Fundamental Theorem of Asset Pricing
|
|
|
- Magnus McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5.450 Recitation
2 o Arbitrage Roughly speaking, an arbitrage is a possibility of profit at zero cost. Often implicit is an assumption that such an arbitrage opportunity is scalable (can repeat it over and over). In this situation, presumably someone with a deep pocket and an ability to recognize the arbitrage opportunity (called arbitrageur) will exploit the arbitrage and in the course will eliminate the arbitrage oppportunity in the market. From the point of view of an average investor, all arbitrage opportunities are already taken up by the arbitrageurs and therefore there is no arbitrage. We re not saying there cannot be an arbitrage arbitrageurs, limits to arbitrage, or systemic mispricing. However, no arbitrage is a very sensible and realistic description of the world we live in. We take no arbitrage as an axiom for the discussion in this class.
3 The condition of no arbitrage is intuitive and primitive. Yet, it s reasonable to imagine that asset prices are determined by the total supply and demand of assets by the entire group of investors, each of whom has his or her own preferences (this approach won t get us far, it s just too difficult to analyze this economy). The breakthrough is the Fundamental Theorem of Asset Pricing. It allows us to study asset prices without having to worry about individual preferences or cross-sectional distribution of investors. The theorem states that the absence of arbitrage is equivalent to the existence of a state price density. One implies the other the implications in both directions are important.
4 State Price Density Another name for the state price density is stochastic discount factor. Recall straightforward bond pricing from 5.40/5.45. B = C + + r 2 ( + r) C T ( + r) (C + P) The terms t are (time) discount factors. They do not (+r) take into account risk. The stochastic discount factor (or state price density) is a generalization of the simple discount factor that incorporates both risk and time value of money. Roughly speaking, state price density is large in bad states where a dollar is more valuable and small in good states where a dollar is less valuable. A state price density can price any asset (where an asset represents a stream of stochastic cashflows) (see page of Lectures otes ).
5 Related Concepts Existence of a state price density is equivalent to existence of two other objects: state prices and risk neutral probabilities. Therefore, by the, no arbitrage is equivalent to existence of any one of the three related objects: state price density, state prices, or risk neutral probabilities. Why have so many different concepts? Each provides a different perspective and insight, but the three concepts, as a group, are really the same thing! In what follows, to fix the idea and simplify notation, assume the following: we have date 0 and date, there are possible states of nature at date, and state i occurs with probability p i.
6 State Price Density Consider an asset that pays off x i dollars in state i at date. The question is what is the value (price) of this asset at date 0. Using the SPD π, we calculate it as follows: P = E [πx] p i π i x i i= In words, the price is the expected value of payoffs, discounted by the state price density.
7 State Prices The state-contingent security in state i is an asset that pays off $ in state i and 0 in all other states. The price of this state-contingent security is the state price in state i, denoted φ i. State prices refer to the vector of state prices (φ,...φ ). Using the state prices, the price of our asset is P = φ i x i i= Intuition: John Cochrane s Happy Meal analogy - The price of a happy meal is the price of a hamburger plus the price of a soft drink plus the price of fries (and plus the price of a toy).
8 Risk eutral Probabilities The actual probabilities are given by (p,...,p ). Are there a different set of probabilities and a risk-free rate such that the price of the asset is given by the expected payoff (under the alternative probabilities) at date, only discounted by the risk-free rate? Call such probabilities (q,...,q ) and the risk-free rate r. Then P = E Q [x] + r q i x + r i= Thinking of an asset price as the expected payoff is somewhat naive because it doesn t take into account risk, but it s not completely wrong! Under the alternative probabilities Q, this is actually correct (hence the name risk neutral probabilities). i
9 The Three Concepts Are Equivalent Existence of state prices existence of state price density φ p i P = φ i x i i= = p i π i x i i= = E [πx] where πi = i. We can also reverse the direction of the proof.
10 Continued Existence of state prices existence of risk neutral probabilities P = φ i x i i= = (φ +...φ = q i x i + r i= φ φ +...φ φi ) φ +...φ i= where we define q i = i and make use of the fact that = φ +...φ. Alternatively, given (q,...,q ) and r, we +r can solve for (φ,...φ ). x i
11 Summary A very intuitive, primitive, and simple restriction of no arbitrage has powerful consequences and guarantees existence of powerful pricing tools (Fundamental Theorem of Asset Pricing). Each of the three objects, state price density, state prices, and risk neutral probabilities, can price any asset (again, an asset is merely a stream of stochastic payoffs). The value of an asset depends on three elements: probabilities, attitude towards risk, and time value of money. The state prices incorporate all three elements. The state price density contain all the information about attitude towards risk and time value of money. The risk neutral probabilities contain all the information about (actual) probabilities and attitude towards risk.
12 MIT OpenCourseWare Analytics of Finance Fall 200 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit:
ECON FINANCIAL ECONOMICS
 ECON 337901 FINANCIAL ECONOMICS Peter Ireland Boston College Fall 2017 These lecture notes by Peter Ireland are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-ShareAlike 4.0 International
ECON 337901 FINANCIAL ECONOMICS Peter Ireland Boston College Fall 2017 These lecture notes by Peter Ireland are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-ShareAlike 4.0 International
Mixed Strategies. Samuel Alizon and Daniel Cownden February 4, 2009
 Mixed Strategies Samuel Alizon and Daniel Cownden February 4, 009 1 What are Mixed Strategies In the previous sections we have looked at games where players face uncertainty, and concluded that they choose
Mixed Strategies Samuel Alizon and Daniel Cownden February 4, 009 1 What are Mixed Strategies In the previous sections we have looked at games where players face uncertainty, and concluded that they choose
Consumption- Savings, Portfolio Choice, and Asset Pricing
 Finance 400 A. Penati - G. Pennacchi Consumption- Savings, Portfolio Choice, and Asset Pricing I. The Consumption - Portfolio Choice Problem We have studied the portfolio choice problem of an individual
Finance 400 A. Penati - G. Pennacchi Consumption- Savings, Portfolio Choice, and Asset Pricing I. The Consumption - Portfolio Choice Problem We have studied the portfolio choice problem of an individual
One-Period Valuation Theory
 One-Period Valuation Theory Part 1: Basic Framework Chris Telmer March, 2013 Develop a simple framework for understanding what the pricing kernel is and how it s related to the economics of risk, return
One-Period Valuation Theory Part 1: Basic Framework Chris Telmer March, 2013 Develop a simple framework for understanding what the pricing kernel is and how it s related to the economics of risk, return
SYSM 6304: Risk and Decision Analysis Lecture 6: Pricing and Hedging Financial Derivatives
 SYSM 6304: Risk and Decision Analysis Lecture 6: Pricing and Hedging Financial Derivatives M. Vidyasagar Cecil & Ida Green Chair The University of Texas at Dallas Email: M.Vidyasagar@utdallas.edu October
SYSM 6304: Risk and Decision Analysis Lecture 6: Pricing and Hedging Financial Derivatives M. Vidyasagar Cecil & Ida Green Chair The University of Texas at Dallas Email: M.Vidyasagar@utdallas.edu October
