State and Local Government Employment and Final Demand (May 2000; Revised March 2009) U.S. Model
|
|
|
- Blaise Joseph
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 State and Local Government Employment and Final Demand (May 2000; Revised March 2009) The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) reports historical state government employment separate from local government employment at the county level. This data is used to estimate state and local final demand as separate components at the county level over history. All of this information together allows us to predict state government employment and final demand separately from local government employment and final demand for the forecast period. The methodology we implemented is based on the following basic assumptions: 1. Final per capita demand for state government employees is different by state but not by local area within a state. 2. Final per capita demand for local government employees is different for each local area (k). 3. Local government demand is always met by the local government in area k, but state government demand is not always met by the state government in local area k. This is because state government employees are usually centralized within a few local areas in a state instead of being distributed throughout the state. In addition, see Predicting State and Local Government Demand in Local Regions Based on Changes in Economic and Demographic Conditions (March 2008) for a full explanation of the state and local government final demand equations. U.S. Model For the U.S. model history, state government final demand is split from the BEA-reported state and local government final demand based on the BEA-reported state government employment as a share of state and local government employment. An analogous approach is used for estimating local government final FD u st,t = (E u st,t/e u stloc,t) * FD u stloc,t FD u loc,t = (E u loc,t/e u stloc,t) * FD u stloc,t FD u st,t = state government final demand for the U.S. in year t E u st,t = state government employment for the U.S. in year t, E u stloc,t = state and local government employment for the U.S. in year t FD u stloc,t = state and local government final demand for the U.S. in year t E u loc,t = local government employment for the U.S. in year t FD u loc,t = local government final demand for the U.S. in year t For the U.S. model forecast, state government final demand is split from the predicted state and local government final demand based on the last history year ratio of state government employment to state and local government employment. An analogous approach is used for predicting local government final FD u st,t = (E u st,t / E u stloc,t) * FD u stloc,t
2 FD u loc,t = (E u loc,t / E u stloc,t) * FD u stloc,t E u st,t = state government employment for the U.S. in the last history year E u stloc,t = state and local government employment for the U.S. in the last history year FD u stloc,t = state and local government final demand for the U.S. in year t E u loc,t = local government employment for the U.S. in the last history year State government employment is split from the predicted state and local government employment based on the predicted state government final demand as a share of predicted state and local government final E u st,t = (FD u st,t/fd u stloc,t) * E u stloc,t E u loc,t = (FD u loc,t/fd u stloc,t) * E u stloc,t E u st,t = state government employment for the U.S. in year t E u stloc,t = state and local government employment for the U.S. in year t E u loc,t = local government employment for the U.S. in year t State Models For a state model history, state government final demand and local government final demand are estimated based on econometric equations that take into account spending as a function of GDP and population. FD s st,t = R s st * [(GDP s t/n s t)/(gdp u t/n u t)] β * (FD u st,t / N u t) * N s t FD s loc,t = R s loc * [(GDP s t/n s t)/(gdp u t/n u t)] γ * (FD u loc,t / N u t) * N s t FD s st,t = state government final demand for the state in year t FD s loc,t = local government final demand for the state in year t R s st = local calibration factor for state government expenditures for the state R s loc = local calibration factor for local government expenditures for the state GDP s t = gross domestic product for the state in year t N s t = total population for the state in year t GDP u t = gross domestic product for the U.S. in year t N u t = total population for the U.S. in year t β = GDP elasticity of state government expenditures γ = GDP elasticity of local government expenditures For a state model forecast, state government final demand is predicted based on the state government final demand spending per person in the state in the last history year, the change in the state government spending per person in the U.S. relative to the last history year, the state s current year population, and the state s GDP per person relative to the nation and the last history year, raised to an econometrically estimated elasticity. An analogous approach is used for predicting local government final
3 FD s st,t = [(GDP s t/n s t)/(gdp u t/n u t)/(gdp s T/N s T)/(GDP u T/N u T)] β * [(FD u st,t / N u t) / (FD u st,t / N u T)] * (N s t/ N s T) * FD s st,t FD s loc,t = [(GDP s t/n s t)/(gdp u t/n u t)/(gdp s T/N s T)/(GDP u T/N u T)] γ * [(FD u loc,t / N u t) / (FD u loc,t / N u T)] * (N s t/ N s T) * FD s loc,t GDP s T = gross domestic product for the state in the last history year GDP u T = gross domestic product for the U.S. in the last history year N s T = total population for the state in the last history year N u T = total population for the U.S. in the last history year FD s st,t = state government final demand for the state in the last history year FD u st,t = state government final demand for the U.S. in the last history year FD s loc,t = local government final demand for the state in the last history year FD u loc,t = local government final demand for the U.S. in the last history year State government employment is predicted by applying the state government employment per dollar of state government final demand in the state to the predicted state government final demand in the state. An analogous approach is used for predicting local government employment. E s st,t = [(E u st,t /FD u st,t)/(e u st,t /FD u st,t)] * (E s st,t /FD s st,t) * FD s st,t E s loc,t = [(E u loc,t /FD u loc,t)/(e u loc,t /FD u loc,t)] * (E s loc,t /FD s loc,t) * FD s loc,t E s st,t = state government employment for the state in year t E s loc,t = local government employment for the state in year t E s st,t = state government employment for the state in the last history year E s loc,t = local government employment for the state in the last history year County Models For a county model history, state government final demand and local government final demand are estimated based on econometric equations that take into account spending as a function of GDP and population. The local calibration factor of the state is adjusted for the region s state and local government employment per capita. FD k st,t = R s st * [(E k st,t/n k T)/(E s st,t/n s T)] * [(GDP k t/n k t)/(gdp u t/n u t)] β * (FD u st,t / N u t) * N k t FD k loc,t = R s loc * [(E k loc,t/n k T)/(E s loc,t/n s T)] * [(GDP k t/n k t)/(gdp u t/n u t)] γ * (FD u loc,t / N u t) * N k t FD k st,t = state government final demand for local area k in year t FD k loc,t = local government final demand for local area k in year t E k st,t = state government employment for local area k in the last history year
4 E k loc,t = local government employment for local area k in the last history year N k T = total population for local area k in the last history year GDP k t = gross domestic product for local area k in year t N k t = total population for local area k in year t For a county model forecast, state government final demand is predicted based on the state government final demand spending per person in the county in the last history year, the change in the state government spending per person in the U.S. relative to the last history year, the local area s current year population, and the local area s GDP per person relative to the nation and the last history year, raised to an econometrically estimated elasticity. An analogous approach is used for predicting local government final FD k st,t = [(GDP k t/n k t)/(gdp u t/n u t)/(gdp k T/N k T)/(GDP u T/N u T)] β * [(FD u st,t / N u t) / (FD u st,t / N u T)] * (N k t/ N k T) * FD k st,t FD k loc,t = [(GDP k t/n k t)/(gdp u t/n u t)/(gdp s T/N s T)/(GDP u T/N u T)] γ * [(FD u loc,t / N u t) / (FD u loc,t / N u T)] * (N k t/ N k T) * FD k loc,t GDP k T = gross domestic product for local area k in the last history year FD k st,t = state government final demand for local area k in the last history year FD k loc,t = local government final demand for local area k in the last history year For a single-region model, state government employment is predicted based on the assumption that if the number of employees per dollar of final demand in the local area equals or exceeds the state average in the last history year, then the proportion of local demand supplied locally is set equal to one and the additional output is an export from that county. An example of this is a county where the state capitol is located. Likewise, if the number of employees per dollar of final demand in the local area is less than the state average in the last history year, then the proportion of local demand supplied locally is less than one, leading to less local employment than the local demand for state services would, on its own, suggest. RPC k st,t = ((FD s st,t / E s st,t) * E k st,t ) / FD k st,t EXP k st,t = ((E k st,t (FD k st,t * (E s st,t / FD s st,t))) / E u st,t ) * E u st,t If RPC < 1 If RPC = 1 E k st,t = [(E u st,t/fd u st,t)/(e u st,t/fd u st,t)] * (E s st,t /FD s st,t) * RPC st,t * FD k st,t E k st,t = {[(E u st,t/fd u st,t)/(e u st,t/fd u st,t)] * (E s st,t /FD s st,t) * FD k st,t} + EXP k st,t RPC k st,t = proportion of the local demand that is supplied locally for local area k in the last history year EXP k st,t = amount of state government employment in local area k based on demand from outside of local area k For a multiregion model, state government employment is predicted based on the assumption that there is state government trade that flows between the regions. Some regions export state government employees (e.g. counties where a state capitol is located) while other regions import state government employees.
