Investigating the Impact of Public Debt on Economic Growth in Jamaica. Tarick Blake * Abstract
|
|
|
- Gavin Silas Fleming
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Investigating the Impact of Public Debt on Economic Growth in Jamaica Working Paper Tarick Blake * Fiscal and Economic Programme Monitoring Department Bank of Jamaica 2015 Abstract The Jamaican economy has been characterized by high levels of public debt concurrent with persistent low economic growth. As such, an understanding of the dynamics between public debt and growth is critical in addressing the obstacles to economic growth. Against this background, the paper investigates the impact of public debt on economic growth using quarterly data from 1990 to The paper employs an autoregressive distributed-lag model, which jointly captures both short-run and long-run effects. The results of the models indicate that the public debt has a non-linear impact on economic growth. Of note, the paper finds that the composition of debt matters, i.e. total public and external debts negatively affect economic growth in excess of 100 per cent and 55 per cent of GDP, respectively. JEL Classification: H62 E62 and D50 Keywords: External Debt, Gross Domestic Product, Auto Regressive Distributive Lag Model * The views expressed in this paper are not necessarily those of the Bank of Jamaica. 1
2 Contents Pages I. Introduction..3 II. III. IV. Literature Review.3 Overview of Public Debt and Economic Growth in Jamaica 6 Data...8 V. Methodology..9 VI. VII. Results and Discussion.12 Conclusion 14 References.16 Appendix 19 2
3 I. Introduction The Jamaican economy has been characterized by high levels of public debt along with persistent low economic growth. As such, an understanding of the dynamics between public debt and growth is critical in addressing the obstacles to economic growth and to improve debt sustainability in Jamaica. Traditionally, the main drivers of economic growth are the level and quality of a country s physical and human capital, technological advancement and the quality of the labour force as well as the country s level of openness to international trade. However, it is now universally accepted that a country s ability to grow also depends critically on its level of indebtedness. Debt financing provides fiscal space to governments which can facilitate growth through higher public investment. However, debt can create higher fiscal imbalances through greater debt servicing attributed, in part, to future increases in loans to repay existing debt. In addition, increase borrowing in the domestic economy can crowd out private sector investment. Further, research has shown that public debt levels have a non-linear impact on growth. Reinhart and Rogoff (2010) find that public debt to GDP in excess of 90 per cent has a negative impact on economic growth. There has been a limited number of studies in Jamaica that analyze the relationship between debt and economic growth. Against this background, the paper investigates the relationship between public debt and economic growth in Jamaica. In addition, the study seeks to determine whether there is evidence of a nonlinear impact of debt on growth and to identify this critical threshold beyond which debt impairs growth. Further, the paper attempts to clarify the impact of external and domestic debt on economic growth. Section two of the paper contains a review of the literature, while section three provides an overview of the relationship between external debt and growth in Jamaica. The data and methodology are outlined in sections four and five while section six contains the results. The conclusion is presented in section seven. II. Literature Review According to the conventional view of public debt (Elmendorf and Mankiw, 1999), in the shortrun output is demand-determined and fiscal deficits (or higher public debt) have a positive effect 3
4 on disposable income, aggregate demand and hence overall output. This positive short-run effect of budget deficits (and higher debt) is likely to be large when the country s output is far from capacity. However, in the long-run Elmendorf and Mankiw (1999) found that the reverse holds. In that if Ricardian Equivalence does not hold, the decrease in public savings brought about by a higher budget deficit will not be fully compensated for by an increase in private savings. 1 As a consequence, national savings will decrease, resulting in lower total investment. This will have a negative effect on GDP, as it leads to a smaller capital stock, higher interest rate, lower labour productivity and wages (Presbitero and Panizza, 2013). Presbitero and Panizza (2013) showed that this negative effect can be amplified by the presence of distortionary taxes. Greiner (2011) argued that the effect of debt on growth depends on the presence of rigidities in the economy. In particular, Greiner (2011) showed that, in a model with no rigidities and elastic labour supply, public debt has a negative effect on labor supply, investment, and economic growth. In the presence of wage rigidities and unemployment, public debt has no effect on the allocation of resources and can have a positive effect on growth if it is used to finance productive investment. Other researchers have also sought to explain theoretically the relationship between debt and economic growth. Presbitero (2010) stated that industrialized countries are better able than developing states to borrow and use domestic and foreign financing in a productive way, without bearing the costs of the disincentive to investment, capital flight, policy volatility and crowding out that generally go hand in hand with large debts. Continuing, the author noted that in developing countries the negative consequences of debt overhang are likely to offset the possible benefits derived from the availability of additional resources. This occurrence results from poor economic management and bad institutions within developing countries. Thus, irrespective of the income level, poor institutions and policies are likely to be the first-order constraints to growth. One of the most prominent paper on debt is Reinhart and Rogoff (2010) where the authors studied the relationship between high public debt levels, growth and inflation in 44 countries using a panel framework. The paper finds that a ratio of public debt to GDP in excess of 90 per 1 Ricardian Equivalence suggests that as governments try to stimulate demand by increasing debt-financed government spending, demand remains unchanged as the public will save excess money to pay for future tax increases that will be initiated to pay off the debt. 4
5 cent has a negative impact on economic growth. Using a dynamic panel based on an endogenous growth model Rother and Checherita (2010) in their study of 12 Euro area countries also found that debt in the range of 90 per cent to 100 per cent of GDP has a negative non-linear impact on growth. The authors showed that debt affects economic growth via its impact on private saving, public investment, total factor productivity as well as sovereign long-term nominal and real interest rates. Presbitero (2010) studied the relationship between external debt and economic growth in 114 developing countries over the period 1980 to 2004 using an ordinary least square and generalized method of moments techniques. He found that public debt has a negative impact on output growth in excess of 90 per cent of GDP in low and middle-income countries. 2 In contrast to the findings of Rother and Checherita (2010), Presbitero (2010) and Reinhart and Rogoff (2010), Simon et al (2014), in their study of the relationship between public debt levels and economic growth in advanced countries, did not find any threshold for debt ratios above which medium-term economic growth are significantly negatively affected. Notwithstanding, the authors did find evidence that higher debt levels are associated with a higher degree of output volatility. Calderón and Fuentes (2013) using a panel framework investigated the relationship between debt and growth in Latin America countries over the period 1970 to The study revealed that debt has a negative impact on economic growth. Notably, they show that strong institutions, high quality domestic policies, and outward-oriented policies partly mitigate the adverse effect of debt on economic growth. In addition, the paper shows that a simultaneous sharp reduction in public debt and an improvement in the policy environment induce an increase in the growth rate per capita of 1.7 percentage points for the Caribbean and 2 percentage points for South America. A number of studies has found that the composition or the type of debt matters. Using an auto regressive distributed lag (ARDL) approach, AKram (2011) examined the impact of public debt on economic growth and investment in Pakistan for the period He finds that the public external debt has a negative relationship with per capita GDP and investment in Pakistan, confirming the existence of a debt overhang effect. Musa et al (2013) examined the relationship 2 Minea and Parent (2012) study the relationship between debt and growth by using the Panel Smooth Threshold Regressions model. They find that public debt is negatively associated with growth when the debt-to-gdp ratio is above 90 per cent and below 115 per cent. 5
6 between economic growth, external debt and domestic debt in Nigeria over the period 1970 to They found that external debt has a negative impact on the economic performance of Nigeria. In contrast, they also show that domestic debt had a positive impact on economic growth through encouraging productivity and hence output growth. Omet el al (2002) studied the impact of external debt on the performance of the Jordan economy during the period 1970 to Using an endogenous growth model, the authors found that the positive effect of external debt on growth rapidly changes as external debt levels increase above the optimal level of 53 per cent of GDP. The authors noted that high debt levels are associated with low growth since a higher distortionary tax burden on capital is required to service debt, leading to a lower rate of return on capital, hence lower investment and growth. Using a dynamic panel data model on 93 developing countries, Ricci et al (2002) examined the impact of external debt on developing countries during the period 1969 to The findings showed that the average impact of debt on per capita growth becomes negative for debt levels above 160 per cent to170 per cent of exports and 35 per cent to 40 per cent of GDP. Hassan and Mamman (2013) examined the contribution of external debt to the economic growth in Nigeria over the period 1970 to 2010, through the use of an ordinary least square model. The authors result showed an inverse relationship between external debt and economic growth in Nigeria. However, Hassan and Mamman (2013) showed that debt service payments have a positive impact on economic growth in Nigeria. The authors explained that as the country pays its debts, it avoids the accumulation of interests and penalties thereby attracting foreign aid, foreign direct investments and other international opportunities that boost the economy in the long-run. With regard to Jamaica, Blavy (2006) in his study on productivity in Jamaica found that debt service crowded out investment in Jamaica, and as a result adversely affects productivity growth. He also showed that low levels of debt in Jamaica are associated with positive growth in productivity. III. Overview of Public Debt and Economic Growth in Jamaica Economic growth in Jamaica has been very low and volatile over the period 1990 to 2014, reflecting the vulnerability of the country to frequent natural disasters, adverse external and 6
