COMBATING MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING INDONESIA PERSPECTIVE
|
|
|
- Sarah Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMBATING MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING INDONESIA PERSPECTIVE by : YUNUS HUSEIN *) I. INTRODUCTION Combating money laundering has been a primary concern for Government of Indonesia (GOI) since the economic and political crises erupted in The GOI paid more attention in eradicating such criminal activities, both because of our domestic needs and to meet our international commitments. It is deemed necessary to eradicate those criminal acts because the domestic crises occurred mainly due to corruption, collusion and nepotism-- fundamental weaknesses that are basically homegrown problems. Moreover, money laundering is not only a national crime but also a transnational crime, therefore it has to be eradicated, among other things by engaging in regional or international cooperation through bilateral or multilateral forums. Internationally, the prevention of the criminal offenses of money laundering has been promoted by the establishment of a task force known as The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) on Money Laundering by the G-7 Summit held in Paris on July Indonesia is yet a member of FATF, but has been a member of the Asia Pacific Group on Money Laundering (APG), an international cooperation organization established in 1997 to cooperate with FATF in the Asia Pacific regions. In June 2001, Indonesia and nineteen other countries were included in the list of NCCTs. The weaknesses focused on by FATF were the absence of Crime of Money Laundering Law that determine money laundering as a criminal offence, loopholes in financial regulation such as the absence of Know Your Customer Principles Regulation for financial institutions, inadequate resources for preventing, detecting and repressing money laundering activities, and the lack of international co-operation. Inclusion of Indonesia in the list of NCCTs has pushed the GOI to take serious measures in a short timeframe relatively, directed particularly remedying weaknesses identified by the FATF. The Government of Indonesia has enacted Law Number 15 Year 2002, the Crime of Money Laundering Law, as amended by Law Number 25 Year This Law stipulates money laundering as criminal offence and the establishment of the Center for Financial Transactions Reporting and Analysis as the independent agency in implementing its duties and authority for preventing and eradicating the criminal offenses of money laundering. Moreover, the GOI, besides moving actively to eradicate the criminal offences of money laundering, has also paid attention to the eradication of terrorism, an activity closely related to money launderers and the proceeds of money laundering crimes. Due to the width of impacts, Indonesia has taken immediate actions to respond the terrorism and terrorists financing activities, which are currently tending to aggressively attack globally. By the Law *) Yunus Husein is the Head of Indonesian Financial Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre (PPATK) 1
2 Number 15 Year 2003 Indonesia criminalized the financing of terrorism, the financing of the terrorist acts and the financing of terrorist organizations as described in the 1999 UN Convention. Law No. 15 Year 2002 concerning the Crime of Money Laundering as amended by Law No. 25 Year 2003 includes the terrorism as one the of predicate offences for money laundering. In addition, the terrorist financing offences are applied when they are committed in or outside of Indonesia. II. IMPROVEMENT OF THE LEGAL SYSTEM 1. The Crime of Money Laundering Law Since 1999 Indonesia has been diligently working toward establishing an effective antimoney laundering regime. This effort culminated in the passage of Law Number 15 Year 2002 in April of This law stipulated important provisions to enhance an anti-money laundering regime, such as: 1) The criminalizing of money laundering activities; 2) The obligation of Providers of Financial Services to submit Suspicious Transaction Reports (STR) and Cash Transaction Reports (CTR); 3) Reporting, investigation, prosecution and justice for criminal offences of money laundering are exempted from the provisions of bank secrecy that are stipulated in Indonesia s Banking Law; 4) Placed the burden of proof, that assets were not from criminal activities on the defendant (Instead of the prosecution having the burden of proving that the assets were derived from criminal activities, the onus is on the criminal to prove that the source of funds is legitimate to purchase asset.); 5) Established the Financial Transactions Reports and Analysis Center (PPATK) as an independent agency with the duty and authority to prevent and eradicate criminal offences of money laundering; 6) Established a clear legal basis for freezing and confiscating the proceeds of crime. In the context of the prevention and eradication of money laundering, Indonesia realizes the importance of international recommendations and best practices. The recommendations have served as essential elements in preparing policies for the prevention and eradication of the criminal offence of money laundering in Indonesia. Measures taken by Indonesia in satisfying these recommendations have been pursued aggressively since June The GOI recognized the negative impact of its inclusion in the NCCT list. As a consequence, Law No. 15 Year 2002 was amended to accommodate the FATF s further recommendations as an indication of Indonesia s commitment to the prevention and eradication of the criminal offence of money laundering in accordance with international best practices. Law No.25 Year 2003 was enacted on 13 October 2003 as an amendment to Law No. 15 Year 2002 concerning the Crime of Money Laundering. Enhancements to Indonesia s antimoney laundering regime included in this amendment include (but are not limited to) the following: 1) The definition of Providers of Financial Services was expanded to incorporate additional financial services related industries. This was meant to anticipate the criminal use of Providers of Financial Services which were not obliged to submit financial transaction reports under Law No. 15 Year ) The definition of Suspicious Transaction Report was amended to include either complete or incomplete financial transactions where there is reasonable grounds to suspect that the funds or assets constitute the proceeds of crime. 2
3 3) The threshold of Rp incorporated into the proceeds of crime definition was removed. 4) The number of predicate offences for money laundering was expanded from 15 to 23 specific types of offences and includes a general catch all for serious offences which includes other serious crimes for which the punishment is 4 (four) or more years in prison. 5) The timeframe for submitting suspicious transaction reports, was reduced from 14 (fourteen) working days to no more than 3 (three) working days. 6) New Anti-Tipping Off provisions to ensure secrecy of STR reports. 7) Provisions regarding mutual legal assistance in money laundering matters so that Indonesian law enforcement officials may cooperate with foreign counterparts in the investigation and prosecution of criminal money laundering offences. 8) Allows the PPATK to take action on new identified developments in international conventions or international recommendations for the prevention and eradication of the crime of money laundering, in a manner consistent with Indonesian laws and regulations. As mentioned above that predicate offences for money laundering was expanded from 5 to 23 specific types of offences. Article 2 of Law stipulates that the proceeds of crime shall be Assets derived from the following criminal acts: a. corruption; b. bribery; c. smuggling of goods; d. smuggling of workers; e. smuggling of immigrants; f. in the banking field; g. in the capital market field; h. in the insurance field; i. narcotics; j. psychotropic substances; k. trade in people; l. illegal trade in arms; m. kidnapping; n. terrorism; o. theft; p. embezzlement; q. fraud; r. currency counterfeiting; s. gambling; t. prostitution; u. in the tax field; v. in the forestry field; 3
4 w. in the environmental field; x. in the maritime field; or y. other offences for which the prescribed penalty is 4 years imprisonment or more; committed in the territory of The Republic of Indonesia or outside the territory of The Republic of Indonesia and where the offence is considered a crime according to Indonesian law. 2. The Criminal Acts of Terrorism Law Although Indonesia has signed but has not ratified the 1999 United Nations International Convention for the Suppression of the Financing of Terrorism, it has fully implemented the convention through Law No. 15 Year Law No. 15 Year 2003 concerns the enactment of Government Regulation in Lieu of Law No. 1 Year 2002 concerning the Eradication of the Criminal Acts of Terrorism. Law Number 15 Year 2003 pertaining the Eradication of the Criminal Acts of Terrorism contains specific provisions that were not found in the existing legislation on the scope of international and transnational jurisdiction and on criminal acts of terrorism that relate to international terrorist activities. This law embodies the government s commitment to implement Article 3 of the Convention Against Terrorist Bombing (1997) and the Convention for the Suppression of the Financing of Terrorism (1999). This law is the umbrella provision for other legislation relating to the eradication of criminal acts of terrorism. It also contains provisions of the financing of terrorist activities as criminal acts of terrorism, strengthening at the same time Indonesia s anti-money laundering regime described above. Furthermore, in term of financing of terrorism activities, Indonesia has criminalized the financing of terrorism, the financing of the terrorist acts and the financing of terrorist organizations as described in the UN Convention. Articles 11 and 12 of Law No. 15 Year 2003 clearly stipulate that the financing of terrorism, the financing of the terrorist acts and the financing of terrorist organizations are crimes and shall be punished by imprisonment for not less than 3 (three) years and not more than 15 (fifteen) years. Law No. 15 Year 2002 concerning the Crime of Money Laundering as amended by Law No. 25 Year 2003 includes the financing of terrorist activities as one the of predicate offences for money laundering. In addition, the terrorist financing offences are applied when they are committed in or outside of Indonesia. Indonesia will take measures necessary to establish its jurisdiction over terrorist financing offences and to submit them to competent domestic authorities if it does not extradite the alleged offender (Chapter II, Articles 3-5 of Law No. 15 Year 2003). Article 32 of Law No. 15 Year 2002 concerning the Crime of Money Laundering as amended by Law No. 25 Year 2003 allows competent authorities to freeze, seize and confiscate the proceeds of terrorism and assets used for terrorist activities. Article 29 of Law No.15 Year 2003 also stipulates the same provision. Law No. 15 Year 2002 concerning the Crime of Money Laundering as amended by Law No. 25 Year 2003 requires financial services providers to make a report (Suspicious Transaction Reports) to competent authorities when they suspect or have reasonable grounds to suspect that funds are linked to, related to, or are to be used for terrorism, terrorist acts or by terrorist organizations (Article 13, Article 2 and Article 1(7)). The Law and relevant regulations issued by Bank Indonesia, Ministry of Finance, and BAPEPAM concerning Implementation KYC Principles, require financial institutions to include information on the originator of fund transfers and retain information on the originator of fund transfers (5 years). 4
