Internet Appendix to Shareholder Litigation and Ownership Structure: Evidence from a Natural Experiment
|
|
|
- Maud Golden
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Internet Appendix to Shareholder Litigation and Ownership Structure: Evidence from a Natural Experiment Alan D. Crane Andrew Koch First Draft: January 14, 2014 May 5, 2016 Crane is at Rice University, acrane@rice.edu. Koch is at University of Pittsburgh, awkoch@pitt.edu. We thank Lauren Cohen (editor), an anonymous associate editor, an anonymous referee, Alex Butler, Kevin Crotty, David De Angelis, Dave Denis, Diane Denis, Ken Lehn, Sébastien Michenaud, Shawn Thomas, Vahap Usyal (discussant), James Weston, and seminar participants at Depaul, University of Pittsburgh, Rice University, and University of Texas Alumni Conference for their helpful comments.
2 In this appendix we report several robustness checks and supplemental results that support the analysis in Shareholder Litigation and Ownership Structure: Evidence from a Natural Experiment. The following tables and figures are included in this appendix: 1. Table A1 presents detailed definitions of the variables used in the paper. These include the details on the treatment classification as well as control variables and additional variables of interest. 2. Table A2 presents additional robustness samples for the results in Table 3 of the text. These include a constant composition sample (Panel A) and sample that includes only firms that are at least 5 years old (Panel B). This table shows that our results are not driven by the entry of new firms with different ownership structures, but rather by changes in the ownership structures of existing firms. 3. Table A3 presents robustness to Table 4 of the paper. Panel A of Table A3 is the same specification presented in Table 4, but reports all coefficients that were suppressed for space in the paper. Panel B includes a shorter sample period ( ) to show that the results are not sensitive to the number of years selected on either side of the treatment. 4. Table A4 presents robustness to definitions of ownership concentration and number of larger owners. In the paper, ownership concentration is defined as the concentration of the 20 largest owners and a large owner is defined as one with a position size of 2% or greater. In this table, we replicate the results of Table 3 and Table 4 under different thresholds for each of these outcomes. ˆ Panel A: Replication of Table 3 under four different thresholds of ownership concentration. 1
3 ˆ Panel B: Replication of Table 4 under four different thresholds of ownership concentration. ˆ Panel C: Replication of Table 3 under six different definitions of a large owner. ˆ Panel D: Replication of Table 4 under six different definitions of a large owner. 5. Figure A1 presents the results from placebo regressions. In this figure, we replicate the specification from Table 3 randomizing states to treatment groups. The histograms plot the point estimates and t-statistics from 5,000 randomizations. The vertical red lines show the estimate under the true treatment assignment. 2
4 Table A1: Variable Appendix Variable Definition Ninth Indicator variable equal to one if the headquarters location in 1998 is one of the following: CA,WA,OR,ID,AZ,MT,NV,AK,HI and zero otherwise. Post 1999 Indicator variable equal to one if the observation is after Treatment Interaction equal to Ninth*Post Book Equity Compustat variables ceq+txdb, minus preferred stock, which equals Compustat pstkrv or pstkl or upstk in that order, based on data availability. ln(market Equity) The natural of Compustat variables prcc c*cshpri. ln(market to Book) The natural log of Compustat variables ((prcc c*cshpri)+(dlc+dltt)+pstkl-txditc)/at ) Dividend Payer An indicator variable equal to one if Compustat variables (dvp+dvc) is greater than zero and zero otherwise. ROA Compustat variables (oibdp/at) and winsorized at the 1% level. Annual Return Compounded monthly CRSP returns for the 12 months prior to the reporting period. Institutional Ownership Number of shares owned by institutions (per Thomson-Reuters 13f) as a percent of total shares outstanding. Ownership Concentration Natural log of (ownership of the top 20 owners/(1-ownership of the top 20 owners)). Number of Large Owners Count of the number of institutional owners with positions greater than 2% of the firm s value. State Net Tax Revenue Annual state tax revenue minus subsidies obtained from the Bureau of Economic Analysis. State GDP per Capita Annual GDP by state obtained from the Bureau of Economic Analysis State Unemployment Annual state unemployment obtained from the Bureau of Labor Statistics. State Population Annual state population estimates from Federal Reserve Economic Data. High Vol Indicator variable equal to one if the standard deviation of daily returns over 1998 is in the top quartile and zero otherwise. High Negative Skewness Indicator variable equal to one if the skewness of daily returns over 1998 is in the bottom quartile and zero otherwise. Low Minimum Return Indicator variable equal to one if firm s minimum monthly return in 1998 is in the bottom quartile and zero otherwise. California Indicator variable equal to one if the firm is headquartered in California and zero otherwise. Tech Industry Indicator variable equal to one if the firm s SIC code is one of the following: 2830, 2831, 2833, 2834, 2835, 2836, 3570, 3680, 3681, 3682, 3683, 3684, 3685, 3686, 3687, 3688, 3689, 3695, 7373, 3622, 3661, 3662, 3663, 3664, 3665, 3666, 3669, 3679, 3810, or Ninth Circuit Covariance The sensitivity of firm i s return to a portfolio of Ninth Circuit firms estimated by ri,t = αi + β i M MKTt + β i N Nintht + ɛ i,t and averaged over each firm in the industry. High Ninth Covariance Indicator variable equal to one if the firm s Ninth Circuit Covariance is in the top quartile. Zero CAR Indicator variable equal to one if the firm s 3-day return around the 1999 ruling is within the cross-sectional interquartile range. Connected Owner COj = i owner i in firm j. ω i j C i where Ci is the clustering coefficient of large owner (2%) i and ω i j is the ownership of large 3
5 Table A2: The Effect of Litigation Laws on Ownership This table presents a difference in difference estimation of the effect of the 1999 Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals decision on ownership structure. Each column estimates the effect on a different measure of ownership structure, including Institutional Ownership, Ownership Concentration, and the Number of Large Positions. These variables are defined in Appendix A. Each panel estimates the effect on different samples as indicated in the sub-caption. The main variable of interest, Treatment, is the interaction of two indicator variables, Ninth Circuit and Post Ninth Circuit takes a value of one if the firm is subject to (headquartered in) the 1999 ruling of the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals and Post 1999 takes a value of one if the observation is after Dividend Payer t 1 is an indicator variable equal to one if the firm the paid a dividend in the prior year, and zero otherwise. Ln(Market Equity) t 1 is the natural log of the lagged dollar market equity value(in millions deflated to 2005 dollars) of the firm and Ln(Market to Book) t 1 measures the natural log of the lag ratio of market value of equity to book value of equity. ROA t 1 is the lagged measure of operating income before interest and depreciation scaled by prior periods total assets. Annual returns measure the compounded monthly returns for the 12 months prior to the reporting period. Standard errors are clustered by firm with t-statistics reported in parenthesis and significance represented according to: p < 0.10, p < 0.05, p < Panel A: Constant Composition Sample Inst. Ownership Ownership Concentration Number of Large Positions Treatment 5.88*** 0.23** 0.77** (3.17) (2.24) (2.45) Ln(Market Equity) t *** 0.37*** 0.82*** (13.09) (8.90) (7.49) Ln(Market to Book) t *** -0.20*** -0.71*** (-5.63) (-3.37) (-4.75) Dividend Payer t *** (-2.89) (-1.48) (-0.76) ROA t ** 0.36** 0.74* (2.19) (2.18) (1.77) Annual Return t (-0.69) (-1.24) (-0.36) State Net Tax Revenue t * (1.09) (0.01) (1.95) State GDP per Capita t (-0.32) (-0.75) (0.51) State Unemployment t (0.92) (-0.36) (0.49) Population t *** (-1.49) (-1.16) (-3.53) Observations Year Effects YES YES YES Firm Effects YES YES YES 4