7 internal shocks and social conflicts. On average, Jamaica s real GDP grew by 0.5 per cent between 1990 and Jamaica s low economic growth over the period can be partly explained by the financial crisis that the country experienced during the late 1990 s and the impact of the international financial crisis in 2008, which contributed to the persistent contraction in economic growth throughout 2008 to These factors combined with a large public debt-to-gdp ratio, often created macroeconomic uncertainty, high unemployment, emigration, declining external competiveness, limited access to finance by the private sector given the narrow scope of the financial sector, as well as rising crime rates, which dampened output growth in Jamaica over the period (Blavy, 2006). Jamaica is regarded as one the most highly indebted countries in the world. The country s debt to GDP ratio increased from 31.7 per cent in FY1990/91 to per cent in FY2014/15, while the domestic and external debt to GDP ratio grew from 7.3 per cent and 24.4 per cent in FY1990/91, respectively, to 67.5 per cent and 63.1 per cent in FY2014/15. 3 One of the primary factors which contributed to the increase in debt was the Government s bailout of the financial sector in the 1990s, which added approximately 40 per cent of GDP to the public debt (Government of Jamaica, 2011). In addition, persistent fiscal deficits, due in part to low economic growth, as well as the absorption of debt from loss making public entities by the Central Government and the exposure of the debt to exchange rate deprecation contributed to Jamaica s high debt over the period (CaPRI, 2008). Figure1 (below) shows that there tends to be a faster build-up in debt at lower levels of GDP growth. In addition, when GDP growth declines, there is larger increase in total debt. Notably, there is a stronger negative relationship between Jamaica s economic growth and the external debt. Against the background of the economic and fiscal challenges faced by the Government, Jamaica entered a Stand-by Agreement in 2010 with the International Monetary Fund and subsequently an Extended Fund Facility (EFF) in To date, the EFF programme has resulted in significant improvement in Jamaica s macro economy. This improvement has generated, in part, confidence in the domestic economy, both from the domestic and international markets. In this 3 Debt calculation includes central government direct and guaranteed, including PetroCaribe debt and BOJ debt. 7
8 context, Jamaica s real GDP expanded on average by 0.6 per cent during FY2013/14 to FY2014/15, relative to an average contraction of 0.8 per cent over FY2009/10 to FY2012/13. Similarly, Jamaica s debt to GDP ratio fell from per cent in FY2010/11 to in FY2014/15 (see Figure 1). Figure 1: Public Debt and Economic Growth in Jamaica IV. Data The study utilizes quarterly data from 1990 to The change in real GDP is used as a measure of economic growth while investment is measured by the change in gross fixed capital formation. The paper measures debt burden by the ratio of debt to nominal GDP, the ratio of external debt to nominal GDP and the ratio of domestic debt to nominal GDP. Openness to trade is measured by the total of imports and exports divided by nominal GDP. The openness indicator is included to capture the impact of globalization and free trade on economic growth. Notably, the long-run coefficient on openness is expected to be positive. The short-run estimate is expected to be negative. This is in a context where Jamaica is highly dependent on imports. Given that the country has consistently recorded trade deficits, the increasing levels of trade in the absence of significant rise in exports should have a negative impact on GDP. The other independent variable is labour, measured as Jamaica employed labour force. The long-run 4 Data obtained from the Ministry of Finance, the Statistical Institute of Jamaica and the Bank of Jamaica. 8
9 coefficient on labour is expected to be positive based on economic growth theory. However, the short-run coefficient on labour could be negative due to the findings of Blavy (2006) that labour productivity in Jamaica is generally low, which could have a negative impact on economic growth. The final independent variable is inflation, which captures uncertainty in the economy. The model includes a dummy variable to capture the structural breaks in the economy due mainly to the local financial crisis. All variables are logged and first differenced. The Phillips Perron-Test for unit root revealed that most of the variables in the model are I (0) while the others were stationary after taking the first difference (see Table 1, Appendix). In addition, the first difference of all variables were normally distributed based on the Jarque-Bera test. V. Methodology To gauge the relationship between public debt and economic growth, an ARDL approach was used. The ARDL approach allows the inclusion of dynamic variables to mitigate the impact of the endogeneity of the explanatory variables (Ekanayake (2012). Furthermore, the general to specific modeling procedure provides consistent estimators when the variables of concern are of different orders of integration. This feature minimized the possibility of estimating spurious relations, while retaining long-run information (Ekanayake (2012). Additionally, for a finite sample, the ARDL methodology provides precise estimators and valid t-statistics (Pesaran, et al. 2001). Another advantage of working with ARDL specification is that all of the independent variables enter the equation with a lag, which mitigates any contemporaneous causation from the dependent variable to the independent variables, which could bias the estimates (Catao and Terrones 2003). In addition, the ARDL model is selected on the basis that the model specification has no bias to the order of integration of the variables when assessing a long-run relationship compared to other error correction models, such as the vector error correction model, which requires all variables to be integrated of the same order (Scarlett, 2011). The ARDL model has the advantage of yielding consistent estimates of the long-run coefficients that are asymptotically normal. Furthermore, the estimation of the model can be carried out using ordinary least squares (OLS) from which the long-run relationships can be ascertained. However, the ARDL approach employs only a single reduced form equation and therefore it is necessary to 9
10 avoid bi-directional causality between the main variables of concern (Ekanayake, 2012). In this regard, this study carries out Granger causality tests to determine the causality between variables. The ARDL framework implemented in its log format is outlined below: p y t = β 0 + y t 1 + λ j t 1 + θx J,t 1 + k=1 Ω p k y t k + k=1 Г k j t k + q l=0 α J X J,t 1 + ε t...(e1) In the model, the dependent variable Y t (which is measured by the change in real GDP), ϳ the main explanatory variable (measure by ratio of debt to GDP) and explanatory variables X J (which include, investments, inflation, labour, and openness) enter the ARDL regression with lag of order p and q, respectively. The coefficients on the level effects are and θ with the long-run effects estimated as - θ and - λ, with representing the convergence parameter (speed of adjustment to the long run relationship). Additionally, the short run coefficients are Ω, Г and α. Given that the research is interested in assessing whether there exists a non-linear impact of government debt on growth, a quadratic equation in debt is included in the model. The latter is used to capture the impact of increasing levels of debt on economic growth. This is outline in the model below: 2 y t = β 0 + y t 1 + λ j t 1 + λ j t 1 + θx J,t 1 + k=1 Ω k y t k + k=1 Г k j t k + p k=1 q Г 2 k j t k + l=0 α J X J,t 1 + ε t (E2) p p Where: ϳ 2 is the non-linear variable, which is derive by squaring the ratio of debt to GDP. If the coefficients on the linear and quadratic debt terms are significantly deferent from zero then the hypothesis of a non-linear effect of debt on economic growth would be confirmed in Jamaica. Given the existence of a non-linear relationship between debt and economic growth, equation 3 attempts to identify the level of debt at which the non-linear relationship holds by including 10
11 dummy variables to capture specific debt levels. In this regard, the ARDL model employed is as follows: p y t = β 0 + y t 1 + λ j t 1 + θx J,t 1 + k=1 Ω p k y t k + k=1 Г k j t k + q l=0 α J X J,t 1 + D i,t + ε t.. (E3) Where D i,t captures respective debt levels of interest. To investigate the relationship between the debt public (and the composition of debt) and economic growth in Jamaica the study estimates several models. The first model (Model 1), which is derived from equation 2, has real GDP as the dependent variable, the main independent variable as the ratio of debt to GDP along with the quadratic term in debt and the vector X consisting of the other independent variables. These are investment, lag real GDP, the ratio of openness to GDP, labour, and a dummy variable to capture the impact of structural changes in the economy. The second model (M2) seeks to determine the level at which debt negatively affect economic growth. Model 2 consist of M1 (excluding the quadratic debt terms) along with a dummy variable to capture the threshold that debt negatively affect economic growth. The third model (M3) seeks to capture the impact of domestic and external debt on economic growth. M3 replicates M1 by replacing the main independent variable, ratio of debt to GDP, with the ratios of domestic and external debt to GDP along with their quadratic terms. The model also includes the CPI variable. The final model (M4), seeks to determine the level at which domestic and external debt negatively affect growth. This model is built from M3 by replacing the quadratic terms with two dummy variables that capture the threshold that domestic and external debt negatively affect economic growth. To test the existence of a long-run relationship between the variables under investigation a Wald test was employed (i.e. Ho: β1=β2=β3= β4= β5=0). The Wald test statistic is compared with the bound test critical values tabulated by Pesaran, et al. (2001). If the Wald test statistics were greater than the upper bound of the critical value, the null hypothesis can be rejected to conclude that there exists a long-run relation between the variables of concern. If it were smaller than the lower bound critical value, the null hypothesis cannot be rejected. Finally, if it falls within the 11