5 EXPMR k st,t = ( k f s T * IMPMR l st,t) If all regions are in one state kf s T = EXPMR k st,t / IMPMR l st,t where l є s and IMPMR l st,t = sum of imports for all counties in the state If a multi-county model when k and g are not in the same state kf g T = 0 EXPMR k st,t =((FD s st,t / E s st,t) * E k st,t) - FD k st,t If negative EXPMR k st,t = 0 IMPMR l st,t = FD l st,t - ((FD s st,t / E s st,t) * E l st,t) If negative IMPMR l st,t = 0 IMPMR l st,t = FD l st,t - (((FD s st,t/e s st,t)*((fd u st,t/e u st,t)/(fd u st,t/e u st,t))*e l st,t) If negative IMPMR l st,t = 0 If RPC < 1 If RPC = 1 E k st,t = [(E u st,t/fd u st,t)/(e u st,t/fd u st,t)] * (E s st,t /FD s st,t) * RPC k st,t * FD k st,t E k st,t = [(E u st,t/fd u st,t)/(e u st,t/fd u st,t)] * (E s st,t /FD s st,t) * (FD k st,t + EXPMR k st,t) EXPMR k st,t = amount of state government in local area k attributable to demand in the other model regions, for time period t kf s T = state government trade flow coefficient for local area k within a state s, for the last history year IMPMR l st,t = amount of state government that local area l (where l є s) demands but is not able to supply, in time period t Local government employment is predicted by applying the local government employment per dollar of local government final demand in the county in the last history year, updated for the current year s change in national local government employment per dollar of local government final demand relative to the last history year, to the predicted local government final demand in the local area. E k loc,t = [(E u loc,t/fd u loc,t)/(e u loc,t/fd u loc,t)] * (E k loc,t /FD k loc,t) * FD k loc,t
Regional unemployment and welfare effects of the EU transport policies:
 Regional unemployment and welfare effects of the EU transport policies: recent results from an applied general equilibrium model Artem Korzhenevych, Johannes Broecker Institute for Regional Research, CAU-Kiel,
Regional unemployment and welfare effects of the EU transport policies: recent results from an applied general equilibrium model Artem Korzhenevych, Johannes Broecker Institute for Regional Research, CAU-Kiel,
The Measurement Procedure of AB2017 in a Simplified Version of McGrattan 2017
 The Measurement Procedure of AB2017 in a Simplified Version of McGrattan 2017 Andrew Atkeson and Ariel Burstein 1 Introduction In this document we derive the main results Atkeson Burstein (Aggregate Implications
The Measurement Procedure of AB2017 in a Simplified Version of McGrattan 2017 Andrew Atkeson and Ariel Burstein 1 Introduction In this document we derive the main results Atkeson Burstein (Aggregate Implications
Economic Impact of the Oklahoma Manufacturing Sector Winter 2018 Prepared by Prepared for
 Economic Impact of the Oklahoma Manufacturing Sector Winter 2018 Prepared by Prepared for Population, Labor Force, & Employment Summary Population in any given year is determined by adding the net natural
Economic Impact of the Oklahoma Manufacturing Sector Winter 2018 Prepared by Prepared for Population, Labor Force, & Employment Summary Population in any given year is determined by adding the net natural
v1.7 (changes from PI + v1.6r)
 v1.7 (changes from PI + v1.6r) Major Economic Data Sources Employment County BEA LAPI (sector industries; 2001-2013) 1 2 State BEA SPI (summary industries; 1998-2013) 3 National BEA SPI (summary industries;
v1.7 (changes from PI + v1.6r) Major Economic Data Sources Employment County BEA LAPI (sector industries; 2001-2013) 1 2 State BEA SPI (summary industries; 1998-2013) 3 National BEA SPI (summary industries;
The Effect of Interventions to Reduce Fertility on Economic Growth. Quamrul Ashraf Ashley Lester David N. Weil. Brown University.
 The Effect of Interventions to Reduce Fertility on Economic Growth Quamrul Ashraf Ashley Lester David N. Weil Brown University December 2007 Goal: analyze quantitatively the economic effects of interventions
The Effect of Interventions to Reduce Fertility on Economic Growth Quamrul Ashraf Ashley Lester David N. Weil Brown University December 2007 Goal: analyze quantitatively the economic effects of interventions
Forecasting State and Local Government Spending: Model Re-estimation. January Equation
 Forecasting State and Local Government Spending: Model Re-estimation January 2015 Equation The REMI government spending estimation assumes that the state and local government demand is driven by the regional
Forecasting State and Local Government Spending: Model Re-estimation January 2015 Equation The REMI government spending estimation assumes that the state and local government demand is driven by the regional
Gross Domestic Product: What It Is and How It Is Measured. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all final user goods and services
 Gross Domestic Product: What It Is and How It Is Measured Tawni Hunt Ferrarini Northern Michigan University James Gwartney Florida State University Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all
Gross Domestic Product: What It Is and How It Is Measured Tawni Hunt Ferrarini Northern Michigan University James Gwartney Florida State University Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the market value of all
Objectives of the lecture
 Assessing the External Position Bank Indonesia International Workshop and Seminar Central Bank Policy Mix: Issues, Challenges, and Policies Jakarta, 9-13 April 2018 Rajan Govil The views expressed herein
Assessing the External Position Bank Indonesia International Workshop and Seminar Central Bank Policy Mix: Issues, Challenges, and Policies Jakarta, 9-13 April 2018 Rajan Govil The views expressed herein
Movement of Capital: Multinational Corporations and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) EC 378 November 30, December 5, 2006
 Movement of Capital: Multinational Corporations and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) EC 378 November 30, December 5, 2006 Motivation Factor movements and trade: o Over one quarter of world trade is intra-firm
Movement of Capital: Multinational Corporations and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) EC 378 November 30, December 5, 2006 Motivation Factor movements and trade: o Over one quarter of world trade is intra-firm
Empirical appendix of Public Expenditure Distribution, Voting, and Growth
 Empirical appendix of Public Expenditure Distribution, Voting, and Growth Lorenzo Burlon August 11, 2014 In this note we report the empirical exercises we conducted to motivate the theoretical insights
Empirical appendix of Public Expenditure Distribution, Voting, and Growth Lorenzo Burlon August 11, 2014 In this note we report the empirical exercises we conducted to motivate the theoretical insights
Aggregated Binary Logit Modal-Split Model Calibration: An Evaluation for Istanbul
 Aggregated Binary Logit Modal-Split Model Calibration: An Evaluation for Istanbul H. B. Celikoglu a,1 and M. Akad a,2 a Technical University of Istanbul Dept. of Transportation, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Aggregated Binary Logit Modal-Split Model Calibration: An Evaluation for Istanbul H. B. Celikoglu a,1 and M. Akad a,2 a Technical University of Istanbul Dept. of Transportation, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
v2.2 (changes from PI + v2.1)
 v2.2 (changes from PI + v2.1) Major Economic Data Sources Employment County BEA LAPI (sector industries; 2001-2016) 1 State BEA SPI (summary industries; 2001-2016) 2 National BEA SPI (summary industries;
v2.2 (changes from PI + v2.1) Major Economic Data Sources Employment County BEA LAPI (sector industries; 2001-2016) 1 State BEA SPI (summary industries; 2001-2016) 2 National BEA SPI (summary industries;
Real Business Cycles in Emerging Countries?