6 Panel B: Firms Older than 5 Years Inst. Ownership Ownership Concentration Number of Large Positions Treatment 5.83*** 0.19*** 0.78*** (4.53) (2.67) (3.75) Ln(Market Equity) t *** 0.32*** 0.82*** (19.93) (12.62) (13.38) Ln(Market to Book) t *** -0.14*** -0.44*** (-5.31) (-3.90) (-5.31) Dividend Payer t *** (-3.81) (-1.45) (-1.36) ROA t *** 0.36*** 0.65*** (2.85) (3.47) (3.17) Annual Return t (-0.07) (-0.30) (1.25) State Net Tax Revenue t (0.43) (-0.37) (1.41) State GDP per Capita t (-1.17) (-0.42) (-0.13) State Unemployment t (-0.26) (-0.02) (0.84) Population t * *** (-1.80) (-0.80) (-3.62) Observations Year Effects YES YES YES Firm Effects YES YES YES 5
7 Table A3: Difference in Difference Regression: Propensity Matched Sample (Alternative Samples) This table presents a difference in difference estimation of the effect of the 1999 Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals decision on institutional ownership. The regression is estimated on a propensity matched sample. Panel A presents the treatment effect regressions. Each column estimates the effect on a different measure of ownership structure, including Institutional Ownership, Ownership Concentration, and the Number of Large Positions. These variables are defined in Appendix A. The main variable of interest, Treatment, is the interaction of two indicator variables, Ninth Circuit and Post Ninth Circuit takes a value of one if the firm is subject to (headquartered in) the 1999 ruling of the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals and Post 1999 takes a value of one if the observation is after Dividend Payer t 1 is an indicator variable equal to one if the firm the paid a dividend in the prior year, and zero otherwise. Ln(Market Equity) t 1 is the natural log of the lagged dollar market equity value(in millions deflated to 2005 dollars) of the firm and Ln(Market to Book) t 1 measures the natural log of the lag ratio of market value of equity to book value of equity. ROA t 1 is the lagged measure of operating income before interest and depreciation scaled by prior periods total assets. Annual returns measure the compounded monthly returns for the 12 months prior to the reporting period. Panel B presents the treatment effect estimation over a shorter window, from Standard errors are clustered by firm with t-statistics reported in parenthesis and significance represented according to: p < 0.10, p < 0.05, p < Panel A: Propensity Matched Sample: All Covariates Reported Inst. Ownership Ownership Concentration Number of Large Positions Treatment 6.49*** 0.23*** 0.87*** (4.90) (3.12) (4.14) Ln(Market Equity) t *** 0.34*** 0.74*** (18.86) (12.22) (11.42) Ln(Market to Book) t *** -0.20*** -0.46*** (-5.93) (-4.94) (-4.68) Dividend Payer t *** -0.10** (-3.39) (-2.20) (-1.35) ROA t *** 0.44*** 0.79*** (3.11) (3.69) (3.32) Annual Return t * (1.11) (1.52) (1.77) State Net Tax Revenue t * (0.46) (-0.17) (1.81) State GDP per Capita t (-0.13) (-0.34) (0.11) State Unemployment t (0.53) (0.34) (1.01) Population t *** (-1.42) (-0.92) (-3.46) Observations Year Effects YES YES YES Firm Effects YES YES YES Panel B: Propensity Matched Sample Inst. Ownership Ownership Concentration Number of Large Positions Treatment 3.99*** 0.17*** 0.54*** (3.46) (2.66) (2.82) Ln(Market Equity) t *** 0.31*** 0.60*** (11.43) (8.86) (7.10) Ln(Market to Book) t * (-1.13) (-1.78) (-0.98) Dividend Payer t (-1.24) (-0.84) (-0.56) ROA t ** 0.28** 0.51 (2.44) (2.00) (1.64) Annual Return t (0.51) (0.42) (0.73) State Net Tax Revenue t (-0.54) (-0.51) (0.28) State GDP per Capita t (-0.04) (-1.27) (0.40) State Unemployment t (1.50) (0.85) (0.25) Population t (-0.35) (-0.35) (-1.25) Observations Year Effects YES YES YES Firm Effects YES 6 YES YES
8 Table A4: Difference in Difference Regression: Different thresholds for Large Owners This table presents a difference in difference estimation of the effect of the 1999 Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals decision on institutional ownership. Each column estimates the effect on a different measure of ownership concentration. The dependent variables are defined in Appendix I. The main variable of interest, Treatment, is the interaction of two indicator variables, Ninth Circuit and Post Ninth Circuit that takes a value of one if the firm is subject to (headquartered in) the 1999 ruling of the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals. Dividend Payert 1 is an indicator variable equal to one if the firm the paid a dividend in the prior year, and zero otherwise. Ln(Market Equity)t 1 is the natural log of the lagged dollar market equity value(in millions deflated to 2005 dollars) of the firm and Ln(Market to Book)t 1 measures the natural log of the lag ratio of market value of equity to book value of equity. ROAt 1 is the lagged measure of operating income before interest and depreciation scaled by prior periods total assets. Annual returns measure the compounded monthly returns for the 12 months prior to the reporting period. Panel A: Baseline Sample - Concentration Concent. of Top 5 Concent. of Top 10 Concent. of Top 20 Concent. of Top 50 Treatment 0.11** 0.14** 0.18*** 0.24*** (2.02) (2.36) (2.90) (3.61) Ln(Market Equity)t *** 0.27*** 0.34*** 0.43*** (10.79) (12.86) (15.15) (18.17) Ln(Market to Book)t *** -0.15*** -0.16*** -0.18*** (-4.74) (-4.87) (-5.04) (-5.50) Dividend Payert * -0.09** (-1.43) (-1.48) (-1.67) (-2.17) ROAt *** 0.37*** 0.42*** 0.45*** (3.53) (4.01) (4.35) (4.47) Annual Returnt ** 0.02** (0.79) (1.55) (2.22) (2.56) State Net Tax Revenuet (-1.16) (-1.04) (-0.76) (-0.39) State GDP per Capitat (-0.05) (-0.20) (-0.39) (-0.78) State Unemploymentt (0.02) (0.09) (0.09) (0.01) Populationt (0.30) (0.17) (-0.00) (-0.34) Observations Year Effects YES YES YES YES Firm Effects YES YES YES YES 7
9 Panel B: Propensity Score Matched Sample - Concentration Concent. of Top 5 Concent. of Top 10 Concent. of Top 20 Concent. of Top 50 Treatment 0.15** 0.18** 0.22*** 0.29*** (2.25) (2.56) (3.04) (3.65) Ln(Market Equity)t *** 0.28*** 0.34*** 0.43*** (8.87) (10.55) (12.37) (14.69) Ln(Market to Book)t *** -0.20*** -0.21*** -0.23*** (-4.73) (-4.93) (-5.09) (-5.33) Dividend Payert ** -0.09** -0.10** -0.12** (-2.20) (-2.10) (-2.15) (-2.43) ROAt *** 0.39*** 0.43*** 0.46*** (2.96) (3.31) (3.58) (3.75) Annual Returnt * (0.51) (1.10) (1.59) (1.87) State Net Tax Revenuet (-0.58) (-0.51) (-0.22) (0.25) State GDP per Capitat (-0.38) (-0.47) (-0.56) (-0.88) State Unemploymentt (0.45) (0.46) (0.43) (0.32) Populationt (-0.34) (-0.45) (-0.67) (-0.99) Observations Year Effects YES YES YES YES Firm Effects YES YES YES YES 8
10 Panel C: Baseline Sample - Number of Positions Num 1% Num 2% Num 3% Num 4% Num 5% Num 10% Treatment 1.31*** 0.59*** 0.28** 0.18* 0.14* 0.04 (4.41) (3.38) (2.34) (1.93) (1.82) (1.34) Ln(Market Equity)t *** 0.83*** 0.41*** 0.24*** 0.16*** 0.03** (21.21) (15.49) (10.26) (7.74) (6.52) (2.54) Ln(Market to Book)t *** -0.41*** -0.29*** -0.25*** -0.22*** (-4.39) (-5.49) (-5.14) (-5.78) (-6.54) (-1.57) Dividend Payert ** -0.20** -0.13** ** -0.04** (-2.23) (-2.16) (-2.05) (-1.51) (-2.21) (-2.22) ROAt *** 0.83*** 0.46*** 0.24** (4.85) (4.07) (3.05) (2.05) (0.93) (-0.63) Annual Returnt *** 0.06** ** -0.01** (3.73) (2.30) (0.52) (-0.74) (-2.41) (-2.58) State Net Tax Revenuet * (1.07) (1.65) (0.54) (-0.17) (-0.65) (0.29) State GDP per Capitat (-1.39) (-0.86) (-0.32) (-0.78) (-0.21) (-0.94) State Unemploymentt (-0.45) (0.41) (1.19) (0.47) (-0.15) (-0.76) Populationt *** -0.09*** -0.05* (-1.64) (-3.68) (-2.71) (-1.89) (-0.79) (0.59) Observations Year Effects YES YES YES YES YES YES Firm Effects YES YES YES YES YES YES 9
11 Panel D: Propensity Score Matched Sample - Number of Positions Num 1% Num 2% Num 3% Num 4% Num 5% Num 10% Treatment 1.64*** 0.87*** 0.45*** 0.27** 0.19** 0.05 (4.43) (4.14) (3.17) (2.36) (2.05) (1.32) Ln(Market Equity)t *** 0.74*** 0.36*** 0.20*** 0.14*** 0.03** (16.49) (11.42) (7.86) (5.85) (5.06) (2.14) Ln(Market to Book)t *** -0.46*** -0.37*** -0.33*** -0.28*** -0.04** (-3.69) (-4.68) (-5.51) (-6.51) (-7.06) (-2.30) Dividend Payert ** -0.07*** (-1.48) (-1.35) (-1.46) (-1.39) (-2.52) (-2.74) ROAt *** 0.79*** 0.49*** 0.28** (4.62) (3.32) (2.68) (2.12) (0.98) (-0.19) Annual Returnt *** 0.06* (2.83) (1.77) (0.47) (0.33) (-1.51) (-1.58) State Net Tax Revenuet * (1.18) (1.81) (0.99) (-0.12) (0.03) (0.20) State GDP per Capitat (-0.56) (0.11) (0.44) (-0.43) (0.17) (0.10) State Unemploymentt * (0.36) (1.01) (1.66) (0.24) (-0.13) (-0.46) Populationt *** -0.12*** -0.06* (-1.50) (-3.46) (-2.73) (-1.68) (-1.27) (0.35) Observations Year Effects YES YES YES YES YES YES Firm Effects YES YES YES YES YES YES 10
