|
|
|
- Barnaby Mitchell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 of 5 Article : Social Health Insurance Development Social Health Insurance Development as an Integral Part of the National Health Policy: Recent Reform in the Indonesian Health Insurance System Adang Setiana ** Deputy Coordination for Social Welfare, Coordinating Ministry for People's Welfare the Republic of Indonesia, Jakarta, deputi1@menkokesra.go.id Abstract The concept of Social Health Insurance (SHI) has the potential to achieve universal coverage to ensure that every body will get access to medical care he/she needs. In line with the Indonesian National Health Policy that has put the rights to health care in the Constitution amended in 2002, recently the Indonesian government has reformed the National Social Security Law that also provides the foundation for a National Health Insurance Program (NHIP) is enacted on October 19 th, The concept of social health insurance has been poorly understood in Indonesia. Most people understand social health insurance as program for the poor. This misunderstanding has caused difficulties in introducing Social Health Insurance in Indonesia; even though a social health insurance program for the government employees has been implemented since 1968, and a social health insurance program for private employees since Several International organisations, such as GTZ, European Union, ILO, and WHO provided technical assistance to expand health insurance through social security reform. The new Cabinet chaired by President Susilo Bambang Yudoyono has a strong commitment to provide access to health care for every body, a policy that is in line with the concept of social health insurance. As a start, the Ministry of Health has insured about 60 million of the poorest Indonesians by paying their contributions to Askes, the insurance scheme for civil servants. The paper will discuss the existing implementation of SHI in Indonesia, the expansion of coverage to 60 million poorest Indonesians, and the political process and economic feasibility for expansion of social health insurance coverage for 220 million people. A qualitative analysis will be presented on political process, conflict of interests, oppositions, and prolonged debates on the expansion of coverage as a National Health Policy. Short-term evaluation of the existing policy will also be discussed. Introduction Indonesia is a country located between Asia and Australia comprising more than 17,000 islands spread over about 5,000 Km length and 3,500 Km width crossing the equator line. More than half of the population are living below 1.6 a day, the standard poverty line defined by the World Bank. Successful family planning programs implemented in the last thirty years, have controlled population growth, and Indonesia has now an annual population growth rate of 1.3 %. However, due to low education level, the unemployment rate remains high, and the wage level is low. The GDP per capita in 2005 was at 850 (= US$ 1,050). Actually, Indonesia had achieved a GDP per capita of more than US$ 1,200 in But the exchange and financial crisis of 1997 that hit Asia decreased the Indonesian economy followed by political crises resulting in a sharp fall of the country's GDP and economic competitiveness. Currently, the political and economic stability are improved significantly. Although, some smallscaled political unrest occurred in areas, the political commitment of the current government to improve Indonesia's stability in politic, economy and investment conditions, as well as the people's welfare, has been gaining trust from the international community. At the same time, social security, including social health insurance scheme has received significant commitment. Traditionally, to provide health services, Indonesia provides public health centres, sub-health centres (both stationary and mobile) and public hospitals. User fees are determined by local governments using fee for service payment system. This user fees hinder access to severe health problems where expensive and multiple medical procedures are needed. In addition, people perceive that the services in public health care providers are in poor quality. The better off who demand higher quality services may visit private clinics of the same doctors, who work in the centre, in the afternoon and pay much higher fees. One important factor for equitable access to primary health services is the proximity to the population. The Indonesian health policy mandates local government to build one health centre for every 30,000 inhabitants, and one sub-health centre for every 10,000 inhabitants. A public health centre has a staff of at least one physician (general practitioner), several nurses and midwives, other health related personnel and administrative staff. A sub-health centre has at least one nurse or a midwife plus few administrative staff to provide very basic health services to the community. There are currently more than 7,000 health centres and more than 21,000 sub-health centres throughout Indonesia (MoH, 2001). In addition, there are about 50,000 doctors who offer private medical services in their offices with various degrees of charges. It has to be pointed out that there is no regulation on private medical fees in Indonesia. Public hospitals, providing secondary and tertiary care, consist of four types: (1) small district hospitals (less than 50 beds with four specialists: internist, obstetric-gynaecologist, surgeon, and paediatrician) provide basic secondary care at district level, (2) municipality hospitals ( beds with more than four specialties) deliver secondary and tertiary care for a larger district, (3) provincial hospital ( beds with a variety of specialists) providing more specialised referral care at provincial level, and (4) regional and national hospitals (up to 1,500 beds) designed to provide top (national) referral care. Users of public hospitals are charged according to the number and type of services received (regulated and subsidised fees-for-service system in public facilities). User charges at health centres and third-class rooms of public hospitals cover about % of the unit costs, depending on the type of facility. Currently Indonesia has about 700 public hospitals across the country, and in addition there are about 600 private hospitals owned by various organisations and companies. The growing numbers of privately owned and foreign investor hospitals are competing to sell higher quality services to the richest quintile of the population. Until recently, there has been great inequity in access across income groups, even in public hospital services, and not to mention in private hospitals. Additional problems such as geographical (distance) and cultural (education and beliefs) barriers remain significant factors for low access to hospital services. A study by Thabrany (2005) indicates that in 2001 the richest 10 % of the population consumed more than 400 hospital days per 1,000 people, and members of Askes and Jamsostek (insured) had more than 500 and thus more than the non-insured. On the other hand, hospital days incurred less than 100 per 1,000 people for the poorest 10 % of the population and the uninsured. Physicians working at health centres and public hospitals are public servants receiving low basic salaries. To supplement their income, every medical staff working with the government is allowed to work in private clinics after office hours. Nurses and midwives are officially not given this kind of privileges; however in practice they also have private practices (especially in small towns or districts). The charges in private clinics run by the same physicians working in public facilities in the morning are 3 to 10 times higher than the public sector fees. Social Health Insurance Systems before Reform Social-Economic Survey of 2004 indicated that 20.6 % of the 220 million Indonesians are covered by any kind of health insurance. About seven percent of the population were covered by Askes
2 Page 2 of 5 (civil-servant social health insurance scheme), the most comprehensive scheme in the country. Currently there are many health insurance schemes, including Askes, social health insurance for private employees (Jamsostek), community health insurance, private commercial health insurance, and employer-covered health insurance. The benefits of those insurance schemes are not comparable one to another, and one should not assume that the 20.6 % of the population covered by health insurance are completely free from financial risks once they are suffer from a severe or catastrophic illness. The legal bases for the Askes scheme are the Government Regulations No 69/1991, No 6/1992, and No 28/2003. The scheme covers about 13.8 million beneficiaries comprising about 4.5 million affiliated employees and 9.3 million dependents. All civil servants and civil service pensioners, personnel of the armed forces, and veterans are mandated to contribute 2 % of their basic salary monthly, regardless of their marital status. In the past, the government, as employer did not contribute. Starting in 2004, the government started to contribute 0.25 % to match the 2% employee contribution. The government contribution is to be increased annually by 0.25% of employee salary to reach the matching of 2% (fifty-fifty contribution) by Regardless of an employee's wage level, all beneficiaries are entitled to a comprehensive health benefits considered medically necessary. With regard to non-medical services, however, benefits are differentiated in two different levels. Highest rank civil servants are entitled to first class rooms and boards in public hospital, while the low and middle range employees and their dependents have access to second class rooms only. All other health benefits, deemed medically necessary, are not discriminated by ranks. The Askes scheme is covering benefits delivered in contracted provider network consisting mainly of public health centres and public hospitals. Services rendered out side the network are not covered. Contracted providers are paid prospectively by capitation, per case or per diem. The Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Internal Affairs determine the level of provider payment in order to ensure Askes' financial solvency. Besides social health insurance for government employees, private employees are covered under Jamsostek scheme. The legal bases for Jamsostek are the Social Security Law No 3/1992 and the Government Regulation No 14/1993. All employers having 10 or more employees are obliged to insure their employees through Jamsostek. However, the Law prescribes that (1) the employers that prefer better health benefits may opt out from the scheme; (2) only employers are mandated to pay contribution of 3 % (for singles) and 6 % (for married employees) of the wages; (3) the scheme set a wage ceiling that has not been changed since 1993 at one million Rupiah (equivalent to 80 ) salary per month, freezing revenues for SHI contributions while costs of medical care continue to rise; (4) the benefits are provided to employees and family members up to a maximum of three children; (5) some expensive medical procedures such as cancer treatment and haemodialysis are not covered fully; and (6) coverage terminated when employees are retired or loss their jobs. The membership has grown very slowly from 199,000 members in 1991 to 2.74 million people (1.26 million employees) in the year Due to opt out option, only a small number of employers, mostly small and medium size, are enrolling their employees to Jamsostek while larger employers opted out of Jamsostek to buy private health insurance or provide their other types of health benefits. By 2005 Jamsostek covers less than 5 % of eligible employees. On the other hand, 19.8 million employees were enrolled in the other three Jamsostek programs (occupational accident scheme, death benefit scheme, and provident fund scheme) since the beginning of the implementation of Jamsostek Law, but only about 8 million members were actively paying contribution in 2004 (Jamsostek 2005). Even