STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE. Part 1 - Explanatory note Part 2 - Definition of terms 30-33
|
|
|
- Brice Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Contents Part 1 - Explanatory note 1-29 Part 2 - Definition of terms Part 3 - Standard accounting practice Part 4 - Part 5 - Legal and International Stock Exchange requirements in Great Britain and Northern Ireland Legal and International Stock Exchange requirements in the Republic of Ireland Part 6 - Compliance with International Accounting Standard No. 14 Reporting Financial Information by Segment' 64 Appendix - Illustrative segmental report 1
2 Segmental Reporting (Issued June 1990) The provisions of this statement of standard accounting practice should be read in conjunction with the Explanatory foreword to accounting standards and need not be applied to immaterial items. PART 1 - EXPLANATORY NOTE Purpose of segmental information 1 Many entities carry on several classes of business or operate in several geographical areas, with different rates of profitability, different opportunities for growth and different degrees of risk. It is not usually possible for the user of the financial statements of such an entity to make judgements about either the nature of the entity's different activities or their contribution to the entity's overall financial results unless the financial statements provide some segmental analysis of the information they contain. The purpose of segmental information is, therefore, to provide information to assist the users of financial statements: to appreciate more thoroughly the results and financial position of the entity by permitting a better understanding of the entity's past performance and thus a better assessment of its future prospects; and to be aware of the impact that changes in significant components of a business may have on the business as a whole. 2 This accounting standard should ensure as far as possible that the segmental information reported by an entity is disclosed on a consistent basis, year by year. However, caution should be exercised if comparing similar segments in different entities, because, in addition to any differences in accounting policies adopted, the basis of accounting for inter-segment sales or the treatment of common costs may not be consistent between entities. Scope and applicability 3 This accounting standard contains provisions relating to the statutory segmental disclosure requirements contained in companies legislation in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland. All companies are required to comply with these provisions. 2
3 4 This accounting standard also contains provisions relating to the disclosure of intersegment turnover, geographical segment result, segment net assets, origin of turnover, and segmental information about associated undertakings, which are not required by companies legislation. These provisions apply to any entity that: (c) is a public limited company or has a public limited company as a subsidiary; or is a banking or insurance company or group (as defined for the purposes of Part VII of the Companies Act 1985); or exceeds the criteria, multiplied in each case by 10, for defining a medium-sized company under Section 248 of the Companies Act 1985, as amended from time to time by statutory instrument. However, a subsidiary that is not a public limited company or a banking or insurance company need not comply with these provisions if its parent provides segmental information in compliance with this accounting standard. 5 All entities are encouraged to apply the provisions of this accounting standard in all financial statements intended to give a true and fair view of the financial position and profit or loss. 6 Where, in the opinion of the directors, the disclosure of any information required by this accounting standard would be seriously prejudicial to the interests of the reporting entity, that information need not be disclosed; but the fact that any such information has not been disclosed must be stated. This repeats the exemption contained in paragraph 55(5) of Schedule 4 to the Companies Act 1985* in the wider context of this accounting standard. Determining reportable segments 7 Information contained in financial statements can be segmented in two principal ways - by class of business and geographically. The Companies Act 1985 recognises both of these bases in paragraph 55 of Schedule 4, referring to the geographical areas as 'markets'. Paragraph 55 states that in analysing the source (in terms of either business or market) of turnover or profit or loss the directors should have regard to the manner in which the company's activities are organised. Paragraph 55 also states that it is for the directors to determine whether the company has carried on business of two or more classes or has supplied markets that differ substantially from each other and that where, in the opinion of the directors, the classes of business or the markets do not differ substantially from each other they may be treated as one. * Throughout this statement of standard accounting practice, references to paragraph 55 of Schedule 4 to the Companies Act 1985 should be read in the Republic of Ireland as references to paragraph 41 of the Schedule to the Companies (Amendment) Act
4 8 In identifying separate reportable segments, the director should have regard to the overall purpose of presenting segmental information (as set out in paragraph l) and the need of the user of the financial statements to be informed where an entity carries on operations in different classes of business or in different geographical areas that: earn a return on investment that is out of line with the remainder of the business; or are subject to different degrees of risk; or (c) have experienced different rates of growth; or (d) have different potentials for future development. 9 Each class of business or geographical segment that is significant to an entity as a whole should be identified as a reportable segment. For the purposes of this accounting standard a segment should normally be regarded as significant if: (c) its third party turnover is ten per cent or more of the total third party turnover of the entity; or its segment result, whether profit or loss, is ten per cent or more of the combined result of all segments in profit or of all segments in loss, whichever combined result is the greater; or its net assets are ten per cent or more of the total net assets of the entity. 10 The directors should review the definitions of the segments annually and re -define them when appropriate. In doing so the directors should have regard to the fundamental objective of this accounting standard, which is to achieve, as far as possible, consistency and comparability between years. Classes of business 11 A separate class of business is a distinguishable component of an entity that provides a separate product or service or a separate group of related products or services. 12 When deciding whether or not an entity operates in different classes of business, the directors should take into account the following factors: the nature of the products or services; the nature of the production processes; (c) the markets in which the products or services are sold; (d) the distribution channels for the products; (e) the manner in which the entity's activities are organised; (f) any separate legislative framework relating to part of the business, for example, a bank or an insurance company. 4
5 13 Although it is possible to identify certain characteristics that differentiate between classes of business, no single set of characteristics is universally applicable nor is any single characteristic determinative in all cases. Consequently, determination of an entity's classes of business must depend on the judgement of the directors. Geographical segments 14 A geographical segment is a geographical area comprising an individual country or a group of countries in which an entity operates, or to which it supplies products or services. 15 Ageographical analysis should help the user of the financial statements to assess the extent to which an entity's operations are subject to factors such as the following: expansionist or restrictive economic climates; stable or unstable political regimes; (c) exchange control regulations; (d) exchange rate fluctuations. 16 It is not practicable to define a method of grouping that will reflect all the differences between international business environments and that would apply to all entities. The selected grouping should reflect the purpose of presenting segmental information (as set out in paragraph l) and the factors noted in paragraphs 8 and 15. Although geographical proximity may indicate similar economic trends and risks, this will not necessarily be the case. Information to be disclosed General 17 The entity should define in its financial statements each reported class of business and geographical segment. Turnover 18 The factors listed in paragraph 15 apply both to the geographical locations of the entity's operations and to the geographical locations of its markets. The user of the financial statements gains a fuller understanding of the entity's exposure to these factors, if turnover is disclosed according to both location of operations and location of markets. For the purposes of this accounting standard, origin of turnover is the geographical area from which products or services are supplied to a third party or another segment. Destination of turnover is the geographical area to which goods or services are supplied. Because disclosure relating to segment results and net assets will generally be based on location of operations, an analysis of turnover on the same basis will enable the user to match turnover, result and net assets on a consistent basis, and to relate all three to the perceived risks and opportunities of the segments. For these reasons this accounting standard requires the disclosure of sales by origin, but reporting entities should also disclose turnover by destination unless there is no material difference between the two. If there is no material difference, a statement to that effect is required. 5
