CASH MANAGEMENT SERVICES IN CHINA
|
|
|
- Jewel Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASH MANAGEMENT SERVICES IN CHINA BA 691 June 24, 2002 Li Liu
2 During the past twenty years, China has undergone significant changes and reforms, especially after the launch of its open door economic reform policy in Many multinational corporations view China as the next growth market. China s entry into the World Trade Organization has induced even more interest from foreign investors. (Cheung, 1) One issue that foreign investors concerned about is how to effectively manage its cash to ensure smooth operation. Foreign investments is one of the primary drivers for China s economic growth, thus cash management services play a critical role in the development of its economy. China still lags other countries in the implementation of modern cash management techniques, however there will be significant changes to the banking industry in the next few years that can improve the cash management services offered. Business Environment China has made continuous effort to reform the national economy, especially at the structural and institutional levels. So, there are some improvements in the operating environment. Businesses are operating in a partial market system with more diversified ownership structure. The economy is no longer completely controlled by the government because privately owned enterprises are becoming major players. A labor market is developing, especially in the private sector due to greater labor mobility. Many of the peasants have moved to cities to find jobs, providing laborer for the manufacturing and service industries. (Tsang, p1) Enterprises now enjoy a greater autonomy in terms of decision-making. Government no longer dictates all decisions involving investment, production, and output. Shareholding companies have been established and are openly traded on stock
3 markets worldwide. (Tsang, p1) Many of the state owned enterprises are listed on the stock market with the government owning more than fifty percent of the shares and the rest are in the hands of private or institutional investors. Thus private investors can have some impact on the operations of state owned businesses. China has also made some significant changes in the financial environment during the past few years. China has formally established a central bank and is going through a gradual commercialization of the state banks. The foreign exchange trading system is unified and market-based. The exchange rate for the renminbi (RMB), China s official currency, is stable because it is pegged to the US dollar. China s securities market is slowly developing as transaction volume increases and more enterprises become publicly traded companies. China now even has a small market for trading stocks denominated in US dollar. A set of regulations and laws were developed to govern the inflow of foreign capital. (Tsang, p1) There is a quicker pace in decentralization of the foreign trade system and trade barriers have reduced. After China has entered the WTO, reduction in tariffs, quotas, and other barriers would encourage more foreign investments. Chinese government has established preferential policies such as tax incentives to attract foreign investors. (Tsang, p1-2) China has currently shifted its development focus from the east coast to the western region, thus many favorable incentives are offered to draw foreign investors to the western provinces. So, the changes in both the operating and financial environments have improved the overall business environment that is more favorable toward foreign investors.
4 Investment Methods Foreign investors can choose from different methods depending on the specific needs and requirements of each individual investment. Equity joint venture is considered China s most popular foreign investment form and is the preferred method of the Chinese government. Detailed regulations are enforced to cover issues such as capital contributions, management independence, labor, leverage level, and accounting and financial management. Equity joint ventures are attractive when there is a relatively well-developed regulatory environment. The second investment form is cooperative joint venture (CJV), which has a simpler regulatory framework when compared with equity joint venture. CJV provides investors with more freedom to structure their investments according to their business requirements, so it is popular with Hong Kong investors who set up basic processing operations in China. A main advantage of CJV is the flexibility to build a simple management structure that helps reduce operating costs. (Tsang, 2) Equity joint venture and cooperative joint venture are the two most common forms of foreign investment, but there are three other forms that investors can choose from. A foreign business can establish a wholly foreign owned enterprise (WFOE). China published Wholly Foreign Owned Enterprise Law in 1986 and issued its implementation rules in The benefit of operating a WFOE is that foreign investors have greater control over its management and operations. On the other hand, this form of investment requires large capital outlay because everything has to be done from scratch. A simpler way of entering the market is to open representative offices in strategic locations because this would require minimal upfront capital commitment. However, representative offices can only engage in non-direct business activities, such as
5 consulting, market research, sourcing, and procurement. The benefit of open an office versus other forms of investment is the short period of time needed to obtain approval, usually within two to three months. Another form of indirect foreign investment that is gaining popularity is to acquire a listed or unlisted joint stock company s shares from an existing shareholder. The investor may also acquire newly issued shares directly from the joint stock company. This form of investment allows the investors to bypass the original examination and approval process involved in setting up the foreign investment enterprise. (Cheung, p1-2) Banking System China has a multi-tiered banking system with the People s Bank of China (PBOC) at the center. During the past ten years, the PBOC has been increasingly acting as a central bank, transferring its commercial activities to other institutions. Unlike the US Federal Reserve, the PBOC is not independent because it still reports to the State Council, an executive organization of the Chinese Government. In its central bank capacity, the PBOC lends to commercial banks, trades in government bonds, and controls interest rates and reserve requirements. (Wegner, p1) The four largest banks in China are the state-run specialized banks: the Agricultural Bank of China, the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Construction Bank and the Bank of China. China established three policy banks in 1994 to provide lending to support selected government policies and these are the Agriculture Development Bank, Export and Import Bank of China, and State Development Bank. The five national commercial banks currently in operation are the Bank of Communication, China Everbright Bank, China International Trust and Investment
6 Corporation Industrial Bank, China Minsheng Bank, and Huaxia Bank. In addition, nine regional commercial banks serve their specific regions within China. Cooperative banks that are created by merging the urban credit entities are allowed to engage in limited banking activities. (Cheung, p2) All of the policy, national, regional, and cooperative banks are relatively small in size compared to the state-run banks. Also, government appoints most of the bank presidents because usually the government holds a majority ownership. The finance, investment, and leasing companies, as well as foreign banks all just play a supplementary role in the system. (Cheung, p2) In 1996, the People s Bank of China announced that the following four banks are allowed to conduct RMB business in Shanghai: Bank of Tokyo-Mitsubishi, Citibank, HSBC, and the Industrial Bank of Japan. Then in early 1997, the approval was given to a second group of foreign banks, which are Banquez Indosuez, Dai-Ichi Kangyo Bank, Sanwa Bank, Shanghai-Paris International Bank, and Standard Chartered Bank. Currently there are twenty-five foreign banks in Shanghai and eight in Shenzhen that offer RMB services to foreign nationals and businesses. (Tsang, p4) In 1998, the foreign banks were allowed to lend or borrow RMB directly from the inter-bank market, and conduct bond and bond repurchase trading through the market. The branches of foreign banks are now permitted to offer RMB services in other regions of the country. Regulation The State Administration of Foreign Exchange, which directly reports to the People s Bank of China, is responsible for maintaining control over all foreign exchange transactions by local and foreign financial institutions. (Wegner, p1) Since 1996, foreign expenditure classified as current account items such as import payments and export
7 proceeds can be freely exchanged through designated banks. The convertibility of capital account items, which are items of inflow and outflow of assets and liabilities, are subject to more restrictive controls imposed by the State Administration for Foreign Exchange. Foreign enterprises can keep the income from current account items in their settlement account in foreign currencies if the amount does not exceed the limits set by the SAFE. Any excess must be sold to designated banks. The foreign enterprise s amount of the limits is based on the paid-up capital and the import and export activities. (Tsang, p4) All foreign currency borrowings for local Chinese businesses must be first approved by SAFE regardless whether local or foreign banks provide the funding. Foreign companies are required to register foreign debt with the SAFE office in their region when it makes an overseas borrowing. The SAFE can cancel a foreign enterprise s Foreign Debt Registration Certificate if it fails to execute draw down within 120 days after the first draw down date as stated in the bank contract. Borrowers are not permitted to deposit borrowed funds overseas or convert borrowed funds into RMB without approval from the SAFE. Since 1998, China no longer allows foreign and domestic banks to help clients redeem hard currency loans ahead of maturity if this is not provided for in loan agreements. The rule means that foreign bankers cannot help clients secure RMB borrowings from mainland banks for conversion into hard currency to redeem loans. (Tsang, p4-5) In recent years, China has allowed the establishment of foreign investment holding companies through which foreign companies may own interest in a number of foreign enterprises. Then in 1996, China started to the establishment of finance companies that can provide services such as taking and RMB and FX deposits from, and