12 Figure A1: Placebo Treatment Group Coefficient Estimates and t-statistics This figure presents the results of 5,000 placebo regressions where states are randomly assigned to treatment. Each coefficient and t-statistic is estimated following the specification from Table 3, Panel A. (a) Institutional Ownership Placebo Simulations - Coefficients (b) Concentration Placebo Simulations - Coefficients (c) Number of Large Owners Placebo Simulations - Coefficients (d) Institutional Ownership Placebo Simulations - t-stat (e) Concentration Placebo Simulations - t-stat (f) Number of Large Owners Placebo Simulations - t-stat 11
Institutional Investor Cliques and Governance: Internet Appendix
 Institutional Investor Cliques and Governance: Internet Appendix Alan D. Crane Jones Graduate School of Business Rice University Andrew Koch Katz Graduate School of Business University of Pittsburgh Sébastien
Institutional Investor Cliques and Governance: Internet Appendix Alan D. Crane Jones Graduate School of Business Rice University Andrew Koch Katz Graduate School of Business University of Pittsburgh Sébastien
Internet Appendix for: Cyclical Dispersion in Expected Defaults
 Internet Appendix for: Cyclical Dispersion in Expected Defaults March, 2018 Contents 1 1 Robustness Tests The results presented in the main text are robust to the definition of debt repayments, and the
Internet Appendix for: Cyclical Dispersion in Expected Defaults March, 2018 Contents 1 1 Robustness Tests The results presented in the main text are robust to the definition of debt repayments, and the
Internet Appendix for: Cyclical Dispersion in Expected Defaults
 Internet Appendix for: Cyclical Dispersion in Expected Defaults João F. Gomes Marco Grotteria Jessica Wachter August, 2017 Contents 1 Robustness Tests 2 1.1 Multivariable Forecasting of Macroeconomic Quantities............
Internet Appendix for: Cyclical Dispersion in Expected Defaults João F. Gomes Marco Grotteria Jessica Wachter August, 2017 Contents 1 Robustness Tests 2 1.1 Multivariable Forecasting of Macroeconomic Quantities............
Appendix A. Mathematical Appendix
 Appendix A. Mathematical Appendix Denote by Λ t the Lagrange multiplier attached to the capital accumulation equation. The optimal policy is characterized by the first order conditions: (1 α)a t K t α
Appendix A. Mathematical Appendix Denote by Λ t the Lagrange multiplier attached to the capital accumulation equation. The optimal policy is characterized by the first order conditions: (1 α)a t K t α
Online Appendix to. The Value of Crowdsourced Earnings Forecasts
 Online Appendix to The Value of Crowdsourced Earnings Forecasts This online appendix tabulates and discusses the results of robustness checks and supplementary analyses mentioned in the paper. A1. Estimating
Online Appendix to The Value of Crowdsourced Earnings Forecasts This online appendix tabulates and discusses the results of robustness checks and supplementary analyses mentioned in the paper. A1. Estimating
1. Logit and Linear Probability Models
 INTERNET APPENDIX 1. Logit and Linear Probability Models Table 1 Leverage and the Likelihood of a Union Strike (Logit Models) This table presents estimation results of logit models of union strikes during
INTERNET APPENDIX 1. Logit and Linear Probability Models Table 1 Leverage and the Likelihood of a Union Strike (Logit Models) This table presents estimation results of logit models of union strikes during
Do Investors Value Dividend Smoothing Stocks Differently? Internet Appendix
 Do Investors Value Dividend Smoothing Stocks Differently? Internet Appendix Yelena Larkin, Mark T. Leary, and Roni Michaely April 2016 Table I.A-I In table I.A-I we perform a simple non-parametric analysis
Do Investors Value Dividend Smoothing Stocks Differently? Internet Appendix Yelena Larkin, Mark T. Leary, and Roni Michaely April 2016 Table I.A-I In table I.A-I we perform a simple non-parametric analysis
Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? Francesco Decarolis (Boston University)
 Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? 1) Data Francesco Decarolis (Boston University) The dataset was assembled from data made publicly available by CMS
Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? 1) Data Francesco Decarolis (Boston University) The dataset was assembled from data made publicly available by CMS
Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? Francesco Decarolis (Boston University)
 Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? 1) Data Francesco Decarolis (Boston University) The dataset was assembled from data made publicly available by CMS
Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? 1) Data Francesco Decarolis (Boston University) The dataset was assembled from data made publicly available by CMS
Ownership, Concentration and Investment
 Ownership, Concentration and Investment Germán Gutiérrez and Thomas Philippon January 2018 Abstract The US business sector has under-invested relative to profits, funding costs, and Tobin s Q since the
Ownership, Concentration and Investment Germán Gutiérrez and Thomas Philippon January 2018 Abstract The US business sector has under-invested relative to profits, funding costs, and Tobin s Q since the
Credit Cycles and Financial Verification
 Online Appendix to: Credit Cycles and Financial Verification Petro Lisowsky University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sloan School of Management and Norwegian Center
Online Appendix to: Credit Cycles and Financial Verification Petro Lisowsky University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sloan School of Management and Norwegian Center
Local Culture and Dividends
 Local Culture and Dividends Erdem Ucar I empirically investigate whether geographical variations in local culture, as proxied by local religion, affect dividend demand and corporate dividend policy for
Local Culture and Dividends Erdem Ucar I empirically investigate whether geographical variations in local culture, as proxied by local religion, affect dividend demand and corporate dividend policy for
CEO Attributes, Compensation, and Firm Value: Evidence from a Structural Estimation. Internet Appendix
 CEO Attributes, Compensation, and Firm Value: Evidence from a Structural Estimation Internet Appendix A. Participation constraint In evaluating when the participation constraint binds, we consider three
CEO Attributes, Compensation, and Firm Value: Evidence from a Structural Estimation Internet Appendix A. Participation constraint In evaluating when the participation constraint binds, we consider three
Supplemental Table I. WTO impact by industry
 Supplemental Table I. WTO impact by industry This table presents the influence of WTO accessions on each three-digit NAICS code based industry for the manufacturing sector. The WTO impact is estimated
Supplemental Table I. WTO impact by industry This table presents the influence of WTO accessions on each three-digit NAICS code based industry for the manufacturing sector. The WTO impact is estimated
Internet Appendix to Broad-based Employee Stock Ownership: Motives and Outcomes *
 Internet Appendix to Broad-based Employee Stock Ownership: Motives and Outcomes * E. Han Kim and Paige Ouimet This appendix contains 10 tables reporting estimation results mentioned in the paper but not
Internet Appendix to Broad-based Employee Stock Ownership: Motives and Outcomes * E. Han Kim and Paige Ouimet This appendix contains 10 tables reporting estimation results mentioned in the paper but not
Internet Appendix for Does Banking Competition Affect Innovation? 1. Additional robustness checks
 Internet Appendix for Does Banking Competition Affect Innovation? This internet appendix provides robustness tests and supplemental analyses to the main results presented in Does Banking Competition Affect
Internet Appendix for Does Banking Competition Affect Innovation? This internet appendix provides robustness tests and supplemental analyses to the main results presented in Does Banking Competition Affect
Online Appendix to Do Short-Sellers. Trade on Private Information or False. Information?