6 19 Inter-segment sales and transfers are often a material part of the total turnover of the reportable segments and in such cases they should be analysed segmentally and shown separately. The geographical analysis of inter-segment turnover should be disclosed by origin. Analysis by destination usually has little or no value and would not normally be provided. 20 The Companies Act 1985 and the Companies (Northern Ireland) Order 1986 contain provisions exempting banking and insurance companies and groups from the requirement to disclose turnover in certain circumstances. In the Republic of Ireland, similar exemptions are extended to special classes of companies (banking, discount and insurance companies) under the Companies Act Certain other entities - for example, building societies - are subject to different statutory rules from those applied to companies. Where turnover is not required by statute to be disclosed, it is not required by this accounting standard to be disclosed segmentally. The fact that such turnover has not been disclosed segmentally should be stated. Segment result 21 The entity should disclose the result of each reportable segment before accounting for taxation, minority interests and extraordinary items. The geographical analysis of segment result should normally be based on the areas from which products or services are supplied. 22 In the majority of entities, different classes of business or geographical segments are financed by different proportions of interest-bearing debt and equity. The interest earned or incurred by individual segments are therefore a result of the entity's overall financial policy rather than a proper reflection of the results of the various segments. Consequently, comparisons of profit between segments or between different years for the same segment are likely to be meaningless if interest is included in arriving at the result. For these reasons, it will normally be appropriate for segment results to be disclosed before taking account of interest. However, where all or part of the entity's business is to earn and/or incur interest (as in the financial sector, for example), or where interest income or expense is central to the business (as in the contracting or travel businesses, for example), interest should normally be included in arriving at the segment result. Common costs 23 Common costs are costs relating to more than one segment. They should be treated in the way that the directors deem most appropriate in pursuance of the objectives of segmental reporting. Entities may apportion some common costs for the purposes of internal reporting and, in such cases, it may be reasonable for such costs to be similarly apportioned for external reporting purposes. If the apportionment would be misleading, common costs should not be apportioned in the segmental disclosures but should be deducted from the total of the segment results. Costs that are directly attributable to individual reportable segments are not common costs for the purposes of this accounting standard and therefore should be allocated to those segments, irrespective of the fact that they may have been borne by a different segment or by the Head Office. 6
7 Segment net assets 24 The net assets of each reportable segment should be disclosed. In most cases these will be the non-interest bearing operating assets less the non- interest bearing operating liabilities. However, to the extent that the segment result is disclosed after accounting for interest as described in paragraph 22, the corresponding interest-bearing operating assets and liabilities should also be included. 25 Segment operating assets and liabilities may include assets and liabilities relating exclusively to one segment and also an allocated portion of assets and liabilities that relate jointly to more than one segment. Assets and liabilities used jointly by more than one segment should be allocated to the segments on a reasonable basis. Assets and liabilities that are not used in the operations of any segment should not be allocated to segments. Operating assets of a segment should not normally include loans or advances to, or investments in, another segment unless interest therefrom has been included in arriving at the segment result on the basis set out in paragraph 22. Associated undertakings 26 Sometimes associated undertakings form a significant part of a reporting entity's results or assets. In such circumstances the following information should be analysed segmentally and shown separately in the segmental report: the reporting entity's share of the profits or losses of associated undertakings before accounting for taxation, minority interests and extraordinary items; and the reporting entity's share of the net assets of associated undertakings (including goodwill to the extent that it has not been written off) stated, where possible, after attributing fair values to the net assets at the date of acquisition of the interest in each associated undertaking. However, it is recognised that this information might be unobtainable or publication might be prejudicial to the business of the associate. In such circumstances the disclosure is not required but the reason for non- disclosure should be stated by way of note, together with a brief description of the omitted business or businesses. 27 For the purposes of this accounting standard, associated companies form a significant part of the reporting entity's results or assets if, in total, they account for at least 20% of the total result or 20% of the total net assets of the reporting entity. General 28 The total of the amounts disclosed by segment should agree with the related total in the financial statements. If it does not, the reporting entity should provide a reconciliation between the two figures. Reconciling items should be properly identified and explained. 29 Comparative figures for the previous accounting period should be provided. If a change is made to the definitions of the segments or to the accounting policies that are adopted for reporting segmental information, the nature of the change should be disclosed. The reason for the change and the effect of the change should be stated. The previous year's figures should be restated to reflect the change. 7
8 PART 2 - DEFINITION OF TERMS 30 A class of business is a distinguishable component of an entity that provides a separate product or service or a separate group of related products or services. 31 A geographical segment is a geographical area comprising an individual country or group of countries in which an entity operates, or to which it supplies products or services. 32 Origin of turnover is the geographical segment from which products or services are supplied to a third party or to another segment. 33 Destination of turnover is the geographical segment to which products or services are supplied. PART 3 - STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 34 If an entity has two or more classes of business, or operates in two or more geographical segments which differ substantially from each other, it should define its classes of business and geographical segments in its financial statements, and it should report with respect to each class of business and geographical segment the following financial information: (c) turnover, distinguishing between (i) turnover derived from external customers and (ii) turnover derived from other segments; result, before accounting for taxation, minority interests and extraordinary items; and net assets. The reporting entity should disclose the geographical segmentation of turnover by origin. It should also disclose turnover to third parties by destination or state where appropriate that this amount is not materially different from turnover to third parties by origin. Segment result will normally be disclosed before taking account of interest. However, where all or part of the entity's business is to earn and/or incur interest, or where interest income or expense is central to the business, interest should normally be included in arriving at the segment result. Net assets will normally be non-interest bearing operating assets less the non-interest bearing operating liabilities, but to the extent that the segment result is disclosed after accounting for interest the corresponding interest-bearing assets or liabilities should also be included. 35 When both parent and consolidated financial statements are presented, segmental information should be presented on the basis of the consolidated financial statements. 8
9 36 The reporting entity should disclose the following information segmentally in relation to its associated undertakings if these account for at least 20% of its total result or 20% of its total net assets: the entity's share of the results of associated undertakings before accounting for taxation, minority interests and extraordinary items: and the entity's share of the net assets of associated undertakings (including goodwill to the extent it has not been written off) stated, where possible, after attributing fair values to the net assets at the date of acquisition of the interest in each associated undertaking. The segmental disclosure should be of the aggregate amounts for all associated undertakings for which the information is available and should be shown separately in the segmental report. However, this information need not be disclosed if it is unobtainable or publication would be prejudicial to the business of the associate. In such circumstances, the reason for non -disclosure should be stated by way of note, together with a brief description of the omitted business or businesses. 37 The total of the amounts disclosed by segment should agree with the related total in the financial statements. If it does not, the reporting entity should provide a reconciliation between the two amounts. Reconciling items should be properly identified and explained. 38 Comparative figures for the previous accounting period should be provided. If, however, on the first occasion on which an entity provides a segmental report the necessary information is not readily available, comparative figures need not be provided. 39 The directors should re-define the segments when appropriate. If a change is made to the definitions of the segments or to the accounting policies that are adopted for reporting segmental information, the nature of the change should be disclosed. The reason for the change and its effect should be stated. The previous year's figures should be re-stated to reflect the change. 40 This accounting standard contains provisions relating to the statutory segmental disclosure requirements contained in companies legislation in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland. All companies are required to comply with these provisions. 9
10 41 This accounting standard also contains provisions relating to segmental disclosures which are not required by companies legislation*. These provisions apply to any entity that: (c) is a public limited company or that has a public limited company as a subsidiary; or is a banking or insurance company or group (as defined for the purposes of Part VII of the Companies Act 1985); or exceeds the criteria, multiplied in each case by 10, for defining a medium-sized company under section 247** of the Companies Act 1985, as amended from time to time by statutory instrument. However, a subsidiary that is not a public limited company or a banking or insurance company need not comply with these provisions if its parent provides segmental disclosures in compliance with this accounting standard. 42 All other entities are encouraged to apply the provisions of this accounting standard in all financial statements intended to give a true and fair view of the financial position and profit or loss. 43 Where, in the opinion of the directors, the disclosure of any information required by this accounting standard would be seriously prejudicial to the interests of the reporting entity, that information need not be disclosed. The fact that any such information has not been disclosed must be stated. 44 Entities that are not required by statute to disclose turnover in their financial statements are not required by this accounting standard to disclose turnover segmentally. The fact that turnover has not been disclosed segmentally should be stated in the financial statements. Reporting entities applying the Financial Reporting Standard for Smaller Entities are exempt from this accounting standard. Date from which effective 45 The provisions of this statement of standard accounting practice should be adopted as soon as possible and regarded as standard in respect of financial statements relating to accounting periods beginning on or after 1 July * Disclosures not required by the Companies Act 1985 are those set out in paragraphs 34ii, 34 insofar as it relates to geographical segment result, 34(c), 34 in so far as it relates to origin of turnover, and 36. ** Equivalent legal references Great Britain Northern Ireland Republic of Ireland Companies Act 1985 Companies (Northern Companies (Amendment) Ireland) Order 1986 Act 1986 Section 247 Article 256 Section 8 (as amended) 10
