The International Financial Architecture
|
|
|
- Lorin Jacobs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUNDAY APRIL 27, 2008 The International Financial Architecture Development, Global Economics Jeffrey A. Frankel JUNE 1999 The G-7 and the rest of the international financial policymaking community has, over the last eight months, made a variety of reforms to try to reduce the frequency and severity of international financial crises. The reforms include steps to improve transparency, strengthen financial systems, and involve the private sector more fully in rescue packages. These measures are worthwhile, regardless of whether critics are right that they are too small to merit the label new financial architecture. However, innovations in several areas would be so fundamental as to merit unquestionably that appellation. One is the question of liberalization of international capital flows, and how rapid it should be. Another is the question of exchange rate regimes, and how flexible they should be. No single currency regime is right for all countries or at all times. The choice of exchange-rate arrangement should depend on the particular circumstances facing the country in question. This proposition may sound obvious. But it needs to be stated. Recent experience has many lessons to offer. There is a danger of over-generalizing, however--of applying a given lesson to all countries regardless of circumstances. Five such propositions are currently heard. Five Common Propositions Regarding Exchange-Rate Regimes The first proposition is that countries should generally move to increased exchange-rate flexibility. We hear this particularly from policymakers who have tried over the last two years to help fight speculative pressures against exchange-rate targets in Thailand, Korea, Indonesia, Russia, and Brazil, where the attempts ended in costly crashes. When exchange rates float, there is no target that needs defending. A second (diametrically opposed) proposition is that all countries should move toward enhanced institutional commitment to fixing the exchange rate. After all, none of those crisis-influenced currencies had been literally or formally fixed to the dollar. Enthusiasts point to currency boards that have successfully weathered the storms in Hong Kong and Argentina. Some even go further and suggest full official dollarization. They take encouragement from the euro-eleven's successful move to a common currency on January 1, 1999.
2 A third proposition is that countries in general must move increasingly in either direction on exchange-rate regimes--free-floating or firm-fixing--but that the intermediate regimes such as target zones are no longer tenable (See Figure 1 for definitions). This proposition, too, is in danger of being applied too broadly. Figure 1: Definitions of Nine Major Exchange Rate Regimes, Ranged Along the Continuum from the Most Flexible to the Strongest Fixed-Rate Commitment FLEXIBLE CORNER 1. Free floating--the absence of regular intervention in the foreign exchange market 2. Managed float--the absence of a specific target for the exchange rate INTERMEDIATE REGIMES 3. Target zone, or band--a margin of fluctuation around some central rate 4. Basket peg--fixing not to a single foreign currency but to a weighted average of other currencies 5. Crawling peg--a preannounced policy of devaluing a bit each week 6. Adjustable peg--fixing the exchange rate, but without any open-ended commitment to resist devaluation or revaluation in the presence of a large balance of payments deficit or surplus FIXED CORNER 7. Truly fixed peg--fixing, committing to buy or sell however much foreign currency is necessary at a given exchange rate, with a firm and lasting intention of maintaining the policy 8. Currency board--three defining characteristics: fixing not just by policy but by law, backing increases in the monetary base one-for-one with foreign exchange reserves, and allowing balance of payments deficits to tighten monetary policy and thereby adjust spending automatically 9. Monetary union--the adoption of a foreign currency as legal tender. This includes the special case of official dollarization The fourth proposition is the prediction that the world is breaking up into a few big currency blocs as European countries give up their currencies for the euro and Western Hemisphere countries give up theirs for the dollar. (The perceived trends in the first two blocs have recently become more plausible in light of the success of the European Monetary Union (EMU) and talk in Latin America of dollarization. Not so the yen bloc, however.) The final proposition is the opposite of the fourth. Some, particularly among European leaders, believe that the most important reform is to stabilize the cross-rates between the dollar, euro, and yen and let
3 smaller countries do what they will, rather than stabilizing the exchange rates within each bloc and letting the three major currencies continue to float freely. Some Countries Should Fix Firmly What are the characteristics that make a country more suited for fixed rather than flexible rates? The classic list includes: small size, openness to trade, high labor mobility, availability of a fiscal mechanism to cushion downturns, and a high correlation of the local business cycle with that of the country to which a currency peg, or fix, is contemplated. These attributes are well known among economists as criteria for political units to join in an optimum currency area (OCA). Countries that have these characteristics are likely to see big benefits from exchange-rate stability, and are also less likely to need monetary independence in the first place. Easy examples are Panama (dollar) and Luxembourg (euro). The classic OCA criteria list needs to be updated, particularly if we are talking about prerequisites for the most rigid institutional arrangements--a currency board, full dollarization or a monetary union. Argentina, for example, is not an especially small open economy. But it has had a currency board since 1991 that has been largely successful in the face of severe challenges. (The government announced in January that it was considering abandoning the peso altogether in favor of official adoption of the U.S. dollar as legal tender.) First and foremost to be added to the list of criteria for a rigid peg is a strong need to import monetary stability due to either a history of hyperinflation, an absence of credible public institutions, or unusually large exposure to nervous investors. The willingness of Argentina to give up monetary independence derives from its past history of hyperinflation and a domestic political consensus that the experience must not be repeated. It is also useful for a fixed-exchange-rate candidate to have extensive integration with one particular large trading partner or currency area, or a craving for future integration of this sort. The appropriateness of currency boards in Estonia, Lithuania, and Bulgaria, for example, derives from their desire for integration with the European Union. The next requirements are access to an adequate level of reserves, and a strong, well-supervised and regulated financial system. Otherwise, the country might simply convert currency-crisis vulnerability into banking-crisis vulnerability. Finally, the existence of the rule of law is a necessary condition for a currency board, though not necessarily for dollarization. Otherwise, putting the currency peg in the law accomplishes little. Proclaiming a currency board does not, as is sometimes asserted, automatically guarantee the credibility of a fixed-rate peg (see Figure 1); a currency board is not credibility in a bottle. It is unlikely to be successful unless accompanied by solid fundamentals. The Dollar and Euro Should Float Freely Fixing is not the right course for all countries. To begin with the opposite extreme, the United States meets the criterion for an independent, free-floating currency. We have a large economy. The states of the union are more highly integrated with each other than they are with the rest of the world. There is more movement of trade, labor, and fiscal transfers--and a higher correlation of the business cycle--within
