Chapter 2. International Flow of Funds. Lecture Outline. Balance of Payments Current Account Capital and Financial Accounts
|
|
|
- Silvester Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds Lecture Outline Balance of Payments Current Account Capital and Financial Accounts International Trade Flows Distribution of U.S. Exports and Imports U.S. Balance of Trade Trend International Trade Issues Events That Increase International Trade Trade Friction Factors Affecting International Trade Flows Impact of Inflation Impact of National Income Impact of Government Policies Impact of Exchange Rates Interaction of Factors Correcting a Balance of Trade Deficit Limitations of a Weak Home Currency Solution International Capital Flows Distribution of DFI by U.S. Firms Distribution of DFI in the U.S. Factors Affecting Direct Foreign Investment Factors Affecting International Portfolio Investment Agencies that Facilitate International Flows How Trade Affects an MNC s Value from the U.S. Edition. May not be scanned, copied, duplicated, or posted to a publicly accessible website, in whole or in part.
2 2 International Flow of Funds Chapter Theme This chapter provides an overview of the international environment surrounding MNCs. The chapter is macro-oriented in that it discusses international payments on a country-by-country basis. This macro discussion is useful information for an MNC since the MNC can be affected by changes in a country s current account and capital account positions. Topics to Stimulate Class Discussion 1. Is a current account deficit something to worry about? 2. If a government wants to correct a current account deficit, why can t it simply enforce restrictions on imports? 3. Why don t exchange rates always adjust to correct current account deficits? POINT/COUNTER-POINT: Should Trade Restrictions be Used to Influence Human Rights Issues? POINT: Yes. Some countries do not protect human rights in the same manner as the U.S. At times, the U.S. should threaten to restrict U.S. imports from or investment in a country if it does not correct human rights violations. The U.S. should use its large international trade and investment as leverage to ensure that human rights violations do not occur. Other countries with a history of human rights violations are more likely to honor human rights if their economic conditions are threatened. COUNTER-POINT: No. International trade and human rights are two separate issues. International trade should not be used as the weapon to enforce human rights. Firms engaged in international trade should not be penalized by the human rights violations of a government. If the U.S. imposes trade restrictions to enforce human rights, the country will retaliate. Thus, the U.S. firms that export to that foreign country will be adversely affected. By imposing trade sanctions, the U.S. government is indirectly penalizing the MNCs that are attempting to conduct business in specific foreign countries. Trade sanctions cannot solve every difference in the beliefs or morals between the more developed countries and the developing countries. By restricting trade, the U.S. will slow down the economic progress of developing countries. WHO IS CORRECT? Use the Internet to learn more about this issue. Which argument do you support? Offer your own opinion on this issue. ANSWER: There is no perfect solution, but the tradeoff should be recognized. When trade is used as the means to correct human rights problems, those firms that initiated their business in other countries could suffer major losses. These firms may argue that they are mistreated by such restrictions, and that the country of concern will not necessarily improve its human rights record even with the restrictions. Yet, if the U.S. ignores the human rights issue, it will be criticized for being too capitalistic, and unwilling to help solve social problems in the world.
3 International Flow of Funds 3 Answers to End of Chapter Questions 1. Effects of Tariffs. Assume a simple world in which the U.S. exports soft drinks and beer to France and imports wine from France. If the U.S. imposes large tariffs on the French wine, explain the likely impact on the values of the U.S. beverage firms, U.S. wine producers, the French beverage firms, and the French wine producers. ANSWER: The U.S. wine producers benefit from the U.S. tariffs, while the French wine producers are adversely affected. The French government would likely retaliate by imposing tariffs on the U.S. beverage firms, which would adversely affect their value. The French beverage firms would benefit. 2. IMF. a. What are some of the major objectives of the IMF? ANSWER: Major IMF objectives are to (1) promote cooperation among countries on international monetary issues, (2) promote stability in exchange rates, (3) provide temporary funds to member countries attempting to correct imbalances of international payments, (4) promote free mobility of capital funds across countries, and (5) promote free trade. b. How is the IMF involved in international trade? ANSWER: The IMF in involved in international trade because it attempts to stabilize international payments, and trade represents a significant portion of the international payments. 3. Currency Effects. When South Korea s export growth stalled, some South Korean firms suggested that South Korea s primary export problem was the weakness in the Japanese yen. How would you interpret this statement? ANSWER: One of South Korea s primary competitors in exporting is Japan, which produces and exports many of the same types of products to the same countries. When the Japanese yen is weak, some importers switch to Japanese products in place of South Korean products. For this reason, it is often suggested that South Korea s primary export problem is weakness in the Japanese yen. 4. Exchange Rate Effect on Trade Balance. Would the U.S. balance of trade deficit be larger or smaller if the dollar depreciates against all currencies, versus depreciating against some currencies but appreciated against others? Explain. ANSWER: If the dollar weakens against all currencies, the U.S. balance of trade deficit will likely be smaller. Some U.S. importers would have more seriously considered purchasing their goods in the U.S. if most or all currencies simultaneously strengthened against the dollar. Conversely, if some currencies weaken against the dollar, the U.S. importers may have simply shifted their importing from one foreign country to another. 5. Impact on International Trade. Why do you think international trade volume has increased over time? In general, how are inefficient firms affected by the reduction in trade restrictions among countries and the continuous increase in international trade?
4 4 International Flow of Funds ANSWER. International trade volume has increased because of the reduction in trade restrictions over time. It may have also increased for many other reasons, such as increased information flow (via Internet etc.) between firms in different countries. Inefficient firms are adversely affected if they have to face tougher competition from foreign firms as a result of a reduction in trade restrictions. 6. Government Restrictions. How can government restrictions affect international payments among countries? ANSWER: Governments can place tariffs or quotas on imports to restrict imports. They can also place taxes on income from foreign securities, thereby discouraging investors from purchasing foreign securities. If they loosen restrictions, they can encourage international payments among countries. 7. Effects of the Euro. Explain how the existence of the euro may affect U.S. international trade. ANSWER: The euro allowed for a single currency among many European countries. It could encourage firms in those countries to trade among each other since there is no exchange rate risk. This would possibly cause them to trade less with the U.S. The euro can increase trade within Europe because it eliminates the need for several European countries to exchange currencies when trading with each other. 8. Inflation Effect on Trade. a. How would a relatively high home inflation rate affect the home country s current account, other things being equal? ANSWER: A high inflation rate tends to increase imports and decrease exports, thereby increasing the current account deficit, other things equal. b. Is a negative current account harmful to a country? Discuss. ANSWER: This question is intended to encourage opinions and does not have a perfect solution. A negative current account is thought to reflect lost jobs in a country, which is unfavorable. Yet, the foreign importing reflects strong competition from foreign producers, which may keep prices (inflation) low. 9. Demand for Exports. A relatively small U.S. balance of trade deficit is commonly attributed to a strong demand for U.S. exports. What do you think is the underlying reason for the strong demand for U.S. exports? ANSWER: The strong demand for U.S. exports is commonly attributed to strong foreign economies or to a weak dollar. 10. Balance of Payments. a. Of what is the current account generally composed? ANSWER: The current account balance is composed of (1) the balance of trade, (2) the net amount of payments of interest to foreign investors and from foreign investment, (3) payments from international tourism, and (4) private gifts and grants.