5 3. Special Protection for Witnesses and Reporting Parties The Government Regulation No.57 year 2003 pertaining Special Protection for Witnesses and Reporting Parties of the Crime of Money Laundering has been passed on 12 November The substances of this draft consist of the protection that shall be forthwith implemented without any delay as from the obtainment of an indication of suspicious financial transaction; and forms special protection that include protection of personal safety and or the safety of the relevant person s family against physical or mental threat, maintenance of confidentiality of the identity of the witnesses or reporting parties, giving testimony during court examination without being confronted with the suspect, and change of identity of the witnesses or reporting parties. III. INDONESIA s ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING (AML) REGIME 1. Indonesia s AML Schema Financial Service Providers (FSP) - Reporting Parties International Cooperation Indonesia n Police (Investigat or) Attorney General Office (Prosecutor ) Court PPATK Bank Indonesia Bape pam DGFI Ministry of Finance tcustoms Financial Sector Law Enforcement & Judicial Sector President Parliament Public NCC a. Reporting Parties (Financial Services Providers) Article 1 of Law No. 15 Year 2002 concerning the Crime of Money Laundering as amended by Law No. 25 Year 2003 defines a Provider of Financial Services as any person providing services in the financial field or other services in relation to finance, including but not limited to banks, financial institutions, securities companies, mutual fund managers, custodians, trust agents, depository and settlement agencies, foreign exchange traders, pension funds, insurance companies and the post office. Providers of Financial Services are obligated to submit reports to the PPATK as follows: a. Suspicious Financial Transactions; b. Cash Financial Transactions to a cumulative total of Rp.500,000, (five hundred million rupiah) or more or an equivalent amount in another currency, made either in one transaction or in several transactions within 1 (one) business day. 5
6 b. Bank Indonesia Bank Indonesia, the Central Bank of Indonesia, was established in Its objectives and tasks are governed by Law No. 23 Year 1999 concerning Bank Indonesia (Bank Indonesia Act). Under the Bank Indonesia Act, Bank Indonesia has as its primary objective to maintain the stability of the Rupiah currency. To achieve this goal, Bank Indonesia has the authority to formulate monetary policy, to regulate and safeguard the payment system, and to regulate and supervise banks. Bank Indonesia s functions to regulate and supervise banks is further elaborated on in Law No. 7 Year 1992 concerning Banking as amended by Law No. 10 Year 1998 (Banking Act). As governed in the Banking Act, in carrying out its duty as the regulator and supervisor of banks, Bank Indonesia shall have the power to license, prescribe regulation, supervise, and impose sanctions; upon the banking system, which consists of Commercial Banks, Rural Banks and Islamic (Syaria) Banks. As bank supervisor, Bank Indonesia is responsible for the supervision of the implementation of anti-money laundering (AML) policy, which includes implementation of KYC principles in the banking industry. Bank Indonesia s objective in this matter is to ensure that banks are not being utilized as targets and or mediums for money laundering activities since banks are the financial institutions most used by money launderers. c. BAPEPAM (Capital Market Supervisory Agency) Guidance, regulation, and day-to-day supervision of the capital market is undertaken by BAPEPAM in order to implement fair and efficient capital market activities and to protect the interests of investors and the public as set forth in Law No. 8 Year 1995 concerning the Capital Market. BAPEPAM is responsible for providing full disclosure of capital markets to the public and protecting public interests from malpractice in the capital market. Under Law No. 8 Year 1995 concerning the Capital Market, BAPEPAM has a strong legal foundation for carrying out enforcement actions as well as the important role of capital market development. d. Directorate General of Financial Institutions (DGFI) The Directorate General of Financial Institutions is a government agency under the Ministry of Finance, responsible for supervising non-bank financial institutions, including insurance, pension funds, and mutual funds firms. In line with the wide scope of financial institutions that is responsible for, the DGFI supervises Providers of Financial Services through its various directorates, namely Directorate of Banking and Financial Institutions, Directorate of Insurance, and Directorate of Pension Funds. The Directorates under the DGFI are authorized to provide licenses, to act as a regulator and to supervise Providers of Financial Services under their jurisdiction. Implementation is carried out by the subdirectorates. 2. The Indonesian Financial Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre ( PPATK ) The PPATK (Indonesian Financial Transactions Reporting and Analysis Center) is an independent body that reports directly to the President and became fully operational on 20 October The PPATK is Indonesia s Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) and as such will be the pivotal agency in the anti-money laundering regime. PPATK is lead by a Head appointed under the authority of the Act. The Head is assisted by four Deputy Heads comprising Deputy Head of Analysis, Research and Inter Agency Cooperation, Deputy Head of Legal and Compliance, Deputy Head of Technology and Information, and Deputy Head of Administration. The responsibilities of the Head and Deputy Heads have been set out at a high level in Presidential Decree No. 81 Year 2003 concerning the Organizational Structure and Working Procedure of the PPATK. 6
7 a. Duties and Powers Article 26 of Law No. 15 Year 2002 concerning the Crime of Money Laundering as amended by Law No. 25 Year 2003 states that in implementing its functions, the PPATK shall have the following duties: 1) to collect, maintain, analyse and evaluate information obtained by the PPATK in accordance with this Law; 2) to monitor records in the exempt registry prepared by Providers of Financial Services; 3) to prepare guidelines of procedures for reporting of suspicious financial transactions; 4) to provide advice and assistance to relevant authorities concerning information obtained by the PPATK in accordance with the provisions of this Law; 5) to issue guidelines and publications to Providers of Financial Services concerning their obligations as set forth in this Law or in other prevailing laws and regulations, and to assist in detecting suspicious customer behavior; 6) to provide recommendations to the Government concerning measures for the prevention and eradication of money laundering; 7) to report to the Police and the Public Prosecutor's Office the results of analyses of financial transactions which indicate money laundering; 8) to prepare and provide reports regarding the results of analyses of financial transactions and other activities once every 6 (six) months to the President, the House of Representatives (DPR) and to agencies authorized to supervise Providers of Financial Services. 9) to provide information to the public concerning its institutional performance, to the extent that such disclosure is not contrary to the provisions of this Law. Article 27 of Law No. 15 Year 2002 concerning the Crime of Money Laundering as amended by Law No. 25 Year 2003 states that in executing its duties, the PPATK shall have the following powers: 1) to request and receive reports from Providers of Financial Services; 2) to request information concerning the progress of investigations or prosecutions of money laundering that have been reported to investigators or public prosecutors; 3) to audit Providers of Financial Services for compliance with the provisions of this Law and guidelines for reporting financial transactions; 4) to grant exemptions from the reporting obligation for Cash Financial Transactions referred to in Article 13(1)(b). To implement its duties and powers, Presidential Decree No. 81 Year 2003 concerning the Organizational Structure and Operational Procedures of the PPATK and the Presidential Decree No. 82 Year 2003 concerning the PPATK s Authorities were enacted, both of which were issued on 3 November b. Attribution It is commonly acknowledged that FIU may range from units conducting a sort of intelligence tasks (such as tapping phone calls) to units that just do some paper work (documentation review). In this regards, as mandated by the money laundering Law and the Presidential Decree No. 82 Year 2003 concerning the PPATK s Authorities, PPATK is attributed by administrative power only, among other things are as follows: to request and receive reports, Suspicious Transaction Reports and Cash Transaction Reports, from Financial Service Providers; 7
8 to request additional information from Financial Service Providers, in case reports provided by Financial Service Providers are not reliable enough; to request assistance and information from domestic and foreign agencies for its purposes in analyzing any suspicious financial transaction in preventing and eradicating the crimes of money laundering; and many other administrative powers. Therefore, in term of conducting its function as FIU, PPATK is not attributed by investigative powers and other intelligence duties, such as tapping phone calls, doing under cover, on-site investigative, and others. c. Suspicious Financial Transaction Report handling Reporting Process PPATK has received a number of Suspicious Financial Transaction Reports (STRs). Care is being taken within PPATK to ensure that the right procedures are being set up within PPATK to receive, process, evaluate and disseminate the reports, with associated financial data where it exists, in an effective and timely manner. To facilitate the submission of STRs from PFSs, PPATK accepts STRs from PFSs in two forms: - In writing, both letters and facsimiles; or - Electronic data through a computerized on-line system. In the initial stages most STRs will be submitted manually. The PPATK is planning for an eventual switch to an almost entirely electronic submission system once the necessary computer infrastructure is in place. PPATK will also receive Cash Transaction Reports (CTRs) effective in April 1, The system required to enable the computerized on-line system is being developed. Analysis Process The intelligence to be provided by PPATK to law enforcement agencies will be greatly enhanced when supplemented by additional information or intelligence. PPATK has powers to acquire a range of additional data sources to complement PPATK data in its analysis of reports. If the existing data available in the PPATK s database is not significant then the PPATK may obtain additional information from PFSs or other parties, such as the Indonesian National Police, Attorney General, Directorate General of Tax, and Bank Indonesia. All sources that might have pertinent information related to the STRs being analyzed will be used. In the event that the desired information is possessed by a foreign state then the PPATK may request assistance in obtaining additional information from the FIU in that jurisdiction. The analysis currently is done manually however, in the long-term, it is expected that computerized analytical programs will be employed to assist the analysis effort. The availability of support software will make the PPATK s STR analysis significantly more effective. Specialized training in forensic accounting procedures will be sought from countries that have relevant expertise to pass to the PPATK analysis team. This training should be in the form of long-term placement of PPATK officers in actual working environments and the placement of forensic accounting mentors within PPATK. Dissemination If there is any indication of the commission of a money laundering crime from the analysis of an STR then the result will be handed over to the National Police as primary investigators and to the Attorney General for follow-up. 8
