Financial Accounting (F3/FFA) February 2013 to January 2014
|
|
|
- Jacob Taylor
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Financial Accounting (F3/FFA) February 2013 to January 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE STRUCTURE OF THE SYLLABUS AND STUDY GUIDE Relational diagram with other papers This diagram shows direct and indirect links between this paper and other papers preceding or following it. Some papers are directly underpinned by other papers. These links are shown as solid line arrows. The links between papers where there is only an indirect link and no required underpinning are shown as dotted line arrows. The relational diagram therefore indicates where you are expected to have underpinning knowledge and where it would be useful to review previous learning before undertaking study. Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective of the paper and indicates in the broadest sense the capabilities to be developed within the paper. Main capabilities This paper s aim is broken down into several main capabilities which divide the syllabus and study guide into discrete sections. Relational diagram of main capabilities This diagram illustrates the flows and links between the main capabilities (sections) of the syllabus and should be used as an aid to planning teaching and learning in a structured way. Syllabus rationale This is a narrative explaining how the syllabus is structured and how the main capabilities are linked. The rationale also explains in further detail what the examination intends to assess and why. Detailed syllabus This shows the breakdown of the main capabilities (sections) of the syllabus into subject areas. This is the blueprint for the detailed study guide. Approach to examining the syllabus This section briefly explains the structure of the examination and how it is assessed. Study Guide This is the main document that students and learning and content providers should use as the basis of their studies, instruction and materials respectively. Examinations will be based on the detail of the study guide which comprehensively identifies what could be assessed in any examination session. The study guide is a precise reflection and breakdown of the syllabus. It is divided into sections based on the main capabilities identified in the syllabus. These sections are divided into subject areas which relate to the sub-capabilities included in the detailed syllabus. Subject areas are broken down into sub-headings which describe the detailed outcomes that could be assessed in examinations. These outcomes are described using verbs indicating what exams may require students to demonstrate, and the broad intellectual level at which these may need to be demonstrated (*see intellectual levels below). Learning Materials ACCA's Approved Learning Partner - content (ALPc) is the programme through which ACCA approves learning materials from high quality content providers designed to support study towards ACCA s qualifications. ACCA has one Platinum Approved Learning Partner content which is BPP Learning Media. In addition, there are a number of Gold Approved Learning Partners - content. For information about ACCA's Approved Learning Partners - content, please go ACCA's Content Provider Directory. The Directory also lists materials by Subscribers, these materials have not been quality assured by 1
2 ACCA but may be helpful if used in conjunction with approved learning materials. You will also find details of Examiner suggested Additional Reading which may be a useful supplement to approved learning materials. ACCA's Content Provider Directory can be found here HUhttp:// ontent_provider_directory/search/uh. Relevant articles will also be published in Student Accountant. LEVEL OF ASSESSMENTS INTELLECTUAL DEMAND ACCA qualifications are designed to progressively broaden and deepen the knowledge and skills demonstrated by the student at a range of levels on their way through each qualification. Throughout, the study guides assess both knowledge and skills. Therefore a clear distinction is drawn, within each subject area, between assessing knowledge and skills and in assessing their application within an accounting or business context. The assessment of knowledge is denoted by a superscript K and the assessment of skills is denoted by the superscript S. VALUE OF ASSESSMENTS EDUCATION RECOGNITION ACCA seeks to enhance the education recognition of its qualifications on both national and international education frameworks, and with educational authorities and partners globally. In doing so, ACCA aims to ensure that its qualifications are recognized and valued by governments, regulatory authorities and employers across all sectors. To this end, ACCA qualifications are currently recognized on the education frameworks in several countries. Please refer to for further information. All FIA examinations are assessed by two-hour paper based and computer based examinations. The pass mark for all FIA examination papers is 50%. GUIDE TO EXAMINATION ASSESSMENT ACCA reserves the right to examine anything contained within any study guide at any examination session. This includes knowledge, techniques, principles, theories, and concepts as specified. For the financial accounting, audit and tax papers, except where indicated otherwise, ACCA will publish examinable documents once a year to indicate exactly what regulations and legislation could potentially be assessed within identified examination sessions. Examinations regulation issued or legislation passed on or before 30 th September annually, will be assessed from June 1 st of the following year to May 31 st of the year after. Please refer to the examinable documents for the paper (where relevant) for further information. Regulation issued or legislation passed in accordance with the above dates may be examinable even if the effective date is in the future. The term issued or passed relates to when regulation or legislation has been formally approved. The term effective relates to when regulation or legislation must be applied to entity transactions and business practices. The study guide offers more detailed guidance on the depth and level at which the examinable documents will be examined. The study guide should therefore be read in conjunction with the examinable documents list. GUIDE TO EXAM STRUCTURE The structure of examinations varies within and between modules and levels. The FIA examinations contain 100% compulsory questions to encourage candidates to study across the breadth of each syllabus. 2
3 Qualification Structure The qualification structure requires candidates who wish to be awarded the Diploma in Accounting and Business to pass the F1/FAB, F2/FMA and the F3/FFA examinations and successfully complete the Foundations in Professionalism module F1/FAB F2/FMA F3/FFA FiP* = Diploma in Accounting and Business * Foundations in Professionalism Syllabus Structure 'The Foundations in Accountancy suite of qualifications is designed so that a student can progress through three discrete levels; Introductory Certificate level, Intermediate Certificate level and the Diploma level. Students are recommended to enter FIA at the level which is most appropriate to their needs and to take examinations in order, but this is not a mandatory requirement P2 ACCA F7 FIA FFA F3 FA2 FA1 3