4 our borders than across our borders. Fluctuations in the exchange rate are simply not as important to us as they are to most countries. We do not want to subordinate our monetary policy to conditions abroad. Thus, the advantages of floating overwhelm the advantages of fixing. This does not mean that the U.S. authorities should never intervene in the foreign-exchange market at all. An occasional purchase or sale of foreign exchange is appropriate, if necessary to maintain in the marketplace a sense of two-way risk (rates can go up as easily as down), or to nudge the dollar exchange rate on those few occasions when it is far out of line. Purely parenthetically, the question has arisen of what U.S. exchange rate policy might be like under the newly nominated Secretary of the Treasury. One cannot resist putting forward the alliterative theory of the dollar (Figure 2). Over the last twenty-five years, the secretaries whose names begin with the letter "B" have been perceived as bashing the dollar, as it depreciated during their terms, whereas the dollar was revived under secretaries whose names begin with "R." In the mid-1970s, it remained steady under the last secretary whose name began with "S." This is probably the appropriate characterization for the current outlook under Lawrence Summers, as well. Figure 2: Trend of Dollar Exchange Rates by Term of Treasury Secretary, Percent Per Annum Treasury Secretary Term G10 Effective Exchange Rate William E. Simon May 8, January 20, W. Michael Blumenthal January 23, August 4, G. William Miller August 7, January 20, Donald T. Regan January 22, February 1, James A. Baker, III February 4, August 17, Nicholas F. Brady September 15, January 17, Lloyd M. Bentsen January 20, December 22, Robert E. Rubin January 11, December 31, Source: Federal Reserve Board (1999) and U.S. Department of Treasury (1999). What of the new EMU? The eleven members do not satisfy the classic criteria for an OCA as well as the fifty American states do. And still less do the other four members of the European Union who have not yet decided whether to join. Labor mobility, income correlations, and federal fiscal cushions are all lower than
5 within the United States. Nevertheless, trade integration and labor mobility within Europe are increasing over time, and as they do, the correlation of national business cycles can be expected to increase as well. Thus, European countries will, with the passage of time, come increasingly to satisfy the criteria for a common currency. But the theory of the optimum currency area suggests that the euro, dollar and yen should continue in the future to float freely against each other. Are Intermediate Regimes No Longer Feasible? Most countries are somewhere in between the big United States and little Luxembourg. Until recently, many experts believed that countries intermediate with respect to size, openness, and the other optimum currency area criteria were probably suited to intermediate exchange-rate regimes. However, suddenly the view has become common that such regimes are not sustainable in a world of large-scale financial flows and, therefore, countries are being pushed to the corners of either firm-fixing or free-floating. What is the logic behind the proposition that countries must choose between firm-fixing and free-floating? At first glance, it appears to be a corollary to the principle of the impossible trinity. That principle says that a country must give up one of three goals: exchange-rate stability, monetary independence, or financialmarket integration. It cannot have all three simultaneously (Figure 3). One can attain any pair of attributes--the first two at the apex marked capital controls, the second two at the point marked monetary union, or the other two at the point marked pure float. But one cannot be on all three sides simultaneously. The general trend of financial integration has pushed most countries toward the lower part of the graph. If one is at the bottom leg of the triangle, the choice is narrowed down to a simple decision regarding the degree of exchange-rate flexibility. But even under perfect capital mobility, there is nothing to prevent the country from choosing an intermediate solution between floating and monetary union. Whence, then, the hypothesis of the vanishing intermediate regime? Recent history makes it understandable that some would flee the soft middle ground of the intermediate regimes and seek the
6 bedrock of the corners. Most of the intermediate regimes have been tried, and have failed, often spectacularly so. Contrary to claims that currencies in Mexico, Thailand, Indonesia, Korea, Russia, or Brazil were formally pegged to the dollar when their recent crises hit, they actually were following varieties of bands, baskets, and crawling pegs (See Figure 1 for definitions). Perhaps when international investors are lacking in confidence and risk-tolerance--the conditions that have characterized emerging markets from 1997 to governments can reclaim confidence only by proclaiming policies that are so simple and so transparent that investors can verify instantly that the government is, in fact, following them. Market participants can verify the announcement of a simple dollar peg simply by checking if today's exchange rate differs from yesterday's. Alternatively, it may be that the search for a single regime that will eliminate currency speculation as an issue is doomed to fail (without capital flow restrictions). The rejection of the middle ground is then explained simply as a rejection of where most countries have been, with no reasonable expectation that the sanctuaries of monetary union or free-floating will, in fact, be any better. Therefore, a blanket recommendation to avoid the middle regimes in favor of firm-fixing or free-floating would not be appropriate. When Should Capital Flows Be Restricted? As noted, a country that has fully opened its financial markets cannot have both a fixed exchange rate and an independent monetary policy. If the exchange rate is fixed, then such a country must accept the interest rate that it is given by the world financial market. But a country with restrictions on the crossborder movement of capital can set both the exchange rate and the interest rate, without fearing a tidal wave of capital flows. One cannot help noticing that China, with its still heavily controlled capital account, has been able to withstand the recent turmoil in emerging markets to a better degree than Hong Kong, even though the latter has far sounder macroeconomic and structural policies. A variety of measures to slow international capital flows are possible. The efficacy of restrictions on inflows is likely to be greater than controls on outflows, in part because it is easier to scare capital off than to keep it in against its will. Moreover, restrictions may have a useful role to play as a temporary measure when a country faces a large surge of inflows. After several years of controls, policymakers may have a better idea whether their country is the next tiger, justifying the inflows, or merely the subject of a speculative bubble. Statistical evidence suggests that the composition of inflow is a significant leading indicator of the probability of currency crashes occurring. The higher the reliance on foreign direct investment, the lower the probability of crisis. The higher the reliance on foreign-currency borrowing that is short term and/or handled through banks, the higher the probability of crisis. This conclusion lends support to proposals for restrictions that would seek to change the composition of capital inflows, rather than changing the total magnitude. Penalties on short-term inflows might shift the composition toward longer maturities. Restrictions in Chile and Colombia appear to have succeeded in changing the composition of the capital inflow in this way.
7 One promising possibility is the idea of placing some penalty on short-term bank borrowing from abroad in foreign currency, perhaps in the form of requiring a non-interest-earning deposit with the central bank. The application of higher reserve requirements than are placed on other forms of bank borrowing need not be inconsistent with the pursuit of properly timed liberalization of the overall capital account. Rather, it would fall well within the kind of enhanced prudential banking regulation that the United States and the International Monetary Fund have for some time urged on developing countries, and for which the need has become increasingly obvious in the wake of the Asian crisis. Conclusion The overarching lesson regarding restrictions on capital flows is analogous to the lesson regarding exchange-rate regimes: there is no single answer that suits all countries. Circumstances are critical. As countries approach the level of economic development attained by the industrialized countries, they should evolve domestic financial systems that are correspondingly well-developed, and should achieve full integration into the world financial system. In the meantime, certain well-targeted inflow restrictions might be appropriate for some countries, particularly at certain stages of the boom-bust cycle. In the case of exchange-rate regimes, other country attributes are relevant. Arrangements to fix exchange rates make the most sense for small open economies, or those that have a desperate need to import monetary and financial stability. Larger countries, like the United States, the European Union, and Japan, should float their currencies. Some countries that are intermediate in size and openness should continue to adopt intermediate regimes. While the dollar and the euro will be the two important international currencies in the coming decade, forecasts that most countries in the Western Hemisphere may or should give up their currencies in favor of the dollar, or those in the Eastern Hemisphere in favor of the euro or some other currency, are greatly exaggerated. Admittedly, however, emerging-market countries face problems that industrialized countries do not. Heightened financial integration means that finicky global investors must be satisfied, and, in some cases, this increasingly requires the kind of transparency or verifiability that is afforded only by the two corner solutions of firm-fixing or free-floating.