8 making RMB and FX loans to, group companies. Finance companies do have to maintain specified financial ratios and are under the supervision of PBOC. In 1999, supplementary provisions governing holding companies allow these companies to invest in non-manufacturing entities such as research and development, conduct domestic trade and distribution, as well as foreign trade. (Tsang, 5) Clearing System Clearing systems in China are classified as in-city and cross-city. In-city RMB payments- which are settled by paper instruments such as checks, drafts, or debit adviceare cleared within a local settlement and drafts exchange bureau run by the PBOC. There are usually two clearing runs per day in the larger cities. For cross-city payments, the PBOC administers the China National Automated Payments System (CNAPS), a nationwide clearing system linking different banks. The system covers more than 800 locations across China and a number of foreign banks are participating members. Some Chinese banks, including the four state owned banks, have developed independent electronic funds transfer system to facilitate cross-city, cross-branch but not cross-bank payments. Payments in which the remitter and the beneficiary are with the same bank are now cleared through these in-house systems. If the systems are among the Big Four, the transfers can be credited to the beneficiary s account within 24 hours. For some local banks, express clearing involving larger branches can even be done within two hours. (Cheung, p3) However, for cross-city payments of RMB 500,000 or more, a separate system run by the PBOC must be used to detect fraud and minimize delay. Shenzhen, which is located very close to Hong Kong, already uses Batched Electronic
9 Payments System (BEPS) and real-time gross settlement system (RTGS), as well as cross-bank ATMs and Point of Sale (POS) infrastructure. (Tsang, p6) Cash Management A main issue that treasurers in China often identified is that many cash management techniques commonly used elsewhere are not relevant in China. Complex regulations, FX controls, limited investment products, unique operating conditions, and developing banking infrastructure mean many cash management techniques widely used in other parts of Asia cannot be readily implemented on the mainland. Companies with significant and diverse operations in China often find it difficult to keep track of their cash positions and transactions across the country. The consequence is idle and excessive funds sitting in some accounts, with unexpected funding shortfalls and unnecessary borrowings in others. This often leads to an inefficient use of the company s financial resources, and to higher interest costs. (Tsang, p6) Given China s relatively restricted financial environment, finance managers and treasurers overseeing projects are constantly searching for ways to minimize delays in fund transfers, maximize returns on idle funds, manage RMB exchange risk, facilitate account reporting and maneuver funds among group entities. (Tsang, p5) With the government s gradual relaxation on the domestic banking sector in the recent years, foreign banks are able to offer a wider range of RMB services and serve foreign enterprises from their Shanghai and Shenzhen branches. Also, local financial institutions have greatly increased their efforts in developing cash management products and services, leveraging their vast branch network across the country and decreased regulatory and geographical restrictions placed on their business. (Cheung, p4)
10 In the past few years, foreign investment enterprises have benefited from the increased innovations, competition and collaboration among local and foreign banks, as the end-users of China s financial services. Several years ago, cash management maybe considered basic services such as updating balances and transactions, which were often done manually using faxes, phone banking, and even paper statements. However, companies now can find more effective cash management solutions offered in larger and developed cities. (Cheung, p4) Some of the most effective cash management products in place are often offered as partnered solutions between foreign and local banks. The partnered solution is viewed as best of both worlds because the foreign banks provide the front-end user interface or electronic banking systems, and local banks provide the nationwide network for collections and payments. Foreign banks can utilize their comparatively advanced technology and systems, but are often restricted in their ability to offer nationwide solutions due to their branch network, restricted RMB license and limited customer base. Local banks with their extensive national networks and resources can complement these disadvantages. A number of multinationals use a common cash management structure that usually comprise of one, and at most two, foreign banks with local banks. (Cheung, p4) One example of such an alliance between a foreign bank and local banks is that between May and December 2000, HSBC (Hong Kong Shanghai Bank Corp) formed cash management service alliances with all of China s Big Four state banks. With this alliance, HSBC customers have access to over 26,000 branches of these banks as collection and payment points nationwide. After the implementation of this arrangement,
11 in-country collections are been expedited. HSBC have helped several multinational clients to cut their cash in transit for inward collections from an average of four to five working days to be within 24 hours. (Cheung, p5) Liquidity Management A number of mechanisms and tools are available to help companies when it comes to liquidity management. The techniques available elsewhere in Asia are not as readily available in China, and exceptional approval, if any, must be obtained from the SAFE on a case-by-case basis. (Cheung, p5) Lockbox arrangement is common in the US, yet it is not that popular in China because people are not used to mailing checks through the mail. According to Citibank China, super-account structures, zero balance accounts and daily sweeps can be arranged for cash concentration. However, the sweeping structures are not easily practicable in China. One main issue is that inter-company loans are prohibited in China; thus transactions between group entities can only be executed if there is an underlying transaction between them. As a result, surplus funds in one group entity cannot be fully used by another group entity. Also, transfer or commingling of funds between capital and settlement accounts for foreign currency transactions are not permitted. The purposes of the accounts differ and only specifically related transactions can be executed from each type of account. (Cheung, p5) Due to these restrictions, cash concentration techniques are only useful for units operating under one legal entity; therefore, companies must consider the structure of their operations in China in order to efficiently utilize their cash. Foreign enterprises are working toward holding structures, bringing as many legal entities as possible. Some have set up consolidated sales arrangement allowing various
12 manufacturing facilities of a company inside China sell their products to one single sales entity, which then sends the final invoice to their customers. When a group or company has one legal entity operating from several locations, the bank can monitor the balances held in various accounts and sweep funds across to a concentration account at the appropriate intervals. ( China s Treasury Obstacle Course, p1) Pooling is the notional offset of debit and credit balances, used for the purpose of calculating interest on the net position. Pooling is used where interest offset is required but where account balances must remain segregated; therefore it requires the establishment of overdraft facilities at sub-account level. Pooling offers the benefits of reduction in borrowing costs, transfer costs, and the spread on overdrafts at sub-account level. Pooling may also be used to minimize taxes. (Ashford, p3) In China, however, pooling is not feasible because overdraft facilities are not offered. (Cheung, p5) Corporations that have multiple intra-group cash flows use netting method, whereby payables and receivables among group entities are settled on a net basis. Netting are usually done on a regular basis, such as monthly or bi-monthly, therefore it minimizes float and reduces a company s exposure to foreign exchange risk. (Ashford, p1-2) Netting is also not feasible in China because for foreign currency transactions, setting off inward and outward transactions contradicts China s import and export reconciliation regulations. China requires that each receipt or shipment of physical goods has to be matched with funds paid or received on a standalone basis. Thus, outgoing payments cannot be netted off with the coming receivable since they are considered separate documents and cannot be mixed together. HSBC did help a European multinational to establish a modified netting system involving a gross-in, gross-out
13 arrangement. The arrangement worked because the client has subsidiaries operating in China, which make regular payments overseas and also has overseas subsidiaries that regularly send payments to China for the purchase of equipments. ( China s Treasury Obstacle Course, p1-2) Electronic Banking Electronic banking gained popularity in China during recent years. It has helped to promote competition and accelerated the pace of commercialization of China s banking sector. Electronic banking has enabled foreign and smaller banks with limited branch networks to reach a large number of clients without having the need to invest heavily in network building. Given the widespread locations of foreign investment enterprises and the limited coverage of foreign bank branches in china, electronic banking provides an ideal solution to eliminate the distances involved and to increase efficiency. HSBC has formally secured its approval from the People s Bank of China to provide electronic banking services to foreign businesses in China. Electronic banking services not only enable clients to access balance information, it also provide an electronic means to send the bank secure and authenticated instructions. Foreign bank branches are responsible for ensure that all regulatory and documentation requirements are complied with before acting on customers instructions. (Cheung, p6) Local banks are also investing heavily in electronic banking systems in order to maintain and broaden their customer base and improve efficiency. Services include account enquiry, online securities trading, and online payment options for both personal and corporate clients. Currently electronic and Internet banking services are limited to the major cities. (Cheung, p6) Bank of China was the first to provide online banking
14 services in Then in 1999, China Construction Bank and Industrial and Commercial Bank of China also started to offer on-line banking services. For example, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China has launched a telebanking system where customers can call to reach the voice-activated, automated system or a person-to-person customer service center. The system offers services such as account information, money transfers and exchange foreign currencies. Clients can also access the web site to request the same services. ( Cyber China Up and Running, p1) Language Issue A difference between China and other emerging markets is the language factor. Payments services are manual because all information has to be written in Chinese for clearing and settlement. Foreign banks are trying to use e-banking to automate payments, but automating payments involving city clearing and out-city clearing is very different. If the supplier is within the same city, then check are used, but if in a different city, telegraphic transfers and demand draft are standard. ( China s Treasury Obstacle Course, p2) The process of manually filling in these Chinese characters is very inefficient. Some banks attempt to offer SAP so that the company can send the bulk of their payment files through electronic banking. The success or failure of the e-banking system depends on whether the system can process the characters and show information in Chinese. In many cases, client systems cannot support Chinese. Multinationals from the US usually have their database only in English. The banks have to translate the information to Chinese. Banks can use translation engine software that converts English documents to