9 The PPATK will provide assistance to the National Police and the Attorney General in their investigation and prosecution of money laundering cases. The PPATK also has the authority to request information on the progress of investigations resulting from PPATK reports to the National Police and the Attorney General s Office. The PPATK is expected to provide a valuable contribution to the investigation and prosecution of money laundering crimes. Furthermore, all STRs and other information derived from PFSs or other parties will be maintained in the PPATK s database for possible future use. Statistical Data As of 29 February 2004, PPATK has received 497 STRs from 36 banks and 1 non-bank financial institution. All data includes data handed over by the Special Unit for Banking Investigation at Bank Indonesia, which responsible for the PPATK s functions over banks before October 17, PPATK has disseminated 78 cases from 198 STRs to POLRI. d. Training for PPATK personnel Training is required to build, develop and increase the capacity and effectiveness of PPATK personnel. To improve PPATK capacity, PPATK personnel have been assisted by: a. AusAID technical advisor assisting in the start up management of PPATK; b. USAID/ELIPS legal advisor assisting in the legal and regulatory area; c. AUSTRAC technical advisors assisting in the area of STR analysis, law enforcement liaison, international stream and regulatory and compliance stream; d. ADB Technical Assistance Project run by Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu assisting in the area of developing required guidelines, ensuring practical implementation of CTR, establishing effective and consistent supervision, compliance framework and a training program; e. European Commission technical advisors assisting in IT development. List of training that PPATK personnel have received: No. Modules Donor/Provider Personnel 1. AML Investigation Techniques ADB/Deloitte STR and CTR Analysis ADB/Deloitte Basic Analysis and STR reporting US Gov t./fincen 2 4. AML Prosecution USAID/FSVC 4 5. AML Investigation US Gov t/fbi, IRS 4 6. Financial Investigation AFP 1 7. Complex Financial Crime Investigation US Gov t/ ILEA Bangkok 3 8. Typology workshop Self-funded 2 9. APG Mutual Evaluation training US Gov t Training for trainers ADB/Deloitte Consultation with US Government representatives in Washington DC US Gov t / FSVC 1 9
10 e. Problems There are some problems and challenges faced by PPATK and other relevant agencies based on duties that have been performed by PPATK for the last 12 (twelve) months in developing effective anti money laundering regime Indonesia as follow: 1. Coordination among relevant agencies Considering that the development of effective anti money laundering regime is collective responsibility from all Indonesian communities that its implementation shall be conducted by related institutions, cooperation and coordination among institutions must be implemented absolutely. This shall also apply for the development of good relationship between related institutions and business actors and society generally. 2. Public awareness Given the implementation of AML regime is relatively new for Indonesia s society, increasing public awareness is deemed necessary. 3. PFSs compliance It could not be denied that PFSs are front guard in implementating AML regime due to its role as reporting parties. Therefore, a series of comprehensive regulations should be conducted to boost PFSs compliance in reporting system. 3. Progress of Indonesia s AML Regime a. Know Your Customer Principle KYC With regard to the implementation of Know Your Customer Principles, the Capital Market Supervisory Agency (Bapepam) has issued KYC regulation for securities companies by stipulating a Decision of Head of Bapepam on January 15, The Ministry of Finance has also issued similar regulation for non-bank financial institutions by stipulating the Ministerial Decree on January 30, The issuance of these regulations complements the KYC regulations for banking industry, which has been issued by Bank Indonesia on June 18, 2001, December 13, 2001 (1 st amendment) and on October 17, 2003 (2 nd amendment). Bank Indonesia also has issued KYC regulations for rural banks on October 23, b. Guidelines for Financial Industry in implementing AML regime Reporting guidance for the financial services providers is crucial and becomes a prerequisite for the smooth functioning of the PPATK. Likewise, the general guidance for authorities in financial services is also deemed necessary considering that the provisions on Know Your Customer Principles for banks, capital markets, non-bank financial institutions and other financial services institutions is conducted by respective authority. The issuance of this guidance is aimed at producing the arrangement equality and ensuring compliances of providers of financial services against their reporting obligations. So far PPATK has issued 6 (six) guidelines as follows: i. General Guidelines for Financial Service Providers on Prevention and Eradication of Money Laundering; ii. Guideline for Financial Service Providers (major FSPs) on Identification of Suspicious Financial Transactions; iii. Guideline for Financial Service Providers (major FSPs) on Procedures of Reporting of Suspicious Financial Transactions; 10
11 iv. Guideline for Money Changer and Money Remittance Agent on Identification of Suspicious Financial Transactions; v. Guideline for Money Changer and Money Remittance Agent on Procedures of Reporting of Suspicious Financial Transactions. vi. Guideline for Financial Service Providers on Cash Transaction Reports and Its Reporting Procedures c. Inter-agencies Cooperation 1) Domestic Cooperation For the smoothness of information exchange, particularly in relation to financial intelligence, the PPATK has signed: i) Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Bank Indonesia on February 5, 2003 and October 20, 2003; ii) Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Capital Market Supervisory Agency (Bapepam) on October 20, 2003; iii) Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Directorate General of Financial Institutions on October 28, 2003; iv) Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Directorate General of Tax on October 28, 2003; v) Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Directorate General of Customs and Excise on October 31, 2003; vi) Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR) on 16 January Memorandum of Understandings (in the form of Joint Decree) with Indonesian National Police and Attorney General Office would be signed shortly. 2) International Cooperation In order to enhance Indonesia s capacity to undertake the international exchange of financial intelligence, throughout the course of 2003 PPATK has sought Memoranda of Understanding with 16 FIU s from other jurisdictions. At this stage, Indonesia has established Memoranda of Understanding with AMLO-Thailand (24 March 2003), Bank Negara Malaysia (31 July 2003), KoFIU-Republic of Korea (20 October 2003), and AUSTRAC-Australia (4 February 2003); and has entered into an Exchange of Letters enabling international exchange with Hong Kong. In addition, Indonesia has been a member of APG (Asia Pacific Group on Money Laundering) since year 2000, and plans to participate as member of EGMONT Group in the near future. In this regards, PPATK has sent a letter to the Chair of Egmont Secretariat, the Chair of Legal Working Group and the Chair of Outreach Working Group to seek information and assistance concerning membership admission. d. National Coordination Committee (NCC) To enhance the strategic implementation and coordination of the anti-money laundering regime, the Republic of Indonesia, has established a National Coordination Committee (NCC) on anti-money laundering, a Ministerial-level committee formed to ensure coordination and cooperation between Ministries relevant to the fight against 11
12 money laundering. The initial meeting took place on 30 December 2002 in Jakarta, led by the Coordinating Minister for Political and Security Affairs. Participants in this first meeting included: the Coordinating Minister for Economy, the Minister of Justice and Human Rights, the Minister of Foreign Affairs, the Deputy Attorney General for General Crime, the Governor of Bank Indonesia, the Minister of Finance, the Chief of National Police of the Republic of Indonesia, the Chairman of the Capital Market Supervisory Agency, the Head of the PPATK, the Head of the National Intelligence Agency, the Head of the National Narcotics Agency and the Head of the Terrorism Eradication Coordination Desk. The National Coordination Committee (NCC) established under the authority of Law No. 15 Year 2002 as amended by Law No. 25 Year 2003 and Presidential Decree No. 1 Year 2004 has the following duties: 1) to coordinate the effort for handling the prevention and eradication of the crime of money laundering; 2) to provide recommendations to the President regarding directions and policies for handling the prevention and eradication of the crime of money laundering nationally; 3) to evaluate the implementation of the prevention and eradication of the crime of money laundering; 4) to report progress of the prevention and eradication of the crime of money laundering to the President. In implementing its duties, the NCC is assisted by a working group consists of high officials from the agencies as mentioned above. The NCC working group may involve the representatives of PFSs, experts or other relevant parties in the working group discussions if deemed necessary. e. Technical Assistances Donor Institutions/States Coordination In following up a meeting between the Government of Indonesia and donor institutions/states in Denpasar on December 2002 that decided technical assistances implementation coordination between the PPATK and donors, it has been held coordination meetings regularly (once per 4 months) to discuss technical assistances needs in anti money laundering regime development in Indonesia. The coordination meetings have provided a priority list and also are utilized as forum to exchange information. At this point, the coordination meetings are considered has provided positive benefits for anti money laundering regime development in Indonesia. IV. Final Words As explored above, it could be wrapped up that Government of Indonesia (GOI) has made significant further progress in strengthening its anti-money laundering and anti-terrorism system. It may be represented by the enactment of anti-money laundering Law and criminal acts of terrorism law, the presence of KYC regulation for both banks and non-bank financial institutions, the establishment of Indonesian FIU, the series of guidelines for Financial Services Providers, and other significant actions. The GOI, in addition, is serious in correcting the defects in criminal law and regulations, in upgrading capacity to implement them, and in strengthening cooperative in financial information exchange with overseas agencies. 12