3 Arbitrage pricing theory in discrete time.
 3 Arbitrage pricing theory in discrete time. Orientation. In the examples studied in Chapter 1, we worked with a single period model and Gaussian returns; in this Chapter, we shall drop these assumptions
3 Arbitrage pricing theory in discrete time. Orientation. In the examples studied in Chapter 1, we worked with a single period model and Gaussian returns; in this Chapter, we shall drop these assumptions
ECON FINANCIAL ECONOMICS
 ECON 337901 FINANCIAL ECONOMICS Peter Ireland Boston College Spring 2018 These lecture notes by Peter Ireland are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-ShareAlike 4.0 International
ECON 337901 FINANCIAL ECONOMICS Peter Ireland Boston College Spring 2018 These lecture notes by Peter Ireland are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-ShareAlike 4.0 International
Lecture 8: Introduction to asset pricing
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON Paul Klein Office: Murray Building, 3005 Email: p.klein@soton.ac.uk URL: http://paulklein.se Economics 3010 Topics in Macroeconomics 3 Autumn 2010 Lecture 8: Introduction
THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON Paul Klein Office: Murray Building, 3005 Email: p.klein@soton.ac.uk URL: http://paulklein.se Economics 3010 Topics in Macroeconomics 3 Autumn 2010 Lecture 8: Introduction
18.440: Lecture 32 Strong law of large numbers and Jensen s inequality
 18.440: Lecture 32 Strong law of large numbers and Jensen s inequality Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline A story about Pedro Strong law of large numbers Jensen s inequality 2 Outline A story about Pedro Strong
18.440: Lecture 32 Strong law of large numbers and Jensen s inequality Scott Sheffield MIT 1 Outline A story about Pedro Strong law of large numbers Jensen s inequality 2 Outline A story about Pedro Strong
Ph.D. Preliminary Examination MICROECONOMIC THEORY Applied Economics Graduate Program June 2017
 Ph.D. Preliminary Examination MICROECONOMIC THEORY Applied Economics Graduate Program June 2017 The time limit for this exam is four hours. The exam has four sections. Each section includes two questions.
Ph.D. Preliminary Examination MICROECONOMIC THEORY Applied Economics Graduate Program June 2017 The time limit for this exam is four hours. The exam has four sections. Each section includes two questions.
Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.997 Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.997 Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Derivative Instruments
 Derivative Instruments Paris Dauphine University - Master I.E.F. (272) Autumn 2016 Jérôme MATHIS jerome.mathis@dauphine.fr (object: IEF272) http://jerome.mathis.free.fr/ief272 Slides on book: John C. Hull,
Derivative Instruments Paris Dauphine University - Master I.E.F. (272) Autumn 2016 Jérôme MATHIS jerome.mathis@dauphine.fr (object: IEF272) http://jerome.mathis.free.fr/ief272 Slides on book: John C. Hull,
Projects to Avoid Catastrophes
 Projects to Avoid Catastrophes Robert S. Pindyck April 10, 2013 Abstract How should we evaluate public policies or projects that are intended to reduce the likelihood or potential impact of a catastrophic
Projects to Avoid Catastrophes Robert S. Pindyck April 10, 2013 Abstract How should we evaluate public policies or projects that are intended to reduce the likelihood or potential impact of a catastrophic
Christiano 362, Winter 2006 Lecture #3: More on Exchange Rates More on the idea that exchange rates move around a lot.
 Christiano 362, Winter 2006 Lecture #3: More on Exchange Rates More on the idea that exchange rates move around a lot. 1.Theexampleattheendoflecture#2discussedalargemovementin the US-Japanese exchange
Christiano 362, Winter 2006 Lecture #3: More on Exchange Rates More on the idea that exchange rates move around a lot. 1.Theexampleattheendoflecture#2discussedalargemovementin the US-Japanese exchange
The Fiscal Theory of the Price Level
 The Fiscal Theory of the Price Level 1. Sargent and Wallace s (SW) article, Some Unpleasant Monetarist Arithmetic This paper first put forth the idea of the fiscal theory of the price level, a radical
The Fiscal Theory of the Price Level 1. Sargent and Wallace s (SW) article, Some Unpleasant Monetarist Arithmetic This paper first put forth the idea of the fiscal theory of the price level, a radical
Remarks on Probability
 omp2011/2711 S1 2006 Random Variables 1 Remarks on Probability In order to better understand theorems on average performance analyses, it is helpful to know a little about probability and random variables.
omp2011/2711 S1 2006 Random Variables 1 Remarks on Probability In order to better understand theorems on average performance analyses, it is helpful to know a little about probability and random variables.