15 Chinese and then communicate with the bank through e-banking. ( China s Treasury Obstacle Course, p2) Card Usage Debit cards and ATM cards are still the norm in China, and each bank has developed its own ATM network. The Chinese government has introduced the Golden Card Project, thus with the participation of international card systems operators such as Visa and MasterCard, a more sophisticated card system is in development. Some foreign banks have already formed alliances with local banks so that holders of credit and ATM cards issued by foreign banks outside China can debit their own overseas accounts and withdraw RMB cash. HSBC and other foreign banks have joined the Shanghai ATM network as part of the Golden Card project to develop a nationwide ATM linkup. Shanghai ATM network has partnered with global systems such as Visa/Plus and MasterCard/Cirrus. (Cheung, p5) China is still primarily a cash society and most transactions are made with paper bills. However, for large transactions this could be a problem, thus credit cards are growing in acceptance. An issue with the present credit card system in China is that different local banks issue individual credit cards, which are not interchangeable between different banks. Therefore merchants need to maintain machines from each bank if they want to take the full range of cards from all customers. (Wegner, p2) Hedging Multinational companies have limited opportunity to invest surplus cash in China. Excess cash can only be parked in an overnight deposit because investments in bonds or stocks are not permitted. Companies with large amount of idle cash have to spend it
16 locally, or can either declare a dividend or use the foreign currency to buy capital goods overseas. When there is a huge amount of cash to send outside China, declare a dividend is particularly useful. ( China s Treasury Obstacle Course, p2) Renminbi is a non-convertible currency, so the opportunity to hedge through the use of derivatives is very limited. The only product available in China is the six-month renminbi forward contracts. The contract is offered by the Bank of China and it is restricted to a very few selected enterprises, approved on a case-by-case basis. The hedge can only be used to manage import and export payments, thus it is not possible to hedge long-term capital risks. In some situations, companies can hedge indirectly by booking counter-currency such as British Pound forward against another foreign currency that is relatively stable against the renminbi such as the US dollar. (Tsang, p7) Some companies have found a new way to hedge long-term risks by purchase renminbi non-deliverable forwards offered in Hong Kong. The contract is settled in US dollars, but the People s Bank of China does not sanction the product, thus companies and banks are not willing to discuss the details. Activities in RMB non-deliverable forwards are still limited. About $100 million flow through the market in Hong Kong every week, with reasonably liquid forward curve out to one year. The picture is quite different when it comes to hedging foreign exchange liabilities. Most of the big local Chinese banks offer foreign currency denominated interest rate swaps to local companies. ( China s Treasury Obstacle Course, p2) Relaxations on Regulations Chinese government has announced that foreign banks are allowed to expand in terms of business volume, geographic area, and sources of RMB funding. In terms of
17 business scale, the ratio of foreign banks RMB denominated liabilities to their gross foreign currency denominated liabilities is raised from 35% to 50%. Foreign banks in Shanghai are permitted to expand their client base from Shanghai to Jiangsu and Zhejiang province, while the Shenzhen branches are permitted to expand from Shenzhen to Guangdon, Guangxi and Hunan province. (Tsang, p9) Another area of relaxation is the source of RMB funding. Foreign banks now can borrow RMB loans of over one-year terms from domestic financial institutions. Foreign banks borrowing from the inter-bank market of over seven days are no longer capped by their operating capital. Before the restriction was lifted, the borrowing amount and operating capital must be maintained at a one-to-one ratio. In addition, foreign bank branches of the same bank at different localities with permission to conduct RMB business are allowed to transfer RMB balances between them. Foreign banks are permitted to charge obligations and management fees for organizing syndicated loans up to 0.3% of the total loans arranged. (Tsang, p9) Thus, foreign banks have gained a few ways to receive more capital and increase revenue due to these relaxations on regulations. Impact of WTO Entry on Banking Sector China was recently admitted to the World Trade Organization after almost twenty years of negotiations. China s accession to WTO has four main benefits. First of all, China s foreign trade will expand due to a wider opening of the nation s market to foreign goods and an equal opening of foreign markets to Chinese goods. Second, there will be an increase in the inflow of foreign capital, expertise and technology as more foreign investors seek to benefit from the China market. Third, consumers will benefit from a wider range of choices of products and services. The competition from foreign
18 companies can bring the prices of goods down. Lastly, the quality of China s economy should improve under increasing pressure for adjustment and reform in line with international standards. (Tsang, p9) The issues with inferior quality and patent infringement should decrease from the increased competition. The agreements between Sino-EU and Sino-US also included provisions for the further opening of the banking sector, especially RMB business, which will give almost full market access to foreign banks in five years time. The provisions open the sector to foreign competition and put pressure on Chinese banks to adjust. During the past few year, China s banks have taken numerous steps to enhance their competitiveness in anticipation of the WTO entry. So, the new provisions are unlikely to cause a major shock to the Chinese banking industry. (Tsang, p9-10) Over the last three years, the Chinese government has made conscious effort to strengthen the basics and management of China s banking sector. Chinese government has forced some financial institutions that are not viable to close down their businesses. The central bank has strengthened some external regulations and improved the internal management within the banks. Some other improvements are the capitalization of banks and setting up asset management companies to manage problem loans. In addition, China has opened up the ownership structure of banks through issuing shares to introduce capital market discipline. (Tsang, p10) Even though the opening of markets will bring new opportunities for foreign banks, the foreign banks will most likely be concentrated on penetration of the market s specific, higher-value wholesale or niche sectors. Foreign banks will face a number of challenges. First, China s money and capital markets are still in the stage of infancy and
19 the lack of extensive branch network limits foreign bank s ability to raise RMB funds needed for conducting business. Second, room for interest rate competition is limited until there is a liberalization of bank interest rates. Third, the close relationship built up over time between state banks and state owned enterprises is hard to break. Also, laws and regulations protecting creditors rights are inadequate, thus the difficulties in exercising these rights can limit foreign bank operations. Finally, the cultural barriers such as differences in language, customers, personal relations, and attitudes toward legal obligations can all be limitations to the foreign bank s business. Due to the limiting factors, along with foreign bank s strength in financial expertise and international connections, the wholesale sector is probably foreign banks main area of penetration. The wholesale sector does not need extensive networks and is less sensitive to local and cultural factors. (Cheung, p8) Shared Service Centers and Regional Treasury Centers As investment and activity in China increases, many large multinationals are looking to centralize their operations and achieve better control and economies of scale. With electronic banking becoming more available in China from foreign and local banks, some multinationals are looking into centralize all in-country RMB payment processing. The companies do have to consider whether the entities covered fall into foreign banks RMB catchments areas. A few large multinationals have established Asia-wide payment transactions centers in China, supporting payment processing and operations for multiple countries. (Cheung, p8) Through the establishment of shared service centers and regional treasury centers, there is a change in the attitude of companies towards their cash management operations
20 in Asia. Some multinationals have established shared service centers in Shanghai, but as companies start to establish operations in other regions of the country, they want their cash centers to be close to the manufacturing hubs as possible. The problem with establishing cash management centers in other region is that very few of the large foreign banks have licenses to operate in these cities and have to rely on their alliances with local banks to service clients. Also, the operating costs have increased sharply in recent months, thus no longer making it a cheap option. (Marriott, p2) But as the Chinese banking sector becomes more open, China will become an attractive place for cash management centers in Asia. Conclusion Cash management is becoming one of the important factors when evaluating investment in China as more and more foreign companies consider entering the market. China s cash management development depends on the direction and pace of its reform effort in the financial and banking industry. Despite the latest relaxations, the foreign banks are still restricted in terms of the RMB business. The foreign banks are only allowed access to foreign companies with a ceiling on the volume of their RMB business, and limited availability of RMB funds. Due to foreign banks stronger competitive edge with better management, services, advertising and marketing techniques, a gradual opening is needed to prevent any destabilizing diversion of deposits from state to foreign banks. (Tsang, p10) Another issue to be considered is the uncertainty between China and Taiwan, which could provide opportunity for Sino-US cooperation or may lead to a serious confrontation. Also, China is primarily a cash based society with the nation s cash
21 savings equal to about forty percent of GDP, thus it takes time to change people s attitude and habit toward spending. Reforms in the banking sector will be favorable for the finance and treasury managers future, and we have already seen the success of foreign banks in Shanghai and Shenzhen. Collaboration and cooperation between local and foreign banks will most likely continue. (Cheung, p11) Recently, China even allowed HSBC, a foreign bank, to own a percentage of shares in a state bank. So, in the coming three to five years, the Chinese banking industry will experience significant changes that can move the sector in a positive direction. The improvements in cash management area will definitely help China to attract more investors. Foreign investment is a driving force for China s economic growth, thus the Chinese government should make more effort in changing the banking services. In conclusion, cash management is a key to effective operation and the recent changes in China s cash management area will positively impact China s overall economic development.