11 PART 4 - LEGAL AND INTERNATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE REQUIREMENTS IN GREAT BRITAIN AND NORTHERN IRELAND Company law All paragraph references, unless otherwise indicated, are to the Schedules to the Companies Act 1985 and the Companies (Northern Ireland) Order Paragraph 55(1) of Schedule 4 requires all companies that, in the course of the financial year, have carried on business of two or more classes that (in the opinion of the directors) differ substantially from each other to state: (c) a description of each class of business; the amount of turnover attributable to each class of business; and the amount of the profit or loss of the company before taxation that is, in the opinion of the directors, attributable to each class of business. 47 Paragraph 55(2) of Schedule 4 requires all companies that, in the course of the financial year, have supplied geographical markets that (in the opinion of the directors) differ substantially from each other to state the amount of the turnover attributable to each market. 48 Paragraph 55(3) of Schedule 4 provides that, in analysing the source (in terms of either classes of business or markets) of turnover or profit or loss for the purposes of paragraph 55, the directors of the company shall have regard to the manner in which the company's activities are organised. 49 Paragraph 55(4) of Schedule 4 provides that, for the purposes of paragraph 55: (c) classes of business which, in the opinion of the directors, do not differ substantially from each other shall be treated as one class; markets which, in the opinion of the directors, do not differ substantially from each other shall be treated as one market; and any amounts properly attributable to one class of business or to one market which are not material may be included in the amount stated in respect of another. 50 Paragraph 55(5) of Schedule 4 states that where, in the opinion of the directors, the disclosure of any information required by paragraph 55 would be seriously prejudicial to the interests of the company, that information need not be disclosed but the fact that any such information has not been disclosed must be stated. 11
12 51 Schedule 9 deals with the special provisions for banking and insurance companies and groups. Paragraph 17 of Schedule 9 requires the following matters to be stated by way of note, if not otherwise shown: (c) the turnover for the financial year, except in so far as it is attributable to the business of banking or discounting; if some or all of the turnover is omitted by reason of its being attributable to the business of banking or discounting, the fact that it is so omitted; and the method by which turnover stated is arrived at. 52 Paragraph 17(5) of Schedule 9 provides that a company should not be subject to the requirements of paragraph 17 if it is neither a parent company nor a subsidiary undertaking and the turnover which, apart from sub-paragraph 17(5), would be required to be stated does not exceed 1 million. 53 Schedule 10 deals with the directors' report where accounts are prepared in accordance with the special provisions for banking or insurance companies or groups. Paragraph 2 provides that where a company prepares group accounts in accordance with the special provisions and, in the course of the financial year to which the accounts relate, the group has carried on business of two or more classes (other than banking or discounting of a class prescribed for the purpose of paragraph 17(2) of that Schedule) that in the opinion of the directors differ substantially from each other, there shall be contained in the directors' report a statement of - the proportions in which the turnover for the financial year (so far as stated in the consolidated accounts) is divided amongst those classes (describing them); and as regards business of each class, the extent or approximate extent (expressed in money terms) to which, in the opinion of the directors, the carrying on of business of that class contributed to, or restricted, the profit or loss of the company for that year (before taxation). Classes of business which, in the opinion of the directors, do not differ substantially from each other, are to be treated as one class. International Stock Exchange 54 The International Stock Exchange of the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland Ltd. sets out its requirements for segmental information in the 'Admission of Securities to Listing'. Section 5, Chapter 2, paragraph 21(c) of that publication requires: 'a geographical analysis of both net turnover and contribution to trading results of those trading operations carried on by the company (or group) outside the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland.' 12
13 55 No analysis of the contribution to trading results is required unless the contribution to profit or loss from a specific area is 'abnormal' in nature. 'Abnormal' is defined as substantially out of line with the normal ratio of profit to turnover. PART 5 - LEGALAND INTERNATIONALSTOCK EXCHANGE REQUIREMENTS IN THE REPUBLIC OF IRELAND Company law All paragraph references, unless otherwise indicated, are to the Schedule to the Companies (Amendment) Act Paragraph 41(1) requires all companies that, in the course of the financial year, have carried on business of two or more classes that ( in the opinion of the directors) differ substantially from each other to state: a description of each class of business; and the amount of turnover attributable to each class of business. 57 Paragraph 41(2) requires all companies that, in the course of the financial year, have supplied geographical markets that (in the opinion of the directors) differ substantially from each other, to state the amount of the turnover attributable to each market. 58 Paragraph 41(3) provides that, in analysing the source (in terms of either classes of business or markets) of turnover, the directors of the company shall have regard to the manner in which the company's activities are organised. 59 Paragraph 41(4) provides that, for the purposes of paragraph 41: classes of business which, in the opinion of the directors, do not differ substantially from each other shall be treated as one class; markets which, in the opinion of the directors, do not differ substantially from each other shall be treated as one market; and (c) any amounts properly attributable to one class of business or to one market which are not material may be included in the amount stated in respect of another. 60 Paragraph 41(5) states that where, in the opinion of the directors, the disclosure of any information required by paragraph 41 would be seriously prejudicial to the interests of the company, that information need not be disclosed but the fact that any such information has not been disclosed must be stated. 61 Banking, discount and insurance companies are regarded as special classes of companies and as such come within Part III of the Sixth Schedule to the Companies Act 1963 which exempts them from the disclosure requirements of the Schedule to the Companies (Amendment) Act
14 62 The International Stock Exchange of the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland Ltd. sets out its requirements for segmental information in the 'Admission of Securities to Listing'. Section 5, Chapter 2, paragraph 21(c) of that publication requires: 'a geographical analysis of both net turnover and contribution to trading results of those trading operations carried on by the company (or group) outside the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland'. 63 No analysis of the contribution to trading results is required unless the contribution to profit or loss from a specific area is 'abnormal' in nature. 'Abnormal' is defined as substantially out of line with the normal ratio of profit to turnover. PART 6 - COMPLIANCE WITH INTERNATIONAL ACCOUNTING STANDARD NO. 14 REPORTING FINANCIAL INFORMATION BY SEGMENT 64 Compliance with the requirements of this accounting standard will ensure compliance with IAS 14 in all material respects, except in the following circumstances. (c) This accounting standard does not require the basis of inter-segment pricing to be disclosed. This information must be disclosed in order to comply with IAS 14. This accounting standard requires the disclosure of segment 'net assets', whereas IAS 14 refers to 'assets employed'. However, as stated in paragraph 34, net assets will normally be the non-interest bearing operating assets less the non-interest bearing operating liabilities, and in those cases net assets will not be materially different from assets employed. This accounting standard gives the following exemptions which do not appear in IAS 14. (i) (ii) (iii) An entity need not disclose segmental information if disclosure would be seriously prejudicial to its interests. An entity that is not required by statute to disclose turnover is not required to disclose turnover segmentally. Asubsidiary that is not a public limited company or a banking or insurance company need not make the segmental disclosures required by this accounting standard if its parent does so. 14
15 APPENDIX: ILLUSTRATIVE SEGMENTAL REPORT This Appendix is for general guidance only and does not form part of the Statement of Standard Accounting Practice CLASSES OF BUSINESS Industry A Industry B Other industries Group TURNOVER Total sales 33,000 30,000 42,000 38,000 Inter-segment sales (4,000) Sales to third parties 29,000 30,000 42,000 38,000 26,000 23, ,000 91,000 (12,000) (14,000) (16,000) (14,000) 14,000 9,000 85,000 77,000 PROFIT BEFORE TAXATION Segment profit 3,000 2,500 4,500 4,000 Common costs Operating profit Net interest 1,800 1,500 9,300 8, ,000 7,700 (400) (500) 8,600 7,200 Group share of the profits before taxation of associated undertakings 1,000 1,000 1,400 1, ,400 2,200 Group profit before taxation 11,000 9,400 NETASSETS Segment net assets 17,600 15,000 24,000 25,000 Unallocated assets Group share of the net assets of associated undertakings 10,200 8,000 8,800 9,000 Total net assets 19,400 19,000 61,000 59,000 3,000 3,000 64,000 62, ,000 17,000 83,000 79,000 15