 Real Business Cycles in Emerging Countries? Javier García-Cicco, Roberto Pancrazi and Martín Uribe Published in American Economic Review (2010) Presented by Onursal Bağırgan Real Business Cycles in Emerging
Real Business Cycles in Emerging Countries? Javier García-Cicco, Roberto Pancrazi and Martín Uribe Published in American Economic Review (2010) Presented by Onursal Bağırgan Real Business Cycles in Emerging
Partial Equilibrium Model: An Example. ARTNet Capacity Building Workshop for Trade Research Phnom Penh, Cambodia 2-6 June 2008
 Partial Equilibrium Model: An Example ARTNet Capacity Building Workshop for Trade Research Phnom Penh, Cambodia 2-6 June 2008 Outline Graphical Analysis Mathematical formulation Equations Parameters Endogenous
Partial Equilibrium Model: An Example ARTNet Capacity Building Workshop for Trade Research Phnom Penh, Cambodia 2-6 June 2008 Outline Graphical Analysis Mathematical formulation Equations Parameters Endogenous
Inflation, Output, and Nominal Money. Growth
 Money Money Department of Economics, University of Vienna May 25 th, 2011 Money The AS-AD model dealt with the relation between output and the price level In this chapter we extend the AS-AD model to examine
Money Money Department of Economics, University of Vienna May 25 th, 2011 Money The AS-AD model dealt with the relation between output and the price level In this chapter we extend the AS-AD model to examine
EMBARGOED UNTIL RELEASE AT 3:00 P.M. EST, WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 13, 2016
 NEWS RELEASE EMBARGOED UNTIL RELEASE AT 3:00 P.M. EST, WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 13, 2016 Aya Hamano: (202) 606-9683 (BEA) BEA 16-02 Tanya Harris Joshua: (202) 208-6008 (OIA) THE BUREAU OF ECONOMIC ANALYSIS (BEA)
NEWS RELEASE EMBARGOED UNTIL RELEASE AT 3:00 P.M. EST, WEDNESDAY, JANUARY 13, 2016 Aya Hamano: (202) 606-9683 (BEA) BEA 16-02 Tanya Harris Joshua: (202) 208-6008 (OIA) THE BUREAU OF ECONOMIC ANALYSIS (BEA)
Risk management methodology in Latvian economics
 Risk management methodology in Latvian economics Dr.sc.ing. Irina Arhipova irina@cs.llu.lv Latvia University of Agriculture Faculty of Information Technologies, Liela street 2, Jelgava, LV-3001 Fax: +
Risk management methodology in Latvian economics Dr.sc.ing. Irina Arhipova irina@cs.llu.lv Latvia University of Agriculture Faculty of Information Technologies, Liela street 2, Jelgava, LV-3001 Fax: +
Modeling Tax Return on TV, Film, and Digital Media Incentives in Michigan
 Modeling Tax Return on TV, Film, and Digital Media Incentives in Michigan PREPARED BY Regional Economic Models, Inc. (REMI) Rod Motamedi, Senior Economic Associate Huaqun Li, Ph.D., Regional Economist
Modeling Tax Return on TV, Film, and Digital Media Incentives in Michigan PREPARED BY Regional Economic Models, Inc. (REMI) Rod Motamedi, Senior Economic Associate Huaqun Li, Ph.D., Regional Economist
DRC. Factor Decomposition of Share change of Tertiary Industry in China Comparison with South Korea. Zhaoyuan Xu Shantong Li
 DRC DEVELOPMENT RESEARCH CENTER OF THE STATE COUNCIL Factor Decomposition of Share change of Tertiary DRC Industry in China Comparison with South Korea Zhaoyuan Xu Shantong Li Development Research of the
DRC DEVELOPMENT RESEARCH CENTER OF THE STATE COUNCIL Factor Decomposition of Share change of Tertiary DRC Industry in China Comparison with South Korea Zhaoyuan Xu Shantong Li Development Research of the
New York City Tax Effort: Historical Tables. Gross Taxable Resources: Tables 1 and 2 and Figure 1
 June 2018 New York City Tax Effort: Historical Tables This set of tables and charts traces historical trends in gross taxable resources (GTR) and tax effort in New York City. As in previous IBO reports,
June 2018 New York City Tax Effort: Historical Tables This set of tables and charts traces historical trends in gross taxable resources (GTR) and tax effort in New York City. As in previous IBO reports,
Fiscal Impact Analysis of the North Carolina Rural Job Creation Fund
 Fiscal Impact Analysis of the North Carolina Rural Job Creation Fund Prepared for: Stonehenge Capital Company, LLC. Copyright 2017 All Rights Reserved Economic Impact Group, LLC. Dacula, GA 30019 March
Fiscal Impact Analysis of the North Carolina Rural Job Creation Fund Prepared for: Stonehenge Capital Company, LLC. Copyright 2017 All Rights Reserved Economic Impact Group, LLC. Dacula, GA 30019 March
Main Features. Aid, Public Investment, and pro-poor Growth Policies. Session 4 An Operational Macroeconomic Framework for Ethiopia
 Aid, Public Investment, and pro-poor Growth Policies Addis Ababa, August 16-19, 2004 Session 4 An Operational Macroeconomic Framework for Ethiopia Pierre-Richard Agénor Main features. Public capital and
Aid, Public Investment, and pro-poor Growth Policies Addis Ababa, August 16-19, 2004 Session 4 An Operational Macroeconomic Framework for Ethiopia Pierre-Richard Agénor Main features. Public capital and
U.S. Food Manufacturing Industry: The Choice of Exports vs. FDI
 U.S. Food Manufacturing Industry: The Choice of Exports vs. FDI Mahdi Asgari PhD student, University of Kentucky Mahdi.asgari@uky.edu Selected Paper prepared for presentation at the Southern Agricultural
U.S. Food Manufacturing Industry: The Choice of Exports vs. FDI Mahdi Asgari PhD student, University of Kentucky Mahdi.asgari@uky.edu Selected Paper prepared for presentation at the Southern Agricultural
Capital Income Tax Reform and the Japanese Economy (Very Preliminary and Incomplete)
 Capital Income Tax Reform and the Japanese Economy (Very Preliminary and Incomplete) Gary Hansen (UCLA), Selo İmrohoroğlu (USC), Nao Sudo (BoJ) December 22, 2015 Keio University December 22, 2015 Keio
Capital Income Tax Reform and the Japanese Economy (Very Preliminary and Incomplete) Gary Hansen (UCLA), Selo İmrohoroğlu (USC), Nao Sudo (BoJ) December 22, 2015 Keio University December 22, 2015 Keio
Gravity in the Weightless Economy
 Gravity in the Weightless Economy Wolfgang Keller University of Colorado and Stephen Yeaple Penn State University NBER ITI Summer Institute 2010 1 Technology transfer and firms in international trade How
Gravity in the Weightless Economy Wolfgang Keller University of Colorado and Stephen Yeaple Penn State University NBER ITI Summer Institute 2010 1 Technology transfer and firms in international trade How
Austerity in the Aftermath of the Great Recession
 Austerity in the Aftermath of the Great Recession Christopher L. House University of Michigan and NBER. Christian Proebsting EPFL École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Linda Tesar University of Michigan
Austerity in the Aftermath of the Great Recession Christopher L. House University of Michigan and NBER. Christian Proebsting EPFL École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne Linda Tesar University of Michigan
Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in Some MENA Countries: Theory and Evidence
 Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Topics in Middle Eastern and orth African Economies Quinlan School of Business 1999 Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in Some MEA Countries: Theory
Loyola University Chicago Loyola ecommons Topics in Middle Eastern and orth African Economies Quinlan School of Business 1999 Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Growth in Some MEA Countries: Theory
Online Appendix to: The Composition Effects of Tax-Based Consolidations on Income Inequality. June 19, 2017
 Online Appendix to: The Composition Effects of Tax-Based Consolidations on Income Inequality June 19, 2017 1 Table of contents 1 Robustness checks on baseline regression... 1 2 Robustness checks on composition
Online Appendix to: The Composition Effects of Tax-Based Consolidations on Income Inequality June 19, 2017 1 Table of contents 1 Robustness checks on baseline regression... 1 2 Robustness checks on composition
14.02 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set # 2, Answers
 14.0 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set #, Answers Part I 1. False. The multiplier is 1/ [1- c 1 (1- t)]. The effect of an increase in autonomous spending is dampened because taxes respond proportionally
14.0 Principles of Macroeconomics Problem Set #, Answers Part I 1. False. The multiplier is 1/ [1- c 1 (1- t)]. The effect of an increase in autonomous spending is dampened because taxes respond proportionally
Preliminary draft, please do not quote
 Quantifying the Economic Impact of U.S. Offshoring Activities in China and Mexico a GTAP-FDI Model Perspective Marinos Tsigas (Marinos.Tsigas@usitc.gov) and Wen Jin Jean Yuan ((WenJin.Yuan@usitc.gov) Introduction
Quantifying the Economic Impact of U.S. Offshoring Activities in China and Mexico a GTAP-FDI Model Perspective Marinos Tsigas (Marinos.Tsigas@usitc.gov) and Wen Jin Jean Yuan ((WenJin.Yuan@usitc.gov) Introduction
Aviation Economics & Finance
 Aviation Economics & Finance Professor David Gillen (University of British Columbia )& Professor Tuba Toru-Delibasi (Bahcesehir University) Istanbul Technical University Air Transportation Management M.Sc.
Aviation Economics & Finance Professor David Gillen (University of British Columbia )& Professor Tuba Toru-Delibasi (Bahcesehir University) Istanbul Technical University Air Transportation Management M.Sc.
Economic Growth Chapter 12 Section Main Menu
 Economic Growth 12.3 How do economists measure economic growth? What is capital deepening? How are saving and investing related to economic growth? How does technological progress affect economic growth?
Economic Growth 12.3 How do economists measure economic growth? What is capital deepening? How are saving and investing related to economic growth? How does technological progress affect economic growth?
Introducing OLG-CGE modelling and the National institute General Equilibrium model for studying population Ageing, NiAGE
 Introducing OLG-CGE modelling and the National institute General Equilibrium model for studying population Ageing, NiAGE NIESR, London, February 18, 2013 Katerina Lisenkova Financial support from the Economic
Introducing OLG-CGE modelling and the National institute General Equilibrium model for studying population Ageing, NiAGE NIESR, London, February 18, 2013 Katerina Lisenkova Financial support from the Economic
Domestic and Foreign Debt: Global Projections to 2050
 Domestic and Foreign Debt: Global Projections to 2050 John L Perkins National Institute of Economics and Industry Research, Melbourne. Project LINK, 26 October 2011 Outline Long term model features Government
Domestic and Foreign Debt: Global Projections to 2050 John L Perkins National Institute of Economics and Industry Research, Melbourne. Project LINK, 26 October 2011 Outline Long term model features Government
Chapter 12: Gross Domestic Product and Growth Section 3
 Chapter 12: Gross Domestic Product and Growth Section 3 Objectives 1. Analyze how economic growth is measured. 2. Explain what capital deepening is and how it contributes to economic growth. 3. Analyze
Chapter 12: Gross Domestic Product and Growth Section 3 Objectives 1. Analyze how economic growth is measured. 2. Explain what capital deepening is and how it contributes to economic growth. 3. Analyze
CHAPTER 8. MACROECONOMIC SUPPLY AND DEMAND
 CHAPTER 8. MACROECONOMIC SUPPLY AND DEMAND There are four markets of primary interest to macroeconomics: Product, Credit, Labor, and Foreign Exchange. Each can be modeled using supply and demand. For each
CHAPTER 8. MACROECONOMIC SUPPLY AND DEMAND There are four markets of primary interest to macroeconomics: Product, Credit, Labor, and Foreign Exchange. Each can be modeled using supply and demand. For each
Macroeconomic Analysis and Parametric Control of Economies of the Customs Union Countries Based on the Single Global Multi- Country Model
 Macroeconomic Analysis and Parametric Control of Economies of the Customs Union Countries Based on the Single Global Multi- Country Model Abdykappar A. Ashimov, Yuriy V. Borovskiy, Nikolay Yu. Borovskiy
Macroeconomic Analysis and Parametric Control of Economies of the Customs Union Countries Based on the Single Global Multi- Country Model Abdykappar A. Ashimov, Yuriy V. Borovskiy, Nikolay Yu. Borovskiy
Growth 2. Chapter 6 (continued)
 Growth 2 Chapter 6 (continued) 1. Solow growth model continued 2. Use the model to understand growth 3. Endogenous growth 4. Labor and goods markets with growth 1 Solow Model with Exogenous Labor-Augmenting
Growth 2 Chapter 6 (continued) 1. Solow growth model continued 2. Use the model to understand growth 3. Endogenous growth 4. Labor and goods markets with growth 1 Solow Model with Exogenous Labor-Augmenting
Visualizing GDP: An Inside Look at the Q3 ThirdEstimate
 Visualizing GDP: An Inside Look at the Q3 ThirdEstimate December 24, 2018 by Jill Mislinski of Advisor Perspectives Note: The charts in this commentary have been updated to include the Q3 2018 Third Estimate
Visualizing GDP: An Inside Look at the Q3 ThirdEstimate December 24, 2018 by Jill Mislinski of Advisor Perspectives Note: The charts in this commentary have been updated to include the Q3 2018 Third Estimate
Proximity vs Comparative Advantage: A Quantitative Theory of Trade and Multinational Production
 Proximity vs Comparative Advantage: A Quantitative Theory of Trade and Multinational Production Costas Arkolakis, Natalia Ramondo, Andres Rodriguez-Clare, Stephen Yeaple June 2011 Motivation WSJ (April
Proximity vs Comparative Advantage: A Quantitative Theory of Trade and Multinational Production Costas Arkolakis, Natalia Ramondo, Andres Rodriguez-Clare, Stephen Yeaple June 2011 Motivation WSJ (April
THE VOODOO ECONOMICS OF PHASING OUT OKLAHOMA S PERSONAL INCOME TAX: Kent Olson, Professor of Economics Emeritus, Oklahoma State University