22 Works Cited Ashford, Duncan, Optimizing Cash and Liquidity Management in Asia Pacific, HSBC Global Payments and Cash Management, Jan. 28, 2000, Originally published in HSBC s Guide to Cash And Treasury Management in Asia 2000, Cyber China Up and Running, Oct. 23, 2001, Originally published in Asiamoney, Cheung, Shannon, Cash Management in China, HSBC Global Payments and Cash Management, Dec. 7, 2001, Originally published in HSBC s Guide to Cash And Treasury Management in Asia Pacific 2002, China s Treasury Obstacle Course, May 30, 2002, Originally published in The Asset, Marriott, Cherie, Cash Management: Negotiating China Part I & II, Nov 1, 2001, Tsang, Brian, Cash Management in China, HSBC Global Payments and Cash Management, Feb. 20, 2001, Wegner, Carl, Recent Improvements in the Chinese Banking System, Nov. 6,
23 Bibliography Ashford, Duncan, Optimizing Cash and Liquidity Management in Asia Pacific, HSBC Global Payments and Cash Management, Jan. 28, 2000, Originally published in HSBC s Guide to Cash And Treasury Management in Asia 2000, Ashton, Jonathan, Treasury and Payment Services Through an Internet Window, HSBC Global Payments and Cash Management, Dec. 10, 2001, Bhandari, Maninder, E-enabled Cash Management Solutions, Apr. 1, 2002, Originally published in HSBC s Guide to Cash And Treasury Management in Asia Pacific 2002, Cyber China Up and Running, Oct. 23, 2001, Originally published in Asiamoney, Cheung, Shannon, Cash Management in China, HSBC Global Payments and Cash Management, Dec. 7, 2001, Originally published in HSBC s Guide to Cash And Treasury Management in Asia Pacific 2002, China s Treasury Obstacle Course, May 30, 2002, Originally published in The Asset, Koh, Alex, Implementing Cash Pooling in Asia Pacific, Jan. 28, 2000, Originally published in HSBC s Guide to Cash And Treasury Management in Asia Pacific 2002, Marriott, Cherie, Cash Management: Negotiating China Part I & II, Nov 1, 2001,
24 Tsang, Brian, Cash Management in China, HSBC Global Payments and Cash Management, Feb. 20, 2001, Tam, Alex, A Practical Approach to Cash Management for Asian Corporations, HSBC Global Payments and Cash Management, Apr. 30, 2001, Originally published in HSBC s Guide to Cash And Treasury Management in Asia Pacific 2001, Wegner, Carl, Recent Improvements in the Chinese Banking System, Nov. 6,
Transformation in China: New Opportunities and Challenges
 Transformation in China: New Opportunities and Challenges March 2008 The information contained herein does not constitute and shall not be construed to constitute investment, tax or legal advice by Deutsche
Transformation in China: New Opportunities and Challenges March 2008 The information contained herein does not constitute and shall not be construed to constitute investment, tax or legal advice by Deutsche
LEADING-EDGE CASH MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS
 CHINA CASH OVERVIEW PART 3 LEADING-EDGE CASH MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS OUR SHANGHAI AND SHENZHEN BRANCHES HAVE FULL CAPABILITIES TO MANAGE YOUR CNY ACCOUNTS IN CHINA. In China, ABN AMRO s cash management services
CHINA CASH OVERVIEW PART 3 LEADING-EDGE CASH MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS OUR SHANGHAI AND SHENZHEN BRANCHES HAVE FULL CAPABILITIES TO MANAGE YOUR CNY ACCOUNTS IN CHINA. In China, ABN AMRO s cash management services
Emergence of RMB as an International Currency
 Emergence of RMB as an International Currency Cindy Lo, Partner Allen & Overy, Beijing Office March 2013 1 Agenda An Overview: the Chinese Government s policy objectives and key regulatory developments
Emergence of RMB as an International Currency Cindy Lo, Partner Allen & Overy, Beijing Office March 2013 1 Agenda An Overview: the Chinese Government s policy objectives and key regulatory developments
The Renminbi: Why + How = Now
 Excerpt from Insights 2013 The Renminbi: Why + How = Now Sridhar Kanthadai, Regional Head of Transaction Banking, North Asia Michael Vrontamitis, Regional Head of Product Management, Transaction Banking,
Excerpt from Insights 2013 The Renminbi: Why + How = Now Sridhar Kanthadai, Regional Head of Transaction Banking, North Asia Michael Vrontamitis, Regional Head of Product Management, Transaction Banking,
BOCHK achieved 17.7% year-on-year growth in profit attributable to equity holders from continuing operations in the first half
 28 August 2018 BOCHK achieved 17.7% year-on-year growth in profit attributable to equity holders from continuing operations in the first half BOC Hong Kong (Holdings) Limited ( the Company, stock code
28 August 2018 BOCHK achieved 17.7% year-on-year growth in profit attributable to equity holders from continuing operations in the first half BOC Hong Kong (Holdings) Limited ( the Company, stock code
CHINA s ENTRY INTO THE WTO AND THE FINANCIAL SECTOR
 CHINA s ENTRY INTO THE WTO AND THE FINANCIAL SECTOR Javier Serrado Banco Sabadell-Beijing To open the banking industry is essential part of the basic policy of the China Open Reform. Starting from late
CHINA s ENTRY INTO THE WTO AND THE FINANCIAL SECTOR Javier Serrado Banco Sabadell-Beijing To open the banking industry is essential part of the basic policy of the China Open Reform. Starting from late
Guide to Establishing a Subsidiary in China
 Guide to Establishing a Subsidiary in China by jie chen As China s strength in the global economy continues to grow, businesses need to consider the prospect of establishing operations within its borders.
Guide to Establishing a Subsidiary in China by jie chen As China s strength in the global economy continues to grow, businesses need to consider the prospect of establishing operations within its borders.
RMB Internationalization Status and Its Implications
 International Finance RMB Internationalization Status and Its Implications Hansoo Kim, Research Fellow* 1) China announced the RMB internationalization policy in 2009 and has carried forward many initiatives
International Finance RMB Internationalization Status and Its Implications Hansoo Kim, Research Fellow* 1) China announced the RMB internationalization policy in 2009 and has carried forward many initiatives
China Law Update December 2006
 China Law Update December 2006 table of contents In this issue of China Law Update, we summarize a variety of new banking laws and regulations that were enacted in late 2006. 3 Revised PRC Banking Supervision
China Law Update December 2006 table of contents In this issue of China Law Update, we summarize a variety of new banking laws and regulations that were enacted in late 2006. 3 Revised PRC Banking Supervision
Understanding RQFII The Great Door Opener for China Access
 Markets and Securities Services Investor Services Understanding RQFII The Great Door Opener for China Access By: Stewart Aldcroft, Citi Investor Services Since China first started opening up its capital
Markets and Securities Services Investor Services Understanding RQFII The Great Door Opener for China Access By: Stewart Aldcroft, Citi Investor Services Since China first started opening up its capital
Interest Rate Policies for the People s Republic of China: Some Considerations
 Interest Rate Policies for the People s Republic of China: Some Considerations 1.The Objectives of Interest Rate Policies The rate of interest (and its term structure) is an extremely important instrument
Interest Rate Policies for the People s Republic of China: Some Considerations 1.The Objectives of Interest Rate Policies The rate of interest (and its term structure) is an extremely important instrument
Webinar: A look at the Top-10 China Financial Industry Trends for 2013
 Webinar: A look at the Top-10 China Financial Industry Trends for 2013 February 7th, 2013-17:00 17:45 Beijing Standard Time The webinar will start in a few minutes. For more information about the topics
Webinar: A look at the Top-10 China Financial Industry Trends for 2013 February 7th, 2013-17:00 17:45 Beijing Standard Time The webinar will start in a few minutes. For more information about the topics
2017 Renminbi Internationalisation Survey Report. Together we thrive
 2017 Renminbi Internationalisation Survey Report Together we thrive 2 2017 Renminbi Internationalisation Survey Report HSBC is at the forefront of both offshore and onshore Renminbi (RMB) business: One
2017 Renminbi Internationalisation Survey Report Together we thrive 2 2017 Renminbi Internationalisation Survey Report HSBC is at the forefront of both offshore and onshore Renminbi (RMB) business: One
OCR Economics A-level
 OCR Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 4: The Global Context 4.5 Trade policies and negotiations Notes Different methods of protectionism Protectionism is the act of guarding a country s industries
OCR Economics A-level Macroeconomics Topic 4: The Global Context 4.5 Trade policies and negotiations Notes Different methods of protectionism Protectionism is the act of guarding a country s industries
Business Models in China
 China offers a set of business models quite similar to those of more developed nations. Differences apply not to the business models themselves, but to the specific regulatory and contextual environment
China offers a set of business models quite similar to those of more developed nations. Differences apply not to the business models themselves, but to the specific regulatory and contextual environment
INDUSTRY OVERVIEW SOURCE OF INFORMATION
 3rd Sch3 The information presented in this section is, including certain facts, statistics and data, derived from the CIC Report, which was commissioned by us and from various official government publications
3rd Sch3 The information presented in this section is, including certain facts, statistics and data, derived from the CIC Report, which was commissioned by us and from various official government publications
China Construction Bank Corporation
 ENGLISH TRANSLATION OF THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS FOR THE YEAR FROM 1 JANUARY 2006 TO 31 DECEMBER 2006 IF THERE IS ANY CONFLICT OF MEANING BETWEEN THE CHINESE AND ENGLISH VERSIONS, THE CHINESE VERSION WILL
ENGLISH TRANSLATION OF THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS FOR THE YEAR FROM 1 JANUARY 2006 TO 31 DECEMBER 2006 IF THERE IS ANY CONFLICT OF MEANING BETWEEN THE CHINESE AND ENGLISH VERSIONS, THE CHINESE VERSION WILL
BANKING IN CHINA TEN PRACTICES YOU NEED TO UNDERSTAND
 INTERNATIONAL SERVICES BANKING IN CHINA TEN PRACTICES YOU NEED TO UNDERSTAND By Chris Chen, CertICM, Representative, PNC s Shanghai Representative Office This whitepaper focuses on the top 10 concepts
INTERNATIONAL SERVICES BANKING IN CHINA TEN PRACTICES YOU NEED TO UNDERSTAND By Chris Chen, CertICM, Representative, PNC s Shanghai Representative Office This whitepaper focuses on the top 10 concepts
The Chinese Approach to Capital Account Liberalization: What Do We Learn from Renminbi Banking in Hong Kong?