16 GEOGRAPHICAL SEGMENTS United Kingdom North America Far East TURNOVER Turnover by destination Sales to third parties 34,000 31,000 16,000 14,500 25,000 23,000 Turnover by origin Total sales 38,000 34,000 29,000 27,500 23,000 23,000 Inter-segment sales - - (8,000) (9,000) (9,000) (9,000) Sales to third parties 38,000 34,000 21,000 18,500 14,000 14,000 PROFIT BEFORE TAXATION Segment profit 4,000 2,900 2,500 2,300 1,800 1,900 Common costs Operating profit Net interest Other Group ,000 8,500 85,000 77,000 12,000 10, ,000 95, (17,000) (18,000) 12,000 10,500 85,000 77,000 1, ,300 8, ,000 7,700 (400) (500) 8,600 7,200 Group share of the profit before taxation of associated undertakings 950 1,000 1,450 1, ,400 2,200 Group profit before taxation 11,000 9,400 NET ASSETS Segment net assets 16,000 15,000 25,000 26,000 16,000 15,000 Unallocated assets 4,000 3,000 61,000 59,000 3,000 3,000 64,000 62,000 Group share of net assets of associated undertakings 8,500 7,000 10,500 10, ,000 17,000 Total net assets 83,000 79,000 Unallocated assets consist of assets at the Group's head office in London amounting to 2.4 million ( million) and at the Group's regional office in Hong Kong amounting to 0.6 million ( million) 16
FINANCIAL REPORTING FOR SEGMENTS
 Issued 07/89 New Zealand Society of Accountants STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE NO. 23 1989 FINANCIAL REPORTING FOR SEGMENTS Issued by the Council, New Zealand Society of Accountants CONTENTS
Issued 07/89 New Zealand Society of Accountants STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE NO. 23 1989 FINANCIAL REPORTING FOR SEGMENTS Issued by the Council, New Zealand Society of Accountants CONTENTS
STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE. First issued May 1975, Part 6 added August Revised september Contents
 Parts Contents Paragraphs Part 1 - Explanatory note 1-15 Part 2 - Definition of terms 16-25 Part 3 - Standard accounting practice 26-33 Part 4 - Note on legal requirements in Great Britain and Northern
Parts Contents Paragraphs Part 1 - Explanatory note 1-15 Part 2 - Definition of terms 16-25 Part 3 - Standard accounting practice 26-33 Part 4 - Note on legal requirements in Great Britain and Northern
ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD JULY 1998 STATEMENT STATEMENT P RELIMINARY A NNOUNCEMENTS ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD
 ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD JULY 1998 STATEMENT P RELIMINARY A NNOUNCEMENTS STATEMENT ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD P RELIMINARY A NNOUNCEMENTS This Statement is designed as a formulation and development of
ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD JULY 1998 STATEMENT P RELIMINARY A NNOUNCEMENTS STATEMENT ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD P RELIMINARY A NNOUNCEMENTS This Statement is designed as a formulation and development of
FRS 101 Reduced Disclosure Framework
 Standard Accounting and Reporting Financial Reporting Council March 2018 FRS 101 Reduced Disclosure Framework Disclosure exemptions from EU-adopted IFRS for qualifying entities The FRC's mission is to
Standard Accounting and Reporting Financial Reporting Council March 2018 FRS 101 Reduced Disclosure Framework Disclosure exemptions from EU-adopted IFRS for qualifying entities The FRC's mission is to
FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARDS
 ACCOUNTINGSTANDARDSBOARDSEPTEMBER 1994 FRS 6 CONTENTS Paragraph SUMMARY FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD 6 OBJECTIVE DEFINITIONS 2-3 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 4-39 Scope 4 Use of merger accounting
ACCOUNTINGSTANDARDSBOARDSEPTEMBER 1994 FRS 6 CONTENTS Paragraph SUMMARY FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD 6 OBJECTIVE DEFINITIONS 2-3 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 4-39 Scope 4 Use of merger accounting
FRS 102 The Financial Reporting Standard applicable in the UK and Republic of Ireland
 Standard Accounting and Reporting Financial Reporting Council March 2018 FRS 102 The Financial Reporting Standard applicable in the UK and Republic of Ireland The FRC's mission is to promote transparency
Standard Accounting and Reporting Financial Reporting Council March 2018 FRS 102 The Financial Reporting Standard applicable in the UK and Republic of Ireland The FRC's mission is to promote transparency
Operating Segments. Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 108. Core principle. Scope. Operating segments
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 108 Operating Segments (This Indian Accounting Standard includes paragraphs set in bold type and plain type, which have equal authority. Paragraphs in bold type indicate
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 108 Operating Segments (This Indian Accounting Standard includes paragraphs set in bold type and plain type, which have equal authority. Paragraphs in bold type indicate
SLAS 9. Sri Lanka Accounting Standard 9. Cash Flow Statements
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard 9 Cash Flow Statements 107 Contents Sri Lanka Accounting Standard 9 Cash Flow Statements Objective Scope Paragraphs 1-2 Benefits of Cash Flow Information 3-4 Definitions 5
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard 9 Cash Flow Statements 107 Contents Sri Lanka Accounting Standard 9 Cash Flow Statements Objective Scope Paragraphs 1-2 Benefits of Cash Flow Information 3-4 Definitions 5
Week 4 Operating Segments- IFRS 8
 Week 4 Operating Segments- IFRS 8 Learning Objectives Define the term operating segment Discuss the procedures for reportable segments in IFRS 8 Explain the disclosure procedures in IFRS 8 Scope IFRS 8
Week 4 Operating Segments- IFRS 8 Learning Objectives Define the term operating segment Discuss the procedures for reportable segments in IFRS 8 Explain the disclosure procedures in IFRS 8 Scope IFRS 8
Restatement of 2004 Results under International Financial Reporting Standards. Grafton Group plc
 Restatement of 2004 Results under International Financial Reporting Standards Grafton Group plc 6 July 2005 1 6 July 2005 RESTATEMENT OF 2004 RESULTS UNDER IFRS Grafton Group plc today announces the impact
Restatement of 2004 Results under International Financial Reporting Standards Grafton Group plc 6 July 2005 1 6 July 2005 RESTATEMENT OF 2004 RESULTS UNDER IFRS Grafton Group plc today announces the impact
NOTES TO INTERIM ACCOUNTS
 NOTES TO INTERIM ACCOUNTS 1. BASIS OF PREPARATION OF THE ACCOUNTS The unaudited consolidated interim accounts have been prepared in accordance with Hong Kong Statement of Standard Accounting Practice (
NOTES TO INTERIM ACCOUNTS 1. BASIS OF PREPARATION OF THE ACCOUNTS The unaudited consolidated interim accounts have been prepared in accordance with Hong Kong Statement of Standard Accounting Practice (
Professional Level Essentials Module, Paper P2 (IRL)
 Answers Professional Level Essentials Module, Paper P2 (IRL) Corporate Reporting (Irish) December 2011 Answers 1 (a) Traveler plc Consolidated Statement of Financial Position at 30 November 2011 Assets:
Answers Professional Level Essentials Module, Paper P2 (IRL) Corporate Reporting (Irish) December 2011 Answers 1 (a) Traveler plc Consolidated Statement of Financial Position at 30 November 2011 Assets:
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 108. Operating Segments
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 108 Operating Segments Indian Accounting Standard 108 Operating Segments Contents Paragraphs Core principle 1 Scope 2 4 Operating segments 5 10 Reportable segments
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 108 Operating Segments Indian Accounting Standard 108 Operating Segments Contents Paragraphs Core principle 1 Scope 2 4 Operating segments 5 10 Reportable segments
Report of the Auditors
 69 Report of the Auditors TO THE SHAREHOLDERS OF THE WHARF (HOLDINGS) LIMITED (INCORPORATED IN HONG KONG WITH LIMITED LIABILITY) We have audited the accounts on pages 70 to 117 which have been prepared
69 Report of the Auditors TO THE SHAREHOLDERS OF THE WHARF (HOLDINGS) LIMITED (INCORPORATED IN HONG KONG WITH LIMITED LIABILITY) We have audited the accounts on pages 70 to 117 which have been prepared
International Financial Reporting Standard 8
 International Financial Reporting Standard 8 Operating Segments In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) adopted IAS 14 Segment Reporting, which had originally been issued by the
International Financial Reporting Standard 8 Operating Segments In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) adopted IAS 14 Segment Reporting, which had originally been issued by the
Presentation of Financial Statements
 LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 1 Presentation of Financial Statements Any correspondence regarding this Standard should be addressed to: The Chairman
LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 1 Presentation of Financial Statements Any correspondence regarding this Standard should be addressed to: The Chairman
International Financial Reporting Standards Disclosure Checklist 2004
 International Financial Reporting Standards Disclosure Checklist 2004 Meeting all IFRS requirements www.pwc.com/ifrs PricewaterhouseCoopers (www.pwc.com) is the world s largest professional services organisation.
International Financial Reporting Standards Disclosure Checklist 2004 Meeting all IFRS requirements www.pwc.com/ifrs PricewaterhouseCoopers (www.pwc.com) is the world s largest professional services organisation.
Statement of Recommended Practice. Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships
 Statement of Recommended Practice Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships Effective for periods commencing on or after 1 January 2019. Early adoption is permitted for accounting periods beginning
Statement of Recommended Practice Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships Effective for periods commencing on or after 1 January 2019. Early adoption is permitted for accounting periods beginning
Appendix 1: SSAP 20*: Foreign Currency Translation
 Appendix 1: SSAP 20*: Foreign Currency Translation Contents Part 1 - Explanatory Note Part 2 - Definition of Terms Part 3 - Standard Accounting Practice Individual companies Consolidated financial statements
Appendix 1: SSAP 20*: Foreign Currency Translation Contents Part 1 - Explanatory Note Part 2 - Definition of Terms Part 3 - Standard Accounting Practice Individual companies Consolidated financial statements
STATEMENT OF AUDITING STANDARDS 600 AUDITORS' REPORTS ON FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 STATEMENT OF AUDITING STANDARDS 600 AUDITORS' REPORTS ON FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Issued August 1994; revised April 2000, June 2001; February 2004, September 2004 (name change), December 2005 and October
STATEMENT OF AUDITING STANDARDS 600 AUDITORS' REPORTS ON FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Issued August 1994; revised April 2000, June 2001; February 2004, September 2004 (name change), December 2005 and October
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS!
 NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS! 1.!"#$%&'()*+,-./ 0!"#$%&'()*+,-.$&(/0!"#$%&' ()*+,-.!"#$%&'()*+,-4546 47 2.!"#$%&!"#$%&'()&*+$%&'()!"#$%&'()&*+,-.'*+!"#$%&'!"#()$*+,-!"#$%&'()*+,-../012!"#$!%&'()*+,-./01!"#"$%&'!()*+,-./!"#$%&'(!"#$%&)*+
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS! 1.!"#$%&'()*+,-./ 0!"#$%&'()*+,-.$&(/0!"#$%&' ()*+,-.!"#$%&'()*+,-4546 47 2.!"#$%&!"#$%&'()&*+$%&'()!"#$%&'()&*+,-.'*+!"#$%&'!"#()$*+,-!"#$%&'()*+,-../012!"#$!%&'()*+,-./01!"#"$%&'!()*+,-./!"#$%&'(!"#$%&)*+
SSAP 28 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 28 PROVISIONS, CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND CONTINGENT ASSETS
 SSAP 28 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 28 PROVISIONS, CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND CONTINGENT ASSETS (Issued January 2001) The standards, which have been set in bold italic type, should be read
SSAP 28 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 28 PROVISIONS, CONTINGENT LIABILITIES AND CONTINGENT ASSETS (Issued January 2001) The standards, which have been set in bold italic type, should be read
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-SLFRS 8. Operating Segments
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-SLFRS 8 Operating Segments CONTENTS paragraphs SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD-SLFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS CORE PRINCIPLE 1 SCOPE 2 4 OPERATING SEGMENTS 5 10 REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-SLFRS 8 Operating Segments CONTENTS paragraphs SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD-SLFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS CORE PRINCIPLE 1 SCOPE 2 4 OPERATING SEGMENTS 5 10 REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
Income Taxes. International Accounting Standard 12 IAS 12. IFRS Foundation A625
 International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) adopted IAS 12 Income Taxes, which had originally been issued by the International Accounting
International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes In April 2001 the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) adopted IAS 12 Income Taxes, which had originally been issued by the International Accounting
LAAP BULLETIN 86. Componentisation of Property, Plant & Equipment under the 2010/11 IFRS-based Code JUNE 2010
 LAAP BULLETIN 86 Componentisation of Property, Plant & Equipment under the 2010/11 IFRS-based Code JUNE 2010 The Local Authority Accounting Panel issues LAAP Bulletins to assist practitioners with the
LAAP BULLETIN 86 Componentisation of Property, Plant & Equipment under the 2010/11 IFRS-based Code JUNE 2010 The Local Authority Accounting Panel issues LAAP Bulletins to assist practitioners with the
CAMBODIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS (CAS)
 CAMBODIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS (CAS) 1 - CAS 1 : Presentation of Financial Statements an Audit of Financial Statements 2 - CAS 2 : Inventories 3 - CAS 7 : Cash Flow Statements 4 - CAS 8 : Net profit or
CAMBODIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS (CAS) 1 - CAS 1 : Presentation of Financial Statements an Audit of Financial Statements 2 - CAS 2 : Inventories 3 - CAS 7 : Cash Flow Statements 4 - CAS 8 : Net profit or
SSAP 12 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 12 INCOME TAXES
 SSAP 12 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 12 INCOME TAXES (Issued August 2002) Contents Paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-11 Tax Base 7-11 RECOGNITION OF CURRENT TAX LIABILITIES AND
SSAP 12 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 12 INCOME TAXES (Issued August 2002) Contents Paragraphs OBJECTIVE SCOPE 1-4 DEFINITIONS 5-11 Tax Base 7-11 RECOGNITION OF CURRENT TAX LIABILITIES AND
Report. Review of European enforcers on the implementation of IFRS 8 Operating Segments. 9 November 2011 ESMA/2011/372
 Report Review of European enforcers on the implementation of IFRS 8 Operating Segments 9 November 2011 ESMA/2011/372 Date: 9 November 2011 ESMA/2011/372 Table of Contents I Introduction 4 II Scope of the
Report Review of European enforcers on the implementation of IFRS 8 Operating Segments 9 November 2011 ESMA/2011/372 Date: 9 November 2011 ESMA/2011/372 Table of Contents I Introduction 4 II Scope of the
This version includes amendments resulting from IFRSs issued up to 31 December 2009.
 International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes This version includes amendments resulting from IFRSs issued up to 31 December 2009. IAS 12 Income Taxes was issued by the International Accounting Standards
International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes This version includes amendments resulting from IFRSs issued up to 31 December 2009. IAS 12 Income Taxes was issued by the International Accounting Standards
FRS 102 LIMITED. Example Financial Statements For the year ended 31 December 2015
 Example Financial Statements Introduction These illustrative financial statements are an example of a group and parent company financial statements prepared for the first time in accordance with FRS 102
Example Financial Statements Introduction These illustrative financial statements are an example of a group and parent company financial statements prepared for the first time in accordance with FRS 102
PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL REPORTS
 Institute of Chartered Accountants of New Zealand FINANCIAL REPORTING NO. 2 1994 FRS-2 Issued 05/94 Revised 10/01 PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL REPORTS Issued by the Financial Reporting Standards Board Institute
Institute of Chartered Accountants of New Zealand FINANCIAL REPORTING NO. 2 1994 FRS-2 Issued 05/94 Revised 10/01 PRESENTATION OF FINANCIAL REPORTS Issued by the Financial Reporting Standards Board Institute
Illustrative results under IFRS
 Illustrative results under IFRS 2 June Bradford & Bingley plc Illustrative results under IFRS Introduction Bradford & Bingley plc ( the Group ), along with other European listed entities, is required by
Illustrative results under IFRS 2 June Bradford & Bingley plc Illustrative results under IFRS Introduction Bradford & Bingley plc ( the Group ), along with other European listed entities, is required by
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-SLFRS 8. Operating Segments
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-SLFRS 8 Operating Segments CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD-SLFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS paragraphs CORE PRINCIPLES 1 SCOPE 2 4 OPERATING SEGMENTS 5 10 REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard-SLFRS 8 Operating Segments CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD-SLFRS 8 OPERATING SEGMENTS paragraphs CORE PRINCIPLES 1 SCOPE 2 4 OPERATING SEGMENTS 5 10 REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARDS
 ACCOUNTINGSTANDARDSBOARDSEPTEMBER1994 FRS 7 CONTENTS SUMMARY Paragraph FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD 7 OBJECTIVE 1 DEFINITIONS 2-3 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 4-31 Scope 4 Determining the
ACCOUNTINGSTANDARDSBOARDSEPTEMBER1994 FRS 7 CONTENTS SUMMARY Paragraph FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD 7 OBJECTIVE 1 DEFINITIONS 2-3 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 4-31 Scope 4 Determining the
Guidance Note on Combined and Carve-Out Financial Statements
 Guidance Note on Combined and Carve-Out Financial Statements Introduction 1. Generally, consolidated financial statements of an entity are required to be presented under the relevant legal or regulatory
Guidance Note on Combined and Carve-Out Financial Statements Introduction 1. Generally, consolidated financial statements of an entity are required to be presented under the relevant legal or regulatory
International Financial Reporting Standard 8
 BV2010_IFRS08_PART A.fm Page 237 Thursday, April 1, 2010 9:37 AM International Financial Reporting Standard 8 Operating Segments was issued in November 2006 and its effective date is 1 January 2009. This
BV2010_IFRS08_PART A.fm Page 237 Thursday, April 1, 2010 9:37 AM International Financial Reporting Standard 8 Operating Segments was issued in November 2006 and its effective date is 1 January 2009. This
New Zealand Equivalent to International Financial Reporting Standard 8 Operating Segments (NZ IFRS 8)
 New Zealand Equivalent to International Financial Reporting Standard 8 Operating Segments (NZ IFRS 8) Issued December 2006 and incorporates amendments to 28 February 2014 This Standard was issued by the
New Zealand Equivalent to International Financial Reporting Standard 8 Operating Segments (NZ IFRS 8) Issued December 2006 and incorporates amendments to 28 February 2014 This Standard was issued by the
AIM Rules for Companies (clean) - AIM Notice 50. AIM Rules for Companies
 AIM Rules for Companies (clean) - AIM Notice 50. AIM Rules for Companies March 2018 1 AIM Rules for Companies Introduction 3 Part One AIM Rules 4 Retention and role of a nominated adviser 4 Applicants
AIM Rules for Companies (clean) - AIM Notice 50. AIM Rules for Companies March 2018 1 AIM Rules for Companies Introduction 3 Part One AIM Rules 4 Retention and role of a nominated adviser 4 Applicants
As previously stated, we pride ourselves on the quality of work undertaken. would invite creditors to consider the following points:
 DUFF & PHELPS LTD. PROFESSIONAL FEES - SIP 9 Our mission statement is to provide clients with an outstanding service based on technical excellence, effective problem solving and the highest level of client
DUFF & PHELPS LTD. PROFESSIONAL FEES - SIP 9 Our mission statement is to provide clients with an outstanding service based on technical excellence, effective problem solving and the highest level of client