13 Based on the facts, the GOI expects that all measures taken could lead to the right track in the effort to remove Indonesia from the list of Non Cooperative Countries and Territories (NCCTs) drawn up by the Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF) on the next plenary meeting. Being on the list of the NCCTs has raised the premium for Indonesian economic agents in conducting transactions in the international financial markets. This has increased costs for rebuilding the already shattered economy.** Presented at Program Second Conference on Secure Trade in the APEC Region, Town Hotel-Vina del Mar, Chile March
APG Mutual Evaluation Recommendations May 2002 PROGRESS REPORT. Page I - 1
 I. Legal 1. It is recommended that the monetary threshold in the definition of proceeds of crime in Article 2 be removed and the list of predicate offences in Article 3 be extended to include a broader
I. Legal 1. It is recommended that the monetary threshold in the definition of proceeds of crime in Article 2 be removed and the list of predicate offences in Article 3 be extended to include a broader
THE KINGDOM OF LESOTHO ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBATING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM REGIME
 THE KINGDOM OF LESOTHO ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBATING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM REGIME ----------------------------------------------------------------- NATIONAL STRATEGY JANUARY 2010 1 TABLE OF
THE KINGDOM OF LESOTHO ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBATING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM REGIME ----------------------------------------------------------------- NATIONAL STRATEGY JANUARY 2010 1 TABLE OF
CROSS BORDER STATUTES & OTHER MEASURES TO CURB MONEY LAUNDERING 25 November 2005, Makati Shangrila, Rizal Ballroom Makati, Philippines
 SUMMARY REPORT ON ALA WORKSHOP II Rapporteur: Atty. Diane A. Desierto CROSS BORDER STATUTES & OTHER MEASURES TO CURB MONEY LAUNDERING 25 November 2005, Makati Shangrila, Rizal Ballroom Makati, Philippines
SUMMARY REPORT ON ALA WORKSHOP II Rapporteur: Atty. Diane A. Desierto CROSS BORDER STATUTES & OTHER MEASURES TO CURB MONEY LAUNDERING 25 November 2005, Makati Shangrila, Rizal Ballroom Makati, Philippines
Indonesia s Cross-Border Statutes to Curb Money Laundering Criminal Activities
 Provisional paper. Revised 1: September 25, 2005. Indonesia s Cross-Border Statutes to Curb Money Laundering Criminal Activities By: Agus Brotosusilo* Background It was not until February 11, 2005 when
Provisional paper. Revised 1: September 25, 2005. Indonesia s Cross-Border Statutes to Curb Money Laundering Criminal Activities By: Agus Brotosusilo* Background It was not until February 11, 2005 when
REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA NATIONAL STRATEGY ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING COMBATTING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM
 REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA NATIONAL STRATEGY ON ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBATTING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM 2 GLOSSARY AND ABBREVIATIONS ACC AML AMLAC BoN CFT DNFBPs ESAAMLG FATF FI Anti-Corruption Commission
REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA NATIONAL STRATEGY ON ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBATTING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM 2 GLOSSARY AND ABBREVIATIONS ACC AML AMLAC BoN CFT DNFBPs ESAAMLG FATF FI Anti-Corruption Commission
Council of Europe COMMITTEE OF MINISTERS
 Word FranГais Explanatory Memorandum Council of Europe COMMITTEE OF MINISTERS Recommendation Rec(2001)11 of the Committee of Ministers to member states concerning guiding principles on the fight against
Word FranГais Explanatory Memorandum Council of Europe COMMITTEE OF MINISTERS Recommendation Rec(2001)11 of the Committee of Ministers to member states concerning guiding principles on the fight against
Presented by : Panji Achmad, SH, LL.M Group Head of Analysts. Dakar- Senegal
 Presented by : Panji Achmad, SH, LL.M Group Head of Analysts The Forum on Anti Terrorism and Its Financing 18 19 19 December 2008 Dakar- Senegal 1 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Introduction Why focus on financing
Presented by : Panji Achmad, SH, LL.M Group Head of Analysts The Forum on Anti Terrorism and Its Financing 18 19 19 December 2008 Dakar- Senegal 1 PRESENTATION OUTLINE Introduction Why focus on financing
Practical Implementation of UN Standards and Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF) Recommendations: Challenges and Assistance
 2007/ACT/WKSP/005 Practical Implementation of UN Standards and Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF) Recommendations: Challenges and Assistance Submitted by: United Nations Office on Drugs
2007/ACT/WKSP/005 Practical Implementation of UN Standards and Financial Action Task Force on Money Laundering (FATF) Recommendations: Challenges and Assistance Submitted by: United Nations Office on Drugs
REPORT TO THE FATF PLENARY February 2008
 REPORT TO THE FATF PLENARY February 2008 Ongoing Technical Assistance and Plans 1. Background ADB continues to provide assistance to a number of its developing member countries (DMCs) to enhance their
REPORT TO THE FATF PLENARY February 2008 Ongoing Technical Assistance and Plans 1. Background ADB continues to provide assistance to a number of its developing member countries (DMCs) to enhance their
THE HEAD OF THE INDONESIAN FINANCIAL TRANSACTION REPORTS AND ANALYSIS CENTRE,
 DECREE OF THE HEAD OF THE INDONESIAN FINANCIAL TRANSACTION REPORTS AND ANALYSIS CENTRE NUMBER: 2/1/KEP. PPATK/2003 CONCERNING GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR FINANCIAL SERVICES PROVIDERS ON THE HEAD OF THE INDONESIAN
DECREE OF THE HEAD OF THE INDONESIAN FINANCIAL TRANSACTION REPORTS AND ANALYSIS CENTRE NUMBER: 2/1/KEP. PPATK/2003 CONCERNING GENERAL GUIDELINES FOR FINANCIAL SERVICES PROVIDERS ON THE HEAD OF THE INDONESIAN
ASEAN LAW ASSOCIATION 25TH ANNIVERSARY SPECIAL COMMEMORATIVE SESSION NOVEMBER 2005, MAKATI SHANGRI-LA HOTEL, MANILA, PHILIPPINES
 ASEAN LAW ASSOCIATION 25TH ANNIVERSARY SPECIAL COMMEMORATIVE SESSION 24-27 NOVEMBER 2005, MAKATI SHANGRI-LA HOTEL, MANILA, PHILIPPINES Cross Border Statutes and Other Measures To Curb Money Laundering
ASEAN LAW ASSOCIATION 25TH ANNIVERSARY SPECIAL COMMEMORATIVE SESSION 24-27 NOVEMBER 2005, MAKATI SHANGRI-LA HOTEL, MANILA, PHILIPPINES Cross Border Statutes and Other Measures To Curb Money Laundering
Eva Rossidou Papakyriacou Senior Counsel of the Republic Head of the Unit for Combating Money Laundering (MOKAS)
 Eva Rossidou Papakyriacou Senior Counsel of the Republic Head of the Unit for Combating Money Laundering (MOKAS) The process by which criminals conceal the true origin and ownership of the proceeds of
Eva Rossidou Papakyriacou Senior Counsel of the Republic Head of the Unit for Combating Money Laundering (MOKAS) The process by which criminals conceal the true origin and ownership of the proceeds of
International Monetary Fund Washington, D.C.
 2004 International Monetary Fund April 2004 IMF Country Report No. 04/119 South Africa: Report on the Observance of Standards and Codes FATF Recommendations for Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the
2004 International Monetary Fund April 2004 IMF Country Report No. 04/119 South Africa: Report on the Observance of Standards and Codes FATF Recommendations for Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the
Annual Report. Fiscal Year 2067/68 (2010/11) Financial Information Unit (FIU) Nepal Nepal Rastra Bank
 Annual Report Fiscal Year 2067/68 (2010/11) Financial Information Unit (FIU) Nepal Nepal Rastra Bank ANNUAL REPORT Fiscal Year 2067/68 (20010/11) Financial Information Unit (FIU) Nepal Rastra Bank Baluwatar,
Annual Report Fiscal Year 2067/68 (2010/11) Financial Information Unit (FIU) Nepal Nepal Rastra Bank ANNUAL REPORT Fiscal Year 2067/68 (20010/11) Financial Information Unit (FIU) Nepal Rastra Bank Baluwatar,
EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC)
 Strasbourg, 14 May 2004 MONEYVAL (04) 7Summ EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC) SELECT COMMITTEE OF EXPERTS ON THE EVALUATION OF ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING MEASURES MONEYVAL SECOND ROUND EVALUATION
Strasbourg, 14 May 2004 MONEYVAL (04) 7Summ EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC) SELECT COMMITTEE OF EXPERTS ON THE EVALUATION OF ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING MEASURES MONEYVAL SECOND ROUND EVALUATION
PNG s Anti-Money Laundering & Counter Terrorist Financing Framework
 PNG s Anti-Money Laundering & Counter Terrorist Financing Framework Wilson Onea Deputy Director Financial Analysis and Supervision Unit (FASU) PNG s Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) Presentation Outline
PNG s Anti-Money Laundering & Counter Terrorist Financing Framework Wilson Onea Deputy Director Financial Analysis and Supervision Unit (FASU) PNG s Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU) Presentation Outline
Japan Financial Intelligence Center (JAFIC) Annual Report
 Japan Financial Intelligence Center (JAFIC) Annual Report 2016 JAFIC: Japan Financial Intelligence Center Introduction It has been 10 years since the enactment of the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal
Japan Financial Intelligence Center (JAFIC) Annual Report 2016 JAFIC: Japan Financial Intelligence Center Introduction It has been 10 years since the enactment of the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal
PREVENTION AND ERADICATION OF THE CRIME OF MONEY LAUNDERING IN INDONESIA FISCAL YEAR
 NATIONAL STRATEGY PREVENTION AND ERADICATION OF THE CRIME OF MONEY LAUNDERING IN INDONESIA FISCAL YEAR 2007-2011 Jakarta, March 2007 1 REMARKS OF THE COORDINATING MINISTER IN POLITICAL, LA W AND SECURITY
NATIONAL STRATEGY PREVENTION AND ERADICATION OF THE CRIME OF MONEY LAUNDERING IN INDONESIA FISCAL YEAR 2007-2011 Jakarta, March 2007 1 REMARKS OF THE COORDINATING MINISTER IN POLITICAL, LA W AND SECURITY
Overview of AML/CFT Framework of
 Overview of AML/CFT Framework of The ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF IRAN Feb 2013 2 TITLES 1. Legal-institutional framework on AML/CFT 2. Executive measures, Statistics, facts and figures 3. International Co-operation
Overview of AML/CFT Framework of The ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF IRAN Feb 2013 2 TITLES 1. Legal-institutional framework on AML/CFT 2. Executive measures, Statistics, facts and figures 3. International Co-operation
