Chapter 7. Random Variables
|
|
|
- Julian Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 7 Random Variables
2 Making quantifiable meaning out of categorical data Toss three coins. What does the sample space consist of? HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, TTT, TTH, THT, THH In statistics, we are most interested in numerical outcomes. I don t see any numbers here how could we explore patterns and make predictions when the sample space doesn t seem to be numerical?
3 Two types of Random Variable Probability Models Random Variable Probability Models: 1. Each probability is between 0 and 1 2. The sum of the probabilities of all events is 1. Discrete Variable: Has a countable number of possible values (aka outcomes = X = integers) Continuous Variable: Takes all values in an interval of numbers (aka outcomes = X = any value)
4 First type of random variable probability model: Discrete variables Discrete Variables Probability Distribution organized in table Probabilities of each outcome plotted in histogram X: define outcome All listed here P(X) Corresponding listed here X-axis outcomes, Y-axis Probability
5 Example 1: Create the probability distribution for the sum when two dice are tossed. Create a histogram of these results.
6 Example 2: NHL Goals In 2010, there were 1319 games played in the National Hockey League s regular season. Imagine selecting one of these games at random and then randomly selecting one of the two teams that played in the game. Define the random variable X = number of goals scored by a randomly selected team in a randomly selected game. The table below gives the probability distribution of X: Goals: Probabilit y a. Show that the probability distribution for X is legitimate. b. Make a histogram of the probability distribution. Describe what you see. c. What is the probability that the number of goals scored by a randomly selected team in a randomly selected game is at least 6?
7 Example 2 Answers (a) Show that the probability distribution for X is legitimate. Sum should be 1 (b) Make a histogram of the probability distribution. Describe what you see. Skewed right Most of the time, 2-3 goals are made per game Scoring 8-9 goals is rare (c) What is the probability that the number of goals scored by a randomly selected team in a randomly selected game is at least 6? P(X 6) = = 0.061
8 Mean, or expected value, of Discrete Random Variables Mean of a sample is X bar; Mean of a probability distribution is μ x Mean of random variable x has to take into consideration that all outcomes are not equally likely Each outcome is weighted by its probability
9 Example 3: Mean of rolling a pair of dice Based on the probability distribution from Example 1, calculate the mean sum when rolling a pair of dice μ x = 10.5 The mean of a random variable is the longrun average value of the variable after many repetitions of the chance process. So in this case, if two dice are infinitely tossed the sum would average to be _applet_11_largenums.html
10 Law of Large Numbers The law of large numbers says that with the increase of trials, the actual mean outcome will get closer and closer to μ. The law doesn t say how many trials are needed; it depends on the variability of the random outcomes. The more variable the outcomes, the more trials are needed to ensure the computed mean is close to the theoretical.
11 In Gambling It is because of the Law of Large numbers that the house always wins. There seems to be unpredictability for the gambler, who can afford a handful of bets to play. To him/her, the thrill of the unexpected can be enticing. The house, on the other hand, has thousands and thousands of bets/trials daily, and knows the expected mean of each game s distribution. Though the individual games may vary, over the course of these thousands of bets, they can predict how much money they will make/gamblers will lose.
12 Example 4: Winning and Losing at Roulette There are 38 slots numbered 1 through 36, plus 0 and 00. Half of the slots are red, the other half are black, and 0 and 00 are green. A player places a $1 bet on red. If the ball lands in a red slot, the player gets the original dollar back, plus an additional dollar. If the ball lands on a differentcolored slot, the player loses the dollar bet. What is the player s average gain?
13 What s the player s average gain? a. What are the possible outcomes for this scenario? Lose a dollar, win a dollar b. What are the probabilities with each of these outcomes? 20/38, 18/38 c. To find the average gain, it s not just the average of the two outcomes, since it s more likely that a player will lose a dollar than gain a dollar. In the long-run, the player gains a dollar 18 times out of every 38 games played, and loses $1 the other 20 times. So to calculate the average gain, find the expected value. What do you get? -$0.05: in the long run, the player loses (and the casino gains) five cents per bet.
14 Variance of a discrete random Variable Variance of a random variable X notated as σ 2 x (different from variance of a sample which is notated as s 2 ). Just like with a set of data, variance is found by subtracting the value of the mean from each outcome, square that difference, and take the square root if you want to find standard deviation. In probability distributions, the difference is multiplied by its corresponding probability.
15 Using your TI s to find mean and variance of probability distribution 1. Enter the values of the random variable in L1 2. Enter corresponding probabilities in L2 3. You can make a histogram with Xlist= L1 and Freq: L2 4. To calculate the mean and standard deviation, use command 1-Var Stats L1, L2
16 Practice! Example 5: NHL Goals In 2010, there were 1319 games played in the National Hockey League s regular season. Imagine selecting one of these games at random and then randomly selecting one of the two teams that played in the game. Define the random variable X = number of goals scored by a randomly selected team in a randomly selected game. The table below gives the probability distribution of X: Goals: Probabilit y d. Find and interpret the mean of the random variable X in context. e. Find and interpret the standard deviation of the random variable X in context.
17 Practice Solutions d. Find and interpret the mean of the random variable X in context. The mean njmber of goals for a randomly selected team in a randomly selected game is (If you were to repeat the process over and over again, the mean number of goals scored would be about in the long run.) e. Find and interpret the standard deviation of the random variable X in context. On average, a randomly selected team s number of goals in a randomly selected game will differ from the mean by about 1.63 goals.