CONSOLIDATED PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT For The Six Months Ended June 30, 2003
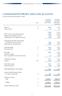 CONSOLIDATED PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT For The Six Months Ended June 30, 2003 Unaudited Unaudited Note (Restated) Turnover 2 5,463 5,576 Other net loss 3 (5) (1) 5,458 5,575 Direct costs and operating expenses
CONSOLIDATED PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT For The Six Months Ended June 30, 2003 Unaudited Unaudited Note (Restated) Turnover 2 5,463 5,576 Other net loss 3 (5) (1) 5,458 5,575 Direct costs and operating expenses
AIM Rules for Companies July AIM Notice 45
 AIM Rules for Companies July 2016 - AIM Notice 45 AIM Rules for Companies July 2016 1 AIM Rules for Companies Introduction 3 Part One AIM Rules 4 Retention and role of a nominated adviser 4 Applicants
AIM Rules for Companies July 2016 - AIM Notice 45 AIM Rules for Companies July 2016 1 AIM Rules for Companies Introduction 3 Part One AIM Rules 4 Retention and role of a nominated adviser 4 Applicants
IN THIS SECTION 128 Independent auditors report 134 Accounting policies
 127 IFRS FINANCIAL STATEMENTS IN THIS SECTION 128 Independent auditors report 134 Accounting policies CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 148 Consolidated income statement 149 Consolidated statement of comprehensive
127 IFRS FINANCIAL STATEMENTS IN THIS SECTION 128 Independent auditors report 134 Accounting policies CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 148 Consolidated income statement 149 Consolidated statement of comprehensive
Good Group (International) Limited
 EY IFRS Core Tools Good Group (International) Limited International GAAP Illustrative interim condensed consolidated financial statements for the period ended 30 June 2015 Based on International Financial
EY IFRS Core Tools Good Group (International) Limited International GAAP Illustrative interim condensed consolidated financial statements for the period ended 30 June 2015 Based on International Financial
Amendments to FRS 102 The Financial Reporting Standard applicable in the UK and Republic of Ireland
 Amendment to Standard Accounting and Reporting Financial Reporting Council July 2015 Amendments to FRS 102 The Financial Reporting Standard applicable in the UK and Republic of Ireland Small entities and
Amendment to Standard Accounting and Reporting Financial Reporting Council July 2015 Amendments to FRS 102 The Financial Reporting Standard applicable in the UK and Republic of Ireland Small entities and
Statement of Cash Flows
 HKAS 7 Revised June 2016August 2017 Hong Kong Accounting Standard 7 Statement of Cash Flows HKAS 7 COPYRIGHT Copyright 2017 Hong Kong Institute of Certified Public Accountants This Hong Kong Financial
HKAS 7 Revised June 2016August 2017 Hong Kong Accounting Standard 7 Statement of Cash Flows HKAS 7 COPYRIGHT Copyright 2017 Hong Kong Institute of Certified Public Accountants This Hong Kong Financial
LIQUIDATIONS A CREDITOR S GUIDE TO INSOLVENCY PRACTITIONERS FEES
 Guidance Note LIQUIDATIONS A CREDITOR S GUIDE TO INSOLVENCY PRACTITIONERS FEES Amended for changes introduced by The Insolvency (England and Wales) Rules 2016 6 April 2017 LIQUIDATIONS - A CREDITORS GUIDE
Guidance Note LIQUIDATIONS A CREDITOR S GUIDE TO INSOLVENCY PRACTITIONERS FEES Amended for changes introduced by The Insolvency (England and Wales) Rules 2016 6 April 2017 LIQUIDATIONS - A CREDITORS GUIDE
CONSOLIDATED PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT
 CONSOLIDATED PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT For the year ended 31 March 2004 (Restated) Note HK$ Million HK$ Million Turnover 3 7,115.9 9,868.0 Other net income/(loss) 4 17.3 (84.0) 7,133.2 9,784.0 Direct costs
CONSOLIDATED PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT For the year ended 31 March 2004 (Restated) Note HK$ Million HK$ Million Turnover 3 7,115.9 9,868.0 Other net income/(loss) 4 17.3 (84.0) 7,133.2 9,784.0 Direct costs
UK/KENYA DOUBLE TAXATION AGREEMENT SIGNED 20 JANUARY 1976 Protocol to the 1973 Agreement. Entered into force 30 September 1977
 UK/KENYA DOUBLE TAXATION AGREEMENT SIGNED 20 JANUARY 1976 Protocol to the 1973 Agreement Entered into force 30 September 1977 The text of this Agreement has been reproduced with the kind permission of
UK/KENYA DOUBLE TAXATION AGREEMENT SIGNED 20 JANUARY 1976 Protocol to the 1973 Agreement Entered into force 30 September 1977 The text of this Agreement has been reproduced with the kind permission of
Chapter 18 EQUITY SECURITIES FINANCIAL INFORMATION. Introduction
 Chapter 18 EQUITY SECURITIES FINANCIAL INFORMATION Introduction 18.01 This Chapter sets out the continuing obligations of a listed issuer with regard to the disclosure of routine financial information
Chapter 18 EQUITY SECURITIES FINANCIAL INFORMATION Introduction 18.01 This Chapter sets out the continuing obligations of a listed issuer with regard to the disclosure of routine financial information
International Standard on Auditing (UK and Ireland) 720
 Standard Audit and Assurance Financial Reporting Council October 2012 International Standard on Auditing (UK and Ireland) 720 Section A The auditor s responsibilities relating to other information in documents
Standard Audit and Assurance Financial Reporting Council October 2012 International Standard on Auditing (UK and Ireland) 720 Section A The auditor s responsibilities relating to other information in documents
The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
 International Accounting Standard 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates This version includes amendments resulting from IFRSs issued up to 31 December 2009. IAS 21 The Effects of Changes
International Accounting Standard 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates This version includes amendments resulting from IFRSs issued up to 31 December 2009. IAS 21 The Effects of Changes
Observations by the Financial Statements Review Committee 1 January December 2009
 Observations by the Financial Statements Review Committee 1 January 2009 31 December 2009 The Financial Statements Review Committee (FSRC) of the Institute reviews audited financial statements with the
Observations by the Financial Statements Review Committee 1 January 2009 31 December 2009 The Financial Statements Review Committee (FSRC) of the Institute reviews audited financial statements with the
ILLUSTRATIVE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2012 International Financial Reporting Standards
 ILLUSTRATIVE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2012 International Financial Reporting Standards A Layout (International) Group Plc Annual report and financial statements For the year ended 31
ILLUSTRATIVE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS YEAR ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2012 International Financial Reporting Standards A Layout (International) Group Plc Annual report and financial statements For the year ended 31
SSAP 33 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 33 DISCONTINUING OPERATIONS
 SSP 33 STTEMENT OF STNDRD OUNTING PRTIE 33 DISONTINUING OPERTIONS (Issued October 2001) The standards, which have been set in bold italic type, should be read in the context of the background material
SSP 33 STTEMENT OF STNDRD OUNTING PRTIE 33 DISONTINUING OPERTIONS (Issued October 2001) The standards, which have been set in bold italic type, should be read in the context of the background material
Financial statements. Contents. Financial statements. Company financial statements
 Contents 93 Directors responsibilities statement 94 Independent auditor s report 99 Consolidated income statement 100 Consolidated statement of comprehensive income/(expense) 101 Consolidated balance sheet
Contents 93 Directors responsibilities statement 94 Independent auditor s report 99 Consolidated income statement 100 Consolidated statement of comprehensive income/(expense) 101 Consolidated balance sheet
Cable & Wireless Guernsey Published Separated Regulatory Accounts. For the year ended 31 March 2012
 Cable & Wireless Guernsey Published Separated Regulatory Accounts For the year ended 31 March 2012 Contents Introduction Basis of preparation of the Published Separated Regulatory Accounts Reference Offer
Cable & Wireless Guernsey Published Separated Regulatory Accounts For the year ended 31 March 2012 Contents Introduction Basis of preparation of the Published Separated Regulatory Accounts Reference Offer
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
 5. SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED) Properties under for sale Properties under for sale are stated at the lower of cost and net realisable value. Net realisable value represents the estimated
5. SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED) Properties under for sale Properties under for sale are stated at the lower of cost and net realisable value. Net realisable value represents the estimated
!"# $%& ()* +%& &),(,#) -.&!/",
 0#% 1234561 789: 5851!"# $%& ()* +%& &),(,#) -.&!/", 07;5 22356 ;851?@A BCDEFE G BCDEF I KLMNOPQROST SU IVW XYPZTOPQN [LKKS\R ]TOR 012345678 45678 44 1851 558 458 5 16 16 ^_`abcdec g hicjkc
0#% 1234561 789: 5851!"# $%& ()* +%& &),(,#) -.&!/", 07;5 22356 ;851?@A BCDEFE G BCDEF I KLMNOPQROST SU IVW XYPZTOPQN [LKKS\R ]TOR 012345678 45678 44 1851 558 458 5 16 16 ^_`abcdec g hicjkc
Chapter 19 EQUITY SECURITIES OVERSEAS ISSUERS. Preliminary
 Chapter 19 EQUITY SECURITIES OVERSEAS ISSUERS Preliminary 19.01 The Exchange Listing Rules apply as much to overseas issuers as they do to Hong Kong issuers, subject to the additional requirements, modifications
Chapter 19 EQUITY SECURITIES OVERSEAS ISSUERS Preliminary 19.01 The Exchange Listing Rules apply as much to overseas issuers as they do to Hong Kong issuers, subject to the additional requirements, modifications
