PART II A MACRO-ECONOMIC METHODOLOGY FOR THE APPRAISAL OF THE EFFECTS OF PRI V A TE FOREIGN INVESTMENTS IN LESS DEVELOPED COUNTRIES
|
|
|
- Veronica Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PART II A MACRO-ECONOMIC METHODOLOGY FOR THE APPRAISAL OF THE EFFECTS OF PRI V A TE FOREIGN INVESTMENTS IN LESS DEVELOPED COUNTRIES
2 TABLE OF CONTENTS SUMMARY OF PART II 53 CHAPTER I. GENERAL INTRODUCTION Introduction 1.2. The appraisal of the effects of PFI 1.3. The quantitative approach in general CHAPTER II. A MODEL OF A LDC's ECONOMY WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO PFI Introduction The PFI sector The external sector of the rest of the economy and the b.o.p Private savings The public sector Investments in the rest of the economy Income for the total economy Demand Employment O. Alternative formulations of some equations Alternative ways of financing investments from abroad 72 Appendix I : Terminology and abbreviations 74 Appendix 2: Ust of symbols 74 Appendix 3: The model 76 CHAPTER III. THE ECONOMIC EFFECTS OF PFI Introduction The effects on investments in the rest of the economy and on the growth of income The effects on the b.o.p Import substitution and export promotion The effects on wages, profits and employment The effects on the distribution of income 82
3 50 PRIVATE FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES 3.7. The effects on government revenue and expenditure 3.8. The effects on private savings 3.9. Substitution effects CHAPTER IV. OTHER ECONOMIC EFFECTS OF PFI NOT CON- SIDERED BY THE MODEL 4.1. Introduction 4.2. The exchange rate 4.3. The internal price system 4.4. The terms of trade 4.5. The external effects 4.6. The demonstration effects 4.7. The savings rate CHAPTER V. THE INTERDEPENDENCE - SIMULTANEOUS AND OVER TIME - OF THE EFFECTS OF PFI Introduction The income effect The b.o.p. effect The private savings effect The public savings effect The interdependence of the effects of PFI 100 CHAPTER V I THE 'CUMULATIVE' EFFECTS OF PFI Introduction The formulation of the cumulative effects Economic interpretation of the cumulative effects A general solution for the cumulative effects A solution in terms of the growth of the cumulative effects 104 CHAPTER VII. THE 'MARGINAL' EFFECTS OF PFI Introduction 7.2. A marginal approach and the related problems 7.3. The marginal effect on the b.o.p The marginal effect on private savings 7.5. The marginal effect on public savings 7.6. The time behaviour of the marginal effects 7.7. The marginal effect on income III III
4 EFFECTS OF PRIV ATE FOREIGN INVESTMENTS The formulation or the four marginal effects and their eco- 115 nomic interpretation CHAPTER VIII. CUMULATIVE AND MARGINAL EFFECTS COMPARED Cumulative vs marginal effects Practical applications of the cumulative and marginal effects A numerical exercise and some variations for the marginal and the cumulative effects The effect on wages, profits, and income distribution The employment effects The substitution effect The impact of the financial mechanism of the annual additions to PFI 131 CHAPTER IX. SECTORAL DISAGGREGATION AND INPUT- OUTPUT ANALYSIS Introduction The sectoral use of the methodology in general The sectoral use of the methodology taking into account just one PFI sector or sub-sector The sectoral use of the methodology taking into account various PFI sectors and/or sub-sectors The introduction of input-output analysis Other possible extentions 142 CHAPTER X. VARIOUS PRACTICAL SITUATIONS AND THE USE OF THE MODEL CHAPTER XI. THE USE OF THE MODEL FOR DECISION MAKING CHAPTER XII. THE USE OF THE MODEL FOR EMPIRICAL IN VESTIGA TIONS CHAPTER XIII. EVALUATION AND CONCLUSIONS 150 LIST OF REFERENCES 152
5 SUMMARY OF PART II This part of the research concentrates on the macro-economic methodology, indicating also how it can be used both for decision making (Chapter XI) and for empirical applications (Chapter XII). The methodological framework presented is not considered to be complete, both because some problems still need a more satisfactory solution, and because some extentions are possible in order to get a better analysis (Chapter IX, in particular). The introduction points out how the approach is meant first of all to be analytical, i.e. limited to the analysis of the effects of PFI, leaving any decision about their acceptibility to the policy makers themselves, for whom it is hoped that the methodology would provide a useful starting point and a base for their decisions (Section 1.2). Furthermore, the approach is meant to be at a macro-economic (sectoral) level, and not a project level. The purpose of the methodology is to quantify the economic effects of PFI in LDC's. A number of such effects is discussed in Chapter III. Attention is given to the more quantifiable ones, and consequently the list may not be complete. Some other economic effects of PFI, not taken into account by the model, are discussed in Chapter IV. The methodology is based on a multi-sectoral dynamic model. A twosector version of this model is given in Chapter II. Two sectors are considered: the 'PFI sector', and the 'rest of the economy' sector. Attention is given to the relations which are more relevant in a study about the effects of PFI; moreover, it is shown how the model could be extended to take into account employment (Section 2.9) and to take into account other ways of financing an investment project from abroad than through PFI (Section 2.l1). The formulation of some equations may raise some questions; Section 2.l 0 discusses briefly why certain specific formulations have been choosen. Finally, in Chapter IX it is pointed out how the model can be extended to become a multi-sectoral one. The purpose of the model presented in Chapter II is not to get a set of full solutions for the endogenous variables it considers, but to provide a starting point for the quantification of the economic effects of PFI. The model is needed in order to have a detailed and consistent picture of a LDC's economy, with special reference to what happens to some key variables as a
6 54 PRIV ATE FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES consequence of the presence of PFI. Starting from the model, it will then be possible to get some quantified expressions for the economic effects of PFI, which are consistent with each other, and which take into account direct and indirect effects. In order to estimate the effects of PFI, the approach proposed is to compare (by difference) a situation with PFI and a situation without PFI, using the model as a basis to get the relations referring to the various effects. Two sets of effects, corresponding to two different approaches, are distinguished in the report. In the NEI terminology, they are called, respectively, the cumulative and the marginal effects of PFI. The cumulative effects (Chapters V and VI) are obtained by difference, comparing, for various variables corresponding to various effects, from time 0 to time t, a situation where PFI is always present, and a situation where PFI is always absent. Since the effects of PFI on some variables 'cumulate' from year to year, this particular terminology was choosen. This can be seen considering, e.g. the cumulative effect on income. Since the increase in GDP from 0 to t is determined by the investments, through the capital-output ratio. the effects of PFI on domestic investments for every year will be present in the cumulative effect referring to time t. And since all other effects are also related to income, this same situation applies also to them. Moreover, for the balance of payments effect (b.o.p.) one must also consider the effects on it in the previous years, which are assumed to represent the debt effect of PFI 1. Consequently, using this approach, it is also possible to point out how the effects of PFI are interdependent simultaneously and over time (Chapter V). The analysis of both cumulative (Chapter VI) and marginal (Chapter VII) effects mainly concentrates on four of them (income, private savings, public savings, and b.o.p.). However, in the report it is also pointed out how it is possible to extend the analysis to some other effects, like the one on employment (Section 8.5) the one on the distribution of income (Section 8.4) and the substitution effect (Section 8.6). The report discusses also how it is possible to take into consideration various practical situations different from the model given in Chapter II, like, e.g., different ways of financing an investment project from abroad, or joint ventures, or also different structural parameters for the two sectors (as it is the case when the Government wants to provide incentives or disincentives to PFI). Chapter X further points out how these various practical situations can be incorporated into the model changing some of the parameters, or introducing 1 For the foreign debt, the model assumes that its annual increase corresponds to the deficit of the b,o.p" equal to the foreign capital inflow (under the assumption of no variations in reserves etc,l.