Finance: Lecture 4 - No Arbitrage Pricing Chapters of DD Chapter 1 of Ross (2005)
 Finance: Lecture 4 - No Arbitrage Pricing Chapters 10-12 of DD Chapter 1 of Ross (2005) Prof. Alex Stomper MIT Sloan, IHS & VGSF March 2010 Alex Stomper (MIT, IHS & VGSF) Finance March 2010 1 / 15 Fundamental
Finance: Lecture 4 - No Arbitrage Pricing Chapters 10-12 of DD Chapter 1 of Ross (2005) Prof. Alex Stomper MIT Sloan, IHS & VGSF March 2010 Alex Stomper (MIT, IHS & VGSF) Finance March 2010 1 / 15 Fundamental
6: MULTI-PERIOD MARKET MODELS
 6: MULTI-PERIOD MARKET MODELS Marek Rutkowski School of Mathematics and Statistics University of Sydney Semester 2, 2016 M. Rutkowski (USydney) 6: Multi-Period Market Models 1 / 55 Outline We will examine
6: MULTI-PERIOD MARKET MODELS Marek Rutkowski School of Mathematics and Statistics University of Sydney Semester 2, 2016 M. Rutkowski (USydney) 6: Multi-Period Market Models 1 / 55 Outline We will examine
Fixed-Income Options
 Fixed-Income Options Consider a two-year 99 European call on the three-year, 5% Treasury. Assume the Treasury pays annual interest. From p. 852 the three-year Treasury s price minus the $5 interest could
Fixed-Income Options Consider a two-year 99 European call on the three-year, 5% Treasury. Assume the Treasury pays annual interest. From p. 852 the three-year Treasury s price minus the $5 interest could
1 Asset Pricing: Replicating portfolios
 Alberto Bisin Corporate Finance: Lecture Notes Class 1: Valuation updated November 17th, 2002 1 Asset Pricing: Replicating portfolios Consider an economy with two states of nature {s 1, s 2 } and with
Alberto Bisin Corporate Finance: Lecture Notes Class 1: Valuation updated November 17th, 2002 1 Asset Pricing: Replicating portfolios Consider an economy with two states of nature {s 1, s 2 } and with
Finance: A Quantitative Introduction Chapter 7 - part 2 Option Pricing Foundations
 Finance: A Quantitative Introduction Chapter 7 - part 2 Option Pricing Foundations Nico van der Wijst 1 Finance: A Quantitative Introduction c Cambridge University Press 1 The setting 2 3 4 2 Finance:
Finance: A Quantitative Introduction Chapter 7 - part 2 Option Pricing Foundations Nico van der Wijst 1 Finance: A Quantitative Introduction c Cambridge University Press 1 The setting 2 3 4 2 Finance:
( 0) ,...,S N ,S 2 ( 0)... S N S 2. N and a portfolio is created that way, the value of the portfolio at time 0 is: (0) N S N ( 1, ) +...
 No-Arbitrage Pricing Theory Single-Period odel There are N securities denoted ( S,S,...,S N ), they can be stocks, bonds, or any securities, we assume they are all traded, and have prices available. Ω
No-Arbitrage Pricing Theory Single-Period odel There are N securities denoted ( S,S,...,S N ), they can be stocks, bonds, or any securities, we assume they are all traded, and have prices available. Ω
Characterization of the Optimum
 ECO 317 Economics of Uncertainty Fall Term 2009 Notes for lectures 5. Portfolio Allocation with One Riskless, One Risky Asset Characterization of the Optimum Consider a risk-averse, expected-utility-maximizing
ECO 317 Economics of Uncertainty Fall Term 2009 Notes for lectures 5. Portfolio Allocation with One Riskless, One Risky Asset Characterization of the Optimum Consider a risk-averse, expected-utility-maximizing
Chapter 23: Choice under Risk
 Chapter 23: Choice under Risk 23.1: Introduction We consider in this chapter optimal behaviour in conditions of risk. By this we mean that, when the individual takes a decision, he or she does not know
Chapter 23: Choice under Risk 23.1: Introduction We consider in this chapter optimal behaviour in conditions of risk. By this we mean that, when the individual takes a decision, he or she does not know
Martingale Pricing Theory in Discrete-Time and Discrete-Space Models
 IEOR E4707: Foundations of Financial Engineering c 206 by Martin Haugh Martingale Pricing Theory in Discrete-Time and Discrete-Space Models These notes develop the theory of martingale pricing in a discrete-time,
IEOR E4707: Foundations of Financial Engineering c 206 by Martin Haugh Martingale Pricing Theory in Discrete-Time and Discrete-Space Models These notes develop the theory of martingale pricing in a discrete-time,
Binomial Trees. Liuren Wu. Zicklin School of Business, Baruch College. Options Markets
 Binomial Trees Liuren Wu Zicklin School of Business, Baruch College Options Markets Binomial tree represents a simple and yet universal method to price options. I am still searching for a numerically efficient,
Binomial Trees Liuren Wu Zicklin School of Business, Baruch College Options Markets Binomial tree represents a simple and yet universal method to price options. I am still searching for a numerically efficient,
Real Options. Katharina Lewellen Finance Theory II April 28, 2003
 Real Options Katharina Lewellen Finance Theory II April 28, 2003 Real options Managers have many options to adapt and revise decisions in response to unexpected developments. Such flexibility is clearly
Real Options Katharina Lewellen Finance Theory II April 28, 2003 Real options Managers have many options to adapt and revise decisions in response to unexpected developments. Such flexibility is clearly
ECON 459 Game Theory. Lecture Notes Auctions. Luca Anderlini Spring 2017
 ECON 459 Game Theory Lecture Notes Auctions Luca Anderlini Spring 2017 These notes have been used and commented on before. If you can still spot any errors or have any suggestions for improvement, please
ECON 459 Game Theory Lecture Notes Auctions Luca Anderlini Spring 2017 These notes have been used and commented on before. If you can still spot any errors or have any suggestions for improvement, please
Fundamental Theorems of Asset Pricing. 3.1 Arbitrage and risk neutral probability measures
 Lecture 3 Fundamental Theorems of Asset Pricing 3.1 Arbitrage and risk neutral probability measures Several important concepts were illustrated in the example in Lecture 2: arbitrage; risk neutral probability
Lecture 3 Fundamental Theorems of Asset Pricing 3.1 Arbitrage and risk neutral probability measures Several important concepts were illustrated in the example in Lecture 2: arbitrage; risk neutral probability
Are Capital Structure Decisions Relevant?
 Are Capital Structure Decisions Relevant? 161 Chapter 17 Are Capital Structure Decisions Relevant? Contents 17.1 The Capital Structure Problem.................... 161 17.2 The Capital Structure Problem
Are Capital Structure Decisions Relevant? 161 Chapter 17 Are Capital Structure Decisions Relevant? Contents 17.1 The Capital Structure Problem.................... 161 17.2 The Capital Structure Problem
To have a concrete example in mind, suppose that we want to price a European call option on a stock that matures in six months.