12 lower and upper bound, the results become inconclusive (Pesaran, et al., 2001). The Wald F test statistics for all models exceeded the upper bound critical value and therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected, confirming a long-run relationship among the variables of interest (see Table 2). The ARDL models employed in the paper are normal distributed based on the Jarque-Bera test. Similarly, none of the ARDL models are found to have serial correlation based on the Breusch- Godfrey Serial Correlation LM test or heteroskedasticity based on the Harvey test (see Table 3). In addition, the Granger causality tests indicate that there is no bi-directional causality between the main variables (see Table 5). VI. Results and Discussion Model 1 estimates the relationship between the public debt and economic growth in Jamaica. The results suggest that public debt has a non-linear impact on economic growth both in the long and short runs as indicated by the statistical significance of the non-linear variable (see Tables 3 & 4 in the appendix). Furthermore, both in the long and short runs, public debt at low levels has a positive impact on economic growth, while public debt at high levels has a negative impact on economic growth. More specifically, in the long-run, at low levels of debt, economic growth increases by 0.06 per cent after a one percentage point increase in the ratio of debt to GDP, while at high levels of debt, a one percentage point increase in the ratio of debt-to-gdp reduces economic growth by 0.02 per cent. Similarly, in the short-run, at high levels of debt, economic growth is reduced by 0.04 per cent after a one percentage point increase in the ratio of debt-to- GDP, while at low levels of debt, a one percentage point in ratio of debt to GDP increases GDP by 0.19 per cent. To gauge the level at which debt negatively affect economic growth in Jamaica the results from Model 2 indicate that ratios of debt to GDP in excess of 100 per cent have a negative and statistical significant impact on economic growth in Jamaica (see Tables 3 & 4 in the appendix). The above results, imply that debt has a statistical and significant inverse relationship with economic growth at high levels in Jamaica. That is, the greater the level of debt, the more the economy growth decreases. This results may partly reflect the use of loan receipts (outside of capital linked loans) on non-productive activities / sectors. Notably, a significant portion of debt proceeds in Jamaica is used to repay other debts rather than to boost capital investment. For 12
13 example, US$1.5 billion of the recent debt raising of US$2.0 billion on the ICM was used to repay debt to Venezuela. In addition, Jamaica s high debt level is largely attributed to the Government s bailout of the financial sector in the 1990s, which added approximately 40 per cent of GDP to the public debt (Government of Jamaica, 2011). Further, the Government s absorption of losses and debt from loss making public entities such as Air Jamaica, Clarendon Alumna Partners and Sugar Company of Jamaica and the exposure of Jamaica debt to exchange rate deprecation also contributed significantly to its high debt levels. The crowding out of the private sector by Government as it seeks to finance its debt payments could also explain the negative relationship. That is, the Jamaican Government borrowed extensively in the domestic bond market, which would have diverted funds away for private sector investment and would have also facilitated an increase in interest rates, which had a further damping impact on economic growth. Notably, the results of the paper is consistent with the findings of Rother and Checherita (2010), Reinhart and Rogoff (2010) and Presbitero (2010) who found that debt has a negative effect on economic growth at certain levels of debt. The signs of the coefficients on the key indicators of growth in Model 1 is generally in line with expectations for the long and short runs. That is the coefficients on investments and labour are positive and statistically significant in the short and long runs, with the exception of labour in the short-run. However, the openness to trade variable was not statistical significant both in the long and short runs. Further, the model is robust based on the standard normality, heteroskedasticity and serial correlation tests. The results from Model 3 which estimates the impact of external and domestic debt on economic growth in Jamaica show that external debt has a non-linear impact on economic growth both in the short and long run as indicated by the statistical significance of the non-linear variable. In addition, both in the long and short runs, external debt at low levels has a positive impact on economic growth, while external debt at high levels has a negative impact on economic growth. With regards to the domestic debt, the results show that in the short-run high levels of domestic debt has a statistical negative impact on economic growth, however, lower levels of debt while having a negative impact on GDP, the relation was not statistically significant. Further in the long-run, while the results show that domestic debt does not have a non-linear relationship with economic growth, domestic debt has an overall positive impact on economic growth. Against 13
14 this background, external debt has a greater statistical negative impact on economic growth in Jamaica. It is possible that domestic debt create additional spending in the economy which is used, in part, to generate additional activity. The signs of the coefficients on the other indicators of growth in Model 3 is generally in line with expectations. The coefficients on investments, openness and labour in the long-run are positive and statistically significant, while in the shortrun the coefficient on investment remains the same, however, the impact from labour and openness while remaining statistically significance are negative. The negative openness coefficient in the short-run may arise from the large import content in production, however, as businesses grow efficiencies improve in the long-run. Similarly, in the short-run the low quality of the Jamaican labour force could have a negative impact on growth as indicated by Blavy (2006) due to low labour productivity. However, as training is received on the job, the contribution of labour to economic growth increases in the long-run. Notably, the model is robust based on the standard normality, heteroskedasticity and serial correlation tests. The results from Model 4 reveal that that ratio of external debt-to-gdp in excess of 55 per cent has a negative and significant impact on economic growth in Jamaica. 5 The results are consistent with the findings of Ricci et al (2002), AKram (2011) and Musa et al (2013) who show that high external debt has a negative impact on economic growth. The results also support Omet et al (2002) findings that high external debt levels are associated with low growth as a higher distortionary tax burden on capital is required to service debt, leading to a lower rate of return on capital, and hence lower investment and economic growth. VII. Conclusion The study explores the relationship between public debt and economic growth in Jamaica from 1990 to 2014 using an ARDL approach. Specifically, the paper investigated the existence of a non-linear relationship between public debt and economic growth. The results indicate that public debt has a non-linear impact on economic growth. Of note, the paper finds that public and external debt negatively affect economic growth in excess of 100 per cent and 55 per cent of 5 The threshold impact for domestic debt was not access given that the non-linear impact in the long-run was not confirmed. 14
15 GDP, respectively. Furthermore, the results indicate that external debt has a greater statistical negative impact on economic growth in Jamaica. The findings are consistent with the results from other studies, specifically those related to developing countries. Given the potential impact of public debt on economic growth in Jamaica, it is imperative that the Government of Jamaica seek to reduce debt levels by implementing sound fiscal and debt management policies. Specifically the Government s debt strategy should be geared towards reducing the country s exposure to external debt given the overwhelming negative impact on growth and to increase financing from the domestic market. Notwithstanding, the Government should expeditiously seek to implement structural reforms geared towards fiscal consolidation, debt management, public sector reform and tax reform, which are necessary for economic expansion as well as for fiscal and debt sustainability. In addition, the strict implementation of fiscal rules, as outlined in the Government s medium-term macroeconomic programme, will be critical for achieving debt and fiscal sustainability. 6 Due to the limited scope of the study, there are some areas that warrant further investigation. A much larger data set and the employment of different methodologies, which capture the impact of maturity structure, interest rate and currency composition of debt, could facilitate further research on the subject area. 6 The fiscal rules put a limits on the Government s ability to incur huge fiscal deficits. 15
16 References Akram, N. (2011). Impact of Public Debt on the economic growth of Pakistan. Centre for Poverty Reduction and Social Policy Development, Islamabad. Blavy, R. (2006). Public Debt and Productivity: The Difficult Quest for Growth in Jamaica. IMF Working Paper Calderon, C. & Fuentes, J. R. (2013). Government Debt and Economic Growth. Inter-American Development Bank Working Paper Series, (424). Caribbean Policy Research Institute (CaPRI). (2008). Jamaica s Debt: Exploring Causes and Strategies. Catao, L., & Terrones. T. (2003, April). Fiscal Deficits and Inflation. IMF Working Paper WP/03/65. Ekanayake, H. K. (2012). The Link between Fiscal Deficit and Inflation: Do Public Sector Wages Matter. Australia South Asia Research Centre, (14). Elmendorf, D. W., and Mankiw, G.N. (1999). Government Debt. Handbook of Macroeconomics 1(25), pp
17 Government of Jamaica. (2011). Fiscal Policy Paper. Greiner, A. (2011). Economic Growth, Public Debt and Welfare: Comparing Three Budget Rules German Economic Review, 12(2), pp Hassan, S. U., & Mamman, A. (2013). External Debt and Economic Growth: Evidence From Nigeria. International Journal of Economics, Business and Finance 1(10). Krugman, P. (1988). Financing vs. Forgiving a Debt Overhang: Some Analytical Issues. NBER Working Paper No (Cambridge, Massachusetts: National Bureau of Economic Research). Minea, A., & Parent. (2012). Is high Public Debt Always Harmful to Economic Growth? Reinhart and Rogoff and some Complex Nonlinearities. Association Francaise de Cliometrie Working Paper, (8). Musa, S., Ahmadu A. H., & Aminu U. (2013). External Debt and Domestic Debt Impact on the Growth of the Nigerian Economy. International J. Educational Research 1 (2). Omet, G., Aktham, M., & Fadwa, K. (2002). External Debt and Economic Growth in Jordan: The Threshold Effect. Faculty of Economics & Administrative Sciences The Hashemite University Jordan. Pesaran, H., Shin, Y., & Smith, R. (2001). Bound Testing Approaches to the Analysis of Level Relationships. Journal of Applied Econometrics, 16(3), Presbitero, A. F. (2008). The Debt-Growth Nexus in Poor Countries: A Reassessment. Economics: The Open-Access. Open-Assessment E-Journal 2. Presbitero, A.F. (2010). Total Public Debt and Growth in Developing Countries. 17
18 Presbitero, A.F., & Panizza, U. (2013). Public Debt and Economic Growth in Advanced Economies: A Survey. Money and Finance Group Working Paper, (78). Reinhart, C. M., & Kenneth S. R. (201). Growth in a Time of Debt. American Economic Review: Papers & Proceedings Ricci, L., Catherine, P., & Helene, P. (2002). External Debt and Growth. IMF Working Paper 02.(69). Rother, P., & Cristina, C. (2010). The Impact of High and Growing Government on Economic Growth: An Empirical Investigation for the Euro Area. ECB Working Paper 12 (37). Scarlett, G.H. (2011). Tax Policy and Economic Growth in Jamaica. Bank of Jamaica Working Paper Simon, J., Sandri, D,. & Pescatori, A. (2014). Debt and Growth: Is There a Magic Threshold? IMF Working Paper 14.(34). 18