if all employees were enrolled, it was still relatively small number of workers was covered by social security scheme as a national labour survey in the year 2000 estimated that there were number of 56.2 million workers in Indonesia (ILO 2000). Data from commercial insurance companies showed that total membership of the private health insurance market in 1999 was only about 4 million people (Djaelani 2002). In addition to the two SHI schemes (Askes and Jamsostek), about 2 million people are insured by the military health services system covering all armed forces, civil servants of the Ministry of Defence, and their families. The New National Agenda of Askeskin: The Most Expansive Initiative After the monetary crisis that hit Indonesia severely in 1997, a series of political, economic, and social reforms have been undertaken in Indonesia. Decentralisation of authority to local governments to run various public services, including health care and health financing, has been the main focus of the reform. The Indonesian Constitution has been amended three times between 1999 and 2002 that had never before occurred during the first 55 years after the country's independence. One of the most important political measures was the reform of social security including health insurance. The constitutional amendment of 2002 obliged the government to establish social security for all citizens. This amendment was followed by the issuance of a law on the National Social Security System ( Sistem Jaminan Sosial Nasional - SJSN) at October 19, The National Social Security System Law mandates employers, including the government, to provide social health insurance (SHI) through Askes or Jamsostek. In addition, for the first time this law mandates the government formally to pay contributions to the SJSN for the low income population to enable them to earn income. Once they work and earn income above the poverty line, they are mandated to contribute for health benefits. One day after the law was enacted; the new cabinet headed by President Susilo Bambang Yudoyono came into power. In the General Five Year Plan, the new cabinet put high priority to improve access to the Indonesian health care system. The new cabinet is willing to relieve the financial burden of the low income groups to meet their health care needs. The initial new agenda was provision of free hospital services in third class room and board in public hospitals then was formulated in line with the stipulation of the SJSN law. The Ministry of Health then designated Askes to administer the initiative and paid contribution on behalf of the poor to Askes. This concept is in line with which all people are mandated to contribute. The only difference is that while the poor has not adequate income (temporarily) to contribute, the government subsidize contribution. Although the detailed regulation of the SJSN law on how and how much the government should contribute is still being formulated, the Ministry of Health has taken a bold initiative to start health insurance for the low income under the name of Askeskin. Since 2005, the new initiative (Askeskin) has extended health insurance coverage to an additional of 60 million people (27 % of the population). Askeskin: The Health Insurance Program for Low Income People In early 2005, the Bureau of Census identified that Indonesia had about 36 million poor people measured by the national poverty line. Before 2005, to compensate increasing prices and cost of living due to increased of oil prices, the government had provided the poor with a health card that entitled the holders to free health care in public health facilities. The fund for the compensation program was distributed directly to public health centres and public hospitals according to the number of the poor individuals within the catchment's area of each facility. The distribution of fund was similar with the concept of capitation payment. Health centres provided primary health care, maternal and child health services, and childbirth; while public hospitals provided outpatient and inpatient care. The evaluation of this program showed many access and equity problems. In one hand utilisation of health services was low while utilisation of public hospitals was much higher than expected. However, the fund allocated to a health facility could not be transferred to other facilities resulting in inequity across facilities and populations. As a pilot project, Askes had initiated a program to provide health care for the poor to which local government contribute monthly on per capita basis in the Musi Banyuasin district in South Sumatra. The program started in 2002 when Askes was contracted by the Musi Banyuasin
3 Page 3 of 5 government to cover 20,000 poor individuals, mostly in remote areas. The district government paid a monthly contribution of Rp. 5,000 per person (equivalent to 0.40 per capita, but this amount was adequate to cover already heavily subsidized user charges in public health facilities). In 2003, the number of poor covered by this program was expanded to 167,000 people (about one-third of the district population) at the same level of contribution. Based on this experience, the Ministry of Health then initiated the extension of the scheme at the national level. This initiative is in accordance with the SJSN law that prescribes mandatory government contribution to insure the poor through a designated social security implementing agency (known as Badan Penyelenggara Jaminan Sosial, BPJS literally means Social Security Corporation, of the law of SJSN). In November 2004, the Ministry of Health discussed with Askes to administer the scheme planned to start in January The official designation of Askes was issued by the Ministerial Decree No of the Minister of Health in December At the beginning, the number of poor covered was 36,146,700 individuals and the monthly contribution was fixed at Rp 5,000 (0.40 ) per capita. In January 2005, the program was started and all basic principles of SJSN were implemented. The fund has been managed by Askes on a not-for-profit basis to cover comprehensive health services equivalent to the health benefits for the government employees. The only different with the government employee's scheme is that for inpatient care, the poor entitle to be confined only in a third class public hospital ward. The program was implemented nationwide in order to ensure portability of health care benefits all over the country. This is very important because the availability and the range of services across districts vary widely. The portability principle ensures the poor to obtain tertiary care in public hospitals across districts or provinces. Six months after the implementation the number of people covered has been increased to 60 million people to accommodate those who are nearly poor who cannot afford to pay the health care needs. The delivery of health benefits has been changed slightly to adjust with previous health card schemes. However, at the beginning of 2006, the whole program resumed to the original concept of covering comprehensive benefits through Askes. Table 2 : Description of Askeskin Program in 2005 and 2006 Scheme Description First Semester 2005 and in 2006 Health insurance, government pays contribution for the poor for comprehensive services to Askes Number of beneficiaries Poor population: 36,146,700 persons Appointment to Askes Budget To cover comprehensive health care Rp. 1 Trillion (80 million ) in the first semester of 2005 Rp 3.7 Trillion (about 300 million Euros) Second Semester 2005 Direct provision of primary care in public health centres. Health insurance scheme cover inpatient only, in third class ward of public hospitals and participated private hospitals The poor and nearly poor: about 60,000,000 persons Outpatient referral and inpatient hospital care Rp trillion (110 million ) Registration of the poor Based on census data collected by the Central Statistics Agency in December 2004, there 36,146,700 poor people to be insured by the Ministry of Health by paying contribution (premium) of Rp 5,000 per person per month. Those data tell the MoH the number of poor people in each district but did not identify names and address of those people. The district government then identified the persons to be insured and sent the names and address to Askes to be issued Askeskin card with which the holders are eligible for comprehensive health benefits. In practice, the identification of beneficiaries was made by the head of a village often with the support of midwives, village's women organisations, and health centres. At the beginning, it was not easy for district government to select the number of poor as allocated by the MoH. Some districts had already similar programs or other poverty alleviation programs with the number of poor (using the district poverty line) resulting in much higher number of poor. The difference in the number of poor between what was insured by the MoH and the number of the poor identified by district sparked protests by the poor and NGOs in some districts to the MoH. Later, the number of poor insured by the MoH via Askes then was increased to 60 million to accommodate the difference. Benefits and Procedures Benefits for the Askeskin program comprise of various levels of health care. Primary health care is provided at health centres, sub-health centres, and midwife services in smaller villages. To be eligible to receive benefits of secondary care provided in district hospitals, a referral from a primary health care provider is required. In case of emergency, however, a patient may visit a public hospital without referral from health centre. Accordingly, a district hospital can refer a patient to a provincial hospital in case of there is insufficient medical equipment or a specialists and the patients need tertiary care. Birth delivery services are provided by accredited midwives at village level or by general practicing physicians working in health centres, hospitals or clinics. Because there are more than 13,000 drug names, drugs are covered only if doctors prescribed drugs listed on the formulary developed by Askes, known in Indonesia as DPHO ( Daftar Plafon Harga Obat, literally means List of Drugs and Prices for Askes members). Finally, the Askes scheme covers also other medical supplies, deemed medically necessary. Due to geographic difficulties in providing basic maternal and child health, other than requiring a freshly graduated general practitioner providing mandatory services in health centres, a midwife is appointed to provide primary maternity care (antenatal care and delivery) in a village. By assigning a midwife in each village to provide services at the village level, access to maternity care was made easier. In addition, the midwife can also provide treatment for simple medical problems and deliver very basic drugs for first aid such as anti-diarrhoea or pain killers or when no physician is available. The midwife is working under the supervision of a physician in health centres. Problems and Constraints The Askeskin is the largest expansion of insuring 60 million people in about a year. Certainly, in the fields there were many technical problems identified. The first difficulty was to identify poor households among the poor and near poor who were eligible for receiving financial assistance in the form of paying contribution for a SHI scheme. Before the Askeskin was implemented, local governments were provided with seed money to create some kind of medical aids where local governments match the fund and create local systems. Overall, local governments claimed that they already covered more than 54 million people (however, the benefits were not comprehensive and varied across districts) whereas the Askeskin started with only 34 million people. Of course, even with much less comprehensive benefits, people who were covered before and then were not eligible for Askeskin would be very disappointed and felt discriminated. This problem was finally overcome by adding MoH commitment to cover up to 60 million people in the second semester of 2005.