 Online Appendix to Do Short-Sellers Trade on Private Information or False Information? by Amiyatosh Purnanandam and Nejat Seyhun December 12, 2017 Purnanandam, amiyatos@umich.edu, University of Michigan,
Online Appendix to Do Short-Sellers Trade on Private Information or False Information? by Amiyatosh Purnanandam and Nejat Seyhun December 12, 2017 Purnanandam, amiyatos@umich.edu, University of Michigan,
Online Appendix of. This appendix complements the evidence shown in the text. 1. Simulations
 Online Appendix of Heterogeneity in Returns to Wealth and the Measurement of Wealth Inequality By ANDREAS FAGERENG, LUIGI GUISO, DAVIDE MALACRINO AND LUIGI PISTAFERRI This appendix complements the evidence
Online Appendix of Heterogeneity in Returns to Wealth and the Measurement of Wealth Inequality By ANDREAS FAGERENG, LUIGI GUISO, DAVIDE MALACRINO AND LUIGI PISTAFERRI This appendix complements the evidence
Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions)
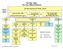 Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions) Total Tax Liability $2,660 Gross Tax Gap: $450 (Voluntary Compliance Rate = 83.1%) Tax Paid Voluntarily & Timely: $2,210 Enforced & Other Late Payments of Tax $65
Tax Gap Map Tax Year 2006 ($ billions) Total Tax Liability $2,660 Gross Tax Gap: $450 (Voluntary Compliance Rate = 83.1%) Tax Paid Voluntarily & Timely: $2,210 Enforced & Other Late Payments of Tax $65
Government Debt and Capital Structure Decisions: International Evidence
 Government Debt and Capital Structure Decisions: International Evidence Irem Demirci Nova SBE Jennifer Huang CKGSB Clemens Sialm UT Austin and NBER Introduction Question: Do corporations adjust their capital
Government Debt and Capital Structure Decisions: International Evidence Irem Demirci Nova SBE Jennifer Huang CKGSB Clemens Sialm UT Austin and NBER Introduction Question: Do corporations adjust their capital
How Are SNAP Benefits Spent? Evidence from a Retail Panel
 How Are SNAP Benefits Spent? Evidence from a Retail Panel Justine Hastings Jesse M. Shapiro Brown University and NBER March 2018 Online Appendix Contents 1 Quantitative model of price misperception 3 List
How Are SNAP Benefits Spent? Evidence from a Retail Panel Justine Hastings Jesse M. Shapiro Brown University and NBER March 2018 Online Appendix Contents 1 Quantitative model of price misperception 3 List
Are Consultants to Blame for High CEO Pay?
 Preliminary Draft Please Do Not Circulate Are Consultants to Blame for High CEO Pay? Kevin J. Murphy Marshall School of Business University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0804 E-mail: kjmurphy@usc.edu
Preliminary Draft Please Do Not Circulate Are Consultants to Blame for High CEO Pay? Kevin J. Murphy Marshall School of Business University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90089-0804 E-mail: kjmurphy@usc.edu
Internet Appendix for Collateral Shocks and Corporate Employment
 Internet Appendix for Collateral Shocks and Corporate Employment Nuri Ersahin Rustom M. Irani University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign March 1, 2018 Appendix IA.I: First-stage for IV estimation This
Internet Appendix for Collateral Shocks and Corporate Employment Nuri Ersahin Rustom M. Irani University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign March 1, 2018 Appendix IA.I: First-stage for IV estimation This
Percentiles, STATA, Box Plots, Standardizing, and Other Transformations
 Percentiles, STATA, Box Plots, Standardizing, and Other Transformations Lecture 3 Reading: Sections 5.7 54 Remember, when you finish a chapter make sure not to miss the last couple of boxes: What Can Go
Percentiles, STATA, Box Plots, Standardizing, and Other Transformations Lecture 3 Reading: Sections 5.7 54 Remember, when you finish a chapter make sure not to miss the last couple of boxes: What Can Go
Internet Appendix for Do General Managerial Skills Spur Innovation?
 Internet Appendix for Do General Managerial Skills Spur Innovation? Cláudia Custódio Imperial College Business School Miguel A. Ferreira Nova School of Business and Economics, ECGI Pedro Matos University
Internet Appendix for Do General Managerial Skills Spur Innovation? Cláudia Custódio Imperial College Business School Miguel A. Ferreira Nova School of Business and Economics, ECGI Pedro Matos University
Internet Appendix for Buyout Activity: The Impact of Aggregate Discount Rates
 Internet Appendix for Buyout Activity: The Impact of Aggregate Discount Rates Valentin Haddad, Erik Loualiche, and Matthew Plosser * In this Internet Appendix we present several robustness tables. IAI
Internet Appendix for Buyout Activity: The Impact of Aggregate Discount Rates Valentin Haddad, Erik Loualiche, and Matthew Plosser * In this Internet Appendix we present several robustness tables. IAI
Supplemental Appendix for Cost Pass-Through to Higher Ethanol Blends at the Pump: Evidence from Minnesota Gas Station Data.
 November 18, 2018 Supplemental Appendix for Cost Pass-Through to Higher Ethanol Blends at the Pump: Evidence from Minnesota Gas Station Data Jing Li, MIT James H. Stock, Harvard University and NBER This
November 18, 2018 Supplemental Appendix for Cost Pass-Through to Higher Ethanol Blends at the Pump: Evidence from Minnesota Gas Station Data Jing Li, MIT James H. Stock, Harvard University and NBER This
Appendix. A.1 Independent Random Effects (Baseline)
 A Appendix A.1 Independent Random Effects (Baseline) 36 Table 2: Detailed Monte Carlo Results Logit Fixed Effects Clustered Random Effects Random Coefficients c Coeff. SE SD Coeff. SE SD Coeff. SE SD Coeff.
A Appendix A.1 Independent Random Effects (Baseline) 36 Table 2: Detailed Monte Carlo Results Logit Fixed Effects Clustered Random Effects Random Coefficients c Coeff. SE SD Coeff. SE SD Coeff. SE SD Coeff.