4 Syllabus financial statements from the individual financial statements of group incorporated entities AIM To develop knowledge and understanding of the underlying principles and concepts relating to financial accounting and technical proficiency in the use of double-entry accounting techniques including the preparation of basic financial statements for single entities and simple groups. The syllabus also introduces basic techniques of interpretation of financial statements. RATIONALE The syllabus for Paper FFA/F3, Foundations of Financial Accounting, introduces the candidate to the fundamentals of the regulatory framework relating to accounts preparation and to the qualitative characteristics of useful information. The syllabus then covers drafting financial statements and to principles of accounts preparation. The syllabus then concentrates in depth on recording, processing, and reporting business transactions and events. The syllabus then covers the use of the trial balance and how to identify and correct errors, and then the preparation of financial statements for incorporated and unincorporated entities. The syllabus then moves in two directions, firstly requiring candidates to be able to conduct a basic interpretation of financial statements; and secondly requiring the preparation of simple consolidated MAIN CAPABILITIES On successful completion of this paper, candidates should be able to: A. Explain the context and purpose of financial reporting B. Define the qualitative characteristics of financial information C. Demonstrate the use of double-entry and accounting systems D. Record transactions and events E. Prepare a trial balance (including identifying and correcting error F. Prepare basic financial statements for incorporated and unincorporated entities. G. Prepare simple consolidated financial statements H. Interpretation of financial statements RELATIONAL DIAGRAM OF MAIN CAPABILITIES The context and purpose of financial reporting (A) The qualitative characteristics of financial information (B) The use of double-entry and accounting systems (C) Recording transactions and events (D) Preparing a trial balance (E) Preparing basic financial statements (F) 4 Preparing simple consolidated statements (G) Interpretation of Financial statements (H)
5 DETAILED SYLLABUS 9. Provisions and contingencies A The context and purpose of financial reporting 10. Capital structure and finance costs 1. The scope and purpose of, financial statements for external reporting 2. Users and stakeholders needs 3. The main elements of financial reports 4. The regulatory framework (legislation and regulation, reasons and limitations, relevance of accounting standards) 5. Duties and responsibilities of those charged with governance. B The qualitative characteristics of financial information 1. The qualitative characteristics of financial information C The use of double-entry and accounting systems 1. Double-entry book-keeping principles including the maintenance of accounting records and sources of accounting information 2. Ledger accounts, books of prime entry, and journals D Recording transactions and events 1. Sales and purchases 2. Cash 3. Inventory 4. Tangible non-current assets 5. Depreciation 6. Intangible non-current assets and amortisation E Preparing a trial balance 1. Trial balance 2. Correction of errors 3. Control accounts and reconciliations 4. Bank reconciliations 5. Suspense accounts F Preparing basic financial statements 1. Statements of financial position 2. Income statements and statements of comprehensive income 3. Disclosure notes 4 Events after the reporting period 5. Statements of cash flows (excluding partnerships) 6. Incomplete records G Preparing simple consolidated financial statements 1. Subsidiaries 2. Associates H Interpretation of financial statements 1. Importance and purpose of analysis of financial statements 2. Ratios 3. Analysis of financial statements 7. Accruals and prepayments 8. Receivables and payables 5
6 APPROACH TO EXAMINING THE SYLLABUS THE SYLLABUS IS ASSESSED BY A TWO HOUR PAPER-BASED OR COMPUTER-BASED EXAMINATION. The syllabus is assessed by a two hour paper-based or computer-based examination. Questions will assess all parts of the syllabus and will include both computational and non-computational elements. The examination will consist of 50 two mark questions. 6
7 Study Guide A THE CONTEXT AND PURPOSE OF FINANCIAL REPORTING 1. The scope and purpose of, financial statements for external reporting a) Define financial reporting recording, analysing and summarising financial data. [K] b) Identify and define types of business entity sole trader, partnership, limited liability company. [K] c) Recognise the legal differences between a sole trader, partnership and a limited liability company. [K] d) Identify the advantages and disadvantages of operating as a limited liability company, sole trader or partnership. [K] e) Understand the nature, principles and scope of financial reporting. [K] 2. Users and stakeholders needs a) Identify the users of financial statements and state and differentiate between their information needs. [K] 3. The main elements of financial reports a) Understand and identify the purpose of each of the main financial statements. [K] b) Define and identify assets, liabilities, equity, revenue and expenses. [K] 4. The regulatory framework a) Understand the role of the regulatory system including the roles of the IFRS Foundation (IFRSF), the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), the IFRS Advisory Council (IFRS AC) and the IFRS Interpretations Committee (IFRS IC). [K] b) Understand the role of International Financial Reporting Standards. [K] 5. Duties and responsibilities of those charged with governance a) Explain what is meant by governance specifically in the context of the preparation of financial statements [K] b) Describe the duties and responsibilities of directors and other parties covering the preparation of the financial statements. [K] B THE QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS OF FINANCIAL INFORMATION 1. The qualitative characteristics of financial information a) Define, understand and apply accounting concepts and qualitative characteristics: [K] i) Fair presentation ii) Going concern iii) Accruals iv) Consistency v) Materiality vi) Relevance vii) Reliability viii)faithful representation ix) Substance over form x) Neutrality xi) Prudence xii) Completeness xiii) Comparability xiv) Understandability xv) Business entity concept b) Understand the balance between qualitative characteristics. [K] C THE USE OF DOUBLE-ENTRY AND ACCOUNTING SYSTEMS 1. Double-entry book-keeping principles including the maintenance of accounting records a) Identify and explain the function of the main data sources in an accounting system. [K] b) Outline the contents and purpose of different types of business documentation, including: quotation, sales order, purchase order, goods received note, goods despatched note, invoice, statement, credit note, debit note, remittance advice, receipt. [K] 7
8 c) Understand and apply the concept of doubleentry accounting and the duality concept. [K] d) Understand and apply the accounting equation. [S] e) Understand how the accounting system contributes to providing useful accounting information and complies with organisational policies and deadlines. [K] f) Identify the main types of business transactions e.g. sales, purchases, payments, receipts. [K] 2. Ledger accounts, books of prime entry and journals a) Identify the main types of ledger accounts and books of prime entry, and understand their nature and function. [K] b) Understand and illustrate the uses of journals and the posting of journal entries into ledger accounts. [S] c) Identify correct journals from given narrative. [S] d) Illustrate how to balance and close a ledger account. [S] D RECORDING TRANSACTIONS AND EVENTS 1. Sales and purchases a) Record sale and purchase transactions in ledger accounts. [S] b) Understand and record sales and purchase returns. [S] c) Understand the general principles of the operation of a sales tax. [K] d) Calculate sales tax on transactions and record the consequent accounting entries. [S] e) Account for discounts allowed and discounts received. [S] 2. Cash a) Record cash transactions in ledger accounts. [S] b) Understand the need for a record of petty cash transactions. [K] 3. Inventory a) Recognise the need for adjustments for inventory in preparing financial statements. [K] b) Record opening and closing inventory. [S] c) Identify the alternative methods of valuing inventory. [K] d) Understand and apply the IASB requirements for valuing inventories. [S] e) Recognise which costs should be included in valuing inventories. [S] f) Understand the use of continuous and period end inventory records. [K] g) Calculate the value of closing inventory using FIFO (first in, first out) and AVCO (average cost). [S] h) Understand the impact of accounting concepts on the valuation of inventory. [K] i) Identify the impact of inventory valuation methods on profit and on assets. [S] 4. Tangible non-current assets a) Define non-current assets. [K] b) Recognise the difference between current and non-current assets. [K] c) Explain the difference between capital and revenue items. [K] d) Classify expenditure as capital or revenue expenditure. [S] e) Prepare ledger entries to record the acquisition and disposal of non-current assets. [S] f) Calculate and record profits or losses on disposal of non-current assets in the income statement including part exchange transactions. [S] 8