4 Page 4 of 5 To avoid misused of Askeskin it was first designed to attach each Askeskin card with a photo of each beneficiary. This ambitious work, putting photo of each individual of more than 36 million people within six months, had caused serious administrative difficulties in taking photo, sticking appropriate photo with name and address of each person, and distributing the card was a nightmare. Finally it was decided distribute the card without photo and to cover all people who claim they are unable to pay user charges as long as they are willing to be confined in a third class room ward in public hospitals, even if they had no Askeskin card. Thus, this decision eliminates administrative problems in identifying each individual eligible for the government program and then if a person actually poor, a card was issued for him/her and the family members. Due to very large country of Indonesia (it spans over about 5,000 Km from East to West and 1,500 Km from North to South), many hospitals and even health centres in small districts are geographically difficult to reach. Covering health care only, though it relieves financial burden to get health care, it does not solve health problems of the poor. Transportation, often an air plane is needed in remote areas, to health facilities hinder the sick to receive treatments provided through Askeskiin. As the MoH budget remains insufficient to cover transportation costs, local governments were urged to support the program by providing transportation costs or by bringing mobiles clinics, including personnel and medical supplies, to remote areas. The Progress Regardless of geographical, technical, and administrative problems, the Askeskin program has brought a reasonable relieve for low income groups to meet their health care needs. The registration of the indigent people has been completed and the cards have been distributed to eligible individuals. The claim data submitted by health care providers indicate evidence that the distribution of cards has been effective, health care providers understood their function, and the poor used their entitlements of health care. At the first semester of 2006, 2.9 million hospital outpatient referral visits and inpatient care have been claimed to Askes (Marisi, 2006). Data of 2005 indicated that about 15 % of the beneficiaries utilized health care in public health centres and hospitals. The following tables shows the total utilisation numbers (Table 3), the corresponding claim expenditures (Table 4), and the epidemiological profile of enrolees (Table 5) (Sutadji, 2006). Table 3 : Reported Health Care Utilisation for the Askeskin Program by September 2005 Description Utilization Ratios to Insured Total visits 50,517, Referral visits 4,051, Secondary health care visits 3,277, Number of admissions 429, Number of haemodialysis cases 437 Table 4 : Distribution of Health Care Costs Incurred (Claimed) for Expensive Medical Procedures, in Indonesian Currency (Rp) as of September 2005 No Medical Procedures Costs incurred (Rp) 1 Heart surgery 3,134,600,000 2 Haemodialysis 643,264,255 3 Cardiac catheterisation 580,000,000 4 Caesarean section 458,831,000 5 Congenital diseases 172,000,000 6 Craniotomy 142,064,000 7 Explorative laparoscopy 119,817,000 8 Radical mastectomy 64,755,000 9 Appendectomy 53,349, Hysterectomy 15,650,000 Total 5,384,330,979 Table 5 : Distribution of Ten-Most Reported Diagnoses among Askesin Beneficiaries Reported by Health Care Providers as of September 2005 N o Conclusion Diagnosis Number of Cases % 1 Unidentified cause of fever 90, Acute diarrhoea 39, Upper respiratory tract infections 37, Typhoid and paratyphoid fever 25, Birth problems/complicated delivery 20, Tuberculosis 11, Dyspepsia 10, Injuries 10, Dengue hemorrhagic fever 8, Bronchial asthma 7, Total 261, Coverage by social health insurance is dominated by formal sector employees and beneficiaries of government subsidized contribution (Askeskin). Among formal sector employments, coverage is limited to all civil servants, military personnel, police personnel, veterans, and less than 5 % of employees of the private sector. In 2005, the government underpinned its strong commitment to increase access to health care by paying social health insurance contributions for the poor as prescribed by the SJSN Law of This program is known as Askeskin is the largest expansion of health insurance in the Indonesian history, may be in the World. Within two years, the Askeskin program covers about 60 million low income people across Indonesia and improves access to health care significantly. This program is expected to accelerate the reduction of maternal and
5 Page 5 of 5 infant mortality to speed up attainment of Millennium Development Goals. References Central Bureau of Census. Indonesian Profile of Jakarta, BPS, 2005 Djaelani. F ( 2002 ). Development of Health Insurance Products in Indonesia. Paper presented at the Asia-Pacific Summit on Health Insurance, Jakarta, May 22-24, 2002 International Labour Office ( 2005 ). Labour Survey of Indonesia. Jakarta, 2000 Jamsostek. Paper presented in SHI seminar. October Jakarta. Marisi U (2006). Askeskin: Concept and the Progress. Paper presented on Workshop on Askeskin for Women Organizations. Cisarua, September 6, 2006 Ministry of Health (MoH) (2001). Health Profile Pusdakes MOH, Jakarta. Sutadji, OA (2006). Progress Report of the Askeskin Program. National Planning Workshop on Health. Medan, March 2006 Thabrany, H (2005). The 36 Years Experience of Health Insurance in Indonesia. Paper presented in IHEA Conference, Barcelona, July 10-13, RESUME: Adang Setiana Date of Birth : 8 July 1953 Education : Ph.D. in Environmental Biology, The University of Manchester, UK (1991) Position : Deputy Coordination for Social Welfare, Coordinating Ministry for People's Welfare, The Republic of Indonesia Scope of Coordination : Implementation of National Social Protection System. Empowerment for Disable and Ageing Persons. Social Assistance in Emergency Response. Address : Jalan Merdeka Barat No.3 Jakarta Pusat Indonesia.
Health Insurance for Poor People in the Province Of Santa Fe, Argentina: The Power of the Clear Model for All
 ARGENTINA Health Insurance for Poor People in the Province Of Santa Fe, Argentina: The Power of the Clear Model for All FAMEDIC and Ministry of Health of Santa Fe. SUMMARY In Argentina, the system is characterized
ARGENTINA Health Insurance for Poor People in the Province Of Santa Fe, Argentina: The Power of the Clear Model for All FAMEDIC and Ministry of Health of Santa Fe. SUMMARY In Argentina, the system is characterized
Increasing equity in health service access and financing: Health strategy, policy achievements and new challenges
 Increasing equity in health service access and financing: Health strategy, policy achievements and new challenges Policy Note Cambodia Health Systems in Transition A WPR/2016/DHS/009 World Health Organization
Increasing equity in health service access and financing: Health strategy, policy achievements and new challenges Policy Note Cambodia Health Systems in Transition A WPR/2016/DHS/009 World Health Organization
The New Mandatory Health Insurance Scheme
 February 2015 Insurance Newsletter The New Mandatory Health Insurance Scheme Taking stock one year after the introduction Key edition highlights Access to basic health insurance and increased insurance
February 2015 Insurance Newsletter The New Mandatory Health Insurance Scheme Taking stock one year after the introduction Key edition highlights Access to basic health insurance and increased insurance
Universal Healthcare. Universal Healthcare. Universal Healthcare. Universal Healthcare
 Universal Healthcare Universal Healthcare In 2004, health care spending in the United States reached $1.9 trillion, and is projected to reach $2.9 trillion in 2009 The annual premium that a health insurer
Universal Healthcare Universal Healthcare In 2004, health care spending in the United States reached $1.9 trillion, and is projected to reach $2.9 trillion in 2009 The annual premium that a health insurer
Number Obstacles in the process. of establishing sustainable. National Health Insurance Scheme: insights from Ghana
 WHO/HSS/HSF/PB/10.01 Number 1 2010 Obstacles in the process of establishing sustainable National Health Insurance Scheme: insights from Ghana Department of Health Systems Financing Health Financing Policy
WHO/HSS/HSF/PB/10.01 Number 1 2010 Obstacles in the process of establishing sustainable National Health Insurance Scheme: insights from Ghana Department of Health Systems Financing Health Financing Policy
OECD Health Committee Survey on Health Systems Characteristics 2016 ROUND
 OECD Health Committee Survey on Health Systems Characteristics 2016 ROUND PART I. HEALTH CARE FINANCING Section 1: Characteristics of basic health care coverage Section 2: Regulation of health insurance