Lecture 20: Exchange Rate Regimes. Prof.J.Frankel
 Lecture 20: Exchange Rate Regimes What exchange rate regimes do countries choose? 1. Classification of exchange rate regimes What regimes should countries choose? 2. Advantages of fixed rates 3. Advantages
Lecture 20: Exchange Rate Regimes What exchange rate regimes do countries choose? 1. Classification of exchange rate regimes What regimes should countries choose? 2. Advantages of fixed rates 3. Advantages
Macro for SCS Nov. 29, International Trade & Finance
 Macro for SCS Nov. 29, 2017 International Trade & Finance The Gains from Trade Do you believe in magic The Gains from Trade Leave the England-Portugal rivalry for the soccer field Criticism of the free
Macro for SCS Nov. 29, 2017 International Trade & Finance The Gains from Trade Do you believe in magic The Gains from Trade Leave the England-Portugal rivalry for the soccer field Criticism of the free
Exchange Rate Regimes
 Exchange Rate Regimes Lecture 2 LIUC 2011 1 How many exchange rate regimes do we have? Hard pegs or no legal tender (23 countries or %12): No separate legal tender (10 countries) The country adopts a foreign
Exchange Rate Regimes Lecture 2 LIUC 2011 1 How many exchange rate regimes do we have? Hard pegs or no legal tender (23 countries or %12): No separate legal tender (10 countries) The country adopts a foreign
Figure: EUR-USD Exchange Rate
 Figure: EUR-USD Exchange Rate SuSe 2013 1 Monetary Policy and EMU: Open Economy Setting Figure: EUR-USD Exchange Rate SuSe 2013 2 Monetary Policy and EMU: Open Economy Setting Figure: Indirect Quotation
Figure: EUR-USD Exchange Rate SuSe 2013 1 Monetary Policy and EMU: Open Economy Setting Figure: EUR-USD Exchange Rate SuSe 2013 2 Monetary Policy and EMU: Open Economy Setting Figure: Indirect Quotation
Ten Lessons Learned from the Korean Crisis Center for International Development, 11/19/99. Jeffrey A. Frankel, Harpel Professor, Harvard University
 Ten Lessons Learned from the Korean Crisis Center for International Development, 11/19/99 Jeffrey A. Frankel, Harpel Professor, Harvard University The crisis has now passed in Korea. The excessive optimism
Ten Lessons Learned from the Korean Crisis Center for International Development, 11/19/99 Jeffrey A. Frankel, Harpel Professor, Harvard University The crisis has now passed in Korea. The excessive optimism
East Asia Crisis of Econ October 8, Team 5 Bryan Darch Svend Egholm Paramdeep Singh Sarah Zullo
 East Asia Crisis of 1997 Econ 7920 October 8, 2008 Team 5 Bryan Darch Svend Egholm Paramdeep Singh Sarah Zullo The East Asian currency crisis of 1997 caused severe distress for the countries of East Asia
East Asia Crisis of 1997 Econ 7920 October 8, 2008 Team 5 Bryan Darch Svend Egholm Paramdeep Singh Sarah Zullo The East Asian currency crisis of 1997 caused severe distress for the countries of East Asia
483 Subject Index. Global Depositiory Receipts, 250 Grassman s law, 148, 160
 Subject Index Adjustabonos, 401-3 Agency for International Development, 100 American depository receipts (ADRs): considered as foreign securities, 250; traded on over-the-counter market, 245 Arbitrage:
Subject Index Adjustabonos, 401-3 Agency for International Development, 100 American depository receipts (ADRs): considered as foreign securities, 250; traded on over-the-counter market, 245 Arbitrage:
Fix or float? Jan 28th 1999 From The Economist print edition
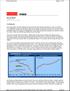 Page 1 of 5 Fix or float? Jan 28th 1999 From The Economist print edition It all depends AT A casual glance, the IMF s attitude towards exchange rates seems extraordinarily erratic. In 1997 the Fund urged
Page 1 of 5 Fix or float? Jan 28th 1999 From The Economist print edition It all depends AT A casual glance, the IMF s attitude towards exchange rates seems extraordinarily erratic. In 1997 the Fund urged
Prepared by Iordanis Petsas To Accompany. by Paul R. Krugman and Maurice Obstfeld
 Chapter 22 Developing Countries: Growth, Crisis, and Reform Prepared by Iordanis Petsas To Accompany International Economics: Theory and Policy, Sixth Edition by Paul R. Krugman and Maurice Obstfeld Chapter
Chapter 22 Developing Countries: Growth, Crisis, and Reform Prepared by Iordanis Petsas To Accompany International Economics: Theory and Policy, Sixth Edition by Paul R. Krugman and Maurice Obstfeld Chapter
Exchange Rate Regimes Revised: January 13, 2012
 The Global Economy Class Notes Exchange Rate Regimes Revised: January 13, 2012 The term exchange rate regimes refers to the various arrangements governments around the world make about international transactions.
The Global Economy Class Notes Exchange Rate Regimes Revised: January 13, 2012 The term exchange rate regimes refers to the various arrangements governments around the world make about international transactions.
9 Right Prices for Interest and Exchange Rates
 9 Right Prices for Interest and Exchange Rates Roberto Frenkel R icardo Ffrench-Davis presents a critical appraisal of the reforms of the Washington Consensus. He criticises the reforms from two perspectives.
9 Right Prices for Interest and Exchange Rates Roberto Frenkel R icardo Ffrench-Davis presents a critical appraisal of the reforms of the Washington Consensus. He criticises the reforms from two perspectives.
Chapter 13 The Open Economy Revisited: the Mundell-Fleming Model and the Exchange-Rate Regime
 Chapter 13 The Open Economy Revisited: the Mundell-Fleming Model and the Exchange-Rate Regime Modified by Yun Wang Eco 3203 Intermediate Macroeconomics Florida International University Summer 2017 2016
Chapter 13 The Open Economy Revisited: the Mundell-Fleming Model and the Exchange-Rate Regime Modified by Yun Wang Eco 3203 Intermediate Macroeconomics Florida International University Summer 2017 2016
19.2 Exchange Rates in the Long Run Introduction 1/24/2013. Exchange Rates and International Finance. The Nominal Exchange Rate
 Chapter 19 Exchange Rates and International Finance By Charles I. Jones International trade of goods and services exceeds 20 percent of GDP in most countries. Media Slides Created By Dave Brown Penn State
Chapter 19 Exchange Rates and International Finance By Charles I. Jones International trade of goods and services exceeds 20 percent of GDP in most countries. Media Slides Created By Dave Brown Penn State
Exchange Rate Regimes and Monetary Policy: Options for China and East Asia
 Exchange Rate Regimes and Monetary Policy: Options for China and East Asia Takatoshi Ito, University of Tokyo and RIETI, and Eiji Ogawa, Hitotsubashi University, and RIETI 3/19/2005 RIETI-BIS Conference
Exchange Rate Regimes and Monetary Policy: Options for China and East Asia Takatoshi Ito, University of Tokyo and RIETI, and Eiji Ogawa, Hitotsubashi University, and RIETI 3/19/2005 RIETI-BIS Conference
The Open Economy Revisited: the Exchange-Rate Regime
 C H A P T E R 12 : the Mundell-Fleming Model and the Exchange-Rate Regime MACROECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved In
C H A P T E R 12 : the Mundell-Fleming Model and the Exchange-Rate Regime MACROECONOMICS SIXTH EDITION N. GREGORY MANKIW PowerPoint Slides by Ron Cronovich 2008 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved In
Lecture 6: Intermediate macroeconomics, autumn Lars Calmfors
 Lecture 6: Intermediate macroeconomics, autumn 2009 Lars Calmfors 1 Topics Systems of fixed exchange rates Interest rate parity under a fixed exchange rate Stabilisation policy under a fixed exchange rate
Lecture 6: Intermediate macroeconomics, autumn 2009 Lars Calmfors 1 Topics Systems of fixed exchange rates Interest rate parity under a fixed exchange rate Stabilisation policy under a fixed exchange rate
Governments and Exchange Rates
 Governments and Exchange Rates Exchange Rate Behavior Existing spot exchange rate covered interest arbitrage locational arbitrage triangular arbitrage Existing spot exchange rates at other locations Existing
Governments and Exchange Rates Exchange Rate Behavior Existing spot exchange rate covered interest arbitrage locational arbitrage triangular arbitrage Existing spot exchange rates at other locations Existing
The Role of Asian Currencies in the International Monetary System
 The Role of Asian Currencies in the International Monetary System Masahiro Kawai Asian Development Bank Institute The Global Monetary and Financial System and Its Governance Tokyo Club Foundation for Global
The Role of Asian Currencies in the International Monetary System Masahiro Kawai Asian Development Bank Institute The Global Monetary and Financial System and Its Governance Tokyo Club Foundation for Global