9 g) Record the revaluation of a non-current asset in ledger accounts, the statement of comprehensive income and in the statement of financial position. [S] h) Calculate the profit or loss on disposal of a revalued asset. [S] i) Illustrate how non-current asset balances and movements are disclosed in financial statements. [S] j) Explain the purpose and function of an asset register. [K] 5. Depreciation a) Understand and explain the purpose of depreciation. [K] b) Calculate the charge for depreciation using straight line and reducing balance methods. [S] c) Identify the circumstances where different methods of depreciation would be appropriate. [K] d) Illustrate how depreciation expense and accumulated depreciation are recorded in ledger accounts. [S] e) Calculate depreciation on a revalued noncurrent asset including the transfer of excess depreciation between the revaluation reserve and retained earnings. [S] f) Calculate the adjustments to depreciation necessary if changes are made in the estimated useful life and/or residual value of a noncurrent asset. [S] g) Record depreciation in the income statement and statement of financial position. [S] 6. Intangible non-current assets and amortisation a) Recognise the difference between tangible and intangible non-current assets. [K] b) Identify types of intangible assets. [K] c) Identify the definition and treatment of research costs and development costs in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards. [K] d) Calculate amounts to be capitalised as development expenditure or to be expensed from given information. [S] e) Explain the purpose of amortisation. [K] f) Calculate and account for the charge for amortisation. [S] 7. Accruals and prepayments a) Understand how the matching concept applies to accruals and prepayments. [K] b) Identify and calculate the adjustments needed for accruals and prepayments in preparing financial statements. [S] c) Illustrate the process of adjusting for accruals and prepayments in preparing financial statements. [S] d) Prepare the journal entries and ledger entries for the creation of an accrual or prepayment. [S] e) Understand and identify the impact on profit and net assets of accruals and prepayments. [S] 8. Receivables and payables a) Explain and identify examples of receivables and payables. [K] b) Identify the benefits and costs of offering credit facilities to customers. [K] c) Understand the purpose of an aged receivables analysis. [K] d) Understand the purpose of credit limits. [K]] e) Prepare the bookkeeping entries to write off an irrecoverable debt. [S] f) Record an irrecoverable debt recovered. [S] g) Identify the impact of irrecoverable debts on the income statement and on the statement of financial position. [S] 9
10 h) Prepare the bookkeeping entries to create and adjust an allowance for receivables. [S] i) Illustrate how to include movements in the allowance for receivables in the income statement and how the closing balance of the allowance should appear in the statement of financial position. [S] j) Account for contras between trade receivables and payables. [S] k) Prepare, reconcile and understand the purpose of supplier statements. [S] l) Classify items as current or non-current liabilities in the statement of financial position. [S] 9. Provisions and contingencies a) Understand the definition of provision, contingent liability and contingent asset. [K] b) Distinguish between and classify items as provisions, contingent liabilities or contingent assets. [K] c) Identify and illustrate the different methods of accounting for provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets. [K] d) Calculate provisions and changes in provisions. [S] e) Account for the movement in provisions. [S] f) Report provisions in the final accounts. [S] 10. Capital structure and finance costs a) Understand the capital structure of a limited liability company including: [K] i) Ordinary shares ii) Preference shares (redeemable and irredeemable) iii) Loan notes. b) Record movements in the share capital and share premium accounts. [S] c) Identify and record the other reserves which may appear in the company statement of financial position. [S] d) Define a bonus (capitalisation) issue and its advantages and disadvantages. [K] e) Define a rights issue and its advantages and disadvantages. [K] f) Record and show the effects of a bonus (capitalisation) issue in the statement of financial position. [S] g) Record and show the effects of a rights issue in the statement of financial position. [S] h) Record dividends in ledger accounts and the financial statements. [S] i) Calculate and record finance costs in ledger accounts and the financial statements. [S] j) Identify the components of the statement of changes in equity. [K] E PREPARING A TRIAL BALANCE 1. Trial balance a) Identify the purpose of a trial balance. [K] b) Extract ledger balances into a trial balance. [S] c) Prepare extracts of an opening trial balance. [S] d) Identify and understand the limitations of a trial balance. [K] 2. Correction of errors a) Identify the types of error which may occur in bookkeeping systems. [K] b) Identify errors which would be highlighted by the extraction of a trial balance. [K] c) Prepare journal entries to correct errors. [S] d) Calculate and understand the impact of errors on the income statement, statement of comprehensive income and statement of financial position. [S] 10
11 3. Control accounts and reconciliations a) Understand the purpose of control accounts for accounts receivable and accounts payable. [K] b) Understand how control accounts relate to the double-entry system. [K] c) Prepare ledger control accounts from given information. [S] d) Perform control account reconciliations for accounts receivable and accounts payable. [S] e) Identify errors which would be highlighted by performing a control account reconciliation. [K] f) Identify and correct errors in control accounts and ledger accounts. [S] 4. Bank reconciliations a) Understand the purpose of bank reconciliations. [K] b) Identify the main reasons for differences between the cash book and the bank statement. [K] c) Correct cash book errors and/or omissions. [S] d) Prepare bank reconciliation statements. [S] e) Derive bank statement and cash book balances from given information. [S] f) Identify the bank balance to be reported in the final accounts. [S] 5. Suspense accounts a) Understand the purpose of a suspense account. [K] b) Identify errors leading to the creation of a suspense account. [K] c) Record entries in a suspense account. [S] d) Make journal entries to clear a suspense account. [S] F PREPARING BASIC FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 1. Statements of financial position a) Recognise how the accounting