5 International Flow of Funds 5 b. Of what is the capital account generally composed? ANSWER: The capital account is composed of all capital investments made between countries, including both direct foreign investment and purchases of securities with maturities exceeding one year. Advanced Questions 11. International Investments. U.S.-based MNCs commonly invest in foreign securities. a. Assume that the dollar is presently weak and is expected to strengthen over time. How will these expectations affect the tendency of U.S. investors to invest in foreign securities? ANSWER: The expectations of a strong dollar would discourage U.S. investors from investing abroad. If the dollar is relatively weak now, U.S. investors need more dollars to make purchase foreign currency (when investing). If the dollar strengthens over their investment horizon, they will exchange the foreign currency (as the investment is liquidated) into dollars at a less favorable exchange rate than the exchange rate at which they converted dollars into the foreign currency. That is, the exchange rate effect would reduce the yield that they earn on their investment. b. Explain how low U.S. interest rates can affect the tendency of U.S.-based MNCs to invest abroad. ANSWER: Low U.S. interest rates can encourage U.S.-based MNCs to invest abroad, as investors seek higher returns on their investment than they can earn in the U.S. c. In general terms, what is the attraction of foreign investments to U.S. investors? ANSWER: The main attraction is potentially higher returns. The international stocks can outperform U.S. stocks, and international bonds can outperform U.S. bonds. However, there is no guarantee that the returns on international investments will be so favorable. Some investors may also pursue international investments to diversify their investment portfolio, which can possibly reduce risk. 12. Exchange Rate Effects on Trade. a. Explain why a stronger dollar could enlarge the U.S. balance of trade deficit. Explain why a weaker dollar could affect the U.S. balance of trade deficit. ANSWER: A stronger dollar makes U.S. exports more expensive to importers and may reduce imports. It makes U.S. imports cheap and may increase U.S. imports. A weaker home currency increases the prices of imports purchased by the home country and reduces the prices paid by foreign businesses for the home country s exports. This should cause a decrease in the home country s demand for imports and an increase in the foreign demand for the home country s exports, and therefore increase the current account. However, this relationship can be distorted by other factors. b. It is sometimes suggested that a floating exchange rate will adjust to reduce or eliminate any current account deficit. Explain why this adjustment would occur. ANSWER: A current account deficit reflects a net sale of the home currency in exchange for other currencies. This places downward pressure on that home currency s value. If the currency weakens, it will reduce the home demand for foreign goods (since goods will now be more
6 6 International Flow of Funds expensive), and will increase the home export volume (since exports will appear cheaper to foreign countries). c. Why does the exchange rate not always adjust to a current account deficit? ANSWER: In some cases, the home currency will remain strong even though a current account deficit exists, since other factors (such as international capital flows) can offset the forces placed on the currency by the current account. 13. Free Trade. There has been considerable momentum to reduce or remove trade barriers in an effort to achieve free trade. Yet, one disgruntled executive of an exporting firm stated, Free trade is not conceivable; we are always at the mercy of the exchange rate. Any country can use this mechanism to impose trade barriers. What does this statement mean? ANSWER: This statement implies that even if there were no explicit barriers, a government could attempt to manipulate exchange rates to a level that would effectively reduce foreign competition. For example, a U.S. firm may be discouraged from attempting to export to Japan if the value of the dollar is very high against the yen. The prices of the U.S. goods from the Japanese perspective are too high because of the strong dollar. The reverse situation could also be possible in which a Japanese exporting firm is priced out of the U.S. market because of a strong yen (weak dollar). [Answer is based on opinion.] Solution to Continuing Case Problem: Blades, Inc. 1. How could a higher level of inflation in Thailand affect Blades (assume U.S. inflation remains constant)? ANSWER: A high level of inflation in Thailand relative to the United States could affect Blades favorably. Generally, if a country s inflation rate increases relative to the countries with which it trades, consumers and corporations within the country will most likely purchase more goods overseas, as local goods become more expensive. Consequently, Blades sales to Thailand may increase. 2. How could competition from firms in Thailand and from U.S. firms conducting business in Thailand affect Blades? ANSWER: Blades would be favorably affected relative to Thai roller blade manufacturers and relative to other U.S. roller blade manufacturers with operations in Thailand. Both groups of firms will likely be forced to raise their prices if they want to maintain the same profit margin should inflation in Thailand increase. This is especially true if both groups of firms source their supplies directly from Thailand, so that the prices of these supplies are subject to the higher inflation in Thailand. Conversely, Blades cost of goods sold incurred in Thailand is relatively small. Consequently, costs will not be subject to the higher level of inflation in Thailand to a great extent and Blades will probably not have to raise its prices to the same extent as Thai roller blade manufacturers or U.S. manufacturers with operations in Thailand. 3. How could a decreasing level of national income in Thailand affect Blades? ANSWER: At first glance, it would appear that a decreasing level of national income in Thailand could hurt Blades financially, as Thai consumers will have less money to spend. Furthermore, this
7 International Flow of Funds 7 effect may be magnified because Blades manufactures a leisure product, which is probably one of the first products Thai consumers will stop buying. The arrangement Blades has with its primary Thai importer mitigates this effect somewhat, since the latter has committed himself to the purchase of a certain number of Speedos annually. Nevertheless, the importer may not offer to renew this arrangement in excess of the original three years if the Thai economy does not improve. 4. How could a continued depreciation of the Thai baht affect Blades? How would it affect Blades relative to U.S. exporters invoicing their roller blades in U.S. dollars? ANSWER: A continued depreciation of the Thai baht would hurt Blades, especially because the firm invoices its roller blades in baht. A continued depreciation of the baht means that the bahtdenominated revenue in Thailand will convert to fewer U.S. dollars. Blades also has some expenses in baht, but this amount is less than the revenue denominated in baht. Although Blades would be hurt by a depreciating baht because its exports are denominated in baht, the demand for Blades products may increase relative to that of its U.S. competitors exporting to Thailand. This is because most of the U.S. firms exporting roller blades to Thailand invoice their products in U.S. dollars. If the baht depreciates, Thai importers will have to convert more baht to dollars in order to pay for the dollar-denominated exports. 5. If Blades increases its business in Thailand and experiences serious financial problems, are there any international agencies that the company could approach for loans or other financial assistance? ANSWER: An agency extending direct loans to corporations involved in international trade is the International Financial Corporation (IFC). Besides extending loans, the IFC may also purchase stock in a corporation, thereby becoming part owner. Solution to Supplemental Case: Maple Leaf Paper Company This case reflects the actual experience of a Canadian exporting firm (although the name and industry have been changed) to the free-trade agreement on January 2, The appreciation in Canadian dollars (resulting from the agreement) offset the tariff, so that the firm was no better off with the free-trade agreement. The case shows that the effects of free trade are not always so obvious and may differ across firms. a. While the tariff allowed for a 12 percent decline in price, the U.S. clients will have to pay more dollars to obtain Canadian dollars in the future, based on the forecast of the exchange rate. The exchange rate is expected to rise by percent. Given that the 12 percent tariff is removed along with the exchange rate movement, the net effect will be an increase in price to U.S. clients of about one percent. Based on the relationship between the price and U.S. demand, the U.S. demand for Maple Leaf paper should decline 3 percent in response to the one percent increase in price. This implies a U.S. demand of 174,600 rolls of paper per year. In Canada, the 20 percent increase in demand (provided in the case) implies an annual demand of 24,000 rolls. Therefore, the total demand for Maple Leaf paper should be around 198,600 rolls, which is slightly less than the total demand in the past. b. The precise forecast is not as important as the general concept here. What seemed to be a favorable event does not benefit Maple Leaf. While the free-trade agreement allows for the
8 8 International Flow of Funds removal of tariffs, it causes a shift in international trade flows, which places upward pressure on the Canadian dollar s value. The appreciation of the Canadian dollar is expected to overwhelm the effect of removing the tariff, forcing the price in U.S. dollars to rise. c. The U.S. exporting firm is not directly affected by the removal of the tariff on Canadian exports, but would benefit from the appreciation of the Canadian dollar. Small Business Dilemma Identifying Factors That Will Affect the Foreign Demand at the Sports Exports Company Identify the factors that affect the current account balance between the U.S. and the U.K. Explain how each factor may possibly affect the British demand for the footballs that are produced by the Sports Exports Company. ANSWER: 1. High inflation in the U.K. could cause a shift in the demand for U.S. products instead of British products. However, at this time there is not a British producer of footballs, so that high British inflation will not cause an increase in the demand for U.S.-produced footballs. 2. High national income in the U.K. could increase the amount of spending by British consumers, and would therefore cause an increase in the demand for footballs produced by the Sports Exports Company. A lower national income in the U.K. would have the opposite effect. 3. Government restrictions could be imposed by the British government on goods (such as the footballs) exported by U.S. firms. However, footballs are not likely to be targeted by the British government as a product that should be subject to restrictions. 4. The exchange rate of the British pound will change over time. However, since the Sports Exports Company is willing to accept pounds when it sells footballs to the distributor, the distributor does not have to convert the pounds into dollars. Therefore, the British demand for footballs is not affected by changes in the value of the pound (unless this causes the Sports Exports Company to change the price it charges for the footballs someday).
