PROTECTION OF INVESTORS IN INDIA
|
|
|
- Oliver Young
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PROTECTION OF INVESTORS IN INDIA *Moushumi Sarmah,Department: Law [ Pursuing LL.M],Gujarat National Law University Abstract: It is usually not possible for a company to encounter any kinds of risks alone due to huge financial burdens upon them. Companies opting for huge projects usually face such kind of situation. To tackle these dangers furthermore to diminish monetary troubles a company in this way normally searches for aid from the public by indulging them to make investments through different ways. Therefore, the security laws came into being to protect the interest of those persons who invest in such a company as investors. Security laws or capital market which are of two types primary market, where securities are sold for the first time and secondary market, where previously issued securities are bought and sold investment protection is provided to them. Investors are protected through structural framework where the regulatory bodies empowered through various Acts, guidelines and regulations maintain smooth functioning and transparency in the security market and through legal framework where the statutory provisions like rules, guidelines circulars etc protect the interests of investors. This paper will shed light upon the following points: Securities market Investor protection- Structural framework Investor protection- Legal framework Conclusions and suggestions The author will be using non-doctrinal and empirical research technique of research methodology. The study adopts Oscola citation style format. The researcher will be using both primary sources such as legislations, treaties and conventions as well as secondary sources of data such as books, articles, journals, reports, cases and judicial interpretations. Key words: Investors, protection, securities law. 1
2 Introduction: An investor is a person who allocates capital with the expectation of a financial return. Generally, the primary concern of an investor is to minimize risk while maximizing return, as opposed to a speculator, who is willing to accept a higher level of risk in the hopes of collecting higher than average. In simple terms, investor is a person or group of persons who invest in a company through a security market while in wider terms an investor is an individual (either natural or artificial) or classes of persons or special entity who or which use to commit money or capital with intention to gain a financial return in terms of profit. In India, security market usually refers to capital market and capital market is broadly divided into primary market and secondary market. Investment is time, energy, or matter spent in the hope of future benefits actualized within a specified date or time frame. Investment has different meanings in economics and finance. In economics, investment is the accumulation of newly produced physical entities, such as factories, machinery, houses, and goods inventories. In finance, investment is buying or creating an asset with the expectation of capital appreciation, dividends (profit), interest earnings, rents or some combination of these returns. Financial investment denotes a business where capitals are invested for procurement of shares of a company through a recognised SE and by which a company is also bound to pay the specified share of a profit to the persons who invested their money in the security market. The term investor protection means a process or a mechanism by which the interest of an investor is protected in the security market. Basically, it denotes the acts done with object to bring and also maintain transparency in procedural aspect while dealing with investor through some regulatory bodies by means of some suitable legislation. In order to protect the interest of the investors, various investors protection mechanisms have been established in India. There are mainly three means i.e mechanisms to protect the interest of investors in the security marketregulatory bodies like SEBI, various Acts and Judiciaries. 2
3 Securities market: A security is a financial instrument that represents: an ownership position in a publicly-traded corporation (stock), a creditor relationship with governmental body or a corporation (bond), or rights to ownership as represented by an option. It is a fungible, negotiable financial instrument that represents some type of financial value. Section 2 (h) of the Security Control Regulation Act, 1956 defines security and it includes shares, scripts, stocks, bonds, debentures, debenture stock or other marketable securities like derivative, government securities, various mutual funds etc. 1 Securities market is a component of the wider financial market where securities can be bought and sold between subjects of the economy, on the basis of demand and supply. It is a place where trading take place with intention to raise money from the investors by the various companies to undertake their projects, expansion of business programmes as these require a huge amount of investments. In India, security market is usually known as capital market which is broadly divided into primary and secondary markets. The primary market is that part of the capital markets that deals with the issue of new securities. The primary market is the market where the securities are sold for the first time. Therefore it is also called the new issue market (NIM). In a primary issue, the securities are issued by the company directly to investors as prescribed under Companies Act, 1956, Listing and other SEBI guidelines. The secondary market, also known as the aftermarket, is the financial market where previously issued securities and financial instruments such as stock, bonds, options, and futures are bought and sold. As secondary market is bigger than primary market therefore investment protection is mainly provided to secondary market. History of securities market: In India in 1875, The Native Share and Stock Brokers Association 2 was established. To control fraud and other illegal transaction in the securities market, the Bombay Securities Contracts Control Act, 1925 was enacted but it failed to do so. Thus, the concept of security market 1 Taxman s SEBI Manual (15 th edn, Taxmann Publications 2010) 2 Now known as Bombay Stock Exchange 3
4 prevailed in the pre- independent era i.e when India was under British rule. Therefore to tackle this problem the A.D Gorwala Committee was formed and based upon its recommendations the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956 was enacted to prevent illegal transaction in the security market. The Capital Issue (Control) Act, 1947 was also enacted to regulate to control over issues of capital. After independence numerous attempts were made to control the activities under security markets through legal framework but it could not succeed to achieve it 3. In 1991 when India adopted the liberalising policy in the industrial sector, it opened the door for the foreign investors in the security market and the concept of security market has been changed drastically. Moreover due to globalisation the business has flourished worldwide. 4 Though a number of scams like Harshad Maheta, Satyam Scam etc took place which directly affected the investors but it didn t stop the investors to invest money in the security market and they continued to do so. In the New Economic Policy adopted by the Government of India due importance was given to the security market by the reform made in the SE. Some of the objects of Indian Security market are as follows: to ensure nationwide trading facilities for all types of securities, provide equal opportunity and scope to all investors to invest their money with the help of advanced technologies, ensure the transparency and safety in the security trading by adopting adequate safety measures. 5 For bringing an economic reform in India, Government made some reforms in the structure of capital market to maintain the consistency between newly adopted liberalising industrial policy and capital market. Thus, the Narasimham Committee 6 was appointed and it made some recommendations like setting up a strong regulatory body by vesting immense power to regulate the capital i.e security market, vesting power to frame its own regulations as per requirement to control the capital market in a better way, free entry to capital market etc. Realising that the present Acts and regulations are not sufficient and an autonomous body must be established to regulate the security market, the Government accepted the recommendations made by the committee and enacted the SEBI Act in SEBI was established under the SEBI Act, Investor Protection: Structural Framework- 3 Tierney Robert B., New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission < uws extension bkln hd & 3 landmarks approved.pdf> accessed 25 March K.Sekhar, Guide to SEBI capital issues debentures and listing ( 3 rd edn, Wadhwa &Company 2003) 5 Objectives of Indian securities market < accessed 26 March In the name of Shri M. Narasimham who was appointed as a chairperson of this committee. 4
5 Structural framework means the various regulatory bodies working in the capital market responsible for the protection of investors at various levels as entrusted by Acts, Regulations and Guidelines. These regulatory bodies provide smooth functioning, maintaining the reputation and transparency in the capital market. The term investor protection means those steps and measures which are required to protect the interest of the investors by enacting suitable legislation, establishing regulatory bodies or by passing of regulations or guidelines for protecting the interest of the investors in the capital market. The term enforcement bodies means the various regulatory bodies which can enforce the right guaranteed to the investors on account of infringement by imposing punishment through various Acts. The enforcement bodies are: SEBI, Central Government, SAT, Tribunal, Judiciary. The four main legislations governing the securities market i.e under which an approach can be made to various regulatory bodies are: (a) the SEBI Act, 1992 which established SEBI to protect investors and develop and regulate securities market; (b) the Companies Act, 2013 which sets out the code of conduct for the corporate sector in relation to issue, allotment and transfer of securities, and disclosures to be made in public issues; (c) the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act, 1956, which provides for regulation of transactions in securities through control over stock exchanges; (d) the Depositories Act, 1996 which provides for electronic maintenance and transfer of ownership of demat securities. SEBI: The main object of SEBI is to preserve the interest of the investor in the capital market 7. Its head office is situated in Bombay and it has various branch offices in Kolkata, Delhi, Chennai and Ahmedabad, Jaipur and Bangalore. It has also opened its new offices in Guwahati, Bhubaneshwar, Patna, Kochi and Chandigarh. 8 Protection done by SEBI under the SEBI Act: 9 Nature of Grievance Mode of taking Section Remedies and against whom it cognizance 7 The preamble of the SEBI says to protect the interests of investors in securities and to promote the development of and to regulate the securities market and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto 8 Securities and exchange board of India < accessed 28 March Adjudication is done by a person i.e, who is not below the rank of divisional chief of the SEBI. 5
6 is made If any intermediaries Section 11C 10 Appoint any person or any person being an investigating associated with authority to security market investigate the matter. engages himself for It may summon to doing certain acts any intermediaries or which amount to any person associated violation of any with the security provision of SEBI market to: furnish Act or involved or necessary will fully allowed to information, produce do any transactions all relevant which infringed the documents, take right of the investors custody of these documents, sought help of a judicial magistrate of 1 st class for search and seizure as per provision of CrPC on account of reasonable appreciation for being destroyed of any documents including records by any intermediaries or other person involved in the security market, can imposed punishment of 10 The language of the provision given in section 11 C is not clear as the starting sentence clearly states while the board has reasonable ground to believe, Sumit Agarwal & Robin Joseph Baby, SEBI Act (Taxmann Publication 2011) 6
7 Imprisonment upto 1yr or fine upto 1crore rupees or with both. Failure to- Section 15 A Penalty of Rs 1lakh furnish any information, return or report etc to SEBI, file any return or to furnish any information, books or upon complaint made by third 11 shall be imposed upon the defaulter for each day during which such failure continues or Rs. 1 crore whichever is less other documents within the specified time under any regulation made by SEBI, maintain books of account or records. If a registered Section 15B Penalty of Rs 1lakh intermediary has shall be imposed failed to enter into a upon the defaulter for contract with his each day during which client as per such failure continues requirement of any 12 or Rs. 1 crore Act, regulation or whichever is less rules. Failure of a registered Section 15 C Penalty of Rs 1lakh 11 The language of the provision given in section 11 C is not clear as the starting sentence clearly states while the board has reasonable ground to believe, Sumit Agarwal &Robin Joseph Baby, SEBI Act (Taxmann Publication 2011) 12 The language of the provision given in section 11 C is not clear as the starting sentence clearly states while the board has reasonable ground to believe,, Sumit Agarwal &Robin Joseph Baby, SEBI Act (Taxmann Publication 2011) 7