equation, accounting treatments as stipulated within sections D, E and examinable documents and business entity convention underlie the statement of financial position. [K] b) Understand the nature of reserves. [K] c) Identify and report reserves in a company statement of financial position. [S] d) Prepare a statement of financial position or extracts as applicable from given information using accounting treatments as stipulated within sections D, E and examinable documents. [S] e) Understand why the heading retained earnings appears in a company statement of financial position. [K] 2. Income statements and statements of comprehensive income a) Prepare an income statement and statement of comprehensive income or extracts as applicable from given information using accounting treatments as stipulated within section D, E and examinable documents. [S] b) Understand how accounting concepts apply to revenue and expenses. [K] c) Calculate revenue, cost of sales, gross profit, profit for the year, and total comprehensive income from given information. [S] d) Disclose items of income and expenditure in the income statement. [S] e) Record income tax in the income statement of a company including the under and overprovision of tax in the prior year. [S] f) Understand the interrelationship between the statement of financial position, income statement and statement of comprehensive income. [K] g) Identify items requiring separate disclosure on the face of the income statement. [K] 11
12 3. Disclosure notes a) Explain the purpose of disclosure notes [K] b) Draft the following disclosure notes [S] i) Non current assets including tangible and in tangible assets ii) Provisions iii) Events after the reporting period iv) Inventory 4. Events after the reporting period a) Define an event after the reporting period in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards. [K] b) Classify events as adjusting or non-adjusting. [S] c) Distinguish between how adjusting and nonadjusting events are reported in the financial statements. [K] 5 Statements of cash flows (excluding partnerships) a) Differentiate between profit and cash flow. [K] b) Understand the need for management to control cash flow. [K] c) Recognise the benefits and drawbacks to users of the financial statements of a statement of cash flows. [K] d) Classify the effect of transactions on cash flows. [S] e) Calculate the figures needed for the statement of cash flows including: [S] i) Cash flows from operating activities ii) Cash flows from investing activities iii) Cash flows from financing activities f) Calculate the cash flow from operating activities using the indirect and direct method. [S] g) Prepare statements of cash flows and extracts from statements of cash flows from given information. [S] h) Identify the treatment of given transactions in a company s statement of cash flows. [K] 6. Incomplete records a) Understand and apply techniques used in incomplete record situations: [S] i) Use of accounting equation ii) Use of ledger accounts to calculate missing figures iii) Use of cash and/or bank summaries iv) Use of profit percentages to calculate missing figures. G PREPARING SIMPLE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 1. Subsidiaries a) Define and describe the following terms in the context of group accounting: [K] i) Parent ii) Subsidiary iii) Control iv) Consolidated or group financial statements v) Non-controlling interest vi) Trade / simple investment b) Identify subsidiaries within a group structure. [K] c) Describe the components of and prepare a consolidated statement of financial position or extracts thereof including: [S] i) Fair value adjustments at acquisition on land and buildings (excluding depreciation adjustments) ii) Fair value of consideration transferred from cash and shares (excluding deferred and contingent consideration) iii) Elimination of inter-company trading balances (excluding cash and goods in transit) iv) Removal of unrealised profit arising on inter-company trading v) Acquisition of subsidiaries part way through the financial year d) Calculate goodwill (excluding impairment of goodwill) using the full goodwill method only as follows: [S] Fair value of consideration X Fair value of non-controlling interest X Less fair value of net assets at acquisition (X) 12
13 Goodwill at acquisition e) Describe the components of and prepare a consolidated statement of comprehensive income or extracts thereof including: [S] i) Elimination of inter-company trading balances (excluding cash and goods in transit) ii) Removal of unrealised profit arising on inter-company trading iii) Acquisition of subsidiaries part way through the financial year X efficient use of resources and financial position [S]. b) Draw valid conclusions from the information contained within the financial statements and present these to the appropriate user of the financial statements. [S] 2. Associates a) Define and identify an associate and significant influence and identify the situations where significant influence or participating interest exists. [K] b) Describe the key features of a parent-associate relationship and be able to identify an associate within a group structure. [K] c) Describe the principle of equity accounting [K] H INTERPRETATION OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 1. Importance and purpose of analysis of financial statements a) Describe how the interpretation and analysis of financial statements is used in a business environment. [K] b) Explain the purpose of interpretation of ratios [K]. 2. Ratios a) Calculate key accounting ratios [S] i) Profitability ii) Liquidity iii) Efficiency iv) Position b) Explain the interrelationships between ratios [K] 3. Analysis of financial statements NOTE OF SIGNIFICANT CHANGES TO STUDY GUIDE PAPER FFA F3 a) Calculate and interpret the relationship between the elements of the financial statements with regard to profitability, liquidity, 13
14 ACCA periodically reviews its qualification syllabuses so that they fully meet the needs of stakeholders such as employers, students, regulatory and advisory bodies and learning providers. Table 1 Additions to FFA F3 There have not been any additions to the 2012 study guide for Table 2 Deletions to FFA F3 There have not been any deletions to the 2012 study guide for
Financial Accounting (FA)/FFA September 2018 to August 2019
 Financial Accounting (FA)/FFA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Financial Accounting (FA)/FFA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Financial Reporting (F7) December 2014 to June 2015
 Financial Reporting (F7) December 2014 to June 2015 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Financial Reporting (F7) December 2014 to June 2015 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016)
 Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016) This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide
Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016) This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide
Financial Reporting (F7) September 2017 to June 2018
 Financial Reporting (F7) September 2017 to June 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Financial Reporting (F7) September 2017 to June 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
(F2/FMA) December 2011
 Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
(F2/FMA) December 2011
 Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Financial Reporting (FR) Syllabus and study guide
 September 2018 to June 2019 Financial Reporting (FR) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
September 2018 to June 2019 Financial Reporting (FR) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Management (FFM) June and December 2013
 Foundations in F inancial Management (FFM) June and December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could
