Svein Gjedrem: The economic outlook for Norway
|
|
|
- Georgina Carter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Svein Gjedrem: The economic outlook for Norway Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), for Norges Bank s regional network, Region East, 19 November Please note that the text below may differ slightly from the actual presentation. The speech is based on the assessments presented at Norges Bank s press conference following the Executive Board s monetary policy meeting on 29 October and Monetary Policy Report 3/08. Financial market imbalances * * * The first signs of an emerging crisis in financial markets came into evidence in early The crisis intensified in August last year and entered a new phase in March this year when the US authorities had to bail out the investment bank Bear Stearns. What began as isolated losses in a small segment of the US housing market gradually had substantial spillover effects on the global financial system. The crisis took a new and dramatic turn when Lehman Brothers, the fourth largest US bank, filed for bankruptcy on 15 September this year. The failure contributed to a weakening of confidence between financial market participants, and many financial markets abroad, but also in Norway, almost stopped functioning. Confidence was further eroded when the crisis spread to US commercial and savings banks. Among other things, bondholders suffered losses after the largest US savings bank Washington Mutual was split up and partially acquired by JPMorgan Chase in the wake of heavy mortgage losses. On 17 September, American International Group (AIG), the largest US insurance company, had to rely on an emergency loan from the Federal Reserve. The company played a key role in the credit default insurance market. The financial crisis has heightened in several European countries. Banks in Belgium, Denmark, France, the Netherlands, the UK, Sweden and Germany have been taken over by the government or other financial institutions. In Iceland, the authorities took over the three largest banks and are now unwinding their international operations. The crisis at these banks prompted a flight from Iceland s national currency which, combined with a property market crash, has triggered a sharp recession. In Norway, the effects of the financial crisis have also occurred more rapidly and become more pronounced than the outlook seemed to imply only recently. Norway is still in a better position than most countries. Capacity utilisation in the Norwegian economy has been very high. The surplus on current account is considerable and government finances are solid. Norwegian banks have limited exposures to international securities. They have suffered only small losses and recorded solid earnings in recent years. Furthermore, the Norwegian banking system is not large relative to the size of the Norwegian economy. In response to the uncertain environment, banks abroad and at home are reluctant to lend to each other and are tightening their credit standards. Credit channels are drying up. Money market rates have increased markedly, and to levels substantially higher than central bank key rates. The fallout has been particularly pronounced in the US, but European interest rates have also risen sharply. The flow of dollars among banks has seized up at times. Other than central bank measures to supply liquidity to banking systems, the authorities in the US and Europe first approached the financial crisis as a succession of problems at individual institutions. In the US, a general package was adopted by Congress on Friday 3 October. USD 700 billion was allocated for purchasing illiquid assets from financial institutions. On 8 October, the UK government announced a number of measures to stabilise financial markets, but with emphasis on providing risk capital. Euro area countries followed suit and on 12 October agreed to take similar action. On 12 November, the strategy for the BIS Review 143/2008 1
2 US crisis package of USD 700 billion was changed to provide the authorities with the scope to inject capital into banks and other financial institutions. There is unusually high uncertainty surrounding economic developments ahead. This is reflected in equity markets among other things. Since spring, stock indices have plummeted both abroad and on the Oslo Stock Exchange. The Oslo Stock Exchange has declined by more than 50 per cent since the peak in May. On 8 October, the central banks in the US, the UK, Canada, the euro area, Switzerland and Sweden implemented coordinated interest rate cuts. The central bank of China also reduced its key rate. On 29 October, the Federal Reserve reduced its key rate by a further 0.5 percentage point. On 6 November, the European Central Bank and the Bank of England reduced their key rates by 0.5 percentage point and 1.5 percentage points, respectively. Market participants expect key rates to be reduced further among most of our trading partners. Norges Bank reduced its key policy rate by a total of 1 percentage point to 4.75 per cent. Norwegian money market rates increased markedly as a result of risk premiums abroad spilling over into the Norwegian market. The eurodollar market has been a widely used source of financing for Norwegian banks. Dollars in this market are used to procure NOK liquidity and to redistribute liquidity among banks. Banks borrow in US dollars and then swap them for NOK. The conditions in financial markets have improved somewhat recently, but access to credit is still limited and risk premiums are high. Premiums are expected to edge down in the coming quarters, but market participants believe that it will take time to restore confidence in banks. Monetary policy influences the economy through several channels, often referred to as the monetary policy transmission mechanism. The relationship between Norges Bank s key policy rate and the effects on activity and inflation has been impaired by money market conditions. The transmission mechanism is not functioning as previously. Money markets have become highly segmented. There is limited turnover and at times it is difficult for foreign operators to satisfy their need for NOK liquidity. Small Norwegian banks that previously borrowed from large banks are now turning directly to Norges Bank for loans. In this period the central bank in Norway, as in other countries, has actually become a marketplace, and the only marketplace, for banks. With a view to curbing the effects of the turbulence Norges Bank has implemented a range of measures to boost liquidity in the banking system. Norges Bank has provided loans with maturities that are longer than normal and has expanded the list of eligible bank collateral for loans. The Storting (Norwegian parliament) has adopted a package providing for an arrangement whereby banks can exchange safe, but today illiquid residential mortgagebacked bonds for highly liquid government securities. Higher money market premiums have led to higher interest rates on loans to both households and firms. As most residential mortgages in Norway are floating-rate loans, money market rates have a greater bearing on Norwegian households than households in most other European countries. Liquidity measures in Norway and other countries have resulted in some decline in premiums. Combined with a reduction in Norges Bank s key policy rate, this has prompted several banks to reduce their deposit and lending rates and to cancel previously announced increases. Interest rates have now fallen back to levels observed before the collapse of Lehman Brothers. Oil prices have fallen by more than USD 80 after peaking in July. Growth in oil demand has fallen as a result of weaker economic developments. Moreover, the fall in demand probably reflects adaptations among households and businesses in the wake of the sharp rise in oil prices up to summer. A stronger dollar, heightened uncertainty and reduced willingness and ability to take risk among financial investors in the futures market for oil may also have contributed to the fall in oil prices. 2 BIS Review 143/2008