19 Appendix Table 1: Unit Root Test Variables Phillips-Perron Test Level 1st Difference Test Statistic Critical Values Test Statistic Critical Values Intercept Trend & Intercept Intercept Trend & Intercept Intercept Trend & Intercept Intercept Trend & Intercept Log Public Debt/GDP *** *** (Log Public Debt/GDP)^ *** *** Log External Debt/GDP *** *** (Log External Debt/GDP)^ ** *** Log Domestic Debt/GDP ** *** Log (Domestic Debt/GDP)^ *** *** Log CPI *** *** Log Real GDP *** *** Log Labour *** Log Openness *** *** Log Investment *** *** Notes: *,**,*** are Mackinnon critical valves for the rejection of the null hypothesis of a unit root at the 10%, 5% and 1% levels respectively. 19
20 Table 2: Bound Test Results Model Wald test F statistic Model *** Model *** Model *** Model *** Notes: Critical Value for Bound Test (Pesaran et, al 2001, p 300) intercept and trend( k=4) :[ 4.617, 5.786] at 1% and [3.539, 4.667] at 5% intercept and trend( k=5) :[ 4.011, 5.331] at 1% and [3.189, 4.329] at 5% intercept and trend( k=8) :[ 3.220, 4.411] at 1% and [2.604, 3.46] at 5% *** and ** indicate significance at 1% and 5%,respectively Table 3: Model 1 to Model 4 Short-run Results 20
21 Results of the General to Specific ARDL Models Variables Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 Coefficient Std. Error Coefficient Std. Error Coefficient Std. Error Coefficient Std. Error L GDP (-1) *** *** *** *** L Public Debt/GDP (-3) *** *** (L Public Debt/GDP)^2 (-1) *** L External Debt/GDP (-3) *** *** (L External Debt/GDP)^2 (-1) ** L Domestic Debt/GDP (-3) ** (L Domestic Debt/GDP)^2 (-1) L Investment (-3) *** *** ** ** L Openess (-3) L Openess (-2) ** L Labour (-3) ** L Labour (-1) *** ** L CPI(-1) *** DL GDP (-3) *** DL GDP (-1) *** *** DL Public Debt/GDP (-1) *** (DL Public Debt/GDP)^2 (-3) ** DL External Debt/GDP (-1) *** ** (DL External Debt/GDP)^2 (-3) ** DL Domestic Debt/GDP (-1) (L Domestic Debt/GDP)^2 (-3) *** DL Investment (-8) * DL Investment (-4) *** DL Openness (-1) ** DL labour(-1) ** DL CPI(-1) *** ** Local Finanical Crisis Dummy *** *** ** ** Public Debt 100 Threshold Dummy ** External Debt 55 Threshold Dummy *** Trend * * *** * constant *** *** *** *** R-Square Jargue-Bera Prob Value Breusch-Godfrey Serial Correlation Test Harvey Test Heteroskedasticity Test White-Heteroscedasticity Robust Standard Errors are included Note: Level of Significance: *----10% Level of Significance: **---5% Level of Significance: ***---1% Dependent Variable: DL GDP Table 4: Model 1 to Model 4 Long-run Results 21
22 Results of the Long Run Coefficents ARDL Models Variables Model 1 Model 2 Model 3 Model 4 L Public Debt/GDP (-3) (L Public Debt/GDP)^2 (-1) L External Debt/GDP (-3) (L External Debt/GDP)^2 (-1) L Domestic Debt/GDP (-3) 0.05 (L Domestic Debt/GDP)^2 (-1) 0.00 L Investment (-3) L Investment (-1) L Openness (-3) L Openness (-2) L labour (-3) L labour (-1) L CPI (-1) Table 5: Granger Causality Tests 22
The Dynamics between Government Debt and Economic Growth in South Asia: A Time Series Approach
 The Empirical Economics Letters, 15(9): (September 16) ISSN 1681 8997 The Dynamics between Government Debt and Economic Growth in South Asia: A Time Series Approach Nimantha Manamperi * Department of Economics,
The Empirical Economics Letters, 15(9): (September 16) ISSN 1681 8997 The Dynamics between Government Debt and Economic Growth in South Asia: A Time Series Approach Nimantha Manamperi * Department of Economics,
Exploring the Link between Fiscal Policy and Inflation in Jamaica. Tarick Blake * Abstract
 Exploring the Link between Fiscal Policy and Inflation in Jamaica Working Paper Tarick Blake * Fiscal and Economic Programme Monitoring Department Bank of Jamaica 2014 Abstract The relationship between
Exploring the Link between Fiscal Policy and Inflation in Jamaica Working Paper Tarick Blake * Fiscal and Economic Programme Monitoring Department Bank of Jamaica 2014 Abstract The relationship between
The Effects of Public Debt on Economic Growth and Gross Investment in India: An Empirical Evidence
 Volume 8, Issue 1, July 2015 The Effects of Public Debt on Economic Growth and Gross Investment in India: An Empirical Evidence Amanpreet Kaur Research Scholar, Punjab School of Economics, GNDU, Amritsar,
Volume 8, Issue 1, July 2015 The Effects of Public Debt on Economic Growth and Gross Investment in India: An Empirical Evidence Amanpreet Kaur Research Scholar, Punjab School of Economics, GNDU, Amritsar,
The Short and Long-Run Implications of Budget Deficit on Economic Growth in Nigeria ( )
 Canadian Social Science Vol. 10, No. 5, 2014, pp. 201-205 DOI:10.3968/4517 ISSN 1712-8056[Print] ISSN 1923-6697[Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The Short and Long-Run Implications of Budget Deficit
Canadian Social Science Vol. 10, No. 5, 2014, pp. 201-205 DOI:10.3968/4517 ISSN 1712-8056[Print] ISSN 1923-6697[Online] www.cscanada.net www.cscanada.org The Short and Long-Run Implications of Budget Deficit
Thi-Thanh Phan, Int. Eco. Res, 2016, v7i6, 39 48
 INVESTMENT AND ECONOMIC GROWTH IN CHINA AND THE UNITED STATES: AN APPLICATION OF THE ARDL MODEL Thi-Thanh Phan [1], Ph.D Program in Business College of Business, Chung Yuan Christian University Email:
INVESTMENT AND ECONOMIC GROWTH IN CHINA AND THE UNITED STATES: AN APPLICATION OF THE ARDL MODEL Thi-Thanh Phan [1], Ph.D Program in Business College of Business, Chung Yuan Christian University Email:
The relationship amongst public debt and economic growth in developing country case of Tunisia
 The relationship amongst public debt and economic growth in developing country case of Tunisia FERHI Sabrine Department of economic, FSEGT Faculty of Economics and Management Tunis Campus EL MANAR 1 sabrineferhi@yahoo.fr
The relationship amongst public debt and economic growth in developing country case of Tunisia FERHI Sabrine Department of economic, FSEGT Faculty of Economics and Management Tunis Campus EL MANAR 1 sabrineferhi@yahoo.fr
Sovereign debt crisis and economic growth: new evidence for the euro area
 Sovereign debt crisis and economic growth: new evidence for the euro area Iuliana Matei 1 Abstract: The recent euro area financial crisis has revived the debates on the macroeconomic impact of sovereign
Sovereign debt crisis and economic growth: new evidence for the euro area Iuliana Matei 1 Abstract: The recent euro area financial crisis has revived the debates on the macroeconomic impact of sovereign
Determinants of Revenue Generation Capacity in the Economy of Pakistan
 2014, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Determinants of Revenue Generation Capacity in the Economy of Pakistan Khurram Ejaz Chandia 1,
2014, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com Determinants of Revenue Generation Capacity in the Economy of Pakistan Khurram Ejaz Chandia 1,
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ECONOMIC GROWTH AND PUBLIC DEBT: A SURVEY OF THE EMPIRICAL LITERATURE
 International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. IV, Issue 9, September 2016 http://ijecm.co.uk/ ISSN 2348 0386 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ECONOMIC GROWTH AND PUBLIC DEBT:
International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management United Kingdom Vol. IV, Issue 9, September 2016 http://ijecm.co.uk/ ISSN 2348 0386 THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ECONOMIC GROWTH AND PUBLIC DEBT:
Sovereign Debt and Economic Growth in the European Monetary Union
 The Park Place Economist Volume 24 Issue 1 Article 8 2016 Sovereign Debt and Economic Growth in the European Monetary Union Joseph 16 Illinois Wesleyan University, jbakke@iwu.edu Recommended Citation,
The Park Place Economist Volume 24 Issue 1 Article 8 2016 Sovereign Debt and Economic Growth in the European Monetary Union Joseph 16 Illinois Wesleyan University, jbakke@iwu.edu Recommended Citation,
Government Tax Revenue, Expenditure, and Debt in Sri Lanka : A Vector Autoregressive Model Analysis
 Government Tax Revenue, Expenditure, and Debt in Sri Lanka : A Vector Autoregressive Model Analysis Introduction Uthajakumar S.S 1 and Selvamalai. T 2 1 Department of Economics, University of Jaffna. 2
Government Tax Revenue, Expenditure, and Debt in Sri Lanka : A Vector Autoregressive Model Analysis Introduction Uthajakumar S.S 1 and Selvamalai. T 2 1 Department of Economics, University of Jaffna. 2
ARE EXPORTS AND IMPORTS COINTEGRATED? EVIDENCE FROM NINE MENA COUNTRIES* HUSEIN, Jamal ** Abstract
 ARE EXPORTS AND IMPORTS COINTEGRATED? EVIDENCE FROM NINE MENA COUNTRIES* HUSEIN, Jamal ** Abstract The aim of this article is to examine the long-run convergence (cointegration) between exports and imports
ARE EXPORTS AND IMPORTS COINTEGRATED? EVIDENCE FROM NINE MENA COUNTRIES* HUSEIN, Jamal ** Abstract The aim of this article is to examine the long-run convergence (cointegration) between exports and imports
Public Debt and Economic Growth Nexus: Evidence from South Asia. Abstract
 Public Debt and Economic Growth Nexus: Evidence from South Asia Abstract It is well established in literature that the public debt and economic growth bear positive and non-linear relationship. However,
Public Debt and Economic Growth Nexus: Evidence from South Asia Abstract It is well established in literature that the public debt and economic growth bear positive and non-linear relationship. However,
The Debt-to-GDP Threshold Effect On Output: A Country- Specific Analysis
 The Debt-to-GDP Threshold Effect On Output: A Country- Specific Analysis by Luke Lechtenberg Abstract: The recent economics literature has focused on establishing a general debt-to-gdp threshold across
The Debt-to-GDP Threshold Effect On Output: A Country- Specific Analysis by Luke Lechtenberg Abstract: The recent economics literature has focused on establishing a general debt-to-gdp threshold across
Structural Cointegration Analysis of Private and Public Investment
 International Journal of Business and Economics, 2002, Vol. 1, No. 1, 59-67 Structural Cointegration Analysis of Private and Public Investment Rosemary Rossiter * Department of Economics, Ohio University,
International Journal of Business and Economics, 2002, Vol. 1, No. 1, 59-67 Structural Cointegration Analysis of Private and Public Investment Rosemary Rossiter * Department of Economics, Ohio University,
MONEY, PRICES, INCOME AND CAUSALITY: A CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN
 The Journal of Commerce, Vol. 4, No. 4 ISSN: 2218-8118, 2220-6043 Hailey College of Commerce, University of the Punjab, PAKISTAN MONEY, PRICES, INCOME AND CAUSALITY: A CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN Dr. Nisar
The Journal of Commerce, Vol. 4, No. 4 ISSN: 2218-8118, 2220-6043 Hailey College of Commerce, University of the Punjab, PAKISTAN MONEY, PRICES, INCOME AND CAUSALITY: A CASE STUDY OF PAKISTAN Dr. Nisar
THE IMPACT OF IMPORT ON INFLATION IN NAMIBIA
 European Journal of Business, Economics and Accountancy Vol. 5, No. 2, 207 ISSN 2056-608 THE IMPACT OF IMPORT ON INFLATION IN NAMIBIA Mika Munepapa Namibia University of Science and Technology NAMIBIA
European Journal of Business, Economics and Accountancy Vol. 5, No. 2, 207 ISSN 2056-608 THE IMPACT OF IMPORT ON INFLATION IN NAMIBIA Mika Munepapa Namibia University of Science and Technology NAMIBIA
An Empirical Analysis on the Relationship between Health Care Expenditures and Economic Growth in the European Union Countries
 An Empirical Analysis on the Relationship between Health Care Expenditures and Economic Growth in the European Union Countries Çiğdem Börke Tunalı Associate Professor, Department of Economics, Faculty
An Empirical Analysis on the Relationship between Health Care Expenditures and Economic Growth in the European Union Countries Çiğdem Börke Tunalı Associate Professor, Department of Economics, Faculty