7 EFFECTS OF PRIVATE FOREIGN INVESTMENTS 55 some new variables, and how the formulations of both cumulative and marginal effects can be modified accordingly. The interdependence -- simultaneously and over time - of the cumulative effects of PFI has been mentioned above. This makes the practical solution of the system which expresses them rather difficult. A general solution could be obtained in terms of a system of difference equations (Section 6.4), while an approximate solution, much more operational for its simplicity, can be obtained considering the rate of growth of the cumulative effects. It is proved that the latter is approximated by the rate of growth of the PFI capital stock (or gross value added), and consequently it is possible to arrive at a solution for the main effects considered (Section 6.5). Such a solution is given as a system of four linear equations, where the four effects are the unknowns. Substituting the value of the parameters, and of the PFI gross value added in a given time t, it is possible to solve it, and to get the numerical value of the four effects. Since, in practice, both for lack of data for a reasonably long period of time, or because the LOe's economy or the PFI capital stock do not behave exactly according to the assumptions of the model, it might be difficult to apply the cumulative approach, also a simpler one has been developed, called the 'marginal' approach" Under the assumption that the situation in time t is given and that one is simply interested in finding out what happens from time t to time t+ 1 as a consequence of the presence of PFI on some variables, the marginal effects are defined as the variation in these variables from t to t+ I imputable to the presence of PFI. This approach is obviously quite different from the cumulative one. The two are compared in Section 8.1, where the reader may also find a useful picture, showing the cumulative and marginal effects on income. The formulation of the marginal effects still involves the presence of lagged endogenous variables. However, it is possible to prove that the rate of growth of these effects is exactly the same as the rate of growth of the PFI capital stock (or gross value added), and consequently it is possible to eliminate the lags. Also the marginal effects are given as a system of four equations, where the four main effects considered are the unknowns and which can be solved once the parameters and the gross value added of the PFI sector in t are given (Section 7.8). The basic difference between the two effects is that the cumulative effects refer to the effects of PFI on certain variables from time 0 to time t, while the marginal effects simply point out the effect imputable to PFI in the development of the economy from time t to time t+ I. These different con-
8 56 PRIVATE FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES cepts point out also the different practical possible uses of the two approaches (Chapter VIII). If detailed information is available for a long period of time, and if the economy and the PFI sector behave according to the relations of the model, then it is possible to use the cumulative approach. If, on the contrary, only data for one or two years are available, it is possible to use the marginal one. The former gives a more complete answer to the question of the economic effects of PFI; if it is not possible to apply it, then the latter can still provide some useful answers. A numerical exercise is given in Section 8.3, with reference to both cumulative and marginal effects. First, a general solution is obtained giving some arbitrary values to the parameters. Then some variations are studied. The exercise proves quite useful both to compare different practical situations reflected in the various alternative values given to some of the parameters, and to get some insights in how the model reacts to some variations in its parameters. As it was said at the beginning of this summary, the last chapters discuss the use of the methodological approach for decision making (Chapter XI) and its use for practical investigations (Chapter XII).
5 NATIONAL ACCOUNTING AND ECONOMIC POLICY DECISIONS (with special reference to the Netherlands)
 5 NATIONAL ACCOUNTING AND ECONOMIC POLICY DECISIONS (with special reference to the Netherlands) by C. A. van den Beld I. INTRODUCTION IN the Netherlands there exists already a long-term tradition in quantitative
5 NATIONAL ACCOUNTING AND ECONOMIC POLICY DECISIONS (with special reference to the Netherlands) by C. A. van den Beld I. INTRODUCTION IN the Netherlands there exists already a long-term tradition in quantitative
Main Features. Aid, Public Investment, and pro-poor Growth Policies. Session 4 An Operational Macroeconomic Framework for Ethiopia
 Aid, Public Investment, and pro-poor Growth Policies Addis Ababa, August 16-19, 2004 Session 4 An Operational Macroeconomic Framework for Ethiopia Pierre-Richard Agénor Main features. Public capital and
Aid, Public Investment, and pro-poor Growth Policies Addis Ababa, August 16-19, 2004 Session 4 An Operational Macroeconomic Framework for Ethiopia Pierre-Richard Agénor Main features. Public capital and
A 2009 Social Accounting Matrix (SAM) for South Africa
 A 2009 Social Accounting Matrix (SAM) for South Africa Rob Davies a and James Thurlow b a Human Sciences Research Council (HSRC), Pretoria, South Africa b International Food Policy Research Institute,
A 2009 Social Accounting Matrix (SAM) for South Africa Rob Davies a and James Thurlow b a Human Sciences Research Council (HSRC), Pretoria, South Africa b International Food Policy Research Institute,
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 ECONOMICS Class XII BLUE PRINT
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 ECONOMICS Class XII Maximum Marks: 00 Time: 3 hours BLUE PRINT Sl. No. Forms of Questions Content Unit Very Short ( Mark) Short Answer (3,4 Marks) Long Answer (6 Marks) Total. Unit
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER 2 ECONOMICS Class XII Maximum Marks: 00 Time: 3 hours BLUE PRINT Sl. No. Forms of Questions Content Unit Very Short ( Mark) Short Answer (3,4 Marks) Long Answer (6 Marks) Total. Unit
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA (SHIFT I) PATTOM ECONOMICS Class XII
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA (SHIFT I) PATTOM ECONOMICS Class XII Time : 3 Hrs. Max. Marks - 100 Note : i. All questions in both the sections are compulsory. ii. iii. iv. Marks for questions are indicated against
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA (SHIFT I) PATTOM ECONOMICS Class XII Time : 3 Hrs. Max. Marks - 100 Note : i. All questions in both the sections are compulsory. ii. iii. iv. Marks for questions are indicated against
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject ST5 Finance and Investment A For 2018 Examinations
 Institute of Actuaries of India Subject ST5 Finance and Investment A For 2018 Examinations Aim The aim of this Finance and Investment Technical subject is to instill in successful candidates the ability
Institute of Actuaries of India Subject ST5 Finance and Investment A For 2018 Examinations Aim The aim of this Finance and Investment Technical subject is to instill in successful candidates the ability
MACROECONOMICS NATIONAL INCOME
 MACROECONOMICS Q. 1. Define intermediate goods. NATIONAL INCOME Q.2. Q.3. Q.4. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
MACROECONOMICS Q. 1. Define intermediate goods. NATIONAL INCOME Q.2. Q.3. Q.4. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
CONTENTS. iii PREFACE
 CONTENTS PREFACE iii CHAPTER 1 Aims, Background, Innovations and Presentation 1 1. Introduction 1 2. Background and innovations 2 2.1. Dynamics 4 (a) Physical capital accumulation 4 (b) Financial asset/liability
CONTENTS PREFACE iii CHAPTER 1 Aims, Background, Innovations and Presentation 1 1. Introduction 1 2. Background and innovations 2 2.1. Dynamics 4 (a) Physical capital accumulation 4 (b) Financial asset/liability
NATIONAL INCOME. be less than NDP FC. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example.