18 Second type of random variable probability model: Continuous variables Random Variable Probability Models Discrete Variable: Continuous Variable: Takes all values in an interval of numbers Because it covers an interval of numbers, X can assume any value within those boundaries, and cannot be organized in a table Probability distribution of X is described by a density curve; the probability of any event is the area under the density curve and above the values of X.
19 Using Density Curves to calculate probability The event displayed (the shaded area) is finding the probability of selecting a random number between 0 and 1; Example 6: Draw a similar diagram to accompany finding P(0.3 X < 0.7.)
20 Differences between variables 1. Probability model for a continuous variable assigns probabilities to INTERVALS of outcomes- not individual outcomes! With continuous random variables, there is no such thing as finding the probability of x = 8. You can find the probability of x > 8 or x 8, but finding the probability of when x = 8 will be zero. This is because with continuous random variables, to find the probability you find area under the curve, and there is no real area for a single value on a curve. 2. We can ignore the distinction between > and in continuous but not discrete variables. Because of the insignificance of a single value among an interval for continuous variables, finding P(x > 8 ) and P(x 8) is indistinguishably different.
21 Normal Distributions The density curve we are most familiar with is a Normal Curve. Remember z = (x-μ)/σ Remember Z-score interprets data as the number of standard deviations above or below the mean. Remember by interpreting any data as a z-score, you can find the area under a normal distribution curve, which equates to probability of data being within these values. Remember N(μ, σ) is our notation for a normal distribution. Remember the mean is the point at which the area under the density curve would balance if it were made out of solid material (center if symmetrical)
22 Example 6: Cheating in School The true population probability that a student will report on another cheating student is 12% Based on a survey of 400 random students, done many times, we expect the average probability to get close to this 0.12 value. (with a standard deviation of 0.016) What is the probability that if I conduct a survey my result will be within the true probability by 2%?
23 Solution Example 6 Draw a diagram Use the given values (that μ=0.12, σ=0.016, and x = 0.10 and 0.14) to interpret these as z-scores. Beyonce will help you find the areas associated with each z-score. Based on the areas you find, determine the desired area to help you answer the question. If the result is less than.10 or greater than.14 P(From table A), P(-1.25 Z 1.25) = and Subtract areas = = % chance that a survey will produce a result within the true probability by 2%.
24 Example 7: Heights of women The heights of young women closely follow the normal distribution with mean μ= 64 inches and standard deviation σ=2.7 inches. If a young woman is chosen at random, find the probability that the chosen woman is between 68 and 70 inches tall. Solution: draw a diagram. There s about a 5.6% chance that a randomly chosen young woman has a height between 68 and 70 inches.
Random Variables. 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. Probability Distribution. Discrete Random Variables. Chapter 6, Section 1
 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables Random Variables A random variable, usually written as X, is a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. There are two types
6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables Random Variables A random variable, usually written as X, is a variable whose possible values are numerical outcomes of a random phenomenon. There are two types
HHH HHT HTH THH HTT THT TTH TTT
 AP Statistics Name Unit 04 Probability Period Day 05 Notes Discrete & Continuous Random Variables Random Variable: Probability Distribution: Example: A probability model describes the possible outcomes
AP Statistics Name Unit 04 Probability Period Day 05 Notes Discrete & Continuous Random Variables Random Variable: Probability Distribution: Example: A probability model describes the possible outcomes
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables
 CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Discrete and Continuous Random
CHAPTER 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 5th Edition Starnes, Tabor, Yates, Moore Bedford Freeman Worth Publishers Discrete and Continuous Random
Chapter 6: Random Variables
 Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous
Chapter 6: Random Variables Section 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE Chapter 6 Random Variables 6.1 Discrete and Continuous
6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. 6.1A Discrete random Variables, Mean (Expected Value) of a Discrete Random Variable
 6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6.1A Discrete random Variables, Mean (Expected Value) of a Discrete Random Variable Random variable Takes numerical values that describe the outcomes of some
6.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 6.1A Discrete random Variables, Mean (Expected Value) of a Discrete Random Variable Random variable Takes numerical values that describe the outcomes of some
6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables. Nov 4 6:53 PM. Objectives
 6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables examples vocab Objectives Today we will... - Compute probabilities using the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. - Calculate and interpret
6.1 Discrete & Continuous Random Variables examples vocab Objectives Today we will... - Compute probabilities using the probability distribution of a discrete random variable. - Calculate and interpret
Part V - Chance Variability
 Part V - Chance Variability Dr. Joseph Brennan Math 148, BU Dr. Joseph Brennan (Math 148, BU) Part V - Chance Variability 1 / 78 Law of Averages In Chapter 13 we discussed the Kerrich coin-tossing experiment.
Part V - Chance Variability Dr. Joseph Brennan Math 148, BU Dr. Joseph Brennan (Math 148, BU) Part V - Chance Variability 1 / 78 Law of Averages In Chapter 13 we discussed the Kerrich coin-tossing experiment.
CHAPTER 10: Introducing Probability
 CHAPTER 10: Introducing Probability The Basic Practice of Statistics 6 th Edition Moore / Notz / Fligner Lecture PowerPoint Slides Chapter 10 Concepts 2 The Idea of Probability Probability Models Probability
CHAPTER 10: Introducing Probability The Basic Practice of Statistics 6 th Edition Moore / Notz / Fligner Lecture PowerPoint Slides Chapter 10 Concepts 2 The Idea of Probability Probability Models Probability
Econ 6900: Statistical Problems. Instructor: Yogesh Uppal
 Econ 6900: Statistical Problems Instructor: Yogesh Uppal Email: yuppal@ysu.edu Lecture Slides 4 Random Variables Probability Distributions Discrete Distributions Discrete Uniform Probability Distribution
Econ 6900: Statistical Problems Instructor: Yogesh Uppal Email: yuppal@ysu.edu Lecture Slides 4 Random Variables Probability Distributions Discrete Distributions Discrete Uniform Probability Distribution
Math 14 Lecture Notes Ch Mean
 4. Mean, Expected Value, and Standard Deviation Mean Recall the formula from section. for find the population mean of a data set of elements µ = x 1 + x + x +!+ x = x i i=1 We can find the mean of the
4. Mean, Expected Value, and Standard Deviation Mean Recall the formula from section. for find the population mean of a data set of elements µ = x 1 + x + x +!+ x = x i i=1 We can find the mean of the
MA 1125 Lecture 14 - Expected Values. Wednesday, October 4, Objectives: Introduce expected values.