Volume 35, Issue 1. Thai-Ha Le RMIT University (Vietnam Campus)
 Volume 35, Issue 1 Exchange rate determination in Vietnam Thai-Ha Le RMIT University (Vietnam Campus) Abstract This study investigates the determinants of the exchange rate in Vietnam and suggests policy
Volume 35, Issue 1 Exchange rate determination in Vietnam Thai-Ha Le RMIT University (Vietnam Campus) Abstract This study investigates the determinants of the exchange rate in Vietnam and suggests policy
The Impact of Tax Policies on Economic Growth: Evidence from Asian Economies
 The Impact of Tax Policies on Economic Growth: Evidence from Asian Economies Ihtsham ul Haq Padda and Naeem Akram Abstract Tax based fiscal policies have been regarded as less policy tool to overcome the
The Impact of Tax Policies on Economic Growth: Evidence from Asian Economies Ihtsham ul Haq Padda and Naeem Akram Abstract Tax based fiscal policies have been regarded as less policy tool to overcome the
Relationship between Inflation and Unemployment in India: Vector Error Correction Model Approach
 Relationship between Inflation and Unemployment in India: Vector Error Correction Model Approach Anup Sinha 1 Assam University Abstract The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between
Relationship between Inflation and Unemployment in India: Vector Error Correction Model Approach Anup Sinha 1 Assam University Abstract The purpose of this study is to investigate the relationship between
MEASURING THE OPTIMAL MACROECONOMIC UNCERTAINTY INDEX FOR TURKEY
 ECONOMIC ANNALS, Volume LXI, No. 210 / July September 2016 UDC: 3.33 ISSN: 0013-3264 DOI:10.2298/EKA1610007E Havvanur Feyza Erdem* Rahmi Yamak** MEASURING THE OPTIMAL MACROECONOMIC UNCERTAINTY INDEX FOR
ECONOMIC ANNALS, Volume LXI, No. 210 / July September 2016 UDC: 3.33 ISSN: 0013-3264 DOI:10.2298/EKA1610007E Havvanur Feyza Erdem* Rahmi Yamak** MEASURING THE OPTIMAL MACROECONOMIC UNCERTAINTY INDEX FOR
jei External Debt and Economic Growth : The Case of Emerging Economy Sami Al Kharusi
 Journal of Economic Integration External Debt and Economic Growth : The Case of Emerging Economy Sami Al Kharusi Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, Oman Mbah Stella Ada Federal University Oye-Ekiti, Ekiti
Journal of Economic Integration External Debt and Economic Growth : The Case of Emerging Economy Sami Al Kharusi Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, Oman Mbah Stella Ada Federal University Oye-Ekiti, Ekiti
An Empirical Study on the Determinants of Dollarization in Cambodia *
 An Empirical Study on the Determinants of Dollarization in Cambodia * Socheat CHIM Graduate School of Economics, Osaka University 1-7 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka, Osaka, 560-0043, Japan E-mail: chimsocheat3@yahoo.com
An Empirical Study on the Determinants of Dollarization in Cambodia * Socheat CHIM Graduate School of Economics, Osaka University 1-7 Machikaneyama, Toyonaka, Osaka, 560-0043, Japan E-mail: chimsocheat3@yahoo.com
A Note on the Oil Price Trend and GARCH Shocks
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive A Note on the Oil Price Trend and GARCH Shocks Li Jing and Henry Thompson 2010 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/20654/ MPRA Paper No. 20654, posted 13. February
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive A Note on the Oil Price Trend and GARCH Shocks Li Jing and Henry Thompson 2010 Online at http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/20654/ MPRA Paper No. 20654, posted 13. February
Journal of Asian Business Strategy Volume 7, Issue 1(2017): 13-22
 Journal of Asian Business Strategy Volume 7, Issue 1(2017): 13-22 http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5006 The role of oil price fluctuations on the USD/EUR exchange rate: an ARDL bounds testing approach
Journal of Asian Business Strategy Volume 7, Issue 1(2017): 13-22 http://aessweb.com/journal-detail.php?id=5006 The role of oil price fluctuations on the USD/EUR exchange rate: an ARDL bounds testing approach
Composition of Foreign Capital Inflows and Growth in India: An Empirical Analysis.
 Composition of Foreign Capital Inflows and Growth in India: An Empirical Analysis. Author Details: Narender,Research Scholar, Faculty of Management Studies, University of Delhi. Abstract The role of foreign
Composition of Foreign Capital Inflows and Growth in India: An Empirical Analysis. Author Details: Narender,Research Scholar, Faculty of Management Studies, University of Delhi. Abstract The role of foreign
Effect of Macroeconomic Variables on Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan
 Effect of Macroeconomic Variables on Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan Mangal 1 Abstract Foreign direct investment is essential for economic growth of a country. It acts as a catalyst for the economic
Effect of Macroeconomic Variables on Foreign Direct Investment in Pakistan Mangal 1 Abstract Foreign direct investment is essential for economic growth of a country. It acts as a catalyst for the economic
A Threshold Multivariate Model to Explain Fiscal Multipliers with Government Debt
 Econometric Research in Finance Vol. 4 27 A Threshold Multivariate Model to Explain Fiscal Multipliers with Government Debt Leonardo Augusto Tariffi University of Barcelona, Department of Economics Submitted:
Econometric Research in Finance Vol. 4 27 A Threshold Multivariate Model to Explain Fiscal Multipliers with Government Debt Leonardo Augusto Tariffi University of Barcelona, Department of Economics Submitted:
A Study on Impact of WPI, IIP and M3 on the Performance of Selected Sectoral Indices of BSE
 A Study on Impact of WPI, IIP and M3 on the Performance of Selected Sectoral Indices of BSE J. Gayathiri 1 and Dr. L. Ganesamoorthy 2 1 (Research Scholar, Department of Commerce, Annamalai University,
A Study on Impact of WPI, IIP and M3 on the Performance of Selected Sectoral Indices of BSE J. Gayathiri 1 and Dr. L. Ganesamoorthy 2 1 (Research Scholar, Department of Commerce, Annamalai University,
Optimal fiscal policy
 Optimal fiscal policy Jasper Lukkezen Coen Teulings Overview Aim Optimal policy rule for fiscal policy How? Four building blocks: 1. Linear VAR model 2. Augmented by linearized equation for debt dynamics
Optimal fiscal policy Jasper Lukkezen Coen Teulings Overview Aim Optimal policy rule for fiscal policy How? Four building blocks: 1. Linear VAR model 2. Augmented by linearized equation for debt dynamics
Equity Price Dynamics Before and After the Introduction of the Euro: A Note*
 Equity Price Dynamics Before and After the Introduction of the Euro: A Note* Yin-Wong Cheung University of California, U.S.A. Frank Westermann University of Munich, Germany Daily data from the German and
Equity Price Dynamics Before and After the Introduction of the Euro: A Note* Yin-Wong Cheung University of California, U.S.A. Frank Westermann University of Munich, Germany Daily data from the German and
Cross- Country Effects of Inflation on National Savings
 Cross- Country Effects of Inflation on National Savings Qun Cheng Xiaoyang Li Instructor: Professor Shatakshee Dhongde December 5, 2014 Abstract Inflation is considered to be one of the most crucial factors
Cross- Country Effects of Inflation on National Savings Qun Cheng Xiaoyang Li Instructor: Professor Shatakshee Dhongde December 5, 2014 Abstract Inflation is considered to be one of the most crucial factors
Economics Bulletin, 2013, Vol. 33 No. 3 pp
 1. Introduction In an attempt to facilitate faster economic growth through greater economic cooperation and free trade, the last four decades have witnessed the formation of major trading blocs and memberships
1. Introduction In an attempt to facilitate faster economic growth through greater economic cooperation and free trade, the last four decades have witnessed the formation of major trading blocs and memberships
The trade balance and fiscal policy in the OECD
 European Economic Review 42 (1998) 887 895 The trade balance and fiscal policy in the OECD Philip R. Lane *, Roberto Perotti Economics Department, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland Columbia University,
European Economic Review 42 (1998) 887 895 The trade balance and fiscal policy in the OECD Philip R. Lane *, Roberto Perotti Economics Department, Trinity College Dublin, Dublin 2, Ireland Columbia University,
Money Market Uncertainty and Retail Interest Rate Fluctuations: A Cross-Country Comparison
 DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS JOHANNES KEPLER UNIVERSITY LINZ Money Market Uncertainty and Retail Interest Rate Fluctuations: A Cross-Country Comparison by Burkhard Raunig and Johann Scharler* Working Paper
DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS JOHANNES KEPLER UNIVERSITY LINZ Money Market Uncertainty and Retail Interest Rate Fluctuations: A Cross-Country Comparison by Burkhard Raunig and Johann Scharler* Working Paper
Institute of Economic Research Working Papers. No. 63/2017. Short-Run Elasticity of Substitution Error Correction Model
 Institute of Economic Research Working Papers No. 63/2017 Short-Run Elasticity of Substitution Error Correction Model Martin Lukáčik, Karol Szomolányi and Adriana Lukáčiková Article prepared and submitted
Institute of Economic Research Working Papers No. 63/2017 Short-Run Elasticity of Substitution Error Correction Model Martin Lukáčik, Karol Szomolányi and Adriana Lukáčiková Article prepared and submitted
A Note on the Oil Price Trend and GARCH Shocks
 A Note on the Oil Price Trend and GARCH Shocks Jing Li* and Henry Thompson** This paper investigates the trend in the monthly real price of oil between 1990 and 2008 with a generalized autoregressive conditional
A Note on the Oil Price Trend and GARCH Shocks Jing Li* and Henry Thompson** This paper investigates the trend in the monthly real price of oil between 1990 and 2008 with a generalized autoregressive conditional
Determinants of foreign direct investment in Malaysia
 Nanyang Technological University From the SelectedWorks of James B Ang 2008 Determinants of foreign direct investment in Malaysia James B Ang, Nanyang Technological University Available at: https://works.bepress.com/james_ang/8/
Nanyang Technological University From the SelectedWorks of James B Ang 2008 Determinants of foreign direct investment in Malaysia James B Ang, Nanyang Technological University Available at: https://works.bepress.com/james_ang/8/
Multiple Regression Approach to Fit Suitable Model for All Share Price Index with Other Important Related Factors
 Multiple Regression Approach to Fit Suitable Model for All Share Price Index with Other Important Related Factors Aboobacker Jahufer and Imras AHM Department of Mathematical Science, Faculty of Applied
Multiple Regression Approach to Fit Suitable Model for All Share Price Index with Other Important Related Factors Aboobacker Jahufer and Imras AHM Department of Mathematical Science, Faculty of Applied
AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF THE PUBLIC DEBT RELEVANCE TO THE ECONOMIC GROWTH OF THE USA
 AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF THE PUBLIC DEBT RELEVANCE TO THE ECONOMIC GROWTH OF THE USA Petar Kurečić University North, Koprivnica, Trg Žarka Dolinara 1, Croatia petar.kurecic@unin.hr Marin Milković University
AN EMPIRICAL ANALYSIS OF THE PUBLIC DEBT RELEVANCE TO THE ECONOMIC GROWTH OF THE USA Petar Kurečić University North, Koprivnica, Trg Žarka Dolinara 1, Croatia petar.kurecic@unin.hr Marin Milković University
Asian Economic and Financial Review THE EFFECT OF OIL INCOME ON REAL EXCHANGE RATE IN IRANIAN ECONOMY. Adibeh Savari. Hassan Farazmand.