MACROECONOMICS. The Open Economy Revisited: the Mundell-Fleming Model and the Exchange-Rate Regime MANKIW N. GREGORY
 C H A P T E R 12 The Open Economy Revisited: the Mundell-Fleming Model and the Exchange-Rate Regime MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2007 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint
C H A P T E R 12 The Open Economy Revisited: the Mundell-Fleming Model and the Exchange-Rate Regime MACROECONOMICS N. GREGORY MANKIW 2007 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved SIXTH EDITION PowerPoint
Outlook for the Chilean Economy
 Outlook for the Chilean Economy Jorge Marshall, Vice-President of the Board, Central Bank of Chile. Address to the Fifth Annual Latin American Banking Conference, Salomon Smith Barney, New York, March
Outlook for the Chilean Economy Jorge Marshall, Vice-President of the Board, Central Bank of Chile. Address to the Fifth Annual Latin American Banking Conference, Salomon Smith Barney, New York, March
Open Economy AS/AD: Applications
 Open Economy AS/AD: Applications Econ 309 Martin Ellison UBC Agenda and References Trilemma Jones, chapter 20, section 7 Euro crisis Jones, chapter 20, section 8 Global imbalances Jones, chapter 29, section
Open Economy AS/AD: Applications Econ 309 Martin Ellison UBC Agenda and References Trilemma Jones, chapter 20, section 7 Euro crisis Jones, chapter 20, section 8 Global imbalances Jones, chapter 29, section
Money and Exchange rates
 Macroeconomic policy Class Notes Money and Exchange rates Revised: December 13, 2011 Latest version available at www.fperri.net/teaching/macropolicyf11.htm So far we have learned that monetary policy can
Macroeconomic policy Class Notes Money and Exchange rates Revised: December 13, 2011 Latest version available at www.fperri.net/teaching/macropolicyf11.htm So far we have learned that monetary policy can
Ian J Macfarlane: Payment imbalances
 Ian J Macfarlane: Payment imbalances Presentation by Mr Ian J Macfarlane, Governor of the Reserve Bank of Australia, to the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing, 12 May 2005. * * * My talk today
Ian J Macfarlane: Payment imbalances Presentation by Mr Ian J Macfarlane, Governor of the Reserve Bank of Australia, to the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Beijing, 12 May 2005. * * * My talk today
Study Questions (with Answers) Lecture 16 Fixed Versus Floating Exchange Rates
 Study Questions (with Answers) Page 1 of 5 (6) Part 1: Multiple Choice Select the best answer of those given. Study Questions (with Answers) Lecture 16 Fixed Versus Floating Exchange Rates 1. Freely floating
Study Questions (with Answers) Page 1 of 5 (6) Part 1: Multiple Choice Select the best answer of those given. Study Questions (with Answers) Lecture 16 Fixed Versus Floating Exchange Rates 1. Freely floating
POLICY BRIEF. Resurgent Capital Flows to Developing Countries: Policies to Improve Their Impact
 J u n e 2 0 1 3 n u m b e r 1 0 Resurgent Capital Flows to Developing Countries: Policies to Improve Their Impact James A. Hanson* Overview Some developing countries have reinstated controls on capital
J u n e 2 0 1 3 n u m b e r 1 0 Resurgent Capital Flows to Developing Countries: Policies to Improve Their Impact James A. Hanson* Overview Some developing countries have reinstated controls on capital
Chapter 6. Government Influence on Exchange Rates. Lecture Outline
 Chapter 6 Government Influence on Exchange Rates Lecture Outline Exchange Rate Systems Fixed Exchange Rate System Freely Floating Exchange Rate System Managed Float Exchange Rate System Pegged Exchange
Chapter 6 Government Influence on Exchange Rates Lecture Outline Exchange Rate Systems Fixed Exchange Rate System Freely Floating Exchange Rate System Managed Float Exchange Rate System Pegged Exchange
Panel on. Policymaking in a Global Context. Remarks by. Robert T. Parry. President and Chief Executive Officer Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco
 Panel on Policymaking in a Global Context Remarks by Robert T. Parry President and Chief Executive Officer Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Delivered at the conference on Crises, Contagion, and Coordination:
Panel on Policymaking in a Global Context Remarks by Robert T. Parry President and Chief Executive Officer Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Delivered at the conference on Crises, Contagion, and Coordination:
that each of you in the audience is finding it to be well worth your time.
 THE FEDERAL RESERVE'S PERSPECTIVE ON FOREIGN BANK REGULATION Remarks by Robert P. Forrestal President and Chief Executive Officer Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Conference
THE FEDERAL RESERVE'S PERSPECTIVE ON FOREIGN BANK REGULATION Remarks by Robert P. Forrestal President and Chief Executive Officer Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Conference
Week 1. Currency Systems and Crises
 Week 1 Currency Systems and Crises Definition An exchange rate is the amount of currency that one needs in order to buy one unit of another currency, or the amount of currency that one receive when selling
Week 1 Currency Systems and Crises Definition An exchange rate is the amount of currency that one needs in order to buy one unit of another currency, or the amount of currency that one receive when selling
Suggested answers to Problem Set 5
 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS SPRING 2006 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY ECONOMICS 182 Suggested answers to Problem Set 5 Question 1 The United States begins at a point like 0 after 1985, where it is in
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS SPRING 2006 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY ECONOMICS 182 Suggested answers to Problem Set 5 Question 1 The United States begins at a point like 0 after 1985, where it is in
UC Berkeley Fall Final examination SOLUTION SHEET
 Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas Econ182 Department of Economics International Monetary Economics UC Berkeley Fall 2004 Final examination SOLUTION SHEET WRITE YOUR ANSWERS TO QUESTION 1 ON PAGES 2-5. 1. [30 points,
Pierre-Olivier Gourinchas Econ182 Department of Economics International Monetary Economics UC Berkeley Fall 2004 Final examination SOLUTION SHEET WRITE YOUR ANSWERS TO QUESTION 1 ON PAGES 2-5. 1. [30 points,
3. If the price of a British pound increases from $1.50 per pound to $1.80 per pound, we say that:
 STUDY GUIDE FINAL ECO41 FALL 2013 UDAYAN ROY Ch 13 National Income Accounting See the questions in Homework 7 and Homework 8. CHAPTER 14 Exchange Rates and Interest Parity 1. How many dollars would it
STUDY GUIDE FINAL ECO41 FALL 2013 UDAYAN ROY Ch 13 National Income Accounting See the questions in Homework 7 and Homework 8. CHAPTER 14 Exchange Rates and Interest Parity 1. How many dollars would it
Government Intervention during the Asian Crisis
 Government Intervention during the Asian Crisis From 990 to 997, Asian countries achieved higher economic growth than any other countries. They were viewed as models for advances in technology and economic
Government Intervention during the Asian Crisis From 990 to 997, Asian countries achieved higher economic growth than any other countries. They were viewed as models for advances in technology and economic
Global Imbalances and Latin America: A Comment on Eichengreen and Park
 3 Global Imbalances and Latin America: A Comment on Eichengreen and Park Barbara Stallings I n Global Imbalances and Emerging Markets, Barry Eichengreen and Yung Chul Park make a number of important contributions
3 Global Imbalances and Latin America: A Comment on Eichengreen and Park Barbara Stallings I n Global Imbalances and Emerging Markets, Barry Eichengreen and Yung Chul Park make a number of important contributions
Presentation. The Boom in Capital Flows and Financial Vulnerability in Asia
 High-level Regional Policy Dialogue on "Asia-Pacific economies after the global financial crisis: Lessons learnt, challenges for building resilience, and issues for global reform" 6-8 September 2011, Manila,
High-level Regional Policy Dialogue on "Asia-Pacific economies after the global financial crisis: Lessons learnt, challenges for building resilience, and issues for global reform" 6-8 September 2011, Manila,
These questions may help you prepare for the upcoming final test at 8:00 am on Wednesday, December 17.
 PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON CHAPTER 20 ECO41 FALL 2014 UDAYAN ROY These questions may help you prepare for the upcoming final test at 8:00 am on Wednesday, December 17. CHAPTER 20 Optimum Currency Areas and
PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON CHAPTER 20 ECO41 FALL 2014 UDAYAN ROY These questions may help you prepare for the upcoming final test at 8:00 am on Wednesday, December 17. CHAPTER 20 Optimum Currency Areas and
The Mundell-Fleming model
 The Mundell-Fleming model 2013 General short run macroeconomic equilibrium Income influences demand for money Goods Market Money Market Interest rates affect aggregate demand in the open the economy Income
The Mundell-Fleming model 2013 General short run macroeconomic equilibrium Income influences demand for money Goods Market Money Market Interest rates affect aggregate demand in the open the economy Income
: Monetary Economics and the European Union. Lecture 8. Instructor: Prof Robert Hill. The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II
 320.326: Monetary Economics and the European Union Lecture 8 Instructor: Prof Robert Hill The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II De Grauwe Chapters 3, 4, 5 1 1. Countries in Trouble in the Eurozone
320.326: Monetary Economics and the European Union Lecture 8 Instructor: Prof Robert Hill The Costs and Benefits of Monetary Union II De Grauwe Chapters 3, 4, 5 1 1. Countries in Trouble in the Eurozone
Test Bank Multinational Business Finance 14th Edition by Eiteman Stonehill Moffett
 Test Bank Multinational Business Finance 14th Edition by Eiteman Stonehill Moffett Solutions Manual for Multinational Business Finance 14th Edition by David K. Eiteman, Arthur I. Stonehill, Michael H.
Test Bank Multinational Business Finance 14th Edition by Eiteman Stonehill Moffett Solutions Manual for Multinational Business Finance 14th Edition by David K. Eiteman, Arthur I. Stonehill, Michael H.
Ch. 2 International Monetary System. Motives for Int l Financial Markets. Motives for Int l Financial Markets
 Ch. 2 International Monetary System Topics Motives for International Financial Markets History of FX Market Exchange Rate Systems Euro Eurocurrency Market Motives for Int l Financial Markets The markets
Ch. 2 International Monetary System Topics Motives for International Financial Markets History of FX Market Exchange Rate Systems Euro Eurocurrency Market Motives for Int l Financial Markets The markets
Chapter 22 (11) Developing Countries: Growth, Crisis, and Reform
 Chapter 22 (11) Developing Countries: Growth, Crisis, and Reform Preview Snapshots of rich and poor countries Characteristics of poor countries Borrowing and debt in poor and middle-income economies The
Chapter 22 (11) Developing Countries: Growth, Crisis, and Reform Preview Snapshots of rich and poor countries Characteristics of poor countries Borrowing and debt in poor and middle-income economies The
Economic Interaction
 Beijing Review Vol. 49, No. 40 (October 5, 2006) Economic Interaction At a hearing before the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission on August 22, 2006, James A. Dorn, Vice President for Academic
Beijing Review Vol. 49, No. 40 (October 5, 2006) Economic Interaction At a hearing before the U.S.-China Economic and Security Review Commission on August 22, 2006, James A. Dorn, Vice President for Academic
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 6
 Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley Spring 2006 Economics 182 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 6 Problem 1: International diversification Because raspberries are nontradable, asset
Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley Spring 2006 Economics 182 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 6 Problem 1: International diversification Because raspberries are nontradable, asset
Study Questions (with Answers) Lecture 20 International Policies for Economic Development: Financial
 Study Questions (with Answers) Page 1 of 5 Study Questions (with Answers) Lecture 20 International Policies for Economic Development: Financial Part 1: Multiple Choice Select the best answer of those given.
Study Questions (with Answers) Page 1 of 5 Study Questions (with Answers) Lecture 20 International Policies for Economic Development: Financial Part 1: Multiple Choice Select the best answer of those given.
Chapter 24 CRISES IN EMERGING MARKETS
 Chapter 24 CRISES IN EMERGING MARKETS The previous chapter extended the IS-LM-BP model to accommodate high capital mobility. Chapter 24 applies that model to the crises that beset some middle-income countries
Chapter 24 CRISES IN EMERGING MARKETS The previous chapter extended the IS-LM-BP model to accommodate high capital mobility. Chapter 24 applies that model to the crises that beset some middle-income countries
Chapter Eleven. The International Monetary System
 Chapter Eleven The International Monetary System Introduction 11-3 The international monetary system refers to the institutional arrangements that govern exchange rates. Floating exchange rates occur when
Chapter Eleven The International Monetary System Introduction 11-3 The international monetary system refers to the institutional arrangements that govern exchange rates. Floating exchange rates occur when
The International Monetary System
 INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Fourth Edition EUN / RESNICK The International Monetary System 2 Chapter Two INTERNATIONAL Chapter Objective: FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT This chapter serves to introduce the
INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Fourth Edition EUN / RESNICK The International Monetary System 2 Chapter Two INTERNATIONAL Chapter Objective: FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT This chapter serves to introduce the
Botswana s exchange rate policy
 BIS Botswana s exchange rate policy Kealeboga Masalila and Oduetse Motshidisi 1. Introduction In the construction of a market-based development strategy, a key policy consideration is the selection of
BIS Botswana s exchange rate policy Kealeboga Masalila and Oduetse Motshidisi 1. Introduction In the construction of a market-based development strategy, a key policy consideration is the selection of
Econ 340. Recall Macro from Econ 102. Recall Macro from Econ 102. Recall Macro from Econ 102. Recall Macro from Econ 102
 Econ 34 Lecture 5 International Macroeconomics Outline: International Macroeconomics Recall Macro from Econ 2 Aggregate Supply and Demand Policies Effects ON the Exchange Expansion Interest Rate Depreciation
Econ 34 Lecture 5 International Macroeconomics Outline: International Macroeconomics Recall Macro from Econ 2 Aggregate Supply and Demand Policies Effects ON the Exchange Expansion Interest Rate Depreciation
The Renminbi and the Global Economy. Robert Mundell. Chinese University of Hong Kong June 3, 2005
 The Renminbi and the Global Economy Robert Mundell Chinese University of Hong Kong June 3, 2005 Topics Rise of China Macroeconomic Condition RMB Issue Recommendations RMB Currency Area in the World Economy,
The Renminbi and the Global Economy Robert Mundell Chinese University of Hong Kong June 3, 2005 Topics Rise of China Macroeconomic Condition RMB Issue Recommendations RMB Currency Area in the World Economy,
to T5? dollar. T4 T1 to T2 but T4 to T5. rate needed to market model) 1 Problem
 Problem Set 4 Determining thee exchange rate (currency market model) 1. Nominal exchange rate. Consider the following tables (T1 to T5) taken from the web site http://www.x rates.com/ /. In tabless T1,
Problem Set 4 Determining thee exchange rate (currency market model) 1. Nominal exchange rate. Consider the following tables (T1 to T5) taken from the web site http://www.x rates.com/ /. In tabless T1,
Global Business Economics. Mark Crosby SEMBA International Economics
 Global Business Economics Mark Crosby SEMBA International Economics The balance of payments and exchange rates Understand the structure of a country s balance of payments. Understand the difference between
Global Business Economics Mark Crosby SEMBA International Economics The balance of payments and exchange rates Understand the structure of a country s balance of payments. Understand the difference between
Chapter 7 Fixed Exchange Rate Regimes and Short Run Macroeconomic Policy
 George Alogoskoufis, International Macroeconomics and Finance Chapter 7 Fixed Exchange Rate Regimes and Short Run Macroeconomic Policy Up to now we have been assuming that the exchange rate is determined
George Alogoskoufis, International Macroeconomics and Finance Chapter 7 Fixed Exchange Rate Regimes and Short Run Macroeconomic Policy Up to now we have been assuming that the exchange rate is determined
CAPITAL FLOWS TO LATIN AMERICA: CHALLENGES AND POLICY RESPONSES. Javier Guzmán Calafell 1