Draft Statement of Recommended Practice. Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships
 Draft Statement of Recommended Practice Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships Effective for periods commencing on or after 1 January 2015 and for any earlier periods in which an entity chooses to
Draft Statement of Recommended Practice Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships Effective for periods commencing on or after 1 January 2015 and for any earlier periods in which an entity chooses to
Draft Statement of Recommended Practice. Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships
 Draft Statement of Recommended Practice Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships Effective for periods commencing on or after 1 January 2019. Early adoption is permitted for accounting periods beginning
Draft Statement of Recommended Practice Accounting by Limited Liability Partnerships Effective for periods commencing on or after 1 January 2019. Early adoption is permitted for accounting periods beginning
Presentation of Financial Statements
 HKAS 1 (Revised) Revised JanuaryAugust 2017 Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2009 Hong Kong Accounting Standard 1 (Revised) Presentation of Financial Statements COPYRIGHT Copyright
HKAS 1 (Revised) Revised JanuaryAugust 2017 Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2009 Hong Kong Accounting Standard 1 (Revised) Presentation of Financial Statements COPYRIGHT Copyright
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21. The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates
 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates 1 2 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Contents Paragraph OBJECTIVE
Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates 1 2 Indian Accounting Standard (Ind AS) 21 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates Contents Paragraph OBJECTIVE
As Re-stated Note
 Group Income Statement For the year ended 30 April 2014 Note Revenue - continuing 2 114,188 98,537 Cost of sales - operating (84,563) (77,904) - impairment charge on inventories 3 (162) (3,539) Gross profit
Group Income Statement For the year ended 30 April 2014 Note Revenue - continuing 2 114,188 98,537 Cost of sales - operating (84,563) (77,904) - impairment charge on inventories 3 (162) (3,539) Gross profit
Statement of Recommended Practice:
 The Association of Investment Companies Statement of Recommended Practice: Financial Statements of Investment Trust Companies and Venture Capital Trusts Issued November 2014 and updated in January 2017
The Association of Investment Companies Statement of Recommended Practice: Financial Statements of Investment Trust Companies and Venture Capital Trusts Issued November 2014 and updated in January 2017
5 5BC G877?H> JKLMNOPQO S TUOVWO S XVNYO
 .!# /01/.!# /2& 3'**$!"#$ &'( )#$$'*&*!' +,$- * 5851 5 789:;;?@?A 5BC DE 012345678 45678 44 1851 8 8 458 5 56214 JKLMNOPQO S TUOVWO S XVNYO SFRS FOR SMALL ENTITIES DISCLOSURE AND
.!# /01/.!# /2& 3'**$!"#$ &'( )#$$'*&*!' +,$- * 5851 5 789:;;?@?A 5BC DE 012345678 45678 44 1851 8 8 458 5 56214 JKLMNOPQO S TUOVWO S XVNYO SFRS FOR SMALL ENTITIES DISCLOSURE AND
Module 5 Statement of Comprehensive Income and Income Statement
 IFRS for SMEs Standard (2015) + Q&As IFRS Foundation Supporting Material for the IFRS for SMEs Standard Module 5 Statement of Comprehensive Income and Income Statement IFRS Foundation Supporting Material
IFRS for SMEs Standard (2015) + Q&As IFRS Foundation Supporting Material for the IFRS for SMEs Standard Module 5 Statement of Comprehensive Income and Income Statement IFRS Foundation Supporting Material
IFRS industry insights
 IFRS Global Office September 2011 IFRS industry insights The new joint s standard insights for the real estate industry IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements may change how investors in the real estate industry account
IFRS Global Office September 2011 IFRS industry insights The new joint s standard insights for the real estate industry IFRS 11 Joint Arrangements may change how investors in the real estate industry account
Taxation of Provisions and Accruals (income tax and corporation tax)
 Taxation of Provisions and Accruals (income tax and corporation tax) Part 04-05-06 This document should be read in conjunction with sections 76A, 76B and 81 of the Taxes Consolidation Act, 1997 Document
Taxation of Provisions and Accruals (income tax and corporation tax) Part 04-05-06 This document should be read in conjunction with sections 76A, 76B and 81 of the Taxes Consolidation Act, 1997 Document
AMF recommendation Financial statements 2006
 AMF recommendation 2006-22 Financial statements 2006 Reference texts: Article 223-1 of the AMF General Regulation Pursuant to EC Regulation 1606/2002 ("IFRS 2005"), European companies with shares admitted
AMF recommendation 2006-22 Financial statements 2006 Reference texts: Article 223-1 of the AMF General Regulation Pursuant to EC Regulation 1606/2002 ("IFRS 2005"), European companies with shares admitted
A SHAREHOLDERS GUIDE TO LIQUIDATORS FEES - ENGLAND AND WALES
 A SHAREHOLDERS GUIDE TO LIQUIDATORS FEES - ENGLAND AND WALES 1. Introduction 1.1 When a company goes into liquidation the costs of the proceedings are paid out of its assets. The members (shareholders),
A SHAREHOLDERS GUIDE TO LIQUIDATORS FEES - ENGLAND AND WALES 1. Introduction 1.1 When a company goes into liquidation the costs of the proceedings are paid out of its assets. The members (shareholders),
Notes to the Financial Statements
 1. CORPORATE INFORMATION The Company was incorporated as an exempted company with limited liability in the Cayman Islands on 26 November 2003 under the Companies Law, Cap. 22 (Law 3 of 1961, as consolidated
1. CORPORATE INFORMATION The Company was incorporated as an exempted company with limited liability in the Cayman Islands on 26 November 2003 under the Companies Law, Cap. 22 (Law 3 of 1961, as consolidated
SSAP 20 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 20 RELATED PARTY DISCLOSURES
 SSAP 20 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 20 RELATED PARTY DISCLOSURES (Issued August 1997) The standards, which have been set in bold italic type, should be read in the context of the background
SSAP 20 STATEMENT OF STANDARD ACCOUNTING PRACTICE 20 RELATED PARTY DISCLOSURES (Issued August 1997) The standards, which have been set in bold italic type, should be read in the context of the background
LIQUIDATION - A MEMBERS GUIDE TO FEES IN ENGLAND AND WALES
 LIQUIDATION - A MEMBERS GUIDE TO FEES IN ENGLAND AND WALES 1 Introduction 1.1 When a Company goes into Members Voluntary Liquidation, the costs of the proceedings are paid out of its assets. A declaration
LIQUIDATION - A MEMBERS GUIDE TO FEES IN ENGLAND AND WALES 1 Introduction 1.1 When a Company goes into Members Voluntary Liquidation, the costs of the proceedings are paid out of its assets. A declaration
Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards Presentation and Disclosure Checklist 2008
 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards Presentation and Disclosure Checklist 2008 Audit Presentation and Disclosure Checklist 2008 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards Presentation and disclosure
Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards Presentation and Disclosure Checklist 2008 Audit Presentation and Disclosure Checklist 2008 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards Presentation and disclosure
PART A NOTES TO THE QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS PURSUANT TO MALAYSIAN FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD ( MFRS ) 134
 PART A NOTES TO THE QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS PURSUANT TO MALAYSIAN FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD ( MFRS ) 134 A1. BASIS OF PREPARATION The condensed consolidated interim financial statements have
PART A NOTES TO THE QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS PURSUANT TO MALAYSIAN FINANCIAL REPORTING STANDARD ( MFRS ) 134 A1. BASIS OF PREPARATION The condensed consolidated interim financial statements have
Diploma in International Financial Reporting and Auditing
 Answers Diploma in International Financial Reporting and Auditing Answers 1 (a) Consolidated Balance Sheet of Holding as at 31 March 2002 $000 $000 Assets Non-current assets Property, plant and equipment
Answers Diploma in International Financial Reporting and Auditing Answers 1 (a) Consolidated Balance Sheet of Holding as at 31 March 2002 $000 $000 Assets Non-current assets Property, plant and equipment
Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets
 LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 20 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets Any correspondence regarding this Standard should be
LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD MASB Standard 20 Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets Any correspondence regarding this Standard should be
Appendix 4B. Half yearly/preliminary final report. Preliminary final (tick)
 Appendix 4B Rules 4.1, 4.3 Introduced 3/6/22. Name of entity COMPUTERSHARE LIMITED ABN or equivalent company reference 5 485 825 Half yearly (tick) Preliminary final (tick) Half year/financial year ended
Appendix 4B Rules 4.1, 4.3 Introduced 3/6/22. Name of entity COMPUTERSHARE LIMITED ABN or equivalent company reference 5 485 825 Half yearly (tick) Preliminary final (tick) Half year/financial year ended
Notes to the Accounts
 Notes to the Accounts 1. Accounting Policies Statement of compliance The Group financial statements consolidate those of the Company and its subsidiaries (together referred to as the Group ), equity account