 Asian Economic and Financial Review journal homepage: http://www.aessweb.com/journals/5002 THE EFFECT OF OIL INCOME ON REAL EXCHANGE RATE IN IRANIAN ECONOMY Adibeh Savari Department of Economics, Science
Asian Economic and Financial Review journal homepage: http://www.aessweb.com/journals/5002 THE EFFECT OF OIL INCOME ON REAL EXCHANGE RATE IN IRANIAN ECONOMY Adibeh Savari Department of Economics, Science
The effect of unemployment on economic growth in South Africa ( )
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The effect of unemployment on economic growth in South Africa (1994-2016) Sibusiso Clement Makaringe and Hlalefang Khobai 19 March 2018 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/85305/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive The effect of unemployment on economic growth in South Africa (1994-2016) Sibusiso Clement Makaringe and Hlalefang Khobai 19 March 2018 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/85305/
Impact of Devaluation on Trade Balance in Pakistan
 Page 16 Oeconomics of Knowledge, Volume 3, Issue 3, 3Q, Summer 2011 Impact of Devaluation on Trade Balance in Pakistan Muhammad ASIF, Lecturer Management Sciences Department CIIT, Abbottabad, Pakistan
Page 16 Oeconomics of Knowledge, Volume 3, Issue 3, 3Q, Summer 2011 Impact of Devaluation on Trade Balance in Pakistan Muhammad ASIF, Lecturer Management Sciences Department CIIT, Abbottabad, Pakistan
Chapter 4 Level of Volatility in the Indian Stock Market
 Chapter 4 Level of Volatility in the Indian Stock Market Measurement of volatility is an important issue in financial econometrics. The main reason for the prominent role that volatility plays in financial
Chapter 4 Level of Volatility in the Indian Stock Market Measurement of volatility is an important issue in financial econometrics. The main reason for the prominent role that volatility plays in financial
The relationship between the government debt and GDP growth: evidence of the Euro area countries
 The relationship between the government debt and GDP growth: evidence of the Euro area countries AUTHORS ARTICLE INFO JOURNAL Stella Spilioti Stella Spilioti (2015). The relationship between the government
The relationship between the government debt and GDP growth: evidence of the Euro area countries AUTHORS ARTICLE INFO JOURNAL Stella Spilioti Stella Spilioti (2015). The relationship between the government
Private Consumption Expenditure in the Eastern Caribbean Currency Union
 Private Consumption Expenditure in the Eastern Caribbean Currency Union by Richard Sutherland Summer Intern, Research Department Central Bank of Barbados, BARBADOS and Post-graduate Student, Department
Private Consumption Expenditure in the Eastern Caribbean Currency Union by Richard Sutherland Summer Intern, Research Department Central Bank of Barbados, BARBADOS and Post-graduate Student, Department
Outward FDI and Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from Germany
 Outward FDI and Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from Germany Outward investment substitutes foreign for domestic production, thereby reducing total output and thus employment in the home (outward investing)
Outward FDI and Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from Germany Outward investment substitutes foreign for domestic production, thereby reducing total output and thus employment in the home (outward investing)
Tax or Spend, What Causes What? Reconsidering Taiwan s Experience
 International Journal of Business and Economics, 2003, Vol. 2, No. 2, 109-119 Tax or Spend, What Causes What? Reconsidering Taiwan s Experience Scott M. Fuess, Jr. Department of Economics, University of
International Journal of Business and Economics, 2003, Vol. 2, No. 2, 109-119 Tax or Spend, What Causes What? Reconsidering Taiwan s Experience Scott M. Fuess, Jr. Department of Economics, University of
VERIFYING OF BETA CONVERGENCE FOR SOUTH EAST COUNTRIES OF ASIA
 Journal of Indonesian Applied Economics, Vol.7 No.1, 2017: 59-70 VERIFYING OF BETA CONVERGENCE FOR SOUTH EAST COUNTRIES OF ASIA Michaela Blasko* Department of Operation Research and Econometrics University
Journal of Indonesian Applied Economics, Vol.7 No.1, 2017: 59-70 VERIFYING OF BETA CONVERGENCE FOR SOUTH EAST COUNTRIES OF ASIA Michaela Blasko* Department of Operation Research and Econometrics University
Macroeconomic Policy: Evidence from Growth Laffer Curve for Sri Lanka. Sujith P. Jayasooriya, Ch.E. (USA) Innovation4Development Consultants
 Macroeconomic Policy: Evidence from Growth Laffer Curve for Sri Lanka Sujith P. Jayasooriya, Ch.E. (USA) Innovation4Development Consultants INTRODUCTION The concept of optimal taxation policies has recently
Macroeconomic Policy: Evidence from Growth Laffer Curve for Sri Lanka Sujith P. Jayasooriya, Ch.E. (USA) Innovation4Development Consultants INTRODUCTION The concept of optimal taxation policies has recently
RE-EXAMINE THE INTER-LINKAGE BETWEEN ECONOMIC GROWTH AND INFLATION:EVIDENCE FROM INDIA
 6 RE-EXAMINE THE INTER-LINKAGE BETWEEN ECONOMIC GROWTH AND INFLATION:EVIDENCE FROM INDIA Pratiti Singha 1 ABSTRACT The purpose of this study is to investigate the inter-linkage between economic growth
6 RE-EXAMINE THE INTER-LINKAGE BETWEEN ECONOMIC GROWTH AND INFLATION:EVIDENCE FROM INDIA Pratiti Singha 1 ABSTRACT The purpose of this study is to investigate the inter-linkage between economic growth
The Bilateral J-Curve: Sweden versus her 17 Major Trading Partners
 Bahmani-Oskooee and Ratha, International Journal of Applied Economics, 4(1), March 2007, 1-13 1 The Bilateral J-Curve: Sweden versus her 17 Major Trading Partners Mohsen Bahmani-Oskooee and Artatrana Ratha
Bahmani-Oskooee and Ratha, International Journal of Applied Economics, 4(1), March 2007, 1-13 1 The Bilateral J-Curve: Sweden versus her 17 Major Trading Partners Mohsen Bahmani-Oskooee and Artatrana Ratha
The Effects of Monetary and Fiscal Policy on the Stock Market in Nigeria
 Journal of Economics and Development Studies March 2018, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 79-85 ISSN: 2334-2382 (Print), 2334-2390 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research
Journal of Economics and Development Studies March 2018, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp. 79-85 ISSN: 2334-2382 (Print), 2334-2390 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). All Rights Reserved. Published by American Research
Foreign Direct Investment and Islamic Banking: A Granger Causality Test
 Foreign Direct Investment and Islamic Banking: A Granger Causality Test Gholamreza Tajgardoon Department of economics of research and training institute for management and development planning President
Foreign Direct Investment and Islamic Banking: A Granger Causality Test Gholamreza Tajgardoon Department of economics of research and training institute for management and development planning President
IMPLICATIONS OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIATION COST ON ECONOMIC GROWTH IN NIGERIA.