Foundations in F inancial Management (FFM) June and December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could
Management (FFM) June and December 2012
 Foundations in F inancial Management (FFM) June and December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could
Foundations in F inancial Management (FFM) June and December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could
Taxation (F6) Poland (POL) June & December 2014
 Taxation (F6) Poland (POL) June & December 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation (F6) Poland (POL) June & December 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation Botswana (BWA) (F6) June & December 2014
 Taxation Botswana (BWA) (F6) June & December 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation Botswana (BWA) (F6) June & December 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Financial Management (F9) June & December 2013
 Financial Management (F9) June & December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Financial Management (F9) June & December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Foundations in Taxation FTX (LSO) June & December 2018
 Foundations in Taxation FTX (LSO) June & December 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed
Foundations in Taxation FTX (LSO) June & December 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed
Taxation (F6) Zimbabwe (ZWE) June & December 2013
 Taxation (F6) Zimbabwe (ZWE) June & December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation (F6) Zimbabwe (ZWE) June & December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Financial Management (F9) 2011
 Financial Management (F9) 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE STRUCTURE
Financial Management (F9) 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE STRUCTURE
Financial Management (F9) June & December 2012
 Financial Management (F9) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Financial Management (F9) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019
 Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Financial Reporting (UK) (F7)
 Financial Reporting (UK) (F7) CR (P2) BA (P3) MAIN CAPABILITIES On successful completion of this paper, candidates should be able to: A Discuss and apply a conceptual framework for financial reporting
Financial Reporting (UK) (F7) CR (P2) BA (P3) MAIN CAPABILITIES On successful completion of this paper, candidates should be able to: A Discuss and apply a conceptual framework for financial reporting
ACCA Paper F3. FIA Diploma in Accounting and Business. Study Text
 ACCA Paper F3 and FIA Diploma in Accounting and Business Financial Accounting (FA/FFA) Study Text ISBN: 978-1-78740-051-1 ii KAPLAN PUBLISHING Contents Page Chapter 1 Introduction to financial reporting
ACCA Paper F3 and FIA Diploma in Accounting and Business Financial Accounting (FA/FFA) Study Text ISBN: 978-1-78740-051-1 ii KAPLAN PUBLISHING Contents Page Chapter 1 Introduction to financial reporting
Taxation (F6) Malawi (MWI) June & December 2012
 Taxation (F6) Malawi (MWI) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation (F6) Malawi (MWI) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Intermediate Bookkeeping
 Intermediate Bookkeeping Course map This document outlines the course structure. Course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: Getting your diploma Lesson 3: How do I study this course? Unit 1: Welcome
Intermediate Bookkeeping Course map This document outlines the course structure. Course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: Getting your diploma Lesson 3: How do I study this course? Unit 1: Welcome
Taxation (F6) Zimbabwe (ZWE) June & December 2014
 Taxation (F6) Zimbabwe (ZWE) June & December 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation (F6) Zimbabwe (ZWE) June & December 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation Vietnam (VNM)(F6) June & December 2017
 Taxation Vietnam (VNM)(F6) June & December 2017 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation Vietnam (VNM)(F6) June & December 2017 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation (F6) Lesotho (LSO) June & December 2017
 Taxation (F6) Lesotho (LSO) June & December 2017 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation (F6) Lesotho (LSO) June & December 2017 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
ACCA Paper F3. FIA Diploma in Accounting and Business. Complete Text
 ACCA Paper F3 and FIA Diploma in Accounting and Business Financial Accounting (FA/FFA) Complete Text British library cataloguing in publication data A catalogue record for this book is available from the
ACCA Paper F3 and FIA Diploma in Accounting and Business Financial Accounting (FA/FFA) Complete Text British library cataloguing in publication data A catalogue record for this book is available from the
Taxation (Cyprus) F6 (CYP) June & December 2014
 Taxation (Cyprus) F6 (CYP) June & December 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation (Cyprus) F6 (CYP) June & December 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Advanced Taxation Singapore (ATX-SGP) (P6)
 June 2018 to March 2019 Advanced Taxation Singapore (ATX-SGP) (P6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall
June 2018 to March 2019 Advanced Taxation Singapore (ATX-SGP) (P6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall
Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2012
 Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) June & December 2012
 Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2016
 Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2016 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2016 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) Exams in the year 1 April 2017 to 31 March 2018
 Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) Exams in the year 1 April 2017 to 31 March 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be
Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) Exams in the year 1 April 2017 to 31 March 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be
Taxation Vietnam (TX-VNM) (F6)
 June and December 2018 Taxation Vietnam (TX-VNM) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
June and December 2018 Taxation Vietnam (TX-VNM) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Taxation Poland (TX- POL) (F6)
 June and December 2018 Taxation Poland (TX- POL) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
June and December 2018 Taxation Poland (TX- POL) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Financial Management (FM) Syllabus and study guide
 September 2018 to June 2019 Financial Management (FM) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
September 2018 to June 2019 Financial Management (FM) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Advanced Taxation Cyprus (ATX- CYP) (P6)
 June & December 2018 Advanced Taxation Cyprus (ATX- CYP) (P6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
June & December 2018 Advanced Taxation Cyprus (ATX- CYP) (P6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Taxation Russia (TX-RUS) (F6)
 June 2018 & December 2018 Taxation Russia (TX-RUS) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
June 2018 & December 2018 Taxation Russia (TX-RUS) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Taxation (Cyprus) F6 (CYP) June & December 2016
 Taxation (Cyprus) F6 (CYP) June & December 2016 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation (Cyprus) F6 (CYP) June & December 2016 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2015
 Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2015 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Advanced Taxation (P6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2015 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation (F6) South Africa (ZAF) June & December 2017