Chapter 2. International Flow of Funds. Lecture Outline. Balance of Payments Current Account Capital and Financial Accounts
 Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds Lecture Outline Balance of Payments Current Account Capital and Financial Accounts Growth in International Trade Events That Increased Trade Volume Impact of Outsourcing
Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds Lecture Outline Balance of Payments Current Account Capital and Financial Accounts Growth in International Trade Events That Increased Trade Volume Impact of Outsourcing
International Corporate Finance
 International Corporate Finance Solution Manual Chapter 2: International Flow of Funds Effects of Tariffs Assume a simple world in which the U.S. exports soft drinks and beer to France and imports wine
International Corporate Finance Solution Manual Chapter 2: International Flow of Funds Effects of Tariffs Assume a simple world in which the U.S. exports soft drinks and beer to France and imports wine
Chapter 6. Government Influence on Exchange Rates. Lecture Outline
 Chapter 6 Government Influence on Exchange Rates Lecture Outline Exchange Rate Systems Fixed Exchange Rate System Freely Floating Exchange Rate System Managed Float Exchange Rate System Pegged Exchange
Chapter 6 Government Influence on Exchange Rates Lecture Outline Exchange Rate Systems Fixed Exchange Rate System Freely Floating Exchange Rate System Managed Float Exchange Rate System Pegged Exchange
Chapter 13. Direct Foreign Investment. Lecture Outline
 Chapter 13 Direct Foreign Investment Lecture Outline Motives for Direct Foreign Investment (DFI) Revenue-Related Motives Cost-Related Motives Comparing Benefits of DFI Among Countries Measuring an MNC's
Chapter 13 Direct Foreign Investment Lecture Outline Motives for Direct Foreign Investment (DFI) Revenue-Related Motives Cost-Related Motives Comparing Benefits of DFI Among Countries Measuring an MNC's
4: Exchange Rate Determination
 4: Exchange Rate Determination Financial managers of MNCs that conduct international business must continuously monitor exchange rates because their cash flows are highly dependent on them. They need to
4: Exchange Rate Determination Financial managers of MNCs that conduct international business must continuously monitor exchange rates because their cash flows are highly dependent on them. They need to
Chapter 9. Forecasting Exchange Rates. Lecture Outline. Why Firms Forecast Exchange Rates
 Chapter 9 Forecasting Exchange Rates Lecture Outline Why Firms Forecast Exchange Rates Forecasting Techniques Technical Forecasting Fundamental Forecasting Market-Based Forecasting Mixed Forecasting Guidelines
Chapter 9 Forecasting Exchange Rates Lecture Outline Why Firms Forecast Exchange Rates Forecasting Techniques Technical Forecasting Fundamental Forecasting Market-Based Forecasting Mixed Forecasting Guidelines
FINC/ECON International Finance Homework Solution
 FINC/ECON 3240 - International Finance Homework Solution Chapter 1 2. Comparative Advantage. a. Explain how the theory of comparative advantage relates to the need for international business. ANSWER: The
FINC/ECON 3240 - International Finance Homework Solution Chapter 1 2. Comparative Advantage. a. Explain how the theory of comparative advantage relates to the need for international business. ANSWER: The
Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds
 Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds 1. Recently, the U.S. experienced an annual balance of trade representing a. a. large surplus (exceeding $100 billion) b. small surplus c. level of zero d. deficit
Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds 1. Recently, the U.S. experienced an annual balance of trade representing a. a. large surplus (exceeding $100 billion) b. small surplus c. level of zero d. deficit
Chapter 11. Managing Transaction Exposure. Lecture Outline. Hedging Payables. Hedging Receivables
 Chapter 11 Managing Transaction Exposure Lecture Outline Policies for Hedging Transaction Exposure Hedging Most of the Exposure Selective Hedging Hedging Payables Forward or Futures Hedge Money Market
Chapter 11 Managing Transaction Exposure Lecture Outline Policies for Hedging Transaction Exposure Hedging Most of the Exposure Selective Hedging Hedging Payables Forward or Futures Hedge Money Market
Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds
 Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds 1. Recently, the U.S. experienced an annual balance of trade representing a. a. large surplus (exceeding $100 billion) b. small surplus c. level of zero d. deficit
Chapter 2 International Flow of Funds 1. Recently, the U.S. experienced an annual balance of trade representing a. a. large surplus (exceeding $100 billion) b. small surplus c. level of zero d. deficit
Chapter 1. Multinational Financial Management. Lecture Outline. Managing the MNC Agency Problems Management Structure of an MNC
 Chapter 1 Multinational Financial Management Lecture Outline Managing the MNC Agency Problems Management Structure of an MNC Why Firms Pursue International Business Theory of Comparative Advantage Imperfect
Chapter 1 Multinational Financial Management Lecture Outline Managing the MNC Agency Problems Management Structure of an MNC Why Firms Pursue International Business Theory of Comparative Advantage Imperfect
Lecture #8: How Scary is the US Trade Deficit?