 NATIONAL INCOME Q. 1. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? Q.2. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? Q.3. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example. Q.4.
NATIONAL INCOME Q. 1. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? Q.2. State the meaning of consumption of fixed capital? Q.3. State the meaning of injection in income flow, with the help of an example. Q.4.
Impact of Foreign Aid on Fiscal Behaviour: A Case Study of Pakistan ( )
 Salman Ahmad 117 Impact of Foreign Aid on Fiscal Behaviour: A Case Study of Pakistan (1980-2000) Salman Ahmad * Abstract Economists have been trying to study the linkages between aid inflow and government
Salman Ahmad 117 Impact of Foreign Aid on Fiscal Behaviour: A Case Study of Pakistan (1980-2000) Salman Ahmad * Abstract Economists have been trying to study the linkages between aid inflow and government
Sample Question Paper Economics. Class XII. Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: Section A: Microeconomics
 Sample Question Paper Economics Class XII Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: 1. All questions in both sections are compulsory. However, there is internal choice in some questions.
Sample Question Paper Economics Class XII Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: 1. All questions in both sections are compulsory. However, there is internal choice in some questions.
Exercise 1 Output Determination, Aggregate Demand and Fiscal Policy
 Fletcher School, Tufts University Exercise 1 Output Determination, Aggregate Demand and Fiscal Policy Prof. George Alogoskoufis The Basic Keynesian Model Consider the following short run keynesian model
Fletcher School, Tufts University Exercise 1 Output Determination, Aggregate Demand and Fiscal Policy Prof. George Alogoskoufis The Basic Keynesian Model Consider the following short run keynesian model
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100. Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 7 PART A
 : 1 : Roll No... Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 7 PART A (Answer Question No.1 which is compulsory and any two of the rest from
: 1 : Roll No... Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 7 PART A (Answer Question No.1 which is compulsory and any two of the rest from
BALANCE SHEET. thousands of PLN
 thousands of PLN BALANCE SHEET Notes 2013 2012 ASSETS I. Non-current assets 603,433 578,820 1. Intangible assets 1 11,119 10,563 2. Property, plant and equipment 2 203,731 211,348 3. Non-current investment
thousands of PLN BALANCE SHEET Notes 2013 2012 ASSETS I. Non-current assets 603,433 578,820 1. Intangible assets 1 11,119 10,563 2. Property, plant and equipment 2 203,731 211,348 3. Non-current investment
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ECONOMICS Class - XII BLUE PRINT
 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ECONOMICS Class - XII Maximum Marks 100 Time : 3 hrs. BLUE PRINT Sl. No. Form of Very Short Short Answer Long Answer Total Questions (1 Mark) (3, 4 Marks) (6 Marks) Content Unit
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II ECONOMICS Class - XII Maximum Marks 100 Time : 3 hrs. BLUE PRINT Sl. No. Form of Very Short Short Answer Long Answer Total Questions (1 Mark) (3, 4 Marks) (6 Marks) Content Unit
ECON 102 (RATNA) FINAL EXAM REVIEW SESSION BY PHUONG VU
 ECON 102 (RATNA) FINAL EXAM REVIEW SESSION BY PHUONG VU TABLE OF CONTENT I. Chapter 19 & 20 II. Chapter 21 &22 III. Chapter 23, 24 & 25. IV. Chapter 26 V. Chapter 27, 28 & 29. VI. Chapter 27, 28 & 29 (cont.)
ECON 102 (RATNA) FINAL EXAM REVIEW SESSION BY PHUONG VU TABLE OF CONTENT I. Chapter 19 & 20 II. Chapter 21 &22 III. Chapter 23, 24 & 25. IV. Chapter 26 V. Chapter 27, 28 & 29. VI. Chapter 27, 28 & 29 (cont.)
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN ERNAKULAM REGION SECOND PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION CLASS XII ECONOMICS (30) Time Allowed- 3 Hours
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN ERNAKULAM REGION SECOND PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION 208-9 CLASS XII ECONOMICS (0) MM-80 Time Allowed- Hours General Instructions: i. All questions in both sections are compulsory.
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN ERNAKULAM REGION SECOND PRE-BOARD EXAMINATION 208-9 CLASS XII ECONOMICS (0) MM-80 Time Allowed- Hours General Instructions: i. All questions in both sections are compulsory.
International Linkages and Domestic Policy
 International Linkages and Domestic Policy 11 Unit highlights: The basis of and gains from international trade Concept of absolute advantage and comparative advantage Balance of paymets Exchange rate system
International Linkages and Domestic Policy 11 Unit highlights: The basis of and gains from international trade Concept of absolute advantage and comparative advantage Balance of paymets Exchange rate system
AN AXIOMATIC APPROACH TO NATIONAL ACCOUNTING: AN OUTLINE. by Odd Aukrust
 Review of Income and Wealth Series 54, Number 4, December 2008 AN AXIOMATIC APPROACH TO NATIONAL ACCOUNTING: AN OUTLINE by Odd Aukrust Central Bureau of Statistics of Norway Reprinted from The Review of
Review of Income and Wealth Series 54, Number 4, December 2008 AN AXIOMATIC APPROACH TO NATIONAL ACCOUNTING: AN OUTLINE by Odd Aukrust Central Bureau of Statistics of Norway Reprinted from The Review of
Balance of Payments in Poland December 2017
 Warsaw, 13 February 2018 Balance of Payments in Poland December 2017 Components of monthly bop are estimated based on monthly and quarterly information reported by residents involved in transactions with
Warsaw, 13 February 2018 Balance of Payments in Poland December 2017 Components of monthly bop are estimated based on monthly and quarterly information reported by residents involved in transactions with
International Trade. International Trade, Exchange Rates, and Macroeconomic Policy. International Trade. International Trade. International Trade
 , Exchange Rates, and 1 Introduction Open economy macroeconomics International trade in goods and services International capital flows Purchases & sales of foreign assets by domestic residents Purchases
, Exchange Rates, and 1 Introduction Open economy macroeconomics International trade in goods and services International capital flows Purchases & sales of foreign assets by domestic residents Purchases
The Multiplier Model
 The Multiplier Model Allin Cottrell March 3, 208 Introduction The basic idea behind the multiplier model is that up to the limit set by full employment or potential GDP the actual level of employment and