OECD Health Committee Survey on Health Systems Characteristics 2016 ROUND PART I. HEALTH CARE FINANCING Section 1: Characteristics of basic health care coverage Section 2: Regulation of health insurance
Social Security Schemes,Pension and Elderly policy in Lao P.D.R
 Social Security Schemes,Pension and Elderly policy in Lao P.D.R Mr. Prasong VONGKHAMCHANH Deputy Director General of Social Security Department National Director of ILO Social Security Project Content
Social Security Schemes,Pension and Elderly policy in Lao P.D.R Mr. Prasong VONGKHAMCHANH Deputy Director General of Social Security Department National Director of ILO Social Security Project Content
Universal health coverage roadmap Private sector engagement to improve healthcare access
 Universal health coverage roadmap Private sector engagement to improve healthcare access Prepared for the World Bank February 2018 Copyright 2017 IQVIA. All rights reserved. National health coverage has
Universal health coverage roadmap Private sector engagement to improve healthcare access Prepared for the World Bank February 2018 Copyright 2017 IQVIA. All rights reserved. National health coverage has
Thailand's Universal Coverage System and Preliminary Evaluation of its Success. Kannika Damrongplasit, Ph.D. UCLA and RAND October 15, 2009
 Thailand's Universal Coverage System and Preliminary Evaluation of its Success Kannika Damrongplasit, Ph.D. UCLA and RAND October 15, 2009 Presentation Outline Country Profile History of Health System
Thailand's Universal Coverage System and Preliminary Evaluation of its Success Kannika Damrongplasit, Ph.D. UCLA and RAND October 15, 2009 Presentation Outline Country Profile History of Health System
The Impact of Community-Based Health Insurance on Access to Care and Equity in Rwanda
 TECH N IC A L B R I E F MARCH 16 Photo by Todd Shapera The Impact of Community-Based Health Insurance on Access to Care and Equity in Rwanda W ith support from The Rockefeller Foundation s Transforming
TECH N IC A L B R I E F MARCH 16 Photo by Todd Shapera The Impact of Community-Based Health Insurance on Access to Care and Equity in Rwanda W ith support from The Rockefeller Foundation s Transforming
HOSPITAL AND DIAGNOSTIC SERVICES INSURANCE ACT REGULATIONS
 c t HOSPITAL AND DIAGNOSTIC SERVICES INSURANCE ACT REGULATIONS PLEASE NOTE This document, prepared by the Legislative Counsel Office, is an office consolidation of this regulation, current to March 31,
c t HOSPITAL AND DIAGNOSTIC SERVICES INSURANCE ACT REGULATIONS PLEASE NOTE This document, prepared by the Legislative Counsel Office, is an office consolidation of this regulation, current to March 31,
Indonesia National Health Accounts 2016 Presented in INAHEA 5 th Conference Jakarta, 31 October 2 November 2018
 Indonesia National Health Accounts 2016 Presented in INAHEA 5 th Conference Jakarta, 31 October 2 November 2018 Total Area (km 2 ) = 1,913,578.68 Number of Islands = 17,504 Indonesia in Brief Population
Indonesia National Health Accounts 2016 Presented in INAHEA 5 th Conference Jakarta, 31 October 2 November 2018 Total Area (km 2 ) = 1,913,578.68 Number of Islands = 17,504 Indonesia in Brief Population
COUNTRY CASE STUDY UNIVERSAL HEALTH INSURANCE IN COSTA RICA. Prepared by: Di McIntyre Health Economics Unit, University of Cape Town
 COUNTRY CASE STUDY UNIVERSAL HEALTH INSURANCE IN COSTA RICA Prepared by: Di McIntyre Health Economics Unit, University of Cape Town Preparation of this material was funded through a grant from the Rockefeller
COUNTRY CASE STUDY UNIVERSAL HEALTH INSURANCE IN COSTA RICA Prepared by: Di McIntyre Health Economics Unit, University of Cape Town Preparation of this material was funded through a grant from the Rockefeller
Social Protection Assessment Based National Dialogue in Indonesia: Existing schemes, gaps, recommendations and scenarios
 Social Protection Assessment Based National Dialogue in Indonesia: Existing schemes, gaps, recommendations and scenarios Jakarta, 13 December 2011 Sinta Satriana Health Official Coverage Jamkesmas and
Social Protection Assessment Based National Dialogue in Indonesia: Existing schemes, gaps, recommendations and scenarios Jakarta, 13 December 2011 Sinta Satriana Health Official Coverage Jamkesmas and
Predictive Analytics in the People s Republic of China
 Predictive Analytics in the People s Republic of China Rong Yi, PhD Senior Consultant Rong.Yi@milliman.com Tel: 781.213.6200 4 th National Predictive Modeling Summit Arlington, VA September 15-16, 2010
Predictive Analytics in the People s Republic of China Rong Yi, PhD Senior Consultant Rong.Yi@milliman.com Tel: 781.213.6200 4 th National Predictive Modeling Summit Arlington, VA September 15-16, 2010
Standard Definitions of Terminology used in Health Insurance Policies (IRDA CIRCULAR NO: IRDA/HLT/CIR/036/02/2013 DATED )
 Standard Definitions of Terminology used in Health Insurance Policies (IRDA CIRCULAR NO: IRDA/HLT/CIR/036/02/2013 DATED 20-02-2013) 1. Accident An accident is a sudden, unforeseen and involuntary event
Standard Definitions of Terminology used in Health Insurance Policies (IRDA CIRCULAR NO: IRDA/HLT/CIR/036/02/2013 DATED 20-02-2013) 1. Accident An accident is a sudden, unforeseen and involuntary event
Union General Hospital. An Equal Opportunity Employer
 Original Date: 02/19/2013 Title: Financial Assistance Policy Department: Patient Financial Services Union General Hospital An Equal Opportunity Employer Date Reviewed: 06/03/2015 Date Revised: 01/19/2016
Original Date: 02/19/2013 Title: Financial Assistance Policy Department: Patient Financial Services Union General Hospital An Equal Opportunity Employer Date Reviewed: 06/03/2015 Date Revised: 01/19/2016
T H E NA I RO B I C A L L TO A C T I O N F O R C L O S I N G T H E I M P L E M E N TA T I O N G A P I N H E A LT H P RO M O T I O N
 T H E NA I RO B I C A L L TO A C T I O N F O R C L O S I N G T H E I M P L E M E N TA T I O N G A P I N H E A LT H P RO M O T I O N 1. INTRODUCTION PURPOSE The Nairobi Call to Action identifies key strategies
T H E NA I RO B I C A L L TO A C T I O N F O R C L O S I N G T H E I M P L E M E N TA T I O N G A P I N H E A LT H P RO M O T I O N 1. INTRODUCTION PURPOSE The Nairobi Call to Action identifies key strategies
The Development of Community-Based Health Insurance in Rwanda: Experiences and Lessons
 TECH N IC A L B R I E F MARCH 2016 Photo by Todd Shapera The Development of Community-Based Health Insurance in Rwanda: Experiences and Lessons W ith support from The Rockefeller Foundation s Transforming
TECH N IC A L B R I E F MARCH 2016 Photo by Todd Shapera The Development of Community-Based Health Insurance in Rwanda: Experiences and Lessons W ith support from The Rockefeller Foundation s Transforming
Glossary of Health Coverage and Medical Terms x
 Glossary of Health Coverage and Medical Terms x x x This glossary defines many commonly used terms, but isn t a full list. These glossary terms and definitions are intended to be educational and may be
Glossary of Health Coverage and Medical Terms x x x This glossary defines many commonly used terms, but isn t a full list. These glossary terms and definitions are intended to be educational and may be
Thai Universal Coverage Scheme: Toward a More Stable System
 Thai Universal Coverage Scheme: Toward a More Stable System Dr. Narin Jaroensubphayanont, Lecturer, College of Local Administration, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen Thailand Researcher, Research Group
Thai Universal Coverage Scheme: Toward a More Stable System Dr. Narin Jaroensubphayanont, Lecturer, College of Local Administration, Khon Kaen University, Khon Kaen Thailand Researcher, Research Group
SUN LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY OF CANADA
 SUN LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY OF CANADA Executive Office: One Sun Life Executive Park Wellesley Hills, MA 02481 (800) 247-6875 www.sunlife.com/us Sun Life Assurance Company of Canada certifies that it has
SUN LIFE ASSURANCE COMPANY OF CANADA Executive Office: One Sun Life Executive Park Wellesley Hills, MA 02481 (800) 247-6875 www.sunlife.com/us Sun Life Assurance Company of Canada certifies that it has
National Health Insurance Policy 2013
 National Health Insurance Policy 2013 1. Background The Interim Constitution of Nepal 2007 provides for free basic health care as a fundamental right of citizens. Accordingly, the Government of Nepal has
National Health Insurance Policy 2013 1. Background The Interim Constitution of Nepal 2007 provides for free basic health care as a fundamental right of citizens. Accordingly, the Government of Nepal has
IRDA STANDARD DEFINITIONS OF TERMINOLOGY USED IN HEALTH INSURANCE POLICIES
 IRDA STANDARD DEFINITIONS OF TERMINOLOGY USED IN HEALTH INSURANCE POLICIES 1. Accident An accident is a sudden, unforeseen and involuntary event caused by external and visible means. [Insurance companies