 Parsons, 2007 Lecture #8: How Scary is the US Trade Deficit? First, the facts: How big IS the US deficit? Well, if we look at the current account, whose largest component is the trade deficit, it was about
Parsons, 2007 Lecture #8: How Scary is the US Trade Deficit? First, the facts: How big IS the US deficit? Well, if we look at the current account, whose largest component is the trade deficit, it was about
International Economics questions Part II
 International Economics questions Part II A country would justify erecting trade barriers, such as tariffs or quotas, to a. make goods cheaper b. expand their markets c. protect domestic jobs d. stimulate
International Economics questions Part II A country would justify erecting trade barriers, such as tariffs or quotas, to a. make goods cheaper b. expand their markets c. protect domestic jobs d. stimulate
International Finance multiple-choice questions
 International Finance multiple-choice questions 1. Spears Co. will receive SF1,000,000 in 30 days. Use the following information to determine the total dollar amount received (after accounting for the
International Finance multiple-choice questions 1. Spears Co. will receive SF1,000,000 in 30 days. Use the following information to determine the total dollar amount received (after accounting for the
Chapter 14. Multinational Capital Budgeting. Lecture Outline
 Chapter 14 Multinational Capital Budgeting Lecture Outline Subsidiary versus Parent Perspective Tax Differentials Restrictions on Remitted Earnings Exchange Rate Movements Input for Multinational Capital
Chapter 14 Multinational Capital Budgeting Lecture Outline Subsidiary versus Parent Perspective Tax Differentials Restrictions on Remitted Earnings Exchange Rate Movements Input for Multinational Capital
Chapter 15. The Foreign Exchange Market. Chapter Preview
 Chapter 15 The Foreign Exchange Market Chapter Preview In the mid-1980s, American businesses became less competitive relative to their foreign counterparts. By the 2000s, though, competitiveness increased.
Chapter 15 The Foreign Exchange Market Chapter Preview In the mid-1980s, American businesses became less competitive relative to their foreign counterparts. By the 2000s, though, competitiveness increased.
BBM2153 Financial Markets and Institutions Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar
 BBM2153 Financial Markets and Institutions Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L8: The Foreign Exchange Market www. notes638.wordpress.com Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd. All rights reserved. 8-1 Chapter
BBM2153 Financial Markets and Institutions Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L8: The Foreign Exchange Market www. notes638.wordpress.com Copyright 2015 Pearson Education, Ltd. All rights reserved. 8-1 Chapter
Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System
 Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding
Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding
2. Interest rates in the United States rise faster than interest rates in Canada.
 Exchange Rates Interaction Between Currencies When Americans buy more foreign goods, U.S. dollars are sold in the international currency market to purchase foreign currencies that are used to pay producers
Exchange Rates Interaction Between Currencies When Americans buy more foreign goods, U.S. dollars are sold in the international currency market to purchase foreign currencies that are used to pay producers
Open Economy. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Open Economy 1 / 66
 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Open Economy 1 / 66 International Flows Definition A closed economy is an economy that does not interact with other economies. Definition An open economy is an economy
Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Open Economy 1 / 66 International Flows Definition A closed economy is an economy that does not interact with other economies. Definition An open economy is an economy
Chapter 10. Measuring Exposure to Exchange Rate Fluctuations. Lecture Outline. Relevance of Exchange Rate Risk
 Chapter 10 Measuring Exposure to Exchange Rate Fluctuations Lecture Outline Relevance of Exchange Rate Risk Transaction Exposure Estimating Net Cash Flows in Each Currency Exposure of an MNC s Portfolio
Chapter 10 Measuring Exposure to Exchange Rate Fluctuations Lecture Outline Relevance of Exchange Rate Risk Transaction Exposure Estimating Net Cash Flows in Each Currency Exposure of an MNC s Portfolio
Macroeconomics in an Open Economy
 Chapter 17 (29) Macroeconomics in an Open Economy Chapter Summary Nearly all economies are open economies that trade with and invest in other economies. A closed economy has no interactions in trade or
Chapter 17 (29) Macroeconomics in an Open Economy Chapter Summary Nearly all economies are open economies that trade with and invest in other economies. A closed economy has no interactions in trade or
AP Macro Unit 3: Int'l Trade and Finance
 Name: Class: Date: AP Macro Unit 3: Int'l Trade and Finance Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The overall U.S. balance of payments
Name: Class: Date: AP Macro Unit 3: Int'l Trade and Finance Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The overall U.S. balance of payments
Chapter 18. The International Financial System Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market
 Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding of foreign assets in the foreign exchange market
Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding of foreign assets in the foreign exchange market
Chapter 1. Multinational Financial Management: An Overview
 Chapter 1 Multinational Financial Management: An Overview 1. The commonly accepted goal of the MNC is to: A) maximize short-term earnings. B) maximize shareholder wealth. C) minimize risk. D) A and C.
Chapter 1 Multinational Financial Management: An Overview 1. The commonly accepted goal of the MNC is to: A) maximize short-term earnings. B) maximize shareholder wealth. C) minimize risk. D) A and C.
Chapter 3 Foreign Exchange Determination and Forecasting
 Chapter 3 Foreign Exchange Determination and Forecasting Note: In the sixth edition of Global Investments, the exchange rate quotation symbols differ from previous editions. We adopted the convention that
Chapter 3 Foreign Exchange Determination and Forecasting Note: In the sixth edition of Global Investments, the exchange rate quotation symbols differ from previous editions. We adopted the convention that
5: Currency Derivatives
 5: Currency Derivatives Given the potential shifts in the supply of or demand for currency (as explained in the previous chapter), fi rms and individuals who have assets denominated in foreign currencies
5: Currency Derivatives Given the potential shifts in the supply of or demand for currency (as explained in the previous chapter), fi rms and individuals who have assets denominated in foreign currencies
OCR Economics A-level
 OCR Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 4: The Global Context 4.5 Trade policies and negotiations Notes Different methods of protectionism Protectionism is the act of guarding a country s industries
OCR Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 4: The Global Context 4.5 Trade policies and negotiations Notes Different methods of protectionism Protectionism is the act of guarding a country s industries
Chapter 15. International Corporate Governance and Control. Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 International Corporate Governance and Control Lecture Outline International Corporate Governance Governance by Board Members Governance by Institutional Investors Governance by Shareholder
Chapter 15 International Corporate Governance and Control Lecture Outline International Corporate Governance Governance by Board Members Governance by Institutional Investors Governance by Shareholder
BBK3273 International Finance
 BBK3273 International Finance Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L2: Exchange Rate Determination www.lecturenotes638.wordpress.com Contents 1. Measuring Exchange Rate Movements 2. How Exchange Rate Movements
BBK3273 International Finance Prepared by Dr Khairul Anuar L2: Exchange Rate Determination www.lecturenotes638.wordpress.com Contents 1. Measuring Exchange Rate Movements 2. How Exchange Rate Movements
Exchange rates and aviation: examining the links
 -50%+ -48% to -50% -44% to -46% -40% to -42% -36% to -38% -32% to -34% -28% to -30% -24% to -26% -20% to -22% -16% to -18% -12% to -14% -8% to -10% -4% to -6% 0% to -2% 0% to 2% 4% to 6% 8% to 10% 12%