 A one period model To have a concrete example in mind, suppose that we want to price a European call option on a stock that matures in six months.. The model setup We will start simple with a one period
A one period model To have a concrete example in mind, suppose that we want to price a European call option on a stock that matures in six months.. The model setup We will start simple with a one period
Economics 2010c: -theory
 Economics 2010c: -theory David Laibson 10/9/2014 Outline: 1. Why should we study investment? 2. Static model 3. Dynamic model: -theory of investment 4. Phase diagrams 5. Analytic example of Model (optional)
Economics 2010c: -theory David Laibson 10/9/2014 Outline: 1. Why should we study investment? 2. Static model 3. Dynamic model: -theory of investment 4. Phase diagrams 5. Analytic example of Model (optional)
Topics in Contract Theory Lecture 5. Property Rights Theory. The key question we are staring from is: What are ownership/property rights?
 Leonardo Felli 15 January, 2002 Topics in Contract Theory Lecture 5 Property Rights Theory The key question we are staring from is: What are ownership/property rights? For an answer we need to distinguish
Leonardo Felli 15 January, 2002 Topics in Contract Theory Lecture 5 Property Rights Theory The key question we are staring from is: What are ownership/property rights? For an answer we need to distinguish
Problem Set 4 Answers
 Business 3594 John H. Cochrane Problem Set 4 Answers ) a) In the end, we re looking for ( ) ( ) + This suggests writing the portfolio as an investment in the riskless asset, then investing in the risky
Business 3594 John H. Cochrane Problem Set 4 Answers ) a) In the end, we re looking for ( ) ( ) + This suggests writing the portfolio as an investment in the riskless asset, then investing in the risky
Risk Aversion, Stochastic Dominance, and Rules of Thumb: Concept and Application
 Risk Aversion, Stochastic Dominance, and Rules of Thumb: Concept and Application Vivek H. Dehejia Carleton University and CESifo Email: vdehejia@ccs.carleton.ca January 14, 2008 JEL classification code:
Risk Aversion, Stochastic Dominance, and Rules of Thumb: Concept and Application Vivek H. Dehejia Carleton University and CESifo Email: vdehejia@ccs.carleton.ca January 14, 2008 JEL classification code:
1 Geometric Brownian motion
 Copyright c 05 by Karl Sigman Geometric Brownian motion Note that since BM can take on negative values, using it directly for modeling stock prices is questionable. There are other reasons too why BM is
Copyright c 05 by Karl Sigman Geometric Brownian motion Note that since BM can take on negative values, using it directly for modeling stock prices is questionable. There are other reasons too why BM is
Exam Quantitative Finance (35V5A1)
 Exam Quantitative Finance (35V5A1) Part I: Discrete-time finance Exercise 1 (20 points) a. Provide the definition of the pricing kernel k q. Relate this pricing kernel to the set of discount factors D
Exam Quantitative Finance (35V5A1) Part I: Discrete-time finance Exercise 1 (20 points) a. Provide the definition of the pricing kernel k q. Relate this pricing kernel to the set of discount factors D
12 Bounds. on Option Prices. Answers to Questions and Problems
 12 Bounds on Option Prices 90 Answers to Questions and Problems 1. What is the maximum theoretical value for a call? Under what conditions does a call reach this maximum value? Explain. The highest price
12 Bounds on Option Prices 90 Answers to Questions and Problems 1. What is the maximum theoretical value for a call? Under what conditions does a call reach this maximum value? Explain. The highest price
Common Knowledge AND Global Games
 Common Knowledge AND Global Games 1 This talk combines common knowledge with global games another advanced branch of game theory See Stephen Morris s work 2 Today we ll go back to a puzzle that arose during
Common Knowledge AND Global Games 1 This talk combines common knowledge with global games another advanced branch of game theory See Stephen Morris s work 2 Today we ll go back to a puzzle that arose during
Roy Model of Self-Selection: General Case
 V. J. Hotz Rev. May 6, 007 Roy Model of Self-Selection: General Case Results drawn on Heckman and Sedlacek JPE, 1985 and Heckman and Honoré, Econometrica, 1986. Two-sector model in which: Agents are income
V. J. Hotz Rev. May 6, 007 Roy Model of Self-Selection: General Case Results drawn on Heckman and Sedlacek JPE, 1985 and Heckman and Honoré, Econometrica, 1986. Two-sector model in which: Agents are income
ECON FINANCIAL ECONOMICS
 ECON 337901 FINANCIAL ECONOMICS Peter Ireland Boston College February 19, 2019 These lecture notes by Peter Ireland are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-ShareAlike 4.0 International
ECON 337901 FINANCIAL ECONOMICS Peter Ireland Boston College February 19, 2019 These lecture notes by Peter Ireland are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommerical-ShareAlike 4.0 International
M.I.T Fall Practice Problems
 M.I.T. 15.450-Fall 2010 Sloan School of Management Professor Leonid Kogan Practice Problems 1. Consider a 3-period model with t = 0, 1, 2, 3. There are a stock and a risk-free asset. The initial stock
M.I.T. 15.450-Fall 2010 Sloan School of Management Professor Leonid Kogan Practice Problems 1. Consider a 3-period model with t = 0, 1, 2, 3. There are a stock and a risk-free asset. The initial stock
Microeconomic Theory III Spring 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 14.123 Microeconomic Theory III Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MIT 14.123 (2009) by
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 14.123 Microeconomic Theory III Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. MIT 14.123 (2009) by
March 30, Why do economists (and increasingly, engineers and computer scientists) study auctions?