Table IA.1 CEO Pay-Size Elasticity and Increased Labor Demand Panel A: IPOs Scaled by Full Sample Industry Average
 Table IA.1 CEO Pay-Size Elasticity and Increased Labor Demand Panel A: IPOs Scaled by Industry Average (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) Ln(Market Value) 0.423 0.419 0.423 0.423 0.255 (33.29) (30.84) (33.29) (33.29)
Table IA.1 CEO Pay-Size Elasticity and Increased Labor Demand Panel A: IPOs Scaled by Industry Average (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) Ln(Market Value) 0.423 0.419 0.423 0.423 0.255 (33.29) (30.84) (33.29) (33.29)
ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables
 ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables 34 Figure A.1: First Page of the Standard Layout 35 Figure A.2: Second Page of the Credit Card Statement 36 Figure A.3: First
ONLINE APPENDIX (NOT FOR PUBLICATION) Appendix A: Appendix Figures and Tables 34 Figure A.1: First Page of the Standard Layout 35 Figure A.2: Second Page of the Credit Card Statement 36 Figure A.3: First
Public Employees as Politicians: Evidence from Close Elections
 Public Employees as Politicians: Evidence from Close Elections Supporting information (For Online Publication Only) Ari Hyytinen University of Jyväskylä, School of Business and Economics (JSBE) Jaakko
Public Employees as Politicians: Evidence from Close Elections Supporting information (For Online Publication Only) Ari Hyytinen University of Jyväskylä, School of Business and Economics (JSBE) Jaakko
Internet Appendix: Costs and Benefits of Friendly Boards during Mergers and Acquisitions. Breno Schmidt Goizueta School of Business Emory University
 Internet Appendix: Costs and Benefits of Friendly Boards during Mergers and Acquisitions Breno Schmidt Goizueta School of Business Emory University January, 2014 A Social Ties Data To facilitate the exposition,
Internet Appendix: Costs and Benefits of Friendly Boards during Mergers and Acquisitions Breno Schmidt Goizueta School of Business Emory University January, 2014 A Social Ties Data To facilitate the exposition,
Online Appendices for
 Online Appendices for From Made in China to Innovated in China : Necessity, Prospect, and Challenges Shang-Jin Wei, Zhuan Xie, and Xiaobo Zhang Journal of Economic Perspectives, (31)1, Winter 2017 Online
Online Appendices for From Made in China to Innovated in China : Necessity, Prospect, and Challenges Shang-Jin Wei, Zhuan Xie, and Xiaobo Zhang Journal of Economic Perspectives, (31)1, Winter 2017 Online
The Impact of Shareholder Taxation on Merger and Acquisition Behavior
 The Impact of Shareholder Taxation on Merger and Acquisition Behavior Eric Ohrn, Grinnell College Nathan Seegert, University of Utah Grinnell College Department of Economics Seminar November 8, 2016 Introduction
The Impact of Shareholder Taxation on Merger and Acquisition Behavior Eric Ohrn, Grinnell College Nathan Seegert, University of Utah Grinnell College Department of Economics Seminar November 8, 2016 Introduction
Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models)
 Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models) Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Example #1... 1 Example #2... 10 Summary Monte Carlo simulation is used to estimate the distribution of variables when
Monte Carlo Simulation (General Simulation Models) Revised: 10/11/2017 Summary... 1 Example #1... 1 Example #2... 10 Summary Monte Carlo simulation is used to estimate the distribution of variables when
Sources of Financing in Different Forms of Corporate Liquidity and the Performance of M&As
 Sources of Financing in Different Forms of Corporate Liquidity and the Performance of M&As Zhenxu Tong * University of Exeter Jian Liu ** University of Exeter This draft: August 2016 Abstract We examine
Sources of Financing in Different Forms of Corporate Liquidity and the Performance of M&As Zhenxu Tong * University of Exeter Jian Liu ** University of Exeter This draft: August 2016 Abstract We examine
Online Appendix for. Explaining Corporate Capital Structure: Product Markets, Leases, and Asset Similarity. Joshua D.
 Online Appendix for Explaining Corporate Capital Structure: Product Markets, Leases, and Asset Similarity Section 1: Data A. Overview of Capital IQ Joshua D. Rauh Amir Sufi Capital IQ (CIQ) is a Standard
Online Appendix for Explaining Corporate Capital Structure: Product Markets, Leases, and Asset Similarity Section 1: Data A. Overview of Capital IQ Joshua D. Rauh Amir Sufi Capital IQ (CIQ) is a Standard
This document consists of three sections: Section IA.1 examines the sensitivity of our
 Internet Appendix for Determinants and Consequences of Information Processing Delay: Evidence from Thomson Reuters Institutional Brokers Estimate System This document consists of three sections: Section
Internet Appendix for Determinants and Consequences of Information Processing Delay: Evidence from Thomson Reuters Institutional Brokers Estimate System This document consists of three sections: Section
Regression Discontinuity and. the Price Effects of Stock Market Indexing
 Regression Discontinuity and the Price Effects of Stock Market Indexing Internet Appendix Yen-Cheng Chang Harrison Hong Inessa Liskovich In this Appendix we show results which were left out of the paper
Regression Discontinuity and the Price Effects of Stock Market Indexing Internet Appendix Yen-Cheng Chang Harrison Hong Inessa Liskovich In this Appendix we show results which were left out of the paper
Deviations from Optimal Corporate Cash Holdings and the Valuation from a Shareholder s Perspective
 Deviations from Optimal Corporate Cash Holdings and the Valuation from a Shareholder s Perspective Zhenxu Tong * University of Exeter Abstract The tradeoff theory of corporate cash holdings predicts that
Deviations from Optimal Corporate Cash Holdings and the Valuation from a Shareholder s Perspective Zhenxu Tong * University of Exeter Abstract The tradeoff theory of corporate cash holdings predicts that
Internet Appendix for: Does Going Public Affect Innovation?
 Internet Appendix for: Does Going Public Affect Innovation? July 3, 2014 I Variable Definitions Innovation Measures 1. Citations - Number of citations a patent receives in its grant year and the following
Internet Appendix for: Does Going Public Affect Innovation? July 3, 2014 I Variable Definitions Innovation Measures 1. Citations - Number of citations a patent receives in its grant year and the following
DazStat. Introduction. Installation. DazStat is an Excel add-in for Excel 2003 and Excel 2007.
 DazStat Introduction DazStat is an Excel add-in for Excel 2003 and Excel 2007. DazStat is one of a series of Daz add-ins that are planned to provide increasingly sophisticated analytical functions particularly
DazStat Introduction DazStat is an Excel add-in for Excel 2003 and Excel 2007. DazStat is one of a series of Daz add-ins that are planned to provide increasingly sophisticated analytical functions particularly
Inflation and the Evolution of Firm-Level Liquid Assets
 Inflation and the Evolution of Firm-Level Liquid Assets Chadwick C. Curtis University of Richmond Julio Garín University of Georgia This Version: April 12, 2017 M. Saif Mehkari University of Richmond Abstract
Inflation and the Evolution of Firm-Level Liquid Assets Chadwick C. Curtis University of Richmond Julio Garín University of Georgia This Version: April 12, 2017 M. Saif Mehkari University of Richmond Abstract
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE doi /mnsc ec
 MANAGEMENT SCIENCE doi 10.1287/mnsc.1100.1159ec e-companion ONLY AVAILABLE IN ELECTRONIC FORM informs 2010 INFORMS Electronic Companion Quality Management and Job Quality: How the ISO 9001 Standard for
MANAGEMENT SCIENCE doi 10.1287/mnsc.1100.1159ec e-companion ONLY AVAILABLE IN ELECTRONIC FORM informs 2010 INFORMS Electronic Companion Quality Management and Job Quality: How the ISO 9001 Standard for
URL:
 Supplemental appendix to Evidence on the Insurance Effect of Redistributive Taxation by Charles Grant, Christos Koulovatianos, Alexander Michaelides, and Mario Padula, Review of Economics and Statistics,
Supplemental appendix to Evidence on the Insurance Effect of Redistributive Taxation by Charles Grant, Christos Koulovatianos, Alexander Michaelides, and Mario Padula, Review of Economics and Statistics,
Internet Appendix for Private Equity Firms Reputational Concerns and the Costs of Debt Financing. Rongbing Huang, Jay R. Ritter, and Donghang Zhang
 Internet Appendix for Private Equity Firms Reputational Concerns and the Costs of Debt Financing Rongbing Huang, Jay R. Ritter, and Donghang Zhang February 20, 2014 This internet appendix provides additional
Internet Appendix for Private Equity Firms Reputational Concerns and the Costs of Debt Financing Rongbing Huang, Jay R. Ritter, and Donghang Zhang February 20, 2014 This internet appendix provides additional
Internet Appendix to Quid Pro Quo? What Factors Influence IPO Allocations to Investors?