The Multiplier Model Allin Cottrell March 3, 208 Introduction The basic idea behind the multiplier model is that up to the limit set by full employment or potential GDP the actual level of employment and
Bhartiya Samruddhi Finance Limited Asset-Liability Management Policy
 Bhartiya Samruddhi Finance Limited Asset-Liability Management Policy I. Goal: The assets and liabilities of Bhartiya Samruddhi Finance Limited of Hyderabad shall be managed in order to maximize shareholders
Bhartiya Samruddhi Finance Limited Asset-Liability Management Policy I. Goal: The assets and liabilities of Bhartiya Samruddhi Finance Limited of Hyderabad shall be managed in order to maximize shareholders
DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated
 DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII Marks - 100 Duration - 3 hrs. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated questions time a candidate is expected to take to answer
DESIGN OF QUESTION PAPER ECONOMICS Class - XII Marks - 100 Duration - 3 hrs. 1. Weightage by types of questions Type Number of Marks Total Estimated questions time a candidate is expected to take to answer
 UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption Goods : Those goods which
UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption Goods : Those goods which
UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER
 1 COMPREHENSIVE COMMERCE UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption
1 COMPREHENSIVE COMMERCE UNIT 6 NATIONAL INCOME POINTS TO REMEMBER Good : In economics a good is defined as any physical object, natural or man-made, that could command a price in the market. Consumption
Introduction to Risk Parity and Budgeting
 Chapman & Hall/CRC FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS SERIES Introduction to Risk Parity and Budgeting Thierry Roncalli CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor
Chapman & Hall/CRC FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS SERIES Introduction to Risk Parity and Budgeting Thierry Roncalli CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor
Assessing the Spillover Effects of Changes in Bank Capital Regulation Using BoC-GEM-Fin: A Non-Technical Description
 Assessing the Spillover Effects of Changes in Bank Capital Regulation Using BoC-GEM-Fin: A Non-Technical Description Carlos de Resende, Ali Dib, and Nikita Perevalov International Economic Analysis Department
Assessing the Spillover Effects of Changes in Bank Capital Regulation Using BoC-GEM-Fin: A Non-Technical Description Carlos de Resende, Ali Dib, and Nikita Perevalov International Economic Analysis Department
 http:/// Guess Paper 2014 Class XII Subject Economics Total Marks: 100 Time:3 Hours. General Instructions: (i) All questions in both the sections are compulsory. (ii) Marks for questions are indicated
http:/// Guess Paper 2014 Class XII Subject Economics Total Marks: 100 Time:3 Hours. General Instructions: (i) All questions in both the sections are compulsory. (ii) Marks for questions are indicated
ECONOMICS. Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 QUESTION PAPER CODE 58/1/1 SECTION - A. 1. Define an indifference curve. 1
 ECONOMICS Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) All questions in both the sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each.
ECONOMICS Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) All questions in both the sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each.
Implementing the Expected Credit Loss model for receivables A case study for IFRS 9
 Implementing the Expected Credit Loss model for receivables A case study for IFRS 9 Corporates Treasury Many companies are struggling with the implementation of the Expected Credit Loss model according
Implementing the Expected Credit Loss model for receivables A case study for IFRS 9 Corporates Treasury Many companies are struggling with the implementation of the Expected Credit Loss model according
Monte Carlo, Resampling, And Other Estimation Tricks. Mauricio Aguiar ti MÉTRICAS, President IFPUG Immediate Past President
 Monte Carlo, Resampling, And Other Estimation Tricks Mauricio Aguiar ti MÉTRICAS, President IFPUG Immediate Past President Agenda Introduction A Simple Example Another Example An Alternative Do It Yourself
Monte Carlo, Resampling, And Other Estimation Tricks Mauricio Aguiar ti MÉTRICAS, President IFPUG Immediate Past President Agenda Introduction A Simple Example Another Example An Alternative Do It Yourself
Economic Life Cycle Deficit and Intergenerational Transfers in Italy: An Analysis Using National Transfer Accounts Methodology
 Economic Life Cycle Deficit and Intergenerational Transfers in Italy: An Analysis Using National Transfer Accounts Methodology Marina Zannella, Graziella Caselli Department of Statistical Sciences, Sapienza
Economic Life Cycle Deficit and Intergenerational Transfers in Italy: An Analysis Using National Transfer Accounts Methodology Marina Zannella, Graziella Caselli Department of Statistical Sciences, Sapienza
SOCIAL ACCOUNTING MATRIX (SAM) AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR MACROECONOMIC PLANNING
 Unpublished Assessed Article, Bradford University, Development Project Planning Centre (DPPC), Bradford, UK. 1996 SOCIAL ACCOUNTING MATRIX (SAM) AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR MACROECONOMIC PLANNING I. Introduction:
Unpublished Assessed Article, Bradford University, Development Project Planning Centre (DPPC), Bradford, UK. 1996 SOCIAL ACCOUNTING MATRIX (SAM) AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR MACROECONOMIC PLANNING I. Introduction:
The World Bank Revised Minimum Standard Model: Concepts and limitations
 Acta Universitatis Wratislaviensis No 3535 Wioletta Nowak University of Wrocław The World Bank Revised Minimum Standard Model: Concepts and limitations JEL Classification: C60, F33, F35, O Keywords: RMSM,
Acta Universitatis Wratislaviensis No 3535 Wioletta Nowak University of Wrocław The World Bank Revised Minimum Standard Model: Concepts and limitations JEL Classification: C60, F33, F35, O Keywords: RMSM,
Inflation, Output, and Nominal Money. Growth
 Money Money Department of Economics, University of Vienna May 25 th, 2011 Money The AS-AD model dealt with the relation between output and the price level In this chapter we extend the AS-AD model to examine
Money Money Department of Economics, University of Vienna May 25 th, 2011 Money The AS-AD model dealt with the relation between output and the price level In this chapter we extend the AS-AD model to examine
The Elasticity of Taxable Income and the Tax Revenue Elasticity