 CAPITAL FLOWS TO LATIN AMERICA: CHALLENGES AND POLICY RESPONSES Javier Guzmán Calafell 1 1. Introduction Capital flows to Latin America and other emerging market regions fell sharply after the collapse
CAPITAL FLOWS TO LATIN AMERICA: CHALLENGES AND POLICY RESPONSES Javier Guzmán Calafell 1 1. Introduction Capital flows to Latin America and other emerging market regions fell sharply after the collapse
POLICY PRESCRIPTIONS FOR EAST ASIA
 POLICY PRESCRIPTIONS FOR EAST ASIA Masaru Yoshitomi* At the Asian Development Bank Institute in Tokyo, we recently produced policy recommendations about how to avoid another financial crisis and, if we
POLICY PRESCRIPTIONS FOR EAST ASIA Masaru Yoshitomi* At the Asian Development Bank Institute in Tokyo, we recently produced policy recommendations about how to avoid another financial crisis and, if we
Developing Countries Chapter 22
 Developing Countries Chapter 22 1. Growth 2. Borrowing and Debt 3. Money-financed deficits and crises 4. Other crises 5. Currency board 6. International financial architecture for the future 1 Growth 1.1
Developing Countries Chapter 22 1. Growth 2. Borrowing and Debt 3. Money-financed deficits and crises 4. Other crises 5. Currency board 6. International financial architecture for the future 1 Growth 1.1
Each of the major international capital market-related crises since 1994
 Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 15, Number 2 Spring 2001 Pages 3 24 Distinguished Lecture on Economics in Government Exchange Rate Regimes: Is the Bipolar View Correct? Stanley Fischer Each of
Journal of Economic Perspectives Volume 15, Number 2 Spring 2001 Pages 3 24 Distinguished Lecture on Economics in Government Exchange Rate Regimes: Is the Bipolar View Correct? Stanley Fischer Each of
Lecture 17: Mundell-Fleming model with perfect capital mobility
 Lecture 17: Mundell-Fleming model with perfect capital mobility Fiscal policy fixed vs. floating rates. Monetary policy fixed vs. floating rates. The Impossible Trinity Application to European monetary
Lecture 17: Mundell-Fleming model with perfect capital mobility Fiscal policy fixed vs. floating rates. Monetary policy fixed vs. floating rates. The Impossible Trinity Application to European monetary
Other similar crisis: Euro, Emerging Markets
 Session 15. Understanding Macroeconomic Crises. Mexican Crisis 1994-95 Other similar crisis: Euro, Emerging Markets Global Scenarios 2017-2021 The Mexican Peso Crisis in 1994: Background An economy that
Session 15. Understanding Macroeconomic Crises. Mexican Crisis 1994-95 Other similar crisis: Euro, Emerging Markets Global Scenarios 2017-2021 The Mexican Peso Crisis in 1994: Background An economy that
POLI 12D: International Relations Sections 1, 6
 POLI 12D: International Relations Sections 1, 6 Spring 2017 TA: Clara Suong Chapter 9 International Monetary Relations 9 INTERNATIONAL MONETARY RELATIONS Core of the Analysis National Monetary Order Fixed
POLI 12D: International Relations Sections 1, 6 Spring 2017 TA: Clara Suong Chapter 9 International Monetary Relations 9 INTERNATIONAL MONETARY RELATIONS Core of the Analysis National Monetary Order Fixed
Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System
 Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding
Economics of Money, Banking, and Fin. Markets, 10e (Mishkin) Chapter 18 The International Financial System 18.1 Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market 1) A central bank of domestic currency and corresponding
Emerging market central banks investment strategies: Tailwind for the euro?
 Economic Research Allianz Group Dresdner Bank Working Paper No.:38, 11.04.2005 Autor: Dr. R. Schäfer Emerging market central banks investment strategies: Tailwind for the euro? The euro has appreciated
Economic Research Allianz Group Dresdner Bank Working Paper No.:38, 11.04.2005 Autor: Dr. R. Schäfer Emerging market central banks investment strategies: Tailwind for the euro? The euro has appreciated
Study Questions. Lecture 16 Fixed Versus Floating Exchange Rates
 Study Questions Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Multiple Choice Select the best answer of those given. Study Questions Lecture 16 Fixed Versus Floating Exchange Rates 1. Freely floating exchange rates describes the
Study Questions Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Multiple Choice Select the best answer of those given. Study Questions Lecture 16 Fixed Versus Floating Exchange Rates 1. Freely floating exchange rates describes the
The Asian Financial Crisis
 The Asian Financial Crisis The Asian crisis 1996 Miraculous growth in EA But some signs of worsening current accounts in Korea and Thailand Signs of worsening financial institutions in Thailand 1997 January
The Asian Financial Crisis The Asian crisis 1996 Miraculous growth in EA But some signs of worsening current accounts in Korea and Thailand Signs of worsening financial institutions in Thailand 1997 January
Threats to Financial Stability in Emerging Markets: The New (Very Active) Role of Central Banks. LILIANA ROJAS-SUAREZ Chicago, November 2011
 Threats to Financial Stability in Emerging Markets: The New (Very Active) Role of Central Banks LILIANA ROJAS-SUAREZ Chicago, November 2011 Currently, the Major Threats to Financial Stability in Emerging
Threats to Financial Stability in Emerging Markets: The New (Very Active) Role of Central Banks LILIANA ROJAS-SUAREZ Chicago, November 2011 Currently, the Major Threats to Financial Stability in Emerging
IV. THE BENEFITS OF FURTHER FINANCIAL INTEGRATION IN ASIA
 IV. THE BENEFITS OF FURTHER FINANCIAL INTEGRATION IN ASIA The need for economic rebalancing in the aftermath of the global financial crisis and the recent surge of capital inflows to emerging Asia have
IV. THE BENEFITS OF FURTHER FINANCIAL INTEGRATION IN ASIA The need for economic rebalancing in the aftermath of the global financial crisis and the recent surge of capital inflows to emerging Asia have
International Finance
 International Finance 7 e édition Christophe Boucher christophe.boucher@u-paris10.fr 1 Session 7 7 e édition Exchange rate regimes and monetary policy spillovers 2 Roadmap 1. Classifying countries by exchange
International Finance 7 e édition Christophe Boucher christophe.boucher@u-paris10.fr 1 Session 7 7 e édition Exchange rate regimes and monetary policy spillovers 2 Roadmap 1. Classifying countries by exchange
Challenges to Central Banking from Globalized Financial Systems
 Challenges to Central Banking from Globalized Financial Systems Conference at the IMF in Washington, D.C., September 16 17, 2002 Mr. Jerzy Pruski, Member of the Monetary Policy Council, National Bank of
Challenges to Central Banking from Globalized Financial Systems Conference at the IMF in Washington, D.C., September 16 17, 2002 Mr. Jerzy Pruski, Member of the Monetary Policy Council, National Bank of
Lectures 13 and 14: Fixed Exchange Rates
 Christiano 362, Winter 2003 February 21 Lectures 13 and 14: Fixed Exchange Rates 1. Fixed versus flexible exchange rates: overview. Over time, and in different places, countries have adopted a fixed exchange
Christiano 362, Winter 2003 February 21 Lectures 13 and 14: Fixed Exchange Rates 1. Fixed versus flexible exchange rates: overview. Over time, and in different places, countries have adopted a fixed exchange
Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 4
 Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley Spring 2006 Economics 182 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 4 Problem 1 : True, False, Uncertain (a) False or Uncertain. In first generation
Department of Economics University of California, Berkeley Spring 2006 Economics 182 Suggested Solutions to Problem Set 4 Problem 1 : True, False, Uncertain (a) False or Uncertain. In first generation
Chapter 9 Essential macroeconomic tools. Baldwin&Wyplosz 2009 The Economics of European Integration, 3 rd Edition
 Chapter 9 Essential macroeconomic tools 2 Background theory A quick refresher on basic macroeconomic principles Application of these principles to the question of exchange rate regimes 3 Output and prices
Chapter 9 Essential macroeconomic tools 2 Background theory A quick refresher on basic macroeconomic principles Application of these principles to the question of exchange rate regimes 3 Output and prices
26/10/2016. The Euro. By 2016 there are 19 member countries and about 334 million people use the. Lithuania entered 1 January 2015
 The Euro 1 The Economics of the Euro 2 The History and Politics of the Euro Prepared by: Fernando Quijano Dickinson State University 1of 88 In 1961 the economist Robert Mundell wrote a paper discussing
The Euro 1 The Economics of the Euro 2 The History and Politics of the Euro Prepared by: Fernando Quijano Dickinson State University 1of 88 In 1961 the economist Robert Mundell wrote a paper discussing
What is Wrong with Market-Oriented Policies?