 Internet Appendix to Quid Pro Quo? What Factors Influence IPO Allocations to Investors? TIM JENKINSON, HOWARD JONES, and FELIX SUNTHEIM* This internet appendix contains additional information, robustness
Internet Appendix to Quid Pro Quo? What Factors Influence IPO Allocations to Investors? TIM JENKINSON, HOWARD JONES, and FELIX SUNTHEIM* This internet appendix contains additional information, robustness
 TABLE I SUMMARY STATISTICS Panel A: Loan-level Variables (22,176 loans) Variable Mean S.D. Pre-nuclear Test Total Lending (000) 16,479 60,768 Change in Log Lending -0.0028 1.23 Post-nuclear Test Default
TABLE I SUMMARY STATISTICS Panel A: Loan-level Variables (22,176 loans) Variable Mean S.D. Pre-nuclear Test Total Lending (000) 16,479 60,768 Change in Log Lending -0.0028 1.23 Post-nuclear Test Default
Geographic Diffusion of Information and Stock Returns
 Geographic Diffusion of Information and Stock Returns Jawad M. Addoum * University of Miami Alok Kumar University of Miami Kelvin Law Tilburg University February 12, 2014 ABSTRACT This study shows that
Geographic Diffusion of Information and Stock Returns Jawad M. Addoum * University of Miami Alok Kumar University of Miami Kelvin Law Tilburg University February 12, 2014 ABSTRACT This study shows that
Online appendix to Mark My Words: Information and the Fear of Declaring an Exchange Rate Regime
 Online appendix to Mark My Words: Information and the Fear of Declaring an Exchange Rate Regime Pierre-Guillaume Méon and Geoffrey Minne In this online appendix, we provide extra evidence complementing
Online appendix to Mark My Words: Information and the Fear of Declaring an Exchange Rate Regime Pierre-Guillaume Méon and Geoffrey Minne In this online appendix, we provide extra evidence complementing
Online Appendix (Not For Publication)
 A Online Appendix (Not For Publication) Contents of the Appendix 1. The Village Democracy Survey (VDS) sample Figure A1: A map of counties where sample villages are located 2. Robustness checks for the
A Online Appendix (Not For Publication) Contents of the Appendix 1. The Village Democracy Survey (VDS) sample Figure A1: A map of counties where sample villages are located 2. Robustness checks for the
Really Uncertain Business Cycles
 Really Uncertain Business Cycles Nick Bloom (Stanford & NBER) Max Floetotto (McKinsey) Nir Jaimovich (Duke & NBER) Itay Saporta-Eksten (Stanford) Stephen J. Terry (Stanford) SITE, August 31 st 2011 1 Uncertainty
Really Uncertain Business Cycles Nick Bloom (Stanford & NBER) Max Floetotto (McKinsey) Nir Jaimovich (Duke & NBER) Itay Saporta-Eksten (Stanford) Stephen J. Terry (Stanford) SITE, August 31 st 2011 1 Uncertainty
For Online Publication. The macroeconomic effects of monetary policy: A new measure for the United Kingdom: Online Appendix
 VOL. VOL NO. ISSUE THE MACROECONOMIC EFFECTS OF MONETARY POLICY For Online Publication The macroeconomic effects of monetary policy: A new measure for the United Kingdom: Online Appendix James Cloyne and
VOL. VOL NO. ISSUE THE MACROECONOMIC EFFECTS OF MONETARY POLICY For Online Publication The macroeconomic effects of monetary policy: A new measure for the United Kingdom: Online Appendix James Cloyne and
Washington University Fall Economics 487. Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3
 Washington University Fall 2001 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3 For this project, you will analyze the behaviour of 10
Washington University Fall 2001 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Monday 10/22 Final Project due Monday 12/3 For this project, you will analyze the behaviour of 10
Random Walks vs Random Variables. The Random Walk Model. Simple rate of return to an asset is: Simple rate of return
 The Random Walk Model Assume the logarithm of 'with dividend' price, ln P(t), changes by random amounts through time: ln P(t) = ln P(t-1) + µ + ε(it) (1) where: P(t) is the sum of the price plus dividend
The Random Walk Model Assume the logarithm of 'with dividend' price, ln P(t), changes by random amounts through time: ln P(t) = ln P(t-1) + µ + ε(it) (1) where: P(t) is the sum of the price plus dividend
 Table I Descriptive Statistics This table shows the breakdown of the eligible funds as at May 2011. AUM refers to assets under management. Panel A: Fund Breakdown Fund Count Vintage count Avg AUM US$ MM
Table I Descriptive Statistics This table shows the breakdown of the eligible funds as at May 2011. AUM refers to assets under management. Panel A: Fund Breakdown Fund Count Vintage count Avg AUM US$ MM
Citation for published version (APA): Shehzad, C. T. (2009). Panel studies on bank risks and crises Groningen: University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Panel studies on bank risks and crises Shehzad, Choudhry Tanveer IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Panel studies on bank risks and crises Shehzad, Choudhry Tanveer IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Has the Propensity to Pay Out Declined?
 Has the Propensity to Pay Out Declined? Gustavo Grullon Rice University grullon@rice.edu 713-348-6138 Bradley Paye Rice University bpaye@rice.edu 713-348-6030 Shane Underwood Rice University shaneu@rice.edu
Has the Propensity to Pay Out Declined? Gustavo Grullon Rice University grullon@rice.edu 713-348-6138 Bradley Paye Rice University bpaye@rice.edu 713-348-6030 Shane Underwood Rice University shaneu@rice.edu
Online Appendix A: Verification of Employer Responses
 Online Appendix for: Do Employer Pension Contributions Reflect Employee Preferences? Evidence from a Retirement Savings Reform in Denmark, by Itzik Fadlon, Jessica Laird, and Torben Heien Nielsen Online
Online Appendix for: Do Employer Pension Contributions Reflect Employee Preferences? Evidence from a Retirement Savings Reform in Denmark, by Itzik Fadlon, Jessica Laird, and Torben Heien Nielsen Online
Acemoglu, et al (2008) cast doubt on the robustness of the cross-country empirical relationship between income and democracy. They demonstrate that
 Acemoglu, et al (2008) cast doubt on the robustness of the cross-country empirical relationship between income and democracy. They demonstrate that the strong positive correlation between income and democracy
Acemoglu, et al (2008) cast doubt on the robustness of the cross-country empirical relationship between income and democracy. They demonstrate that the strong positive correlation between income and democracy
Financial Innovation and Borrowers: Evidence from Peer-to-Peer Lending
 Financial Innovation and Borrowers: Evidence from Peer-to-Peer Lending Tetyana Balyuk BdF-TSE Conference November 12, 2018 Research Question Motivation Motivation Imperfections in consumer credit market
Financial Innovation and Borrowers: Evidence from Peer-to-Peer Lending Tetyana Balyuk BdF-TSE Conference November 12, 2018 Research Question Motivation Motivation Imperfections in consumer credit market
Table 1a (Robustness) Event study of stock returns surrounding announcements of Fortune ranking scores
 Table 1a (Robustness) Event study of stock returns surrounding announcements of Fortune ranking scores This table presents cumulative abnormal returns (CARs) calculated over various intervals surrounding
Table 1a (Robustness) Event study of stock returns surrounding announcements of Fortune ranking scores This table presents cumulative abnormal returns (CARs) calculated over various intervals surrounding
Supplementary Material and Data for Catering Through Nominal Share Prices. Malcolm Baker, Robin Greenwood, and Jeffrey Wurgler October 1, 2008
 Supplementary Material and Data for Catering Through Nominal Share Prices Malcolm Baker, Robin Greenwood, and Jeffrey Wurgler October, 2008 Table A. Data table: Raw Market-to-Book Data. The market-to-book
Supplementary Material and Data for Catering Through Nominal Share Prices Malcolm Baker, Robin Greenwood, and Jeffrey Wurgler October, 2008 Table A. Data table: Raw Market-to-Book Data. The market-to-book
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Addison-Wesley.
 Appendix: Statistics in Action Part I Financial Time Series 1. These data show the effects of stock splits. If you investigate further, you ll find that most of these splits (such as in May 1970) are 3-for-1
Appendix: Statistics in Action Part I Financial Time Series 1. These data show the effects of stock splits. If you investigate further, you ll find that most of these splits (such as in May 1970) are 3-for-1
Stronger Risk Controls, Lower Risk: Evidence from U.S. Bank Holding Companies
 Stronger Risk Controls, Lower Risk: Evidence from U.S. Bank Holding Companies Andrew Ellul 1 Vijay Yerramilli 2 1 Kelley School of Business, Indiana University 2 C. T. Bauer College of Business, University
Stronger Risk Controls, Lower Risk: Evidence from U.S. Bank Holding Companies Andrew Ellul 1 Vijay Yerramilli 2 1 Kelley School of Business, Indiana University 2 C. T. Bauer College of Business, University
Employment protection: Do firms perceptions match with legislation?
 Economics Letters 90 (2006) 328 334 www.elsevier.com/locate/econbase Employment protection: Do firms perceptions match with legislation? Gaëlle Pierre, Stefano Scarpetta T World Bank, 1818 H Street NW,
Economics Letters 90 (2006) 328 334 www.elsevier.com/locate/econbase Employment protection: Do firms perceptions match with legislation? Gaëlle Pierre, Stefano Scarpetta T World Bank, 1818 H Street NW,
starting on 5/1/1953 up until 2/1/2017.
 An Actuary s Guide to Financial Applications: Examples with EViews By William Bourgeois An actuary is a business professional who uses statistics to determine and analyze risks for companies. In this guide,
An Actuary s Guide to Financial Applications: Examples with EViews By William Bourgeois An actuary is a business professional who uses statistics to determine and analyze risks for companies. In this guide,
Online Appendix. Do Funds Make More When They Trade More?