 March 3, 215 Steven A. Matthews, A Technical Primer on Auction Theory I: Independent Private Values, Northwestern University CMSEMS Discussion Paper No. 196, May, 1995. This paper is posted on the course
March 3, 215 Steven A. Matthews, A Technical Primer on Auction Theory I: Independent Private Values, Northwestern University CMSEMS Discussion Paper No. 196, May, 1995. This paper is posted on the course
Advanced Risk Management
 Winter 2014/2015 Advanced Risk Management Part I: Decision Theory and Risk Management Motives Lecture 1: Introduction and Expected Utility Your Instructors for Part I: Prof. Dr. Andreas Richter Email:
Winter 2014/2015 Advanced Risk Management Part I: Decision Theory and Risk Management Motives Lecture 1: Introduction and Expected Utility Your Instructors for Part I: Prof. Dr. Andreas Richter Email:
Fin 501: Asset Pricing Fin 501:
 Lecture 3: One-period Model Pricing Prof. Markus K. Brunnermeier Slide 03-1 Overview: Pricing i 1. LOOP, No arbitrage 2. Forwards 3. Options: Parity relationship 4. No arbitrage and existence of state
Lecture 3: One-period Model Pricing Prof. Markus K. Brunnermeier Slide 03-1 Overview: Pricing i 1. LOOP, No arbitrage 2. Forwards 3. Options: Parity relationship 4. No arbitrage and existence of state
Risk aversion and choice under uncertainty
 Risk aversion and choice under uncertainty Pierre Chaigneau pierre.chaigneau@hec.ca June 14, 2011 Finance: the economics of risk and uncertainty In financial markets, claims associated with random future
Risk aversion and choice under uncertainty Pierre Chaigneau pierre.chaigneau@hec.ca June 14, 2011 Finance: the economics of risk and uncertainty In financial markets, claims associated with random future
European Contingent Claims
 European Contingent Claims Seminar: Financial Modelling in Life Insurance organized by Dr. Nikolic and Dr. Meyhöfer Zhiwen Ning 13.05.2016 Zhiwen Ning European Contingent Claims 13.05.2016 1 / 23 outline
European Contingent Claims Seminar: Financial Modelling in Life Insurance organized by Dr. Nikolic and Dr. Meyhöfer Zhiwen Ning 13.05.2016 Zhiwen Ning European Contingent Claims 13.05.2016 1 / 23 outline
The Pennsylvania State University. The Graduate School. Department of Industrial Engineering AMERICAN-ASIAN OPTION PRICING BASED ON MONTE CARLO
 The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Industrial Engineering AMERICAN-ASIAN OPTION PRICING BASED ON MONTE CARLO SIMULATION METHOD A Thesis in Industrial Engineering and Operations
The Pennsylvania State University The Graduate School Department of Industrial Engineering AMERICAN-ASIAN OPTION PRICING BASED ON MONTE CARLO SIMULATION METHOD A Thesis in Industrial Engineering and Operations
MATH3075/3975 FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS TUTORIAL PROBLEMS
 MATH307/37 FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS TUTORIAL PROBLEMS School of Mathematics and Statistics Semester, 04 Tutorial problems should be used to test your mathematical skills and understanding of the lecture material.
MATH307/37 FINANCIAL MATHEMATICS TUTORIAL PROBLEMS School of Mathematics and Statistics Semester, 04 Tutorial problems should be used to test your mathematical skills and understanding of the lecture material.
Review for Quiz #2 Revised: October 31, 2015
 ECON-UB 233 Dave Backus @ NYU Review for Quiz #2 Revised: October 31, 2015 I ll focus again on the big picture to give you a sense of what we ve done and how it fits together. For each topic/result/concept,
ECON-UB 233 Dave Backus @ NYU Review for Quiz #2 Revised: October 31, 2015 I ll focus again on the big picture to give you a sense of what we ve done and how it fits together. For each topic/result/concept,
4: SINGLE-PERIOD MARKET MODELS
 4: SINGLE-PERIOD MARKET MODELS Marek Rutkowski School of Mathematics and Statistics University of Sydney Semester 2, 2016 M. Rutkowski (USydney) Slides 4: Single-Period Market Models 1 / 87 General Single-Period
4: SINGLE-PERIOD MARKET MODELS Marek Rutkowski School of Mathematics and Statistics University of Sydney Semester 2, 2016 M. Rutkowski (USydney) Slides 4: Single-Period Market Models 1 / 87 General Single-Period
Portfolio Choice. := δi j, the basis is orthonormal. Expressed in terms of the natural basis, x = j. x j x j,
 Portfolio Choice Let us model portfolio choice formally in Euclidean space. There are n assets, and the portfolio space X = R n. A vector x X is a portfolio. Even though we like to see a vector as coordinate-free,
Portfolio Choice Let us model portfolio choice formally in Euclidean space. There are n assets, and the portfolio space X = R n. A vector x X is a portfolio. Even though we like to see a vector as coordinate-free,
Recitation VI. Jiro E. Kondo
 Recitation VI Jiro E. Kondo Summer 2003 Today s Recitation: Capital Structure. I. MM Thm: Capital Structure Irrelevance. II. Taxes and Other Deviations from MM. 1 I. MM Theorem. A company is considering
Recitation VI Jiro E. Kondo Summer 2003 Today s Recitation: Capital Structure. I. MM Thm: Capital Structure Irrelevance. II. Taxes and Other Deviations from MM. 1 I. MM Theorem. A company is considering
Economics and Computation
 Economics and Computation ECON 425/563 and CPSC 455/555 Professor Dirk Bergemann and Professor Joan Feigenbaum Reputation Systems In case of any questions and/or remarks on these lecture notes, please
Economics and Computation ECON 425/563 and CPSC 455/555 Professor Dirk Bergemann and Professor Joan Feigenbaum Reputation Systems In case of any questions and/or remarks on these lecture notes, please
Stochastic Games and Bayesian Games
 Stochastic Games and Bayesian Games CPSC 532l Lecture 10 Stochastic Games and Bayesian Games CPSC 532l Lecture 10, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 Stochastic Games 3 Bayesian Games 4 Analyzing Bayesian
Stochastic Games and Bayesian Games CPSC 532l Lecture 10 Stochastic Games and Bayesian Games CPSC 532l Lecture 10, Slide 1 Lecture Overview 1 Recap 2 Stochastic Games 3 Bayesian Games 4 Analyzing Bayesian
Option Pricing. Chapter Discrete Time
 Chapter 7 Option Pricing 7.1 Discrete Time In the next section we will discuss the Black Scholes formula. To prepare for that, we will consider the much simpler problem of pricing options when there are
Chapter 7 Option Pricing 7.1 Discrete Time In the next section we will discuss the Black Scholes formula. To prepare for that, we will consider the much simpler problem of pricing options when there are
1.1 Interest rates Time value of money
 Lecture 1 Pre- Derivatives Basics Stocks and bonds are referred to as underlying basic assets in financial markets. Nowadays, more and more derivatives are constructed and traded whose payoffs depend on
Lecture 1 Pre- Derivatives Basics Stocks and bonds are referred to as underlying basic assets in financial markets. Nowadays, more and more derivatives are constructed and traded whose payoffs depend on
Introduction to Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes for Finance Lecture Notes
 Introduction to Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes for Finance Lecture Notes Fabio Trojani Department of Economics, University of St. Gallen, Switzerland Correspondence address: Fabio Trojani,
Introduction to Probability Theory and Stochastic Processes for Finance Lecture Notes Fabio Trojani Department of Economics, University of St. Gallen, Switzerland Correspondence address: Fabio Trojani,
BEM 103: Introduction to Finance. Homework 2: time and money
 BEM 03: Introduction to Finance. Homework 2: time and money Solutions October 5, 203. Financial Literacy Answer these questions in 3 steps. ( give an answer to the question, (2 look over the material assigned
BEM 03: Introduction to Finance. Homework 2: time and money Solutions October 5, 203. Financial Literacy Answer these questions in 3 steps. ( give an answer to the question, (2 look over the material assigned
Microeconomics III Final Exam SOLUTIONS 3/17/11. Muhamet Yildiz
 14.123 Microeconomics III Final Exam SOLUTIONS 3/17/11 Muhamet Yildiz Instructions. This is an open-book exam. You can use the results in the notes and the answers to the problem sets without proof, but
14.123 Microeconomics III Final Exam SOLUTIONS 3/17/11 Muhamet Yildiz Instructions. This is an open-book exam. You can use the results in the notes and the answers to the problem sets without proof, but
Beyond Modern Portfolio Theory to Modern Investment Technology. Contingent Claims Analysis and Life-Cycle Finance. December 27, 2007.