 June 2003 In 1999, SigmaBleyzer initiated the International Private Capital Task Force (IPCTF) in Ukraine. Its objective was to benchmark transition economies to identify best practices in government policies
June 2003 In 1999, SigmaBleyzer initiated the International Private Capital Task Force (IPCTF) in Ukraine. Its objective was to benchmark transition economies to identify best practices in government policies
MANAGING CAPITAL FLOWS
 MANAGING CAPITAL FLOWS Yılmaz Akyüz South Centre, Geneva Capital Account Regulations and Global Economic Governance Workshop Organized by UNCTAD and GEGI, Geneva, Palais des Nations, 3-4 October 2013 www.southcentre.int
MANAGING CAPITAL FLOWS Yılmaz Akyüz South Centre, Geneva Capital Account Regulations and Global Economic Governance Workshop Organized by UNCTAD and GEGI, Geneva, Palais des Nations, 3-4 October 2013 www.southcentre.int
TRUE FACTS AND FALSE PERCEPTIONS ABOUT FEDERAL DEFICITS" Remarks by Thomas C. Melzer Rotary Club of Springfield, Missouri December 6, 1988
 TRUE FACTS AND FALSE PERCEPTIONS ABOUT FEDERAL DEFICITS" Remarks by Thomas C. Melzer Rotary Club of Springfield, Missouri December 6, 1988 During the decade of the 1980s, the U.S. has enjoyed spectacular
TRUE FACTS AND FALSE PERCEPTIONS ABOUT FEDERAL DEFICITS" Remarks by Thomas C. Melzer Rotary Club of Springfield, Missouri December 6, 1988 During the decade of the 1980s, the U.S. has enjoyed spectacular
SPP 542 International Financial Policy South Korea s Next Step
 SPP 542 International Financial Policy South Korea s Next Step Date: April 16, 2003 Written by: Tsutomu Hayafuji Mitsuru Ikeda Hironori Yamada 1. South Korean Economy Outlook From the mid-1960s to the
SPP 542 International Financial Policy South Korea s Next Step Date: April 16, 2003 Written by: Tsutomu Hayafuji Mitsuru Ikeda Hironori Yamada 1. South Korean Economy Outlook From the mid-1960s to the
UNIT FIVE (5) The International Monetary Environment and Financial Management in the Global Firm
 UNIT FIVE (5) The International Monetary Environment and Financial Management in the Global Firm Objectives Exchange rates and currencies How exchange rates are determined The monetary and financial systems
UNIT FIVE (5) The International Monetary Environment and Financial Management in the Global Firm Objectives Exchange rates and currencies How exchange rates are determined The monetary and financial systems
The Case for Price Stability with a Flexible Exchange Rate in the New Neoclassical Synthesis Marvin Goodfriend
 The Case for Price Stability with a Flexible Exchange Rate in the New Neoclassical Synthesis Marvin Goodfriend The New Neoclassical Synthesis is a natural starting point for the consideration of welfare-maximizing
The Case for Price Stability with a Flexible Exchange Rate in the New Neoclassical Synthesis Marvin Goodfriend The New Neoclassical Synthesis is a natural starting point for the consideration of welfare-maximizing
Suggested Answers. Department of Economics Economics 115 University of California. Berkeley, CA Spring *SAS = See Answer Sheet
 Department of Economics Economics 115 University of California The 20 th Century World Economy Berkeley, CA 94720 Spring 2009 *SAS = See Answer Sheet Suggested Answers *Sentences copy-and-pasted from Wikipedia
Department of Economics Economics 115 University of California The 20 th Century World Economy Berkeley, CA 94720 Spring 2009 *SAS = See Answer Sheet Suggested Answers *Sentences copy-and-pasted from Wikipedia
Financial crises in Asia and Latin America: Then and now
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Financial crises in Asia and Latin America: Then and now Carmen Reinhart and Graciela Kaminsky University of Maryland, College Park, Department of Economics May 1998
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Financial crises in Asia and Latin America: Then and now Carmen Reinhart and Graciela Kaminsky University of Maryland, College Park, Department of Economics May 1998
Lessons from GFC for Management and Liberalization of Capital Flows in Asia Mario B. Lamberte Director of Research
 Lessons from GFC for Management and Liberalization of Capital Flows in Asia Mario B. Lamberte Director of Research This draws largely on Chapter 1 of the forthcoming book, Managing Capital Flows: Search
Lessons from GFC for Management and Liberalization of Capital Flows in Asia Mario B. Lamberte Director of Research This draws largely on Chapter 1 of the forthcoming book, Managing Capital Flows: Search
A Chile in Transition: Stability Brings Change. Macroeconomics 556 April 13, Alex Rosaen Neerav Shah Elias Walsh
 A Chile in Transition: Stability Brings Change Macroeconomics 556 April 13, 2005 Alex Rosaen Neerav Shah Elias Walsh Since 1996 Chile has enjoyed declining inflation and stable growth. Government has been
A Chile in Transition: Stability Brings Change Macroeconomics 556 April 13, 2005 Alex Rosaen Neerav Shah Elias Walsh Since 1996 Chile has enjoyed declining inflation and stable growth. Government has been
Capital Account Controls and Liberalization: Lessons for India and China
 UBS Investment Research Capital Account Controls and Liberalization: Lessons for India and China Jonathan Anderson November 2003 ANALYST CERTIFICATION AND REQUIRED DISCLOSURES BEGIN ON PAGE 50 UBS does
UBS Investment Research Capital Account Controls and Liberalization: Lessons for India and China Jonathan Anderson November 2003 ANALYST CERTIFICATION AND REQUIRED DISCLOSURES BEGIN ON PAGE 50 UBS does
ROUNDTABLE COMMENTS ON MONETARY AND REGULATORY POLICY IN AN ERA OF GLOBAL MARKETS
 ROUNDTABLE COMMENTS ON MONETARY AND REGULATORY POLICY IN AN ERA OF GLOBAL MARKETS Liliana Rojas-Suarez Institute for International Economics D uring the conference we have heard a lot of stress placed
ROUNDTABLE COMMENTS ON MONETARY AND REGULATORY POLICY IN AN ERA OF GLOBAL MARKETS Liliana Rojas-Suarez Institute for International Economics D uring the conference we have heard a lot of stress placed
Rich and Poor. Indicators of Economic Welfare for 4 groups of countries, 2003 GNP per capita (1995 US$)
 Rich and Poor Indicators of Economic Welfare for 4 groups of countries, 2003 GNP per capita (1995 US$) Life expectancy Low income 450 58 Lower-middle income 1480 69 Upper-middle income 5340 73 High income
Rich and Poor Indicators of Economic Welfare for 4 groups of countries, 2003 GNP per capita (1995 US$) Life expectancy Low income 450 58 Lower-middle income 1480 69 Upper-middle income 5340 73 High income
Mr Thiessen converses on the conduct of monetary policy in Canada under a floating exchange rate system
 Mr Thiessen converses on the conduct of monetary policy in Canada under a floating exchange rate system Speech by Mr Gordon Thiessen, Governor of the Bank of Canada, to the Canadian Society of New York,
Mr Thiessen converses on the conduct of monetary policy in Canada under a floating exchange rate system Speech by Mr Gordon Thiessen, Governor of the Bank of Canada, to the Canadian Society of New York,
The East Asia Financial Crises. Yue-Chim Richard Wong
 The East Asia Financial Crises Yue-Chim Richard Wong The current East Asia financial crises started in Thailand as early as the autumn of 1996. The Thailand baht came under increasing pressure from speculators
The East Asia Financial Crises Yue-Chim Richard Wong The current East Asia financial crises started in Thailand as early as the autumn of 1996. The Thailand baht came under increasing pressure from speculators
The Trans-Pacific Imbalance: A Disaster in the Making?