CRS-2 develop and promote policies to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. 3 Recently, China and South Korea were granted observer status,
 Order Code RS21904 Updated January 30, 2008 Summary The Financial Action Task Force: An Overview James K. Jackson Specialist in International Trade and Finance Foreign Affairs, Defense, and Trade Division
Order Code RS21904 Updated January 30, 2008 Summary The Financial Action Task Force: An Overview James K. Jackson Specialist in International Trade and Finance Foreign Affairs, Defense, and Trade Division
CORRUPTION. A Reference Guide and Information Note. on the use of the FATF Recommendations. to support the fight against Corruption
 FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE CORRUPTION A Reference Guide and Information Note on the use of the FATF Recommendations to support the fight against Corruption The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the
FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE CORRUPTION A Reference Guide and Information Note on the use of the FATF Recommendations to support the fight against Corruption The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the
ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COUNTER FINANCING OF TERRORISM (AML/CFT): TANZANIA PERSPECTIVE
 ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COUNTER FINANCING OF TERRORISM (AML/CFT): TANZANIA PERSPECTIVE S.E. Nyakulinga Assistant Commissioner of Police Money Laundering & Asset Recovery Investigation Unit Outline Definition
ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COUNTER FINANCING OF TERRORISM (AML/CFT): TANZANIA PERSPECTIVE S.E. Nyakulinga Assistant Commissioner of Police Money Laundering & Asset Recovery Investigation Unit Outline Definition
PROJECT AGAINST CORRUPTION IN ALBANIA (PACA) TECHNICAL PAPER
 PROJECT AGAINST CORRUPTION IN ALBANIA (PACA) TECHNICAL PAPER ASSESSMENT OF THE REVISED PROPOSED AMENDMENTS TO THE LAW ON PREVENTION OF MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING Opinion of the Department
PROJECT AGAINST CORRUPTION IN ALBANIA (PACA) TECHNICAL PAPER ASSESSMENT OF THE REVISED PROPOSED AMENDMENTS TO THE LAW ON PREVENTION OF MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING Opinion of the Department
MONEY LAUNDERING - The EU and Malta
 MONEY LAUNDERING - The EU and Malta Author: George Farrugia α Background The new Prevention of Money Laundering Regulations 2003, which have just been published in August, implement the second European
MONEY LAUNDERING - The EU and Malta Author: George Farrugia α Background The new Prevention of Money Laundering Regulations 2003, which have just been published in August, implement the second European
Law on. Combating Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing LAW ON COMBATING MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING
 LAW ON COMBATING MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING Law on Combating Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing PUBLISHED BY: AL ALAWI & CO., ADVOCATES & LEGAL CONSULTANTS CORPORATE ADVISORY GROUP
LAW ON COMBATING MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING Law on Combating Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing PUBLISHED BY: AL ALAWI & CO., ADVOCATES & LEGAL CONSULTANTS CORPORATE ADVISORY GROUP
Content. 1. Introduction of AML/CFT Legislation
 ANNUAL REPORT On 2008 Activities of the Financial Monitoring Center of the Republic of Armenia Central Bank in the Field of Combating Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing Yerevan, 2009 Content This
ANNUAL REPORT On 2008 Activities of the Financial Monitoring Center of the Republic of Armenia Central Bank in the Field of Combating Money Laundering and Terrorism Financing Yerevan, 2009 Content This
Targeting Illicit Financial Flows
 Targeting Illicit Financial Flows Overview What is meant by the term illicit financial flows Who can monitor financial flows How can it be monitored The importance of domestic coordination 2 Illicit financial
Targeting Illicit Financial Flows Overview What is meant by the term illicit financial flows Who can monitor financial flows How can it be monitored The importance of domestic coordination 2 Illicit financial
DRAFT OF LAW OF THE REPUBLIK OF INDONESIA NUMBER... YEAR CONCERNING THE PREVENTION AND ERADICATION OF THE CRIME MONEY LAUNDERING
 Draft Final DRAFT OF LAW OF THE REPUBLIK OF INDONESIA NUMBER... YEAR CONCERNING THE PREVENTION AND ERADICATION OF THE CRIME MONEY LAUNDERING WITH THE BLESSING OF THE ONE ALMIGHTY GOD THE PRESIDENT OF THE
Draft Final DRAFT OF LAW OF THE REPUBLIK OF INDONESIA NUMBER... YEAR CONCERNING THE PREVENTION AND ERADICATION OF THE CRIME MONEY LAUNDERING WITH THE BLESSING OF THE ONE ALMIGHTY GOD THE PRESIDENT OF THE
AML/CFT TRAINING FOR ACCOUNTANTS AND AUDITORS
 AML/CFT TRAINING FOR ACCOUNTANTS AND AUDITORS 1 16 MARCH 2016 BANK USE PROMOTION & SUPPRESSION OF MONEY LAUNDERING UNIT 2 3 What is Money Laundering? the process of concealing illicit gains from criminal
AML/CFT TRAINING FOR ACCOUNTANTS AND AUDITORS 1 16 MARCH 2016 BANK USE PROMOTION & SUPPRESSION OF MONEY LAUNDERING UNIT 2 3 What is Money Laundering? the process of concealing illicit gains from criminal
Papali I T Scanlan: Preventing money laundering and financing of terrorism in Samoa
 Papali I T Scanlan: Preventing money laundering and financing of terrorism in Samoa Speech by Mr Papali I T Scanlan, Governor of the Central Bank of Samoa, at the Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Terrorist
Papali I T Scanlan: Preventing money laundering and financing of terrorism in Samoa Speech by Mr Papali I T Scanlan, Governor of the Central Bank of Samoa, at the Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Terrorist
FATF Mutual Evaluation of Ireland 2017
 FATF Mutual Evaluation of Ireland 2017 Introduction Background The Financial Action Task Force ( FATF ) was established in 1989 with a high level objective that: Financial systems and the broader economy
FATF Mutual Evaluation of Ireland 2017 Introduction Background The Financial Action Task Force ( FATF ) was established in 1989 with a high level objective that: Financial systems and the broader economy
Fifth Report of the Principality of Liechtenstein to the Counter-Terrorism Committee established by Security Council resolution 1373 (2001) 9 May 2006
 Fifth Report of the Principality of Liechtenstein to the Counter-Terrorism Committee established by Security Council resolution 1373 (2001) 9 May 2006 With the following report, Liechtenstein is submitting
Fifth Report of the Principality of Liechtenstein to the Counter-Terrorism Committee established by Security Council resolution 1373 (2001) 9 May 2006 With the following report, Liechtenstein is submitting
S/2004/450. Security Council. United Nations
 United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 3 June 2004 Original: English S/2004/450 Letter dated 1 June 2004 from the Chairman of the Security Council Committee established pursuant to resolution
United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 3 June 2004 Original: English S/2004/450 Letter dated 1 June 2004 from the Chairman of the Security Council Committee established pursuant to resolution
FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS - POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF LESOTHO
 FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS - POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF LESOTHO Covering the period August 2016 July 2017 ESAAMLG (2017), First Round Mutual Evaluation - Post Evaluation Progress Report of
FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS - POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF LESOTHO Covering the period August 2016 July 2017 ESAAMLG (2017), First Round Mutual Evaluation - Post Evaluation Progress Report of
International efforts to combat the. financing of terrorism. 1 Introduction and background. 2 Characteristics of terrorist financing
 International efforts to combat the financing of terrorism Ken Matthews, Financial Stability Department Following the terrorist attacks in September 2001, there have been a number of developments in measures
International efforts to combat the financing of terrorism Ken Matthews, Financial Stability Department Following the terrorist attacks in September 2001, there have been a number of developments in measures
Unofficial Translation
 BANK INDONESIA REGULATION NUMBER: 11/28/PBI/2009 CONCERNING IMPLEMENTATION OF ANTI MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBANTING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM PROGRAM FOR COMMERCIAL BANK WITH THE BLESSINGS OF THE ONE ALMIGHTY
BANK INDONESIA REGULATION NUMBER: 11/28/PBI/2009 CONCERNING IMPLEMENTATION OF ANTI MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBANTING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM PROGRAM FOR COMMERCIAL BANK WITH THE BLESSINGS OF THE ONE ALMIGHTY
Introduction. February, Hirofumi Naito Director for Prevention of Money Laundering. JAFIC: Japan Financial Intelligence Center
 JAFIC: Japan Financial Intelligence Center Introduction Three years have passed since "the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds" fully came into effect, and specified business operators such
JAFIC: Japan Financial Intelligence Center Introduction Three years have passed since "the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds" fully came into effect, and specified business operators such
High-risk and non-cooperative jurisdictions
 High-risk and non-cooperative jurisdictions FATF PUBLIC STATEMENT - 22 February 2013 Paris, 22 February 2013 - The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the global standard setting body for anti-money
High-risk and non-cooperative jurisdictions FATF PUBLIC STATEMENT - 22 February 2013 Paris, 22 February 2013 - The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the global standard setting body for anti-money
Law No. 80 for Promulgating Anti- Money Laundering Law, Amended by Law No. 78 for 2003*
 First Draft 1 Law No. 80 for 2002 Promulgating Anti- Money Laundering Law, Amended by Law No. 78 for 2003* In the Name of the People, The President of the Republic, The People's Assembly approved the following
First Draft 1 Law No. 80 for 2002 Promulgating Anti- Money Laundering Law, Amended by Law No. 78 for 2003* In the Name of the People, The President of the Republic, The People's Assembly approved the following
MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING AMONG MEMBER GOVERNMENTS OF THE CARIBBEAN FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE - NOVEMBER 2011
 MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING AMONG MEMBER GOVERNMENTS OF THE CARIBBEAN FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE - NOVEMBER 2011 CFATF Secretariat Sackville House 35-37 Sackville Street Port-of-Spain Trinidad Tel:(868)
MEMORANDUM OF UNDERSTANDING AMONG MEMBER GOVERNMENTS OF THE CARIBBEAN FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE - NOVEMBER 2011 CFATF Secretariat Sackville House 35-37 Sackville Street Port-of-Spain Trinidad Tel:(868)
The Financial Intelligence Service
 Guernsey Authorities Official Guernsey Government Website: http://www3.gov.gg/ccm/navigation/government/ Financial Investigation Unit (FIU) Website: http://www.guernseyfiu.gov.gg/ The Financial Intelligence