 THE VOODOO ECONOMICS OF PHASING OUT OKLAHOMA S PERSONAL INCOME TAX: Kent Olson, Professor of Economics Emeritus, Oklahoma State University March 14, 2012 It is well known that taxes are one of the variables
THE VOODOO ECONOMICS OF PHASING OUT OKLAHOMA S PERSONAL INCOME TAX: Kent Olson, Professor of Economics Emeritus, Oklahoma State University March 14, 2012 It is well known that taxes are one of the variables
The 2015 Economic Impact Study of the Recreation Vehicle Industry
 The 2015 Economic Impact Study of the Recreation Vehicle Industry Methodology Prepared for Recreation Vehicle Industry Association 1896 Preston White Drive Reston, VA 20191 By John Dunham & Associates,
The 2015 Economic Impact Study of the Recreation Vehicle Industry Methodology Prepared for Recreation Vehicle Industry Association 1896 Preston White Drive Reston, VA 20191 By John Dunham & Associates,
Dissertation Proposal Presentation
 Dissertation Proposal Presentation Economic Growth and Welfare Improvement from High-Speed Internet Theeradej Suabtrirat, PhD in Economics Student. Wednesday, May 6 th, 2015 at 2.30-3.30pm. Economics Library
Dissertation Proposal Presentation Economic Growth and Welfare Improvement from High-Speed Internet Theeradej Suabtrirat, PhD in Economics Student. Wednesday, May 6 th, 2015 at 2.30-3.30pm. Economics Library
APPENDIX A Input-Output Analysis: Technical Description and Application
 APPENDIX A Input-Output Analysis: Technical Description and Application Economic Impacts of Historic Preservation in Florida A-1 A-2 Economic Impacts of Historic Preservation in Florida The Preservation
APPENDIX A Input-Output Analysis: Technical Description and Application Economic Impacts of Historic Preservation in Florida A-1 A-2 Economic Impacts of Historic Preservation in Florida The Preservation
TRS Benefit Payments by Illinois Legislative District & Their Impact on the Illinois Economy
 TRS Benefit Payments by Illinois Legislative District & Their Impact on the Illinois Economy Study Results May 2, 2008 Teachers Retirement System of the State of Illinois Two parts to this study: First
TRS Benefit Payments by Illinois Legislative District & Their Impact on the Illinois Economy Study Results May 2, 2008 Teachers Retirement System of the State of Illinois Two parts to this study: First
Accounting for the Sources of Macroeconomic Tail Risks
 Accounting for the Sources of Macroeconomic Tail Risks Enghin Atalay, Thorsten Drautzburg, and Zhenting Wang January 31, 2018 Abstract Using a multi-industry real business cycle model, we empirically examine
Accounting for the Sources of Macroeconomic Tail Risks Enghin Atalay, Thorsten Drautzburg, and Zhenting Wang January 31, 2018 Abstract Using a multi-industry real business cycle model, we empirically examine
Specific factor endowments and trade I
 Specific factor endowments and trade I Part B: Small open economy Part C: Two open economies (intro) Robert Stehrer The Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies - wiiw April 14, 2015 1 Small
Specific factor endowments and trade I Part B: Small open economy Part C: Two open economies (intro) Robert Stehrer The Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies - wiiw April 14, 2015 1 Small
Macroeconomics CHAPTER 7. Tracking the Macroeconomy
 Macroeconomics CHAPTER 7 Tracking the Macroeconomy PowerPoint Slides by Can Erbil 2006 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved What you will learn in this chapter: How economists use aggregate measures to
Macroeconomics CHAPTER 7 Tracking the Macroeconomy PowerPoint Slides by Can Erbil 2006 Worth Publishers, all rights reserved What you will learn in this chapter: How economists use aggregate measures to
Economic impact, Cargill Fertilizer, Inc
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons College of Business Publications College of Business 6-15-1999 Economic impact, Cargill Fertilizer, Inc Dennis G. Colie University of South Florida. Center for
University of South Florida Scholar Commons College of Business Publications College of Business 6-15-1999 Economic impact, Cargill Fertilizer, Inc Dennis G. Colie University of South Florida. Center for
REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON TRAFFIC FORECASTING AND ECONOMIC PLANNING
 International Civil Aviation Organization 27/8/10 WORKING PAPER REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON TRAFFIC FORECASTING AND ECONOMIC PLANNING Cairo 2 to 4 November 2010 Agenda Item 3 a): Forecasting Methodology (Presented
International Civil Aviation Organization 27/8/10 WORKING PAPER REGIONAL WORKSHOP ON TRAFFIC FORECASTING AND ECONOMIC PLANNING Cairo 2 to 4 November 2010 Agenda Item 3 a): Forecasting Methodology (Presented
Keynesian Views On The Fiscal Multiplier
 Faculty of Social Sciences Jeppe Druedahl (Ph.d. Student) Department of Economics 16th of December 2013 Slide 1/29 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 16th of December 2013 Slide 2/29 The For Today 1 Some 2 A Benchmark
Faculty of Social Sciences Jeppe Druedahl (Ph.d. Student) Department of Economics 16th of December 2013 Slide 1/29 Outline 1 2 3 4 5 16th of December 2013 Slide 2/29 The For Today 1 Some 2 A Benchmark
LECTURE 5 The Effects of Fiscal Changes: Cross-Section Evidence. September 21, 2016
 Economics 210c/236a Fall 2016 Christina Romer David Romer LECTURE 5 The Effects of Fiscal Changes: Cross-Section Evidence September 21, 2016 I. OVERVIEW OF STATE-BASED STUDIES OF THE IMPACT OF FISCAL CHANGES
Economics 210c/236a Fall 2016 Christina Romer David Romer LECTURE 5 The Effects of Fiscal Changes: Cross-Section Evidence September 21, 2016 I. OVERVIEW OF STATE-BASED STUDIES OF THE IMPACT OF FISCAL CHANGES
ECON 3020: ACCELERATED MACROECONOMICS. Question 1: Inflation Expectations and Real Money Demand (20 points)
 ECON 3020: ACCELERATED MACROECONOMICS SOLUTIONS TO PRELIMINARY EXAM 03/05/2015 Instructor: Karel Mertens Question 1: Inflation Expectations and Real Money Demand (20 points) Suppose that the real money
ECON 3020: ACCELERATED MACROECONOMICS SOLUTIONS TO PRELIMINARY EXAM 03/05/2015 Instructor: Karel Mertens Question 1: Inflation Expectations and Real Money Demand (20 points) Suppose that the real money
Simulation Model of the Irish Local Economy: Short and Medium Term Projections of Household Income
 Simulation Model of the Irish Local Economy: Short and Medium Term Projections of Household Income Cathal O Donoghue, John Lennon, Jason Loughrey and David Meredith Teagasc Rural Economy and Development
Simulation Model of the Irish Local Economy: Short and Medium Term Projections of Household Income Cathal O Donoghue, John Lennon, Jason Loughrey and David Meredith Teagasc Rural Economy and Development
Productivity and the Post-1990 U.S. Economy
 Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Research Department Staff Report 350 November 2004 Productivity and the Post-1990 U.S. Economy Ellen R. McGrattan Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and University
Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Research Department Staff Report 350 November 2004 Productivity and the Post-1990 U.S. Economy Ellen R. McGrattan Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis and University
. Fiscal Reform and Government Debt in Japan: A Neoclassical Perspective. May 10, 2013
 .. Fiscal Reform and Government Debt in Japan: A Neoclassical Perspective Gary Hansen (UCLA) and Selo İmrohoroğlu (USC) May 10, 2013 Table of Contents.1 Introduction.2 Model Economy.3 Calibration.4 Quantitative
.. Fiscal Reform and Government Debt in Japan: A Neoclassical Perspective Gary Hansen (UCLA) and Selo İmrohoroğlu (USC) May 10, 2013 Table of Contents.1 Introduction.2 Model Economy.3 Calibration.4 Quantitative
Fiscal and Monetary Policy in the Growth Model. Introduction
 Introduction Fiscal and Monetary Policy in the Growth Model A. Our focus will be on fiscal and monetary policies over a longtime horizon. (ex. 10 years) B. Ex. The federal budget deficit was much higher
Introduction Fiscal and Monetary Policy in the Growth Model A. Our focus will be on fiscal and monetary policies over a longtime horizon. (ex. 10 years) B. Ex. The federal budget deficit was much higher
Export markets and labor allocation in a low-income country. Brian McCaig and Nina Pavcnik. Online Appendix
 Export markets and labor allocation in a low-income country Brian McCaig and Nina Pavcnik Online Appendix Appendix A: Supplemental Tables for Sections III-IV Page 1 of 29 Appendix Table A.1: Growth of
Export markets and labor allocation in a low-income country Brian McCaig and Nina Pavcnik Online Appendix Appendix A: Supplemental Tables for Sections III-IV Page 1 of 29 Appendix Table A.1: Growth of
Practical example of an Economic Scenario Generator
 Practical example of an Economic Scenario Generator Martin Schenk Actuarial & Insurance Solutions SAV 7 March 2014 Agenda Introduction Deterministic vs. stochastic approach Mathematical model Application
Practical example of an Economic Scenario Generator Martin Schenk Actuarial & Insurance Solutions SAV 7 March 2014 Agenda Introduction Deterministic vs. stochastic approach Mathematical model Application
Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Business Commons
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons College of Business Publications College of Business 10-1-2000 Economic contributions - Big Bend Transfer Company : an analysis performed by Center for Economic
University of South Florida Scholar Commons College of Business Publications College of Business 10-1-2000 Economic contributions - Big Bend Transfer Company : an analysis performed by Center for Economic
LECTURE 6 The Effects of Fiscal Changes: Cross-Section Evidence. September 26, 2018
 Economics 210c/236a Fall 2018 Christina Romer David Romer LECTURE 6 The Effects of Fiscal Changes: Cross-Section Evidence September 26, 2018 Office Hours No office hours this Thursday (9/27). Office hours
Economics 210c/236a Fall 2018 Christina Romer David Romer LECTURE 6 The Effects of Fiscal Changes: Cross-Section Evidence September 26, 2018 Office Hours No office hours this Thursday (9/27). Office hours
Entry, Trade Costs and International Business Cycles
 Entry, Trade Costs and International Business Cycles Roberto Fattal and Jose Lopez UCLA SED Meetings July 10th 2010 Entry, Trade Costs and International Business Cycles SED Meetings July 10th 2010 1 /
Entry, Trade Costs and International Business Cycles Roberto Fattal and Jose Lopez UCLA SED Meetings July 10th 2010 Entry, Trade Costs and International Business Cycles SED Meetings July 10th 2010 1 /
The Effectiveness of Non-traditional Monetary Policy and the Inflation Target Policy : The Case of Japan in Comparison with the US
 Economics & Management Series EMS-2013-11 The Effectiveness of Non-traditional Monetary Policy and the Inflation Target Policy : The Case of Japan in Comparison with the US Osamu Nakamura International
Economics & Management Series EMS-2013-11 The Effectiveness of Non-traditional Monetary Policy and the Inflation Target Policy : The Case of Japan in Comparison with the US Osamu Nakamura International
Economic Impacts of the First 5 Placer Children & Families Commission s Funded Programs
 Economic Impacts of the First 5 Placer Children & Families Commission s Funded Programs May 18, 2011 Prepared for: First 5 Placer Children & Families Commission 365 Nevada Street Auburn, CA 95603 530/745-1304
Economic Impacts of the First 5 Placer Children & Families Commission s Funded Programs May 18, 2011 Prepared for: First 5 Placer Children & Families Commission 365 Nevada Street Auburn, CA 95603 530/745-1304
Influence of Monetary and External Trade Shocks on Russian Economy*
 Influence of Monetary and External Trade Shocks on Russian Economy* Vadim Gilmundinov 20 th Inforum World Conference Florence, Italy September 03, 2012 * The study is supported by a Grant of the President
Influence of Monetary and External Trade Shocks on Russian Economy* Vadim Gilmundinov 20 th Inforum World Conference Florence, Italy September 03, 2012 * The study is supported by a Grant of the President
A Tutorial for Understanding Your Hospital s Economic and Community Impact Report. Healthcare Association of New York State April 2003
 A Tutorial for Understanding Your Hospital s Economic and Community Impact Report Healthcare Association of New York State April 2003 Overview of Your Facility-Specific Economic Impact Report Your facility-specific
A Tutorial for Understanding Your Hospital s Economic and Community Impact Report Healthcare Association of New York State April 2003 Overview of Your Facility-Specific Economic Impact Report Your facility-specific
Financial Autarky and International Business Cycles (JME 2002)
 Financial Autarky and International Business Cycles (JME 2002) Jonathan Heathcote and Fabrizio Perri 9/9/2014 Sargent Reading Group Joseba Martinez Jonathan Heathcote and Fabrizio Perri Financial Autarky
Financial Autarky and International Business Cycles (JME 2002) Jonathan Heathcote and Fabrizio Perri 9/9/2014 Sargent Reading Group Joseba Martinez Jonathan Heathcote and Fabrizio Perri Financial Autarky
Return to Capital in a Real Business Cycle Model
 Return to Capital in a Real Business Cycle Model Paul Gomme, B. Ravikumar, and Peter Rupert Can the neoclassical growth model generate fluctuations in the return to capital similar to those observed in
Return to Capital in a Real Business Cycle Model Paul Gomme, B. Ravikumar, and Peter Rupert Can the neoclassical growth model generate fluctuations in the return to capital similar to those observed in
Contract Pricing and Market Efficiency: Can Peer-to-Peer Internet Credit Markets Improve Allocative Efficiency?