IRDA STANDARD DEFINITIONS OF TERMINOLOGY USED IN HEALTH INSURANCE POLICIES 1. Accident An accident is a sudden, unforeseen and involuntary event caused by external and visible means. [Insurance companies
University Health Insurance Plan (UHIP ) your basic health care solution
 University Health Insurance Plan (UHIP ) your basic health care solution For all eligible international residents studying or working at participating universities in Ontario, Canada. Group Policy Numbers:
University Health Insurance Plan (UHIP ) your basic health care solution For all eligible international residents studying or working at participating universities in Ontario, Canada. Group Policy Numbers:
The 12 th ASEAN & Japan High Level Officials Meeting (HLOM) on Caring Societies. Country Reports. Lao PDR. Vientiane
 The 12 th ASEAN & Japan High Level Officials Meeting (HLOM) on Caring Societies Country Reports Lao PDR Vientiane Oct, 2014 Lao PDR 236 800 km 2 Population: 6.6 Mio. - Rural/Urban: 85%/15% Distinct ethnic
The 12 th ASEAN & Japan High Level Officials Meeting (HLOM) on Caring Societies Country Reports Lao PDR Vientiane Oct, 2014 Lao PDR 236 800 km 2 Population: 6.6 Mio. - Rural/Urban: 85%/15% Distinct ethnic
GOVERNMENT OF SOUTHERN SUDAN MINISTRY OF GENDER, SOCIAL WELFARE AND RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS 2009 SOCIAL SECURITY POLICY
 GOVERNMENT OF SOUTHERN SUDAN MINISTRY OF GENDER, SOCIAL WELFARE AND RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS 2009 SOCIAL SECURITY POLICY Introduction The Ministry of Gender, Social Welfare and Religious Affairs has been mandated
GOVERNMENT OF SOUTHERN SUDAN MINISTRY OF GENDER, SOCIAL WELFARE AND RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS 2009 SOCIAL SECURITY POLICY Introduction The Ministry of Gender, Social Welfare and Religious Affairs has been mandated
TARGETING MECHANISMS OF THE SOCIAL SAFETY NET SYSTEMS IN THE COMCEC REGION COUNTRY EXPERIENCE: CAMEROUN
 TARGETING MECHANISMS OF THE SOCIAL SAFETY NET SYSTEMS IN THE COMCEC REGION COUNTRY EXPERIENCE: CAMEROUN I- INTRODUCTION With a surface area of 475,000 km2 and a population of around 22 million people,
TARGETING MECHANISMS OF THE SOCIAL SAFETY NET SYSTEMS IN THE COMCEC REGION COUNTRY EXPERIENCE: CAMEROUN I- INTRODUCTION With a surface area of 475,000 km2 and a population of around 22 million people,
UNIVERSITY OF THE PACIFIC CALIFORNIA VOLUNTARY DISABILITY PLAN. Effective Date of Plan: June 24, 1977
 UNIVERSITY OF THE PACIFIC CALIFORNIA VOLUNTARY DISABILITY PLAN Effective Date of Plan: June 24, 1977 The provisions of this restatement of the Plan apply to Disability Benefit Periods beginning on or after
UNIVERSITY OF THE PACIFIC CALIFORNIA VOLUNTARY DISABILITY PLAN Effective Date of Plan: June 24, 1977 The provisions of this restatement of the Plan apply to Disability Benefit Periods beginning on or after
ACCESS TO CARE FOR THE UNINSURED: AN UPDATE
 September 2003 ACCESS TO CARE FOR THE UNINSURED: AN UPDATE Over 43 million Americans had no health insurance coverage in 2002 according to the latest estimate from the U.S. Census Bureau - an increase
September 2003 ACCESS TO CARE FOR THE UNINSURED: AN UPDATE Over 43 million Americans had no health insurance coverage in 2002 according to the latest estimate from the U.S. Census Bureau - an increase
OFFICE OF INSURANCE REGULATION Life & Health Product Review INDIVIDUAL HEALTH CONTRACT CHECKLIST
 Statute/Rule Description Yes No N/A Page # 69O-154.001 Important Notice must appear in a prominent manner. 69O-154.003 Notice of Insured's Right to Return Policy: The insured has 10 days from receipt of
Statute/Rule Description Yes No N/A Page # 69O-154.001 Important Notice must appear in a prominent manner. 69O-154.003 Notice of Insured's Right to Return Policy: The insured has 10 days from receipt of
CHAPTER I. Standard Definitions of terminology to be used in Health Insurance Policies
 CHAPTER I Standard Definitions of terminology to be used in Health Insurance Policies It has become increasingly necessary to ensure that certain basic terminology being used in Health Insurance policies
CHAPTER I Standard Definitions of terminology to be used in Health Insurance Policies It has become increasingly necessary to ensure that certain basic terminology being used in Health Insurance policies
Republic of Indonesia: Fiscal Aspect of Social Security Reform
 Technical Assistance Report Project Number: P45110-001 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) October 2012 Republic of Indonesia: Fiscal Aspect of Social Security Reform (Financed by the Japan
Technical Assistance Report Project Number: P45110-001 Capacity Development Technical Assistance (CDTA) October 2012 Republic of Indonesia: Fiscal Aspect of Social Security Reform (Financed by the Japan
Birth Age
 Social security system supporting people throughout their lifetime Birth Age 6 12 15 18 20 40 50 60 70 75 Before school School period Child-raising/working period After retirement [Health/medical care]
Social security system supporting people throughout their lifetime Birth Age 6 12 15 18 20 40 50 60 70 75 Before school School period Child-raising/working period After retirement [Health/medical care]
Social Protection Assessment- Based National Dialogue in Indonesia
 INTRO Costing of income security for the elderly Closing the SPF gap for the elderly would cost between 0.09% of GDP ( low scenario) and 0.95% of GDP ( high scenario) by 2020. The low scenario includes:
INTRO Costing of income security for the elderly Closing the SPF gap for the elderly would cost between 0.09% of GDP ( low scenario) and 0.95% of GDP ( high scenario) by 2020. The low scenario includes:
Annex 3 SOCIAL HEALTH INSURANCE IN INDONESIA: CURRENT STATUS AND THE PLAN FOR NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE 1
 Social Health Insurance Annex 3 SOCIAL HEALTH INSURANCE IN INDONESIA: CURRENT STATUS AND THE PLAN FOR NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE 1 Executive Summary The health status of people in Indonesia has improved
Social Health Insurance Annex 3 SOCIAL HEALTH INSURANCE IN INDONESIA: CURRENT STATUS AND THE PLAN FOR NATIONAL HEALTH INSURANCE 1 Executive Summary The health status of people in Indonesia has improved
GLOSSARY. MEDICAID: A joint federal and state program that helps people with low incomes and limited resources pay health care costs.
 GLOSSARY It has become obvious that those speaking about single-payer, universal healthcare and Medicare for all are using those terms interchangeably. These terms are not interchangeable and already have
GLOSSARY It has become obvious that those speaking about single-payer, universal healthcare and Medicare for all are using those terms interchangeably. These terms are not interchangeable and already have
Social Security Programs Throughout the World: Asia and the Pacific, 2008
 Social Security Programs Throughout the World: Asia and the Pacific, 2008 Social Security Administration Office of Retirement and Disability Policy Office of Research, Evaluation, and Statistics 500 E
Social Security Programs Throughout the World: Asia and the Pacific, 2008 Social Security Administration Office of Retirement and Disability Policy Office of Research, Evaluation, and Statistics 500 E
Health Insurance Glossary of Terms
 1 Health Insurance Glossary of Terms On March 23, 2010, President Obama signed the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) into law. When making decisions about health coverage, consumers should
1 Health Insurance Glossary of Terms On March 23, 2010, President Obama signed the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) into law. When making decisions about health coverage, consumers should
SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM Independence - Freedom - Happiness No. 115/2015/ND-CP Hanoi, November 11, 2015 DECREE
 THE GOVERNMENT ------- SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM Independence - Freedom - Happiness --------------- No. 115/2015/ND-CP Hanoi, November 11, 2015 DECREE GUIDANCE ON THE LAW ON SOCIAL INSURANCE REGARDING
THE GOVERNMENT ------- SOCIALIST REPUBLIC OF VIETNAM Independence - Freedom - Happiness --------------- No. 115/2015/ND-CP Hanoi, November 11, 2015 DECREE GUIDANCE ON THE LAW ON SOCIAL INSURANCE REGARDING
University Health Insurance Plan. UHIP your health care solution. Life s brighter under the sun
 University Health Insurance Plan UHIP your health care solution Life s brighter under the sun Sun Life Assurance Company of Canada is the insurer and is a member of the Sun Life Financial group of companies.
University Health Insurance Plan UHIP your health care solution Life s brighter under the sun Sun Life Assurance Company of Canada is the insurer and is a member of the Sun Life Financial group of companies.