8 intermediary after shall be imposed giving reasonable time upon the defaulter for to rectify investor s each day during which grievances such failure continues 13 or Rs. 1 crore whichever is less Commencement of Section 15D Penalty of Rs 1lakh business relating to shall be imposed collective investment upon the defaulter for schemes, mutual each day during which funds without such failure continues obtaining a certificate 14 or Rs. 1 crore from the SEBI, if a whichever is less person registered for collective investment schemes, mutual funds failed to despatch unit certificate of any scheme and to invest money collected under those schemes. If an asset Section 15 E Penalty of Rs 1lakh management shall be imposed company duly upon the defaulter for registered under this each day during which Act failed to comply such failure continues with the rules and or Rs. 1 crore regulations provided whichever is less for imposing restrictions on the 13 Ibid. 14 Ibid. 8
9 asset management companies while dealing with their business 15 If the registered stock Section 15F Penalty of Rs 1lakh broker failed to issue shall be imposed contract notes upon the defaulter for according to the each day during which specified manner such failure continues given by SE of which or Rs. 1 crore he is a member, if the whichever is less registered broker failed to deliver any security instrument or failed to make payment the amount to the investors entitled to get it. If in an insider trading Section 15G Penalty of 25 crores any insider 16 either rupees or three times himself or on behalf of the profit made of other dealt through such insider securities belonged to trading whichever is somebody corporate higher shall be listed on a SE on the imposed basis of any unpublished pricesensitive information 15 A company that registered with SEBI and steers the ship of decision relating to various investments/ disinvestments done by various mutual fund and also theraby manage the assest of mutual fund, however this type of company is registered under Section 11(2) (c) of the SEBI Act, Insider means any person who is or was connected with the company or is deemed to have been connected with the company and is reasonably expected to have access to unpublished price sensitive information in respect of securities of a company or has received or has had access to such unpublished price sensitive information. However for more information please refer the regulation 2(e) of the SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading ) Regulation,
10 etc. Protection done by SEBI under SCRA Act: Nature of Grievance Mode of taking Section Remedies available and against whom it cognizance is made If any SE engaged itself to do certain act which is against the interest of trade or for the interest of investors 17 Section 5 Withdraw of recognition by stating the reason and after giving an opportunity of being heard In case of occurrence Section 12 Suspend the business of any emergencies if of SE by stating the the situation has reason for initially 7 arisen under which days which may for the Central the public interest Government has no 18 extend up to certain option except time as fixed by the suspension of Central Government business of that SE by notification. 17The language of the provision given in concerned section is not clear as it didn t mention clearly, SEBI Manual, (15 th edn, Taxmann publication 2010) 18 Ibid. 10
11 If any person enters Section 23 Imprisonment up to into a contract which 10 years or with fine is against the up to 25 crore rupees provision of Section or with both and Section 16 20, section 18 A 21 or the rules made under Section or does any act in contravention to Section 17, 17 A 23 or 19 24, 21, 21 A, or against the orders of SAT If a person failed to Section 23A Penalty of Rs. 1lakh maintain books of per day during which account as per such failure will direction given in list continue or 1 crore ing agreement or any rupees whichever is by laws less. If a person failed to Section 23 C Penalty of Rs. 1lakh redress i.e rectify the per day during which investor s grievances. such failure will 19Section 13 authorised the Central Govt considering the nature or volume of the transaction of the securities may prohibit certain transaction by Gazette notification. 20 Section 16 says about the power of Central Govt to prohibit ceratin contract in certain cases. 21 Section 18 A talks about contract in derivative and inserted by the Security Laws(Amendment)Act, 1999 which came into effect on 22 nd Feb, Section 30 confers the power on Central Govt to make rule with intention to achieve the better enforcement of this Act Section 17 and 17A talks about licensing of dealers in securities in certain areas and public issue & listing of securities referred to in sub-clause (ie) of clause (h) of section 2. Section 17 A was inserted by the Security Contract Regulation (Amendment)Act, 2007 which came into effect on 28 th day of May, Section 19 talks about the power of Central Govt. regarding prohibition of SE other than those which are not duly registered. 25 These sections talks about the conditions for listing, delisting of securities & right to appeal against the refusal of listing of securities in a public company. Section 21 A inserted by Security Laws (Amendment)Act, 2004 which came into effect on 12th oct,
12 continue or 1 crore rupees whichever is less. If a person Section 23 F Penalty in the form of dematerialised or fine will be imposed deliver the unlisted which shall not securities in excess exceed 25 core rupees. Under Section 11C, 26 in K. Venkataeswarlu vs The Regional Manager SEBI & others 27 observed that power vested under this section to SEBI purely discretionary and no one can challenge it. In this case investigation under this section was sought by constituting a technical body as the matter involves technicalities. The Delhi HC rejected that petition on the ground that such decision purely lies upon SEBI & couldn t be inferred unless arbitrary act or mala fide intention of SEBI has been challenged. Government of India: The central government along with SEBI has been given powers under the SCRA, 1956 to protect the interest of the investors. Nature of Grievance Mode of taking Section Remedies available and against whom it cognizance is made If any SE engaged itself to do certain act which is against the interest of trade or for the interest of investors Section 5 Withdraw of recognition by stating the reason and after giving an opportunity of being heard 26 It gives a discretionary power to SEBI to appoint any outsider if any person associated with security market does any act which amounts to violation of any provisions of SEBI Act or which violates either directly or indirectly the right of any investors to punish accordingly. Inserted by SEBI (Amendment) Act of 2002 which came into effect on 29 th october, Writ petition (Crl.) No 1008/2007 decided on 7 th day of August,
13 In case of occurrence Section 12 Suspend the business of any emergencies if of SE by stating the the situation has reason for initially 7 arisen under which days which may for the Central the public interest Government has no extend up to certain option except time as fixed by the suspension of Central Government business of that SE by notification. In case opening any Section 19 Prohibit certain SE SE other than those from becoming duly organized operational. Security Appellate Tribunal (SAT): The provision relating to SAT is dealt with in Chapter VI B 28. SAT was established to give relief to the investors and to maintain transparency in the security market. Before the SEBI (Amendment) Act, an appeal against the order of SAT lied to HC and then to SC but after this amendment now an appeal can be made directly to the SC against the order of SAT. Section 15 deals with the procedure and powers of SAT. SAT acts a civil court but in Section 15 U (3) it has been mentioned that under certain circumstances under section 193, 196 & 228 of IPC and for the purpose of section 195 & chapter XXVI of Cr.P.C it got the power vested in a criminal court and is entitled to inflict punishment 30. The powers that are entrusted to SEBI are also exercised by SAT as it comes for appeal against the order of SEBI. However, the power 28 Inserted through Securities Laws (Amendment) Act, 1995 which came into effect from 25 th January, Came into effect from 29 th October, Section 193, 196 & 228 respectively deal with punishment for giving false evidence, punishment for using evidence known to be false and punishment for intention insult or interruption to public servant sitting in the Judicial proceeding. Section 195 & chapter XXVI deal with prosecution for contempt of lawful authority of public servants for offence against public justice and for offence relating to documents given in evidence and offences affecting the administration of justice. 13
14 vested in SAT is not much effective as no provision like other statute 31 was made for the enforcement or execution of its orders and sometimes it is proved to be ineffective in respect of investors protection. 32 In State of Karnataka vs. Vishwabharati House Building Cop. Society, 33 it was observed that it is now a settled principle that to render a proper justice and also to give an effective relief to the litigant, the tribunals which have been created to deal with the special matters must have vested power so that it can implement/execute its order properly. Tribunal: The Company Law Board also plays a vital role in protecting the interests of the investors in the capital market. The Companies Act, 2013 provides various provisions which give powers to the CLB for protecting the interests of the investors. They are as follows: Nature of Grievance Mode of taking Section Remedies available and against whom it cognizance is made Any member 34 of a Upon the complaint Section 241 Pass a necessary order company reasonably made by specified as it think fit for the suspected that the acts member of that purpose of protection conducted by a company of investors & before company in a manner that, notice to be which is amount to an given to the Central oppression and cause Govt prejudiced the interest of the public(mainly investors) When any member Upon the complaint Section 242 Pass a necessary order commits made by specified as it think fit for the mismanagement of a member of that purpose of protection 31 Like section 19 of the TRAI Act, 2002 and section 53P of the Competition Act, Alkan Projects Pvt. Ltd vs SEBI 33 AIR 2003 SC The members who are entitled to file a complaint have been specifically provided under Sec 399 of the Act. 14
15 company that company of investors & before amounts to injurious that, notice to be to public interests given to the Central Govt When any member Upon the complaint Section 242 Pass a necessary order commits made by specified as it think fit for the mismanagement of a member of that purpose of protection company by bringing company of investors & before materials changes that,notice to be given to the Central Govt The Tribunal can pass the following orders: To regulate the company s affairs in future [ Sec ] To direct any other members to purchase the share of that company [ Sec. 242] Can terminate or modify or setting aside any agreement [Section 242] etc. Judiciary: The Judiciary also plays an important to protect the interests of the investors. Prior to Security Law (Amendment) Act, 2002 an appeal against the order of SAT can be made in the High Court but after this amendment an appeal against the order of SAT can be made directly to the Supreme Court. However, if a writ petition is filed under Article 226 of the Constitution then High Court plays an important role to protect the interests of the investors. An aggrieved person can approach the SC by two ways: Firstly, if a person is aggrieved by any decision passed by the SEBI he can approach the SAT and if he not satisfied by its decision he can approach the SC. 36 Secondly, an investor can approach the HC by filing a writ petition under Article 226 and if he is not satisfied by the judgement passed by the HC he can move to the SC through an appeal filed under Article 133 (2) of the Indian Constitution Companies Act, Section 15 T, Section 15 Z of the SEBI Act, Article 133(2) - Notwithstanding anything in the article 132 any party appealing to the Supreme Court can under clause (1) may urge as one of the grounds in such appeal that a substantial question of law as to the interpretation of this Constitution has been wrongfully decided. However, prior to that as per provision of Article 132 (1) a certificate 15