3 Commodity prices have dropped sharply since summer. Lower metal prices reflect lower global growth prospects. It may almost seem as though that there has been a bubble in oil and commodity markets which has now burst. The fall in energy and commodity price has resulted in a weakening of Norway s terms of trade. Foreign exchange markets have also been volatile. Interest among investors has shifted away from carry trade to more liquid currencies or own currencies. Since June, low-interest currencies, such as the Japanese yen and the Swiss franc, have appreciated while highinterest currencies, such as the Australian and New Zealand dollar, have depreciated. The US dollar has appreciated from low levels. The krone exchange rate has depreciated since end-june. This partly reflects the financial market turmoil. Low risk willingness had induced investors to scale back their positions in less liquid currencies such as the Norwegian krone. The fall in the price of oil and other commodities has probably also contributed somewhat to the depreciation. The krone exchange rate is expected to appreciate gradually when financial market conditions improve. The fall in terms of trade may nevertheless imply that the krone exchange rate does not return to previous heights. A weaker krone may contribute to underpinning profitability in the export sector. Cost competitiveness in manufacturing has improved in recent quarters. Effects on output, employment and inflation The financial turbulence has weakened the outlook for investment and consumption in many regions of the world. Against the backdrop of losses and structural changes in the financial sector, many large financial institutions will for a long period ahead seek to increase their interest rate margins, reduce lending and risk. Lending standards have been tightened, particularly in the US and the UK, but also in the euro area. Output has fallen in the US, the euro area and the UK, and growth may be negative in the coming quarters. In emerging economies, the cyclical downturn has also come into growing evidence. In several countries, economic growth is being pulled down by both lower market growth in other countries and reduced access to credit. Monetary policy in Norway is oriented towards annual consumer price inflation of close to 2.5 per cent over time. In recent years, inflation has on average been somewhat lower, but fairly close to 2.5 per cent. Low and stable inflation is the most important contribution monetary policy can make to sound economic developments, providing firms and households with an anchor for inflation expectations. Norges Bank operates a flexible inflation targeting regime so that weight is given to both variability in inflation and variability in output and employment when setting interest rates. The Norwegian economy has in general exhibited solid growth since the beginning of the 1990s, although with a mild setback in 2002 and Over the past four years, the mainland economy has been in a sharp upturn, with annual growth averaging well over 4 per cent and particularly vigorous growth in Growth is now slowing markedly in the Norwegian economy. Household consumption has stagnated and house prices are falling. Growth in the Norwegian economy has slowed, while inflation has accelerated. In October, the year-on-year rise in the consumer price index (CPI) was 5.5 per cent. Electricity prices rose sharply through summer after unusually low prices last year. Underlying inflation has also picked up. Inflation adjusted for tax changes and excluding temporary changes in energy prices (CPIXE) was 3½ per cent in October. Wage growth is markedly higher and productivity growth has slowed considerably. The high rate of cost inflation has led to a faster rise in prices for domestically produced goods and services. Prices for imported consumer goods are no longer falling and are now on the rise. The slowdown in the real economy is expected to start pushing down inflation towards next BIS Review 143/2008 3
4 summer. Higher unemployment and weaker corporate profitability will probably lead to low pay increases in the wage negotiations next spring. Energy price inflation will also be considerable lower ahead. In August, the enterprises in Norges Bank s regional network noted that there had been a shift in sentiment in the Norwegian economy. An extra round of calls to some contacts in October indicated that the outlook had worsened since August. The latest reports from enterprises in Region East indicate that demand has declined since summer, with a further drop in September and October. Customers are responding to tighter lending conditions by postponing projects. The changes have occurred rapidly, and there is now considerable uncertainty among our contacts in this region with regard to developments over the next six months. The majority of the enterprises report that they will reduce investment. Many are considering workforce reductions as an alternative if the situation does not change in the New Year. The majority also envisage lower wage and price inflation ahead. In the past year, unemployment has been as low as in the mid-1980s. Seasonally adjusted registered unemployment was 1.8 per cent in October. The enterprises in Norges Bank s regional network are expecting some reduction in the workforce ahead. There has been a slight increase in layoffs. Going forward, enterprises will probably adjust the workforce to lower output growth and reduce the use of overtime. After a long period of high housing investment and rising prices, activity in the housing market is now slowing. Tighter credit conditions are amplifying the fall in house prices. Even though there are variations across regions, the trend in house prices is the same from a more moderate rise at the beginning 2007 to a clear decline at the beginning of Norges Bank s lending survey for the third quarter shows that banks are tightening credit standards for households. Banks announced further tightening ahead. Owing to growing turmoil and liquidity shortages in financial markets, banks have raised their requirements with regard to collateral and borrowers debt-servicing capacity. Growth in household credit has slowed in recent months. House price developments affect building starts, which have decreased in the past year. The decline is sharpest for residential building starts. In October, enterprises in Norges Bank s regional network indicated a very low level of housing starts in the period ahead. Order reserves for commercial buildings and holiday homes are high, however. Commercial construction is largely financed by loans, and may therefore be affected by changes in interest rate and credit conditions. Enterprises in Norges Bank s regional network report that commercial building starts have declined in recent months. Household saving has picked up. Household income accounts show that the savings ratio excluding share dividends has risen, but is still very low and negative. Household borrowing requirements have also decreased somewhat. (Household net lending has picked up slightly.) The financial market crisis has led to higher borrowing costs for banks and has kept bank lending rates at a higher level than developments in the key rate would imply. Households probably need to build up financial buffers and reduce debt, which will in turn weigh down on growth in private consumption ahead. Growth in spending on goods stalled last autumn. There has been a considerable drop in car sales in particular. Norges Bank s regional network also reports a decline in demand for goods related to moving home, such as white and brown goods and refurbishing equipment. Growth in consumption is expected to be very low for a period ahead, but growth in private consumption may pick up again towards the end of next year. Growth in mainland investment has been strong in recent years, but is now moderating. According to the national accounts, corporate investment was still on the rise in the first half of the year, but there was a considerable decline in housing investment. Falling housing starts, reduced order reserves and assessments from the enterprises in Norges Bank s 4 BIS Review 143/2008
5 regional network indicate that housing investment will continue to show a pronounced fall next year. Gross investment is expected to decline by 14 per cent on an annual basis in 2009, remain at a low level in 2010 before picking up in Even though the krone depreciation is curbing the impact, the global downturn is expected to result in lower growth in Norwegian exports. The high level of petroleum investment was an important driving force during the economic upturn, and petroleum investment is expected to remain high in the years ahead. Some investments may be postponed if oil prices fall permanently below USD per barrel, especially small investments and upgrades of fields in operation. Exploration activity may also be cut back. Large field development projects are probably being affected only to a limited extent, while small companies and smaller investment projects may be adversely affected by the reduced availability of credit. Growth in the Norwegian economy slowed markedly in the first half of this year. The effects of the financial crisis will most probably be greater than envisaged only recently. The slowdown in the Norwegian economy seems to be occurring rapidly and to be pronounced. Mainland growth is projected to be very low in 2009, then recover in 2010 and Petroleum investment will buoy up activity. The central government budget will also boost growth in public demand for goods and services. In the Monetary Policy Report, the results of monetary policy assessments are illustrated in a chart showing projections for the interest rate, inflation and capacity utilisation in the economy. We have illustrated the uncertainty surrounding our projections