 MA 5 Lecture 4 - Expected Values Wednesday, October 4, 27 Objectives: Introduce expected values.. Means, Variances, and Standard Deviations of Probability Distributions Two classes ago, we computed the
MA 5 Lecture 4 - Expected Values Wednesday, October 4, 27 Objectives: Introduce expected values.. Means, Variances, and Standard Deviations of Probability Distributions Two classes ago, we computed the
Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379
 Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Overview 6.1 Discrete
Statistical Methods in Practice STAT/MATH 3379 Dr. A. B. W. Manage Associate Professor of Mathematics & Statistics Department of Mathematics & Statistics Sam Houston State University Overview 6.1 Discrete
+ Chapter 7. Random Variables. Chapter 7: Random Variables 2/26/2015. Transforming and Combining Random Variables
 + Chapter 7: Random Variables Section 7.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE + Chapter 7 Random Variables 7.1 7.2 7.2 Discrete
+ Chapter 7: Random Variables Section 7.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables The Practice of Statistics, 4 th edition For AP* STARNES, YATES, MOORE + Chapter 7 Random Variables 7.1 7.2 7.2 Discrete
Chapter 4. Section 4.1 Objectives. Random Variables. Random Variables. Chapter 4: Probability Distributions
 Chapter 4: Probability s 4. Probability s 4. Binomial s Section 4. Objectives Distinguish between discrete random variables and continuous random variables Construct a discrete probability distribution
Chapter 4: Probability s 4. Probability s 4. Binomial s Section 4. Objectives Distinguish between discrete random variables and continuous random variables Construct a discrete probability distribution
Part 1 In which we meet the law of averages. The Law of Averages. The Expected Value & The Standard Error. Where Are We Going?
 1 The Law of Averages The Expected Value & The Standard Error Where Are We Going? Sums of random numbers The law of averages Box models for generating random numbers Sums of draws: the Expected Value Standard
1 The Law of Averages The Expected Value & The Standard Error Where Are We Going? Sums of random numbers The law of averages Box models for generating random numbers Sums of draws: the Expected Value Standard
4.2 Probability Distributions
 4.2 Probability Distributions Definition. A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon. The probability distribution of a random variable tells us what the
4.2 Probability Distributions Definition. A random variable is a variable whose value is a numerical outcome of a random phenomenon. The probability distribution of a random variable tells us what the
Lesson 97 - Binomial Distributions IBHL2 - SANTOWSKI
 Lesson 97 - Binomial Distributions IBHL2 - SANTOWSKI Opening Exercise: Example #: (a) Use a tree diagram to answer the following: You throwing a bent coin 3 times where P(H) = / (b) THUS, find the probability
Lesson 97 - Binomial Distributions IBHL2 - SANTOWSKI Opening Exercise: Example #: (a) Use a tree diagram to answer the following: You throwing a bent coin 3 times where P(H) = / (b) THUS, find the probability
Opening Exercise: Lesson 91 - Binomial Distributions IBHL2 - SANTOWSKI
 08-0- Lesson 9 - Binomial Distributions IBHL - SANTOWSKI Opening Exercise: Example #: (a) Use a tree diagram to answer the following: You throwing a bent coin times where P(H) = / (b) THUS, find the probability
08-0- Lesson 9 - Binomial Distributions IBHL - SANTOWSKI Opening Exercise: Example #: (a) Use a tree diagram to answer the following: You throwing a bent coin times where P(H) = / (b) THUS, find the probability
Probability & Sampling The Practice of Statistics 4e Mostly Chpts 5 7
 Probability & Sampling The Practice of Statistics 4e Mostly Chpts 5 7 Lew Davidson (Dr.D.) Mallard Creek High School Lewis.Davidson@cms.k12.nc.us 704-786-0470 Probability & Sampling The Practice of Statistics
Probability & Sampling The Practice of Statistics 4e Mostly Chpts 5 7 Lew Davidson (Dr.D.) Mallard Creek High School Lewis.Davidson@cms.k12.nc.us 704-786-0470 Probability & Sampling The Practice of Statistics
Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables (1)
 Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables (1) STT 315: Section 201 Instructor: Abdhi Sarkar Acknowledgement: I d like to thank Dr. Ashoke Sinha for allowing me to use and edit the slides.
Statistics for Business and Economics: Random Variables (1) STT 315: Section 201 Instructor: Abdhi Sarkar Acknowledgement: I d like to thank Dr. Ashoke Sinha for allowing me to use and edit the slides.