16 Besides the above ways of approaching the SC, an investor can directly approach the SC under Article 136 of the Constitution. In Jaswant Singh Mills vs. Lakshmi Chandra, 38 the SC interpreted the word Tribunal and laid down two conditions: firstly, it must be an authority or a body constituted by law with power to determine question or disputes affecting the right of a citizen and secondly such a body or authority must determine such question under a duty to act judicially and such duty must be imposed by law. Thus, SEBI is a tribunal as it fulfils both these conditions. Investor Protection: Legal Framework- Legal framework includes the statutory provisions available for protection of the investors. The various rules, regulations, guidelines, schemes and various circulars passed by SEBI time to time for the protection of the investors: SEBI (Stock Broker & Sub Broker) Regulation, 1992: As the investors are not directly connected with the SE and completely rely upon the stock brokers and sub brokers because they play as intermediaries between investors and SE, so for protecting the interest of investors it is necessary to keep regular monitoring on the regular activities of broker and sub brokers and thus this regulation was issued by SEBI. This regulation provides some requirements which must be fulfilled by the stock and sub brokers before starting its business like providing all personal details so that if any fraudulent act or malpractice is done it can be easily traceable. For prohibiting them from such mal practices some mandatory duties are being imposed and it must be followed by each and every stockbrokers. Under Chapter VI, pecuniary penalty can be imposed by SEBI in case of default. SEBI Prohibition of Insider Trading Regulations 1992: Regulation 2 (e) of this regulation says that insider means a person who having connection with a company reasonably expected to have accessed to unpublished price sensitive in respect of securities of company or has received or had access to such unpublished price sensitive information. The term insider trading means certain activities which have been prohibited under regulation 3 i.e either directly or indirectly accessed to any unpublished price sensitive will have to be obtained from the concerned HC under Article 134-A. This article 134 A has been inserted by the Constitutional (44 th Amendment) Act of AIR 1963 SC
17 information and communicates or counsel in lieu of money to any third person. To treat the information as price sensitive information, the aggrieved party will have to prove that such piece of information has effect the security market materially and substantially. As a precautionary measure this regulation has included some preventive measures under which it bounds the individual shareholder including company to disclose all the material information so that their intention can be scrutinised by the SEBI more effectively. SEBI (Prohibition of Fraudulent and unfair trade practices relating to Securities Market) Regulations, 2003: The main object of this Act is to protect the investors from the various fraudulent and unfair trade practices done in the security market. Therefore, SEBI enacted this regulation to prevent these practices in the security market. This regulation specifies the acts which can be amounted as fraud; it also gives a wide scope for investigation against the fraudulent practices along with the details procedure. Thus, strict penal measures can be taken by SEBI like cancellation of certificate, suspension of certificate on account of proof of practicing fraudulent act. SEBI (Ombudsman) Regulations, 2003: This regulation provides for the appointment of Ombudman who is a public officer which will deal with public grievances i.e he will investigate the complaints the complaints made by the public against the government officials on account of infringement of any right of individuals. The main duty of it is to make a proper investigation on complaints regarding non- receipt of share certificates, refund order, dividend and various other matters. SEBI (Investor protection and Education Fund) Regulation, 2009: The main object of this regulation is to protect the interests of the investors through education and by creating awareness among the investors by organizing seminar, research, publication etc. As to provide education requires a huge amount of money therefore a fund named Investor Protection and Education Fund was established in Besides, to improve the method of investor s education an advisory committee was also established. SEBI (Investment Advisers) Regulations, 2013: The main object of this regulation is to keep monitoring on the activities of investment advisors in the capital market. According to Regulation 2 (l) investment advise means advice relating to investing in purchasing, selling or otherwise dealing in securities or investment products, and advice on investment portfolio containing securities or investment products, whether written oral or through any other means of communication for the benefit of the client and shall include 17
18 financial planning and it was given through any newspaper, magazine or any other electronic mode and according to regulation 2 (m) investment adviser means a person who in lieu of consideration provide the investment advice to clients or other persons or group of persons. The regulation provides a detail procedure regarding registration of investment advisor and issue of registration certificate. It also casts some duties on the investment adviser like disclosure of all materials to the client, maintenance of records, to redress all client grievances. Besides it also empowers SEBI to conduct regulate investigation on the conduct of the investment adviser. Conclusion: It can be seen that Indian Capital market has changed gradually and drastically since pre independent era to present scenario especially in post 1991 when the concept of liberalisation was adopted for the industrial sector which compelled the government to make changes in the security market prevailing in India. After liberalization policy and globalization was been adopted in India, it opened the door for the foreign investors and various trade practises in the security market. As a number of scams and illegal trade practises were been taking place in the capital market, the Government realized that the present Acts and regulations are not sufficient and an autonomous body must be established for regulating the security market. Thus, the Narasimham Committee was appointed and it made some recommendations like setting up a strong regulatory body by vesting immense power to regulate the security market. Consequently, SEBI was established under the SEBI Act, Not only SEBI, other enforcement bodies like Central Government, SAT, Tribunal, Judiciary have been given wide powers to enforce the rights guaranteed to the investors on account of infringement by imposing punishment through various Acts. Additionally, various statutory provisions like rules, regulations, guidelines, schemes and circulars which can be passed by SEBI from time to time for the protection of the investors are also been established and enacted. For example: SEBI (Stock Broker & Sub Broker) Regulation, 1992 was issued by SEBI to keep regular monitoring on the regular activities of broker and sub brokers for 18
19 protecting the interests of the investors, SEBI (Investment Advisers) Regulations, 2013 issued by SEBI to keep monitoring on the activities of investment advisors in the capital market etc. References: Primary Sources: Statutes & Legislations- (1) Security Contract Regulation Act, 1956 (2) Bombay Securities Contracts Control Act, 1925 (3) Capital Issue (Control) Act, 1947 (4) Security and Exchange Board of India, 1992 (5) Companies Act, 1956 (6) Companies Act, 2013 (7) Competition Act, 2002 (8) Depositories Act, 1996 (9) Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (10) Constitution of India, 1949 (11) Security Act, 1933 (12) Securities Exchange Act, 1934 (13) Telecom Regulatory of India Act, 2002 (14) Financial Services and Markets Act, 2000 (15) SEBI (Stock Broker & Sub Broker) Regulation,
20 (16) SEBI Prohibition of Insider Trading Regulations 1992 (17) SEBI (Prohibition of Fraudulent and unfair trade practices relating to Securities Market) Regulations, 2003 (18) SEBI (Ombudsman) Regulations, 2003 (19) SEBI (Investor protection and Education Fund) Regulation, 2009 (20) SEBI (Investment Advisers) Regulations, 2013 (21) SEBI( Amendment) Act, 2002 (22) Securities Laws (Amendment) Act, 1995 (23) Security Laws(Amendment)Act, 1999 (24) Security Laws (Amendment)Act, 2004 (25) SCRA (Amendment) Act, 2007 Secondary Sources: Books- (1) SEBI Manual (15 th edn, Taxmann Publications 2010) (2) Sekhar K., Guide to SEBI capital issues debentures and listing (3 rd edn, Wadhwa &Company 2003) (3) Agarwal Sumit &Robin Joseph Baby, SEBI Act (Taxmann Publication 2011) Websites- (1) Tierney Robert B., New York City Landmarks Preservation Commission < accessed 25 March 2015 (2) Objectives of Indian securities market < accessed 26 March 2015 (3) Securities and Exchange Board of India < accessed 28 March
21 21
SEBI Act, /17/2012. Copyrights CA Kamal Garg 1. Objects of the SEBI Act. Establishment of SEBI [Section 3] By: CA Kamal Garg
![SEBI Act, /17/2012. Copyrights CA Kamal Garg 1. Objects of the SEBI Act. Establishment of SEBI [Section 3] By: CA Kamal Garg SEBI Act, /17/2012. Copyrights CA Kamal Garg 1. Objects of the SEBI Act. Establishment of SEBI [Section 3] By: CA Kamal Garg](/thumbs/75/71507216.jpg) SEBI Act, 1992 By: CA Kamal Garg Objects of the SEBI Act 1. Protection of the interests of investors; 2. Promoting orderly and healthy growth of the securities market; 3. Regulation of the securities market
SEBI Act, 1992 By: CA Kamal Garg Objects of the SEBI Act 1. Protection of the interests of investors; 2. Promoting orderly and healthy growth of the securities market; 3. Regulation of the securities market
SEBI Act, 1992 Scheme and Scope of Powers of SEBI
 SEBI Act, 1992 Scheme and Scope of Powers of SEBI National Judicial Academy, Bhopal Lalit Kumar, Partner August 27, 2015 J. Sagar Associates advocates & solicitors Ahmedabad Bengaluru Chennai Gurgaon Hyderabad
SEBI Act, 1992 Scheme and Scope of Powers of SEBI National Judicial Academy, Bhopal Lalit Kumar, Partner August 27, 2015 J. Sagar Associates advocates & solicitors Ahmedabad Bengaluru Chennai Gurgaon Hyderabad
BE it enacted by Parliament in the Fifty-sixth Year of the Republic of India as follows:-
 ~ THE CREDIT INFORMATION COMPANIES (REGULATION) ACT, 2005 # NO. 30 OF 2005 $ [23rd June 2005.] + An Act to provide for regulation of credit information companies and to facilitate efficient distribution
~ THE CREDIT INFORMATION COMPANIES (REGULATION) ACT, 2005 # NO. 30 OF 2005 $ [23rd June 2005.] + An Act to provide for regulation of credit information companies and to facilitate efficient distribution
PROTECTION OF INVESTORS AND SHAREHOLDERS: A CRITICAL STUDY OF ROLE OF SEBI
 PROTECTION OF INVESTORS AND SHAREHOLDERS: A CRITICAL STUDY OF ROLE OF SEBI CHAPTERS CHAPTER 1 : CHAPTER 2 : CHAPTER-3 : CHAPTER-4 : CHAPTER-5 : CHAPTER-6 : CHAPTER-7 : CHAPTER 8- : CHAPTER 9 : CHAPTER
PROTECTION OF INVESTORS AND SHAREHOLDERS: A CRITICAL STUDY OF ROLE OF SEBI CHAPTERS CHAPTER 1 : CHAPTER 2 : CHAPTER-3 : CHAPTER-4 : CHAPTER-5 : CHAPTER-6 : CHAPTER-7 : CHAPTER 8- : CHAPTER 9 : CHAPTER
Legislative Brief The Consumer Protection Bill, 2018
 Legislative Brief The Consumer Protection Bill, 2018 The Consumer Protection Bill, 2018 was introduced in Lok Sabha on January 5, 2018 by the Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution,
Legislative Brief The Consumer Protection Bill, 2018 The Consumer Protection Bill, 2018 was introduced in Lok Sabha on January 5, 2018 by the Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution,
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA (STOCK-BROKERS AND SUB-BROKERS) REGULATIONS, 1992 CONTENTS
 SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA (STOCK-BROKERS AND SUB-BROKERS) REGULATIONS, 1992 CONTENTS CHAPTER I: PRELIMINARY 1. Short title and commencement 2. Definitions CHAPTER II: REGISTRATION OF STOCK
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA (STOCK-BROKERS AND SUB-BROKERS) REGULATIONS, 1992 CONTENTS CHAPTER I: PRELIMINARY 1. Short title and commencement 2. Definitions CHAPTER II: REGISTRATION OF STOCK
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 and Rules, By CA R.Durai Rengaswamy Partner Sambandam Associates Chennai
 Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 and Rules, 2011 By CA R.Durai Rengaswamy Partner Sambandam Associates Chennai 1 1. Formalities and Procedures 1.1. Introduction The Foreign Contribution( Regulation)
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 and Rules, 2011 By CA R.Durai Rengaswamy Partner Sambandam Associates Chennai 1 1. Formalities and Procedures 1.1. Introduction The Foreign Contribution( Regulation)
Securities and Exchange Board of India (Delisting of Equity Shares) Regulations, 2009
 Ministry : Securities and Exchange Board of India Notification No : LAD-NRO/GN/2008-2009/09/165992 Date : 10.06.2009 Securities and Exchange Board of India (Delisting of Equity Shares) Regulations, 2009
Ministry : Securities and Exchange Board of India Notification No : LAD-NRO/GN/2008-2009/09/165992 Date : 10.06.2009 Securities and Exchange Board of India (Delisting of Equity Shares) Regulations, 2009
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA ACT,
 CONTENTS Foreword Authors Note About The Authors From The Editor s Desk About The Editor Supreme Court Judgments High Court Judgments Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) Judgments Authorities Of Other
CONTENTS Foreword Authors Note About The Authors From The Editor s Desk About The Editor Supreme Court Judgments High Court Judgments Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) Judgments Authorities Of Other
Dabba Trading. The Mechanics or Modus Operandi of Dabba Trading
 Dabba Trading A Dabba Trading" also known as "Bucketing" is the process used by brokers to route their client s trades outside the Stock/Commodity exchange. In such trading, the broker either does not
Dabba Trading A Dabba Trading" also known as "Bucketing" is the process used by brokers to route their client s trades outside the Stock/Commodity exchange. In such trading, the broker either does not
Legislative Brief The Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2006
 Legislative Brief The Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2006 The Bill was introduced in the Lok Sabha on March 9, 2006. The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance [Chairperson: Maj. Gen. (Retd.) Bhuwan
Legislative Brief The Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2006 The Bill was introduced in the Lok Sabha on March 9, 2006. The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance [Chairperson: Maj. Gen. (Retd.) Bhuwan
Short title, extent and commencement. Definitions.