Notes to the Accounts 1. Accounting Policies Statement of compliance The Group financial statements consolidate those of the Company and its subsidiaries (together referred to as the Group ), equity account
A RECEIVER S RESPONSIBILITY TO PREFERENTIAL CREDITORS
 1. INTRODUCTION A RECEIVER S RESPONSIBILITY TO PREFERENTIAL CREDITORS 1.1 This statement of insolvency practice is one of a series issued by the Council of the Society with a view to harmonising the approach
1. INTRODUCTION A RECEIVER S RESPONSIBILITY TO PREFERENTIAL CREDITORS 1.1 This statement of insolvency practice is one of a series issued by the Council of the Society with a view to harmonising the approach
Sent electronically through at
 Our Ref.: C/FRSC Sent electronically through email at strategyreview-comm@ifrs.org 22 July 2011 Tom Seidenstein Chief Operating Officer IFRS Foundation 30 Cannon Street, London EC4M 6XH, United Kingdom
Our Ref.: C/FRSC Sent electronically through email at strategyreview-comm@ifrs.org 22 July 2011 Tom Seidenstein Chief Operating Officer IFRS Foundation 30 Cannon Street, London EC4M 6XH, United Kingdom
ADMINISTRATION A CREDITOR S GUIDE TO INSOLVENCY PRACTITIONER FEES
 Guidance Note ADMINISTRATION A CREDITOR S GUIDE TO INSOLVENCY PRACTITIONER FEES Amended for changes introduced by The Insolvency (England and Wales) Rules 2016 6 April 2017 ADMINISTRATION - A CREDITORS
Guidance Note ADMINISTRATION A CREDITOR S GUIDE TO INSOLVENCY PRACTITIONER FEES Amended for changes introduced by The Insolvency (England and Wales) Rules 2016 6 April 2017 ADMINISTRATION - A CREDITORS
STARBUCKS EMEA INVESTMENT LTD. Registered Number Report and Financial Statements. From the 53 week period ending 2 October 2016
 Registered Number 09332791 Report and Financial Statements From the 53 week period ending 2 October 2016 CONTENTS PAGE DIRECTORS AND OTHER INFORMATION 2 STRATEGIC REPORT 3 DIRECTORS REPORT 5 STATEMENT
Registered Number 09332791 Report and Financial Statements From the 53 week period ending 2 October 2016 CONTENTS PAGE DIRECTORS AND OTHER INFORMATION 2 STRATEGIC REPORT 3 DIRECTORS REPORT 5 STATEMENT
Regulatory Deferral Accounts
 LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD Malaysian Financial Reporting Standard 14 Regulatory Deferral Accounts Malaysian Accounting Standards Board 2014 1 This Standard
LEMBAGA PIAWAIAN PERAKAUNAN MALAYSIA MALAYSIAN ACCOUNTING STANDARDS BOARD Malaysian Financial Reporting Standard 14 Regulatory Deferral Accounts Malaysian Accounting Standards Board 2014 1 This Standard
PN (Revised) Revised April 2013; February 2016, September 2017; January 2018
 PN 810.1 (Revised) Revised April 2013; February 2016, September 2017; January 2018 Effective upon issue Practice Note 810.1 (Revised) Insurance Brokers Compliance with the Minimum Requirements Specified
PN 810.1 (Revised) Revised April 2013; February 2016, September 2017; January 2018 Effective upon issue Practice Note 810.1 (Revised) Insurance Brokers Compliance with the Minimum Requirements Specified
Hong Kong Accounting Standard 32 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation
 Hong Kong Accounting Standard 32 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation 1 Contents Hong Kong Accounting Standard 32 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation paragraphs OBJECTIVE 1-3
Hong Kong Accounting Standard 32 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation 1 Contents Hong Kong Accounting Standard 32 Financial Instruments: Disclosure and Presentation paragraphs OBJECTIVE 1-3
Separated Regulatory Accounts
 Separated Regulatory Accounts For the year ended 31 December 2014 Sure (Guernsey) Limited Contents Introduction Basis of preparation of the Separated Regulatory Accounts Reference Offer Based Costs Applicable
Separated Regulatory Accounts For the year ended 31 December 2014 Sure (Guernsey) Limited Contents Introduction Basis of preparation of the Separated Regulatory Accounts Reference Offer Based Costs Applicable
Presentation on Indian Accounting Standards
 Presentation on Indian Accounting Standards By Bharat K Shetty Associate Director Walker, Chandiok & Co 1 Agenda Ind AS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements Ind AS 2 Inventories Ind AS 3 Statement of
Presentation on Indian Accounting Standards By Bharat K Shetty Associate Director Walker, Chandiok & Co 1 Agenda Ind AS 1 Presentation of Financial Statements Ind AS 2 Inventories Ind AS 3 Statement of
Sample Financial Statements 1 For the Year Ended 31 December April 2006
 Sample Financial Statements 1 For the Year Ended 31 December 2005 12 April 2006 Directors report and financial statements For the year ended 31 December 2005 This PDF file is a Read-Only file. For a printable
Sample Financial Statements 1 For the Year Ended 31 December 2005 12 April 2006 Directors report and financial statements For the year ended 31 December 2005 This PDF file is a Read-Only file. For a printable
Statement of Cash Flows
 Sri Lanka Accounting Standard - LKAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows LKAS 7 CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD - LKAS 7 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS OBJECTIVE paragraphs SCOPE 1 BENEFITS OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION
Sri Lanka Accounting Standard - LKAS 7 Statement of Cash Flows LKAS 7 CONTENTS SRI LANKA ACCOUNTING STANDARD - LKAS 7 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS OBJECTIVE paragraphs SCOPE 1 BENEFITS OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION
Examiner s report F7 Financial Reporting June 2013
 Examiner s report F7 Financial Reporting June 2013 General Comments The overall performance of candidates on this diet was rather disappointing compared to the trend of previous recent papers. The main
Examiner s report F7 Financial Reporting June 2013 General Comments The overall performance of candidates on this diet was rather disappointing compared to the trend of previous recent papers. The main
AIM opened on 19 June It is regulated by London Stock Exchange plc.
 PLEASE NOTE this mark-up is provided for indicative purpose only. Please refer to the current AIM Rules for Companies for a definitive version. Mark-up in yellow indicates changes made since the version
PLEASE NOTE this mark-up is provided for indicative purpose only. Please refer to the current AIM Rules for Companies for a definitive version. Mark-up in yellow indicates changes made since the version
International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes. Objective. Scope. Definitions IAS 12
 International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes Objective The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting treatment for income taxes. The principal issue in accounting for income taxes
International Accounting Standard 12 Income Taxes Objective The objective of this Standard is to prescribe the accounting treatment for income taxes. The principal issue in accounting for income taxes
For the six months ended 30 June 2017
 www.pwchk.com Illustrative condensed consolidated interim For the six months ended 30 June 2017 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards PwC s Accounting Technical Publications Manual of accounting IFRS
www.pwchk.com Illustrative condensed consolidated interim For the six months ended 30 June 2017 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standards PwC s Accounting Technical Publications Manual of accounting IFRS
igaap 2005 in your pocket
 igaap 2005 in your pocket A summary of international financial reporting from a UK perspective July 2005 Contents Deloitte guidance 1 Abbreviations used in this publication 2 Current international standards
igaap 2005 in your pocket A summary of international financial reporting from a UK perspective July 2005 Contents Deloitte guidance 1 Abbreviations used in this publication 2 Current international standards
Regulatory Deferral Accounts
 HKFRS 14 Issued February 2014Revised January 2017 Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2016 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standard 14 Regulatory Deferral Accounts COPYRIGHT Copyright
HKFRS 14 Issued February 2014Revised January 2017 Effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2016 Hong Kong Financial Reporting Standard 14 Regulatory Deferral Accounts COPYRIGHT Copyright
Accounting and Reporting Policy FRS 102. Staff Education Note 13 Transition to FRS 102
 Accounting and Reporting Policy FRS 102 Staff Education Note 13 Transition to FRS 102 This Staff Education Note was updated on 8 January 2014 for minor typographical errors in the suggested reconciliations
Accounting and Reporting Policy FRS 102 Staff Education Note 13 Transition to FRS 102 This Staff Education Note was updated on 8 January 2014 for minor typographical errors in the suggested reconciliations
Notes to the Unaudited Interim Financial Statements for the six-month period ended 30 June 2010
 14 China Telecom Corporation Limited Interim Report Notes to the Unaudited Interim Financial Statements 1. Principal activities China Telecom Corporation Limited (the Company ) and its subsidiaries (hereinafter,
14 China Telecom Corporation Limited Interim Report Notes to the Unaudited Interim Financial Statements 1. Principal activities China Telecom Corporation Limited (the Company ) and its subsidiaries (hereinafter,
Good Group (International) Limited
 IFRS Core Tools Good Group (International) Limited Unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statements 30 June 2017 Contents Abbreviations and key... 2 Introduction... 3 Interim condensed consolidated
IFRS Core Tools Good Group (International) Limited Unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statements 30 June 2017 Contents Abbreviations and key... 2 Introduction... 3 Interim condensed consolidated