TOPIC: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 TOPIC: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS There are two types of random variables: A Discrete random variable can take on only specified, distinct values. A Continuous random variable can take on any value within
TOPIC: PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS There are two types of random variables: A Discrete random variable can take on only specified, distinct values. A Continuous random variable can take on any value within
Sec$on 6.1: Discrete and Con.nuous Random Variables. Tuesday, November 14 th, 2017
 Sec$on 6.1: Discrete and Con.nuous Random Variables Tuesday, November 14 th, 2017 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: ü COMPUTE probabilities
Sec$on 6.1: Discrete and Con.nuous Random Variables Tuesday, November 14 th, 2017 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables Learning Objectives After this section, you should be able to: ü COMPUTE probabilities
In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure. mean variance standard deviation
 Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
Name In a binomial experiment of n trials, where p = probability of success and q = probability of failure mean variance standard deviation µ = n p σ = n p q σ = n p q Notation X ~ B(n, p) The probability
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic Probability Distributions: Binomial and Poisson Distributions Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic Probability Distributions: Binomial and Poisson Distributions Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College
X = x p(x) 1 / 6 1 / 6 1 / 6 1 / 6 1 / 6 1 / 6. x = 1 x = 2 x = 3 x = 4 x = 5 x = 6 values for the random variable X
 Calculus II MAT 146 Integration Applications: Probability Calculating probabilities for discrete cases typically involves comparing the number of ways a chosen event can occur to the number of ways all
Calculus II MAT 146 Integration Applications: Probability Calculating probabilities for discrete cases typically involves comparing the number of ways a chosen event can occur to the number of ways all
Chapter 6 Section 1 Day s.notebook. April 29, Honors Statistics. Aug 23-8:26 PM. 3. Review OTL C6#2. Aug 23-8:31 PM
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#2 Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Apr 27-9:20 AM Jan 18-2:13 PM 2 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 3 Ask about 1 and
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM 3. Review OTL C6#2 Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Apr 27-9:20 AM Jan 18-2:13 PM 2 Nov 27-10:28 PM 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 6.9 6.10 6.11 6.12 Nov 27-9:53 PM 3 Ask about 1 and
Examples: Random Variables. Discrete and Continuous Random Variables. Probability Distributions
 Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
Random Variables Examples: Random variable a variable (typically represented by x) that takes a numerical value by chance. Number of boys in a randomly selected family with three children. Possible values:
STAT 201 Chapter 6. Distribution
 STAT 201 Chapter 6 Distribution 1 Random Variable We know variable Random Variable: a numerical measurement of the outcome of a random phenomena Capital letter refer to the random variable Lower case letters
STAT 201 Chapter 6 Distribution 1 Random Variable We know variable Random Variable: a numerical measurement of the outcome of a random phenomena Capital letter refer to the random variable Lower case letters
Probability mass function; cumulative distribution function
 PHP 2510 Random variables; some discrete distributions Random variables - what are they? Probability mass function; cumulative distribution function Some discrete random variable models: Bernoulli Binomial
PHP 2510 Random variables; some discrete distributions Random variables - what are they? Probability mass function; cumulative distribution function Some discrete random variable models: Bernoulli Binomial
Chapter 5 Basic Probability
 Chapter 5 Basic Probability Probability is determining the probability that a particular event will occur. Probability of occurrence = / T where = the number of ways in which a particular event occurs
Chapter 5 Basic Probability Probability is determining the probability that a particular event will occur. Probability of occurrence = / T where = the number of ways in which a particular event occurs
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions. Outline. Outline
 Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
Outline Lecture 9 Probability Distributions 6-1 Introduction 6- Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7- Properties of the Normal Distribution
expected value of X, and describes the long-run average outcome. It is a weighted average.
 X The mean of a set of observations is their ordinary average, whereas the mean of a random variable X is an average of the possible values of X The mean of a random variable X is often called the expected
X The mean of a set of observations is their ordinary average, whereas the mean of a random variable X is an average of the possible values of X The mean of a random variable X is often called the expected
Lecture 9. Probability Distributions
 Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Lecture 9 Probability Distributions Outline 6-1 Introduction 6-2 Probability Distributions 6-3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation 6-4 The Binomial Distribution Outline 7-2 Properties of the Normal Distribution
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section Distributions of Random Variables
 Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 8.1 - Distributions of Random Variables Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section Random Variables and Histograms
 Section 3.1 - Random Variables and Histograms Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Section 3.1 - Random Variables and Histograms Definition: A random variable is a rule that assigns a number to each outcome of an experiment. Example 1: Suppose we toss a coin three times. Then we could
Chapter 7: Random Variables
 Chapter 7: Random Variables 7.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 7.2 Means and Variances of Random Variables 1 Introduction A random variable is a function that associates a unique numerical value
Chapter 7: Random Variables 7.1 Discrete and Continuous Random Variables 7.2 Means and Variances of Random Variables 1 Introduction A random variable is a function that associates a unique numerical value
Mean, Variance, and Expectation. Mean
 3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation The mean, variance, and standard deviation for a probability distribution are computed differently from the mean, variance, and standard deviation for samples. This section
3 Mean, Variance, and Expectation The mean, variance, and standard deviation for a probability distribution are computed differently from the mean, variance, and standard deviation for samples. This section
Discrete Random Variables
 Discrete Random Variables MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives During this lesson we will learn to: distinguish between discrete and continuous
Discrete Random Variables MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives During this lesson we will learn to: distinguish between discrete and continuous
Discrete Random Variables
 Discrete Random Variables MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Objectives During this lesson we will learn to: distinguish between discrete and continuous
Discrete Random Variables MATH 130, Elements of Statistics I J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2017 Objectives During this lesson we will learn to: distinguish between discrete and continuous
Simple Random Sample
 Simple Random Sample A simple random sample (SRS) of size n consists of n elements from the population chosen in such a way that every set of n elements has an equal chance to be the sample actually selected.