 Department of Economics Working Paper Series The Elasticity of Taxable Income and the Tax Revenue Elasticity John Creedy & Norman Gemmell October 2010 Research Paper Number 1110 ISSN: 0819 2642 ISBN: 978
Department of Economics Working Paper Series The Elasticity of Taxable Income and the Tax Revenue Elasticity John Creedy & Norman Gemmell October 2010 Research Paper Number 1110 ISSN: 0819 2642 ISBN: 978
A N ENERGY ECONOMY I NTERAC TION MODEL FOR EGYPT
 A N ENERGY ECONOMY I NTERAC TION MODEL FOR EGYPT RESULTS OF ALTERNATIVE PRICE REFORM SCENARIOS B Y MOTAZ KHORSHID Vice President of the British University in Egypt (BUE) Ex-Vice President of Cairo University
A N ENERGY ECONOMY I NTERAC TION MODEL FOR EGYPT RESULTS OF ALTERNATIVE PRICE REFORM SCENARIOS B Y MOTAZ KHORSHID Vice President of the British University in Egypt (BUE) Ex-Vice President of Cairo University
Public Hearing on Financial Regulation and Supervision
 Bettina Corves-Wunderer Public Hearing on Financial Regulation and Supervision Panel I: To what extent did financial regulation and supervision fail in preventing the crisis? Brussels, February 25 th,
Bettina Corves-Wunderer Public Hearing on Financial Regulation and Supervision Panel I: To what extent did financial regulation and supervision fail in preventing the crisis? Brussels, February 25 th,
Economics of International Financial Policy: ITF 220
 Economics of International Financial Policy: ITF 220 Staff -- Professor: Jeffrey Frankel, Littauer 217 Office hours: Mon.& Tues., 3:00-4:00. Faculty Asst.: Minoo Ghoreishi, Belfer 505 (617) 384-7329 Teaching
Economics of International Financial Policy: ITF 220 Staff -- Professor: Jeffrey Frankel, Littauer 217 Office hours: Mon.& Tues., 3:00-4:00. Faculty Asst.: Minoo Ghoreishi, Belfer 505 (617) 384-7329 Teaching
Chapter 19 Optimal Fiscal Policy
 Chapter 19 Optimal Fiscal Policy We now proceed to study optimal fiscal policy. We should make clear at the outset what we mean by this. In general, fiscal policy entails the government choosing its spending
Chapter 19 Optimal Fiscal Policy We now proceed to study optimal fiscal policy. We should make clear at the outset what we mean by this. In general, fiscal policy entails the government choosing its spending
NEW I-O TABLE AND SAMs FOR POLAND
 Łucja Tomasewic University of Lod Institute of Econometrics and Statistics 41 Rewolucji 195 r, 9-214 Łódź Poland, tel. (4842) 6355187 e-mail: tiase@krysia. uni.lod.pl Draft NEW I-O TABLE AND SAMs FOR POLAND
Łucja Tomasewic University of Lod Institute of Econometrics and Statistics 41 Rewolucji 195 r, 9-214 Łódź Poland, tel. (4842) 6355187 e-mail: tiase@krysia. uni.lod.pl Draft NEW I-O TABLE AND SAMs FOR POLAND
Simple Macroeconomic Model for MDGs based Planning and Policy Analysis. Thangavel Palanivel UNDP Regional Centre in Colombo
 Simple Macroeconomic Model for MDGs based Planning and Policy Analysis Thangavel Palanivel UNDP Regional Centre in Colombo Outline of the presentation MDG consistent Simple Macroeconomic framework (SMF)
Simple Macroeconomic Model for MDGs based Planning and Policy Analysis Thangavel Palanivel UNDP Regional Centre in Colombo Outline of the presentation MDG consistent Simple Macroeconomic framework (SMF)
ACC 121 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING
 PRINCIPLES OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING COURSE DESCRIPTION: Prerequisites: ACC 120 Corequisites: None This course includes a greater emphasis on managerial and cost accounting skills. Emphasis is on managerial
PRINCIPLES OF MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING COURSE DESCRIPTION: Prerequisites: ACC 120 Corequisites: None This course includes a greater emphasis on managerial and cost accounting skills. Emphasis is on managerial
Are we there yet? Adjustment paths in response to Tariff shocks: a CGE Analysis.
 Are we there yet? Adjustment paths in response to Tariff shocks: a CGE Analysis. This paper takes the mini USAGE model developed by Dixon and Rimmer (2005) and modifies it in order to better mimic the
Are we there yet? Adjustment paths in response to Tariff shocks: a CGE Analysis. This paper takes the mini USAGE model developed by Dixon and Rimmer (2005) and modifies it in order to better mimic the
Introduction. Prof. Eric Sims. Fall University of Notre Dame. Sims (ND) Introduction Fall / 26
 Introduction Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2010 Sims (ND) Introduction Fall 2010 1 / 26 Logistics Syllabus and related issues Sims (ND) Introduction Fall 2010 2 / 26 About Me Assistant
Introduction Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2010 Sims (ND) Introduction Fall 2010 1 / 26 Logistics Syllabus and related issues Sims (ND) Introduction Fall 2010 2 / 26 About Me Assistant
Monetary Theory and Policy. Fourth Edition. Carl E. Walsh. The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England
 Monetary Theory and Policy Fourth Edition Carl E. Walsh The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Contents Preface Introduction xiii xvii 1 Evidence on Money, Prices, and Output 1 1.1 Introduction
Monetary Theory and Policy Fourth Edition Carl E. Walsh The MIT Press Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England Contents Preface Introduction xiii xvii 1 Evidence on Money, Prices, and Output 1 1.1 Introduction
Week 11 Answer Key Spring 2015 Econ 210D K.D. Hoover. Week 11 Answer Key
 Week Answer Key Spring 205 Week Answer Key Problem 3.: Start with the inflow-outflow identity: () I + G + EX S +(T TR) + IM Subtract IM (imports) from both sides to get net exports (NX) on the left and
Week Answer Key Spring 205 Week Answer Key Problem 3.: Start with the inflow-outflow identity: () I + G + EX S +(T TR) + IM Subtract IM (imports) from both sides to get net exports (NX) on the left and
Lecture notes 10. Monetary policy: nominal anchor for the system
 Kevin Clinton Winter 2005 Lecture notes 10 Monetary policy: nominal anchor for the system 1. Monetary stability objective Monetary policy was a 20 th century invention Wicksell, Fisher, Keynes advocated
Kevin Clinton Winter 2005 Lecture notes 10 Monetary policy: nominal anchor for the system 1. Monetary stability objective Monetary policy was a 20 th century invention Wicksell, Fisher, Keynes advocated
IB Economics The Level of Overall Economic Activity 2.1: Economic Activity
 IB Economics: www.ibdeconomics.com 2.1 ECONOMIC ACTIVITY: STUDENT LEARNING ACTIVITY Answer the questions that follow. 1. DEFINITIONS Define the following terms: Income Factors of production Land entrepreneurship).
IB Economics: www.ibdeconomics.com 2.1 ECONOMIC ACTIVITY: STUDENT LEARNING ACTIVITY Answer the questions that follow. 1. DEFINITIONS Define the following terms: Income Factors of production Land entrepreneurship).