 Taxation (F6) South Africa (ZAF) June & December 2017 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation (F6) South Africa (ZAF) June & December 2017 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation Singapore (TX- SGP) (F6)
 June 2018 to March 2019 Taxation Singapore (TX- SGP) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
June 2018 to March 2019 Taxation Singapore (TX- SGP) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) Exams in the year 1 April 2015 to 31 March 2016
 Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) Exams in the year 1 April 2015 to 31 March 2016 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be
Taxation - Singapore (SGP) (F6) Exams in the year 1 April 2015 to 31 March 2016 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be
Taxation South Africa (TX-ZAF) (F6)
 June and December 2018 Taxation South Africa (TX-ZAF) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
June and December 2018 Taxation South Africa (TX-ZAF) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Advanced Taxation (UK) (P6) June & December 2013
 Advanced Taxation (UK) (P6) June & December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Advanced Taxation (UK) (P6) June & December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation Malaysia (MYS)(F6) December 2013 & June 2014
 Taxation Malaysia (MYS)(F6) December 2013 & June 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
Taxation Malaysia (MYS)(F6) December 2013 & June 2014 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination
June and December Taxation Romania (F6) Syllabus and study guide
 June and December 2018 Taxation Romania (TX-ROM) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
June and December 2018 Taxation Romania (TX-ROM) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION
 ZIMBABWE MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS FORMS 5-6 2015 2022 Curriculum Development Unit P.O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant Harare All rights reserved 2015 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The
ZIMBABWE MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS FORMS 5-6 2015 2022 Curriculum Development Unit P.O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant Harare All rights reserved 2015 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The
Performance Management (F5) June 2008
 Performance Management (F5) June 2008 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE
Performance Management (F5) June 2008 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE
Taxation (UK) (F6) June & December 2013
 Taxation (UK) (F6) June & December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE
Taxation (UK) (F6) June & December 2013 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE
Foundations in Financial Management (FFM) September 2018 to June 2019
 Foundations in Financial Management (FFM) September 2018 to June 2019 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what
Foundations in Financial Management (FFM) September 2018 to June 2019 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what
Taxation (UK) (F6) June & December 2012
 Taxation (UK) (F6) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE
Taxation (UK) (F6) June & December 2012 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session. THE
Examiner s report F3 & FFA papers For CBE and Paper exams covering January to June 2016
 Examiner s report F3 & FFA papers For CBE and Paper exams covering January to June 2016 General Comments There are two sections to the examination paper and all of the questions are compulsory. Section
Examiner s report F3 & FFA papers For CBE and Paper exams covering January to June 2016 General Comments There are two sections to the examination paper and all of the questions are compulsory. Section
Taxation (F6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2015
 Taxation (F6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2015 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation (F6) Malta (MLA) June & December 2015 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting
 Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FA2-MA2.X Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Intermediate course orientation
Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FA2-MA2.X Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Intermediate course orientation
Foundations in Taxation FTX (UK) June and December 2018
 Foundations in Taxation FTX (UK) June and December 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed
Foundations in Taxation FTX (UK) June and December 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed
Advanced Financial Management (AFM)
 September 2018 to June 2019 Advanced Financial Management (AFM) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall
September 2018 to June 2019 Advanced Financial Management (AFM) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS GCE ORDINARY LEVEL (SYLLABUS 7092) INTRODUCTION The syllabus aims to develop an understanding of the principles and concepts of accounting and their applications in a variety of
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS GCE ORDINARY LEVEL (SYLLABUS 7092) INTRODUCTION The syllabus aims to develop an understanding of the principles and concepts of accounting and their applications in a variety of
Examiner s report F3 & FFA papers For CBE and Paper exams covering July to December 2017
 Examiner s report F3 & FFA papers For CBE and Paper exams covering July to December 2017 General Comments There are two sections to the examination paper and all of the questions are compulsory. Section
Examiner s report F3 & FFA papers For CBE and Paper exams covering July to December 2017 General Comments There are two sections to the examination paper and all of the questions are compulsory. Section
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 7110 GCE O Level FOR EXAMINATION IN Exclusions
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 7110 GCE O Level FOR EXAMINATION IN 2008 Exclusions This syllabus must not be offered in the same session with any of the following syllabuses: 0452 Accounting 0614 Accounting (Botswana)
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 7110 GCE O Level FOR EXAMINATION IN 2008 Exclusions This syllabus must not be offered in the same session with any of the following syllabuses: 0452 Accounting 0614 Accounting (Botswana)
Advanced Taxation (UK) (P6) Exams in the year 1 April 2017 to 31 March 2018
 Advanced Taxation (UK) (P6) Exams in the year 1 April 2017 to 31 March 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed
Advanced Taxation (UK) (P6) Exams in the year 1 April 2017 to 31 March 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwer
 qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwer Advanced Financial Management tyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuio pasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghj klzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxc vbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbn
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwer Advanced Financial Management tyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuio pasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasd fghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghj klzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxc vbnmqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbn
Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting
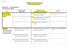 Suggested Revised BAFS Curriculum Draft as at 30 January 2013 Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting Topic Books of Original Entry and Types of Ledgers Explanatory Notes (original
Suggested Revised BAFS Curriculum Draft as at 30 January 2013 Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting Topic Books of Original Entry and Types of Ledgers Explanatory Notes (original