Simple Random Sample A simple random sample (SRS) of size n consists of n elements from the population chosen in such a way that every set of n elements has an equal chance to be the sample actually selected.
The binomial distribution
 The binomial distribution The coin toss - three coins The coin toss - four coins The binomial probability distribution Rolling dice Using the TI nspire Graph of binomial distribution Mean & standard deviation
The binomial distribution The coin toss - three coins The coin toss - four coins The binomial probability distribution Rolling dice Using the TI nspire Graph of binomial distribution Mean & standard deviation
Binomial Random Variable - The count X of successes in a binomial setting
 6.3.1 Binomial Settings and Binomial Random Variables What do the following scenarios have in common? Toss a coin 5 times. Count the number of heads. Spin a roulette wheel 8 times. Record how many times
6.3.1 Binomial Settings and Binomial Random Variables What do the following scenarios have in common? Toss a coin 5 times. Count the number of heads. Spin a roulette wheel 8 times. Record how many times
Statistics for IT Managers
 Statistics for IT Managers 95-796, Fall 212 Course Overview Instructor: Daniel B. Neill (neill@cs.cmu.edu) TAs: Eli (Han) Liu, Kats Sasanuma, Sriram Somanchi, Skyler Speakman, Quan Wang, Yiye Zhang (see
Statistics for IT Managers 95-796, Fall 212 Course Overview Instructor: Daniel B. Neill (neill@cs.cmu.edu) TAs: Eli (Han) Liu, Kats Sasanuma, Sriram Somanchi, Skyler Speakman, Quan Wang, Yiye Zhang (see
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS
 FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
FINAL REVIEW W/ANSWERS ( 03/15/08 - Sharon Coates) Concepts to review before answering the questions: A population consists of the entire group of people or objects of interest to an investigator, while
Mathacle. PSet Stats, Concepts In Statistics Level Number Name: Date: Distribution Distribute in anyway but normal
 Distribution Distribute in anyway but normal VI. DISTRIBUTION A probability distribution is a mathematical function that provides the probabilities of occurrence of all distinct outcomes in the sample
Distribution Distribute in anyway but normal VI. DISTRIBUTION A probability distribution is a mathematical function that provides the probabilities of occurrence of all distinct outcomes in the sample
CHAPTER 4 DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
 CHAPTER 4 DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS A random variable is the description of the outcome of an experiment in words. The verbal description of a random variable tells you how to find or calculate
CHAPTER 4 DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS A random variable is the description of the outcome of an experiment in words. The verbal description of a random variable tells you how to find or calculate
Review of commonly missed questions on the online quiz. Lecture 7: Random variables] Expected value and standard deviation. Let s bet...
![Review of commonly missed questions on the online quiz. Lecture 7: Random variables] Expected value and standard deviation. Let s bet... Review of commonly missed questions on the online quiz. Lecture 7: Random variables] Expected value and standard deviation. Let s bet...](/thumbs/83/87696499.jpg) Recap Review of commonly missed questions on the online quiz Lecture 7: ] Statistics 101 Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel OpenIntro quiz 2: questions 4 and 5 September 20, 2011 Statistics 101 (Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel)
Recap Review of commonly missed questions on the online quiz Lecture 7: ] Statistics 101 Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel OpenIntro quiz 2: questions 4 and 5 September 20, 2011 Statistics 101 (Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel)
Theoretical Foundations
 Theoretical Foundations Probabilities Monia Ranalli monia.ranalli@uniroma2.it Ranalli M. Theoretical Foundations - Probabilities 1 / 27 Objectives understand the probability basics quantify random phenomena
Theoretical Foundations Probabilities Monia Ranalli monia.ranalli@uniroma2.it Ranalli M. Theoretical Foundations - Probabilities 1 / 27 Objectives understand the probability basics quantify random phenomena
4.1 Probability Distributions
 Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
Probability and Statistics Mrs. Leahy Chapter 4: Discrete Probability Distribution ALWAYS KEEP IN MIND: The Probability of an event is ALWAYS between: and!!!! 4.1 Probability Distributions Random Variables
Discrete Probability Distribution
 1 Discrete Probability Distribution Key Definitions Discrete Random Variable: Has a countable number of values. This means that each data point is distinct and separate. Continuous Random Variable: Has
1 Discrete Probability Distribution Key Definitions Discrete Random Variable: Has a countable number of values. This means that each data point is distinct and separate. Continuous Random Variable: Has
Section M Discrete Probability Distribution
 Section M Discrete Probability Distribution A random variable is a numerical measure of the outcome of a probability experiment, so its value is determined by chance. Random variables are typically denoted
Section M Discrete Probability Distribution A random variable is a numerical measure of the outcome of a probability experiment, so its value is determined by chance. Random variables are typically denoted
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#4 Chapter 6.2 rules for means and variances Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at random and
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda 1. Review OTL C6#4 Chapter 6.2 rules for means and variances Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Nov 21-8:16 PM Working out Choose a person aged 19 to 25 years at random and
Probability Distributions
 Chapter 6 Discrete Probability Distributions Section 6-2 Probability Distributions Definitions Let S be the sample space of a probability experiment. A random variable X is a function from the set S into
Chapter 6 Discrete Probability Distributions Section 6-2 Probability Distributions Definitions Let S be the sample space of a probability experiment. A random variable X is a function from the set S into
the number of correct answers on question i. (Note that the only possible values of X i