Capabilities of Correlation-Regression Analysis for Forecasting of Value Added Tax
 Capabilities of Correlation-Regression Analysis for Forecasting of Value Added Tax Doi:10.5901/mjss.2016.v7n1p24 Abstract Margarita S. Irizepova Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Chair of Finance, Credit,
Capabilities of Correlation-Regression Analysis for Forecasting of Value Added Tax Doi:10.5901/mjss.2016.v7n1p24 Abstract Margarita S. Irizepova Ph.D., Associate Professor of the Chair of Finance, Credit,
1 The Solow Growth Model
 1 The Solow Growth Model The Solow growth model is constructed around 3 building blocks: 1. The aggregate production function: = ( ()) which it is assumed to satisfy a series of technical conditions: (a)
1 The Solow Growth Model The Solow growth model is constructed around 3 building blocks: 1. The aggregate production function: = ( ()) which it is assumed to satisfy a series of technical conditions: (a)
ANALYSIS OF TAX AND TRADE INCENTIVES FOR FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT: THE CASE OF VIETNAM
 ANALYSIS OF TAX AND TRADE INCENTIVES FOR FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT: THE CASE OF VIETNAM A thesis presented by Le Minh Tuan to The Committee on Higher Degrees in Public Policy in partial fulfillment of
ANALYSIS OF TAX AND TRADE INCENTIVES FOR FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT: THE CASE OF VIETNAM A thesis presented by Le Minh Tuan to The Committee on Higher Degrees in Public Policy in partial fulfillment of
ECONOMICS QUESTION PAPER CODE 58/1/1 SECTION - A
 ECONOMICS Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) All questions in both the sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each
ECONOMICS Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 100 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) All questions in both the sections are compulsory. Marks for questions are indicated against each
Appendix to Zendesk, Inc Analyst & Investor Day
 Appendix to Zendesk, Inc. 2017 Analyst & Investor Day Important Disclosures Regarding the Analyst and Investor Day Materials This presentation and the accompanying oral presentation include forward-looking
Appendix to Zendesk, Inc. 2017 Analyst & Investor Day Important Disclosures Regarding the Analyst and Investor Day Materials This presentation and the accompanying oral presentation include forward-looking
Downloaded from
 XII ECONOMICS SURE SHOT SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS MICROECONOMICS UNIT - INTRODUCTION Q. Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. 3 Q.2 Discuss the central problems of an economy. Why do they
XII ECONOMICS SURE SHOT SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS MICROECONOMICS UNIT - INTRODUCTION Q. Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. 3 Q.2 Discuss the central problems of an economy. Why do they
Solutions To Problem Set Five
 Lecture 6 Simultaneous equilibrium in both goods and financial markets in the IS LM model () Idea: Any point on the IS curve represents the equilibrium level of output at an interest rate in the goods
Lecture 6 Simultaneous equilibrium in both goods and financial markets in the IS LM model () Idea: Any point on the IS curve represents the equilibrium level of output at an interest rate in the goods
TABLE OF CONTENTS. I. Executive Summary I-1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Organization Budget Document Organization 1 I. Executive Summary I-1 II. III. IV. Port View A. The Port of Seattle II-1 B. History of the Port of Seattle II-1 C. Facilities and Services
TABLE OF CONTENTS Organization Budget Document Organization 1 I. Executive Summary I-1 II. III. IV. Port View A. The Port of Seattle II-1 B. History of the Port of Seattle II-1 C. Facilities and Services
Mob.=
 Sample Question Paper Economics (030) Class XII (2014-15) Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 100 Instructions: 1. All questions in both sections are compulsory. However, there is internal choice in some questions.
Sample Question Paper Economics (030) Class XII (2014-15) Time : 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 100 Instructions: 1. All questions in both sections are compulsory. However, there is internal choice in some questions.
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Organization Budget Document Organization 1. I. Executive Summary I-1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS Organization Budget Document Organization 1 I. Executive Summary I-1 II. III. IV. Port View A. The Port of Seattle II-1 B. History of the Port of Seattle II-1 C. Facilities and Services
TABLE OF CONTENTS Organization Budget Document Organization 1 I. Executive Summary I-1 II. III. IV. Port View A. The Port of Seattle II-1 B. History of the Port of Seattle II-1 C. Facilities and Services
EMPIRE RESOURCES, INC.
 EMPIRE RESOURCES, INC. Empire Resources Reports Strong Year-Over-Year Growth For Fourth Quarter 2014 And Full Year Net Sales Increase 23% from Fourth Quarter of 2013 to $138.1 Million; Full Year 2014 Sales
EMPIRE RESOURCES, INC. Empire Resources Reports Strong Year-Over-Year Growth For Fourth Quarter 2014 And Full Year Net Sales Increase 23% from Fourth Quarter of 2013 to $138.1 Million; Full Year 2014 Sales
Modern Public Economics
 Modern Public Economics Second edition Raghbendra Jha B 366815 Routledge Taylor Si Francis Group LONDON AND NEW YORK Contents List of tables List of figures Preface Preface to the first edition xiv xv
Modern Public Economics Second edition Raghbendra Jha B 366815 Routledge Taylor Si Francis Group LONDON AND NEW YORK Contents List of tables List of figures Preface Preface to the first edition xiv xv
National Minimum Wage in South Africa: Quantification of Impact
 National Minimum Wage in South Africa: Quantification of Impact Asghar Adelzadeh, Ph.D. Director and Chief Economic Modeller Applied Development Research Solutions (ADRS) (asghar@adrs-global.com) Cynthia
National Minimum Wage in South Africa: Quantification of Impact Asghar Adelzadeh, Ph.D. Director and Chief Economic Modeller Applied Development Research Solutions (ADRS) (asghar@adrs-global.com) Cynthia
INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTANCY AND FINANCE
 INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTANCY AND FINANCE TITLES IN THIS SERIES Published R. J. Briston Introduction to Accountancy and Finance H. K. Jaeger The Structure of Consolidated Accounting Ernest Laidler Variance
INTRODUCTION TO ACCOUNTANCY AND FINANCE TITLES IN THIS SERIES Published R. J. Briston Introduction to Accountancy and Finance H. K. Jaeger The Structure of Consolidated Accounting Ernest Laidler Variance
Volume 29, Issue 3. Application of the monetary policy function to output fluctuations in Bangladesh
 Volume 29, Issue 3 Application of the monetary policy function to output fluctuations in Bangladesh Yu Hsing Southeastern Louisiana University A. M. M. Jamal Southeastern Louisiana University Wen-jen Hsieh
Volume 29, Issue 3 Application of the monetary policy function to output fluctuations in Bangladesh Yu Hsing Southeastern Louisiana University A. M. M. Jamal Southeastern Louisiana University Wen-jen Hsieh
General Equilibrium Analysis Part II A Basic CGE Model for Lao PDR
 Analysis Part II A Basic CGE Model for Lao PDR Capacity Building Workshop Enhancing Capacity on Trade Policies and Negotiations in Laos May 8-10, 2017 Vientienne, Lao PDR Professor Department of Economics
Analysis Part II A Basic CGE Model for Lao PDR Capacity Building Workshop Enhancing Capacity on Trade Policies and Negotiations in Laos May 8-10, 2017 Vientienne, Lao PDR Professor Department of Economics
October An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution.
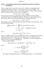 October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
MODEL VULNERABILITY Author: Mohammad Zolfaghari CatRisk Solutions
 BACKGROUND A catastrophe hazard module provides probabilistic distribution of hazard intensity measure (IM) for each location. Buildings exposed to catastrophe hazards behave differently based on their
BACKGROUND A catastrophe hazard module provides probabilistic distribution of hazard intensity measure (IM) for each location. Buildings exposed to catastrophe hazards behave differently based on their
1 What do you mean by Net Export? 2 Define Current Transfers? 3 Who is considered as normal resident of country?
 1 What do you mean by Net Export? 2 Define Current Transfers? 3 Who is considered as normal resident of country? 4 What do you ean by economic territory? 5. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? 6.
1 What do you mean by Net Export? 2 Define Current Transfers? 3 Who is considered as normal resident of country? 4 What do you ean by economic territory? 5. When will be NDP MP be less than NDP FC? 6.