using fan charts. The width of the fan charts is based on historical disturbances, and therefore expresses the average that covers periods of high and low uncertainty. There is now unusually high uncertainty surrounding future developments in inflation and output and hence surrounding interest rate developments. It is difficult to determine probabilities of different outcomes of the ongoing financial crisis. In such decision-making situations it may be appropriate to implement measures that can reduce the uncertainty and stave off particularly adverse outcomes for the economy. This now implies a more active monetary policy than normal, both in interest rate setting and through liquidity policy measures. When setting the key policy rate, we must also take account of developments in premiums in money market rates, other bank funding costs and bank deposit and lending rates. Weight has been given to moving forward the reduction in the key policy rate so that lending rates for households and firms can gradually be reduced. Norwegian banks, households and some businesses have increased their borrowings considerably in recent years. It is important that the necessary deleveraging does not take place too abruptly. Lower interest rates, combined with liquidity measures, may curb the impact of the financial crisis on output and inflation. At the monetary policy meeting on 29 October, Norges Bank s Executive Board decided to reduce the key policy rate by 0.50 percentage point to 4.75 per cent. The Executive Board's assessment was that the key policy rate may lie in the interval 4-5 per cent in the period to the publication of the next Monetary Policy Report in March 2009, unless the Norwegian economy is exposed to new major shocks. Thank you for your attention! BIS Review 143/2008 5
6 6 BIS Review 143/2008
7 BIS Review 143/2008 7
8 8 BIS Review 143/2008
9 BIS Review 143/2008 9
10 10 BIS Review 143/2008
11 BIS Review 143/
12 12 BIS Review 143/2008
13 BIS Review 143/
14 14 BIS Review 143/2008
15 BIS Review 143/
16 16 BIS Review 143/2008
17 BIS Review 143/
18 18 BIS Review 143/2008
19 BIS Review 143/
20 20 BIS Review 143/2008
21 BIS Review 143/
22 22 BIS Review 143/2008
Jan F Qvigstad: Outlook for the Norwegian economy
 Jan F Qvigstad: Outlook for the Norwegian economy Address by Mr Jan F Qvigstad, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at Sparebank 1 Fredrikstad, 4 November 2009. The text below may
Jan F Qvigstad: Outlook for the Norwegian economy Address by Mr Jan F Qvigstad, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at Sparebank 1 Fredrikstad, 4 November 2009. The text below may
Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy
 Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy Introductory statement by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the hearing before the Standing Committee on Finance and Economic
Svein Gjedrem: The conduct of monetary policy Introductory statement by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the hearing before the Standing Committee on Finance and Economic
Svein Gjedrem: Interest rates, the exchange rate and the outlook for the Norwegian economy
 Svein Gjedrem: Interest rates, the exchange rate and the outlook for the Norwegian economy Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Mid-Norway Chamber of Commerce
Svein Gjedrem: Interest rates, the exchange rate and the outlook for the Norwegian economy Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Mid-Norway Chamber of Commerce
Svein Gjedrem: The outlook for the Norwegian economy
 Svein Gjedrem: The outlook for the Norwegian economy Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Bergen Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Bergen, 11 April 2007.
Svein Gjedrem: The outlook for the Norwegian economy Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Bergen Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Bergen, 11 April 2007.
Jarle Bergo: Monetary policy and the cyclical situation
 Jarle Bergo: Monetary policy and the cyclical situation Speech by Mr Jarle Bergo, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at a meeting with local authorities and the business community,
Jarle Bergo: Monetary policy and the cyclical situation Speech by Mr Jarle Bergo, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at a meeting with local authorities and the business community,
Svein Gjedrem: Interest rate developments
 Svein Gjedrem: Interest rate developments Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the annual conference hosted by the Norwegian Federation of State Employees Unions,
Svein Gjedrem: Interest rate developments Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the annual conference hosted by the Norwegian Federation of State Employees Unions,
Svein Gjedrem: The outlook for the Norwegian economy and monetary policy assessments
 Svein Gjedrem: The outlook for the Norwegian economy and monetary policy assessments Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at a presentation of the Monetary Policy
Svein Gjedrem: The outlook for the Norwegian economy and monetary policy assessments Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at a presentation of the Monetary Policy
Svein Gjedrem: On business cycles, monetary policy and property markets
 Svein Gjedrem: On business cycles, monetary policy and property markets Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Næringseiendom conference, Bergen, 12 May 2006.
Svein Gjedrem: On business cycles, monetary policy and property markets Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Næringseiendom conference, Bergen, 12 May 2006.
Svein Gjedrem: The economic outlook in Norway
 Svein Gjedrem: The economic outlook in Norway Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Norges Bank, Oslo, 22 March 2007.
Svein Gjedrem: The economic outlook in Norway Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Norges Bank, Oslo, 22 March 2007.
Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and aspects of economic developments
 Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and aspects of economic developments Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of the Central Bank of Norway, Ålesund, 12 October 2005. Please note that the text below may differ
Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and aspects of economic developments Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of the Central Bank of Norway, Ålesund, 12 October 2005. Please note that the text below may differ
New information since the October 2011 Monetary Policy Report (3/11) 1
 Meeting 14 March 2012 New information since the October 2011 Monetary Policy Report (3/11) 1 International economy According to preliminary figures, GDP for Norway s main trading partners fell by 0.2 percent
Meeting 14 March 2012 New information since the October 2011 Monetary Policy Report (3/11) 1 International economy According to preliminary figures, GDP for Norway s main trading partners fell by 0.2 percent
Øystein Olsen: The economic outlook
 Øystein Olsen: The economic outlook Address by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Oslo, 29 March 2011. The address is based
Øystein Olsen: The economic outlook Address by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Oslo, 29 March 2011. The address is based
Jarle Bergo: The economic outlook
 Jarle Bergo: The economic outlook Address by Mr Jarle Bergo, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Norges Bank, Oslo, 31 March 2005. The address
Jarle Bergo: The economic outlook Address by Mr Jarle Bergo, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Norges Bank, Oslo, 31 March 2005. The address
Jarle Bergo: The economic situation, global uncertainty and monetary policy
 Jarle Bergo: The economic situation, global uncertainty and monetary policy Speech by Mr Jarle Bergo, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Annual General Meeting of ACI Norge
Jarle Bergo: The economic situation, global uncertainty and monetary policy Speech by Mr Jarle Bergo, Deputy Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Annual General Meeting of ACI Norge
Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and the outlook for the Norwegian economy
 Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and the outlook for the Norwegian economy Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Mid-Norway Chamber of Commerce and Industry,
Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and the outlook for the Norwegian economy Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Mid-Norway Chamber of Commerce and Industry,
Evaluation of Norges Bank's projections for 2004
 Evaluation of Norges Bank's projections for 2004 Per Espen Lilleås, economist in the Economics Department 1 The assessments of capacity utilisation in the Norwegian economy in 2004, measured by estimates
Evaluation of Norges Bank's projections for 2004 Per Espen Lilleås, economist in the Economics Department 1 The assessments of capacity utilisation in the Norwegian economy in 2004, measured by estimates
Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and the labour market
 Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and the labour market Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the conference to mark the 10th anniversary of the Federation of Norwegian
Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy and the labour market Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the conference to mark the 10th anniversary of the Federation of Norwegian
Norwegian economy. Economic trends Economic Survey 3/2001
 Economic trends Economic Survey 3/2001 Norwegian economy The fear of a demand-driven increase in inflation has so far induced Norges Bank to maintain high interest rates. Changes in figures from the quarterly
Economic trends Economic Survey 3/2001 Norwegian economy The fear of a demand-driven increase in inflation has so far induced Norges Bank to maintain high interest rates. Changes in figures from the quarterly
Svein Gjedrem: The krone exchange rate and competitiveness in the business sector
 Svein Gjedrem: The krone exchange rate and competitiveness in the business sector Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Federation of Norwegian Process Industries,
Svein Gjedrem: The krone exchange rate and competitiveness in the business sector Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Federation of Norwegian Process Industries,
December. Monetary Policy Report. with financial stability assessment
 December Monetary Policy Report with financial stability assessment Norges Bank Oslo Address: Bankplassen Postal address: Postboks 79 Sentrum, 7 Oslo Phone: +7 Fax: +7 E-mail: central.bank@norges-bank.no
December Monetary Policy Report with financial stability assessment Norges Bank Oslo Address: Bankplassen Postal address: Postboks 79 Sentrum, 7 Oslo Phone: +7 Fax: +7 E-mail: central.bank@norges-bank.no
Svein Gjedrem: The central bank s instruments
 Svein Gjedrem: The central bank s instruments Lecture by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of the Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Centre for Monetary Economics (CME)/BI Norwegian School of Management,
Svein Gjedrem: The central bank s instruments Lecture by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of the Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Centre for Monetary Economics (CME)/BI Norwegian School of Management,
Jean-Pierre Roth: Recent economic and financial developments in Switzerland
 Jean-Pierre Roth: Recent economic and financial developments in Switzerland Introductory remarks by Mr Jean-Pierre Roth, Chairman of the Governing Board of the Swiss National Bank and Chairman of the Board
Jean-Pierre Roth: Recent economic and financial developments in Switzerland Introductory remarks by Mr Jean-Pierre Roth, Chairman of the Governing Board of the Swiss National Bank and Chairman of the Board
MONETARY POLICY REPORT WITH FINANCIAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT
 7 DECEMBER MONETARY POLICY REPORT WITH FINANCIAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT Norges Bank Oslo 7 Address: Bankplassen Postal address: Postboks 79 Sentrum, 7 Oslo Phone: +7 Fax: +7 E-mail: central.bank@norges-bank.no
7 DECEMBER MONETARY POLICY REPORT WITH FINANCIAL STABILITY ASSESSMENT Norges Bank Oslo 7 Address: Bankplassen Postal address: Postboks 79 Sentrum, 7 Oslo Phone: +7 Fax: +7 E-mail: central.bank@norges-bank.no
Monetary Policy Report October
 Monetary Policy Report October Reports from the Central Bank of Norway No. / Monetary Policy Report / Norges Bank Oslo Address: Bankplassen Postal address: Postboks 9 Sentrum, Oslo Phone: + Fax: + E-mail:
Monetary Policy Report October Reports from the Central Bank of Norway No. / Monetary Policy Report / Norges Bank Oslo Address: Bankplassen Postal address: Postboks 9 Sentrum, Oslo Phone: + Fax: + E-mail:
Monetary policy assessment of 12 March 2009 Swiss National Bank takes decisive action to forcefully relax monetary conditions
 Communications P.O. Box, CH-8022 Zurich Telephone +41 44 631 31 11 Fax +41 44 631 39 10 Zurich, 12 March 2009 Monetary policy assessment of 12 March 2009 Swiss National Bank takes decisive action to forcefully
Communications P.O. Box, CH-8022 Zurich Telephone +41 44 631 31 11 Fax +41 44 631 39 10 Zurich, 12 March 2009 Monetary policy assessment of 12 March 2009 Swiss National Bank takes decisive action to forcefully
Svein Gjedrem: Housing finance in Norway
 Svein Gjedrem: Housing finance in Norway Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Norwegian Covered Bond Forum, Oslo, 27 January 2010. The text below may differ
Svein Gjedrem: Housing finance in Norway Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Norwegian Covered Bond Forum, Oslo, 27 January 2010. The text below may differ
Economic Survey 2/2013. Norwegian economy. Economic trends
 Economic trends Economic growth among Norway s trading partners remains very low. Growth in the euro area is at a complete standstill, and unemployment is generally very high and rising. Growth in the
Economic trends Economic growth among Norway s trading partners remains very low. Growth in the euro area is at a complete standstill, and unemployment is generally very high and rising. Growth in the
Macroeconomic and financial market developments. February 2014
 Macroeconomic and financial market developments February 2014 Background material to the abridged minutes of the Monetary Council meeting 18 February 2014 Article 3 (1) of the MNB Act (Act CXXXIX of 2013
Macroeconomic and financial market developments February 2014 Background material to the abridged minutes of the Monetary Council meeting 18 February 2014 Article 3 (1) of the MNB Act (Act CXXXIX of 2013
Svein Gjedrem: Inflation targeting in an oil economy
 Svein Gjedrem: Inflation targeting in an oil economy Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at Sparebanken Møre, Ålesund, 4 June 2002. Please note that the text
Svein Gjedrem: Inflation targeting in an oil economy Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at Sparebanken Møre, Ålesund, 4 June 2002. Please note that the text
Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy in an open economy
 Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy in an open economy Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Confederation of Higher Education Unions, Kongsberg, 13 November 2002.
Svein Gjedrem: Monetary policy in an open economy Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Confederation of Higher Education Unions, Kongsberg, 13 November 2002.
Indonesia: Changing patterns of financial intermediation and their implications for central bank policy
 Indonesia: Changing patterns of financial intermediation and their implications for central bank policy Perry Warjiyo 1 Abstract As a bank-based economy, global factors affect financial intermediation
Indonesia: Changing patterns of financial intermediation and their implications for central bank policy Perry Warjiyo 1 Abstract As a bank-based economy, global factors affect financial intermediation
Corporate and Household Sectors in Austria: Subdued Growth of Indebtedness
 Corporate and Household Sectors in Austria: Subdued Growth of Indebtedness Stabilization of Corporate Sector Risk Indicators The Austrian Economy Slows Down Against the background of the renewed recession
Corporate and Household Sectors in Austria: Subdued Growth of Indebtedness Stabilization of Corporate Sector Risk Indicators The Austrian Economy Slows Down Against the background of the renewed recession
Summary and Economic Outlook
 Pentti Vartia Managing director Pasi Sorjonen Head of forecasting group 1.1 Summary The world economy started to recover rapidly at the start of the year. Despite this rebound in activity, near-term growth
Pentti Vartia Managing director Pasi Sorjonen Head of forecasting group 1.1 Summary The world economy started to recover rapidly at the start of the year. Despite this rebound in activity, near-term growth
Economic Activity Report
 Economic Activity Report FOR THE SCANDINAVIAN COUNTRIES October 2007 New developments since June highlights Some unrest in the financial markets, but it will pass International economy In the spring and
Economic Activity Report FOR THE SCANDINAVIAN COUNTRIES October 2007 New developments since June highlights Some unrest in the financial markets, but it will pass International economy In the spring and
BANK OF FINLAND ARTICLES ON THE ECONOMY
 BANK OF FINLAND ARTICLES ON THE ECONOMY Table of Contents Global economy to grow steadily 3 FORECAST FOR THE GLOBAL ECONOMY Global economy to grow steadily TODAY 1:00 PM BANK OF FINLAND BULLETIN 1/2017
BANK OF FINLAND ARTICLES ON THE ECONOMY Table of Contents Global economy to grow steadily 3 FORECAST FOR THE GLOBAL ECONOMY Global economy to grow steadily TODAY 1:00 PM BANK OF FINLAND BULLETIN 1/2017
Øystein Olsen: How does the key policy rate operate?