Guernsey Authorities Official Guernsey Government Website: http://www3.gov.gg/ccm/navigation/government/ Financial Investigation Unit (FIU) Website: http://www.guernseyfiu.gov.gg/ The Financial Intelligence
Strasbourg, 6 November 2015 C198-COP(2015)PROG3-ANALYSIS
 Strasbourg, 6 November 2015 C198-COP(2015)PROG3-ANALYSIS CONFERENCE OF THE PARTIES Council of Europe Convention on Laundering, Search, Seizure and Confiscation of the Proceeds from Crime and on the Financing
Strasbourg, 6 November 2015 C198-COP(2015)PROG3-ANALYSIS CONFERENCE OF THE PARTIES Council of Europe Convention on Laundering, Search, Seizure and Confiscation of the Proceeds from Crime and on the Financing
High-risk and non-cooperative jurisdictions
 High-risk and non-cooperative jurisdictions FATF PUBLIC STATEMENT - 19 October 2012 Paris, 19 October 2012 - The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the global standard setting body for antimoney laundering
High-risk and non-cooperative jurisdictions FATF PUBLIC STATEMENT - 19 October 2012 Paris, 19 October 2012 - The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is the global standard setting body for antimoney laundering
INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY LAUNDERING IN WEST AFRICA. Second Follow Up Report. Mutual Evaluation SIERRA LEONE
 INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY LAUNDERING IN WEST AFRICA Second Follow Up Report Mutual Evaluation SIERRA LEONE MAY 2009 2014 GIABA. All rights reserved. No reproduction or translation of
INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY LAUNDERING IN WEST AFRICA Second Follow Up Report Mutual Evaluation SIERRA LEONE MAY 2009 2014 GIABA. All rights reserved. No reproduction or translation of
EXPLANATORY NOTE ON ANTI MONEY LAUNDERING (AMENDMENT) ACT Zulkifli Hasan Faculty of Syariah and Law Islamic Science University of Malaysia
 EXPLANATORY NOTE ON ANTI MONEY LAUNDERING (AMENDMENT) ACT 2003 Zulkifli Hasan Faculty of Syariah and Law Islamic Science University of Malaysia 1.0 INTRODUCTION Malaysian government took a step in combating
EXPLANATORY NOTE ON ANTI MONEY LAUNDERING (AMENDMENT) ACT 2003 Zulkifli Hasan Faculty of Syariah and Law Islamic Science University of Malaysia 1.0 INTRODUCTION Malaysian government took a step in combating
Anti-Money-laundering and Countering the Financing of Terrorism
 Anti-Money-laundering and Countering the Financing of Terrorism A Partnership for National Unity Georgetown March 2014 1 A Partnership for National Unity 61 Hadfield Street, Werk-en-Rust Georgetown Co-operative
Anti-Money-laundering and Countering the Financing of Terrorism A Partnership for National Unity Georgetown March 2014 1 A Partnership for National Unity 61 Hadfield Street, Werk-en-Rust Georgetown Co-operative
FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF LESOTHO. Covering the period August 2017 July 2018
 FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF LESOTHO Covering the period August 2017 July 2018 ESAAMLG (2018), First Round Mutual Evaluation Post Evaluation Progress Report of Lesotho
FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF LESOTHO Covering the period August 2017 July 2018 ESAAMLG (2018), First Round Mutual Evaluation Post Evaluation Progress Report of Lesotho
INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY LAUNDERING IN WEST AFRICA. Fifth Follow Up Report. Mutual Evaluation
 INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY LAUNDERING IN WEST AFRICA Fifth Follow Up Report Mutual Evaluation THE GAMBIA NOVEMBER 2012 2014 GIABA. All rights reserved. No reproduction or translation
INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY LAUNDERING IN WEST AFRICA Fifth Follow Up Report Mutual Evaluation THE GAMBIA NOVEMBER 2012 2014 GIABA. All rights reserved. No reproduction or translation
Strasbourg, 11 February 2000 PC -R-EV (99) 28 Summ. EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC)
 Strasbourg, 11 February 2000 PC -R-EV (99) 28 Summ. EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC) Select Committee of Experts on the Evaluation of Anti-Money Laundering Measures (PC -R-E V ) FIRST MUTUAL
Strasbourg, 11 February 2000 PC -R-EV (99) 28 Summ. EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC) Select Committee of Experts on the Evaluation of Anti-Money Laundering Measures (PC -R-E V ) FIRST MUTUAL
Legal Framework on Asset Recovery The United Nations Convention Against Corruption 1. Oliver Stolpe UNODC
 Legal Framework on Asset Recovery The United Nations Convention Against Corruption 1 Introduction Oliver Stolpe UNODC 1. Asset recovery represents an entirely new field of international law and international
Legal Framework on Asset Recovery The United Nations Convention Against Corruption 1 Introduction Oliver Stolpe UNODC 1. Asset recovery represents an entirely new field of international law and international
The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia
 COMMITTEE OF EXPERTS ON THE EVALUATION OF ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING MEASURES AND THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM (MONEYVAL) MONEYVAL(2009)33 The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Progress report 1 21 September
COMMITTEE OF EXPERTS ON THE EVALUATION OF ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING MEASURES AND THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM (MONEYVAL) MONEYVAL(2009)33 The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Progress report 1 21 September
E-booklet. APEC Counter Terrorism Working Group (CTWG)
 E-booklet APEC Counter Terrorism Working Group (CTWG) November 2018 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS PRESENTATION...... 3 CHAPTER I: UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL (UNSC) RESOLUTIONS ON FINANCING OF TERRORISM AND
E-booklet APEC Counter Terrorism Working Group (CTWG) November 2018 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS PRESENTATION...... 3 CHAPTER I: UNITED NATIONS SECURITY COUNCIL (UNSC) RESOLUTIONS ON FINANCING OF TERRORISM AND
Unofficial Translation
 Unofficial Translation Prakas on Structures Duties and Functions of the Cambodia Financial Intelligence Unit The Governor of the National Bank of Cambodia - With reference to the Constitution of the Kingdom
Unofficial Translation Prakas on Structures Duties and Functions of the Cambodia Financial Intelligence Unit The Governor of the National Bank of Cambodia - With reference to the Constitution of the Kingdom
Anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism the Reserve Bank s responsibilities and approach
 Anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism the Reserve Bank s responsibilities and approach Hamish Armstrong Taking action to reduce money laundering and the financing of terrorism
Anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism the Reserve Bank s responsibilities and approach Hamish Armstrong Taking action to reduce money laundering and the financing of terrorism
Indonesia Short Form Report - May 2017
 Sanctions: FAFT AML Deficient Higher Risk Areas Medium Risk Areas None No Non - Compliance with FATF 40 + 9 Recommendations US Dept of State Money Laundering Assessment Not on EU White list equivalent
Sanctions: FAFT AML Deficient Higher Risk Areas Medium Risk Areas None No Non - Compliance with FATF 40 + 9 Recommendations US Dept of State Money Laundering Assessment Not on EU White list equivalent
Organization of American States OAS Inter-American Drug Abuse Control Commission CICAD. Multilateral Evaluation Mechanism MEM.
 Organization of American States OAS Inter-American Drug Abuse Control Commission CICAD Multilateral Evaluation Mechanism MEM Bolivia 2005 PROGRESS REPORT IN DRUG CONTROL IMPLEMENTATION OF RECOMMENDATIONS
Organization of American States OAS Inter-American Drug Abuse Control Commission CICAD Multilateral Evaluation Mechanism MEM Bolivia 2005 PROGRESS REPORT IN DRUG CONTROL IMPLEMENTATION OF RECOMMENDATIONS
ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING/ COUNTERING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM STRATEGY GROUP
 ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING/ COUNTERING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM STRATEGY GROUP AN ISLAND STRATEGY TO COUNTER MONEY LAUNDERING AND THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM UPDATE MARCH 2011 Contents 1 Introduction...3 2
ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING/ COUNTERING THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM STRATEGY GROUP AN ISLAND STRATEGY TO COUNTER MONEY LAUNDERING AND THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM UPDATE MARCH 2011 Contents 1 Introduction...3 2
FATF Report to the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors
 FATF Report to the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors April 2019 The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an independent inter-governmental body that develops and promotes policies to protect
FATF Report to the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors April 2019 The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an independent inter-governmental body that develops and promotes policies to protect
Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing: Definitions and Explanations
 Chapter I Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing: Definitions and Explanations A. What Is Money Laundering? B. What is Terrorist Financing? C. The Link Between Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing
Chapter I Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing: Definitions and Explanations A. What Is Money Laundering? B. What is Terrorist Financing? C. The Link Between Money Laundering and Terrorist Financing
Executive Summary EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Key Findings. Preface
 Executive Summary Preface EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. This report provides a summary of the anti-money laundering and combating the financing of terrorism (AML/CFT) measures in place in Singapore as at the date
Executive Summary Preface EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 1. This report provides a summary of the anti-money laundering and combating the financing of terrorism (AML/CFT) measures in place in Singapore as at the date
How are legal arrangements (express trusts and trust-like agreements) formed in the United States?
 USA Response: Collection of Information Regarding Implementation of Resolution 7/2 of the Conference of States Parties to the UN Convention against Corruption In response to the Secretariat s request for
USA Response: Collection of Information Regarding Implementation of Resolution 7/2 of the Conference of States Parties to the UN Convention against Corruption In response to the Secretariat s request for
CONTEMPORARY MEASURES FOR EFFECTIVE INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION
 CONTEMPORARY MEASURES FOR EFFECTIVE INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION Loh Yoon Min * I. INTRODUCTION 1. There is a growing importance to build and maintain close working cooperation with foreign agencies as corruptors
CONTEMPORARY MEASURES FOR EFFECTIVE INTERNATIONAL COOPERATION Loh Yoon Min * I. INTRODUCTION 1. There is a growing importance to build and maintain close working cooperation with foreign agencies as corruptors
International Monetary Fund Washington, D.C.