 IMPLICATIONS OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIATION COST ON ECONOMIC GROWTH IN NIGERIA. Dr. Nwanne, T. F. I. Ph.D, HCIB Department of Accounting/Finance, Faculty of Management and Social Sciences Godfrey Okoye University,
IMPLICATIONS OF FINANCIAL INTERMEDIATION COST ON ECONOMIC GROWTH IN NIGERIA. Dr. Nwanne, T. F. I. Ph.D, HCIB Department of Accounting/Finance, Faculty of Management and Social Sciences Godfrey Okoye University,
DYNAMIC FEEDBACK BETWEEN MONEY SUPPLY, EXCHANGE RATES AND INFLATION IN SRI LANKA
 Journal of Applied Economics and Business DYNAMIC FEEDBACK BETWEEN MONEY SUPPLY, EXCHANGE RATES AND INFLATION IN SRI LANKA O. G. Dayaratna-Banda 1*, R. C. P. Padmasiri 2 1 Department of Economics and Statistics,
Journal of Applied Economics and Business DYNAMIC FEEDBACK BETWEEN MONEY SUPPLY, EXCHANGE RATES AND INFLATION IN SRI LANKA O. G. Dayaratna-Banda 1*, R. C. P. Padmasiri 2 1 Department of Economics and Statistics,
Threshold Analysis of Fiscal Deficits with Respect to Monetary Growth: Evidence from Nigeria
 Threshold Analysis of Fiscal Deficits with Respect to Monetary Growth: Evidence from Nigeria Sanusi Kazeem Abimbola School of Economics, Accounting & IT, North West University, Vaal Triangle Campus, South
Threshold Analysis of Fiscal Deficits with Respect to Monetary Growth: Evidence from Nigeria Sanusi Kazeem Abimbola School of Economics, Accounting & IT, North West University, Vaal Triangle Campus, South
DATABASE AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
 CHAPTER III DATABASE AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY The nature of the present study Direct Tax Reforms in India: A Comparative Study of Pre and Post-liberalization periods is such that it requires secondary
CHAPTER III DATABASE AND RESEARCH METHODOLOGY The nature of the present study Direct Tax Reforms in India: A Comparative Study of Pre and Post-liberalization periods is such that it requires secondary
Determinants of Cyclical Aggregate Dividend Behavior
 Review of Economics & Finance Submitted on 01/Apr./2012 Article ID: 1923-7529-2012-03-71-08 Samih Antoine Azar Determinants of Cyclical Aggregate Dividend Behavior Dr. Samih Antoine Azar Faculty of Business
Review of Economics & Finance Submitted on 01/Apr./2012 Article ID: 1923-7529-2012-03-71-08 Samih Antoine Azar Determinants of Cyclical Aggregate Dividend Behavior Dr. Samih Antoine Azar Faculty of Business
Inflation and inflation uncertainty in Argentina,
 U.S. Department of the Treasury From the SelectedWorks of John Thornton March, 2008 Inflation and inflation uncertainty in Argentina, 1810 2005 John Thornton Available at: https://works.bepress.com/john_thornton/10/
U.S. Department of the Treasury From the SelectedWorks of John Thornton March, 2008 Inflation and inflation uncertainty in Argentina, 1810 2005 John Thornton Available at: https://works.bepress.com/john_thornton/10/
The other half of the public debt economic growth relationship: a note on Reinhart and Rogoff
 European Journal of Economics and Economic Policies: Intervention, Vol. 12 No. 1, 2015, pp. 20 28 The other half of the public debt economic growth relationship: a note on Reinhart and Rogoff Yannis Dafermos*
European Journal of Economics and Economic Policies: Intervention, Vol. 12 No. 1, 2015, pp. 20 28 The other half of the public debt economic growth relationship: a note on Reinhart and Rogoff Yannis Dafermos*
Available online at ScienceDirect. Energy Procedia 75 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 2658 2664 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Impact of Energy Consumption, GDP & Fiscal Deficit
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 75 (2015 ) 2658 2664 The 7 th International Conference on Applied Energy ICAE2015 Impact of Energy Consumption, GDP & Fiscal Deficit
Determinants of Unemployment: Empirical Evidence from Palestine
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Determinants of Unemployment: Empirical Evidence from Palestine Gaber Abugamea Ministry of Education&Higher Education 14 October 2018 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/89424/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Determinants of Unemployment: Empirical Evidence from Palestine Gaber Abugamea Ministry of Education&Higher Education 14 October 2018 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/89424/
Public Expenditure on Capital Formation and Private Sector Productivity Growth: Evidence
 ISSN 2029-4581. ORGANIZATIONS AND MARKETS IN EMERGING ECONOMIES, 2012, VOL. 3, No. 1(5) Public Expenditure on Capital Formation and Private Sector Productivity Growth: Evidence from and the Euro Area Jolanta
ISSN 2029-4581. ORGANIZATIONS AND MARKETS IN EMERGING ECONOMIES, 2012, VOL. 3, No. 1(5) Public Expenditure on Capital Formation and Private Sector Productivity Growth: Evidence from and the Euro Area Jolanta
Factors Affecting the Movement of Stock Market: Evidence from India
 Factors Affecting the Movement of Stock Market: Evidence from India V. Ramanujam Assistant Professor, Bharathiar School of Management and Entrepreneur Development, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, Tamil
Factors Affecting the Movement of Stock Market: Evidence from India V. Ramanujam Assistant Professor, Bharathiar School of Management and Entrepreneur Development, Bharathiar University, Coimbatore, Tamil
Oil Price Effects on Exchange Rate and Price Level: The Case of South Korea
 Oil Price Effects on Exchange Rate and Price Level: The Case of South Korea Mirzosaid SULTONOV 東北公益文科大学総合研究論集第 34 号抜刷 2018 年 7 月 30 日発行 研究論文 Oil Price Effects on Exchange Rate and Price Level: The Case
Oil Price Effects on Exchange Rate and Price Level: The Case of South Korea Mirzosaid SULTONOV 東北公益文科大学総合研究論集第 34 号抜刷 2018 年 7 月 30 日発行 研究論文 Oil Price Effects on Exchange Rate and Price Level: The Case
A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF REAL AND PREDICTED INFLATION CONVERGENCE IN CEE COUNTRIES DURING THE ECONOMIC CRISIS
 A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF REAL AND PREDICTED INFLATION CONVERGENCE IN CEE COUNTRIES DURING THE ECONOMIC CRISIS Mihaela Simionescu * Abstract: The main objective of this study is to make a comparative analysis
A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF REAL AND PREDICTED INFLATION CONVERGENCE IN CEE COUNTRIES DURING THE ECONOMIC CRISIS Mihaela Simionescu * Abstract: The main objective of this study is to make a comparative analysis
Volume 29, Issue 3. Application of the monetary policy function to output fluctuations in Bangladesh
 Volume 29, Issue 3 Application of the monetary policy function to output fluctuations in Bangladesh Yu Hsing Southeastern Louisiana University A. M. M. Jamal Southeastern Louisiana University Wen-jen Hsieh
Volume 29, Issue 3 Application of the monetary policy function to output fluctuations in Bangladesh Yu Hsing Southeastern Louisiana University A. M. M. Jamal Southeastern Louisiana University Wen-jen Hsieh
GMM for Discrete Choice Models: A Capital Accumulation Application
 GMM for Discrete Choice Models: A Capital Accumulation Application Russell Cooper, John Haltiwanger and Jonathan Willis January 2005 Abstract This paper studies capital adjustment costs. Our goal here
GMM for Discrete Choice Models: A Capital Accumulation Application Russell Cooper, John Haltiwanger and Jonathan Willis January 2005 Abstract This paper studies capital adjustment costs. Our goal here
Cash holdings determinants in the Portuguese economy 1
 17 Cash holdings determinants in the Portuguese economy 1 Luísa Farinha Pedro Prego 2 Abstract The analysis of liquidity management decisions by firms has recently been used as a tool to investigate the
17 Cash holdings determinants in the Portuguese economy 1 Luísa Farinha Pedro Prego 2 Abstract The analysis of liquidity management decisions by firms has recently been used as a tool to investigate the
Government expenditure and Economic Growth in MENA Region
 Available online at http://sijournals.com/ijae/ Government expenditure and Economic Growth in MENA Region Mohsen Mehrara Faculty of Economics, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran Email: mmehrara@ut.ac.ir
Available online at http://sijournals.com/ijae/ Government expenditure and Economic Growth in MENA Region Mohsen Mehrara Faculty of Economics, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran Email: mmehrara@ut.ac.ir
Savings Investment Correlation in Developing Countries: A Challenge to the Coakley-Rocha Findings
 Savings Investment Correlation in Developing Countries: A Challenge to the Coakley-Rocha Findings Abu N.M. Wahid Tennessee State University Abdullah M. Noman University of New Orleans Mohammad Salahuddin*
Savings Investment Correlation in Developing Countries: A Challenge to the Coakley-Rocha Findings Abu N.M. Wahid Tennessee State University Abdullah M. Noman University of New Orleans Mohammad Salahuddin*
Debt Financing and Real Output Growth: Is There a Threshold Effect?
 Debt Financing and Real Output Growth: Is There a Threshold Effect? M. Hashem Pesaran Department of Economics & USC Dornsife INET, University of Southern California, USA and Trinity College, Cambridge,
Debt Financing and Real Output Growth: Is There a Threshold Effect? M. Hashem Pesaran Department of Economics & USC Dornsife INET, University of Southern California, USA and Trinity College, Cambridge,
Testing the Stability of Demand for Money in Tonga
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Testing the Stability of Demand for Money in Tonga Saten Kumar and Billy Manoka University of the South Pacific, University of Papua New Guinea 12. June 2008 Online at
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Testing the Stability of Demand for Money in Tonga Saten Kumar and Billy Manoka University of the South Pacific, University of Papua New Guinea 12. June 2008 Online at
Linkage between Gold and Crude Oil Spot Markets in India-A Cointegration and Causality Analysis
 Linkage between Gold and Crude Oil Spot Markets in India-A Cointegration and Causality Analysis Narinder Pal Singh Associate Professor Jagan Institute of Management Studies Rohini Sector -5, Delhi Sugandha
Linkage between Gold and Crude Oil Spot Markets in India-A Cointegration and Causality Analysis Narinder Pal Singh Associate Professor Jagan Institute of Management Studies Rohini Sector -5, Delhi Sugandha
Macroeconomic Fundamental and Stock Price Index in Southeast Asia Countries: A Comparative Study
 International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues ISSN: 2146-4138 available at http: www.econjournals.com International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 2017, 7(2), 182-187. Macroeconomic
International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues ISSN: 2146-4138 available at http: www.econjournals.com International Journal of Economics and Financial Issues, 2017, 7(2), 182-187. Macroeconomic
ARDL Approach for Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Pakistan ( ): An Empirical Study
 Global Journal of Quantitative Science Vol. 3. No.2. June 2016 Issue. Pp.9-14 ARDL Approach for Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Pakistan (1961-2013): An Empirical Study Zahid Iqbal 1,