Diploma in International Financial Reporting December 2018 to June 2019
 Diploma in International Financial Reporting December 2018 to June 2019 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed
Diploma in International Financial Reporting December 2018 to June 2019 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed
IAB LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING TO INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS (Qualification Accreditation Number 500/3370/
 IAB LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING TO INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS (Qualification Accreditation Number 500/3370/ INTRODUCTION The overall aim of this qualification is to accredit candidates knowledge and understanding
IAB LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING TO INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS (Qualification Accreditation Number 500/3370/ INTRODUCTION The overall aim of this qualification is to accredit candidates knowledge and understanding
Taxation Malaysia (MYS)(F6) Exams in the year 1 October 2017 to 30 September 2018
 Taxation Malaysia (MYS)(F6) Exams in the year 1 October 2017 to 30 September 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could
Taxation Malaysia (MYS)(F6) Exams in the year 1 October 2017 to 30 September 2018 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could
IAB Level 3 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (RQF) Qualification Specification
 IAB Level 3 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (RQF) Qualification Specification Contents 1 Introduction to the qualification... 2 2 Statement of level... 2 3 Aims... 2 4 Target groups... 3 5 Entry
IAB Level 3 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (RQF) Qualification Specification Contents 1 Introduction to the qualification... 2 2 Statement of level... 2 3 Aims... 2 4 Target groups... 3 5 Entry
Taxation Pakistan (PKN)(F6) June & December 2017
 Taxation Pakistan (PKN)(F6) June & December 2017 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation Pakistan (PKN)(F6) June & December 2017 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Advanced Taxation Malta (ATX-MLA) Syllabus and study guide
 Advanced Taxation Malta (ATX-MLA) Syllabus and study guide June and December 2019 Summary of content Introduction 1. Intellectual levels 2. Learning hours and educational recognition 3. Guide to ACCA examination
Advanced Taxation Malta (ATX-MLA) Syllabus and study guide June and December 2019 Summary of content Introduction 1. Intellectual levels 2. Learning hours and educational recognition 3. Guide to ACCA examination
LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
 LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Lesotho General Certificate of Secondary Education Syllabus Accounting 0187 For examination in November 2018 National Curriculum Development Centre in
LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Lesotho General Certificate of Secondary Education Syllabus Accounting 0187 For examination in November 2018 National Curriculum Development Centre in
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING PART I
 PART I SECTION 1 CPA CIFA STUDY TEXT KASNEB JULY 2018 SYLLABUS Revised on: January 2019 www.someakenya.com Contact: Page 1 SYLLABUS PAPER NO 1: GENERAL OBJECTIVE This paper is intended to equip the candidate
PART I SECTION 1 CPA CIFA STUDY TEXT KASNEB JULY 2018 SYLLABUS Revised on: January 2019 www.someakenya.com Contact: Page 1 SYLLABUS PAPER NO 1: GENERAL OBJECTIVE This paper is intended to equip the candidate
ACCOUNTING FRAMEWORK(P1)
 (P1) KNOWLEDGE LEVEL TAX COMPLIANCE MALAW T THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS IN MALAWI I N Copyright The Institute of Chartered Accountants in Malawi 2014 The Institute of Chartered Accountants in
(P1) KNOWLEDGE LEVEL TAX COMPLIANCE MALAW T THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS IN MALAWI I N Copyright The Institute of Chartered Accountants in Malawi 2014 The Institute of Chartered Accountants in
IAB Level 4 Certificate in International Accounting Standards and IFRS 603/3017/X. Qualification Specification
 IAB Level 4 Certificate in International Accounting Standards and IFRS 603/3017/X Qualification Specification Contents 1 Introduction to the qualification... 2 2 Statement of level... 2 3 Aims... 2 4 Target
IAB Level 4 Certificate in International Accounting Standards and IFRS 603/3017/X Qualification Specification Contents 1 Introduction to the qualification... 2 2 Statement of level... 2 3 Aims... 2 4 Target
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION
 Republic of Namibia MINISTRY OF EDUCATION NAMIBIA SENIOR SECONDARY CERTIFICATE (NSSC) ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS ORDINARY LEVEL SYLLABUS CODE: 4345 GRADES 11-12 2010 DEVELOPED IN COLLABORATION WITH UNIVERSITY
Republic of Namibia MINISTRY OF EDUCATION NAMIBIA SENIOR SECONDARY CERTIFICATE (NSSC) ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS ORDINARY LEVEL SYLLABUS CODE: 4345 GRADES 11-12 2010 DEVELOPED IN COLLABORATION WITH UNIVERSITY
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education 0452 Accounting November 2014 Principal Examiner Report for Teachers
 ACCOUNTING Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education Paper 0452/11 Paper 11 Key Messages Questions can be set on any section of the syllabus and a good knowledge of all sections
ACCOUNTING Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education Paper 0452/11 Paper 11 Key Messages Questions can be set on any section of the syllabus and a good knowledge of all sections
FFA. Financial Accounting. OpenTuition.com ACCA FIA exams. Free resources for accountancy students
 September/December 2015 exams OpenTuition.com Free resources for accountancy students ACCA FIA F3 FFA Financial Accounting Please spread the word about OpenTuition, so that all ACCA students can benefit.
September/December 2015 exams OpenTuition.com Free resources for accountancy students ACCA FIA F3 FFA Financial Accounting Please spread the word about OpenTuition, so that all ACCA students can benefit.
ACCA Paper F3. Financial Accounting (INT) Class Notes
 ACCA Paper F3 Financial Accounting (INT) Class Notes June 2011 The Accountancy College Limited January 2011 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
ACCA Paper F3 Financial Accounting (INT) Class Notes June 2011 The Accountancy College Limited January 2011 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
Advanced Taxation United Kingdom (ATX-UK) (P6)
 June 2018 to March 2019 Advanced Taxation United Kingdom (ATX-UK) (P6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the
June 2018 to March 2019 Advanced Taxation United Kingdom (ATX-UK) (P6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the
Advanced Financial Accounting
 Advanced Financial Accounting Course Text Professional, Practical, Proven www.accountingtechniciansireland.ie 100034 Adv_ Fin_Acc_15 - Manual.indb 1 04/08/2015 15:19 100034 Adv_ Fin_Acc_15 - Manual.indb
Advanced Financial Accounting Course Text Professional, Practical, Proven www.accountingtechniciansireland.ie 100034 Adv_ Fin_Acc_15 - Manual.indb 1 04/08/2015 15:19 100034 Adv_ Fin_Acc_15 - Manual.indb
Mapping of. AAT s Accounting Qualifications (Revised 2016) SQA s HNC/HND Accounting (G9M5 15/G9M6 16)
 Mapping of AAT s Qualifications (Revised 2016) to SQA s HNC/HND (G9M5 15/G9M6 16) AAT s 1 Qualifications have been credit and levelled against the QCF and the SCQF. These revised Competence Based Qualifications
Mapping of AAT s Qualifications (Revised 2016) to SQA s HNC/HND (G9M5 15/G9M6 16) AAT s 1 Qualifications have been credit and levelled against the QCF and the SCQF. These revised Competence Based Qualifications
Please spread the word about OpenTuition, so that all ACCA students can benefit.