 6851_ch08_137_153 16/9/02 19:48 Page 137 8 8.1 (a) No: There is no fixed n (i.e., there is no definite upper limit on the number of defects). (b) Yes: It is reasonable to believe that all responses are
6851_ch08_137_153 16/9/02 19:48 Page 137 8 8.1 (a) No: There is no fixed n (i.e., there is no definite upper limit on the number of defects). (b) Yes: It is reasonable to believe that all responses are
Section 7.5 The Normal Distribution. Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution
 Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Section 7.6 Application of the Normal Distribution A random variable that may take on infinitely many values is called a continuous random variable. A continuous probability distribution is defined by
Introduction to Statistics I
 Introduction to Statistics I Keio University, Faculty of Economics Continuous random variables Simon Clinet (Keio University) Intro to Stats November 1, 2018 1 / 18 Definition (Continuous random variable)
Introduction to Statistics I Keio University, Faculty of Economics Continuous random variables Simon Clinet (Keio University) Intro to Stats November 1, 2018 1 / 18 Definition (Continuous random variable)
Chapter 6: Random Variables. Ch. 6-3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables
 Chapter : Random Variables Ch. -3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables X 0 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 0 0 P(X) 3???????? 4 4 When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested in whether
Chapter : Random Variables Ch. -3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables X 0 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 0 0 P(X) 3???????? 4 4 When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested in whether
12. THE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION
 12. THE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION Eg: The top line on county ballots is supposed to be assigned by random drawing to either the Republican or Democratic candidate. The clerk of the county is supposed to make
12. THE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION Eg: The top line on county ballots is supposed to be assigned by random drawing to either the Republican or Democratic candidate. The clerk of the county is supposed to make
12. THE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION
 12. THE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION Eg: The top line on county ballots is supposed to be assigned by random drawing to either the Republican or Democratic candidate. The clerk of the county is supposed to make
12. THE BINOMIAL DISTRIBUTION Eg: The top line on county ballots is supposed to be assigned by random drawing to either the Republican or Democratic candidate. The clerk of the county is supposed to make
Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc.
 Chapter 8 Measures of Center Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc. Data that can only be integer
Chapter 8 Measures of Center Data that can be any numerical value are called continuous. These are usually things that are measured, such as height, length, time, speed, etc. Data that can only be integer
5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5 5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions A random variable (r.v.) can be either continuous or discrete. It takes on the possible values of an experiment. It
Chapter 5 5.2 Random Variables, Probability Histograms and Probability Distributions A random variable (r.v.) can be either continuous or discrete. It takes on the possible values of an experiment. It
Lecture 6 Probability
 Faculty of Medicine Epidemiology and Biostatistics الوبائيات واإلحصاء الحيوي (31505204) Lecture 6 Probability By Hatim Jaber MD MPH JBCM PhD 3+4-7-2018 1 Presentation outline 3+4-7-2018 Time Introduction-
Faculty of Medicine Epidemiology and Biostatistics الوبائيات واإلحصاء الحيوي (31505204) Lecture 6 Probability By Hatim Jaber MD MPH JBCM PhD 3+4-7-2018 1 Presentation outline 3+4-7-2018 Time Introduction-
The normal distribution is a theoretical model derived mathematically and not empirically.
 Sociology 541 The Normal Distribution Probability and An Introduction to Inferential Statistics Normal Approximation The normal distribution is a theoretical model derived mathematically and not empirically.
Sociology 541 The Normal Distribution Probability and An Introduction to Inferential Statistics Normal Approximation The normal distribution is a theoretical model derived mathematically and not empirically.
Chapter 9. Idea of Probability. Randomness and Probability. Basic Practice of Statistics - 3rd Edition. Chapter 9 1. Introducing Probability
 Chapter 9 Introducing Probability BPS - 3rd Ed. Chapter 9 1 Idea of Probability Probability is the science of chance behavior Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run but has a regular and predictable
Chapter 9 Introducing Probability BPS - 3rd Ed. Chapter 9 1 Idea of Probability Probability is the science of chance behavior Chance behavior is unpredictable in the short run but has a regular and predictable
The Binomial distribution
 The Binomial distribution Examples and Definition Binomial Model (an experiment ) 1 A series of n independent trials is conducted. 2 Each trial results in a binary outcome (one is labeled success the other
The Binomial distribution Examples and Definition Binomial Model (an experiment ) 1 A series of n independent trials is conducted. 2 Each trial results in a binary outcome (one is labeled success the other
Business Statistics 41000: Probability 4
 Business Statistics 41000: Probability 4 Drew D. Creal University of Chicago, Booth School of Business February 14 and 15, 2014 1 Class information Drew D. Creal Email: dcreal@chicagobooth.edu Office:
Business Statistics 41000: Probability 4 Drew D. Creal University of Chicago, Booth School of Business February 14 and 15, 2014 1 Class information Drew D. Creal Email: dcreal@chicagobooth.edu Office:
6.1 Binomial Theorem
 Unit 6 Probability AFM Valentine 6.1 Binomial Theorem Objective: I will be able to read and evaluate binomial coefficients. I will be able to expand binomials using binomial theorem. Vocabulary Binomial
Unit 6 Probability AFM Valentine 6.1 Binomial Theorem Objective: I will be able to read and evaluate binomial coefficients. I will be able to expand binomials using binomial theorem. Vocabulary Binomial
Shifting our focus. We were studying statistics (data, displays, sampling...) The next few lectures focus on probability (randomness) Why?