-50%+ -48% to -50% -44% to -46% -40% to -42% -36% to -38% -32% to -34% -28% to -30% -24% to -26% -20% to -22% -16% to -18% -12% to -14% -8% to -10% -4% to -6% 0% to -2% 0% to 2% 4% to 6% 8% to 10% 12%
Lower prices. Lower costs, esp. wages. Higher productivity. Higher quality/more desirable exports. Greater natural resources. Higher interest rates
 1 Goods market Reason to Hold Currency To acquire goods and services from that country Important in... Long run (years to decades) Currency Will Appreciate If... Lower prices Lower costs, esp. wages Higher
1 Goods market Reason to Hold Currency To acquire goods and services from that country Important in... Long run (years to decades) Currency Will Appreciate If... Lower prices Lower costs, esp. wages Higher
Determination of Interest Rates
 Chapter 2 Determination of Interest Rates Outline Loanable Funds Theory Household Demand for Loanable Funds Business Demand for Loanable Funds Government Demand for Loanable Funds Foreign Demand for Loanable
Chapter 2 Determination of Interest Rates Outline Loanable Funds Theory Household Demand for Loanable Funds Business Demand for Loanable Funds Government Demand for Loanable Funds Foreign Demand for Loanable
Investment Insights. International Strategy: Understanding Currency Movements
 International Strategy: Understanding Currency Movements Executive Summary In the past few years, international investing or the purchase of non-u.s. securities has become increasingly popular. We believe
International Strategy: Understanding Currency Movements Executive Summary In the past few years, international investing or the purchase of non-u.s. securities has become increasingly popular. We believe
A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy
 A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy PowerPoint Slides prepared by: Andreea CHIRITESCU Eastern Illinois University 1 Market for Loanable Funds In an open economy S = I + NCO Saving = Domestic investment
A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy PowerPoint Slides prepared by: Andreea CHIRITESCU Eastern Illinois University 1 Market for Loanable Funds In an open economy S = I + NCO Saving = Domestic investment
8: Relationships among Inflation, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates
 8: Relationships among Inflation, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates Infl ation rates and interest rates can have a significant impact on exchange rates (as explained in Chapter 4) and therefore can infl
8: Relationships among Inflation, Interest Rates, and Exchange Rates Infl ation rates and interest rates can have a significant impact on exchange rates (as explained in Chapter 4) and therefore can infl
Open Economy. Sherif Khalifa. Sherif Khalifa () Open Economy 1 / 70
 Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Open Economy 1 / 70 Definition A closed economy is an economy that does not interact with other economies. Definition An open economy is an economy that interacts freely
Sherif Khalifa Sherif Khalifa () Open Economy 1 / 70 Definition A closed economy is an economy that does not interact with other economies. Definition An open economy is an economy that interacts freely
Long-Term Debt Financing
 18 Long-Term Debt Financing CHAPTER OBJECTIVES The specific objectives of this chapter are to: explain how an MNC uses debt financing in a manner that minimizes its exposure to exchange rate risk, explain
18 Long-Term Debt Financing CHAPTER OBJECTIVES The specific objectives of this chapter are to: explain how an MNC uses debt financing in a manner that minimizes its exposure to exchange rate risk, explain
Protectionism. The term free-trade describes the process of lowering protectionist barriers and thereby realizing those gains from trade.
 Protectionism Protectionism Protectionism: is the placement of legal restrictions on international trade and includes tariffs, quotas, subsidies, and other bureaucratic barriers Despite the obvious gains
Protectionism Protectionism Protectionism: is the placement of legal restrictions on international trade and includes tariffs, quotas, subsidies, and other bureaucratic barriers Despite the obvious gains
Assignment 13 (Chapter 14)
 Assignment 13 (Chapter 14) 1. According to the absorption approach, the economic circumstances that best warrant a currency devaluation is where the domestic economy faces: a) Unemployment coupled with
Assignment 13 (Chapter 14) 1. According to the absorption approach, the economic circumstances that best warrant a currency devaluation is where the domestic economy faces: a) Unemployment coupled with
Ch. 2 International Flow of Funds. Balance of Payments. Current Account
 Ch. 2 International Flow of Funds Topics Balance of Payments International Trade Flows International Capital Flows Agencies that Facilitate International Flows Balance of Payments Definition: Measurement
Ch. 2 International Flow of Funds Topics Balance of Payments International Trade Flows International Capital Flows Agencies that Facilitate International Flows Balance of Payments Definition: Measurement
The Case for Not Currency Hedging Foreign Equity Investments: A U.S. Investor s Perspective
 The Case for Not Currency Hedging Foreign Equity Investments: A U.S. Investor s Perspective April 14, 2015 by Catherine LeGraw of GMO EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Investors often ask about GMO s approach to currency
The Case for Not Currency Hedging Foreign Equity Investments: A U.S. Investor s Perspective April 14, 2015 by Catherine LeGraw of GMO EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Investors often ask about GMO s approach to currency
ANURAG GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS School of Business Management ( ) International Financial Management (A94003/F) TEACHING PLAN ( )
 ANURAG GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS School of Business Management (2014-16) International Financial Management (A94003/F) TEACHING PLAN (2016-17) Name of the Faculty: Ch. Siva Priya S.NO TOPIC NO. OF CLASSES
ANURAG GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS School of Business Management (2014-16) International Financial Management (A94003/F) TEACHING PLAN (2016-17) Name of the Faculty: Ch. Siva Priya S.NO TOPIC NO. OF CLASSES
Economy at Risk: The Growing U.S. Trade Deficit
 Economy at Risk: The Growing U.S. Trade Deficit Statement by Professor Robert A. Blecker Department of Economics American University Washington, DC 20016-8029 blecker@american.edu Presented at AFL-CIO/USBIC
Economy at Risk: The Growing U.S. Trade Deficit Statement by Professor Robert A. Blecker Department of Economics American University Washington, DC 20016-8029 blecker@american.edu Presented at AFL-CIO/USBIC
Unit 4 Study Guide: Macroeconomics & International Economics
 Name: Unit 4 Study Guide: Macroeconomics & International Economics Standards: SSEMA2 Explain the role and functions of the Federal Reserve System. b. Describe the organization of the Federal Reserve System
Name: Unit 4 Study Guide: Macroeconomics & International Economics Standards: SSEMA2 Explain the role and functions of the Federal Reserve System. b. Describe the organization of the Federal Reserve System
Chapter 2 Foreign Exchange Parity Relations
 Chapter 2 Foreign Exchange Parity Relations Note: In the sixth edition of Global Investments, the exchange rate quotation symbols differ from previous editions. We adopted the convention that the first
Chapter 2 Foreign Exchange Parity Relations Note: In the sixth edition of Global Investments, the exchange rate quotation symbols differ from previous editions. We adopted the convention that the first
How Is Global Trade Financed? (EA)
 How Is Global Trade Financed? (EA) For countries to trade goods and services, they must also trade their currencies. If you have ever visited a foreign country, such as Mexico, you know that you must exchange
How Is Global Trade Financed? (EA) For countries to trade goods and services, they must also trade their currencies. If you have ever visited a foreign country, such as Mexico, you know that you must exchange
ECON EOC Practice Test: Unit Four
 ECON EOC Practice Test: Unit Four 1) If the federal government spends more than it collects in revenue, then A) it is running a surplus. B) the inflation rate should decline. C) it is running a deficit.
ECON EOC Practice Test: Unit Four 1) If the federal government spends more than it collects in revenue, then A) it is running a surplus. B) the inflation rate should decline. C) it is running a deficit.
Types of Exposure. Forward Market Hedge. Transaction Exposure. Forward Market Hedge. Forward Market Hedge: an Example INTERNATIONAL FINANCE.