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) APPRAISAL STAGE
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) APPRAISAL STAGE Project Name Kosovo Health Project
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) APPRAISAL STAGE Project Name Kosovo Health Project
POLICY BRIEF. Figure 1: Total, general government, and private expenditures on health as percentages of GDP
 POLICY BRIEF Financial Burden of Health Payments in Mongolia The World Health Report 2010 drew attention to the fact that each year 150 million people globally are facing catastrophic health expenditures,
POLICY BRIEF Financial Burden of Health Payments in Mongolia The World Health Report 2010 drew attention to the fact that each year 150 million people globally are facing catastrophic health expenditures,
1. Key provisions of the Law on social integration of the disabled
 Social integration of the disabled in Lithuania Teodoras Medaiskis Vilnius University Eglė Čaplikienė Ministry of Social Security and Labour I. Key information 1. Key provisions of the Law on social integration
Social integration of the disabled in Lithuania Teodoras Medaiskis Vilnius University Eglė Čaplikienė Ministry of Social Security and Labour I. Key information 1. Key provisions of the Law on social integration
Summary Plan Description
 For Wage Employees of Ispat Inland Inc. Program of Insurance Benefits III () Summary Plan Description Effective Pursuant to the Agreement Dated August 1, 1999 This Summary Plan Description contains two
For Wage Employees of Ispat Inland Inc. Program of Insurance Benefits III () Summary Plan Description Effective Pursuant to the Agreement Dated August 1, 1999 This Summary Plan Description contains two
Colombia REACHING THE POOR WITH HEALTH SERVICES. Using Proxy-Means Testing to Expand Health Insurance for the Poor. Public Disclosure Authorized
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized REACHING THE POOR WITH HEALTH SERVICES Colombia s poor now stand a chance of holding
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized REACHING THE POOR WITH HEALTH SERVICES Colombia s poor now stand a chance of holding
Social Health Protection In Lao PDR
 Social Health Protection In Lao PDR Presented by Lao Team in the International Forum on the development of Social Health Protection in the Southeast Asian Region Hanoi, 27-28/10/2014 Presentation Outline
Social Health Protection In Lao PDR Presented by Lao Team in the International Forum on the development of Social Health Protection in the Southeast Asian Region Hanoi, 27-28/10/2014 Presentation Outline
THE SEVENTH CZECH REPORT ON THE FULFILMENT OF THE EUROPEAN CODE OF SOCIAL SECURITY. for the period from 1 July 2008 to 30 June 2009
 THE SEVENTH CZECH REPORT ON THE FULFILMENT OF THE EUROPEAN CODE OF SOCIAL SECURITY for the period from 1 July 2008 to 30 June 2009 List of applicable legislation: SECTION I Part II Medical Care Act No
THE SEVENTH CZECH REPORT ON THE FULFILMENT OF THE EUROPEAN CODE OF SOCIAL SECURITY for the period from 1 July 2008 to 30 June 2009 List of applicable legislation: SECTION I Part II Medical Care Act No
America s Uninsured Population
 STATEMENT OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS AMERICAN SOCIETY OF INTERNAL MEDICINE TO THE COMMITTEE ON WAYS AND MEANS, SUBCOMMITTEE ON HEALTH UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES APRIL 4, 2001 The
STATEMENT OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF PHYSICIANS AMERICAN SOCIETY OF INTERNAL MEDICINE TO THE COMMITTEE ON WAYS AND MEANS, SUBCOMMITTEE ON HEALTH UNITED STATES HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES APRIL 4, 2001 The
Evolution Health Plan Table of benefits
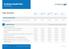 Evolution Health Plan Table of benefits Standard Standard Plus Comprehensive Premium Elite Overall maximum limit This is the maximum amount of money we will pay to, or on behalf of, each insured person
Evolution Health Plan Table of benefits Standard Standard Plus Comprehensive Premium Elite Overall maximum limit This is the maximum amount of money we will pay to, or on behalf of, each insured person
Pocket Statistics. The Social Insurance Institution of Finland
 Pocket Statistics 2015 The Social Insurance Institution of Finland pocket statistics The Social Insurance Institution 2015 General 1 Pensions 7 Disability 12 Health insurance 13 Rehabilitation 20 Unemployment
Pocket Statistics 2015 The Social Insurance Institution of Finland pocket statistics The Social Insurance Institution 2015 General 1 Pensions 7 Disability 12 Health insurance 13 Rehabilitation 20 Unemployment
TERMS OF REFERENCE HEALTH INSURANCE PROVIDER
 TERMS OF REFERENCE HEALTH INSURANCE PROVIDER The World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF) is one of a network of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR). As a global leader in agroforestry
TERMS OF REFERENCE HEALTH INSURANCE PROVIDER The World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF) is one of a network of the Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR). As a global leader in agroforestry
Hospital Indemnity Insurance HI-2200
 Hospital Indemnity Insurance HI-2200 APSB-21396-0709 (AL,AK,AR,CO,DE,GA IA,LA,KY,MI,MO,MS,NE,NM,OH,OR,RI,SC,TN,TX,WV) APS-1883 Generic-EE Summary of Benefits Benefit Description Hospital Confinement Level
Hospital Indemnity Insurance HI-2200 APSB-21396-0709 (AL,AK,AR,CO,DE,GA IA,LA,KY,MI,MO,MS,NE,NM,OH,OR,RI,SC,TN,TX,WV) APS-1883 Generic-EE Summary of Benefits Benefit Description Hospital Confinement Level
Summary of Benefits and Coverage Distribution Instructions
 Summary of Benefits and Coverage Distribution Instructions Federal law requires you, as an employer, to provide your employees with a Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC) at certain times. You can read
Summary of Benefits and Coverage Distribution Instructions Federal law requires you, as an employer, to provide your employees with a Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC) at certain times. You can read
Definitions for Key Terms can be found on page 4
 THIS IS A STATEMENT OF COVERAGE FOR THE LA SIERRA UNIVERSITY CALIFORNIA VOLUNTARY PLAN. THE PROVISIONS OF THIS STATEMENT APPLY TO DISABILITY AND PAID FAMILY LEAVE BENEFIT PERIODS BEGINNING ON OR AFTER
THIS IS A STATEMENT OF COVERAGE FOR THE LA SIERRA UNIVERSITY CALIFORNIA VOLUNTARY PLAN. THE PROVISIONS OF THIS STATEMENT APPLY TO DISABILITY AND PAID FAMILY LEAVE BENEFIT PERIODS BEGINNING ON OR AFTER
Evaluating and Reporting: Accounting for Performance
 S E C T I O N 8 Evaluating and Reporting: Accounting for Performance About this section I This section describes possible ap p ro a ches to account for perfo rmance accord i n g to the key requirements
S E C T I O N 8 Evaluating and Reporting: Accounting for Performance About this section I This section describes possible ap p ro a ches to account for perfo rmance accord i n g to the key requirements
TURKEY. Aggregate spending are linearly estimated from 2000 to 2004 using 1999 and 2005 data.
 TURKEY Monetary unit Social expenditures are expressed in millions of New Turkish liras (TRY). General notes: The individual country notes of the OECD Benefits and Wages ( www.oecd.org/social/benefitsand-wages.htm
TURKEY Monetary unit Social expenditures are expressed in millions of New Turkish liras (TRY). General notes: The individual country notes of the OECD Benefits and Wages ( www.oecd.org/social/benefitsand-wages.htm
MINISTRY OF HEALTH APPLICATION FOR MEDICAL CARD (To be submitted to the nearest Hospital or Health Centre)
 MINISTRY OF HEALTH APPLICATION FOR MEDICAL CARD (To be submitted to the nearest Hospital or Health Centre) WARNING: Any person who, with a view to obtaining a medical card, either for himself or for any
MINISTRY OF HEALTH APPLICATION FOR MEDICAL CARD (To be submitted to the nearest Hospital or Health Centre) WARNING: Any person who, with a view to obtaining a medical card, either for himself or for any
Health Financing in Indonesia
 Executive Summary In 2004, the Indonesian government committed to provide health insurance coverage to its entire population through a mandatory health insurance program. As of 2008, its public budget
Executive Summary In 2004, the Indonesian government committed to provide health insurance coverage to its entire population through a mandatory health insurance program. As of 2008, its public budget
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK
 ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR: INO 34149 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE (Financed from the Japan Special Fund) TO THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA FOR PREPARING THE SECOND DECENTRALIZED HEALTH SERVICES PROJECT November 2001
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR: INO 34149 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE (Financed from the Japan Special Fund) TO THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA FOR PREPARING THE SECOND DECENTRALIZED HEALTH SERVICES PROJECT November 2001
Hong He Min-Min Lyu Nari Park May 2, 2012 South Korea Health Care System South Korea formed a Universal Healthcare system in 1977 which is controlled
 Hong He Min-Min Lyu Nari Park May 2, 2012 South Korea Health Care System South Korea formed a Universal Healthcare system in 1977 which is controlled by the government and managed under the NHIC (National
Hong He Min-Min Lyu Nari Park May 2, 2012 South Korea Health Care System South Korea formed a Universal Healthcare system in 1977 which is controlled by the government and managed under the NHIC (National
LAO PDR: SOCIAL SECURITY
 SERIES: SOCIAL SECURITY EXTENSION INITATIVES IN EAST ASIA LAO PDR: SOCIAL SECURITY ILO Subregional Office for East Asia Decent Work for All Asian Decent Work Decade Country Paper Social Securiy in Lao
SERIES: SOCIAL SECURITY EXTENSION INITATIVES IN EAST ASIA LAO PDR: SOCIAL SECURITY ILO Subregional Office for East Asia Decent Work for All Asian Decent Work Decade Country Paper Social Securiy in Lao
PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA LAW OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA NUMBER 24 OF 2011 CONCERNING THE SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATIVE BODY
 PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA LAW OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA NUMBER 24 OF 2011 CONCERNING THE SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATIVE BODY BY THE GRACE OF GOD ALMIGHTY, PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA
PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA LAW OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA NUMBER 24 OF 2011 CONCERNING THE SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATIVE BODY BY THE GRACE OF GOD ALMIGHTY, PRESIDENT OF THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA
Presentation to SAMA Conference 2015
 Presentation to SAMA Conference 2015 NHI MODEL, RELATIONSHIP TO FINANCE AND ITS EFFECTS ON PUBLIC AND PRIVATE MEDICAL PRACTITIONERS Date: 19 SEPTEMBER 2015 Venue: Sandton Convention Centre Dr Aquina Thulare
Presentation to SAMA Conference 2015 NHI MODEL, RELATIONSHIP TO FINANCE AND ITS EFFECTS ON PUBLIC AND PRIVATE MEDICAL PRACTITIONERS Date: 19 SEPTEMBER 2015 Venue: Sandton Convention Centre Dr Aquina Thulare
This is only a summary. Important Questions $500 $1,000 $500 $1,000. Why this Matters: $50 $4,850 $9,700 $2,000 $4, of 10
 This is only a summary. Important Questions Answers $500 $1,000 $500 $1,000 Why this Matters: $50 $4,850 $9,700 $2,000 $4,000 1 of 10 Common Medical Event Services You May Need In-network Out-of-network
This is only a summary. Important Questions Answers $500 $1,000 $500 $1,000 Why this Matters: $50 $4,850 $9,700 $2,000 $4,000 1 of 10 Common Medical Event Services You May Need In-network Out-of-network
CZECH REPUBLIC Overview of the tax-benefit system
 CZECH REPUBLIC 2004 1. Overview of the tax-benefit system Czech citizens are secured (protected) by three social security systems, i.e. by the social insurance, state social support and social assistance.
