Basic pension
Problems and Prospects of Policy Evaluation System of Central Government in Japan. Nobuo AZUMA* (Director, Study Division, Board of Audit)
 Problems and Prospects of Policy Evaluation System of Central Government in Japan Problems and Prospects of Policy Evaluation System of Central Government in Japan Nobuo AZUMA* (Director, Study Division,
Problems and Prospects of Policy Evaluation System of Central Government in Japan Problems and Prospects of Policy Evaluation System of Central Government in Japan Nobuo AZUMA* (Director, Study Division,
Product Strategy for the Corporate Market Group Pension Insurance
 FALIA Invitational Seminar in Japan Product Development Strategy Course Product Strategy for the Corporate Market Group Pension Insurance May 26 th, 2014 Tomoaki Kanoko Group Pension Business Unit The
FALIA Invitational Seminar in Japan Product Development Strategy Course Product Strategy for the Corporate Market Group Pension Insurance May 26 th, 2014 Tomoaki Kanoko Group Pension Business Unit The
(Unofficial Translation) Consolidated Summary Report under Japanese GAAP for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2012 May 15, 2012
 (Unofficial Translation) Consolidated Summary Report under Japanese GAAP for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2012 May 15, 2012 Company Name: Stock exchange listings: Tokyo Code Number: 8750 URL: http://www.dai-ichi-life.co.jp/
(Unofficial Translation) Consolidated Summary Report under Japanese GAAP for the Fiscal Year Ended March 31, 2012 May 15, 2012 Company Name: Stock exchange listings: Tokyo Code Number: 8750 URL: http://www.dai-ichi-life.co.jp/
Financial Section. Non-Consolidated Balance Sheet Meiji Yasuda Life Insurance Company
 Financial Section Non-Consolidated Balance Sheet Meiji Yasuda Life Insurance Company As of March 31, 2011 and 2010 Yen ASSETS Cash and deposits: Cash... 578 628 $ 6.9 Deposits... 203,245 375,446 2,444.3
Financial Section Non-Consolidated Balance Sheet Meiji Yasuda Life Insurance Company As of March 31, 2011 and 2010 Yen ASSETS Cash and deposits: Cash... 578 628 $ 6.9 Deposits... 203,245 375,446 2,444.3
Continuation of measures against large volume purchase of shares of the Company (Defense Measures Against Takeover)
 [Translation] May 16, 2013 To Whom It May Concern Sadao Yoshino, President, Director Heiwa Real Estate Co., Ltd. 1-10, Nihonbashi Kabuto-cho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo (Code No. 8803) First Section of Tokyo, Osaka
[Translation] May 16, 2013 To Whom It May Concern Sadao Yoshino, President, Director Heiwa Real Estate Co., Ltd. 1-10, Nihonbashi Kabuto-cho, Chuo-ku, Tokyo (Code No. 8803) First Section of Tokyo, Osaka
Part 1. Major Trends in Personnel Administration in the Past Year. Ensuring Proper Remuneration for Public Employees
 Part 1. Chapter 1. Major Trends in Personnel Administration in the Past Year Ensuring Proper Remuneration for Public Employees - On August 7, 2014, the NPA made the Recommendation to the Diet and the Cabinet
Part 1. Chapter 1. Major Trends in Personnel Administration in the Past Year Ensuring Proper Remuneration for Public Employees - On August 7, 2014, the NPA made the Recommendation to the Diet and the Cabinet