 The Trans-Pacific Imbalance: A Disaster in the Making? C. Fred Bergsten Director, Institute for International Economics Speech at the 16 th General Meeting of the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council (PECC),
The Trans-Pacific Imbalance: A Disaster in the Making? C. Fred Bergsten Director, Institute for International Economics Speech at the 16 th General Meeting of the Pacific Economic Cooperation Council (PECC),
Yen and Yuan RIETI, Tokyo
 Yen and Yuan RIETI, Tokyo November 2, 21 In the first half of his talk, Dr. Kwan, senior fellow at RIETI, argued that Asian currencies should be pegged to a currency basket, with the Japanese yen comprising
Yen and Yuan RIETI, Tokyo November 2, 21 In the first half of his talk, Dr. Kwan, senior fellow at RIETI, argued that Asian currencies should be pegged to a currency basket, with the Japanese yen comprising
The Evolution of the International Monetary System. Professor Keith Pilbeam City University, London
 The Evolution of the International Monetary System Professor Keith Pilbeam City University, London The Postwar International Monetary System some highlights Bretton Woods 1949-72 sets up IMF, fixes dollar
The Evolution of the International Monetary System Professor Keith Pilbeam City University, London The Postwar International Monetary System some highlights Bretton Woods 1949-72 sets up IMF, fixes dollar
Simultaneous Equilibrium in Output and Financial Markets: The Short Run Determination of Output, the Exchange Rate and the Current Account
 Fletcher School, Tufts University Simultaneous Equilibrium in Output and Financial Markets: The Short Run Determination of Output, the Exchange Rate and the Current Account Prof. George Alogoskoufis The
Fletcher School, Tufts University Simultaneous Equilibrium in Output and Financial Markets: The Short Run Determination of Output, the Exchange Rate and the Current Account Prof. George Alogoskoufis The
Latin American Finance
 MMost countries in Latin America have made serious strides toward reforming their economies in the last 15 years, opening their markets to trade and foreign investment, reducing government budget deficits,
MMost countries in Latin America have made serious strides toward reforming their economies in the last 15 years, opening their markets to trade and foreign investment, reducing government budget deficits,
Capital Account Liberalization in China
 *All opinions expressed herein are the author s own and do not necessarily reflect the views of any of the organisations with which the author is affiliated. Capital Account Liberalization in China Lawrence
*All opinions expressed herein are the author s own and do not necessarily reflect the views of any of the organisations with which the author is affiliated. Capital Account Liberalization in China Lawrence
Chapter 29 The Global Economy and Policy Principles of Economics in Context (Goodwin et al)
 Chapter 29 The Global Economy and Policy Principles of Economics in Context (Goodwin et al) Chapter Overview This chapter will take you through the basics of international trade and finance. The chapter
Chapter 29 The Global Economy and Policy Principles of Economics in Context (Goodwin et al) Chapter Overview This chapter will take you through the basics of international trade and finance. The chapter
The Case for Chinese Capital Controls. Global Economics Monthly February 2016
 Global Economics Monthly February 2016 The Case for Chinese Capital Controls Robert Kahn, Steven A. Tananbaum Senior Fellow for International Economics O V E R V I E W Bottom line: Japanese Central Bank
Global Economics Monthly February 2016 The Case for Chinese Capital Controls Robert Kahn, Steven A. Tananbaum Senior Fellow for International Economics O V E R V I E W Bottom line: Japanese Central Bank
Asian Financial Crisis. Jianing Li/Wei Ye/Jingyan Zhang 2018/11/29
 Asian Financial Crisis Jianing Li/Wei Ye/Jingyan Zhang 2018/11/29 Causes--Current account deficit 1. Liberalization of capital markets. 2. Large capital inflow due to the interest rates fall in developed
Asian Financial Crisis Jianing Li/Wei Ye/Jingyan Zhang 2018/11/29 Causes--Current account deficit 1. Liberalization of capital markets. 2. Large capital inflow due to the interest rates fall in developed
Currency Asymmetry, Global Imbalance, and the Needed Reform of Global Monetary System
 Currency Asymmetry, Global Imbalance, and the Needed Reform of Global Monetary System FAN Gang National Economic Research Institute China Reform Foundation May 2006 1.China s trade balance In most of past
Currency Asymmetry, Global Imbalance, and the Needed Reform of Global Monetary System FAN Gang National Economic Research Institute China Reform Foundation May 2006 1.China s trade balance In most of past
Welcome to: International Finance
 Welcome to: International Finance Introduction & International Monetary System Reading: Chapter 1 (p1-3) & Chapter 2 Why is International Finance Important? ٣ Why is International Finance Important? In
Welcome to: International Finance Introduction & International Monetary System Reading: Chapter 1 (p1-3) & Chapter 2 Why is International Finance Important? ٣ Why is International Finance Important? In
Currency Crises: Theory and Evidence
 Currency Crises: Theory and Evidence Lecture 3 IME LIUC 2008 1 The most dramatic form of exchange rate volatility is a currency crisis when an exchange rate depreciates substantially in a short period.
Currency Crises: Theory and Evidence Lecture 3 IME LIUC 2008 1 The most dramatic form of exchange rate volatility is a currency crisis when an exchange rate depreciates substantially in a short period.
Economics Higher level Paper 2
 Economics Higher level Paper 2 Tuesday 5 May 2015 (morning) 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. You are not permitted access to any
Economics Higher level Paper 2 Tuesday 5 May 2015 (morning) 1 hour 30 minutes Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. You are not permitted access to any