 Online Appendix to accompany Do Funds Make More When They Trade More? Ľuboš Pástor Robert F. Stambaugh Lucian A. Taylor April 4, 2016 This Online Appendix presents additional empirical results, mostly
Online Appendix to accompany Do Funds Make More When They Trade More? Ľuboš Pástor Robert F. Stambaugh Lucian A. Taylor April 4, 2016 This Online Appendix presents additional empirical results, mostly
Online Appendix Table 1. Robustness Checks: Impact of Meeting Frequency on Additional Outcomes. Control Mean. Controls Included
 Online Appendix Table 1. Robustness Checks: Impact of Meeting Frequency on Additional Outcomes Control Mean No Controls Controls Included (Monthly- Monthly) N Specification Data Source Dependent Variable
Online Appendix Table 1. Robustness Checks: Impact of Meeting Frequency on Additional Outcomes Control Mean No Controls Controls Included (Monthly- Monthly) N Specification Data Source Dependent Variable
Investment and Capital Constraints: Repatriations Under the American Jobs Creation Act
 Investment and Capital Constraints: Repatriations Under the American Jobs Creation Act Online Appendix: Additional Results I) Description of AJCA Repatriation Restrictions. This is a more complete description
Investment and Capital Constraints: Repatriations Under the American Jobs Creation Act Online Appendix: Additional Results I) Description of AJCA Repatriation Restrictions. This is a more complete description
Economic Development and the Margins of Trade: Are the Least Developed Countries Different?
 Economic Development and the Margins of Trade: Are the Least Developed Countries Different? Jesse Mora (Occidental College) Michael Olabisi (Michigan State University) August 3, 2018 Abstract The growing
Economic Development and the Margins of Trade: Are the Least Developed Countries Different? Jesse Mora (Occidental College) Michael Olabisi (Michigan State University) August 3, 2018 Abstract The growing
Interest Rate Pass-Through: Mortgage Rates, Household Consumption, and Voluntary Deleveraging. Online Appendix
 Interest Rate Pass-Through: Mortgage Rates, Household Consumption, and Voluntary Deleveraging Marco Di Maggio, Amir Kermani, Benjamin J. Keys, Tomasz Piskorski, Rodney Ramcharan, Amit Seru, Vincent Yao
Interest Rate Pass-Through: Mortgage Rates, Household Consumption, and Voluntary Deleveraging Marco Di Maggio, Amir Kermani, Benjamin J. Keys, Tomasz Piskorski, Rodney Ramcharan, Amit Seru, Vincent Yao
Playing to the Gallery: Corporate Policies and Equity Research Analysts
 Playing to the Gallery: Corporate Policies and Equity Research Analysts François Degeorge University of Lugano - Swiss Finance Institute François Derrien HEC Paris Ambrus Kecskés Virginia Tech Sébastien
Playing to the Gallery: Corporate Policies and Equity Research Analysts François Degeorge University of Lugano - Swiss Finance Institute François Derrien HEC Paris Ambrus Kecskés Virginia Tech Sébastien
Internet Appendix to Leverage Constraints and Asset Prices: Insights from Mutual Fund Risk Taking
 Internet Appendix to Leverage Constraints and Asset Prices: Insights from Mutual Fund Risk Taking In this Internet Appendix, we provide further discussion and additional empirical results to evaluate robustness
Internet Appendix to Leverage Constraints and Asset Prices: Insights from Mutual Fund Risk Taking In this Internet Appendix, we provide further discussion and additional empirical results to evaluate robustness
The cross section of expected stock returns
 The cross section of expected stock returns Jonathan Lewellen Dartmouth College and NBER This version: March 2013 First draft: October 2010 Tel: 603-646-8650; email: jon.lewellen@dartmouth.edu. I am grateful
The cross section of expected stock returns Jonathan Lewellen Dartmouth College and NBER This version: March 2013 First draft: October 2010 Tel: 603-646-8650; email: jon.lewellen@dartmouth.edu. I am grateful
The Persistent Effect of Temporary Affirmative Action: Online Appendix
 The Persistent Effect of Temporary Affirmative Action: Online Appendix Conrad Miller Contents A Extensions and Robustness Checks 2 A. Heterogeneity by Employer Size.............................. 2 A.2
The Persistent Effect of Temporary Affirmative Action: Online Appendix Conrad Miller Contents A Extensions and Robustness Checks 2 A. Heterogeneity by Employer Size.............................. 2 A.2
Dot Plot: A graph for displaying a set of data. Each numerical value is represented by a dot placed above a horizontal number line.
 Introduction We continue our study of descriptive statistics with measures of dispersion, such as dot plots, stem and leaf displays, quartiles, percentiles, and box plots. Dot plots, a stem-and-leaf display,
Introduction We continue our study of descriptive statistics with measures of dispersion, such as dot plots, stem and leaf displays, quartiles, percentiles, and box plots. Dot plots, a stem-and-leaf display,
APPENDIX to Pyramidal Ownership and the Creation of New Firms
 APPENDIX to Pyramidal Ownership and the Creation of New Firms This Appendix reports additional results that we discuss but do not tabulate in the main text of the paper. The content is summarized below,
APPENDIX to Pyramidal Ownership and the Creation of New Firms This Appendix reports additional results that we discuss but do not tabulate in the main text of the paper. The content is summarized below,
Internet Appendix for Corporate Cash Shortfalls and Financing Decisions. Rongbing Huang and Jay R. Ritter. August 31, 2017
 Internet Appendix for Corporate Cash Shortfalls and Financing Decisions Rongbing Huang and Jay R. Ritter August 31, 2017 Our Figure 1 finds that firms that have a larger are more likely to run out of cash
Internet Appendix for Corporate Cash Shortfalls and Financing Decisions Rongbing Huang and Jay R. Ritter August 31, 2017 Our Figure 1 finds that firms that have a larger are more likely to run out of cash
Conflict in Whispers and Analyst Forecasts: Which One Should Be Your Guide?
 Abstract Conflict in Whispers and Analyst Forecasts: Which One Should Be Your Guide? Janis K. Zaima and Maretno Agus Harjoto * San Jose State University This study examines the market reaction to conflicts
Abstract Conflict in Whispers and Analyst Forecasts: Which One Should Be Your Guide? Janis K. Zaima and Maretno Agus Harjoto * San Jose State University This study examines the market reaction to conflicts
AP STATISTICS FALL SEMESTSER FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP STATISTICS Name: FALL SEMESTSER FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Period: *Go over Vocabulary Notecards! *This is not a comprehensive review you still should look over your past notes, homework/practice, Quizzes,
AP STATISTICS Name: FALL SEMESTSER FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Period: *Go over Vocabulary Notecards! *This is not a comprehensive review you still should look over your past notes, homework/practice, Quizzes,
Washington University Fall Economics 487
 Washington University Fall 2009 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Tuesday 11/10 Final Project due Wednesday 12/9 (by 5:00pm) (20% penalty per day if the project is
Washington University Fall 2009 Department of Economics James Morley Economics 487 Project Proposal due Tuesday 11/10 Final Project due Wednesday 12/9 (by 5:00pm) (20% penalty per day if the project is
ONLINE APPENDIX. Concentrated Powers: Unilateral Executive Authority and Fiscal Policymaking in the American States
 ONLINE APPENDIX Concentrated Powers: Unilateral Executive Authority and Fiscal Policymaking in the American States As noted in Note 13 of the manuscript document, discrepancies exist between using Thad
ONLINE APPENDIX Concentrated Powers: Unilateral Executive Authority and Fiscal Policymaking in the American States As noted in Note 13 of the manuscript document, discrepancies exist between using Thad
Factors in the returns on stock : inspiration from Fama and French asset pricing model
 Lingnan Journal of Banking, Finance and Economics Volume 5 2014/2015 Academic Year Issue Article 1 January 2015 Factors in the returns on stock : inspiration from Fama and French asset pricing model Yuanzhen
Lingnan Journal of Banking, Finance and Economics Volume 5 2014/2015 Academic Year Issue Article 1 January 2015 Factors in the returns on stock : inspiration from Fama and French asset pricing model Yuanzhen
Dividend Changes and Future Profitability
 THE JOURNAL OF FINANCE VOL. LVI, NO. 6 DEC. 2001 Dividend Changes and Future Profitability DORON NISSIM and AMIR ZIV* ABSTRACT We investigate the relation between dividend changes and future profitability,
THE JOURNAL OF FINANCE VOL. LVI, NO. 6 DEC. 2001 Dividend Changes and Future Profitability DORON NISSIM and AMIR ZIV* ABSTRACT We investigate the relation between dividend changes and future profitability,
Firm Manipulation and Take-up Rate of a 30 Percent. Temporary Corporate Income Tax Cut in Vietnam
 Firm Manipulation and Take-up Rate of a 30 Percent Temporary Corporate Income Tax Cut in Vietnam Anh Pham June 3, 2015 Abstract This paper documents firm take-up rates and manipulation around the eligibility
Firm Manipulation and Take-up Rate of a 30 Percent Temporary Corporate Income Tax Cut in Vietnam Anh Pham June 3, 2015 Abstract This paper documents firm take-up rates and manipulation around the eligibility
SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE APPENDIX FOR: TECHNOLOGY AND COLLECTIVE ACTION: THE EFFECT OF CELL PHONE COVERAGE ON POLITICAL VIOLENCE IN AFRICA
 SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE APPENDIX FOR: TECHNOLOGY AND COLLECTIVE ACTION: THE EFFECT OF CELL PHONE COVERAGE ON POLITICAL VIOLENCE IN AFRICA 1. CELL PHONES AND PROTEST The Afrobarometer survey asks whether respondents
SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE APPENDIX FOR: TECHNOLOGY AND COLLECTIVE ACTION: THE EFFECT OF CELL PHONE COVERAGE ON POLITICAL VIOLENCE IN AFRICA 1. CELL PHONES AND PROTEST The Afrobarometer survey asks whether respondents
The Comovements Along the Term Structure of Oil Forwards in Periods of High and Low Volatility: How Tight Are They?