 PART I GOVERNMENT OF PUNJAB DEPARTMENT OF LEGAL AND LEGISLATIVE AFFAIRS, PUNJAB NOTIFICATION The 19th April, 2018 No.12-Leg./2018.-The following Act of the Legislature of the State of Punjab received the
PART I GOVERNMENT OF PUNJAB DEPARTMENT OF LEGAL AND LEGISLATIVE AFFAIRS, PUNJAB NOTIFICATION The 19th April, 2018 No.12-Leg./2018.-The following Act of the Legislature of the State of Punjab received the
SEBI & ITS FUNCTIONS
 SEBI & ITS FUNCTIONS Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was set up in 1988 to regulate the functions of securities market. SEBI promotes orderly and healthy development in the stock market but initially
SEBI & ITS FUNCTIONS Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was set up in 1988 to regulate the functions of securities market. SEBI promotes orderly and healthy development in the stock market but initially
Liability of Banks for Aiding and Abetting in Tax Evasion and Money Laundering
 LÉGALÍCS Liability of Banks for Aiding and Abetting in Tax Evasion and Money Laundering The information provided herein is of general nature and not intended to address the circumstances of any particular
LÉGALÍCS Liability of Banks for Aiding and Abetting in Tax Evasion and Money Laundering The information provided herein is of general nature and not intended to address the circumstances of any particular
Legislative Brief. The Companies Bill, Highlights of the Bill. Key Issues and Analysis
 Legislative Brief The Companies Bill, 2009 The Bill was introduced in the Lok Sabha on 3 rd August, 2009. Recent Briefs: The Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Bill, 2007 June 25, 2009 The Protection and Utilisation
Legislative Brief The Companies Bill, 2009 The Bill was introduced in the Lok Sabha on 3 rd August, 2009. Recent Briefs: The Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Bill, 2007 June 25, 2009 The Protection and Utilisation
DIRECT TAX DISPUTE RESOLUTION SCHEME, Nanubhai Desai & Co.
 DIRECT TAX DISPUTE RESOLUTION SCHEME, 2016 Nanubhai Desai & Co. Contents ELIGIBILITY FOR DECLARATION... 3 PERIOD OF DECLARATION... 4 DECLARATION OF TAX PAYABLE... 5 DECLARATION AND CONDITIONS OF DECLARATION...
DIRECT TAX DISPUTE RESOLUTION SCHEME, 2016 Nanubhai Desai & Co. Contents ELIGIBILITY FOR DECLARATION... 3 PERIOD OF DECLARATION... 4 DECLARATION OF TAX PAYABLE... 5 DECLARATION AND CONDITIONS OF DECLARATION...
CONTENTS COMPARATIVE TABLES SHOWING PROVISIONS OF COMPANIES ACT 2013 & COMPANIES ACT 1956 & VICE VERSA
 CONTENTS COMPARATIVE TABLES SHOWING PROVISIONS OF COMPANIES ACT 2013 & COMPANIES ACT 1956 & VICE VERSA u u u Table showing sections of Companies Act, 2013 & Corresponding Provisions of Companies Act, 1956
CONTENTS COMPARATIVE TABLES SHOWING PROVISIONS OF COMPANIES ACT 2013 & COMPANIES ACT 1956 & VICE VERSA u u u Table showing sections of Companies Act, 2013 & Corresponding Provisions of Companies Act, 1956
CA FINAL SEBI ACT 1992 SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA ACT, 1992 ESTABLISHMENT OF SEBI SEC 3 & 4. HO at Mumbai
 SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA ACT, 1992 ESTABLISHMENT OF SEBI SEC 3 & 4 One Chairman By CG by issuing a notification in the Official Gazette. HO at Mumbai SEBI is a body corporate having perpetual
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA ACT, 1992 ESTABLISHMENT OF SEBI SEC 3 & 4 One Chairman By CG by issuing a notification in the Official Gazette. HO at Mumbai SEBI is a body corporate having perpetual
Registered Valuers and Valuation
 Corporate Advisory Division Registered Valuers and Valuation A means to build a credible discipline of valuation Background The MCA has on October 18, 2017 notified the Companies (Registered Valuers and
Corporate Advisory Division Registered Valuers and Valuation A means to build a credible discipline of valuation Background The MCA has on October 18, 2017 notified the Companies (Registered Valuers and
A DOSSIER: BILLS ON UNORGANISED WORKERS
 The Bill Proposed by National Commission for Enterprises in the Unorganised Sector 2005, which was discussed at Indian Labour Conference, December 2005 UNORGANISED SECTOR WORKERS (CONDITIONS OF WORK &
The Bill Proposed by National Commission for Enterprises in the Unorganised Sector 2005, which was discussed at Indian Labour Conference, December 2005 UNORGANISED SECTOR WORKERS (CONDITIONS OF WORK &
THE GAZETTE OF INDIA EXTRAORDINARY. PART II - SECTION 3 - SUB-SECTION (ii) PUBLISHED BY AUTHORITY NOTIFICATION. MUMBAI, THE 16th DAY OF MAY, 1996
 THE GAZETTE OF INDIA EXTRAORDINARY PART II - SECTION 3 - SUB-SECTION (ii) PUBLISHED BY AUTHORITY NOTIFICATION MUMBAI, THE 16th DAY OF MAY, 1996 SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA (DEPOSITORIES AND
THE GAZETTE OF INDIA EXTRAORDINARY PART II - SECTION 3 - SUB-SECTION (ii) PUBLISHED BY AUTHORITY NOTIFICATION MUMBAI, THE 16th DAY OF MAY, 1996 SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA (DEPOSITORIES AND
I. INTRODUCTION. 2015, RHIMRJ, All Rights Reserved Page 1 of 8 ISSN: (Online)
 ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) RESEARCH HUB International Multidisciplinary Research Journal (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com Analysis of SEBI Regulations for Delisting of Equity Shares
ISSN: 2349-7637 (Online) RESEARCH HUB International Multidisciplinary Research Journal (RHIMRJ) Research Paper Available online at: www.rhimrj.com Analysis of SEBI Regulations for Delisting of Equity Shares
The Payment of Wages Act The Minimum Wages Act The Payment of Bonus Act The Equal Remuneration Act
 Wage Legislation Learning Objectives: The Payment of Wages Act The Minimum Wages Act The Payment of Bonus Act The Equal Remuneration Act Chapter Nine Wage Legislation 1 Structure: 1. Introduction 2. The
Wage Legislation Learning Objectives: The Payment of Wages Act The Minimum Wages Act The Payment of Bonus Act The Equal Remuneration Act Chapter Nine Wage Legislation 1 Structure: 1. Introduction 2. The
REGULATIONS GOVERNING THE BOMBAY STOCK EXCHANGE
 REGULATIONS GOVERNING THE BOMBAY STOCK EXCHANGE Why Regulation? Do you know what a security is? Our laws provide an inclusive definition of securities. It says that securities include shares, bonds, debentures,
REGULATIONS GOVERNING THE BOMBAY STOCK EXCHANGE Why Regulation? Do you know what a security is? Our laws provide an inclusive definition of securities. It says that securities include shares, bonds, debentures,
Service tax. (d) substitute the word "client" with the words "any person" in the specified taxable services;
 Page 1 of 8 Service tax Clause 85 seeks to amend Chapter V of the Finance Act ' 1994 relating to service tax in the following manner, namely:-(/) sub-clause (A) seeks to amend section 65 of the said Act,
Page 1 of 8 Service tax Clause 85 seeks to amend Chapter V of the Finance Act ' 1994 relating to service tax in the following manner, namely:-(/) sub-clause (A) seeks to amend section 65 of the said Act,
Inspection and Investigation
 Inspection and Investigation By: CA Kamal Garg Inspection by Inspecting Officers [Section 209A] Inspecting Officers (IO): 1. Registrar; 2. Officer authorised by CG; 3. Officer authorised by SEBI Inspection
Inspection and Investigation By: CA Kamal Garg Inspection by Inspecting Officers [Section 209A] Inspecting Officers (IO): 1. Registrar; 2. Officer authorised by CG; 3. Officer authorised by SEBI Inspection
INTENSIVE STUDY COURSE ON SEBI RULES AND REGULATIONS
 1 INTENSIVE STUDY COURSE ON SEBI RULES AND REGULATIONS LIABILITIES UNDER SECURITIES LAWS Presented by: Dipali Sheth, Partner, MDP & Partners 2 BACKGROUND The Securities and Exchange Board of India ( SEBI
1 INTENSIVE STUDY COURSE ON SEBI RULES AND REGULATIONS LIABILITIES UNDER SECURITIES LAWS Presented by: Dipali Sheth, Partner, MDP & Partners 2 BACKGROUND The Securities and Exchange Board of India ( SEBI
Companies Act 2013 Sections List
 1 Short title, extent,commencement and application 2 Definitions 3 Formation of company 4 Memorandum 5 Articles 6 Act to override memorandum, articles, etc 7 Incorporation of company 8 Formation of companies
1 Short title, extent,commencement and application 2 Definitions 3 Formation of company 4 Memorandum 5 Articles 6 Act to override memorandum, articles, etc 7 Incorporation of company 8 Formation of companies
THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA
 74 CHAPTER - 3 THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. INTRODUCTION The Securities and Exchange Board of
74 CHAPTER - 3 THE SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1. INTRODUCTION The Securities and Exchange Board of
Scope of the Study: The study is restricted only to the protection of consumers interests and rights in India.