 ACCA COURSE NOTES June 2014 Examinations ACCA F3 FIA FFA Financial Accounting Please spread the word about OpenTuition, so that all ACCA students can benefit. ONLY with your support can the site exist
ACCA COURSE NOTES June 2014 Examinations ACCA F3 FIA FFA Financial Accounting Please spread the word about OpenTuition, so that all ACCA students can benefit. ONLY with your support can the site exist
Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011
 www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011 Note for Exams Officers: Before making Final Entries, please check
www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011 Note for Exams Officers: Before making Final Entries, please check
ICAN MID DIET LIVE CLASS FOR MAY DIET 2015 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Introduction to financial accounting Recording non-current assets and depreciation
 ICAN MID DIET LIVE CLASS FOR MAY DIET 2015 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Introduction to financial accounting Recording non-current assets and depreciation Compiling financial statement Compiling financial statement
ICAN MID DIET LIVE CLASS FOR MAY DIET 2015 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Introduction to financial accounting Recording non-current assets and depreciation Compiling financial statement Compiling financial statement
Activity to Develop and Demonstrate Competence. Describe the nature, scope and purposes of financial statements and their related records and accounts
 Paper 1 Financial Accounting Aim This paper aims at testing students understanding of the basic accounting principles, and their ability to apply concepts of financial accounting and methods to record
Paper 1 Financial Accounting Aim This paper aims at testing students understanding of the basic accounting principles, and their ability to apply concepts of financial accounting and methods to record
ACCOUNTING 2 (TC6) TECHNICIAN DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING ACCOUNTING 2 (TC6) THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS IN MALAWI
 TECHNICIAN DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING MALAW T THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS IN MALAWI I N January 2014 January 2014 BUSINE S S ACCOUNTING/2 CO L A W ( T N C 8 ) ACHNC NICIAN DIPLOM TECHNICIAN DIPLOMA
TECHNICIAN DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTING MALAW T THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS IN MALAWI I N January 2014 January 2014 BUSINE S S ACCOUNTING/2 CO L A W ( T N C 8 ) ACHNC NICIAN DIPLOM TECHNICIAN DIPLOMA
MINISTRY OF EDUCATION
 Republic of Namibia MINISTRY OF EDUCATION NAMIBIA SENIOR SECONDARY CERTIFICATE (NSSC) ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS HIGHER LEVEL SYLLABUS CODE: 8335 GRADES 11-12 2010 DEVELOPED IN COLLABORATION WITH UNIVERSITY OF
Republic of Namibia MINISTRY OF EDUCATION NAMIBIA SENIOR SECONDARY CERTIFICATE (NSSC) ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS HIGHER LEVEL SYLLABUS CODE: 8335 GRADES 11-12 2010 DEVELOPED IN COLLABORATION WITH UNIVERSITY OF
P7 Financial Accounting and Tax Principles
 Financial Management Pillar Managerial Level Paper P7 Financial Accounting and Tax Principles 26 November 2009 Thursday Afternoon Session Instructions to candidates You are allowed three hours to answer
Financial Management Pillar Managerial Level Paper P7 Financial Accounting and Tax Principles 26 November 2009 Thursday Afternoon Session Instructions to candidates You are allowed three hours to answer
Taxation United Kingdom (TX-UK) (F6)
 June 2018 to March 2019 Taxation United Kingdom (TX-UK) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
June 2018 to March 2019 Taxation United Kingdom (TX-UK) (F6) Syllabus and study guide Guide to structure of the syllabus and study guide Overall aim of the syllabus This explains briefly the overall objective
Advanced Financial Accounting
 Advanced Financial Accounting Course Text Professional, Practical, Proven www.accountingtechniciansireland.ie 111321_Adv_ Fin_Acc_17 - Manual.indb 1 02/06/2017 11:20 111321_Adv_ Fin_Acc_17 - Manual.indb
Advanced Financial Accounting Course Text Professional, Practical, Proven www.accountingtechniciansireland.ie 111321_Adv_ Fin_Acc_17 - Manual.indb 1 02/06/2017 11:20 111321_Adv_ Fin_Acc_17 - Manual.indb
Diploma in IFRS. Units with Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria
 Diploma in IFRS Units with Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria Unit 1-IASB and regulatory framework Understand the need and role of the regulatory system Describe the impact of globalization Describe
Diploma in IFRS Units with Learning Outcomes and Assessment Criteria Unit 1-IASB and regulatory framework Understand the need and role of the regulatory system Describe the impact of globalization Describe
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding
Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education 0452 Accounting June 2014 Principal Examiner Report for Teachers
 ACCOUNTING Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education Paper 0452/11 Paper 11 Key Messages Question 1 consisted of ten multiple choice items covering topics across the whole syllabus.
ACCOUNTING Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education Paper 0452/11 Paper 11 Key Messages Question 1 consisted of ten multiple choice items covering topics across the whole syllabus.
AM01 Syllabus (2019): Accounting AM SYLLABUS (2019) SYLLABUS
 ACCOUNTING AM SYLLABUS (2019) AM01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop the students financial literacy,
ACCOUNTING AM SYLLABUS (2019) AM01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop the students financial literacy,
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS GCE Ordinary Level (2017) (Syllabus 7175) CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 2 AIMS 2 ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES 3 SCHEME OF ASSESSMENT 4 USE OF CALCULATORS 4 SYLLABUS OUTLINE 5 SUBJECT CONTENT
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS GCE Ordinary Level (2017) (Syllabus 7175) CONTENTS Page INTRODUCTION 2 AIMS 2 ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES 3 SCHEME OF ASSESSMENT 4 USE OF CALCULATORS 4 SYLLABUS OUTLINE 5 SUBJECT CONTENT
Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (VRQ)
 L2 Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20093) SPECIFICATION Issue 3 First teaching from September 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting
L2 Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting (VRQ) (ASE20093) SPECIFICATION Issue 3 First teaching from September 2015 Pearson LCCI Level 2 Certificate in Bookkeeping and Accounting
Dawood Public School. Course Outline for Principles of Accounts. Class X
 Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus Code 7110 Course Books: Dawood Public School Course Outline for 2013-2014 Principles of Accounts Class X 1. Wood, Frank, Business Accounting, FT Pitman
Cambridge O Level Principles of Accounts Syllabus Code 7110 Course Books: Dawood Public School Course Outline for 2013-2014 Principles of Accounts Class X 1. Wood, Frank, Business Accounting, FT Pitman
Institute of Certified Bookkeepers
 Making you count Institute of Certified Bookkeepers Level II Certificate in Bookkeeping Syllabus from April 2014 1 Level II Certificate in Bookkeeping from April 2014 Course Code L2C Introduction Level
Making you count Institute of Certified Bookkeepers Level II Certificate in Bookkeeping Syllabus from April 2014 1 Level II Certificate in Bookkeeping from April 2014 Course Code L2C Introduction Level
Taxation Pakistan (PKN)(F6) June & December 2015
 Taxation Pakistan (PKN)(F6) June & December 2015 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
Taxation Pakistan (PKN)(F6) June & December 2015 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with planning study and to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any examination session.
+44 (0) International Accounting Standards (IAS) Guidance: Terminology and Presentation
 internationalenquiries@ediplc.com +44 (0) 2476 518951 www.lcci.org.uk International Accounting Standards (IAS) Guidance: Terminology and Presentation Contents Introduction 3 1 First Level 4 1.1 Terminology
internationalenquiries@ediplc.com +44 (0) 2476 518951 www.lcci.org.uk International Accounting Standards (IAS) Guidance: Terminology and Presentation Contents Introduction 3 1 First Level 4 1.1 Terminology
IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS
 IM Syllabus (2020): Accounting IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial
IM Syllabus (2020): Accounting IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ)
 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ) (ASE3012X) L3 SPECIFICATION Issue 2 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ) (ASE3012X) Specification Issue 2 Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications
Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ) (ASE3012X) L3 SPECIFICATION Issue 2 Pearson LCCI Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (VRQ) (ASE3012X) Specification Issue 2 Edexcel, BTEC and LCCI qualifications
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding of accounting
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding of accounting