 2011 International Monetary Fund September 2011 IMF Country Report No. 11/267 Kuwait: Report on Observance of Standards and Codes FATF Recommendations for Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing
2011 International Monetary Fund September 2011 IMF Country Report No. 11/267 Kuwait: Report on Observance of Standards and Codes FATF Recommendations for Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing
Govern d Andorra Missió Permanent del Principat d Andorra a l OSCE NOTE VERBALE
 Govern d Andorra Missió Permanent del Principat d Andorra a l OSCE FSC.EMI/42/10 1 April 2010 ENGLISH only NOTE VERBALE The Permanent Mission of the Principality of Andorra to the Organization for Security
Govern d Andorra Missió Permanent del Principat d Andorra a l OSCE FSC.EMI/42/10 1 April 2010 ENGLISH only NOTE VERBALE The Permanent Mission of the Principality of Andorra to the Organization for Security
Presentation with respect to the FATF. Prakash Mungra GM Supervisory Issues
 Presentation with respect to the FATF Mutual Evaluation Report Aruba Prakash Mungra GM Supervisory Issues 1 Contents presentation I. 40 + 9 FATF Recommendations II. FATF evaluation of 24 November - 5 December
Presentation with respect to the FATF Mutual Evaluation Report Aruba Prakash Mungra GM Supervisory Issues 1 Contents presentation I. 40 + 9 FATF Recommendations II. FATF evaluation of 24 November - 5 December
2007 Money Laundering Prevention No.2 SAMOA
 2007 Money Laundering Prevention No.2 SAMOA Arrangement of Provisions PART I PRELIMINARY 1. Short Title and Commencement 2. Interpretation 3. Secrecy Obligations Overridden PART II ANTI MONEY LAUNDERING
2007 Money Laundering Prevention No.2 SAMOA Arrangement of Provisions PART I PRELIMINARY 1. Short Title and Commencement 2. Interpretation 3. Secrecy Obligations Overridden PART II ANTI MONEY LAUNDERING
Strasbourg, 11 February 2000 PC -R-EV (99) 27 Summ. EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC)
 Strasbourg, 11 February 2000 PC -R-EV (99) 27 Summ. EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC) Select Committee of Experts on the Evaluation of Anti-Money Laundering Measures (PC -R-E V ) FIRST MUTUAL
Strasbourg, 11 February 2000 PC -R-EV (99) 27 Summ. EUROPEAN COMMITTEE ON CRIME PROBLEMS (CDPC) Select Committee of Experts on the Evaluation of Anti-Money Laundering Measures (PC -R-E V ) FIRST MUTUAL
MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING IN THE CORPORATE SERVICE PROVIDERS SECTOR. Domestic Trends
 MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING IN THE CORPORATE SERVICE PROVIDERS SECTOR Domestic Trends 31 May 2016 AGENDA ML/TF Trends National Risk Assessment Findings Sector Vulnerabilities Shell companies
MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING IN THE CORPORATE SERVICE PROVIDERS SECTOR Domestic Trends 31 May 2016 AGENDA ML/TF Trends National Risk Assessment Findings Sector Vulnerabilities Shell companies
ORGANIZATION OF AMERICAN STATES Inter-American Drug Abuse Control Commission (CICAD)
 OEA/Ser.L/XIV.6.1 MEM/INF.2004 Add.27 ORGANIZATION OF AMERICAN STATES Inter-American Drug Abuse Control Commission (CICAD) Multilateral Evaluation Mechanism (MEM) Governmental Expert Group (GEG) EVALUATION
OEA/Ser.L/XIV.6.1 MEM/INF.2004 Add.27 ORGANIZATION OF AMERICAN STATES Inter-American Drug Abuse Control Commission (CICAD) Multilateral Evaluation Mechanism (MEM) Governmental Expert Group (GEG) EVALUATION
DR. ABDULLAHI SHEHU DIRECTOR GENERAL INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY LAUNDERING IN WEST AFRICA (GIABA)
 TAKING COUNTER-FINANCING OF TERRORISM FORWARD: STRENGTHENING STATES' CAPACITIES AND INTERNATIONAL AND REGIONAL COOPERATION DR. ABDULLAHI SHEHU DIRECTOR GENERAL INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY
TAKING COUNTER-FINANCING OF TERRORISM FORWARD: STRENGTHENING STATES' CAPACITIES AND INTERNATIONAL AND REGIONAL COOPERATION DR. ABDULLAHI SHEHU DIRECTOR GENERAL INTER-GOVERNMENTAL ACTION GROUP AGAINST MONEY
Webinar 01: AML/CFT Requirements Overview. 4 th July 2018
 Webinar 01: AML/CFT Requirements Overview 4 th July 2018 About Your Presenter Neil has a unique background in financial crime risk management, spanning 25 years. This includes working within Law Enforcement
Webinar 01: AML/CFT Requirements Overview 4 th July 2018 About Your Presenter Neil has a unique background in financial crime risk management, spanning 25 years. This includes working within Law Enforcement
NATIONAL STRATEGY AGAINST MONEY LAUNDERING AND THE FINANCING OF TERRORISM
 Pursuant to Article 45(1) of the Law on Government (Official Gazette of RS, No 55/05, 71/05 corr., 101/07, 65/08, 16/2011, 68/2012 CC decision, 72/2012, 7/2014 CC decision and 44/2014), The Government
Pursuant to Article 45(1) of the Law on Government (Official Gazette of RS, No 55/05, 71/05 corr., 101/07, 65/08, 16/2011, 68/2012 CC decision, 72/2012, 7/2014 CC decision and 44/2014), The Government
ASEAN Law Association. And. Meetings of the Governing Council and Standing Committee. Manila, Philippines
 ASEAN Law Association 25 th Anniversary Special Commemorative Session And Meetings of the Governing Council and Standing Committee 24 th -27 th November 2005 Manila, Philippines CROSS-BORDER STATUTES AND
ASEAN Law Association 25 th Anniversary Special Commemorative Session And Meetings of the Governing Council and Standing Committee 24 th -27 th November 2005 Manila, Philippines CROSS-BORDER STATUTES AND
APG ANNUAL BUSINESS PLAN
 APG ANNUAL BUSINESS PLAN 2018 2019 Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering Approved and adopted, 24 July 2018 APG Annual Business Plan 2018 2019 Applications for permission to reproduce all or part of this
APG ANNUAL BUSINESS PLAN 2018 2019 Asia/Pacific Group on Money Laundering Approved and adopted, 24 July 2018 APG Annual Business Plan 2018 2019 Applications for permission to reproduce all or part of this
ZIMBABWE NATIONAL ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBATING FINANCING OF TERRORISM STRATEGIC PLAN FOR THE PERIOD:
 ZIMBABWE NATIONAL ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBATING FINANCING OF TERRORISM STRATEGIC PLAN FOR THE PERIOD: 2015-2018 JUNE 2015 1 P a g e Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 VISION STATEMENT... 3 MISSION
ZIMBABWE NATIONAL ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING AND COMBATING FINANCING OF TERRORISM STRATEGIC PLAN FOR THE PERIOD: 2015-2018 JUNE 2015 1 P a g e Table of Contents INTRODUCTION... 3 VISION STATEMENT... 3 MISSION
INSTRUCTION (NUMBER 02/2017) FOR FINANCIAL SERVICES BUSINESSES BUSINESS FROM SENSITIVE SOURCES
 INSTRUCTION (NUMBER 02/2017) FOR FINANCIAL SERVICES BUSINESSES 10 April 2017 BUSINESS FROM SENSITIVE SOURCES This Instruction is made under section 49(7) of the Criminal Justice (Proceeds of Crime) (Bailiwick
INSTRUCTION (NUMBER 02/2017) FOR FINANCIAL SERVICES BUSINESSES 10 April 2017 BUSINESS FROM SENSITIVE SOURCES This Instruction is made under section 49(7) of the Criminal Justice (Proceeds of Crime) (Bailiwick
FATF Report to the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors
 FATF Report to the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors March 2018 FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an independent inter-governmental body that develops
FATF Report to the G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors March 2018 FINANCIAL ACTION TASK FORCE The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an independent inter-governmental body that develops
Chapter IV Fight against Money Laundering
 Chapter IV Fight against Money Laundering Structure of the presentation Legal framework Institutional framework and Capacities Plans EU legal framework Directive 2005/60 EC (the Third AMLD ); Directive
Chapter IV Fight against Money Laundering Structure of the presentation Legal framework Institutional framework and Capacities Plans EU legal framework Directive 2005/60 EC (the Third AMLD ); Directive
JERSEY FINANCIAL SERVICES COMMISSION 5 TH ANNIVERSARY SEMINAR FATF REVISED 40 RECOMMENDATIONS
 JERSEY FINANCIAL SERVICES COMMISSION 5 TH ANNIVERSARY SEMINAR 1. Introduction 1.0 The FATF Forty Recommendations have been revised and these revised Recommendations are with immediate effect the new international
JERSEY FINANCIAL SERVICES COMMISSION 5 TH ANNIVERSARY SEMINAR 1. Introduction 1.0 The FATF Forty Recommendations have been revised and these revised Recommendations are with immediate effect the new international
CHAPTER 423 THE ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING ACT PRINCIPAL LEGISLATION ARRANGEMETN OF SECTIONS PART I PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS
 CHAPTER 423 THE ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING ACT PRINCIPAL LEGISLATION ARRANGEMETN OF SECTIONS Section Title PART I PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS 1. Short title. 2. Application. 3. Interpretation. PART II THE FINANCIAL
CHAPTER 423 THE ANTI-MONEY LAUNDERING ACT PRINCIPAL LEGISLATION ARRANGEMETN OF SECTIONS Section Title PART I PRELIMINARY PROVISIONS 1. Short title. 2. Application. 3. Interpretation. PART II THE FINANCIAL
CROSS-BORDER STATUTES AND OTHER MEASURES TO CURB MONEY LAUNDERING IN SINGAPORE. 1. Money laundering" is the process whereby the proceeds of criminal
 CROSS-BORDER STATUTES AND OTHER MEASURES TO CURB MONEY LAUNDERING IN SINGAPORE Lee Seiu Kin, SC 1 Second Solicitor-General, Singapore Introduction 1. Money laundering" is the process whereby the proceeds
CROSS-BORDER STATUTES AND OTHER MEASURES TO CURB MONEY LAUNDERING IN SINGAPORE Lee Seiu Kin, SC 1 Second Solicitor-General, Singapore Introduction 1. Money laundering" is the process whereby the proceeds