Read The Invisible Man by H.G Wells and write a Book Review discussing the following aspects:
 CLASS - XII COMMERCE ENGLISH Read The Invisible Man by H.G Wells and write a Book Review discussing the following aspects: a. The novel as a cautionary tale b. Griffin as the anti-hero c. The adaptations
CLASS - XII COMMERCE ENGLISH Read The Invisible Man by H.G Wells and write a Book Review discussing the following aspects: a. The novel as a cautionary tale b. Griffin as the anti-hero c. The adaptations
Midterm 2 Review. ECON 30020: Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Sims University of Notre Dame, Spring 2018
 Midterm 2 Review ECON 30020: Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Sims University of Notre Dame, Spring 2018 The second midterm will take place on Thursday, March 29. In terms of the order of coverage,
Midterm 2 Review ECON 30020: Intermediate Macroeconomics Professor Sims University of Notre Dame, Spring 2018 The second midterm will take place on Thursday, March 29. In terms of the order of coverage,
LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1. Learning outcomes
 LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1 Learning outcomes After studying this unit, you should be able to: Define foreign exchange Know foreign exchange markets functions of foreign exchange market methods affecting
LESSON - 26 FOREIGN EXCHANGE - 1 Learning outcomes After studying this unit, you should be able to: Define foreign exchange Know foreign exchange markets functions of foreign exchange market methods affecting
DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL ASSIGNMENT ( ) SUBJECT: ECONOMICS (030) CLASS -XII
 DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL ASSIGNMENT (2017-18) SUBJECT: ECONOMICS (030) CLASS -XII UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1. Discuss the central problem of Economy? 2. What do you mean by production possibility frontier? 3.
DEHRADUN PUBLIC SCHOOL ASSIGNMENT (2017-18) SUBJECT: ECONOMICS (030) CLASS -XII UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1. Discuss the central problem of Economy? 2. What do you mean by production possibility frontier? 3.
1. GROSS NATIONAL INCOME AND THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS
 1. GROSS NATIONAL INCOME AND THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS Gross National Income... 3 Investment, Savings and the Current Account... 6 U.S. Savings and Current Account Experience... 7 The Balance of Payments
1. GROSS NATIONAL INCOME AND THE BALANCE OF PAYMENTS Gross National Income... 3 Investment, Savings and the Current Account... 6 U.S. Savings and Current Account Experience... 7 The Balance of Payments
List of tables List of boxes List of screenshots Preface to the third edition Acknowledgements
 Table of List of figures List of tables List of boxes List of screenshots Preface to the third edition Acknowledgements page xii xv xvii xix xxi xxv 1 Introduction 1 1.1 What is econometrics? 2 1.2 Is
Table of List of figures List of tables List of boxes List of screenshots Preface to the third edition Acknowledgements page xii xv xvii xix xxi xxv 1 Introduction 1 1.1 What is econometrics? 2 1.2 Is
Gehrke: Macroeconomics Winter term 2012/13. Exercises
 Gehrke: 320.120 Macroeconomics Winter term 2012/13 Questions #1 (National accounts) Exercises 1.1 What are the differences between the nominal gross domestic product and the real net national income? 1.2
Gehrke: 320.120 Macroeconomics Winter term 2012/13 Questions #1 (National accounts) Exercises 1.1 What are the differences between the nominal gross domestic product and the real net national income? 1.2
FISCAL CONSOLIDATION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH: A CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN. Ahmed Waqar Qasim Muhammad Ali Kemal Omer Siddique
 FISCAL CONSOLIDATION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH: A CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN Ahmed Waqar Qasim Muhammad Ali Kemal Omer Siddique Introduction Occasional spurts in economic growth but not sustainable. Haphazard growth
FISCAL CONSOLIDATION AND ECONOMIC GROWTH: A CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN Ahmed Waqar Qasim Muhammad Ali Kemal Omer Siddique Introduction Occasional spurts in economic growth but not sustainable. Haphazard growth
/
 SAMPLE QUESTIN PAPER 2 Economics Class II Time allowed: 3hrs Maximum Marks: 100 General Instructions: i. All questions in both the sections are compulsory. ii. Marks for questions are indicated against
SAMPLE QUESTIN PAPER 2 Economics Class II Time allowed: 3hrs Maximum Marks: 100 General Instructions: i. All questions in both the sections are compulsory. ii. Marks for questions are indicated against
Stabilization Policy and the AS/AD
 Stabilization Policy and the AS/AD Week 10 Vivaldo Mendes Dep. of Economics Instituto Universitário de Lisboa 25 November 2017 (Vivaldo Mendes ISCTE-IUL ) Macroeconomics I (L0271) 25 November 2014 1 /
Stabilization Policy and the AS/AD Week 10 Vivaldo Mendes Dep. of Economics Instituto Universitário de Lisboa 25 November 2017 (Vivaldo Mendes ISCTE-IUL ) Macroeconomics I (L0271) 25 November 2014 1 /
Lectures µy, ε,weseethata
 Lectures 13-14 The effect of changes in foreign demand on output and net exports Suppose that foreign income is increased by 4Y. For simplicity, assume that Y = Y TB. Figure 12-4 A rise in foreign
Lectures 13-14 The effect of changes in foreign demand on output and net exports Suppose that foreign income is increased by 4Y. For simplicity, assume that Y = Y TB. Figure 12-4 A rise in foreign
Microeconomic Foundations I Choice and Competitive Markets. David M. Kreps
 Microeconomic Foundations I Choice and Competitive Markets David M. Kreps PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS PRINCETON AND OXFORD Contents Preface xiii Chapter One. Choice, Preference, and Utility 1 1.1. Consumer
Microeconomic Foundations I Choice and Competitive Markets David M. Kreps PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PRESS PRINCETON AND OXFORD Contents Preface xiii Chapter One. Choice, Preference, and Utility 1 1.1. Consumer
1 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 1
 Contents Preface xvii 1 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 1 1.1 Measuring Business Cycles 1 1.2 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 4 1.3 Business Cycles in Poor, Emerging, and Rich Countries 7 1.4
Contents Preface xvii 1 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 1 1.1 Measuring Business Cycles 1 1.2 Business-Cycle Facts Around the World 4 1.3 Business Cycles in Poor, Emerging, and Rich Countries 7 1.4
Exercise 2 Short Run Output and Interest Rate Determination in an IS-LM Model
 Fletcher School, Tufts University Exercise 2 Short Run Output and Interest Rate Determination in an IS-LM Model Prof. George Alogoskoufis The IS LM Model Consider the following short run keynesian model
Fletcher School, Tufts University Exercise 2 Short Run Output and Interest Rate Determination in an IS-LM Model Prof. George Alogoskoufis The IS LM Model Consider the following short run keynesian model
Final Term Papers. Fall 2009 (Session 03a) ECO401. (Group is not responsible for any solved content) Subscribe to VU SMS Alert Service
 Fall 2009 (Session 03a) ECO401 (Group is not responsible for any solved content) Subscribe to VU SMS Alert Service To Join Simply send following detail to bilal.zaheem@gmail.com Full Name Master Program
Fall 2009 (Session 03a) ECO401 (Group is not responsible for any solved content) Subscribe to VU SMS Alert Service To Join Simply send following detail to bilal.zaheem@gmail.com Full Name Master Program
Notes II: Consumption-Saving Decisions, Ricardian Equivalence, and Fiscal Policy. Julio Garín Intermediate Macroeconomics Fall 2018
 Notes II: Consumption-Saving Decisions, Ricardian Equivalence, and Fiscal Policy Julio Garín Intermediate Macroeconomics Fall 2018 Introduction Intermediate Macroeconomics Consumption/Saving, Ricardian
Notes II: Consumption-Saving Decisions, Ricardian Equivalence, and Fiscal Policy Julio Garín Intermediate Macroeconomics Fall 2018 Introduction Intermediate Macroeconomics Consumption/Saving, Ricardian
Eco202 Review, April 2011, Prof. Bill Even. I. Introduction. A. The causes of the great recession B. Government responses to great recession
 Eco202 Review, April 2011, Prof. Bill Even I. Introduction. A. The causes of the great recession B. Government responses to great recession II. III. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth A. Definition
Eco202 Review, April 2011, Prof. Bill Even I. Introduction. A. The causes of the great recession B. Government responses to great recession II. III. Chapter 4: Measuring GDP and Economic Growth A. Definition
Hui Zhou. China's Monetary Policy. Regulation and Financial. Risk Prevention. The Study of Effectiveness. and Appropriateness.