 Øystein Olsen: How does the key policy rate operate? Speech by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Centre for Monetary Economics (CME), BI Norwegian Business School,
Øystein Olsen: How does the key policy rate operate? Speech by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Centre for Monetary Economics (CME), BI Norwegian Business School,
Svein Gjedrem: Management of the Government Pension Fund Global
 Svein Gjedrem: Management of the Government Pension Fund Global Introductory statement by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the hearing before the Standing Committee
Svein Gjedrem: Management of the Government Pension Fund Global Introductory statement by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the hearing before the Standing Committee
Monetary Policy Update December 2007
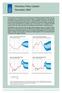 Monetary Policy Update December 7 At its meeting on 8 December, the Executive Board of the Riksbank decided to hold the repo rate unchanged at per cent. During the first half of 8 it is expected that the
Monetary Policy Update December 7 At its meeting on 8 December, the Executive Board of the Riksbank decided to hold the repo rate unchanged at per cent. During the first half of 8 it is expected that the
Antonio Fazio: Overview of global economic and financial developments in first half 2004
 Antonio Fazio: Overview of global economic and financial developments in first half 2004 Address by Mr Antonio Fazio, Governor of the Bank of Italy, to the ACRI (Association of Italian Savings Banks),
Antonio Fazio: Overview of global economic and financial developments in first half 2004 Address by Mr Antonio Fazio, Governor of the Bank of Italy, to the ACRI (Association of Italian Savings Banks),
Øystein Olsen: The purpose and scope of monetary policy
 Øystein Olsen: The purpose and scope of monetary policy Speech by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Centre for Monetary Economics (CME) / BI Norwegian Business
Øystein Olsen: The purpose and scope of monetary policy Speech by Mr Øystein Olsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the Centre for Monetary Economics (CME) / BI Norwegian Business
Svein Gjedrem: From oil and gas to financial assets Norway s Government Pension Fund Global
 Svein Gjedrem: From oil and gas to financial assets Norway s Government Pension Fund Global Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the conference Commodities,
Svein Gjedrem: From oil and gas to financial assets Norway s Government Pension Fund Global Speech by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the conference Commodities,
Svein Gjedrem: The role of the Central Bank
 Svein Gjedrem: The role of the Central Bank Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Fafo Institute for Labour and Social Research and the Norwegian Power and
Svein Gjedrem: The role of the Central Bank Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to the Fafo Institute for Labour and Social Research and the Norwegian Power and
BOFIT Forecast for Russia
 BOFIT Forecast for Russia 24.9.2015 BOFIT Russia Team BOFIT Forecast for Russia 2015 2017 Bank of Finland BOFIT Institute for Economies in Transition Bank of Finland BOFIT Institute for Economies in Transition
BOFIT Forecast for Russia 24.9.2015 BOFIT Russia Team BOFIT Forecast for Russia 2015 2017 Bank of Finland BOFIT Institute for Economies in Transition Bank of Finland BOFIT Institute for Economies in Transition
Svein Gjedrem: Economic perspectives
 Svein Gjedrem: Economic perspectives Annual address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the meeting of the Supervisory Council of Norges Bank, Oslo, February * * *
Svein Gjedrem: Economic perspectives Annual address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the meeting of the Supervisory Council of Norges Bank, Oslo, February * * *
Svein Gjedrem: The economic outlook
 Svein Gjedrem: The economic outlook Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Norges Bank, Oslo, 8 April 2010. * * * The
Svein Gjedrem: The economic outlook Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), to invited foreign embassy representatives, Norges Bank, Oslo, 8 April 2010. * * * The
Editor: Felix Ewert. The Week Ahead Key Events 2 8 Oct, 2017
 Editor: Felix Ewert The Week Ahead Key Events 2 8 Oct, 2017 Monday 2, 08.30 SWE: PMI Manufacturing (Sep) Index SEB Cons. Prev. PMI 60.5 -- 54.7 Manufacturing PMI showed an unexpectedly large fall in August.
Editor: Felix Ewert The Week Ahead Key Events 2 8 Oct, 2017 Monday 2, 08.30 SWE: PMI Manufacturing (Sep) Index SEB Cons. Prev. PMI 60.5 -- 54.7 Manufacturing PMI showed an unexpectedly large fall in August.
Lars Heikensten: The Swedish economy and monetary policy
 Lars Heikensten: The Swedish economy and monetary policy Speech by Mr Lars Heikensten, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at a seminar arranged by the Stockholm Chamber of Commerce and Veckans Affärer,
Lars Heikensten: The Swedish economy and monetary policy Speech by Mr Lars Heikensten, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at a seminar arranged by the Stockholm Chamber of Commerce and Veckans Affärer,
OVERVIEW. The EU recovery is firming. Table 1: Overview - the winter 2014 forecast Real GDP. Unemployment rate. Inflation. Winter 2014 Winter 2014
 OVERVIEW The EU recovery is firming Europe's economic recovery, which began in the second quarter of 2013, is expected to continue spreading across countries and gaining strength while at the same time
OVERVIEW The EU recovery is firming Europe's economic recovery, which began in the second quarter of 2013, is expected to continue spreading across countries and gaining strength while at the same time
An interim assessment
 What is the economic outlook for OECD countries? An interim assessment Paris, 8 September 2011 11h00 Paris time Pier Carlo Padoan OECD Chief Economist and Deputy Secretary-General Activity has come close
What is the economic outlook for OECD countries? An interim assessment Paris, 8 September 2011 11h00 Paris time Pier Carlo Padoan OECD Chief Economist and Deputy Secretary-General Activity has come close
Economic Survey. Economic developments in Norway Forecasts
 Economic Survey Economic developments in Norway Forecasts 2017-2020 3/2017 Economic Survey 3/2017 Norwegian economy Economic developments in Norway After being in a cyclical downturn for almost three
Economic Survey Economic developments in Norway Forecasts 2017-2020 3/2017 Economic Survey 3/2017 Norwegian economy Economic developments in Norway After being in a cyclical downturn for almost three
Macroeconomic and financial market developments. March 2014
 Macroeconomic and financial market developments March 2014 Background material to the abridged minutes of the Monetary Council meeting 25 March 2014 Article 3 (1) of the MNB Act (Act CXXXIX of 2013 on
Macroeconomic and financial market developments March 2014 Background material to the abridged minutes of the Monetary Council meeting 25 March 2014 Article 3 (1) of the MNB Act (Act CXXXIX of 2013 on
NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA. Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report May Dr Jorgovanka Tabaković, Governor
 NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report May Dr Jorgovanka Tabaković, Governor Belgrade, May Ladies and gentlemen, representatives of the press, dear colleagues, Welcome
NATIONAL BANK OF SERBIA Speech at the presentation of the Inflation Report May Dr Jorgovanka Tabaković, Governor Belgrade, May Ladies and gentlemen, representatives of the press, dear colleagues, Welcome
Svein Gjedrem: Economic perspectives
 Svein Gjedrem: Economic perspectives Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the meeting of the Supervisory Council of Norges Bank, Oslo, 17 February 2005. The
Svein Gjedrem: Economic perspectives Address by Mr Svein Gjedrem, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), at the meeting of the Supervisory Council of Norges Bank, Oslo, 17 February 2005. The
Table 1.1. A comparison between the present forecast and the previous forecast in selected areas.