CZECH REPUBLIC 2004 1. Overview of the tax-benefit system Czech citizens are secured (protected) by three social security systems, i.e. by the social insurance, state social support and social assistance.
MOVING FROM A GENERAL SUBSIDY INTO A TARGETED ONE: INDONESIAN EXPERIENCE IN FUEL SUBSIDY AND SOCIAL PROTECTION REFORM
 OFFICE OF THE VICE PRESIDENT THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA MOVING FROM A GENERAL SUBSIDY INTO A TARGETED ONE: INDONESIAN EXPERIENCE IN FUEL SUBSIDY AND SOCIAL PROTECTION REFORM Dr. Bambang Widianto Deputy
OFFICE OF THE VICE PRESIDENT THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA MOVING FROM A GENERAL SUBSIDY INTO A TARGETED ONE: INDONESIAN EXPERIENCE IN FUEL SUBSIDY AND SOCIAL PROTECTION REFORM Dr. Bambang Widianto Deputy
Sharing Country Experiences in Social Protection: CAMBODIA: Increasing Employability of Workers 1
 Sharing Country Experiences in Social Protection: CAMBODIA: Increasing Employability of Workers 1 The social security system in Cambodia is still at an early stage of development and currently includes
Sharing Country Experiences in Social Protection: CAMBODIA: Increasing Employability of Workers 1 The social security system in Cambodia is still at an early stage of development and currently includes
N I H S at a e e o f Re R a e d a ines e s Joe S e S oloane
 NHI State of Readiness Joe Seoloane 1 The South African Envisaged Model of NHI Mandatory Enrolment For all citizens and Legal Residents No financial or other barriers equal access to all health care services
NHI State of Readiness Joe Seoloane 1 The South African Envisaged Model of NHI Mandatory Enrolment For all citizens and Legal Residents No financial or other barriers equal access to all health care services
ACCIDENTAL DEATH AND DISMEMBERMENT & MEDICAL COVERAGE FORM
 Named Insured: Policy Number: Effective: Policy Year From: To: Company Name: ACE American Insurance Company Premium: [ ] Included [ ] $ Due When Coverage Begins ACCIDENTAL DEATH AND DISMEMBERMENT & MEDICAL
Named Insured: Policy Number: Effective: Policy Year From: To: Company Name: ACE American Insurance Company Premium: [ ] Included [ ] $ Due When Coverage Begins ACCIDENTAL DEATH AND DISMEMBERMENT & MEDICAL
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) APPRAISAL STAGE Report No.: PIDA Project Name. Region. Country
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) APPRAISAL STAGE Report No.: PIDA32577 Project Name
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) APPRAISAL STAGE Report No.: PIDA32577 Project Name
Glossary of Health Coverage and Medical Terms
 Glossary of Health Coverage and Medical Terms This glossary defines many commonly used terms, but isn t a full list. These glossary terms and definitions are intended to be educational and may be different
Glossary of Health Coverage and Medical Terms This glossary defines many commonly used terms, but isn t a full list. These glossary terms and definitions are intended to be educational and may be different
Accident and Sickness
 Accident and Sickness Proof of Loss Form Important Information Notice to Insured/Claimant: Please answer all the questions completely and accurately. Indicate N.A. where question is not applicable. To
Accident and Sickness Proof of Loss Form Important Information Notice to Insured/Claimant: Please answer all the questions completely and accurately. Indicate N.A. where question is not applicable. To
World Health Organization 2009
 World Health Organization 2009 This document is not a formal publication of the World Health Organization (WHO), and all rights are reserved by the Organization. The document may, however, be freely reviewed,
World Health Organization 2009 This document is not a formal publication of the World Health Organization (WHO), and all rights are reserved by the Organization. The document may, however, be freely reviewed,
STUDENT ACCIDENT INSURANCE PLAN
 STUDENT ACCIDENT INSURANCE PLAN Designed for Students of: (the Policyholder ) 2016-2017 Policy Number US 562772 Underwritten by: United States Fire Insurance Company SJC 16/17 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...4
STUDENT ACCIDENT INSURANCE PLAN Designed for Students of: (the Policyholder ) 2016-2017 Policy Number US 562772 Underwritten by: United States Fire Insurance Company SJC 16/17 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction...4
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK
 ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR:INO 34147 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE (Cofinanced by the Government of the United Kingdom) TO THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA FOR INTEGRATION OF POVERTY CONSIDERATIONS IN DECENTRALIZED EDUCATION
ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK TAR:INO 34147 TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE (Cofinanced by the Government of the United Kingdom) TO THE REPUBLIC OF INDONESIA FOR INTEGRATION OF POVERTY CONSIDERATIONS IN DECENTRALIZED EDUCATION
Country Report of Lao PDR
 Country Report of Lao PDR Bouathep PHOUMINDR, MD, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine Specialist Vice Dean, Faculty of Medical Technology Head of Rehabilitation Medicine Department E-mail: bouathep@hotmail.com
Country Report of Lao PDR Bouathep PHOUMINDR, MD, PhD Rehabilitation Medicine Specialist Vice Dean, Faculty of Medical Technology Head of Rehabilitation Medicine Department E-mail: bouathep@hotmail.com
PART 3 - ARMENIA: NON-INCOME DIMENSIONS OF POVERTY
 PART 3 - ARMENIA: NON-INCOME DIMENSIONS OF POVERTY 109 110 Chapter 8: Health and Poverty Healthy society is not only a critical precondition for the socio-economic development of any country, but also
PART 3 - ARMENIA: NON-INCOME DIMENSIONS OF POVERTY 109 110 Chapter 8: Health and Poverty Healthy society is not only a critical precondition for the socio-economic development of any country, but also
ADDRESSING PUBLIC PRIVATE SECTOR INEQUALITIES PROFESSOR EMERITUS YOSUF VERIAVA
 ADDRESSING PUBLIC PRIVATE SECTOR INEQUALITIES PROFESSOR EMERITUS YOSUF VERIAVA HEALTH INEQUALITY AND INEQUITY Disparity: Is there a difference in the health status rates between population groups? Inequality:
ADDRESSING PUBLIC PRIVATE SECTOR INEQUALITIES PROFESSOR EMERITUS YOSUF VERIAVA HEALTH INEQUALITY AND INEQUITY Disparity: Is there a difference in the health status rates between population groups? Inequality:
Dr. Winai Sawasdivorn. National Health Security Office. Thailand
 Universal Coverage experience of Thailand Dr. Winai Sawasdivorn Secretary General National Health Security Office 1 Thailand Provinces 76 Districts 876 Tambons (communes) 7,255 Villages 68,839 Source:
Universal Coverage experience of Thailand Dr. Winai Sawasdivorn Secretary General National Health Security Office 1 Thailand Provinces 76 Districts 876 Tambons (communes) 7,255 Villages 68,839 Source:
Chicago Public Schools Policy Manual
 Chicago Public Schools Policy Manual Title: FAMILY AND MEDICAL LEAVE ACT (FMLA) Section: 513.1 Board Report: 17-1206-PO1 Date Adopted: December 6, 2017 Policy: THE CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER RECOMMENDS: That
Chicago Public Schools Policy Manual Title: FAMILY AND MEDICAL LEAVE ACT (FMLA) Section: 513.1 Board Report: 17-1206-PO1 Date Adopted: December 6, 2017 Policy: THE CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER RECOMMENDS: That
UNIVERSAL HEALTH COVERAGE: holding countries to account
 UNIVERSAL HEALTH COVERAGE: holding countries to account UHC AND SUSTAINABLE FINANCING Dr Ravindra Rannan-Eliya Director Health Policy Institute Sri Lanka WHAT IS UHC? WHO definition all people receiving
UNIVERSAL HEALTH COVERAGE: holding countries to account UHC AND SUSTAINABLE FINANCING Dr Ravindra Rannan-Eliya Director Health Policy Institute Sri Lanka WHAT IS UHC? WHO definition all people receiving
Mitigating the Impact of the Global Economic Crisis on Household Health Spending
 50834 Mitigating the Impact of the Global Economic Crisis on Household Health Spending Elizabeth Docteur Key Messages The economic crisis is impacting the ability of households in ECA countries to pay
50834 Mitigating the Impact of the Global Economic Crisis on Household Health Spending Elizabeth Docteur Key Messages The economic crisis is impacting the ability of households in ECA countries to pay
OFFICE OF INSURANCE REGULATION Life & Health Product Review FRANCHISE HEALTH CONTRACT CHECKLIST
 Statute/Rule Description Yes No N/A Page # 69O-125.001(3)(f) 69O-154.104 69O-154.105(1) 69O-154.105(2) 69O-154.105(3) 69O-154.105(4) 69O-154.105(5) 69O-154.105(6) 69O-154.105(7) 69O-154.105(8) 69O-154.105(9)
Statute/Rule Description Yes No N/A Page # 69O-125.001(3)(f) 69O-154.104 69O-154.105(1) 69O-154.105(2) 69O-154.105(3) 69O-154.105(4) 69O-154.105(5) 69O-154.105(6) 69O-154.105(7) 69O-154.105(8) 69O-154.105(9)
EZ2DoBizWith. A Supplemental Out-of-Pocket Medical Expense Policy. American Public Life Insurance Company. MEDlink. MEDlink B Rev.