 Hui Zhou China's Monetary Policy Regulation and Financial Risk Prevention The Study of Effectiveness and Appropriateness & Springer Contents 1 Literature Review and Research Framework 1 1.1 Literature
Hui Zhou China's Monetary Policy Regulation and Financial Risk Prevention The Study of Effectiveness and Appropriateness & Springer Contents 1 Literature Review and Research Framework 1 1.1 Literature
A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy. Chapter 30
 A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy Chapter 30 Key Macroeconomic Variables in an Open Economy The important macroeconomic variables of an open economy include: net exports net foreign investment
A Macroeconomic Theory of the Open Economy Chapter 30 Key Macroeconomic Variables in an Open Economy The important macroeconomic variables of an open economy include: net exports net foreign investment
Appendix A Specification of the Global Recursive Dynamic Computable General Equilibrium Model
 Appendix A Specification of the Global Recursive Dynamic Computable General Equilibrium Model The model is an extension of the computable general equilibrium (CGE) models used in China WTO accession studies
Appendix A Specification of the Global Recursive Dynamic Computable General Equilibrium Model The model is an extension of the computable general equilibrium (CGE) models used in China WTO accession studies
Estimating the Impact of Oil Prices and Interest Rates on the S&P 500
 Estimating the Impact of Oil Prices and Interest Rates on the S&P 500 January 13, 2015 by Eric Stubbs Advisor Perspectives welcomes guest contributions. The views presented here do not necessarily represent
Estimating the Impact of Oil Prices and Interest Rates on the S&P 500 January 13, 2015 by Eric Stubbs Advisor Perspectives welcomes guest contributions. The views presented here do not necessarily represent
Aggregate demand, aggregate supply and fiscal policy. Rush October 2014
 Aggregate demand, aggregate supply and fiscal policy Rush October 2014 Fiscal policy quick start In your notes (not to turn in), answer: What is fiscal policy? What might be the goals of EXPANSIONARY fiscal
Aggregate demand, aggregate supply and fiscal policy Rush October 2014 Fiscal policy quick start In your notes (not to turn in), answer: What is fiscal policy? What might be the goals of EXPANSIONARY fiscal
Mthuli Ncube Professor of Public Policy, Blavatnik School of Government, University of Oxford
 Global Growth and Financial Spillovers and the South African Macro-economy Mthuli Ncube Professor of Public Policy, Blavatnik School of Government, University of Oxford Nombulelo Gumata Economist, South
Global Growth and Financial Spillovers and the South African Macro-economy Mthuli Ncube Professor of Public Policy, Blavatnik School of Government, University of Oxford Nombulelo Gumata Economist, South
Suggested Solutions to Assignment 7 (OPTIONAL)
 EC 450 Advanced Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Wilfrid Laurier University Winter 2008 Suggested Solutions to Assignment 7 (OPTIONAL) Part B Problem Solving Questions
EC 450 Advanced Macroeconomics Instructor: Sharif F. Khan Department of Economics Wilfrid Laurier University Winter 2008 Suggested Solutions to Assignment 7 (OPTIONAL) Part B Problem Solving Questions
Modeling fiscal policy in a small, open, resourcerich
 Modeling fiscal policy in a small, open, resourcerich economy Norwegian experiences Ådne Cappelen Statistics Norway 1 MMU, Dec.2017 Outline Resource richness and fiscal policies Implications for private
Modeling fiscal policy in a small, open, resourcerich economy Norwegian experiences Ådne Cappelen Statistics Norway 1 MMU, Dec.2017 Outline Resource richness and fiscal policies Implications for private
What is Macroeconomics?
 Introduction ti to Macroeconomics MSc Induction Simon Hayley Simon.Hayley.1@city.ac.uk it What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole. It studies aggregate effects, such as:
Introduction ti to Macroeconomics MSc Induction Simon Hayley Simon.Hayley.1@city.ac.uk it What is Macroeconomics? Macroeconomics looks at the economy as a whole. It studies aggregate effects, such as:
Solving Risk Conditions Optimization Problem in Portfolio Models
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 6(9): 669-673, 2012 ISSN 1991-8178 Solving Risk Conditions Optimization Problem in Portfolio Models Reza Nazari Department of Economics, Tabriz branch,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 6(9): 669-673, 2012 ISSN 1991-8178 Solving Risk Conditions Optimization Problem in Portfolio Models Reza Nazari Department of Economics, Tabriz branch,
Unit-8: Profit Planning
 Unit-8: Profit Planning Introduction : Modern business world is full of competition, indecision and exposed to different types of risks. This complexity of managerial problems has led to the development
Unit-8: Profit Planning Introduction : Modern business world is full of competition, indecision and exposed to different types of risks. This complexity of managerial problems has led to the development
Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? Francesco Decarolis (Boston University)
 Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? 1) Data Francesco Decarolis (Boston University) The dataset was assembled from data made publicly available by CMS
Web Appendix for: Medicare Part D: Are Insurers Gaming the Low Income Subsidy Design? 1) Data Francesco Decarolis (Boston University) The dataset was assembled from data made publicly available by CMS
Topic 10: Asset Valuation Effects
 Topic 10: Asset Valuation Effects Part1: Document Asset holding developments - The relaxation of capital account restrictions in many countries over the last two decades has produced dramatic increases
Topic 10: Asset Valuation Effects Part1: Document Asset holding developments - The relaxation of capital account restrictions in many countries over the last two decades has produced dramatic increases
6 The Open Economy. This chapter:
 6 The Open Economy This chapter: Balance of Payments Accounting Savings and Investment in the Open Economy Determination of the Trade Balance and the Exchange Rate Mundell Fleming model Exchange Rate Regimes
6 The Open Economy This chapter: Balance of Payments Accounting Savings and Investment in the Open Economy Determination of the Trade Balance and the Exchange Rate Mundell Fleming model Exchange Rate Regimes