 English summary 1. Short term forecast Since the beginning of 1 the international economy has experienced relatively low growth rates. This downturn in economic growth has been followed by a substantial
English summary 1. Short term forecast Since the beginning of 1 the international economy has experienced relatively low growth rates. This downturn in economic growth has been followed by a substantial
QUARTERLY REPORT FOURTH QUARTER 1998
 MAIN FEATURES The EU currencies appreciated by 5% against the US dollar but fell by 10.5% against the Japanese yen. These currency movements contributed to a small gain (about 1%) in the Union s average
MAIN FEATURES The EU currencies appreciated by 5% against the US dollar but fell by 10.5% against the Japanese yen. These currency movements contributed to a small gain (about 1%) in the Union s average
Economic Survey December 2006 English Summary
 Economic Survey December English Summary. Short term outlook Reaching an annualized growth rate of.5 per cent in the first half of, GDP growth in Denmark has turned out considerably stronger than expected
Economic Survey December English Summary. Short term outlook Reaching an annualized growth rate of.5 per cent in the first half of, GDP growth in Denmark has turned out considerably stronger than expected
THE IMPACT OF THE FINANCIAL CRISIS ON THE INTERNATIONAL COMMERCE
 Scientific Bulletin Economic Sciences, Vol. 8 (14) THE IMPACT OF THE FINANCIAL CRISIS ON THE INTERNATIONAL COMMERCE Professor PhD Ion CIUREA Assistant professor Cornelia MIU University of Pitesti, University
Scientific Bulletin Economic Sciences, Vol. 8 (14) THE IMPACT OF THE FINANCIAL CRISIS ON THE INTERNATIONAL COMMERCE Professor PhD Ion CIUREA Assistant professor Cornelia MIU University of Pitesti, University
5. Bulgarian National Bank Forecast of Key
 5. Bulgarian National Bank Forecast of Key Macroeconomic Indicators for 2018 2020 This issue of Economic Review includes the of key macroeconomic indicators for the 2018 2020 period. It is based on information
5. Bulgarian National Bank Forecast of Key Macroeconomic Indicators for 2018 2020 This issue of Economic Review includes the of key macroeconomic indicators for the 2018 2020 period. It is based on information
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2017)
 Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2017) October 31, 2017 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue expanding on the back of highly accommodative financial
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (October 2017) October 31, 2017 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue expanding on the back of highly accommodative financial
Balance-Sheet Adjustments and the Global Economy
 November 16, 2009 Bank of Japan Balance-Sheet Adjustments and the Global Economy Speech at the Paris EUROPLACE Financial Forum in Tokyo Masaaki Shirakawa Governor of the Bank of Japan Introduction Thank
November 16, 2009 Bank of Japan Balance-Sheet Adjustments and the Global Economy Speech at the Paris EUROPLACE Financial Forum in Tokyo Masaaki Shirakawa Governor of the Bank of Japan Introduction Thank
MINUTES OF THE MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE MEETING 4 AND 5 NOVEMBER 2009
 Publication date: 18 November 2009 MINUTES OF THE MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE MEETING 4 AND 5 NOVEMBER 2009 These are the minutes of the Monetary Policy Committee meeting held on 4 and 5 November 2009. They
Publication date: 18 November 2009 MINUTES OF THE MONETARY POLICY COMMITTEE MEETING 4 AND 5 NOVEMBER 2009 These are the minutes of the Monetary Policy Committee meeting held on 4 and 5 November 2009. They
Joseph S Tracy: A strategy for the 2011 economic recovery
 Joseph S Tracy: A strategy for the 2011 economic recovery Remarks by Mr Joseph S Tracy, Executive Vice President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, at Dominican College, Orangeburg, New York, 28
Joseph S Tracy: A strategy for the 2011 economic recovery Remarks by Mr Joseph S Tracy, Executive Vice President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, at Dominican College, Orangeburg, New York, 28
Finland falling further behind euro area growth
 BANK OF FINLAND FORECAST Finland falling further behind euro area growth 30 JUN 2015 2:00 PM BANK OF FINLAND BULLETIN 3/2015 ECONOMIC OUTLOOK Economic growth in Finland has been slow for a prolonged period,
BANK OF FINLAND FORECAST Finland falling further behind euro area growth 30 JUN 2015 2:00 PM BANK OF FINLAND BULLETIN 3/2015 ECONOMIC OUTLOOK Economic growth in Finland has been slow for a prolonged period,
Monetary Policy Report 1/12. Charts
 Monetary Policy Report / Charts Chart. Projected output gap¹) for Norway's trading partners. Percent. Q Q - - - - MPR / MPR / - - - - - 8 ) The output gap measures the percentage deviation between GDP
Monetary Policy Report / Charts Chart. Projected output gap¹) for Norway's trading partners. Percent. Q Q - - - - MPR / MPR / - - - - - 8 ) The output gap measures the percentage deviation between GDP
Economic Survey. Economic developments in Norway Forecasts
 Economic Survey Economic developments in Norway Forecasts 2015-2018 4/2015 Economic Survey 4/2015 Norwegian economy Economic trends The cyclical downturn in Norway has now lasted for over a year, primarily
Economic Survey Economic developments in Norway Forecasts 2015-2018 4/2015 Economic Survey 4/2015 Norwegian economy Economic trends The cyclical downturn in Norway has now lasted for over a year, primarily
Financial Stability 2
 Reports from the Central Bank of Norway No. 6/3 Financial Stability 3 N o v e m b e r Financial Stability is published twice a year and this report and the Inflation Report together comprise Norges Bank
Reports from the Central Bank of Norway No. 6/3 Financial Stability 3 N o v e m b e r Financial Stability is published twice a year and this report and the Inflation Report together comprise Norges Bank
Egil Matsen: The equity share in the Government Pension Fund Global
 Egil Matsen: The equity share in the Government Pension Fund Global Introductory statement by Mr Egil Matsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), Oslo, 1 December 2016. Accompanying slides
Egil Matsen: The equity share in the Government Pension Fund Global Introductory statement by Mr Egil Matsen, Governor of Norges Bank (Central Bank of Norway), Oslo, 1 December 2016. Accompanying slides
Svante Öberg: The economic situation
 Svante Öberg: The economic situation Speech by Mr Svante Öberg, First Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, to the Västerbotten Chamber of Commerce, Umeå, 5 August. * * * My message today can be summarised
Svante Öberg: The economic situation Speech by Mr Svante Öberg, First Deputy Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, to the Västerbotten Chamber of Commerce, Umeå, 5 August. * * * My message today can be summarised
Postponed recovery. The advanced economies posted a sluggish growth in CONJONCTURE IN FRANCE OCTOBER 2014 INSEE CONJONCTURE
 INSEE CONJONCTURE CONJONCTURE IN FRANCE OCTOBER 2014 Postponed recovery The advanced economies posted a sluggish growth in Q2. While GDP rebounded in the United States and remained dynamic in the United
INSEE CONJONCTURE CONJONCTURE IN FRANCE OCTOBER 2014 Postponed recovery The advanced economies posted a sluggish growth in Q2. While GDP rebounded in the United States and remained dynamic in the United
December 2018 Eurosystem staff macroeconomic projections for the euro area 1
 December 2018 Eurosystem staff macroeconomic projections for the euro area 1 Real GDP growth weakened unexpectedly in the third quarter of 2018, partly reflecting temporary production bottlenecks experienced