 HKIMR First International Conference on the Chinese Economy The Chinese Approach to Capital Account Liberalization: What Do We Learn from Renminbi Banking in Hong Kong? Dong HE Hong Kong Monetary Authority
HKIMR First International Conference on the Chinese Economy The Chinese Approach to Capital Account Liberalization: What Do We Learn from Renminbi Banking in Hong Kong? Dong HE Hong Kong Monetary Authority
ANZ ASIA INVESTOR TOUR 2014
 ANZ ASIA INVESTOR TOUR 214 AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND BANKING GROUP LIMITED 23 JULY 214 STEVE BELLOTTI MANAGING DIRECTOR Global Markets & Loans Global Markets and Global Loans are two of the three product
ANZ ASIA INVESTOR TOUR 214 AUSTRALIA AND NEW ZEALAND BANKING GROUP LIMITED 23 JULY 214 STEVE BELLOTTI MANAGING DIRECTOR Global Markets & Loans Global Markets and Global Loans are two of the three product
Canada: A RMB Hub for the Americas
 Canada: A RMB Hub for the Americas 3 74 % Canadian companies are embracing trade with Mainland China. 74% of Canadian companies surveyed expect to increase trade with the country in the next 12 months
Canada: A RMB Hub for the Americas 3 74 % Canadian companies are embracing trade with Mainland China. 74% of Canadian companies surveyed expect to increase trade with the country in the next 12 months
Tariff of Accounts and Services for Personal Customers
 Tariff of Accounts and Services for Personal Customers Enquiry Hotline: 800 830 2880 www.hsbc.com.cn Issued by HSBC Bank (China) Company Limited This tariff (as may be amended or supplemented from time
Tariff of Accounts and Services for Personal Customers Enquiry Hotline: 800 830 2880 www.hsbc.com.cn Issued by HSBC Bank (China) Company Limited This tariff (as may be amended or supplemented from time
China s Securities Market Development: Lessons from Hong Kong and Other Asian Markets. Xiao Geng 1
 China s Securities Market Development: Lessons from Hong Kong and Other Asian Markets Xiao Geng 1 Draft: 15 January 2003 Achievements of China s securities market In a little more than a decade s time,
China s Securities Market Development: Lessons from Hong Kong and Other Asian Markets Xiao Geng 1 Draft: 15 January 2003 Achievements of China s securities market In a little more than a decade s time,
China Financial Reforms: In need of further deregulation
 China Financial Reforms: In need of further deregulation Mingchun Sun 1 Summary Over the past decade, the Chinese government has implemented a series of financial reforms and transformed its financial
China Financial Reforms: In need of further deregulation Mingchun Sun 1 Summary Over the past decade, the Chinese government has implemented a series of financial reforms and transformed its financial
BOC Hong Kong ( Holdings ) delivered solid results with profit attributable to the equity holders of HK$11.2 billion
 29 Aug 2013 BOC Hong Kong ( Holdings ) delivered solid results with profit attributable to the equity holders of HK$11.2 billion BOC Hong Kong ( Holdings ) Limited 2013 Interim Results Financial Highlights
29 Aug 2013 BOC Hong Kong ( Holdings ) delivered solid results with profit attributable to the equity holders of HK$11.2 billion BOC Hong Kong ( Holdings ) Limited 2013 Interim Results Financial Highlights
A D VA N C E D S P C F U N D S P C NOVEMBER 2018 十一
 A D VA N C E D F U N D S P C S P C NOVEMBER 2018 十一 SPC ( ) ( ) 2018 8 ( ) ** : ( ) Citibank Europe plc, Luxembourg Branch AA ( )Inc AA ( )Inc AA ( )Inc AA ( ) AA ( ) AA 2.05% AA AA ( ) AA ( ) ( ) 6 30
A D VA N C E D F U N D S P C S P C NOVEMBER 2018 十一 SPC ( ) ( ) 2018 8 ( ) ** : ( ) Citibank Europe plc, Luxembourg Branch AA ( )Inc AA ( )Inc AA ( )Inc AA ( ) AA ( ) AA 2.05% AA AA ( ) AA ( ) ( ) 6 30
Newsletter No. 137 (EN) Setting up an Asian Hub: Why and Where
 Setting up an Asian Hub: Why and Where April 2015 All rights reserved Lorenz & Partners 2015 Although Lorenz & Partners always pays great attention on updating information provided in newsletters and brochures
Setting up an Asian Hub: Why and Where April 2015 All rights reserved Lorenz & Partners 2015 Although Lorenz & Partners always pays great attention on updating information provided in newsletters and brochures
Establishment of a Wholly Foreign-owned Enterprise
 Establishment of a Wholly Foreign-owned Enterprise Wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs) are entities established under the Law of the People s Republic of China on WFOEs (the WFOE Law ). By definition,
Establishment of a Wholly Foreign-owned Enterprise Wholly foreign-owned enterprises (WFOEs) are entities established under the Law of the People s Republic of China on WFOEs (the WFOE Law ). By definition,
Bank Readiness for Interest Rate Liberalization in China
 1 FINANCE WORKING PAPER Bank Readiness for Interest Rate Liberalization in China Liu Mingkang 1 August 2013 1 Special thanks to the China Banking Association for their help in designing the survey and
1 FINANCE WORKING PAPER Bank Readiness for Interest Rate Liberalization in China Liu Mingkang 1 August 2013 1 Special thanks to the China Banking Association for their help in designing the survey and
BMO Mutual Funds 2015
 BMO Mutual Funds 2015 Semi-Annual Financial Statements BMO Short-Term Income Class NOTICE OF NO AUDITOR REVIEW OF THE SEMI-ANNUAL FINANCIAL STATEMENTS BMO Investments Inc., the Manager of the Fund, appoints
BMO Mutual Funds 2015 Semi-Annual Financial Statements BMO Short-Term Income Class NOTICE OF NO AUDITOR REVIEW OF THE SEMI-ANNUAL FINANCIAL STATEMENTS BMO Investments Inc., the Manager of the Fund, appoints
HSBC Collective Investment Trust HSBC Asia Pacific ex Japan Equity Volatility Focused Fund
 Important information: The Fund invests mainly in Asia Pacific ex Japan Equity. The Fund is subject to the risks of investing in emerging markets. The Fund may invest in financial derivative instruments
Important information: The Fund invests mainly in Asia Pacific ex Japan Equity. The Fund is subject to the risks of investing in emerging markets. The Fund may invest in financial derivative instruments
HSBC PRIVATE BANK 2017 INVESTMENT OUTLOOK: GO WEST OR EAST. Bond Yield to Come Down, Focus on Growth Opportunities in the US & Asia
 News Release HSBC PRIVATE BANK 2017 INVESTMENT OUTLOOK: GO WEST OR EAST Bond Yield to Come Down, Focus on Growth Opportunities in the US & Asia Following a surprising and turbulent 2016, global financial
News Release HSBC PRIVATE BANK 2017 INVESTMENT OUTLOOK: GO WEST OR EAST Bond Yield to Come Down, Focus on Growth Opportunities in the US & Asia Following a surprising and turbulent 2016, global financial
Monetary Policy and Interest Rate Reform
 Thomas Shik Senior Economist thomasshik@hangseng.com Monetary Policy and Interest Rate Reform The benchmark lending rate set by the People s Bank of China (PBOC) has remained the key reference for banks
Thomas Shik Senior Economist thomasshik@hangseng.com Monetary Policy and Interest Rate Reform The benchmark lending rate set by the People s Bank of China (PBOC) has remained the key reference for banks
ASF Hong Kong Market Report
 HONG KONG ECONOMY ASF 2016 - Hong Kong Market Report Background As everyone knows, Hong Kong has a very good geographic location, it is surround by sea and backup by a huge China market. HK has taken a
HONG KONG ECONOMY ASF 2016 - Hong Kong Market Report Background As everyone knows, Hong Kong has a very good geographic location, it is surround by sea and backup by a huge China market. HK has taken a
May Panda Bonds. Overview and current development in the interbank market
 May 2016 Panda Bonds Overview and current development in the interbank market What you need to know As at the end of February 2016, the issuers in the interbank market were mainly international development
May 2016 Panda Bonds Overview and current development in the interbank market What you need to know As at the end of February 2016, the issuers in the interbank market were mainly international development
Offshore RMB Market Update
 Offshore RMB Market Update Ricky Li Economics and Strategic Planning Department Bank of China (Hong Kong) Limited November 2014 Offshore RMB Market Update A. Offshore RMB Bond Market Update B. RMB Internationalization
Offshore RMB Market Update Ricky Li Economics and Strategic Planning Department Bank of China (Hong Kong) Limited November 2014 Offshore RMB Market Update A. Offshore RMB Bond Market Update B. RMB Internationalization
In the usual course of business the application of a dilution adjustment will be triggered mechanically and on a consistent basis.
 Schroder Investment Management (Hong Kong) Limited Level 33, Two Pacific Place 88 Queensway, Hong Kong ( ) 88 33 Tel +852 2521 1633 Fax +852 2530 9095 www.schroders.com.hk IMPORTANT: This letter is important
Schroder Investment Management (Hong Kong) Limited Level 33, Two Pacific Place 88 Queensway, Hong Kong ( ) 88 33 Tel +852 2521 1633 Fax +852 2530 9095 www.schroders.com.hk IMPORTANT: This letter is important
IUMI 2014 Hong Kong Conference Building Expertise for a Changing World
 IUMI 2014 Hong Kong Conference Building Expertise for a Changing World Keynote Address by the Hon Mrs Laura Cha Chairman of Financial Services Development Council, Hong Kong 22 September 2014 The Shift
IUMI 2014 Hong Kong Conference Building Expertise for a Changing World Keynote Address by the Hon Mrs Laura Cha Chairman of Financial Services Development Council, Hong Kong 22 September 2014 The Shift
The Internationalization of the RMB: A Treasury Perspective
 ctc guide to The Internationalization of the RMB: A Treasury Perspective Executive Summary Underwritten by: CTC GUIDE: The Internationalization of the RMB: A Treasury Perspective Executive Summary The
ctc guide to The Internationalization of the RMB: A Treasury Perspective Executive Summary Underwritten by: CTC GUIDE: The Internationalization of the RMB: A Treasury Perspective Executive Summary The
Global RMB Clearing Service. Bank of China Head Office Clearing Department Apr. 2018
 Global RMB Clearing Service Bank of China Head Office Clearing Department Apr. 2018 CONTENT I. Global RMB Clearing II. BOC RMB Clearing Service III. BOC s Strength 1. Overview of RMB Internationalization
Global RMB Clearing Service Bank of China Head Office Clearing Department Apr. 2018 CONTENT I. Global RMB Clearing II. BOC RMB Clearing Service III. BOC s Strength 1. Overview of RMB Internationalization
Economic Reform without Losers: Twenty Years of Chinese Experience ( )
 Economic Reform without Losers: Twenty Years of Chinese Experience (1979-1999) Lawrence J. Lau, Yingyi Qian and Gérard Roland Department of Economics Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-6072, U.S.A.