 Types of Exposure INTERNATIONAL FINANCE Chapter 8 Transaction exposure sensitivity of realized domestic currency values of the firm s contractual cash flows denominated in foreign currencies to unexpected
Types of Exposure INTERNATIONAL FINANCE Chapter 8 Transaction exposure sensitivity of realized domestic currency values of the firm s contractual cash flows denominated in foreign currencies to unexpected
29 Exchange Rates and International Capital Flows
 29 Exchange Rates and International Capital Flows Figure 29.1 Trade Around the World Is a trade deficit between the United States and the European Union good or bad for the U.S. economy? (Credit: modification
29 Exchange Rates and International Capital Flows Figure 29.1 Trade Around the World Is a trade deficit between the United States and the European Union good or bad for the U.S. economy? (Credit: modification
Lecture 13 International Trade: Economics 181 Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Multinational Corporations (MNCs)
 Lecture 13 International Trade: Economics 181 Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Multinational Corporations (MNCs) REMEMBER: Midterm NEXT TUESDAY. Office hours next week: Monday, 12 to 2 for Ann Harrison
Lecture 13 International Trade: Economics 181 Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Multinational Corporations (MNCs) REMEMBER: Midterm NEXT TUESDAY. Office hours next week: Monday, 12 to 2 for Ann Harrison
Closed vs. Open Economies
 Closed vs. Open Economies! A closed economy does not interact with other economies in the world.! An open economy interacts freely with other economies around the world. 1 Percent of GDP The U.S. Economy
Closed vs. Open Economies! A closed economy does not interact with other economies in the world.! An open economy interacts freely with other economies around the world. 1 Percent of GDP The U.S. Economy
Chapter 25 The Exchange Rate and the Balance of Payments The Foreign Exchange Market
 Chapter 25 The Exchange Rate and the Balance of Payments 25.1 The Foreign Exchange Market 1) Foreign currency is A) the market for foreign exchange. B) the price at which one currency exchanges for another
Chapter 25 The Exchange Rate and the Balance of Payments 25.1 The Foreign Exchange Market 1) Foreign currency is A) the market for foreign exchange. B) the price at which one currency exchanges for another
Role of Financial Markets and Institutions
 International Financial Management By Jeff Madura Solution Manual 11th Edition International Financial Management By Jeff Madura Solution Manual 11th Edition Test Bank. Completed download Solutions Manual
International Financial Management By Jeff Madura Solution Manual 11th Edition International Financial Management By Jeff Madura Solution Manual 11th Edition Test Bank. Completed download Solutions Manual
Chapter 8 Outline. Transaction exposure Should the Firm Hedge? Contractual hedge Risk Management in practice
 Chapter 8 Outline Transaction exposure Should the Firm Hedge? Contractual hedge Risk Management in practice 1 / 51 Transaction exposure Transaction exposure measures gains or losses that arise from the
Chapter 8 Outline Transaction exposure Should the Firm Hedge? Contractual hedge Risk Management in practice 1 / 51 Transaction exposure Transaction exposure measures gains or losses that arise from the
International Economics
 International Economics Unit 5 Pretest As we learn about International Economics, let s see what you already know. Remember do the best you can, but don t stress this assessment doesn t count toward your
International Economics Unit 5 Pretest As we learn about International Economics, let s see what you already know. Remember do the best you can, but don t stress this assessment doesn t count toward your
Econ 340. Recall Macro from Econ 102. Recall Macro from Econ 102. Recall Macro from Econ 102. Recall Macro from Econ 102
 Econ 34 Lecture 5 International Macroeconomics Outline: International Macroeconomics Recall Macro from Econ 2 Aggregate Supply and Demand Policies Effects ON the Exchange Expansion Interest Rate Depreciation
Econ 34 Lecture 5 International Macroeconomics Outline: International Macroeconomics Recall Macro from Econ 2 Aggregate Supply and Demand Policies Effects ON the Exchange Expansion Interest Rate Depreciation
Growth and Inflation Prospects and Monetary Policy
 Growth and Inflation Prospects and Monetary Policy 1. Growth and Inflation Prospects and Monetary Policy The Thai economy expanded by slightly less than the previous projection due to weaker-than-anticipated
Growth and Inflation Prospects and Monetary Policy 1. Growth and Inflation Prospects and Monetary Policy The Thai economy expanded by slightly less than the previous projection due to weaker-than-anticipated
Edexcel Economics A-level
 Edexcel Economics A-level Unit 4: The Global Economy Topic 2: Trade and the World Economy 2.4 Trade liberalisation Notes Types of trading blocs (regional trade agreements and bilateral trade agreements):
Edexcel Economics A-level Unit 4: The Global Economy Topic 2: Trade and the World Economy 2.4 Trade liberalisation Notes Types of trading blocs (regional trade agreements and bilateral trade agreements):
gement JEFF MADURA "Fldfida'J&lantic University .,. ;. O r> Ll.l K 1 i UNIVERSnAT LIECHTENSTEIN Blbllothett SOUTH-WESTERN CENGAGE Learning- " ^ si-
 f f >' ' '^11 ABRIDGED 10TH EDITION gement JEFF MADURA "Fldfida'J&lantic University Ll.l K 1 i.,. ;. O r> UNIVERSnAT LIECHTENSTEIN Blbllothett /, " ^ si- -A- SOUTH-WESTERN CENGAGE Learning- Australia Brazil
f f >' ' '^11 ABRIDGED 10TH EDITION gement JEFF MADURA "Fldfida'J&lantic University Ll.l K 1 i.,. ;. O r> UNIVERSnAT LIECHTENSTEIN Blbllothett /, " ^ si- -A- SOUTH-WESTERN CENGAGE Learning- Australia Brazil
18 INTERNATIONAL FINANCE* Chapter. Key Concepts
 Chapter 18 INTERNATIONAL FINANCE* Key Concepts Financing International Trade The balance of payments accounts measure international transactions. Current account records exports, imports, net interest,
Chapter 18 INTERNATIONAL FINANCE* Key Concepts Financing International Trade The balance of payments accounts measure international transactions. Current account records exports, imports, net interest,
The Foreign Exchange Market
 The Foreign Exchange Market Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The market in which foreign currencies are traded is known as the: A. stock
The Foreign Exchange Market Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The market in which foreign currencies are traded is known as the: A. stock
foreign, and hence it is where the prices of many currencies are set. The price of foreign money is
 Chapter 2: The BOP and the Foreign Exchange Market The foreign exchange market is the market where domestic money can be exchanged for foreign, and hence it is where the prices of many currencies are set.
Chapter 2: The BOP and the Foreign Exchange Market The foreign exchange market is the market where domestic money can be exchanged for foreign, and hence it is where the prices of many currencies are set.