December 2018 Eurosystem staff macroeconomic projections for the euro area 1 Real GDP growth weakened unexpectedly in the third quarter of 2018, partly reflecting temporary production bottlenecks experienced
Minutes of the Monetary Policy Council decision-making meeting held on 6 July 2016
 Minutes of the Monetary Policy Council decision-making meeting held on 6 July 2016 At the meeting, members of the Monetary Policy Council discussed monetary policy against the background of macroeconomic
Minutes of the Monetary Policy Council decision-making meeting held on 6 July 2016 At the meeting, members of the Monetary Policy Council discussed monetary policy against the background of macroeconomic
The Riksbank s Company Interviews
 The Riksbank s Company Interviews DECEMBER 2008 JANUARY 2009 2 the riksbank s company interviews n The Riksbank s company interviews December 2008 January 2009 Ongoing decline in economic activity and
The Riksbank s Company Interviews DECEMBER 2008 JANUARY 2009 2 the riksbank s company interviews n The Riksbank s company interviews December 2008 January 2009 Ongoing decline in economic activity and
LESS DYNAMIC GROWTH AMID HIGH UNCERTAINTY
 OVERVIEW: The European economy has moved into lower gear amid still robust domestic fundamentals. GDP growth is set to continue at a slower pace. LESS DYNAMIC GROWTH AMID HIGH UNCERTAINTY Interrelated
OVERVIEW: The European economy has moved into lower gear amid still robust domestic fundamentals. GDP growth is set to continue at a slower pace. LESS DYNAMIC GROWTH AMID HIGH UNCERTAINTY Interrelated
Executive Board meeting. 31 October 2012
 Executive Board meeting October % % 7% 9% Baseline scenarios with fan charts in MPR / Percent 7-9 9 MPR / MPR / 7 - - - - Output gap 9 CPIXE 9 - - - Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Key policy
Executive Board meeting October % % 7% 9% Baseline scenarios with fan charts in MPR / Percent 7-9 9 MPR / MPR / 7 - - - - Output gap 9 CPIXE 9 - - - Sources: Statistics Norway and Norges Bank Key policy
NBIM Quarterly Performance Report Second quarter 2007
 NBIM Quarterly Performance Report Second quarter 2007 Government Pension Fund Global Norges Bank s foreign exchange reserves Investment portfolio Buffer portfolio Government Petroleum Insurance Fund Norges
NBIM Quarterly Performance Report Second quarter 2007 Government Pension Fund Global Norges Bank s foreign exchange reserves Investment portfolio Buffer portfolio Government Petroleum Insurance Fund Norges
World Economic outlook
 Frontier s Strategy Note: 01/23/2014 World Economic outlook IMF has just released the World Economic Update on the 21st January 2015 and we are displaying the main points here. Even with the sharp oil
Frontier s Strategy Note: 01/23/2014 World Economic outlook IMF has just released the World Economic Update on the 21st January 2015 and we are displaying the main points here. Even with the sharp oil
Monetary Policy Report 1/09
 .. Monetary Policy Report / Governor Svein Gjedrem London, March Norwegian banks equity capital ) Per cent of total assets. - Sources: Klovland (), Statistics Norway and Norges Bank ) Includes savings
.. Monetary Policy Report / Governor Svein Gjedrem London, March Norwegian banks equity capital ) Per cent of total assets. - Sources: Klovland (), Statistics Norway and Norges Bank ) Includes savings
1 World Economy. Value of Finnish Forest Industry Exports Fell by Almost a Quarter in 2009
 1 World Economy The recovery in the world economy that began during 2009 has started to slow since spring 2010 as stocks are replenished and government stimulus packages are gradually brought to an end.
1 World Economy The recovery in the world economy that began during 2009 has started to slow since spring 2010 as stocks are replenished and government stimulus packages are gradually brought to an end.
Minutes of the Monetary Policy Council decision-making meeting held on 2 September 2015
 Minutes of the Monetary Policy Council decision-making meeting held on 2 September 2015 Members of the Monetary Policy Council discussed monetary policy against the background of the current and expected
Minutes of the Monetary Policy Council decision-making meeting held on 2 September 2015 Members of the Monetary Policy Council discussed monetary policy against the background of the current and expected
Christopher Kent: Financial conditions and the Australian dollar - recent developments
 Christopher Kent: Financial conditions and the Australian dollar - recent developments Address by Mr Christopher Kent, Assistant Governor (Financial Markets) of the Reserve Bank of Australia, to the XE
Christopher Kent: Financial conditions and the Australian dollar - recent developments Address by Mr Christopher Kent, Assistant Governor (Financial Markets) of the Reserve Bank of Australia, to the XE
Perspectives on the U.S. Economy
 Perspectives on the U.S. Economy Presentation for Irish Institute Seminar, April 14, 2008 Bob Murphy Department of Economics Boston College Three Perspectives 1. Historical Overview of U.S. Economic Performance
Perspectives on the U.S. Economy Presentation for Irish Institute Seminar, April 14, 2008 Bob Murphy Department of Economics Boston College Three Perspectives 1. Historical Overview of U.S. Economic Performance
Monetary Policy Report April 2018
 Monetary Policy Report April 18 Monetary Policy Report The Riksbank s Monetary Policy Report is published six times a year. The report describes the deliberations made by the Riksbank when deciding what
Monetary Policy Report April 18 Monetary Policy Report The Riksbank s Monetary Policy Report is published six times a year. The report describes the deliberations made by the Riksbank when deciding what
Lars Heikensten: Monetary policy and the economic situation
 Lars Heikensten: Monetary policy and the economic situation Speech by Mr Lars Heikensten, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Handelsbanken, Karlstad, 26 January 2004. * * * It is nice to meet a group
Lars Heikensten: Monetary policy and the economic situation Speech by Mr Lars Heikensten, Governor of the Sveriges Riksbank, at Handelsbanken, Karlstad, 26 January 2004. * * * It is nice to meet a group
The international environment
 The international environment This article (1) discusses developments in the global economy since the August 1999 Quarterly Bulletin. Domestic demand growth remained strong in the United States, and with
The international environment This article (1) discusses developments in the global economy since the August 1999 Quarterly Bulletin. Domestic demand growth remained strong in the United States, and with
Economic outlook. Address by Central Bank Governor Svein Gjedrem to invited foreign embassy representatives. Norges Bank 18 March 2004
 Economic outlook Address by Central Bank Governor Svein Gjedrem to invited foreign embassy representatives Norges Bank 1 March SG Diplomat 1.. Long-term interest rates Per cent 15 1 9 Norway US Germany
Economic outlook Address by Central Bank Governor Svein Gjedrem to invited foreign embassy representatives Norges Bank 1 March SG Diplomat 1.. Long-term interest rates Per cent 15 1 9 Norway US Germany
Ryuzo Miyao: Economic activity and prices in Japan and monetary policy
 Ryuzo Miyao: Economic activity and prices in Japan and monetary policy Summary of a speech by Mr Ryuzo Miyao, Member of the Policy Board of the Bank of Japan, at a meeting with business leaders, Tokushima,
Ryuzo Miyao: Economic activity and prices in Japan and monetary policy Summary of a speech by Mr Ryuzo Miyao, Member of the Policy Board of the Bank of Japan, at a meeting with business leaders, Tokushima,
The reasons why inflation has moved away from the target and the outlook for inflation.