Economic Reform without Losers: Twenty Years of Chinese Experience (1979-1999) Lawrence J. Lau, Yingyi Qian and Gérard Roland Department of Economics Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-6072, U.S.A.
Towards Global Expansions of Japanese Companies. and Financial Institutions
 Towards Global Expansions of Japanese Companies and Financial Institutions Public-Private Financial Roundtable Global Expansion Task Force 1. Purpose Contents 2. Status of global expansion of Japanese
Towards Global Expansions of Japanese Companies and Financial Institutions Public-Private Financial Roundtable Global Expansion Task Force 1. Purpose Contents 2. Status of global expansion of Japanese
THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED 2014 INTERIM CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS
 4 August 2014 THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED 2014 INTERIM CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS Profit before tax down 38% to HK$59,096m (HK$95,550m in the first half of ). Attributable
4 August 2014 THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED 2014 INTERIM CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS Profit before tax down 38% to HK$59,096m (HK$95,550m in the first half of ). Attributable
Navigating the China market - Sustaining high growth through innovations
 Navigating the China market - Sustaining high growth through innovations Louis Cheung Group President Sept 2010 P.0 May, 2010 Summary Ⅰ THE CHINA GROWTH STORY Despite recent volatility, the Chinese market
Navigating the China market - Sustaining high growth through innovations Louis Cheung Group President Sept 2010 P.0 May, 2010 Summary Ⅰ THE CHINA GROWTH STORY Despite recent volatility, the Chinese market
January Premier Schedule of Services and Tariffs
 January 2013 Premier Schedule of Services and Tariffs General Conditions: 1- The Bank reserves the right to levy additional charges for services and change the fees and charges at its sole discretion.
January 2013 Premier Schedule of Services and Tariffs General Conditions: 1- The Bank reserves the right to levy additional charges for services and change the fees and charges at its sole discretion.
Corporate Cash Management. Steven M. Bragg
 Corporate Cash Management Steven M. Bragg Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Introduction to Cash Management... 1 The Nature of Cash Management... 1 The Cash Manager Job... 2 Account Maintenance... 3 Debt Management...
Corporate Cash Management Steven M. Bragg Table of Contents Chapter 1 - Introduction to Cash Management... 1 The Nature of Cash Management... 1 The Cash Manager Job... 2 Account Maintenance... 3 Debt Management...
China s GDP slows out of double-digit growth
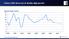 China s GDP slows out of double-digit growth Percent change, annual 16 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 198 1985 199 1995 2 25 21 215 Source: International Monetary Fund. China s growth forecasts slows among Asian countries
China s GDP slows out of double-digit growth Percent change, annual 16 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 198 1985 199 1995 2 25 21 215 Source: International Monetary Fund. China s growth forecasts slows among Asian countries
ANNOUNCEMENT OF 2011 INTERIM RESULTS
 Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited and The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited take no responsibility for the contents of this announcement, make no representation as to its accuracy or completeness
Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited and The Stock Exchange of Hong Kong Limited take no responsibility for the contents of this announcement, make no representation as to its accuracy or completeness
Guide to Financial Management Course Number: 6431
 Guide to Financial Management Course Number: 6431 Test Questions: 1. Objectives of managerial finance do not include: A. Employee profits. B. Stockholders wealth maximization. C. Profit maximization. D.
Guide to Financial Management Course Number: 6431 Test Questions: 1. Objectives of managerial finance do not include: A. Employee profits. B. Stockholders wealth maximization. C. Profit maximization. D.
The USD/CNY Adjustment Is It Complete?
 The USD/CNY Adjustment Is It Complete? Derek Halpenny European Head of Global Currency Research European Central Bank June 29 1 Substantial REER Appreciation 1 USD/CNY vs Renminbi REER 9 8 7 6 5 12 11
The USD/CNY Adjustment Is It Complete? Derek Halpenny European Head of Global Currency Research European Central Bank June 29 1 Substantial REER Appreciation 1 USD/CNY vs Renminbi REER 9 8 7 6 5 12 11
Reform of Global Reserve System and China s Choice 1
 Reform of Global Reserve System and China s Choice 1 Liqing Zhang Professor and Dean, School of Finance, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing Email: zhlq@cufe.edu.cn 1. Why the Regime should
Reform of Global Reserve System and China s Choice 1 Liqing Zhang Professor and Dean, School of Finance, Central University of Finance and Economics, Beijing Email: zhlq@cufe.edu.cn 1. Why the Regime should
THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED 2014 CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS
 23 February 2015 THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS Pre-tax profit HK$111,189m (HK$144,756m in ) tributable profit HK$86,428m (HK$119,009m in ) Return
23 February 2015 THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS Pre-tax profit HK$111,189m (HK$144,756m in ) tributable profit HK$86,428m (HK$119,009m in ) Return
PRODUCT KEY FACTS SWS STRATEGIC INVESTMENT FUNDS Shenyin Wanguo RMB Mainland Investment Fund September 2017
 Issuer: Shenwan Hongyuan Asset Management (Asia) Limited PRODUCT KEY FACTS SWS STRATEGIC INVESTMENT FUNDS Shenyin Wanguo RMB Mainland Investment Fund September 2017 This statement provides you with key
Issuer: Shenwan Hongyuan Asset Management (Asia) Limited PRODUCT KEY FACTS SWS STRATEGIC INVESTMENT FUNDS Shenyin Wanguo RMB Mainland Investment Fund September 2017 This statement provides you with key
Unravel the complexities of RMB Internationalisation The Rising Role of RMB- A Corporate Perspective 24 May 2012 PUBLIC
 Unravel the complexities of RMB Internationalisation The Rising Role of RMB- A Corporate Perspective 24 May 2012 1. RMB Internationalisation Overview A Global Trade Currency A Global Investment Currency
Unravel the complexities of RMB Internationalisation The Rising Role of RMB- A Corporate Perspective 24 May 2012 1. RMB Internationalisation Overview A Global Trade Currency A Global Investment Currency
Edexcel Economics A-level
 Edexcel Economics A-level Unit 4: The Global Economy Topic 2: Trade and the World Economy 2.4 Trade liberalisation Notes Types of trading blocs (regional trade agreements and bilateral trade agreements):
Edexcel Economics A-level Unit 4: The Global Economy Topic 2: Trade and the World Economy 2.4 Trade liberalisation Notes Types of trading blocs (regional trade agreements and bilateral trade agreements):
Offshore Renminbi (CNH) Market: Opportunities Continue to Expand Silicon Valley Bank. January 13, 2012
 Offshore Renminbi (CNH) Market: Opportunities Continue to Expand Silicon Valley Bank January 13, 2012 1 Panelists Ed Sauve, Senior Advisor GFS, Silicon Valley Bank Mark Noble, Senior Foreign Exchange Trader,
Offshore Renminbi (CNH) Market: Opportunities Continue to Expand Silicon Valley Bank January 13, 2012 1 Panelists Ed Sauve, Senior Advisor GFS, Silicon Valley Bank Mark Noble, Senior Foreign Exchange Trader,
Globalization of Korea s Foreign Exchange System. Seoul Asian Financial Forum. June 4, Michael Hellbeck
 Globalization of Korea s Foreign Exchange System Seoul Asian Financial Forum June 4, 2012 Michael Hellbeck COO & Head of Regulatory Affairs Standard Chartered Bank Korea 2 Agenda Introduction to Standard
Globalization of Korea s Foreign Exchange System Seoul Asian Financial Forum June 4, 2012 Michael Hellbeck COO & Head of Regulatory Affairs Standard Chartered Bank Korea 2 Agenda Introduction to Standard
Treasurers cash management practices in mainland China. In-depth fundamentals to help build an effective cash management structure
 Treasurers cash management practices in mainland China In-depth fundamentals to help build an effective cash management structure Today s presenters Marc Monyek Senior Manager, EY Financial Accounting
Treasurers cash management practices in mainland China In-depth fundamentals to help build an effective cash management structure Today s presenters Marc Monyek Senior Manager, EY Financial Accounting
PRODUCT KEY FACTS. Quick Facts. What is this product?