 International Journal of Emerging Research in Management &Technology Research Article February 2017 A Review of Effectiveness of Consumer Protection Act, 1986 Bhisham Datt. PGT Commerce, Jawahar Navodaya
International Journal of Emerging Research in Management &Technology Research Article February 2017 A Review of Effectiveness of Consumer Protection Act, 1986 Bhisham Datt. PGT Commerce, Jawahar Navodaya
ARTECH POWER PRODUCTS LIMITED CODE OF CORPORATE DISCLOSURE PRACTICES CODE OF CONDUCT FOR PREVENTION OF INSIDR TRADING
 ARTECH POWER PRODUCTS LIMITED CODE OF CORPORATE DISCLOSURE PRACTICES AND CODE OF CONDUCT FOR PREVENTION OF INSIDR TRADING ARTECH POWER PRODUCTS LIMTED Code of practices and procedures for fair disclosure
ARTECH POWER PRODUCTS LIMITED CODE OF CORPORATE DISCLOSURE PRACTICES AND CODE OF CONDUCT FOR PREVENTION OF INSIDR TRADING ARTECH POWER PRODUCTS LIMTED Code of practices and procedures for fair disclosure
Insurance (Amendment) Act
 Insurance (Amendment) Act An Act to amend the Insurance Act (Chapter 142 of the 2002 Revised Edition). Be it enacted by the President with the advice and consent of the Parliament of Singapore, as follows:
Insurance (Amendment) Act An Act to amend the Insurance Act (Chapter 142 of the 2002 Revised Edition). Be it enacted by the President with the advice and consent of the Parliament of Singapore, as follows:
MOOT PROBLEM. 5 TH GNLU MOOT ON SECURITIES & INVESTMENT LAW, 2019 Page 1 of 8
 MOOT PROBLEM 1. In January 2009, the Forward Markets Commission (the FMC ) had granted approval to the Bharat Commodity Exchange (the BCX ), a national level multicommodity derivative exchange which was
MOOT PROBLEM 1. In January 2009, the Forward Markets Commission (the FMC ) had granted approval to the Bharat Commodity Exchange (the BCX ), a national level multicommodity derivative exchange which was
PARLIAMENT OF THE DEMOCRATIC SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF SRI LANKA
 PARLIAMENT OF THE DEMOCRATIC SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF SRI LANKA BUDGETARY RELIEF ALLOWANCE OF WORKERS ACT, No. 4 OF 2016 [Certified on 23rd March, 2016] Printed on the Order of Government Published as a Supplement
PARLIAMENT OF THE DEMOCRATIC SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF SRI LANKA BUDGETARY RELIEF ALLOWANCE OF WORKERS ACT, No. 4 OF 2016 [Certified on 23rd March, 2016] Printed on the Order of Government Published as a Supplement
PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY
 PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY (A Central University) DIRECTORATE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION Security Market Operations Paper Code: MBFM 4004 MBA - FINANCE IV - Semester TABLE OF CONTENTS UNIT TITLE PAGE NO. I Security
PONDICHERRY UNIVERSITY (A Central University) DIRECTORATE OF DISTANCE EDUCATION Security Market Operations Paper Code: MBFM 4004 MBA - FINANCE IV - Semester TABLE OF CONTENTS UNIT TITLE PAGE NO. I Security
Annexure II Test Objectives. NISM-Series-IIIA. Securities Intermediaries Compliance (Non-Fund) Certification Examination
 Annexure II Test Objectives NISM-Series-IIIA Securities Intermediaries Compliance (Non-Fund) Certification Examination Part A Understanding the Financial and Regulatory Structure in India Unit 1: Introduction
Annexure II Test Objectives NISM-Series-IIIA Securities Intermediaries Compliance (Non-Fund) Certification Examination Part A Understanding the Financial and Regulatory Structure in India Unit 1: Introduction
Adjustment of International Taxes Act
 Adjustment of International Taxes Act INTRODUCTION Details of Enactment and Amendment Enactment: This Act was enacted in 1995 opportunely at this time when the World Trade Organization (WTO) is about to
Adjustment of International Taxes Act INTRODUCTION Details of Enactment and Amendment Enactment: This Act was enacted in 1995 opportunely at this time when the World Trade Organization (WTO) is about to
GOVERNMENT GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA. N$7.00 WINDHOEK - 5 November 2010 No. 4598
 GOVERNMENT GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA N$7.00 WINDHOEK - 5 November 2010 No. 4598 CONTENTS Page GOVERNMENT NOTICE No. 247 Promulgation of Banking Institutions Amendment Act, 2010 (Act No. 14 of
GOVERNMENT GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA N$7.00 WINDHOEK - 5 November 2010 No. 4598 CONTENTS Page GOVERNMENT NOTICE No. 247 Promulgation of Banking Institutions Amendment Act, 2010 (Act No. 14 of
NSE IFSC CLEARING CORPORATION LIMITED BYE LAWS ARRANGEMENT OF CHAPTERS. I. Definitions Regulations Clearing Members. Clearing and Settlement of Deals
 NSE IFSC CLEARING CORPORATION LIMITED BYE LAWS ARRANGEMENT OF CHAPTERS Chapter Description I. Definitions II. Regulations III. Clearing Members IV. Clearing and Settlement of Deals V. Dealings by Clearing
NSE IFSC CLEARING CORPORATION LIMITED BYE LAWS ARRANGEMENT OF CHAPTERS Chapter Description I. Definitions II. Regulations III. Clearing Members IV. Clearing and Settlement of Deals V. Dealings by Clearing
(Pursuant to Securities Exchange Board of India, (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015)
 BGR ENERGY SYSTEMS LIMITED CODE OF CONDUCT FOR TRADING BY INSIDERS (Pursuant to Securities Exchange Board of India, (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015) OBJECTIVE OF THE CODE This Code of
BGR ENERGY SYSTEMS LIMITED CODE OF CONDUCT FOR TRADING BY INSIDERS (Pursuant to Securities Exchange Board of India, (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015) OBJECTIVE OF THE CODE This Code of
THE GAMBIA FREE ZONES ACT 2001
 THE GAMBIA FREE ZONES ACT 2001 ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS Sections Part I - Preliminary 1. Short title 2. Interpretation Part II - Administration 3. Administration of this Act 4. Objectives of the Agency
THE GAMBIA FREE ZONES ACT 2001 ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS Sections Part I - Preliminary 1. Short title 2. Interpretation Part II - Administration 3. Administration of this Act 4. Objectives of the Agency
THE EMPLOYEES' OLD-AGE BENEFITS ACT 1976 ACT No. XIV OF 1976
 THE EMPLOYEES' OLD-AGE BENEFITS ACT 1976 ACT No. XIV OF 1976 [15th April, 1976] to repeal and re-enact the law relating to old-age benefits for the persons employed in industrial, commercial and other
THE EMPLOYEES' OLD-AGE BENEFITS ACT 1976 ACT No. XIV OF 1976 [15th April, 1976] to repeal and re-enact the law relating to old-age benefits for the persons employed in industrial, commercial and other
Inspection, Search, Seizure and Arrest
 Chapter XIV Inspection, Search, Seizure and Arrest 67. Power of inspection, search and seizure 68. Inspection of goods in movement 69. Power to arrest 70. Power to summon persons to give evidence and produce
Chapter XIV Inspection, Search, Seizure and Arrest 67. Power of inspection, search and seizure 68. Inspection of goods in movement 69. Power to arrest 70. Power to summon persons to give evidence and produce
Foreign Contribution Regulation Rules, 2011
 Foreign Contribution Regulation Rules, 2011 1. Short title and commencement (1) These rules may be called the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Rules, 2011. (2) They shall come into force on the date on
Foreign Contribution Regulation Rules, 2011 1. Short title and commencement (1) These rules may be called the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Rules, 2011. (2) They shall come into force on the date on
A2X TRADING RULES. A2X Rules. Page 1
 A2X TRADING RULES Page 1 SECTION CONTENT OF THE RULES PAGE NUMBER Index Index 2 Introduction Introduction 3 Section 1 Definitions and interpretation 4 Section 2 Applications for and termination of Membership
A2X TRADING RULES Page 1 SECTION CONTENT OF THE RULES PAGE NUMBER Index Index 2 Introduction Introduction 3 Section 1 Definitions and interpretation 4 Section 2 Applications for and termination of Membership
THE CODE FOR PREVENTION OF INSIDER TRADING IN THE SECURITIES OF INDIANOIL
 INDIAN OIL CORPORATION LIMITED [CIN L23201MH1959GOI011388] Regd. Office: IndianOil Bhawan, G-9, Ali Yavar Jung Marg, Bandra (E), Mumbai 400051 Ph: (022)26447327 Fax: (022)26447961 Email id: investors@indianoil.in
INDIAN OIL CORPORATION LIMITED [CIN L23201MH1959GOI011388] Regd. Office: IndianOil Bhawan, G-9, Ali Yavar Jung Marg, Bandra (E), Mumbai 400051 Ph: (022)26447327 Fax: (022)26447961 Email id: investors@indianoil.in