Global Journal of Quantitative Science Vol. 3. No.2. June 2016 Issue. Pp.9-14 ARDL Approach for Determinants of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in Pakistan (1961-2013): An Empirical Study Zahid Iqbal 1,
Research note: Contribution of foreign direct investment to the tourism sector in Fiji: an empirical study
 Tourism Economics, 2014, 20 (6), 1357 1362 doi: 10.5367/te.2013.0358 Research note: Contribution of foreign direct investment to the tourism sector in Fiji: an empirical study T. K. JAYARAMAN School of
Tourism Economics, 2014, 20 (6), 1357 1362 doi: 10.5367/te.2013.0358 Research note: Contribution of foreign direct investment to the tourism sector in Fiji: an empirical study T. K. JAYARAMAN School of
THE INFLATION - INFLATION UNCERTAINTY NEXUS IN ROMANIA
 THE INFLATION - INFLATION UNCERTAINTY NEXUS IN ROMANIA Daniela ZAPODEANU University of Oradea, Faculty of Economic Science Oradea, Romania Mihail Ioan COCIUBA University of Oradea, Faculty of Economic
THE INFLATION - INFLATION UNCERTAINTY NEXUS IN ROMANIA Daniela ZAPODEANU University of Oradea, Faculty of Economic Science Oradea, Romania Mihail Ioan COCIUBA University of Oradea, Faculty of Economic
Economic Growth and Convergence across the OIC Countries 1
 Economic Growth and Convergence across the OIC Countries 1 Abstract: The main purpose of this study 2 is to analyze whether the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) countries show a regional economic
Economic Growth and Convergence across the OIC Countries 1 Abstract: The main purpose of this study 2 is to analyze whether the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) countries show a regional economic
INVESTMENT AND THE GOLDEN RULE IN THE EUROPEAN UNION
 INVESTMENT AND THE GOLDEN RULE IN THE EUROPEAN UNION Abstract Ada Cristina MARINESCU, PhD Student We will study in this paper the relation between public investment, public debt and fiscal rules in the
INVESTMENT AND THE GOLDEN RULE IN THE EUROPEAN UNION Abstract Ada Cristina MARINESCU, PhD Student We will study in this paper the relation between public investment, public debt and fiscal rules in the
Dynamics of Twin Deficits in South Asian Countries
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Dynamics of Twin Deficits in South Asian Countries Kinza Mumtaz and Kashif Munir University of Central Punjab 9 September 2016 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/74592/
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Dynamics of Twin Deficits in South Asian Countries Kinza Mumtaz and Kashif Munir University of Central Punjab 9 September 2016 Online at https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/74592/
Foreign direct investment and profit outflows: a causality analysis for the Brazilian economy. Abstract
 Foreign direct investment and profit outflows: a causality analysis for the Brazilian economy Fernando Seabra Federal University of Santa Catarina Lisandra Flach Universität Stuttgart Abstract Most empirical
Foreign direct investment and profit outflows: a causality analysis for the Brazilian economy Fernando Seabra Federal University of Santa Catarina Lisandra Flach Universität Stuttgart Abstract Most empirical
Impact of Stock Market, Trade and Bank on Economic Growth for Latin American Countries: An Econometrics Approach
 Science Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics 2018; 6(1): 1-6 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjams doi: 10.11648/j.sjams.20180601.11 ISSN: 2376-9491 (Print); ISSN: 2376-9513 (Online) Impact
Science Journal of Applied Mathematics and Statistics 2018; 6(1): 1-6 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjams doi: 10.11648/j.sjams.20180601.11 ISSN: 2376-9491 (Print); ISSN: 2376-9513 (Online) Impact
Exchange Rate Impact on Growth in Jamaica. Taffi Bryson
 Exchange Rate Impact on Growth in Jamaica Taffi Bryson Outline Motivation Objectives Empirical Literature Data and Methodology Results Conclusion and Policy Discussion Motivation To what extent can exchange
Exchange Rate Impact on Growth in Jamaica Taffi Bryson Outline Motivation Objectives Empirical Literature Data and Methodology Results Conclusion and Policy Discussion Motivation To what extent can exchange
An Econometric Assessment of the Impact of Inflation on Economic Growth: A Case Study of Zimbabwe Economy
 Economics 2018; 7(1): 17-22 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/eco doi: 10.11648/j.eco.20180701.13 ISSN: 2376-659X (Print); ISSN: 2376-6603 (Online) An Econometric Assessment of the Impact of Inflation
Economics 2018; 7(1): 17-22 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/eco doi: 10.11648/j.eco.20180701.13 ISSN: 2376-659X (Print); ISSN: 2376-6603 (Online) An Econometric Assessment of the Impact of Inflation
Public Debt and Economic Growth in Sri Lanka: Is There Any Threshold Level for Pubic Debt?
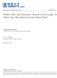 Economics & Management Series EMS-2013-22 Public Debt and Economic Growth in Sri Lanka: Is There Any Threshold Level for Pubic Debt? Hemantha Kumara Alumnus 2013, International University of Japan N. S.
Economics & Management Series EMS-2013-22 Public Debt and Economic Growth in Sri Lanka: Is There Any Threshold Level for Pubic Debt? Hemantha Kumara Alumnus 2013, International University of Japan N. S.
An Analysis Of Determinants Of Private Investment In Pakistan
 Page 18 An Analysis Of Determinants Of Private Investment In Pakistan Mahnaz Muhammad Ali Lecturer, department of Economics The Islamia University Bahawalpur, Pakistan Abstract Salma Shaheen Lecturer,
Page 18 An Analysis Of Determinants Of Private Investment In Pakistan Mahnaz Muhammad Ali Lecturer, department of Economics The Islamia University Bahawalpur, Pakistan Abstract Salma Shaheen Lecturer,
IMPACT OF TRADE OPENNESS ON MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES AND GDP GROWTH IN PAKISTAN AND INDIA
 IMPACT OF TRADE OPENNESS ON MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES AND GDP GROWTH IN PAKISTAN AND INDIA Himayatullah Khan 1*, Alena Fedorova 2, Saira Rasul 3 1 Prof. Dr. The University of Agriculture, Peshawar-Pakistan,
IMPACT OF TRADE OPENNESS ON MACROECONOMIC VARIABLES AND GDP GROWTH IN PAKISTAN AND INDIA Himayatullah Khan 1*, Alena Fedorova 2, Saira Rasul 3 1 Prof. Dr. The University of Agriculture, Peshawar-Pakistan,
Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth Relationship in Nigeria
 International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 2 No. 17 www.ijbssnet.com 244 Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth Relationship in Nigeria Sikiru Jimoh Babalola (Corresponding Author) Lecturer Department
International Journal of Business and Social Science Vol. 2 No. 17 www.ijbssnet.com 244 Fiscal Policy and Economic Growth Relationship in Nigeria Sikiru Jimoh Babalola (Corresponding Author) Lecturer Department
Comparative analysis of monetary and fiscal Policy: a case study of Pakistan
 MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Comparative analysis of monetary and fiscal Policy: a case study of Pakistan Syed Tehseen Jawaid and Imtiaz Arif and Syed Muhammad Naeemullah December 2010 Online at
MPRA Munich Personal RePEc Archive Comparative analysis of monetary and fiscal Policy: a case study of Pakistan Syed Tehseen Jawaid and Imtiaz Arif and Syed Muhammad Naeemullah December 2010 Online at
Trade Openness and Disaggregated Import Demand in East African Countries
 Modern Economy, 2017, 8, 667-689 http://www.scirp.org/journal/me ISSN Online: 2152-7261 ISSN Print: 2152-7245 Trade Openness and Disaggregated Import Demand in East African Countries Micah Samuel Gaalya
Modern Economy, 2017, 8, 667-689 http://www.scirp.org/journal/me ISSN Online: 2152-7261 ISSN Print: 2152-7245 Trade Openness and Disaggregated Import Demand in East African Countries Micah Samuel Gaalya
Exchange Rate and Economic Performance - A Comparative Study of Developed and Developing Countries
 IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-issn: 2278-487X. Volume 8, Issue 1 (Jan. - Feb. 2013), PP 116-121 Exchange Rate and Economic Performance - A Comparative Study of Developed and Developing
IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-issn: 2278-487X. Volume 8, Issue 1 (Jan. - Feb. 2013), PP 116-121 Exchange Rate and Economic Performance - A Comparative Study of Developed and Developing
Overview. o Introduction. o Review of Literature. o Methodology and Data. o Findings and Discussion. o Conclusion
 o Introduction Overview o Review of Literature o Methodology and Data o Findings and Discussion o Conclusion Introduction An economy has comparative advantage if it is more productive than another. Some
o Introduction Overview o Review of Literature o Methodology and Data o Findings and Discussion o Conclusion Introduction An economy has comparative advantage if it is more productive than another. Some
Inflation and Stock Market Returns in US: An Empirical Study
 Inflation and Stock Market Returns in US: An Empirical Study CHETAN YADAV Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce, Delhi School of Economics, University of Delhi Delhi (India) Abstract: This paper
Inflation and Stock Market Returns in US: An Empirical Study CHETAN YADAV Assistant Professor, Department of Commerce, Delhi School of Economics, University of Delhi Delhi (India) Abstract: This paper
Impact of Trade Openness on Exports Growth, Imports Growth and Trade Balance of Pakistan
 Forman Journal of Economic Studies Vol. 8, 2012 (January December) pp. 63-81 Impact of Trade Openness on Exports Growth, Imports Growth and Trade Balance of Pakistan M. Aslam Chaudhary and Baber Amin 1
Forman Journal of Economic Studies Vol. 8, 2012 (January December) pp. 63-81 Impact of Trade Openness on Exports Growth, Imports Growth and Trade Balance of Pakistan M. Aslam Chaudhary and Baber Amin 1
MACROECONOMIC DYNAMICS OF INCOME GROWTH: EVIDENCES FROM ARDL BOUND APPROACH, GMM AND DYNAMIC OLS ABSTRACT
 MACROECONOMIC DYNAMICS OF INCOME GROWTH: EVIDENCES FROM ARDL BOUND APPROACH, GMM AND DYNAMIC OLS Dr. Muhammad Mustafa School of Business South Carolina State University Orangeburg, SC 29117 USA Dr. Haile
MACROECONOMIC DYNAMICS OF INCOME GROWTH: EVIDENCES FROM ARDL BOUND APPROACH, GMM AND DYNAMIC OLS Dr. Muhammad Mustafa School of Business South Carolina State University Orangeburg, SC 29117 USA Dr. Haile
An Econometric Analysis of Impact of Public Expenditure on Industrial Growth in Nigeria
 International Journal of Economics and Finance; Vol. 6, No. 10; 2014 ISSN 1916-971X E-ISSN 1916-9728 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education An Econometric Analysis of Impact of Public Expenditure
International Journal of Economics and Finance; Vol. 6, No. 10; 2014 ISSN 1916-971X E-ISSN 1916-9728 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education An Econometric Analysis of Impact of Public Expenditure
Volume. 3, No. 2 July - December 2016 sijmb.iba-suk.edu.pk. Financing the Fiscal Deficit in Pakistan: Evidence on Ricardian Equivalence
 Volume. 3, No. 2 July - December 2016 sijmb.iba-suk.edu.pk Financing the Fiscal Deficit in Pakistan: Evidence on Ricardian Equivalence Neelma Shamsi 1 The University of Lahore, Sargodha Campus, Pakistan
Volume. 3, No. 2 July - December 2016 sijmb.iba-suk.edu.pk Financing the Fiscal Deficit in Pakistan: Evidence on Ricardian Equivalence Neelma Shamsi 1 The University of Lahore, Sargodha Campus, Pakistan