 Beyond Modern Portfolio Theory to Modern Investment Technology Contingent Claims Analysis and Life-Cycle Finance December 27, 2007 Zvi Bodie Doriana Ruffino Jonathan Treussard ABSTRACT This paper explores
Beyond Modern Portfolio Theory to Modern Investment Technology Contingent Claims Analysis and Life-Cycle Finance December 27, 2007 Zvi Bodie Doriana Ruffino Jonathan Treussard ABSTRACT This paper explores
Answer Key: Problem Set 4
 Answer Key: Problem Set 4 Econ 409 018 Fall A reminder: An equilibrium is characterized by a set of strategies. As emphasized in the class, a strategy is a complete contingency plan (for every hypothetical
Answer Key: Problem Set 4 Econ 409 018 Fall A reminder: An equilibrium is characterized by a set of strategies. As emphasized in the class, a strategy is a complete contingency plan (for every hypothetical
Modeling the Real Term Structure
 Modeling the Real Term Structure (Inflation Risk) Chris Telmer May 2013 1 / 23 Old school Old school Prices Goods? Real Return Real Interest Rate TIPS Real yields : Model The Fisher equation defines the
Modeling the Real Term Structure (Inflation Risk) Chris Telmer May 2013 1 / 23 Old school Old school Prices Goods? Real Return Real Interest Rate TIPS Real yields : Model The Fisher equation defines the
Department of Mathematics. Mathematics of Financial Derivatives
 Department of Mathematics MA408 Mathematics of Financial Derivatives Thursday 15th January, 2009 2pm 4pm Duration: 2 hours Attempt THREE questions MA408 Page 1 of 5 1. (a) Suppose 0 < E 1 < E 3 and E 2
Department of Mathematics MA408 Mathematics of Financial Derivatives Thursday 15th January, 2009 2pm 4pm Duration: 2 hours Attempt THREE questions MA408 Page 1 of 5 1. (a) Suppose 0 < E 1 < E 3 and E 2
The Binomial Model for Stock Options
 2 The Binomial Model for Stock Options 2.1 The Basic Model We now discuss a simple one-step binomial model in which we can determine the rational price today for a call option. In this model we have two
2 The Binomial Model for Stock Options 2.1 The Basic Model We now discuss a simple one-step binomial model in which we can determine the rational price today for a call option. In this model we have two
FINANCIAL OPTIMIZATION. Lecture 5: Dynamic Programming and a Visit to the Soft Side
 FINANCIAL OPTIMIZATION Lecture 5: Dynamic Programming and a Visit to the Soft Side Copyright c Philip H. Dybvig 2008 Dynamic Programming All situations in practice are more complex than the simple examples
FINANCIAL OPTIMIZATION Lecture 5: Dynamic Programming and a Visit to the Soft Side Copyright c Philip H. Dybvig 2008 Dynamic Programming All situations in practice are more complex than the simple examples
The Black Model and the Pricing of Options on Assets, Futures and Interest Rates. Richard Stapleton, Guenter Franke
 The Black Model and the Pricing of Options on Assets, Futures and Interest Rates Richard Stapleton, Guenter Franke September 23, 2005 Abstract The Black Model and the Pricing of Options We establish a
The Black Model and the Pricing of Options on Assets, Futures and Interest Rates Richard Stapleton, Guenter Franke September 23, 2005 Abstract The Black Model and the Pricing of Options We establish a
Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.997 Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.997 Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MATH 5510 Mathematical Models of Financial Derivatives. Topic 1 Risk neutral pricing principles under single-period securities models
 MATH 5510 Mathematical Models of Financial Derivatives Topic 1 Risk neutral pricing principles under single-period securities models 1.1 Law of one price and Arrow securities 1.2 No-arbitrage theory and
MATH 5510 Mathematical Models of Financial Derivatives Topic 1 Risk neutral pricing principles under single-period securities models 1.1 Law of one price and Arrow securities 1.2 No-arbitrage theory and
Basic Arbitrage Theory KTH Tomas Björk
 Basic Arbitrage Theory KTH 2010 Tomas Björk Tomas Björk, 2010 Contents 1. Mathematics recap. (Ch 10-12) 2. Recap of the martingale approach. (Ch 10-12) 3. Change of numeraire. (Ch 26) Björk,T. Arbitrage
Basic Arbitrage Theory KTH 2010 Tomas Björk Tomas Björk, 2010 Contents 1. Mathematics recap. (Ch 10-12) 2. Recap of the martingale approach. (Ch 10-12) 3. Change of numeraire. (Ch 26) Björk,T. Arbitrage
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES FINS 5574 FINANCIAL DECISION-MAKING UNDER UNCERTAINTY Instructor Dr. Pascal Nguyen Office: #3071 Email: pascal@unsw.edu.au Consultation hours: Friday 14:00 17:00 Appointments
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES FINS 5574 FINANCIAL DECISION-MAKING UNDER UNCERTAINTY Instructor Dr. Pascal Nguyen Office: #3071 Email: pascal@unsw.edu.au Consultation hours: Friday 14:00 17:00 Appointments
The text book to this class is available at
 The text book to this class is available at www.springer.com On the book's homepage at www.financial-economics.de there is further material available to this lecture, e.g. corrections and updates. Financial
The text book to this class is available at www.springer.com On the book's homepage at www.financial-economics.de there is further material available to this lecture, e.g. corrections and updates. Financial
Lecture 8: Asset pricing
 BURNABY SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY BRITISH COLUMBIA Paul Klein Office: WMC 3635 Phone: (778) 782-9391 Email: paul klein 2@sfu.ca URL: http://paulklein.ca/newsite/teaching/483.php Economics 483 Advanced Topics