Chapter 13 Exchange Rates, Business Cycles, and Macroeconomic Policy in the Open Economy
 Chapter 13 Exchange Rates, Business Cycles, and Macroeconomic Policy in the Open Economy 1 Goals of Chapter 13 Two primary aspects of interdependence between economies of different nations International
Chapter 13 Exchange Rates, Business Cycles, and Macroeconomic Policy in the Open Economy 1 Goals of Chapter 13 Two primary aspects of interdependence between economies of different nations International
How the Foreign Exchange Market Works
 OpenStax-CNX module: m48784 1 How the Foreign Exchange Market Works OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of
OpenStax-CNX module: m48784 1 How the Foreign Exchange Market Works OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of
Assignment 6. Deadline: July 29, 2005
 ECON 1010C Principles of Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Atkinson College York University Summer 2005 Assignment 6 Deadline: July 29, 2005 Part A Multiple-Choice Questions
ECON 1010C Principles of Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Atkinson College York University Summer 2005 Assignment 6 Deadline: July 29, 2005 Part A Multiple-Choice Questions
Appendix: Analysis of Exchange Rates Pursuant to the Act
 Appendix: Analysis of Exchange Rates Pursuant to the Act Introduction Although reaching judgments about whether countries manipulate the rate of exchange between their currency and the United States dollar
Appendix: Analysis of Exchange Rates Pursuant to the Act Introduction Although reaching judgments about whether countries manipulate the rate of exchange between their currency and the United States dollar
FINANCE REVIEW. Page 1 of 5
 Correlation: A perfect positive correlation means as X increases, Y increases at the same rate Y Corr =.0 X A perfect negative correlation means as X increases, Y decreases at the same rate Y Corr = -.0
Correlation: A perfect positive correlation means as X increases, Y increases at the same rate Y Corr =.0 X A perfect negative correlation means as X increases, Y decreases at the same rate Y Corr = -.0
Discussion in the Boardroom
 APPENDIX E Discussion in the Boardroom This exercise is intended to apply many of the key concepts presented in the text to broad issues that are discussed by managers who make financial decisions. It
APPENDIX E Discussion in the Boardroom This exercise is intended to apply many of the key concepts presented in the text to broad issues that are discussed by managers who make financial decisions. It
Management of Transaction Exposure
 INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Seventh Edition EUN / RESNICK Management of Transaction Exposure 8 Chapter Eight INTERNATIONAL Chapter Objective: FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT This chapter discusses various
INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Seventh Edition EUN / RESNICK Management of Transaction Exposure 8 Chapter Eight INTERNATIONAL Chapter Objective: FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT This chapter discusses various
TOPIC 9. International Economics
 TOPIC 9 International Economics 2 Goals of Topic 9 What is the exchange rate? NX back!! What is the link between the exchange rate and net exports? What is the trade deficit? How do different shocks affect
TOPIC 9 International Economics 2 Goals of Topic 9 What is the exchange rate? NX back!! What is the link between the exchange rate and net exports? What is the trade deficit? How do different shocks affect
Answers to Questions: Chapter 7
 Answers to Questions in Textbook 1 Answers to Questions: Chapter 7 1. Any international transaction that creates a payment of money to a U.S. resident generates a credit. Any international transaction
Answers to Questions in Textbook 1 Answers to Questions: Chapter 7 1. Any international transaction that creates a payment of money to a U.S. resident generates a credit. Any international transaction
Management of Transaction Exposure
 INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Seventh Edition EUN / RESNICK 8-0 Copyright 2015 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Management of Transaction Exposure 8 Chapter Eight INTERNATIONAL
INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Seventh Edition EUN / RESNICK 8-0 Copyright 2015 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Management of Transaction Exposure 8 Chapter Eight INTERNATIONAL
Management of Transaction Exposure
 INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Seventh Edition EUN / RESNICK 8-0 Copyright 2015 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Management of Transaction Exposure 8 Chapter Eight INTERNATIONAL
INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Seventh Edition EUN / RESNICK 8-0 Copyright 2015 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Management of Transaction Exposure 8 Chapter Eight INTERNATIONAL
14.05 Intermediate Applied Macroeconomics Problem Set 5
 14.05 Intermediate Applied Macroeconomics Problem Set 5 Distributed: November 15, 2005 Due: November 22, 2005 TA: Jose Tessada Frantisek Ricka 1. Rational exchange rate expectations and overshooting The
14.05 Intermediate Applied Macroeconomics Problem Set 5 Distributed: November 15, 2005 Due: November 22, 2005 TA: Jose Tessada Frantisek Ricka 1. Rational exchange rate expectations and overshooting The
Chapter 19 (8) International Monetary Systems: An Historical Overview
 Chapter 19 (8) International Monetary Systems: An Historical Overview Preview Goals of macroeconomic policies internal and external balance Gold standard era 1870 1914 International monetary system during
Chapter 19 (8) International Monetary Systems: An Historical Overview Preview Goals of macroeconomic policies internal and external balance Gold standard era 1870 1914 International monetary system during
Introduction to Economics. MACROECONOMICS Chapter 6 International Economics
 Introduction to Economics MACROECONOMICS Chapter 6 International Economics contents 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Theory of Comparative Advantage Gains from International Trade Trade Barriers Balance of Payments
Introduction to Economics MACROECONOMICS Chapter 6 International Economics contents 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Theory of Comparative Advantage Gains from International Trade Trade Barriers Balance of Payments
Government Intervention during the Asian Crisis
 Government Intervention during the Asian Crisis From 990 to 997, Asian countries achieved higher economic growth than any other countries. They were viewed as models for advances in technology and economic
Government Intervention during the Asian Crisis From 990 to 997, Asian countries achieved higher economic growth than any other countries. They were viewed as models for advances in technology and economic
To hedge or not to hedge? Evaluating currency exposure in global equity portfolios
 To hedge or not to hedge? Evaluating currency exposure in global equity portfolios Research brief January 2015 Falling home bias means that investors are increasing their allocations to foreign assets,
To hedge or not to hedge? Evaluating currency exposure in global equity portfolios Research brief January 2015 Falling home bias means that investors are increasing their allocations to foreign assets,
1 World Economy. Value of Finnish Forest Industry Exports Fell by Almost a Quarter in 2009
 1 World Economy The recovery in the world economy that began during 2009 has started to slow since spring 2010 as stocks are replenished and government stimulus packages are gradually brought to an end.
1 World Economy The recovery in the world economy that began during 2009 has started to slow since spring 2010 as stocks are replenished and government stimulus packages are gradually brought to an end.
Edexcel (A) Economics A-level
 Edexcel (A) Economics A-level Theme 4: A Global Perspective 4.1 International Economics 4.1.8 Exchange rates Notes Exchange rate systems The exchange rate of a currency is the weight of one currency relative
Edexcel (A) Economics A-level Theme 4: A Global Perspective 4.1 International Economics 4.1.8 Exchange rates Notes Exchange rate systems The exchange rate of a currency is the weight of one currency relative
Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets 6e (Mishkin) Chapter 1 Why Study Money, Banking, and Financial Markets?
 Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets 6e (Mishkin) Chapter 1 Why Study Money, Banking, and Financial Markets? Download full Test Bank for Economics of Money, Banking and Financial Markets
Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets 6e (Mishkin) Chapter 1 Why Study Money, Banking, and Financial Markets? Download full Test Bank for Economics of Money, Banking and Financial Markets
Edexcel (B) Economics A-level
 Edexcel (B) Economics A-level Theme 3: The Global Economy 3.1 Globalisation 3.1.5 Exchange rate changes Notes Impact of changes in exchange rates and the possible effects on: A reduction in the exchange
Edexcel (B) Economics A-level Theme 3: The Global Economy 3.1 Globalisation 3.1.5 Exchange rate changes Notes Impact of changes in exchange rates and the possible effects on: A reduction in the exchange
file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder (13)/CourseComp...
 file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder (13)/CourseComp... COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down
file:///c:/users/moha/desktop/mac8e/new folder (13)/CourseComp... COURSES > BA121 > CONTROL PANEL > POOL MANAGER > POOL CANVAS Add, modify, and remove questions. Select a question type from the Add drop-down
Emerging market central banks investment strategies: Tailwind for the euro?