 Probability Introduction Shifting our focus We were studying statistics (data, displays, sampling...) The next few lectures focus on probability (randomness) Why? What is Probability? Probability is used
Probability Introduction Shifting our focus We were studying statistics (data, displays, sampling...) The next few lectures focus on probability (randomness) Why? What is Probability? Probability is used
MAKING SENSE OF DATA Essentials series
 MAKING SENSE OF DATA Essentials series THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Copyright by City of Bradford MDC Prerequisites Descriptive statistics Charts and graphs The normal distribution Surveys and sampling Correlation
MAKING SENSE OF DATA Essentials series THE NORMAL DISTRIBUTION Copyright by City of Bradford MDC Prerequisites Descriptive statistics Charts and graphs The normal distribution Surveys and sampling Correlation
The Binomial and Geometric Distributions. Chapter 8
 The Binomial and Geometric Distributions Chapter 8 8.1 The Binomial Distribution A binomial experiment is statistical experiment that has the following properties: The experiment consists of n repeated
The Binomial and Geometric Distributions Chapter 8 8.1 The Binomial Distribution A binomial experiment is statistical experiment that has the following properties: The experiment consists of n repeated
Unit2: Probabilityanddistributions. 3. Normal distribution
 Announcements Unit: Probabilityanddistributions 3 Normal distribution Sta 101 - Spring 015 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science February, 015 Peer evaluation 1 by Friday 11:59pm Office hours:
Announcements Unit: Probabilityanddistributions 3 Normal distribution Sta 101 - Spring 015 Duke University, Department of Statistical Science February, 015 Peer evaluation 1 by Friday 11:59pm Office hours:
Probability Distribution
 Probability Distribution CK-12 Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Probability Distribution CK-12 Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters
 Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
Chapter 7 Sampling Distributions and Point Estimation of Parameters Part 1: Sampling Distributions, the Central Limit Theorem, Point Estimation & Estimators Sections 7-1 to 7-2 1 / 25 Statistical Inferences
Chapter 4 and 5 Note Guide: Probability Distributions
 Chapter 4 and 5 Note Guide: Probability Distributions Probability Distributions for a Discrete Random Variable A discrete probability distribution function has two characteristics: Each probability is
Chapter 4 and 5 Note Guide: Probability Distributions Probability Distributions for a Discrete Random Variable A discrete probability distribution function has two characteristics: Each probability is
The topics in this section are related and necessary topics for both course objectives.
 2.5 Probability Distributions The topics in this section are related and necessary topics for both course objectives. A probability distribution indicates how the probabilities are distributed for outcomes
2.5 Probability Distributions The topics in this section are related and necessary topics for both course objectives. A probability distribution indicates how the probabilities are distributed for outcomes
Chapter 4 Random Variables & Probability. Chapter 4.5, 6, 8 Probability Distributions for Continuous Random Variables
 Chapter 4.5, 6, 8 Probability for Continuous Random Variables Discrete vs. continuous random variables Examples of continuous distributions o Uniform o Exponential o Normal Recall: A random variable =
Chapter 4.5, 6, 8 Probability for Continuous Random Variables Discrete vs. continuous random variables Examples of continuous distributions o Uniform o Exponential o Normal Recall: A random variable =
Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics
 Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 3.-3.3 3. Random Variables and Histograms A is a rule that assigns precisely one real number to each outcome of an experiment. We usually denote
Chapter 3: Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 3.-3.3 3. Random Variables and Histograms A is a rule that assigns precisely one real number to each outcome of an experiment. We usually denote
Chapter 5: Discrete Probability Distributions
 Chapter 5: Discrete Probability Distributions Section 5.1: Basics of Probability Distributions As a reminder, a variable or what will be called the random variable from now on, is represented by the letter
Chapter 5: Discrete Probability Distributions Section 5.1: Basics of Probability Distributions As a reminder, a variable or what will be called the random variable from now on, is represented by the letter
Chance/Rossman ISCAM II Chapter 0 Exercises Last updated August 28, 2014 ISCAM 2: CHAPTER 0 EXERCISES
 ISCAM 2: CHAPTER 0 EXERCISES 1. Random Ice Cream Prices Suppose that an ice cream shop offers a special deal one day: The price of a small ice cream cone will be determined by rolling a pair of ordinary,
ISCAM 2: CHAPTER 0 EXERCISES 1. Random Ice Cream Prices Suppose that an ice cream shop offers a special deal one day: The price of a small ice cream cone will be determined by rolling a pair of ordinary,
ECO220Y Introduction to Probability Readings: Chapter 6 (skip section 6.9) and Chapter 9 (section )
 ECO220Y Introduction to Probability Readings: Chapter 6 (skip section 6.9) and Chapter 9 (section 9.1-9.3) Fall 2011 Lecture 6 Part 2 (Fall 2011) Introduction to Probability Lecture 6 Part 2 1 / 44 From
ECO220Y Introduction to Probability Readings: Chapter 6 (skip section 6.9) and Chapter 9 (section 9.1-9.3) Fall 2011 Lecture 6 Part 2 (Fall 2011) Introduction to Probability Lecture 6 Part 2 1 / 44 From
Random variables. Discrete random variables. Continuous random variables.
 Random variables Discrete random variables. Continuous random variables. Discrete random variables. Denote a discrete random variable with X: It is a variable that takes values with some probability. Examples:
Random variables Discrete random variables. Continuous random variables. Discrete random variables. Denote a discrete random variable with X: It is a variable that takes values with some probability. Examples:
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017
 ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
ECON 214 Elements of Statistics for Economists 2016/2017 Topic The Normal Distribution Lecturer: Dr. Bernardin Senadza, Dept. of Economics bsenadza@ug.edu.gh College of Education School of Continuing and
Chapter 8. Variables. Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc.