 PRODUCT KEY FACTS Mirae Asset Horizons Exchange Traded Funds Series- September 2018 Issuer: Mirae Asset Global Investments (Hong Kong) Limited This is an exchange traded fund. This statement provides you
PRODUCT KEY FACTS Mirae Asset Horizons Exchange Traded Funds Series- September 2018 Issuer: Mirae Asset Global Investments (Hong Kong) Limited This is an exchange traded fund. This statement provides you
HSBC Global Investment Funds ("HSBC GIF") Société d'investissement à capital variable
 HSBC Global Investment Funds ("HSBC GIF") Société d'investissement à capital variable 16, Boulevard d'avranches, L-1160 Luxembourg Grand Duchy of Luxembourg R.C.S. Luxembourg No. B 25 087 Luxembourg, 6
HSBC Global Investment Funds ("HSBC GIF") Société d'investissement à capital variable 16, Boulevard d'avranches, L-1160 Luxembourg Grand Duchy of Luxembourg R.C.S. Luxembourg No. B 25 087 Luxembourg, 6
October 2012 Hong Kong Sustainable Development Research Institute Edmund Ho
 Featured Article: Role of Hong Kong as a RMB Offshore Center October 2012 Hong Kong Sustainable Development Research Institute Edmund Ho Introduction The economy of China developed rapidly after the open
Featured Article: Role of Hong Kong as a RMB Offshore Center October 2012 Hong Kong Sustainable Development Research Institute Edmund Ho Introduction The economy of China developed rapidly after the open
Report on the Philippines
 Arctic Circle This report provides helpful information on the current business environment in the Philippines. It is designed to assist companies in doing business and establishing effective banking arrangements.
Arctic Circle This report provides helpful information on the current business environment in the Philippines. It is designed to assist companies in doing business and establishing effective banking arrangements.
Manager and RQFII Holder: E Fund Management (Hong Kong) Co., Limited Bank of Communications Trustee Limited
 PRODUCT KEY FACTS E Fund Investment Fund Series- E Fund (HK) RMB Fixed Income Fund E Fund Management (Hong Kong) Co., Limited November 2018 This statement provides you with key information about E Fund
PRODUCT KEY FACTS E Fund Investment Fund Series- E Fund (HK) RMB Fixed Income Fund E Fund Management (Hong Kong) Co., Limited November 2018 This statement provides you with key information about E Fund
Internationalization of the RMB: Developments, Problems and Policies
 Internationalization of the RMB: Developments, Problems and Policies 23 October 2015 Zheng Liansheng Outline Introduction The development of RMB internationalization RMB Offshore markets The problems behind
Internationalization of the RMB: Developments, Problems and Policies 23 October 2015 Zheng Liansheng Outline Introduction The development of RMB internationalization RMB Offshore markets The problems behind
Accountant s Guide to Financial Management - Final Exam 100 Questions 1. Objectives of managerial finance do not include:
 Accountant s Guide to Financial Management - Final Exam 100 Questions 1. Objectives of managerial finance do not include: Employee profits B. Stockholders wealth maximization Profit maximization Social
Accountant s Guide to Financial Management - Final Exam 100 Questions 1. Objectives of managerial finance do not include: Employee profits B. Stockholders wealth maximization Profit maximization Social
2013 The year of the renminbi
 2013 The year of the renminbi Economic and regulatory conditions affecting the renminbi are unfolding quickly. This document reflects HSBC s views on how the development of the renminbi will unfold as
2013 The year of the renminbi Economic and regulatory conditions affecting the renminbi are unfolding quickly. This document reflects HSBC s views on how the development of the renminbi will unfold as
General Tariff for Fusion Customers Issue Date: August 2018
 General Tariff for Fusion Customers Issue Date: August 2018 Tariff applies on accounts, facilities, services and transactions used/made for business purposes only. 2 Issue Date: August 2018 Contents General
General Tariff for Fusion Customers Issue Date: August 2018 Tariff applies on accounts, facilities, services and transactions used/made for business purposes only. 2 Issue Date: August 2018 Contents General
Medium-term Business Plan
 Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Inc. Medium-term Business Plan Tokyo, May 15, 2012 --- Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Inc. (MUFG) announced today that it has formulated its medium-term business plan for
Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Inc. Medium-term Business Plan Tokyo, May 15, 2012 --- Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Inc. (MUFG) announced today that it has formulated its medium-term business plan for
Terms otherwise not defined in this letter will have the same meaning as those defined in the current prospectus of the Fund (the Prospectus ).
 HSBC Global Asset Management (Singapore) Limited 21 Collyer Quay #06-01 HSBC Building Singapore 049320 T: 65 6658 2900 F: 65 6225 4324 www.assetmanagement.hsbc.com/sg April 6, 2018 This document is important
HSBC Global Asset Management (Singapore) Limited 21 Collyer Quay #06-01 HSBC Building Singapore 049320 T: 65 6658 2900 F: 65 6225 4324 www.assetmanagement.hsbc.com/sg April 6, 2018 This document is important
Global Banking Service
 Arctic Circle This report provides helpful information on the current business environment in Taiwan. It is designed to assist companies in doing business and establishing effective banking arrangements.
Arctic Circle This report provides helpful information on the current business environment in Taiwan. It is designed to assist companies in doing business and establishing effective banking arrangements.
Tariff of Accounts and Services
 For Private Banking Customers (Effective from 31 December 2016) Tariff of Accounts and Services HSBC Bank (China) Company Limited Incorporated in the PRC with limited liability This tariff is formulated
For Private Banking Customers (Effective from 31 December 2016) Tariff of Accounts and Services HSBC Bank (China) Company Limited Incorporated in the PRC with limited liability This tariff is formulated
Hong Kong s s Expanding Role as an Offshore RMB Centre
 Hong Kong s s Expanding Role as an Offshore RMB Centre Goldman Sachs Global Macro Conference Peter Pang Deputy Chief Executive Hong Kong Monetary Authority 22 February 211 Mainland s s Phenomenal Growth
Hong Kong s s Expanding Role as an Offshore RMB Centre Goldman Sachs Global Macro Conference Peter Pang Deputy Chief Executive Hong Kong Monetary Authority 22 February 211 Mainland s s Phenomenal Growth
Financial Section. Contents. 1 Management s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
 Financial Section 2017 Fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 Contents 1 Management s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations 7 Consolidated Statement of Financial Position 9
Financial Section 2017 Fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 Contents 1 Management s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations 7 Consolidated Statement of Financial Position 9
TALKING Points. FDI in China s Middle Enterprise Sector. Lim Lee Meng RSM Chio Lim
 TALKING Points FDI in China s Middle Enterprise Sector Lim Lee Meng RSM Chio Lim July 2008 July 2008 TALKING Points Inbound foreign direct investment in China, a sphere long dominated by large multinationals,
TALKING Points FDI in China s Middle Enterprise Sector Lim Lee Meng RSM Chio Lim July 2008 July 2008 TALKING Points Inbound foreign direct investment in China, a sphere long dominated by large multinationals,
Effective From 23 October, 2017 GN (10/2017) Service Charges. An Easy guide to banking fees
 Effective From 23 October, 2017 GN150-65 (10/2017) Service Charges An Easy guide to banking fees Contents relationship banking plans 1-2 deposit account-related 2-4 foreign exchange services 4-5 outward
Effective From 23 October, 2017 GN150-65 (10/2017) Service Charges An Easy guide to banking fees Contents relationship banking plans 1-2 deposit account-related 2-4 foreign exchange services 4-5 outward
UNIT FIVE (5) The International Monetary Environment and Financial Management in the Global Firm
 UNIT FIVE (5) The International Monetary Environment and Financial Management in the Global Firm Objectives Exchange rates and currencies How exchange rates are determined The monetary and financial systems
UNIT FIVE (5) The International Monetary Environment and Financial Management in the Global Firm Objectives Exchange rates and currencies How exchange rates are determined The monetary and financial systems
INVESTING IN CHINA - NEW CHALLENGES, PROBLEMS AND ISSUES - (Written by Mary Zhu under the editorial supervision of Adriana Morrison)
 INVESTING IN CHINA - NEW CHALLENGES, PROBLEMS AND ISSUES - (Written by Mary Zhu under the editorial supervision of Adriana Morrison) REGULATORY REGIME FOR FOREIGN INVESTMENT Economic Overview Foreign Direct
INVESTING IN CHINA - NEW CHALLENGES, PROBLEMS AND ISSUES - (Written by Mary Zhu under the editorial supervision of Adriana Morrison) REGULATORY REGIME FOR FOREIGN INVESTMENT Economic Overview Foreign Direct
FTSE Emerging incl. China Overseas
 FTSE Emerging incl. China Overseas non-r/qfii GDP Weighted Index Do you weight for the China A-shares inclusion? As the opening up of the Chinese equities market continues, international market participants
FTSE Emerging incl. China Overseas non-r/qfii GDP Weighted Index Do you weight for the China A-shares inclusion? As the opening up of the Chinese equities market continues, international market participants
Mackenzie Growth ETF Portfolio
 management report Management s Responsibility for Financial Reporting The accompanying financial statements have been prepared by Mackenzie Financial Corporation, as Manager of Mackenzie Growth ETF Portfolio