 Economic Research Allianz Group Dresdner Bank Working Paper No.:38, 11.04.2005 Autor: Dr. R. Schäfer Emerging market central banks investment strategies: Tailwind for the euro? The euro has appreciated
Economic Research Allianz Group Dresdner Bank Working Paper No.:38, 11.04.2005 Autor: Dr. R. Schäfer Emerging market central banks investment strategies: Tailwind for the euro? The euro has appreciated
Introduction to Foreign Exchange Slides for International Finance (KOM Chapter 14)
 Slides for International Finance (KOM Chapter 14) American University 2011-09-01 Preview Introduction to Exchange Rates Basics exchange rate concepts Exchange rates and the cost of foreign goods The foreign
Slides for International Finance (KOM Chapter 14) American University 2011-09-01 Preview Introduction to Exchange Rates Basics exchange rate concepts Exchange rates and the cost of foreign goods The foreign
CIE Economics AS-level
 CIE Economics AS-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy a) Aggregate Demand (AD) and Aggregate Supply (AS) analysis Notes Determinants of AD: Aggregate demand is the total demand in the economy. It measures spending
CIE Economics AS-level Topic 4: The Macroeconomy a) Aggregate Demand (AD) and Aggregate Supply (AS) analysis Notes Determinants of AD: Aggregate demand is the total demand in the economy. It measures spending
Why I Worry About the Trade Deficit
 Why I Worry About the Trade Deficit by Ernest H. Preeg Senior Fellow, Hudson Institute Statement before the Trade Deficit Review Commission Washington, DC, September 9, 1999 There are four reasons why
Why I Worry About the Trade Deficit by Ernest H. Preeg Senior Fellow, Hudson Institute Statement before the Trade Deficit Review Commission Washington, DC, September 9, 1999 There are four reasons why
4.3.1 What are the causes and effects of globalisation?
 Economics Unit 4 Revision Guide 4.3.1 What are the causes and effects of globalisation? Definition of globalisation (from Peter Jay): The ability to produce any goods (or service) anywhere in the world,
Economics Unit 4 Revision Guide 4.3.1 What are the causes and effects of globalisation? Definition of globalisation (from Peter Jay): The ability to produce any goods (or service) anywhere in the world,
INTERNATIONAL FINANCE MBA 926
 INTERNATIONAL FINANCE MBA 926 1. Give a full definition of the market for foreign exchange. Answer: Broadly defined, the foreign exchange (FX) market encompasses the conversion of purchasing power from
INTERNATIONAL FINANCE MBA 926 1. Give a full definition of the market for foreign exchange. Answer: Broadly defined, the foreign exchange (FX) market encompasses the conversion of purchasing power from
The World s Reserve Currency A Gift and a Curse
 Meketa Investment Group Research Series Since World War II, the U.S. dollar has served as the world s reserve currency. This arrangement has played no small part in the dominance of the U.S. economy since
Meketa Investment Group Research Series Since World War II, the U.S. dollar has served as the world s reserve currency. This arrangement has played no small part in the dominance of the U.S. economy since
Chapter 17: Macroeconomics in an Open Economy
 Chapter 17: Macroeconomics in an Open Economy Yulei Luo SEF of HKU April 16, 2012 Learning Objectives 1. Explain how the balance of payments is calculated. 2. Explain how exchange rates are determined
Chapter 17: Macroeconomics in an Open Economy Yulei Luo SEF of HKU April 16, 2012 Learning Objectives 1. Explain how the balance of payments is calculated. 2. Explain how exchange rates are determined
University of Siegen
 University of Siegen Faculty of Economic Disciplines, Department of economics Univ. Prof. Dr. Jan Franke-Viebach Seminar Risk and Finance Summer Semester 2008 Topic 4: Hedging with currency futures Name
University of Siegen Faculty of Economic Disciplines, Department of economics Univ. Prof. Dr. Jan Franke-Viebach Seminar Risk and Finance Summer Semester 2008 Topic 4: Hedging with currency futures Name
Yen and Yuan RIETI, Tokyo
 Yen and Yuan RIETI, Tokyo November 2, 21 In the first half of his talk, Dr. Kwan, senior fellow at RIETI, argued that Asian currencies should be pegged to a currency basket, with the Japanese yen comprising
Yen and Yuan RIETI, Tokyo November 2, 21 In the first half of his talk, Dr. Kwan, senior fellow at RIETI, argued that Asian currencies should be pegged to a currency basket, with the Japanese yen comprising
Edexcel (B) Economics A-level
 Edexcel (B) Economics A-level Theme 2: The Wider Economic Environment 2.5 The Economic Cycle 2.5.2 Circular flow of income, expenditure and output Notes The circular flow of income Firms and households
Edexcel (B) Economics A-level Theme 2: The Wider Economic Environment 2.5 The Economic Cycle 2.5.2 Circular flow of income, expenditure and output Notes The circular flow of income Firms and households
$57.2bn. Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way. Economic and Financial Analysis
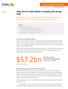 Economic and Financial Analysis 6 April 2018 Global Economics 6 April 2018 Article Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way Macroeconomic policy, not just trade barriers, affects the trade deficit.
Economic and Financial Analysis 6 April 2018 Global Economics 6 April 2018 Article Why the US trade deficit is heading the wrong way Macroeconomic policy, not just trade barriers, affects the trade deficit.
Comments on The International Price System, by Gita Gopinath. Charles Engel University of Wisconsin
 Comments on The International Price System, by Gita Gopinath Charles Engel University of Wisconsin I thank the organizers of this conference for inviting me to discuss this very interesting paper by Gita
Comments on The International Price System, by Gita Gopinath Charles Engel University of Wisconsin I thank the organizers of this conference for inviting me to discuss this very interesting paper by Gita
CASE FAIR OSTER. International Trade, Comparative Advantage, and Protectionism. Trade Surpluses and Deficits
 PEARSON PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N CASE FAIR OSTER Prepared by: Fernando Quijano w/shelly Tefft 2of 49 PART IV THE WORLD ECONOMY International Trade, Comparative Advantage,
PEARSON PRINCIPLES OF MICROECONOMICS E L E V E N T H E D I T I O N CASE FAIR OSTER Prepared by: Fernando Quijano w/shelly Tefft 2of 49 PART IV THE WORLD ECONOMY International Trade, Comparative Advantage,
CHAPTER 31 INTERNATIONAL CORPORATE FINANCE
 Corporate Finance 11 th edition Solutions Manual Ross, Westerfield, Jaffe, and Jordan Completed download Solutions Manual, Answers, Instructors Resource Manual, Case Solutions, Excel Solutions are included:
Corporate Finance 11 th edition Solutions Manual Ross, Westerfield, Jaffe, and Jordan Completed download Solutions Manual, Answers, Instructors Resource Manual, Case Solutions, Excel Solutions are included:
ANALYSIS. Trade & Balance of Payments. Suppose the Belgian government decreases a tariff on all the automobiles it imports from abroad.
 ANALYSIS Trade & Balance of Payments Suppose the Belgian government decreases a tariff on all the automobiles it imports from abroad. A) Will each of the following groups benefit from this action? Explain.
ANALYSIS Trade & Balance of Payments Suppose the Belgian government decreases a tariff on all the automobiles it imports from abroad. A) Will each of the following groups benefit from this action? Explain.