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Rules, 2011
 Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Rules, 2011 NOTIFICATION NO. G.S.R. 349(E), DATED 29-4-2011 In exercise of the powers conferred by section 48 of the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 (42 of
Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Rules, 2011 NOTIFICATION NO. G.S.R. 349(E), DATED 29-4-2011 In exercise of the powers conferred by section 48 of the Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 (42 of
NEW CONCEPTS UNDER COMPANIES ACT, 2013
 NEW CONCEPTS UNDER COMPANIES ACT, 2013 Presented at: (WIRC-ICAI Mumbai Branch) Presented by: CA. Manoj Pati ACA, DISA Partner Kanu Doshi Associates Content OVERVIEW OF COMPANIES ACT,2013 Why there was
NEW CONCEPTS UNDER COMPANIES ACT, 2013 Presented at: (WIRC-ICAI Mumbai Branch) Presented by: CA. Manoj Pati ACA, DISA Partner Kanu Doshi Associates Content OVERVIEW OF COMPANIES ACT,2013 Why there was
CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks
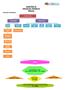 CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks Key Concepts in nutshell: CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL MARKET: It refers to the market which creates and exchanges financial assets. FUNCTIONS OF FINANICIAL
CONCEPT MAPPING: CHAPTER 10 FINANCIAL MARKETS 8Marks Key Concepts in nutshell: CONCEPT OF FINANCIAL MARKET: It refers to the market which creates and exchanges financial assets. FUNCTIONS OF FINANICIAL
C.A. No. 3237/1998 & 3247/1998 (Under Art. 136 of the Constitution of India) INDIAN OIL CORPORATION LTD...APPELLANT
 ITM SCHOOL OF LAW - MOOT COURT EXERCISE BEFORE THE HON BLE SUPREME COURT OF INDIA AT NEW DELHI C.A. No. 3237/1998 & 3247/1998 (Under Art. 136 of the Constitution of India) IN THE MATTER OF INDIAN OIL CORPORATION
ITM SCHOOL OF LAW - MOOT COURT EXERCISE BEFORE THE HON BLE SUPREME COURT OF INDIA AT NEW DELHI C.A. No. 3237/1998 & 3247/1998 (Under Art. 136 of the Constitution of India) IN THE MATTER OF INDIAN OIL CORPORATION
Compounding of Contraventions under FEMA
 Compounding of Contraventions under FEMA The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India - Western India Regional Council 5 th August 2017 Naresh Ajwani Chartered Accountant FEMA complex law FEMA is a
Compounding of Contraventions under FEMA The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India - Western India Regional Council 5 th August 2017 Naresh Ajwani Chartered Accountant FEMA complex law FEMA is a
CS SAROJ KUMAR RAY, FCS
 COMPANIES ACT 2013 CS SAROJ KUMAR RAY, FCS FOCUS AREAS AUDIT & AUDITORS CHAPTER X : AUDITORS Appointment/ Eligibility etc. Removal/ Resignation Penal Provisions Others Sec. 139 : Appointment of Auditors
COMPANIES ACT 2013 CS SAROJ KUMAR RAY, FCS FOCUS AREAS AUDIT & AUDITORS CHAPTER X : AUDITORS Appointment/ Eligibility etc. Removal/ Resignation Penal Provisions Others Sec. 139 : Appointment of Auditors
CHAPTER I PREAMBLE THE CODE
 CHAPTER I CODE OF CONDUCT TO REGULATE, MONITOR AND REPORT TRADING BY INSIDERS (PURSUANT TO SECURITIES EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA, (PROHIBITION OF INSIDER TRADING) REGULATIONS, 2015 PREAMBLE The Securities
CHAPTER I CODE OF CONDUCT TO REGULATE, MONITOR AND REPORT TRADING BY INSIDERS (PURSUANT TO SECURITIES EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA, (PROHIBITION OF INSIDER TRADING) REGULATIONS, 2015 PREAMBLE The Securities
Section of Ordinance (X of 1965) Section of Ordinance (V of 2013) Amended Text
 AMENDMENTS IN THE PROVINCIAL EMPLOYEES SOCIAL SECURITY ORDINANCE, 1965 (THROUGH THE PROVINCIAL EMPLOYEES SOCIAL SECURITY (AMENDMENT) ORDINANCE, 2013) (ORDINANCE NO. V OF 2013) (LAW DEPTT: NOTIFICATION
AMENDMENTS IN THE PROVINCIAL EMPLOYEES SOCIAL SECURITY ORDINANCE, 1965 (THROUGH THE PROVINCIAL EMPLOYEES SOCIAL SECURITY (AMENDMENT) ORDINANCE, 2013) (ORDINANCE NO. V OF 2013) (LAW DEPTT: NOTIFICATION
MEGHALAYA ACT NO. 5 OF 2005.
 MEGHALAYA ACT NO. 5 OF 2005. As passed by the Meghalaya Legislative Assembly Received the assent of the Governor on the 30th April,2005. Published in the Meghalaya Extra Ordinary issue dt.30th April,2005.
MEGHALAYA ACT NO. 5 OF 2005. As passed by the Meghalaya Legislative Assembly Received the assent of the Governor on the 30th April,2005. Published in the Meghalaya Extra Ordinary issue dt.30th April,2005.
Legislative Brief The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Bill, 2006
 Legislative Brief The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Bill, 2006 The Bill was introduced in the Rajya Sabha on December 18, 2006. The Bill has been referred to the Department-related Parliamentary Standing
Legislative Brief The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Bill, 2006 The Bill was introduced in the Rajya Sabha on December 18, 2006. The Bill has been referred to the Department-related Parliamentary Standing
DISCLAIMER. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 DISCLAIMER The Suggested Answers hosted in the website do not constitute the basis for evaluation of the students answers in the examination. The answers are prepared by the Faculty of the Board of Studies
DISCLAIMER The Suggested Answers hosted in the website do not constitute the basis for evaluation of the students answers in the examination. The answers are prepared by the Faculty of the Board of Studies
$~ * IN THE HIGH COURT OF DELHI AT NEW DELHI. Advocate. Versus
 $~ * IN THE HIGH COURT OF DELHI AT NEW DELHI + CRL.M.C. 1990/2010 PREM KUMAR Judgment delivered on:08 th February, 2016 Represented by: Advocate. Versus... Petitioner Mr. Yogesh Verma, CUSTOMS... Respondent
$~ * IN THE HIGH COURT OF DELHI AT NEW DELHI + CRL.M.C. 1990/2010 PREM KUMAR Judgment delivered on:08 th February, 2016 Represented by: Advocate. Versus... Petitioner Mr. Yogesh Verma, CUSTOMS... Respondent
THE BANKING LAWS (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2011
 1 As INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA Bill No. 18 of 2011 5 10 THE BANKING LAWS (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2011 A BILL further to amend the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of
1 As INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA Bill No. 18 of 2011 5 10 THE BANKING LAWS (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2011 A BILL further to amend the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, the Banking Companies (Acquisition and Transfer of
Solomon Islands. UNCTAD Compendium of Investment Laws. The Foreign Investment Bill 2005 (2006)
 UNCTAD Compendium of Investment Laws Solomon Islands The Foreign Investment Bill 2005 (2006) Note The Investment Laws Navigator is based upon sources believed to be accurate and reliable and is intended
UNCTAD Compendium of Investment Laws Solomon Islands The Foreign Investment Bill 2005 (2006) Note The Investment Laws Navigator is based upon sources believed to be accurate and reliable and is intended
3.8 THE PAYMENT OF GRATUITY ACT, 1972
 3.8 THE PAYMENT OF GRATUITY ACT, 1972 1. APPLICABILITY OF THE ACT Initial Applicability (Sec.1(3) The Act applies to (a) Every Factory, Mine, Oilfield, Plantation, Port and Railway Company, (b) Every Shop
3.8 THE PAYMENT OF GRATUITY ACT, 1972 1. APPLICABILITY OF THE ACT Initial Applicability (Sec.1(3) The Act applies to (a) Every Factory, Mine, Oilfield, Plantation, Port and Railway Company, (b) Every Shop
SEBI Order and Satyam Scandal: Much Needed Impetus
 SEBI Order and Satyam Scandal: Much Needed Impetus GAURAV ARORA M. SUPRITHA PRODATURI INTRODUCTION 1. More than five years ago Corporate India was taken aback when the founder of Satyam Computer Services
SEBI Order and Satyam Scandal: Much Needed Impetus GAURAV ARORA M. SUPRITHA PRODATURI INTRODUCTION 1. More than five years ago Corporate India was taken aback when the founder of Satyam Computer Services
ASSESSMENT, OFFENCES & PENALTIES UNDER GST. CA SAURABH PUNYANI B.COM, L.L.B., FCA, DISA, CCA M NO ,
 ASSESSMENT, OFFENCES & PENALTIES UNDER GST CA SAURABH PUNYANI B.COM, L.L.B., FCA, DISA, CCA M NO. 9423680948, E-MAIL : casaurabhpunyani@gmail.com SELF ASSESSMENT YAAR..SAB KAAM MUJHE HI KARNA PADTA HAI.!!!
ASSESSMENT, OFFENCES & PENALTIES UNDER GST CA SAURABH PUNYANI B.COM, L.L.B., FCA, DISA, CCA M NO. 9423680948, E-MAIL : casaurabhpunyani@gmail.com SELF ASSESSMENT YAAR..SAB KAAM MUJHE HI KARNA PADTA HAI.!!!