 The Comovements Along the Term Structure of Oil Forwards in Periods of High and Low Volatility: How Tight Are They? Massimiliano Marzo and Paolo Zagaglia This version: January 6, 29 Preliminary: comments
The Comovements Along the Term Structure of Oil Forwards in Periods of High and Low Volatility: How Tight Are They? Massimiliano Marzo and Paolo Zagaglia This version: January 6, 29 Preliminary: comments
Hedge fund Activism. Updated tables and figures. Hyunseob Kim Johnson Graduate School of Management Cornell University Ithaca, NY 14853, USA
 Hedge fund Activism Updated tables and figures Alon Brav Fuqua School of Business Duke University Durham, NC 27708, USA Wei Jiang Columbia Business School New York, NY 10027, USA Hyunseob Kim Johnson Graduate
Hedge fund Activism Updated tables and figures Alon Brav Fuqua School of Business Duke University Durham, NC 27708, USA Wei Jiang Columbia Business School New York, NY 10027, USA Hyunseob Kim Johnson Graduate
Conservatism and stock return skewness
 Conservatism and stock return skewness DEVENDRA KALE*, SURESH RADHAKRISHNAN, and FENG ZHAO Naveen Jindal School of Management, University of Texas at Dallas, 800 West Campbell Road, Richardson, Texas 75080
Conservatism and stock return skewness DEVENDRA KALE*, SURESH RADHAKRISHNAN, and FENG ZHAO Naveen Jindal School of Management, University of Texas at Dallas, 800 West Campbell Road, Richardson, Texas 75080
A Rising Tide Lifts All Boats? IT growth in the US over the last 30 years
 A Rising Tide Lifts All Boats? IT growth in the US over the last 30 years Nicholas Bloom (Stanford) and Nicola Pierri (Stanford)1 March 25 th 2017 1) Executive Summary Using a new survey of IT usage from
A Rising Tide Lifts All Boats? IT growth in the US over the last 30 years Nicholas Bloom (Stanford) and Nicola Pierri (Stanford)1 March 25 th 2017 1) Executive Summary Using a new survey of IT usage from
Institutional Investor Monitoring Motivation and the Marginal Value of Cash
 Institutional Investor Monitoring Motivation and the Marginal Value of Cash Chao Yin 1 1 ICMA Centre, Henley Business School, University of Reading Abstract This paper examines whether the motivation of
Institutional Investor Monitoring Motivation and the Marginal Value of Cash Chao Yin 1 1 ICMA Centre, Henley Business School, University of Reading Abstract This paper examines whether the motivation of
Online appendix to Understanding Weak Capital Investment: the Role of Market Concentration and Intangibles
 Online appendix to Understanding Weak Capital Investment: the Role of Market Concentration and Intangibles Nicolas Crouzet and Janice Eberly This version: September 6, 2018 We report results of the analysis
Online appendix to Understanding Weak Capital Investment: the Role of Market Concentration and Intangibles Nicolas Crouzet and Janice Eberly This version: September 6, 2018 We report results of the analysis
Appendix A: Descriptive Statistics
 Supplementary appendices for Graeme T. Boushey and Robert J. McGrath. N.d. (forthcoming). Experts, Amateurs, and Bureaucratic Influence in the American States. Journal of Public Administration Research
Supplementary appendices for Graeme T. Boushey and Robert J. McGrath. N.d. (forthcoming). Experts, Amateurs, and Bureaucratic Influence in the American States. Journal of Public Administration Research
Risk, Insurance and Wages in General Equilibrium. A. Mushfiq Mobarak, Yale University Mark Rosenzweig, Yale University
 Risk, Insurance and Wages in General Equilibrium A. Mushfiq Mobarak, Yale University Mark Rosenzweig, Yale University 750 All India: Real Monthly Harvest Agricultural Wage in September, by Year 730 710
Risk, Insurance and Wages in General Equilibrium A. Mushfiq Mobarak, Yale University Mark Rosenzweig, Yale University 750 All India: Real Monthly Harvest Agricultural Wage in September, by Year 730 710
Online Appendix for Unemployment Insurance as a Housing Market Stabilizer
 Online Appendix for Unemployment Insurance as a Housing Market Stabilizer By JOANNE W. HSU, DAVID A. MATSA, AND BRIAN T. MELZER * Appendix A. Using LPS to calculate extended benefits effect on the probability
Online Appendix for Unemployment Insurance as a Housing Market Stabilizer By JOANNE W. HSU, DAVID A. MATSA, AND BRIAN T. MELZER * Appendix A. Using LPS to calculate extended benefits effect on the probability
1 Payroll Tax Legislation 2. 2 Severance Payments Legislation 3
 Web Appendix Contents 1 Payroll Tax Legislation 2 2 Severance Payments Legislation 3 3 Difference-in-Difference Results 5 3.1 Senior Workers, 1997 Change............................... 5 3.2 Young Workers,
Web Appendix Contents 1 Payroll Tax Legislation 2 2 Severance Payments Legislation 3 3 Difference-in-Difference Results 5 3.1 Senior Workers, 1997 Change............................... 5 3.2 Young Workers,
The Role of APIs in the Economy
 The Role of APIs in the Economy Seth G. Benzell, Guillermo Lagarda, Marshall Van Allstyne June 2, 2016 Abstract Using proprietary information from a large percentage of the API-tool provision and API-Management
The Role of APIs in the Economy Seth G. Benzell, Guillermo Lagarda, Marshall Van Allstyne June 2, 2016 Abstract Using proprietary information from a large percentage of the API-tool provision and API-Management
The Consistency between Analysts Earnings Forecast Errors and Recommendations
 The Consistency between Analysts Earnings Forecast Errors and Recommendations by Lei Wang Applied Economics Bachelor, United International College (2013) and Yao Liu Bachelor of Business Administration,
The Consistency between Analysts Earnings Forecast Errors and Recommendations by Lei Wang Applied Economics Bachelor, United International College (2013) and Yao Liu Bachelor of Business Administration,
STAT 157 HW1 Solutions
 STAT 157 HW1 Solutions http://www.stat.ucla.edu/~dinov/courses_students.dir/10/spring/stats157.dir/ Problem 1. 1.a: (6 points) Determine the Relative Frequency and the Cumulative Relative Frequency (fill
STAT 157 HW1 Solutions http://www.stat.ucla.edu/~dinov/courses_students.dir/10/spring/stats157.dir/ Problem 1. 1.a: (6 points) Determine the Relative Frequency and the Cumulative Relative Frequency (fill