BURNABY SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY BRITISH COLUMBIA Paul Klein Office: WMC 3635 Phone: (778) 782-9391 Email: paul klein 2@sfu.ca URL: http://paulklein.ca/newsite/teaching/483.php Economics 483 Advanced Topics
So we turn now to many-to-one matching with money, which is generally seen as a model of firms hiring workers
 Econ 805 Advanced Micro Theory I Dan Quint Fall 2009 Lecture 20 November 13 2008 So far, we ve considered matching markets in settings where there is no money you can t necessarily pay someone to marry
Econ 805 Advanced Micro Theory I Dan Quint Fall 2009 Lecture 20 November 13 2008 So far, we ve considered matching markets in settings where there is no money you can t necessarily pay someone to marry
Stochastic Finance - A Numeraire Approach
 Stochastic Finance - A Numeraire Approach Stochastické modelování v ekonomii a financích 28th November and 5th December 2011 1 Motivation for Numeraire Approach 1 Motivation for Numeraire Approach 2 1
Stochastic Finance - A Numeraire Approach Stochastické modelování v ekonomii a financích 28th November and 5th December 2011 1 Motivation for Numeraire Approach 1 Motivation for Numeraire Approach 2 1
Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.997 Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 15.997 Practice of Finance: Advanced Corporate Risk Management Spring 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
INTRODUCTION TO ARBITRAGE PRICING OF FINANCIAL DERIVATIVES
 INTRODUCTION TO ARBITRAGE PRICING OF FINANCIAL DERIVATIVES Marek Rutkowski Faculty of Mathematics and Information Science Warsaw University of Technology 00-661 Warszawa, Poland 1 Call and Put Spot Options
INTRODUCTION TO ARBITRAGE PRICING OF FINANCIAL DERIVATIVES Marek Rutkowski Faculty of Mathematics and Information Science Warsaw University of Technology 00-661 Warszawa, Poland 1 Call and Put Spot Options
Lecture Notes 1
 4.45 Lecture Notes Guido Lorenzoni Fall 2009 A portfolio problem To set the stage, consider a simple nite horizon problem. A risk averse agent can invest in two assets: riskless asset (bond) pays gross
4.45 Lecture Notes Guido Lorenzoni Fall 2009 A portfolio problem To set the stage, consider a simple nite horizon problem. A risk averse agent can invest in two assets: riskless asset (bond) pays gross
The Birth of Financial Bubbles
 The Birth of Financial Bubbles Philip Protter, Cornell University Finance and Related Mathematical Statistics Issues Kyoto Based on work with R. Jarrow and K. Shimbo September 3-6, 2008 Famous bubbles
The Birth of Financial Bubbles Philip Protter, Cornell University Finance and Related Mathematical Statistics Issues Kyoto Based on work with R. Jarrow and K. Shimbo September 3-6, 2008 Famous bubbles
- Introduction to Mathematical Finance -
 - Introduction to Mathematical Finance - Lecture Notes by Ulrich Horst The objective of this course is to give an introduction to the probabilistic techniques required to understand the most widely used
- Introduction to Mathematical Finance - Lecture Notes by Ulrich Horst The objective of this course is to give an introduction to the probabilistic techniques required to understand the most widely used
Optimal Debt Contracts
 Optimal Debt Contracts David Andolfatto February 2008 1 Introduction As an introduction, you should read Why is There Debt, by Lacker (1991). As Lackernotes,thestrikingfeatureofadebtcontractisthatdebtpaymentsare
Optimal Debt Contracts David Andolfatto February 2008 1 Introduction As an introduction, you should read Why is There Debt, by Lacker (1991). As Lackernotes,thestrikingfeatureofadebtcontractisthatdebtpaymentsare
4 Martingales in Discrete-Time
 4 Martingales in Discrete-Time Suppose that (Ω, F, P is a probability space. Definition 4.1. A sequence F = {F n, n = 0, 1,...} is called a filtration if each F n is a sub-σ-algebra of F, and F n F n+1
4 Martingales in Discrete-Time Suppose that (Ω, F, P is a probability space. Definition 4.1. A sequence F = {F n, n = 0, 1,...} is called a filtration if each F n is a sub-σ-algebra of F, and F n F n+1
DRAFT. 1 exercise in state (S, t), π(s, t) = 0 do not exercise in state (S, t) Review of the Risk Neutral Stock Dynamics
 Chapter 12 American Put Option Recall that the American option has strike K and maturity T and gives the holder the right to exercise at any time in [0, T ]. The American option is not straightforward
Chapter 12 American Put Option Recall that the American option has strike K and maturity T and gives the holder the right to exercise at any time in [0, T ]. The American option is not straightforward
Dynamic Portfolio Choice II
 Dynamic Portfolio Choice II Dynamic Programming Leonid Kogan MIT, Sloan 15.450, Fall 2010 c Leonid Kogan ( MIT, Sloan ) Dynamic Portfolio Choice II 15.450, Fall 2010 1 / 35 Outline 1 Introduction to Dynamic
Dynamic Portfolio Choice II Dynamic Programming Leonid Kogan MIT, Sloan 15.450, Fall 2010 c Leonid Kogan ( MIT, Sloan ) Dynamic Portfolio Choice II 15.450, Fall 2010 1 / 35 Outline 1 Introduction to Dynamic
Integrating rational functions (Sect. 8.4)
 Integrating rational functions (Sect. 8.4) Integrating rational functions, p m(x) q n (x). Polynomial division: p m(x) The method of partial fractions. p (x) (x r )(x r 2 ) p (n )(x). (Repeated roots).
Integrating rational functions (Sect. 8.4) Integrating rational functions, p m(x) q n (x). Polynomial division: p m(x) The method of partial fractions. p (x) (x r )(x r 2 ) p (n )(x). (Repeated roots).