 Contract Pricing and Market Efficiency: Can Peer-to-Peer Internet Credit Markets Improve Allocative Efficiency? June 28, 2016 Extended Abstract In this paper I examine the effects of contract terms offered
Contract Pricing and Market Efficiency: Can Peer-to-Peer Internet Credit Markets Improve Allocative Efficiency? June 28, 2016 Extended Abstract In this paper I examine the effects of contract terms offered
Core methodology I: Sector analysis of MDG determinants
 UNDP UN-DESA UN-ESCAP Core methodology I: Sector analysis of MDG determinants Rob Vos (UN-DESA/DPAD) Presentation prepared for the inception and training workshop of the project Assessing Development Strategies
UNDP UN-DESA UN-ESCAP Core methodology I: Sector analysis of MDG determinants Rob Vos (UN-DESA/DPAD) Presentation prepared for the inception and training workshop of the project Assessing Development Strategies
VIEWPOINT state tax notes
 Multi-Tax Incidence Analysis In a Microsimulation Environment by Eric Cook Eric Cook began his career as a revenue estimator with Congress s Joint Committee on Taxation in 1983. He joined PwC in 1987,
Multi-Tax Incidence Analysis In a Microsimulation Environment by Eric Cook Eric Cook began his career as a revenue estimator with Congress s Joint Committee on Taxation in 1983. He joined PwC in 1987,
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture II: Production Function and Profit Maximization
 Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture II: Production Function and Profit Maximization Kai Hao Yang 09/26/2017 1 Production Function Just as consumer theory uses utility function a function that assign
Elements of Economic Analysis II Lecture II: Production Function and Profit Maximization Kai Hao Yang 09/26/2017 1 Production Function Just as consumer theory uses utility function a function that assign
Multipliers: User s guide
 Federal Planning Bureau Economic analyses and forecasts Multipliers: User s guide Final demand multipliers are a standard application of Leontief s traditional input output model. They measure the response
Federal Planning Bureau Economic analyses and forecasts Multipliers: User s guide Final demand multipliers are a standard application of Leontief s traditional input output model. They measure the response
GDP and National Accounts
 GDP and National Accounts National accounts show technically no recession yeeah! 1of 18 Accounting (I) Some Accounting Definitions A stock variable is measured at one specific time, and represents a quantity
GDP and National Accounts National accounts show technically no recession yeeah! 1of 18 Accounting (I) Some Accounting Definitions A stock variable is measured at one specific time, and represents a quantity
Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income
 Macroeconomics 6 th edition # Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income Modified by Yulin Hou For Principle of Macroeconomics Florida International University Summer 2017 pyright 2017 Pearson
Macroeconomics 6 th edition # Chapter 8 GDP: # Measuring Total Production and Income Modified by Yulin Hou For Principle of Macroeconomics Florida International University Summer 2017 pyright 2017 Pearson
Fiscal Policies for Innovation and Growth
 Fiscal Policies for Innovation and Growth CARLOS MULAS-GRANADOS INTERNATIONAL MONETARY FUND ECFIN WORKSHOP JANUARY 24TH, 2016 1 Outline Growth: Three a state of alert pillars of innovation: a role for
Fiscal Policies for Innovation and Growth CARLOS MULAS-GRANADOS INTERNATIONAL MONETARY FUND ECFIN WORKSHOP JANUARY 24TH, 2016 1 Outline Growth: Three a state of alert pillars of innovation: a role for
Income Convergence in the South: Myth or Reality?
 Income Convergence in the South: Myth or Reality? Buddhi R. Gyawali Research Assistant Professor Department of Agribusiness Alabama A&M University P.O. Box 323 Normal, AL 35762 Phone: 256-372-5870 Email:
Income Convergence in the South: Myth or Reality? Buddhi R. Gyawali Research Assistant Professor Department of Agribusiness Alabama A&M University P.O. Box 323 Normal, AL 35762 Phone: 256-372-5870 Email:
Tax Cuts for Whom? Heterogeneous Effects of Income Tax Changes on Growth and Employment
 Tax Cuts for Whom? Heterogeneous Effects of Income Tax Changes on Growth and Employment Owen Zidar Chicago Booth and NBER December 1, 2014 Owen Zidar (Chicago Booth) Tax Cuts for Whom? December 1, 2014
Tax Cuts for Whom? Heterogeneous Effects of Income Tax Changes on Growth and Employment Owen Zidar Chicago Booth and NBER December 1, 2014 Owen Zidar (Chicago Booth) Tax Cuts for Whom? December 1, 2014
Monetary and Fiscal Policies: Sustainable Fiscal Policies
 Monetary and Fiscal Policies: Sustainable Fiscal Policies Behzad Diba Georgetown University May 2013 (Institute) Monetary and Fiscal Policies: Sustainable Fiscal Policies May 2013 1 / 13 What is Sustainable?
Monetary and Fiscal Policies: Sustainable Fiscal Policies Behzad Diba Georgetown University May 2013 (Institute) Monetary and Fiscal Policies: Sustainable Fiscal Policies May 2013 1 / 13 What is Sustainable?
Does health capital have differential effects on economic growth?
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Commerce - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Business 2013 Does health capital have differential effects on economic growth? Arusha V. Cooray University of
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Commerce - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Business 2013 Does health capital have differential effects on economic growth? Arusha V. Cooray University of
Exchange Rate Pass Through Inflation in Thailand
 Exchange Rate Pass Through Inflation in Thailand Panit Wattanakoon 1 1 Faculty of Economics Thammasat University Setthathat 2011 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Inflation in Thailand from 2000 to 2010 3 Literature
Exchange Rate Pass Through Inflation in Thailand Panit Wattanakoon 1 1 Faculty of Economics Thammasat University Setthathat 2011 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Inflation in Thailand from 2000 to 2010 3 Literature
Financial Development and Economic Growth: The Role of Energy Consumption
 ISSN(E):2522-2260 ISSN(P):2522-2252 Indexing/Abstracting Financial Development and Economic Growth: The Role of Energy Consumption Author(s) Hafiz Muhammad Abubakar Siddique 1 Sadaf Usman 2 Junaid Ishaq
ISSN(E):2522-2260 ISSN(P):2522-2252 Indexing/Abstracting Financial Development and Economic Growth: The Role of Energy Consumption Author(s) Hafiz Muhammad Abubakar Siddique 1 Sadaf Usman 2 Junaid Ishaq
Foreign Trade and the Exchange Rate
 Foreign Trade and the Exchange Rate Chapter 12 slide 0 Outline Foreign trade and aggregate demand The exchange rate The determinants of net exports A A model of the real exchange rates The IS curve and
Foreign Trade and the Exchange Rate Chapter 12 slide 0 Outline Foreign trade and aggregate demand The exchange rate The determinants of net exports A A model of the real exchange rates The IS curve and
IS Curve Figure S = I + G T + NX. In case of (1) closed economy: NX = 0 (2) balanced budget: T = G S = I
 Curve Figure = + G T + NX n case of (1) closed economy: NX = 0 (2) balanced budget: T = G = Private aving = nvestment Note that if G-T or NX changes then so do and nvestment and Real nterest Rate i (exp.)
Curve Figure = + G T + NX n case of (1) closed economy: NX = 0 (2) balanced budget: T = G = Private aving = nvestment Note that if G-T or NX changes then so do and nvestment and Real nterest Rate i (exp.)
UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO 1 st Finance Junior Workshop Program. Monetary Policy and Welfare Issues in the Economy with Shifting Trend Inflation
 UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO 1 st Finance Junior Workshop Program Monetary Policy and Welfare Issues in the Economy with Shifting Trend Inflation Le Thanh Ha (GRIPS) (30 th March 2017) 1. Introduction Exercises
UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO 1 st Finance Junior Workshop Program Monetary Policy and Welfare Issues in the Economy with Shifting Trend Inflation Le Thanh Ha (GRIPS) (30 th March 2017) 1. Introduction Exercises
Measuring Domestic Output and National Income
 Chapter 27 Measuring Domestic Output and National Income Assessing the Economy s Performance National income accounting measures economy s overall performance Bureau of Economic Analysis compiles National
Chapter 27 Measuring Domestic Output and National Income Assessing the Economy s Performance National income accounting measures economy s overall performance Bureau of Economic Analysis compiles National
Economics 689 Texas A&M University
 Horizontal FDI Economics 689 Texas A&M University Horizontal FDI Foreign direct investments are investments in which a firm acquires a controlling interest in a foreign firm. called portfolio investments
Horizontal FDI Economics 689 Texas A&M University Horizontal FDI Foreign direct investments are investments in which a firm acquires a controlling interest in a foreign firm. called portfolio investments
GDP, PERSONAL INCOME AND GROWTH
 GDP, PERSONAL INCOME AND GROWTH PART 2: IMPACT OF PERSONAL INCOME CHANGES ON NEVADA GROWTH INTRODUCTION Nevada has been heavily hit by the recession, with unemployment rates of 13.4% as of October 2011,
GDP, PERSONAL INCOME AND GROWTH PART 2: IMPACT OF PERSONAL INCOME CHANGES ON NEVADA GROWTH INTRODUCTION Nevada has been heavily hit by the recession, with unemployment rates of 13.4% as of October 2011,
Fiscal Devaluations in a Model with Capital
 Fiscal Devaluations in a Model with Capital Emmanuel Farhi Harvard University Gita Gopinath Harvard University Oleg Itskhoki Princeton University First Draft: June 3 2011 This Draft: September 25 2014
Fiscal Devaluations in a Model with Capital Emmanuel Farhi Harvard University Gita Gopinath Harvard University Oleg Itskhoki Princeton University First Draft: June 3 2011 This Draft: September 25 2014
Data Development for Regional Policy Analysis
 Data Development for Regional Policy Analysis David Roland-Holst UC Berkeley ASEM/DRC Workshop on Capacity for Regional Research on Poverty and Inequality in China Monday-Tuesday, March 27-28, 2006 Contents
Data Development for Regional Policy Analysis David Roland-Holst UC Berkeley ASEM/DRC Workshop on Capacity for Regional Research on Poverty and Inequality in China Monday-Tuesday, March 27-28, 2006 Contents
GROWTH PROSPECTS OF EMERGING MARKET ECONOMIES IN EUROPE
 EME-REPORT 6.9.27 GROWTH PROSPECTS OF EMERGING MARKET ECONOMIES IN EUROPE HOW FAST WILL THEY CATCH UP WITH THE OLD WEST? TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive summary 3 1. Introduction 6 2. The starting point 8
EME-REPORT 6.9.27 GROWTH PROSPECTS OF EMERGING MARKET ECONOMIES IN EUROPE HOW FAST WILL THEY CATCH UP WITH THE OLD WEST? TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive summary 3 1. Introduction 6 2. The starting point 8
White Pine County Economic Overview
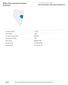 Economic Overview Population (2016) 10,105 Jobs (2016) 4,597 Average Earnings (2016) $65,033 Unemployed (2/2016) 229 GRP (2014) $996,944,330 Exports (2014) $1,789,478,088 Imports (2014) $1,181,738,119
Economic Overview Population (2016) 10,105 Jobs (2016) 4,597 Average Earnings (2016) $65,033 Unemployed (2/2016) 229 GRP (2014) $996,944,330 Exports (2014) $1,789,478,088 Imports (2014) $1,181,738,119
Oil Shocks and the Zero Bound on Nominal Interest Rates
 Oil Shocks and the Zero Bound on Nominal Interest Rates Martin Bodenstein, Luca Guerrieri, Christopher Gust Federal Reserve Board "Advances in International Macroeconomics - Lessons from the Crisis," Brussels,
Oil Shocks and the Zero Bound on Nominal Interest Rates Martin Bodenstein, Luca Guerrieri, Christopher Gust Federal Reserve Board "Advances in International Macroeconomics - Lessons from the Crisis," Brussels,
UN DESA Capacity Development Project on Belt and Road Initiative and SDGs
 UN DESA Capacity Development Project on Belt and Road Initiative and SDGs meeting with the CCIEE delegation 19 October 2018 Vito Intini and Wen Shi United Nations, New York HQ UN Sustainable Development
UN DESA Capacity Development Project on Belt and Road Initiative and SDGs meeting with the CCIEE delegation 19 October 2018 Vito Intini and Wen Shi United Nations, New York HQ UN Sustainable Development
Financial Economics: Risk Aversion and Investment Decisions
 Financial Economics: Risk Aversion and Investment Decisions Shuoxun Hellen Zhang WISE & SOE XIAMEN UNIVERSITY March, 2015 1 / 50 Outline Risk Aversion and Portfolio Allocation Portfolios, Risk Aversion,
Financial Economics: Risk Aversion and Investment Decisions Shuoxun Hellen Zhang WISE & SOE XIAMEN UNIVERSITY March, 2015 1 / 50 Outline Risk Aversion and Portfolio Allocation Portfolios, Risk Aversion,
The Big Picture. Macro Principles. Lecture 1
 What is Macroeconomics? GDP Other Measures The Big Picture Macro Principles Lecture 1 Growth Fluctuations Today s Topics The main ideas in this lecture What do we mean by macroeconomics? What are the major
What is Macroeconomics? GDP Other Measures The Big Picture Macro Principles Lecture 1 Growth Fluctuations Today s Topics The main ideas in this lecture What do we mean by macroeconomics? What are the major
Pyramiding, Productive Efficiency, and Revenue under a Gross Receipts Tax
 Pyramiding, Productive Efficiency, and Revenue under a Gross Receipts Tax Andre J. Barbe Department of Economics Rice University FTA Revenue Estimation & Tax Research Conference October 24, 2012 Barbe
Pyramiding, Productive Efficiency, and Revenue under a Gross Receipts Tax Andre J. Barbe Department of Economics Rice University FTA Revenue Estimation & Tax Research Conference October 24, 2012 Barbe
1. Consider the aggregate production functions for Wisconsin and Minnesota: Production Function for Wisconsin
 Economics 102 Fall 2017 Homework #4 Due 11/14/2017 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework (legibly)
Economics 102 Fall 2017 Homework #4 Due 11/14/2017 Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework (legibly)
Capital-goods imports, investment-specific technological change and U.S. growth
 Capital-goods imports, investment-specific technological change and US growth Michele Cavallo Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System Anthony Landry Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas October 2008
Capital-goods imports, investment-specific technological change and US growth Michele Cavallo Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System Anthony Landry Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas October 2008
Testing the predictions of the Solow model: What do the data say?
 Testing the predictions of the Solow model: What do the data say? Prediction n 1 : Conditional convergence: Countries at an early phase of capital accumulation tend to grow faster than countries at a later
Testing the predictions of the Solow model: What do the data say? Prediction n 1 : Conditional convergence: Countries at an early phase of capital accumulation tend to grow faster than countries at a later