Short-term Insurance Act 4 of 1998 (GG 1832) brought into force on 1 July 1998 by GN 142/1998 (GG 1887) ACT
 (GG 1832) brought into force on 1 July 1998 by GN 142/1998 (GG 1887) as amended by Namibia Financial Institutions Supervisory Authority Act 3 of 2001 (GG 2521) brought into force on 14 May 2001 by GN 85/2001
(GG 1832) brought into force on 1 July 1998 by GN 142/1998 (GG 1887) as amended by Namibia Financial Institutions Supervisory Authority Act 3 of 2001 (GG 2521) brought into force on 14 May 2001 by GN 85/2001
Part III Insurance Consultation Contd
 8.7 Penal Provisions Part III Insurance Consultation Contd 8.8.1 Section 102-105C prescribe penalties for contravention of or default in complying with the provisions of the Act; false statement in document;
8.7 Penal Provisions Part III Insurance Consultation Contd 8.8.1 Section 102-105C prescribe penalties for contravention of or default in complying with the provisions of the Act; false statement in document;
Adjudication Procedure, Recovery of Tax, Penalty and Arrest Provisions K E V I N S H A H C H A R T E R E D A C C O U N T A N T
 Adjudication Procedure, Recovery of Tax, Penalty and Arrest Provisions K E V I N S H A H C H A R T E R E D A C C O U N T A N T Adjudication Procedure What is adjudication? 0 Adjudicate means to hear or
Adjudication Procedure, Recovery of Tax, Penalty and Arrest Provisions K E V I N S H A H C H A R T E R E D A C C O U N T A N T Adjudication Procedure What is adjudication? 0 Adjudicate means to hear or
LONG-TERM INSURANCE ACT NO. 52 OF 1998 DATE OF COMMENCEMENT: 1 JANUARY, 1999 ACT
 LONG-TERM INSURANCE ACT NO. 52 OF 1998 DATE OF COMMENCEMENT: 1 JANUARY, 1999 ACT To provide for the registration of long-term insurers; for the control of certain activities of long-term insurers and intermediaries;
LONG-TERM INSURANCE ACT NO. 52 OF 1998 DATE OF COMMENCEMENT: 1 JANUARY, 1999 ACT To provide for the registration of long-term insurers; for the control of certain activities of long-term insurers and intermediaries;
CHAPTER - 5 STATUTORY REQUIREMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS & AUDIT OF DIVIDENDS
 CHAPTER - 5 STATUTORY REQUIREMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS & AUDIT OF DIVIDENDS MAINTENANCE OF BOOKS OF ACCOUNT Sec. 209(1) of Companies Act, 1956 requires every company to keep at its registered office
CHAPTER - 5 STATUTORY REQUIREMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS & AUDIT OF DIVIDENDS MAINTENANCE OF BOOKS OF ACCOUNT Sec. 209(1) of Companies Act, 1956 requires every company to keep at its registered office
AND WHEREAS the President is satisfied that circumstances exist which render it necessary to take immediate action;
 3. Microfinance Institutions Ordinance, 2001 (Ordinance No. LV of 2001) (Gazette of Pakistan dated 16 th October, 2001) An Ordinance to regulate the establishment, business and operations of microfinance
3. Microfinance Institutions Ordinance, 2001 (Ordinance No. LV of 2001) (Gazette of Pakistan dated 16 th October, 2001) An Ordinance to regulate the establishment, business and operations of microfinance
CHAPTER 10 Financial Market
 CHAPTER 10 Financial Market A financial market refers to a market where the creation and exchange of financial assets (such as shares and debentures) takes place. Allocative Function of Financial Market
CHAPTER 10 Financial Market A financial market refers to a market where the creation and exchange of financial assets (such as shares and debentures) takes place. Allocative Function of Financial Market
THE GUJARAT VALUE ADDED TAX (AMENDMENT) BILL, GUJARAT BILL NO. 7 OF A BILL. further to amend the Gujarat Value Added Tax Act, 2003.
 THE GUJARAT VALUE ADDED TAX (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2006. GUJARAT BILL NO. 7 OF 2006. A BILL further to amend the Gujarat Value Added Tax Act, 2003. It is hereby enacted in the Fifty-seventh Year of the Republic
THE GUJARAT VALUE ADDED TAX (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2006. GUJARAT BILL NO. 7 OF 2006. A BILL further to amend the Gujarat Value Added Tax Act, 2003. It is hereby enacted in the Fifty-seventh Year of the Republic
Securities Industry (Amendment) Act, Act, Act 590 ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS
 Securities Industry (Amendment) Act, Act, 2000 2000 Act 590 Section ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS 1. Section 1 of P.N.D.C.L. 333 amended 2. Section 2 of P.N.D.C.L. 333 amended 3. Section 5 of P.N.D.C.L. 333
Securities Industry (Amendment) Act, Act, 2000 2000 Act 590 Section ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS 1. Section 1 of P.N.D.C.L. 333 amended 2. Section 2 of P.N.D.C.L. 333 amended 3. Section 5 of P.N.D.C.L. 333
International Research Journal of Interdisciplinary & Multidisciplinary Studies (IRJIMS)
 International Research Journal of Interdisciplinary & Multidisciplinary Studies (IRJIMS) A Peer-Reviewed Monthly Research Journal ISSN: 2394-7969 (Online), ISSN: 2394-7950 (Print) Volume-II, Issue-VIII,
International Research Journal of Interdisciplinary & Multidisciplinary Studies (IRJIMS) A Peer-Reviewed Monthly Research Journal ISSN: 2394-7969 (Online), ISSN: 2394-7950 (Print) Volume-II, Issue-VIII,
AN EASY OR COMPLEX CONCEPT OF DEBT RECOVERY
 AN EASY OR COMPLEX CONCEPT OF DEBT RECOVERY **AJAY SOLANKY & AKSHAY PANDEY India is a large country and being a large country, there are variety of economical challenges faced by the people of India and
AN EASY OR COMPLEX CONCEPT OF DEBT RECOVERY **AJAY SOLANKY & AKSHAY PANDEY India is a large country and being a large country, there are variety of economical challenges faced by the people of India and
Bill No. 2 Retirement Benefits Sector Liberalisation Bill 2011
 THE RETIREMENT BENEFITS SECTOR LIBERALISATION BILL, 2011 ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES Clause 1. Commencement 2. Interpretation PART I PRELIMINARY PART II LIBERALISATION OF THE RETIREMENT BENEFITS SECTOR 3. Liberalisation
THE RETIREMENT BENEFITS SECTOR LIBERALISATION BILL, 2011 ARRANGEMENT OF CLAUSES Clause 1. Commencement 2. Interpretation PART I PRELIMINARY PART II LIBERALISATION OF THE RETIREMENT BENEFITS SECTOR 3. Liberalisation
INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT (INCOME TAX RELIEF) ACT
 INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT (INCOME TAX RELIEF) ACT ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS Pioneer conditions 1. Publication of list of pioneer industries and products and issuing of pioneer certificates. 2. Mode of application
INDUSTRIAL DEVELOPMENT (INCOME TAX RELIEF) ACT ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS Pioneer conditions 1. Publication of list of pioneer industries and products and issuing of pioneer certificates. 2. Mode of application
OFFSHORE BANKING ACT 1990 (Act 443) ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS. Part I. Preliminary. Part II. Licensing Of Offshore Banks. Part III
 OFFSHORE BANKING ACT 1990 (Act 443) ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS Part I Section Preliminary 1. Short title and commencement 2. Interpretation 3. Functions, powers and duties of the Bank Part II Licensing Of
OFFSHORE BANKING ACT 1990 (Act 443) ARRANGEMENT OF SECTIONS Part I Section Preliminary 1. Short title and commencement 2. Interpretation 3. Functions, powers and duties of the Bank Part II Licensing Of
Microfinance Institutions Ordinance 2001
 Microfinance Institutions Ordinance 2001 (LV of 2001) (As amended up to 1 st July 2007) 1 ORDINANCE NO. LV OF 2001 An Ordinance to regulate the establishment, business and operations of microfinance institutions.
Microfinance Institutions Ordinance 2001 (LV of 2001) (As amended up to 1 st July 2007) 1 ORDINANCE NO. LV OF 2001 An Ordinance to regulate the establishment, business and operations of microfinance institutions.
NETHERLANDS - ARBITRATION ACT DECEMBER 1986 CODE OF CIVIL PROCEDURE - BOOK IV: ARBITRATION TITLE ONE - ARBITRATION IN THE NETHERLANDS
 NETHERLANDS - ARBITRATION ACT DECEMBER 1986 CODE OF CIVIL PROCEDURE - BOOK IV: ARBITRATION TITLE ONE - ARBITRATION IN THE NETHERLANDS SECTION ONE - ARBITRATION AGREEMENT AND APPOINTMENT OF ARBITRATOR Article
NETHERLANDS - ARBITRATION ACT DECEMBER 1986 CODE OF CIVIL PROCEDURE - BOOK IV: ARBITRATION TITLE ONE - ARBITRATION IN THE NETHERLANDS SECTION ONE - ARBITRATION AGREEMENT AND APPOINTMENT OF ARBITRATOR Article
ANGUILLA TRUST COMPANIES AND OFFSHORE BANKING ACT, 2000 TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1 - PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS PART 2 - OFFSHORE BANKING BUSINESS
 ANGUILLA TRUST COMPANIES AND OFFSHORE BANKING ACT, 2000 1. Interpretation 2. Application TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1 - PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS PART 2 - OFFSHORE BANKING BUSINESS 3. Interpretation 4. Licence
ANGUILLA TRUST COMPANIES AND OFFSHORE BANKING ACT, 2000 1. Interpretation 2. Application TABLE OF CONTENTS PART 1 - PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS PART 2 - OFFSHORE BANKING BUSINESS 3. Interpretation 4. Licence
[ADJUDICATION ORDER NO. PKB/AO 37/2011]
![[ADJUDICATION ORDER NO. PKB/AO 37/2011] [ADJUDICATION ORDER NO. PKB/AO 37/2011]](/thumbs/72/66418023.jpg) BEFORE THE ADJUDICATING OFFICER SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA [ADJUDICATION ORDER NO. PKB/AO 37/2011] UNDER SECTION 15-I OF SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA ACT, 1992 READ WITH RULE 5 OF
BEFORE THE ADJUDICATING OFFICER SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA [ADJUDICATION ORDER NO. PKB/AO 37/2011] UNDER SECTION 15-I OF SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE BOARD OF INDIA ACT, 1992 READ WITH RULE 5 OF
REGULATORY FRAMEWORK GOVERNING INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS IN INDIA
 CHAPTER 4 REGULATORY FRAMEWORK GOVERNING INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS IN INDIA This chapter presents the regulatory framework governing the issuance of IPOs through public offer, book building and online route.
CHAPTER 4 REGULATORY FRAMEWORK GOVERNING INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERINGS IN INDIA This chapter presents the regulatory framework governing the issuance of IPOs through public offer, book building and online route.