 Chapter 8 Random Variables Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 8.1 What is a Random Variable? Random Variable: assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or,
Chapter 8 Random Variables Copyright 2004 Brooks/Cole, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. 8.1 What is a Random Variable? Random Variable: assigns a number to each outcome of a random circumstance, or,
Chapter 6 Section 3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 6 Section 3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested whether a particular outcome does or does
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 6 Section 3: Binomial and Geometric Random Variables When the same chance process is repeated several times, we are often interested whether a particular outcome does or does
Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review
 Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review Multiple Choice 1. Jay Olshansky from the University of Chicago was quoted in Chance News as arguing that for the average life expectancy to reach 100, 18% of people
Name Period AP Statistics Unit 5 Review Multiple Choice 1. Jay Olshansky from the University of Chicago was quoted in Chance News as arguing that for the average life expectancy to reach 100, 18% of people
Probability Distributions for Discrete RV
 Probability Distributions for Discrete RV Probability Distributions for Discrete RV Definition The probability distribution or probability mass function (pmf) of a discrete rv is defined for every number
Probability Distributions for Discrete RV Probability Distributions for Discrete RV Definition The probability distribution or probability mass function (pmf) of a discrete rv is defined for every number
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Chapter7 Probability Distributions and Statistics Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number of boys in
Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a
 Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a Announcements: There are some office hour changes for Nov 5, 8, 9 on website Week 5 quiz begins after class today and ends at
Homework: Due Wed, Nov 3 rd Chapter 8, # 48a, 55c and 56 (count as 1), 67a Announcements: There are some office hour changes for Nov 5, 8, 9 on website Week 5 quiz begins after class today and ends at
Expected Value of a Random Variable
 Knowledge Article: Probability and Statistics Expected Value of a Random Variable Expected Value of a Discrete Random Variable You're familiar with a simple mean, or average, of a set. The mean value of
Knowledge Article: Probability and Statistics Expected Value of a Random Variable Expected Value of a Discrete Random Variable You're familiar with a simple mean, or average, of a set. The mean value of
Density curves. (James Madison University) February 4, / 20
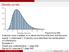 Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Density curves Figure 6.2 p 230. A density curve is always on or above the horizontal axis, and has area exactly 1 underneath it. A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. Example
Example - Let X be the number of boys in a 4 child family. Find the probability distribution table:
 Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Chapter8 Probability Distributions and Statistics Section 8.1 Distributions of Random Variables tthe value of the result of the probability experiment is a RANDOM VARIABLE. Example - Let X be the number
Honors Statistics. Daily Agenda
 Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Write a program to generate random numbers. I've decided to give them free will. A Skip 4, 12, 16 Apr 25-10:55 AM Toss 4 times Suppose you
Honors Statistics Aug 23-8:26 PM Daily Agenda Aug 23-8:31 PM 1 Write a program to generate random numbers. I've decided to give them free will. A Skip 4, 12, 16 Apr 25-10:55 AM Toss 4 times Suppose you
10-3 Probability Distributions
 Identify the random variable in each distribution, and classify it as discrete or continuous. Explain your reasoning. 1. the number of pages linked to a Web page The random variable X is the number of
Identify the random variable in each distribution, and classify it as discrete or continuous. Explain your reasoning. 1. the number of pages linked to a Web page The random variable X is the number of
Continuous Random Variables and the Normal Distribution
 Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables and the Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possible outcomes or an infinite number of possible
Chapter 6 Continuous Random Variables and the Normal Distribution Continuous random variables are used to approximate probabilities where there are many possible outcomes or an infinite number of possible
MATH 446/546 Homework 1:
 MATH 446/546 Homework 1: Due September 28th, 216 Please answer the following questions. Students should type there work. 1. At time t, a company has I units of inventory in stock. Customers demand the
MATH 446/546 Homework 1: Due September 28th, 216 Please answer the following questions. Students should type there work. 1. At time t, a company has I units of inventory in stock. Customers demand the
Elementary Statistics Blue Book. The Normal Curve
 Elementary Statistics Blue Book How to work smarter not harder The Normal Curve 68.2% 95.4% 99.7 % -4-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 4 Z Scores John G. Blom May 2011 01 02 TI 30XA Key Strokes 03 07 TI 83/84 Key Strokes
Elementary Statistics Blue Book How to work smarter not harder The Normal Curve 68.2% 95.4% 99.7 % -4-3 -2-1 0 1 2 3 4 Z Scores John G. Blom May 2011 01 02 TI 30XA Key Strokes 03 07 TI 83/84 Key Strokes
Random variables The binomial distribution The normal distribution Other distributions. Distributions. Patrick Breheny.
 Distributions February 11 Random variables Anything that can be measured or categorized is called a variable If the value that a variable takes on is subject to variability, then it the variable is a random
Distributions February 11 Random variables Anything that can be measured or categorized is called a variable If the value that a variable takes on is subject to variability, then it the variable is a random
Business Statistics 41000: Probability 3
 Business Statistics 41000: Probability 3 Drew D. Creal University of Chicago, Booth School of Business February 7 and 8, 2014 1 Class information Drew D. Creal Email: dcreal@chicagobooth.edu Office: 404
Business Statistics 41000: Probability 3 Drew D. Creal University of Chicago, Booth School of Business February 7 and 8, 2014 1 Class information Drew D. Creal Email: dcreal@chicagobooth.edu Office: 404
AP STATISTICS FALL SEMESTSER FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE
 AP STATISTICS Name: FALL SEMESTSER FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Period: *Go over Vocabulary Notecards! *This is not a comprehensive review you still should look over your past notes, homework/practice, Quizzes,
AP STATISTICS Name: FALL SEMESTSER FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE Period: *Go over Vocabulary Notecards! *This is not a comprehensive review you still should look over your past notes, homework/practice, Quizzes,