 BANK OF ENGLAND Mark Carney Governor The Rt Hon George Osborne Chancellor of the Exchequer HM Treasury 1 Horse Guards Road London SW1A2HQ 12 May 2016 On 12 April, the Office for National Statistics (ONS)
BANK OF ENGLAND Mark Carney Governor The Rt Hon George Osborne Chancellor of the Exchequer HM Treasury 1 Horse Guards Road London SW1A2HQ 12 May 2016 On 12 April, the Office for National Statistics (ONS)
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Global Economic Environment
 The global economy grew strongly in the first half of 2007, although turbulence in financial markets has clouded prospects. While the 2007 forecast has been little affected, the baseline projection for
The global economy grew strongly in the first half of 2007, although turbulence in financial markets has clouded prospects. While the 2007 forecast has been little affected, the baseline projection for
Economic Survey. Economic developments in Norway Forecasts
 Economic Survey Economic developments in Norway Forecasts 08-0 /08 Contents Economic developments in Norway... Contractionary fiscal policy in 08 neutral going forward... 5 The interest rate will be raised
Economic Survey Economic developments in Norway Forecasts 08-0 /08 Contents Economic developments in Norway... Contractionary fiscal policy in 08 neutral going forward... 5 The interest rate will be raised
TREASURY AND FEDERAL RESERVE FOREIGN EXCHANGE OPERATIONS
 TREASURY AND FEDERAL RESERVE FOREIGN EXCHANGE OPERATIONS April-June During the second quarter of, the dollar depreciated 7.3 percent against the Japanese yen but gained 4.2 percent against the German mark.
TREASURY AND FEDERAL RESERVE FOREIGN EXCHANGE OPERATIONS April-June During the second quarter of, the dollar depreciated 7.3 percent against the Japanese yen but gained 4.2 percent against the German mark.
Consumer Instalment Credit Expansion
 Consumer Instalment Credit Expansion EXPANSION OF instalment credit reached a high in the summer of 1959, and then moderated in the fourth quarter. In early 1960 expansion increased, but at a slower rate
Consumer Instalment Credit Expansion EXPANSION OF instalment credit reached a high in the summer of 1959, and then moderated in the fourth quarter. In early 1960 expansion increased, but at a slower rate
ECONOMIC OUTLOOK No.80
 ECONOMIC OUTLOOK No.8 Press Conference Paris, 8th November h Jean-Philippe Cotis Chief Economist For a video link to the press conference and related material : www.oecd.org/oecdeconomicoutlook Summary
ECONOMIC OUTLOOK No.8 Press Conference Paris, 8th November h Jean-Philippe Cotis Chief Economist For a video link to the press conference and related material : www.oecd.org/oecdeconomicoutlook Summary
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2010)
 April 30, 2010 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2010) The Bank's View 1 The global economy has emerged from the sharp deterioration triggered by the financial crisis and has
April 30, 2010 Bank of Japan Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (April 2010) The Bank's View 1 The global economy has emerged from the sharp deterioration triggered by the financial crisis and has
Global Update. 6 th October, Global Prospects. Contacts: Madan Sabnavis Chief Economist
 Global Update Global Prospects 6 th October, 2010 Contacts: Madan Sabnavis Chief Economist 91-022-6754 3489 Samruddha Paradkar Associate Economist 91-022-6754 3407 Krithika Subramanian Associate Economist
Global Update Global Prospects 6 th October, 2010 Contacts: Madan Sabnavis Chief Economist 91-022-6754 3489 Samruddha Paradkar Associate Economist 91-022-6754 3407 Krithika Subramanian Associate Economist
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2018)
 Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2018) January 23, 2018 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue expanding on the back of highly accommodative financial
Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (January 2018) January 23, 2018 Bank of Japan The Bank's View 1 Summary Japan's economy is likely to continue expanding on the back of highly accommodative financial
1. Inflation target policy how does it work?
 Mr. Heikensten discusses recent economic and monetary policy developments in Sweden Speech by the Deputy Governor of the Bank of Sweden, Mr. Lars Heikensten, at the Local Authorities Economics Seminar
Mr. Heikensten discusses recent economic and monetary policy developments in Sweden Speech by the Deputy Governor of the Bank of Sweden, Mr. Lars Heikensten, at the Local Authorities Economics Seminar
Gertrude Tumpel-Gugerell: The financial crisis looking back and the way forward
 Gertrude Tumpel-Gugerell: The financial crisis looking back and the way forward Speech by Ms Gertrude Tumpel-Gugerell, Member of the Executive Board of the European Central Bank, at the conference Rien
Gertrude Tumpel-Gugerell: The financial crisis looking back and the way forward Speech by Ms Gertrude Tumpel-Gugerell, Member of the Executive Board of the European Central Bank, at the conference Rien
Economic Survey August 2006 English Summary
 Economic Survey August English Summary. Short term outlook In several respects, the upswing in the Danish economy is stronger than expected in the May survey: private sector employment has increased strongly,
Economic Survey August English Summary. Short term outlook In several respects, the upswing in the Danish economy is stronger than expected in the May survey: private sector employment has increased strongly,
Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review
 Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review August 14 th, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist Capital Markets Division, Economics Department 1 Please see disclaimer on the last page of this report Key Issues Global
Global Macroeconomic Monthly Review August 14 th, 2018 Arie Tal, Research Economist Capital Markets Division, Economics Department 1 Please see disclaimer on the last page of this report Key Issues Global
World Payments Stresses in
 World Payments Stresses in 1956-57 INTERNATIONAL TRANSACTIONS in the year ending June 1957 resulted in net transfers of gold and dollars from foreign countries to the United States. In the four preceding
World Payments Stresses in 1956-57 INTERNATIONAL TRANSACTIONS in the year ending June 1957 resulted in net transfers of gold and dollars from foreign countries to the United States. In the four preceding