management report Management s Responsibility for Financial Reporting The accompanying financial statements have been prepared by Mackenzie Financial Corporation, as Manager of Mackenzie Growth ETF Portfolio
CEPA: Cross-boundary Business Opportunities. Edward Leung Chief Economist, HKTDC 18 September 2009
 CEPA: Cross-boundary Business Opportunities Edward Leung Chief Economist, HKTDC 18 September 2009 4 Major Concerns on CEPA: - What are the main provisions of CEPA? - Who qualifies? - What are the benefits
CEPA: Cross-boundary Business Opportunities Edward Leung Chief Economist, HKTDC 18 September 2009 4 Major Concerns on CEPA: - What are the main provisions of CEPA? - Who qualifies? - What are the benefits
Supplementary Information
 I DIFFERENCES BETWEEN IFRS AND CAS CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION There are no differences in the Group s operating results for the six month periods ended and 2016 or total equity as at and as at
I DIFFERENCES BETWEEN IFRS AND CAS CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL INFORMATION There are no differences in the Group s operating results for the six month periods ended and 2016 or total equity as at and as at
Service Introduction. 1.1 Application Method. 1.2 System Requirement
 Welcome to CBS Online. You can now manage your corporate bank accounts more conveniently over the internet anytime, anywhere. CBS Online is applicable to most of the operating system of tablets, mobile
Welcome to CBS Online. You can now manage your corporate bank accounts more conveniently over the internet anytime, anywhere. CBS Online is applicable to most of the operating system of tablets, mobile
UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO INTERNAL AUDIT DEPARTMENT MANAGE CASH FLOW
 The following control objectives provide a basis for strengthening your control environment for the process of managing cash flow. When you select an objective, you will access a list of the associated
The following control objectives provide a basis for strengthening your control environment for the process of managing cash flow. When you select an objective, you will access a list of the associated
 http://e-asia.uoregon.edu HONG KONG TRADE SUMMARY The U.S. trade surplus with Hong Kong was $6.5 billion in 2004, an increase of $1.8 billion from $4.7 billion in 2003. U.S. goods exports in 2004 were
http://e-asia.uoregon.edu HONG KONG TRADE SUMMARY The U.S. trade surplus with Hong Kong was $6.5 billion in 2004, an increase of $1.8 billion from $4.7 billion in 2003. U.S. goods exports in 2004 were
Capital account management in China. Yu Yongding CAFRAL Conference, New Delhi, Jan 12, 2014
 Capital account management in China Yu Yongding CAFRAL Conference, New Delhi, Jan 12, 2014 China now is more sympathetic with capital account liberalization, but why? since 2003, and especially since 2009
Capital account management in China Yu Yongding CAFRAL Conference, New Delhi, Jan 12, 2014 China now is more sympathetic with capital account liberalization, but why? since 2003, and especially since 2009
Transformation and Development in a New Environment
 Transformation and Development in a New Environment China Life Insurance Company Limited November 28, 2013 Agenda Section I Section II Section III Features of the Current Life Insurance Industry in China
Transformation and Development in a New Environment China Life Insurance Company Limited November 28, 2013 Agenda Section I Section II Section III Features of the Current Life Insurance Industry in China
Increasing Competition among Markets for Offshore Renminbi Business
 Increasing Competition among Markets for Offshore Renminbi Business Eiichi Sekine Chief Representative, Beijing Representative Office Nomura Institute of Capital Markets Research Masanobu Iwatani Financial
Increasing Competition among Markets for Offshore Renminbi Business Eiichi Sekine Chief Representative, Beijing Representative Office Nomura Institute of Capital Markets Research Masanobu Iwatani Financial
Legal Issues for Foreign Companies doing Business in China Nordic Centre, Fudan University, March 26, 2012
 Legal Issues for Foreign Companies doing Business in China Nordic Centre, Fudan University, March 26, 2012 Qi Tong CMS, China Room 2801-2812, Plaza 66 Tower 2 Tel: 0086-(0)21-6289 6363 1266 Nanjing Road
Legal Issues for Foreign Companies doing Business in China Nordic Centre, Fudan University, March 26, 2012 Qi Tong CMS, China Room 2801-2812, Plaza 66 Tower 2 Tel: 0086-(0)21-6289 6363 1266 Nanjing Road
SUMMARY. Our Business Model We primarily provide the following financial services to individual, institutional and corporate clients:
 This summary aims to give you an overview of the information contained in this prospectus. As this is a summary, it does not contain all the information that may be important to you. You should read the
This summary aims to give you an overview of the information contained in this prospectus. As this is a summary, it does not contain all the information that may be important to you. You should read the
Tariff of Accounts and Services for Personal Customers
 Tariff of Accounts and Services for Personal Customers This tariff (as may be amended or supplemented from time to time) applies to services provided by the Mainland China branches of the Bank to their
Tariff of Accounts and Services for Personal Customers This tariff (as may be amended or supplemented from time to time) applies to services provided by the Mainland China branches of the Bank to their
KCSL Formation of WFOE
 KCSL Formation of WFOE CHINA INTRODUCTION TO WFOE The Wholly Owned Foreign Enterprise (WOFE) is a Limited liability company wholly owned by the foreign investor(s). In China, WOFEs were originally conceived
KCSL Formation of WFOE CHINA INTRODUCTION TO WFOE The Wholly Owned Foreign Enterprise (WOFE) is a Limited liability company wholly owned by the foreign investor(s). In China, WOFEs were originally conceived
32. Management of financial risks
 298 F CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 32. Management of financial risks General information on financial risks As a result of its businesses and the global
298 F CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS 32. Management of financial risks General information on financial risks As a result of its businesses and the global
THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED 2012 CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS. Pre-tax profit up 19% to HK$108,729m (HK$91,370m in 2011).
 News Release 4 March 2013 THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS Pre-tax profit up 19% to HK$108,729m (HK$91,370m in ). tributable profit up 23% to HK$83,008m
News Release 4 March 2013 THE HONGKONG AND SHANGHAI BANKING CORPORATION LIMITED CONSOLIDATED RESULTS HIGHLIGHTS Pre-tax profit up 19% to HK$108,729m (HK$91,370m in ). tributable profit up 23% to HK$83,008m
Supporting International Trade
 Supporting International Trade Rob Keller Head of UK Region, Trade Finance July 2012 Supporting International Trade 1. Hong Kong gateway to China 2. Trading considerations: risk, funding, visibility &
Supporting International Trade Rob Keller Head of UK Region, Trade Finance July 2012 Supporting International Trade 1. Hong Kong gateway to China 2. Trading considerations: risk, funding, visibility &
BMO Mutual Funds 2015
 BMO Mutual Funds 2015 Semi-Annual Financial Statements BMO Conservative ETF Portfolio NOTICE OF NO AUDITOR REVIEW OF THE SEMI-ANNUAL FINANCIAL STATEMENTS BMO Investments Inc., the Manager of the Fund,
BMO Mutual Funds 2015 Semi-Annual Financial Statements BMO Conservative ETF Portfolio NOTICE OF NO AUDITOR REVIEW OF THE SEMI-ANNUAL FINANCIAL STATEMENTS BMO Investments Inc., the Manager of the Fund,
Pricing Guide from Regulators
 Pricing Guide from Regulators Version 2013-03 Z1 RMB Account Service Rate Min. Max. Z3 Rate Min. Max. Z1.1 Outward Remittance Z3.1 Draft Issuance of Bank Accepted Draft (BAD) 0.05% Z1.1.1 Via HVPS - -
Pricing Guide from Regulators Version 2013-03 Z1 RMB Account Service Rate Min. Max. Z3 Rate Min. Max. Z1.1 Outward Remittance Z3.1 Draft Issuance of Bank Accepted Draft (BAD) 0.05% Z1.1.1 Via HVPS - -
Standard Chartered Bank (China) Limited Retail Banking Service Tariff Table Version 1
 Standard Chartered Bank (China) Limited Retail Banking Service Tariff Table 2019 Version 1 01/01/2019 Important Note: 1. This Tariff Table is formulated by Standard Chartered Bank (China) Limited (the
Standard Chartered Bank (China) Limited Retail Banking Service Tariff Table 2019 Version 1 01/01/2019 Important Note: 1. This Tariff Table is formulated by Standard Chartered Bank (China) Limited (the
Being selective key to navigating
 Link to Article on website Being selective key to navigating China s new, investorfriendly policies Rex Lo, Managing Director of Business Development at BEA Union Investment, talks to Hubbis about China
Link to Article on website Being selective key to navigating China s new, investorfriendly policies Rex Lo, Managing Director of Business Development at BEA Union Investment, talks to Hubbis about China
The Internationalisation of the Renminbi
 Tel: (852)3550-7070; Fax: (852)2104-6938 Email: lawrence@lawrencejlau.hk; WebPages: www.igef.cuhk.edu.hk/ljl *All opinions expressed herein are the author s own and do not necessarily reflect the views
Tel: (852)3550-7070; Fax: (852)2104-6938 Email: lawrence@lawrencejlau.hk; WebPages: www.igef.cuhk.edu.hk/ljl *All opinions expressed herein are the author s own and do not necessarily reflect the views
Cash and Treasury Management Country Report JAPAN
 Underwritten by Cash and Treasury Management Country Report Executive Summary Banking The Japanese central bank is the Bank of Japan (BOJ). Bank supervision is performed by the Federal Services Agency
Underwritten by Cash and Treasury Management Country Report Executive Summary Banking The Japanese central bank is the Bank of Japan (BOJ). Bank supervision is performed by the Federal Services Agency