Slides III - Complete Markets
 Slides III - Complete Markets Julio Garín University of Georgia Macroeconomic Theory II (Ph.D.) Spring 2017 Macroeconomic Theory II Slides III - Complete Markets Spring 2017 1 / 33 Outline 1. Risk, Uncertainty,
Slides III - Complete Markets Julio Garín University of Georgia Macroeconomic Theory II (Ph.D.) Spring 2017 Macroeconomic Theory II Slides III - Complete Markets Spring 2017 1 / 33 Outline 1. Risk, Uncertainty,
Ph.D. Preliminary Examination MICROECONOMIC THEORY Applied Economics Graduate Program August 2017
 Ph.D. Preliminary Examination MICROECONOMIC THEORY Applied Economics Graduate Program August 2017 The time limit for this exam is four hours. The exam has four sections. Each section includes two questions.
Ph.D. Preliminary Examination MICROECONOMIC THEORY Applied Economics Graduate Program August 2017 The time limit for this exam is four hours. The exam has four sections. Each section includes two questions.
Infinitely Repeated Games
 February 10 Infinitely Repeated Games Recall the following theorem Theorem 72 If a game has a unique Nash equilibrium, then its finite repetition has a unique SPNE. Our intuition, however, is that long-term
February 10 Infinitely Repeated Games Recall the following theorem Theorem 72 If a game has a unique Nash equilibrium, then its finite repetition has a unique SPNE. Our intuition, however, is that long-term
ECON 301: General Equilibrium V (Public Goods) 1. Intermediate Microeconomics II, ECON 301. General Equilibrium V: Public Goods
 ECON 301: General Equilibrium V (Public Goods) 1 Intermediate Microeconomics II, ECON 301 General Equilibrium V: Public Goods In our last discussion on externality, we found that as long as property rights
ECON 301: General Equilibrium V (Public Goods) 1 Intermediate Microeconomics II, ECON 301 General Equilibrium V: Public Goods In our last discussion on externality, we found that as long as property rights
Introduction Random Walk One-Period Option Pricing Binomial Option Pricing Nice Math. Binomial Models. Christopher Ting.
 Binomial Models Christopher Ting Christopher Ting http://www.mysmu.edu/faculty/christophert/ : christopherting@smu.edu.sg : 6828 0364 : LKCSB 5036 October 14, 2016 Christopher Ting QF 101 Week 9 October
Binomial Models Christopher Ting Christopher Ting http://www.mysmu.edu/faculty/christophert/ : christopherting@smu.edu.sg : 6828 0364 : LKCSB 5036 October 14, 2016 Christopher Ting QF 101 Week 9 October
October An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution.
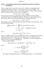 October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
October 13..18.4 An Equilibrium of the First Price Sealed Bid Auction for an Arbitrary Distribution. We now assume that the reservation values of the bidders are independently and identically distributed
ADVANCED MACROECONOMIC TECHNIQUES NOTE 6a
 316-406 ADVANCED MACROECONOMIC TECHNIQUES NOTE 6a Chris Edmond hcpedmond@unimelb.edu.aui Introduction to consumption-based asset pricing We will begin our brief look at asset pricing with a review of the
316-406 ADVANCED MACROECONOMIC TECHNIQUES NOTE 6a Chris Edmond hcpedmond@unimelb.edu.aui Introduction to consumption-based asset pricing We will begin our brief look at asset pricing with a review of the
Help Session 7. David Sovich. Washington University in St. Louis
 Help Session 7 Davi Sovich Washington University in St. Louis TODAY S AGENDA Toay we will learn how to price using Arrow securities We will then erive Q using Arrow securities ARROW SECURITIES IN THE BINOMIAL
Help Session 7 Davi Sovich Washington University in St. Louis TODAY S AGENDA Toay we will learn how to price using Arrow securities We will then erive Q using Arrow securities ARROW SECURITIES IN THE BINOMIAL
Socially-Optimal Design of Crowdsourcing Platforms with Reputation Update Errors
 Socially-Optimal Design of Crowdsourcing Platforms with Reputation Update Errors 1 Yuanzhang Xiao, Yu Zhang, and Mihaela van der Schaar Abstract Crowdsourcing systems (e.g. Yahoo! Answers and Amazon Mechanical
Socially-Optimal Design of Crowdsourcing Platforms with Reputation Update Errors 1 Yuanzhang Xiao, Yu Zhang, and Mihaela van der Schaar Abstract Crowdsourcing systems (e.g. Yahoo! Answers and Amazon Mechanical
Stochastic Manufacturing & Service Systems. Discrete-time Markov Chain
 ISYE 33 B, Fall Week #7, September 9-October 3, Introduction Stochastic Manufacturing & Service Systems Xinchang Wang H. Milton Stewart School of Industrial and Systems Engineering Georgia Institute of
ISYE 33 B, Fall Week #7, September 9-October 3, Introduction Stochastic Manufacturing & Service Systems Xinchang Wang H. Milton Stewart School of Industrial and Systems Engineering Georgia Institute of
Lecture 16: Delta Hedging
 Lecture 16: Delta Hedging We are now going to look at the construction of binomial trees as a first technique for pricing options in an approximative way. These techniques were first proposed in: J.C.
Lecture 16: Delta Hedging We are now going to look at the construction of binomial trees as a first technique for pricing options in an approximative way. These techniques were first proposed in: J.C.
Dynamic Asset Pricing Model
 Econometric specifications University of Pavia March 2, 2007 Outline 1 Introduction 2 3 of Excess Returns DAPM is refutable empirically if it restricts the joint distribution of the observable asset prices
Econometric specifications University of Pavia March 2, 2007 Outline 1 Introduction 2 3 of Excess Returns DAPM is refutable empirically if it restricts the joint distribution of the observable asset prices
Regret Minimization and Security Strategies
 Chapter 5 Regret Minimization and Security Strategies Until now we implicitly adopted a view that a Nash equilibrium is a desirable outcome of a strategic game. In this chapter we consider two alternative
Chapter 5 Regret Minimization and Security Strategies Until now we implicitly adopted a view that a Nash equilibrium is a desirable outcome of a strategic game. In this chapter we consider two alternative
1 Two Period Exchange Economy
 University of British Columbia Department of Economics, Macroeconomics (Econ 502) Prof. Amartya Lahiri Handout # 2 1 Two Period Exchange Economy We shall start our exploration of dynamic economies with
University of British Columbia Department of Economics, Macroeconomics (Econ 502) Prof. Amartya Lahiri Handout # 2 1 Two Period Exchange Economy We shall start our exploration of dynamic economies with