Role of Banking Ombudsman in Banking Reforms
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Role of Banking Ombudsman in Banking Reforms Yogesh Kolekar Ismailsaheb Mulla Law College, Satara 19 December 2016 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/75660/ MPRA
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Role of Banking Ombudsman in Banking Reforms Yogesh Kolekar Ismailsaheb Mulla Law College, Satara 19 December 2016 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/75660/ MPRA
LOANS MADE/ ADVANCE GIVEN/ SECURITY PROVIDED BY THE COMPANY
 Sl No DESCRIPTION PAGE NO LOANS TO DIRECTORS 1 Loans to Directors 2 2 Exclusions 2 3 Loans Given/ Security provided/ Guanrantee given by Holding Company to 2 Its Wholly owned Subsidiary Company 4 Any Person
Sl No DESCRIPTION PAGE NO LOANS TO DIRECTORS 1 Loans to Directors 2 2 Exclusions 2 3 Loans Given/ Security provided/ Guanrantee given by Holding Company to 2 Its Wholly owned Subsidiary Company 4 Any Person
Sri Lanka Accounting and Auditing Standards Act, No.15 of [Certified on 25 th August, 1995]
![Sri Lanka Accounting and Auditing Standards Act, No.15 of [Certified on 25 th August, 1995] Sri Lanka Accounting and Auditing Standards Act, No.15 of [Certified on 25 th August, 1995]](/thumbs/79/80255828.jpg) [Certified on 25 th August, 1995] L.D O. 85/98 AN ACT TO PROVIDE FOR THE ESTABLISHMENT OF SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARDS AND SRI LANKA AND AUDITING STANDARDS; TO ESTABLISH THE SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
[Certified on 25 th August, 1995] L.D O. 85/98 AN ACT TO PROVIDE FOR THE ESTABLISHMENT OF SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARDS AND SRI LANKA AND AUDITING STANDARDS; TO ESTABLISH THE SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
Enrolled Copy H.B. 70 HEALTH DISCOUNT PROGRAM CONSUMER PROTECTION ACT. Chief Sponsor: James A. Dunnigan Senate Sponsor: Michael G.
 Enrolled Copy H.B. 70 HEALTH DISCOUNT PROGRAM CONSUMER PROTECTION ACT 2005 GENERAL SESSION STATE OF UTAH Chief Sponsor: James A. Dunnigan Senate Sponsor: Michael G. Waddoups LONG TITLE General Description:
Enrolled Copy H.B. 70 HEALTH DISCOUNT PROGRAM CONSUMER PROTECTION ACT 2005 GENERAL SESSION STATE OF UTAH Chief Sponsor: James A. Dunnigan Senate Sponsor: Michael G. Waddoups LONG TITLE General Description:
Florida Senate SB 1106
 By Senator Flores 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 A bill to be entitled An act relating to limited purpose international trust company representative
By Senator Flores 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 A bill to be entitled An act relating to limited purpose international trust company representative
DIRECT TAX REVIEW VERENDRA KALRA & CO OCTOBER Inside this edition. Like always, Like never before
 VERENDRA KALRA & CO CHARTERED A CCOUNTANTS Like always, Like never before DIRECT TAX REVIEW OCTOBER 2018 Inside this edition AO's order rejecting ITR without providing opportunity to rectify defect u/s
VERENDRA KALRA & CO CHARTERED A CCOUNTANTS Like always, Like never before DIRECT TAX REVIEW OCTOBER 2018 Inside this edition AO's order rejecting ITR without providing opportunity to rectify defect u/s
MANAGERIAL REMUNERATION SECTION AND SCHEDUL V- ANALYSIS
 MANAGERIAL REMUNERATION SECTION 196 198 AND SCHEDUL V- ANALYSIS Sl Description Page No. No. 1 Conditions for Appointment of MD/Whole Time Director/ Manager 3 2 Extension to Age Limit 3 3 Appointment Procedure
MANAGERIAL REMUNERATION SECTION 196 198 AND SCHEDUL V- ANALYSIS Sl Description Page No. No. 1 Conditions for Appointment of MD/Whole Time Director/ Manager 3 2 Extension to Age Limit 3 3 Appointment Procedure
MODEL QUESTION PAPER FOR LIMITED INSOLVENCY EXAMINATION
 MODEL QUESTION PAPER FOR LIMITED INSOLVENCY EXAMINATION 1 When can a bank initiate a corporate insolvency resolution process in relation to a corporate debtor? a) On determination of default by National
MODEL QUESTION PAPER FOR LIMITED INSOLVENCY EXAMINATION 1 When can a bank initiate a corporate insolvency resolution process in relation to a corporate debtor? a) On determination of default by National
Irish Statute Book. Insurance Act, Quick Search Search for word(s) / phrase in Title of Act or Statutory Instrument
 Quick Search Search for word(s) / phrase in Title of Act or Statutory Instrument Enter Search Acts SIs More Search Options Help Disclaimer Irish Statute Book Produced by the Office of the Attorney General
Quick Search Search for word(s) / phrase in Title of Act or Statutory Instrument Enter Search Acts SIs More Search Options Help Disclaimer Irish Statute Book Produced by the Office of the Attorney General
GENERAL INSURANCE AGENTS REGISTRATION REGULATIONS
 GENERAL INSURANCE AGENTS REGISTRATION REGULATIONS 1. SHORT TITLE AND COMMENCEMENT These Regulations may be cited as the General Insurance Agents Registration Regulations (hereinafter referred to as these
GENERAL INSURANCE AGENTS REGISTRATION REGULATIONS 1. SHORT TITLE AND COMMENCEMENT These Regulations may be cited as the General Insurance Agents Registration Regulations (hereinafter referred to as these
INSPECTION-SEARCH-SEIZURE & ARREST!!
 INSPECTION-SEARCH-SEIZURE & ARREST!! (CHAPTER XIV OF THE CENTRAL GOODS AND SERVICES TAX ACT, 2017 ) The Definitive Provisions In the GST Act to prevent and punish the evasion of tax -By Prakhar Jain ARUN
INSPECTION-SEARCH-SEIZURE & ARREST!! (CHAPTER XIV OF THE CENTRAL GOODS AND SERVICES TAX ACT, 2017 ) The Definitive Provisions In the GST Act to prevent and punish the evasion of tax -By Prakhar Jain ARUN
Acceptance of Deposits by Companies - CA.B. Kalyan Srinath,
 Acceptance of Deposits by Companies - CA.B. Kalyan Srinath, sbkalyan@gmail.com 1. Introduction: The Companies Act, 2013 was assented by the President of India on 29, August 2013 and Published in the Official
Acceptance of Deposits by Companies - CA.B. Kalyan Srinath, sbkalyan@gmail.com 1. Introduction: The Companies Act, 2013 was assented by the President of India on 29, August 2013 and Published in the Official
IN THE HIGH COURT OF DELHI AT NEW DELHI SUBJECT : THE COMPANIES ACT, 1956 Date of decision: 1st May, 2012 CO.APP. No.24/2012
 IN THE HIGH COURT OF DELHI AT NEW DELHI SUBJECT : THE COMPANIES ACT, 1956 Date of decision: 1st May, 2012 CO.APP. No.24/2012 NATIONAL INSTT. OF TECHNOLOGY TRUST...Appellant Through: Mr. Sudhir Nandrajog,
IN THE HIGH COURT OF DELHI AT NEW DELHI SUBJECT : THE COMPANIES ACT, 1956 Date of decision: 1st May, 2012 CO.APP. No.24/2012 NATIONAL INSTT. OF TECHNOLOGY TRUST...Appellant Through: Mr. Sudhir Nandrajog,
THE ARBITRATION AND CONCILIATION (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2018
 1 As INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA Bill No. 100 of 2018 THE ARBITRATION AND CONCILIATION (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2018 A BILL further to amend the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996. BE it enacted by Parliament
1 As INTRODUCED IN LOK SABHA Bill No. 100 of 2018 THE ARBITRATION AND CONCILIATION (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2018 A BILL further to amend the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996. BE it enacted by Parliament
ADJUSTMENT OF INTERNATIONAL TAXES ACT
 ADJUSTMENT OF INTERNATIONAL TAXES ACT Act No. 4981, Dec. 6, 1995 Amended by Act No. 5193, Dec. 30, 1996 Act No. 5581, Dec. 28, 1998 Act No. 5584, Dec. 28, 1998 Act No. 6299, Dec. 29, 2000 Act No. 6304,
ADJUSTMENT OF INTERNATIONAL TAXES ACT Act No. 4981, Dec. 6, 1995 Amended by Act No. 5193, Dec. 30, 1996 Act No. 5581, Dec. 28, 1998 Act No. 5584, Dec. 28, 1998 Act No. 6299, Dec. 29, 2000 Act No. 6304,
Jebel Ali Free Zone Authority JEBEL ALI FREE ZONE AUTHORITY OFFSHORE COMPANIES REGULATIONS 2018
 Jebel Ali Free Zone Authority JEBEL ALI FREE ZONE AUTHORITY OFFSHORE COMPANIES REGULATIONS 2018 Jebel Ali Free Zone Authority PART 1: GENERAL... 7 1. TITLE... 7 2. LEGISLATIVE AUTHORITY... 7 3. DATE OF
Jebel Ali Free Zone Authority JEBEL ALI FREE ZONE AUTHORITY OFFSHORE COMPANIES REGULATIONS 2018 Jebel Ali Free Zone Authority PART 1: GENERAL... 7 1. TITLE... 7 2. LEGISLATIVE AUTHORITY... 7 3. DATE OF
ARBITRATION ACT. May 29, 2016>
 ARBITRATION ACT Wholly Amended by Act No. 6083, Dec. 31, 1999 Amended by Act No. 6465, Apr. 7, 2001 Act No. 6626, Jan. 26, 2002 Act No. 10207, Mar. 31, 2010 Act No. 11690, Mar. 23, 2013 Act No. 14176,
ARBITRATION ACT Wholly Amended by Act No. 6083, Dec. 31, 1999 Amended by Act No. 6465, Apr. 7, 2001 Act No. 6626, Jan. 26, 2002 Act No. 10207, Mar. 31, 2010 Act No. 11690, Mar. 23, 2013 Act No. 14176,
RULES Table of Contents
 CENTRAL SECURITIES DEPOSITORY COMPANY OF BOTSWANA LIMITED RULES Table of Contents Introduction 3 Page Section Title 1 Legal and Contractual Framework 3 2 Definitions and Interpretations 6 3 Nominated Transfer
CENTRAL SECURITIES DEPOSITORY COMPANY OF BOTSWANA LIMITED RULES Table of Contents Introduction 3 Page Section Title 1 Legal and Contractual Framework 3 2 Definitions and Interpretations 6 3 Nominated Transfer