ISRAEL: FOLLOW-UP TO THE PHASE 3 REPORT & RECOMMENDATIONS
 ISRAEL: FOLLOW-UP TO THE PHASE 3 REPORT & RECOMMENDATIONS November 2017 This report, submitted by Israel for discussion at the Working Group on Bribery s June 2017 plenary, provides information on the
ISRAEL: FOLLOW-UP TO THE PHASE 3 REPORT & RECOMMENDATIONS November 2017 This report, submitted by Israel for discussion at the Working Group on Bribery s June 2017 plenary, provides information on the
Guidelines on Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Financing of Terrorism
 Guidelines on Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Financing of Terrorism Prudential Supervision Department Document Issued: 1. Introduction (1) This document sets out guidelines issued under section 78(3)
Guidelines on Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Financing of Terrorism Prudential Supervision Department Document Issued: 1. Introduction (1) This document sets out guidelines issued under section 78(3)
Mutual Evaluation Report. Anti money laundering and counter terrorist financing measures in Samoa 2015
 ` Anti money laundering and counter terrorist financing measures Samoa Mutual Evaluation Report September 2015 Anti money laundering and counter terrorist financing measures in Samoa 2015 The Asia/Pacific
` Anti money laundering and counter terrorist financing measures Samoa Mutual Evaluation Report September 2015 Anti money laundering and counter terrorist financing measures in Samoa 2015 The Asia/Pacific
Regional Risk Spotlight: An Interview with Michael Kim of Kobre & Kim on South Korea s Anti-Money Laundering Laws
 Regional Risk Spotlight: An Interview with Michael Kim of Kobre & Kim on South Korea s Anti-Money Laundering Laws By Megan Zwiebel While anti-corruption compliance is a focus for many companies, anti-money
Regional Risk Spotlight: An Interview with Michael Kim of Kobre & Kim on South Korea s Anti-Money Laundering Laws By Megan Zwiebel While anti-corruption compliance is a focus for many companies, anti-money
Consultation Paper. The Review of the Standards Preparation for the 4 th Round of Mutual Evaluation. Second public consultation
 Financial Action Task Force Groupe d action financière Consultation Paper The Review of the Standards Preparation for the 4 th Round of Mutual Evaluation Second public consultation June 2011 THE FINANCIAL
Financial Action Task Force Groupe d action financière Consultation Paper The Review of the Standards Preparation for the 4 th Round of Mutual Evaluation Second public consultation June 2011 THE FINANCIAL
BRIEFING NOTE ON THE BAILIWICK OF GUERNSEY S NATIONAL RISK ASSESSMENT 7 July 2016
 BRIEFING NOTE ON THE BAILIWICK OF GUERNSEY S NATIONAL RISK ASSESSMENT 7 July 2016 Introduction The purpose of this briefing note is to provide financial services businesses, prescribed businesses and e-gambling
BRIEFING NOTE ON THE BAILIWICK OF GUERNSEY S NATIONAL RISK ASSESSMENT 7 July 2016 Introduction The purpose of this briefing note is to provide financial services businesses, prescribed businesses and e-gambling
Legislative Decree No. 33 The President of the Republic, Acting in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution, Hereby decrees the following:
 Legislative Decree No. 33 The President of the Republic, Acting in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution, Hereby decrees the following: Article 1 The following terms and expressions shall
Legislative Decree No. 33 The President of the Republic, Acting in accordance with the provisions of the Constitution, Hereby decrees the following: Article 1 The following terms and expressions shall
JOINT RESOLUTION OF THE GOVERNOR OF BANK OF MONGOLIA AND CHAIR OF THE FINANCIAL REGULATORY COMMISSION
 JOINT RESOLUTION OF THE GOVERNOR OF BANK OF MONGOLIA AND CHAIR OF THE FINANCIAL REGULATORY COMMISSION Date: June 30, 2016 Ulaanbaatar No A-162/195 In terms of article 19.2.3 of The Law on Money laundering
JOINT RESOLUTION OF THE GOVERNOR OF BANK OF MONGOLIA AND CHAIR OF THE FINANCIAL REGULATORY COMMISSION Date: June 30, 2016 Ulaanbaatar No A-162/195 In terms of article 19.2.3 of The Law on Money laundering
Anti-money Laundering Bulletin
 April 2015 (revised) Anti-money Laundering Bulletin Frequently Asked Questions on Suspicious Transaction Reporting Supplement to AMLB1 HONG KONG INSTITUTE OF CERTIFIED PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS Anti-Money Laundering/
April 2015 (revised) Anti-money Laundering Bulletin Frequently Asked Questions on Suspicious Transaction Reporting Supplement to AMLB1 HONG KONG INSTITUTE OF CERTIFIED PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS Anti-Money Laundering/
NOTICE TO BANKS MONETARY AUTHORITY OF SINGAPORE ACT, CAP. 186
 MAS 626 2 July 2007 Last revised on 23 January 2013 (Refer to endnotes for history of amendments) NOTICE TO BANKS MONETARY AUTHORITY OF SINGAPORE ACT, CAP. 186 PREVENTION OF MONEY LAUNDERING AND COUNTERING
MAS 626 2 July 2007 Last revised on 23 January 2013 (Refer to endnotes for history of amendments) NOTICE TO BANKS MONETARY AUTHORITY OF SINGAPORE ACT, CAP. 186 PREVENTION OF MONEY LAUNDERING AND COUNTERING
Second Evaluation Round
 DIRECTORATE GENERAL OF HUMAN RIGHTS AND LEGAL AFFAIRS DIRECTORATE OF MONITORING Strasbourg, 5 December 2008 Public Greco RC-II (2006) 3E Addendum Second Evaluation Round Addendum to the Compliance Report
DIRECTORATE GENERAL OF HUMAN RIGHTS AND LEGAL AFFAIRS DIRECTORATE OF MONITORING Strasbourg, 5 December 2008 Public Greco RC-II (2006) 3E Addendum Second Evaluation Round Addendum to the Compliance Report
FATF Report to the G20 Leaders Summit
 FATF Report to the G20 Leaders Summit November 2018 The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an independent inter-governmental body that develops and promotes policies to protect the global financial
FATF Report to the G20 Leaders Summit November 2018 The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) is an independent inter-governmental body that develops and promotes policies to protect the global financial
S/2003/385. Security Council. United Nations
 United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 31 March 2003 Original: English S/2003/385 Letter dated 26 March 2003 from the Chairman of the Security Council Committee established pursuant to resolution
United Nations Security Council Distr.: General 31 March 2003 Original: English S/2003/385 Letter dated 26 March 2003 from the Chairman of the Security Council Committee established pursuant to resolution
THE REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA LAW ON COMBATING MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING CHAPTER 1 GENERAL PROVISIONS
 THE REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA LAW ON COMBATING MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING Adopted May 26, 2008 CHAPTER 1 GENERAL PROVISIONS The purpose of this Law is to protect the rights, freedoms, and legitimate
THE REPUBLIC OF ARMENIA LAW ON COMBATING MONEY LAUNDERING AND TERRORISM FINANCING Adopted May 26, 2008 CHAPTER 1 GENERAL PROVISIONS The purpose of this Law is to protect the rights, freedoms, and legitimate
Mutual Evaluation Report
 Inter-Governmental Action Group Against Money Laundering in West Africa Mutual Evaluation Report Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism Executive Summary Report 18 September 2008
Inter-Governmental Action Group Against Money Laundering in West Africa Mutual Evaluation Report Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism Executive Summary Report 18 September 2008
Use of the FATF AML/CTF Toolkit
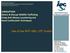 APEC Pathfinder Dialogue IV STRENGTHENING THE FIGHT AGAINST ILLICIT TRADE AND CORRUPTION Partnerships for Sustainable Security CORRUPTION Detect & Disrupt Wildlife Trafficking Using Anti-Money Laundering
APEC Pathfinder Dialogue IV STRENGTHENING THE FIGHT AGAINST ILLICIT TRADE AND CORRUPTION Partnerships for Sustainable Security CORRUPTION Detect & Disrupt Wildlife Trafficking Using Anti-Money Laundering
FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS - POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF SWAZILAND
 FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS - POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF SWAZILAND Covering the period August 2016 July 2017 ESAAMLG (2017), First Round Mutual Evaluation - Post Evaluation Progress Report of
FIRST ROUND MUTUAL EVALUATIONS - POST EVALUATION PROGRESS REPORT OF SWAZILAND Covering the period August 2016 July 2017 ESAAMLG (2017), First Round Mutual Evaluation - Post Evaluation Progress Report of
OFFICE FOR PREVENTION OF LAUNDERING OF PROCEEDS DERIVED FROM CRIMINAL ACTIVITY Report for 2014
 1 OFFICE FOR PREVENTION OF LAUNDERING OF PROCEEDS DERIVED FROM CRIMINAL ACTIVITY Report for 2014 1. General description of the Control Service Legal basis The new Law On the Prevention of Money Laundering
1 OFFICE FOR PREVENTION OF LAUNDERING OF PROCEEDS DERIVED FROM CRIMINAL ACTIVITY Report for 2014 1. General description of the Control Service Legal basis The new Law On the Prevention of Money Laundering
Objectives for FATF XXV ( ) Paper by the incoming President
 Objectives for FATF XXV (2013-2014) Paper by the incoming President Main tasks for the FATF in 2013-2014, in line with the Ministerial Mandate of 20 April 2012: I. INTRODUCTION Promoting and facilitating
Objectives for FATF XXV (2013-2014) Paper by the incoming President Main tasks for the FATF in 2013-2014, in line with the Ministerial Mandate of 20 April 2012: I. INTRODUCTION Promoting and facilitating