 American Public Life Insurance Company EZ2DoBizWith A Supplemental Out-of-Pocket Medical Expense Policy MEDlink MEDlink B Rev. (07/04) Here s How the Hospital MEDlink Plan Works for You: THREE MAJOR BENEFITS:
American Public Life Insurance Company EZ2DoBizWith A Supplemental Out-of-Pocket Medical Expense Policy MEDlink MEDlink B Rev. (07/04) Here s How the Hospital MEDlink Plan Works for You: THREE MAJOR BENEFITS:
MAKING HEALTH INSURANCE MARKETS WORK FOR THE POOR IN SOUTH AFRICA
 MAKING HEALTH INSURANCE MARKETS WORK FOR THE POOR IN SOUTH AFRICA Jeremy Leach Roseanne da Silva IAAHS 2007 IAA Health Section Colloquium 13 th 16 th May 2007 CTICC www.iaahs2007.com FinMark Trust Independent
MAKING HEALTH INSURANCE MARKETS WORK FOR THE POOR IN SOUTH AFRICA Jeremy Leach Roseanne da Silva IAAHS 2007 IAA Health Section Colloquium 13 th 16 th May 2007 CTICC www.iaahs2007.com FinMark Trust Independent
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Project Name PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Health Sector Support Project
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Project Name PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Health Sector Support Project
OVERVIEW OF YOUR BENEFITS
 OVERVIEW OF YOUR BENEFITS 9 IMPORTANT PHONE NUMBERS Rochester Benefit Fund Office (585) 244-0830 For questions about eligibility, Coordination of Benefits, your 1199SEIU Health Benefits ID card, prescription
OVERVIEW OF YOUR BENEFITS 9 IMPORTANT PHONE NUMBERS Rochester Benefit Fund Office (585) 244-0830 For questions about eligibility, Coordination of Benefits, your 1199SEIU Health Benefits ID card, prescription
Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC) & Uniform Glossary A Supplement to the Insurance & Benefits Information Guide
 2017-2018 Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC) & Uniform Glossary A Supplement to the 2017-2018 Insurance & Benefits Information Guide Nassau County School Board 1201 Atlantic Avenue Fernandina Beach,
2017-2018 Summary of Benefits and Coverage (SBC) & Uniform Glossary A Supplement to the 2017-2018 Insurance & Benefits Information Guide Nassau County School Board 1201 Atlantic Avenue Fernandina Beach,
Long-term care the problem of sustainable financing (Ljubljana, November 2014) 1
 Long-term care the problem of sustainable financing (Ljubljana, 18-19 November 2014) 1 Matěj Lipský Social Services Centre Tloskov Vojtěška Hervertová Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs 1. How would
Long-term care the problem of sustainable financing (Ljubljana, 18-19 November 2014) 1 Matěj Lipský Social Services Centre Tloskov Vojtěška Hervertová Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs 1. How would
Disability Coverage. Disability benefits help protect your income if you have an illness or injury that keeps you from working.
 Disability Coverage Disability benefits help protect your income if you have an illness or injury that keeps you from working. Plan Highlights If you enroll in the voluntary STD benefit, you will be eligible
Disability Coverage Disability benefits help protect your income if you have an illness or injury that keeps you from working. Plan Highlights If you enroll in the voluntary STD benefit, you will be eligible
GENERALI WORLDCHOICE DEDUCTIBLE OPTIONS
 GENERALI WORLDCHOICE DEDUCTIBLE OPTIONS Group Health Plan Benefit Summary Comprehensive Major Medical Benefit Pre-Authorization through Generali Worldwide is required for certain Medical Services (1) otherwise
GENERALI WORLDCHOICE DEDUCTIBLE OPTIONS Group Health Plan Benefit Summary Comprehensive Major Medical Benefit Pre-Authorization through Generali Worldwide is required for certain Medical Services (1) otherwise
Exhibit ES-1. Total National Health Expenditures (NHE), Current Projection and Alternative Scenarios
 Exhibit ES-1. Total National Health Expenditures (NHE), 2009 2020 Current Projection and Alternative Scenarios NHE in trillions $6 $5 Current projection (6.7% annual growth) Path proposals (5.5% annual
Exhibit ES-1. Total National Health Expenditures (NHE), 2009 2020 Current Projection and Alternative Scenarios NHE in trillions $6 $5 Current projection (6.7% annual growth) Path proposals (5.5% annual
IdealCare Limited-Benefit Health Insurance. NationalWay Association. Online Fitness & Nutrition Center Online Health Manager Nurse Hotline
 BENEFIT INFORMATION IdealCare Limited-Benefit Health Insurance IdealCare Limited-Benefit Health Insurance brought to you through membership in NationalWay Association Included in this plan: Association
BENEFIT INFORMATION IdealCare Limited-Benefit Health Insurance IdealCare Limited-Benefit Health Insurance brought to you through membership in NationalWay Association Included in this plan: Association
Underwritten by Guardrisk Insurance Company, Guardrisk is a registered and authorised Financial Services Provider FSP Number 75
 Gap Cover Extended Cancer Cover Extended Dentistry Cover Medical Premium Waiver Underwritten by Guardrisk Insurance Company, Guardrisk is a registered and authorised Financial Services Provider FSP Number
Gap Cover Extended Cancer Cover Extended Dentistry Cover Medical Premium Waiver Underwritten by Guardrisk Insurance Company, Guardrisk is a registered and authorised Financial Services Provider FSP Number
The reform experience of Estonia
 The reform experience of Estonia Dr. Ewout van Ginneken Department of Health Care Management Berlin University of Technology WHO Collaborating Centre for Health Systems, Research and Management European
The reform experience of Estonia Dr. Ewout van Ginneken Department of Health Care Management Berlin University of Technology WHO Collaborating Centre for Health Systems, Research and Management European
Panel T17a P07 Session 1. Title of the panel. Going Universal? Universal Health Coverage on Paper and in Practice. Title of the paper.
 3 rd International Conference on Public Policy (ICPP3) June 28-30, 2017 Singapore Panel T17a P07 Session 1 Title of the panel Going Universal? Universal Health Coverage on Paper and in Practice Title of
3 rd International Conference on Public Policy (ICPP3) June 28-30, 2017 Singapore Panel T17a P07 Session 1 Title of the panel Going Universal? Universal Health Coverage on Paper and in Practice Title of
Performance-Based Intergovernmental Transfers
 Performance-Based Intergovernmental Transfers Brazil s Family Health Program And Argentina s PLAN NACER Program Jerry La Forgia World Bank National Workshop for Results-Based Financing for Health Jaipur,
Performance-Based Intergovernmental Transfers Brazil s Family Health Program And Argentina s PLAN NACER Program Jerry La Forgia World Bank National Workshop for Results-Based Financing for Health Jaipur,
Evolution Health Plan (Asia Pacific) Table of benefits
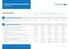 Evolution Health Plan (Asia Pacific) Table of benefits Standard Standard Plus Comprehensive Premium Elite 1 Overall maximum sum insured This is the maximum amount of money we will pay to or on behalf of
Evolution Health Plan (Asia Pacific) Table of benefits Standard Standard Plus Comprehensive Premium Elite 1 Overall maximum sum insured This is the maximum amount of money we will pay to or on behalf of
World Bank Seminar User fees for health care: Protecting the Poor
 World Bank Seminar User fees for health care: Protecting the Poor The case of Thailand Ursula Giedion Population: Background 62.4 million Population under poverty line National: 12.8% Urban: 17.2% Rural:
World Bank Seminar User fees for health care: Protecting the Poor The case of Thailand Ursula Giedion Population: Background 62.4 million Population under poverty line National: 12.8% Urban: 17.2% Rural:
