B.Com(General) 1 st year FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING I
|
|
|
- Bridget Hall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 B.Com(General) 1 st year FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING I Module I Unit I Unit II Introduction Final accounts 20 Financial & Management accounting; Qualitative characteristics of accounting information. Double entry book keeping system Basic accounting equation, meaning of assets, liabilities, equity, revenue expenses. Accounting Cycle - Recording of transaction: Journal, Ledger preparation of Trial Balance. Bases of accounting; cash basis accrual basis. Basic concepts conventions: entity, money measurement, going concern, cost, realisation, accruals, periodicity, consistency, prudence (conservatism), materiality, matching full disclosures. 8 Preparation of financial statements: of sole proprietorship business entities from a trial balance Manufacturing, Trading, P/L A/c Balance Sheet Concepts for determination of business income Revenue recognition: Meaning of revenue; objective; timing of recognition. Recognition of expenses. Inventories: meaning. Significance of inventory valuation. Lower of cost or market The nature of depreciation. The accounting concept of depreciation. Factors in the measurement of depreciation. Methods of computing depreciation: straight line method diminishing balance method; Disposal of depreciable assets; change in method of charging depreciation. Accounting for depreciation: Asset-depreciation, Asset-provision. Reserves provisions: Capital revenue expenditures receipts: general introduction only. Adjustment rectification 8
2 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING I Module II Unit - I Unit - II Unit - III Unit - IV Unit - V Final accounts Preparation of financial statements: a) from incomplete records b) of non-profit organisation 16 Accounting for special sales transaction Consignment: Basic features; difference with sales. Recording in the books of Consignor at cost & at invoice price, Valuation of unsold stock; Ordinary commission. Treatment valuation of abnormal & normal loss. Special commission; Del credere commission (with without bad debt) - use of Consignment Debtors A/C. Recording in the books of Consignee Accounting for sale on approval 8 Sectional Self balancing ledger Concept of sectional balancing, preparation of control accounts. Self balancing Ledger: advantages; Recording process; 8 Insurance claim for loss of stock for loss of profit Loss of stock: Physical & ownership concept; concept of under-insurance average clause; computation of claim with price change; consideration of unusual selling line; price reduction etc. Loss of profit: Concept insured & uninsured sting charges, GP rate, short sales increased cost of working, average clause computation of claim ( simple type ) 8 Partnership accounts-i P/L Appropriation account; Capital & Current account; Guarantee by firm, by partner both ; correction of appropriation items with retrospective effect. Change in constitution of firm change in P/S ratio, admission, retirement retirement cum admission treatment of Goodwill, revaluation of assets & liabilities (with/without alteration of books), treatment of reserve adjustment relating to capital; treatment of Joint Life Policy, Death of a partner 16
3 BUSINESS REGULATORY FRAMEWORK Module I Unit - I Unit - II Unit - III Unit - IV Unit - V The Indian Contract Act, 1872 I Introduction Essential elements of a valid contract, classification of contracts 1.2 Offer Acceptance: meaning, rules relating to valid offer acceptance; communication of offer acceptance; revocation of offer acceptance 1.3 Consideration : definition ; essential elements, types of consideration ; no consideration no contract it s exceptions 1.4 Capacity of Parties: Competency to contract; minor; persons of unsound mind; persons disqualified by other laws 1.5 Consent: definition of consent free consent; 20 The Sale of Goods Act, Introduction: definition; goods their classification; sale a agreement to sell; essential elements of contract of sale; sale distinguished from hire purchase instalment sale 2.2 Conditions Warranties: distinction between condition warranty; implied conditions warranties 2.3 Doctrine of Caveat Emptor its exceptions 2.4 Transfer of Ownership: passing of property from the seller to the buyer 2.5 Transfer of Title by Non-owners: unpaid seller his rights 12 Indian Partnership Act, Partnership: meaning - partner, firm firm name; essential elements; true test of partnership 3.2 Types of Partner: partnership distinguished from co-ownership, company, club; partnership by estoppel or holding out; limited partnership 3.3 Registration of Partnership Firm: consequences of nonregistration 3.4 Minor s Position in Partnership 3.5 Rights Duties of the Partner: relation of partners with third parties; implied authority of a partner restrictions on the implied authority of a partner 12 The Negotiable Instruments Act, Negotiable Instruments: definition, features; Promissory Note, Bill of Exchange Cheque essential elements; distinction between Promissory Note, Bill of Exchange Cheque; types of cheques modes of crossing cheques; inchoate stamped instrument; accommodation bill; fictitious bill 4.2 Endorsement types of endorsement 4.3 Holder Holder in Due Course: rights of holder in due course 4.4 Dishonour of Negotiable Instruments: modes of dishonour; consequences; notice of dishonour; 12 Consumer Protection Act, Introduction: objective of the Act, definitions of complaint, consumer; consumer dispute, goods, services, etc. 5.2 Objectives of Central Council State Council 5.3 Consumer Dispute Redressal Agencies: composition jurisdiction of district forum, State Commission National Commission 5.4 Manner of Lodging a Complaint: procedure of complaint; findings of District Forum, Appeal 6
4 coercion; undue influence; fraud; misrepresentation; mistake 1.6 Void Voidable Agreements: definitions; distinction between void illegal agreement; wagering agreement 1.7 Discharge of Contracts: meaning; methods of termination or discharge of contract 1.8 Special Contracts: definition only contingent contract; quasi contract; contract of indemnity; contract of guarantee; bailment; pledge 3.6 Dissolution of Firms: meaning grounds of dissolution Noting; Protest
5 BUSINESS REGULATORY FRAMEWORK Module II INDIAN COMPANY LAW Unit - I Unit - II Unit - III Unit - IV Unit - V Introduction definitions, features types of Companies; private company public company differences, conversion of private company into public company vice versa 12 Memorum of Association Articles of Association, distinction, alteration of Memorum Articles of Association, Doctrine of Ultra Vires Indoor Management; Prospectus- form content- statutory requirements of a prospectus; additional disclosures in prospectus statement in lieu of prospectus statement by experts, Shelf prospectus, red- herring prospectus, abridged prospectus, misstatement in prospectus its consequences; minimum subscription; Dematerialized 12 Formation of Company: essential steps, procedure for registration incorporation, certificate of incorporation commencement of business; promoters legal status, duties, liabilities remuneration; allotment of shares 8 Share Capital equity preference shares; stock; sweat equity shares; ESOP(Employees stock option scheme); rights issue; share certificate share warrants - distinction; bonus shares; transfer transmission of shares; buy back of shares; debentureclassification 14 Board of Management Directorqualification, disqualification, appointment, legal position; number of directorship ; removal, Resignation of Director; duties, liabilities, powers of board of directors; Managing Director qualification, appointment; Company Meetings - quorum, resolution, Minutes; Winding up modes, Grounds for compulsory voluntary winding up 14
6 shares
7 PRINCIPLES MANAGEMENT & BUSINESS COMMUNICATION PRINCIPLES MANAGEMENT Module I Unit - I Unit - II Unit - III Unit - IV Unit -VI Unit - VII Unit -VIII Unit -IX Introduction to Management: Management - definition, importance, functions; Nature-as profession, science art, universality of management; Levels of management; managerial tasks skills N O L 5 Different Schools of Management Thought: Classical Schoolcontributions of Taylor Fayol; Neoclassical School- Human Relations approach Behavioural Science approach; Modern School- Systems approach Contingency approach L 12 Planning: concept, importance, types, steps, premises, barriers to effective planning remedial measures; Strategic Planningconcept; Forecastingconcept, techniques L 12 Organizing : concept, importance, principles, different organization models - Line & Staff, Functional; Departmentation need, basis, principles; Delegation of Authorityelement s, steps, barriers; Centralisation Decentralization of Authority; Span of Management - concept determining factors N OL Motivation: concept, importance, contributions of McGregor, Maslow, Herzberg N O L 8 Leaders hip: concept, importan ce, types, leadershi p traits; Tannenb aum & Schmidt s Model Blake & Mouton s Model N O L 8 Coordinati on: concept, significa nce, principle s, techniqu es N O L 2 Coordination: concept, significance, principles, techniques N O L 4
8 PRINCIPLES MANAGEMENT & BUSINESS COMMUNICATION BUSINESS COMMUNICATION MODULE II Unit - I Unit - II Unit - III Unit - IV Introduction: definition, objectives, importance, elements, process, forms, models; levels of analysis of business communication; principles of effective communication, barriers to Communication remedial measures, role of communication in conflict resolution Types of Communication: formal informal communication; grapevine; characteristics of corporate communication; communication network Tools of Communication: emergence of communication technology; modern forms of communication Fax, , Video Conferencing Drafting notice, circular, resolution, minutes, report; CV writing, business letter writing offer letter, quotation, status enquiry, confirmation, execution, refusal cancellation of order, recommendation, credit collection, claim, bank loan 20
9 ECOMICS I Module- I Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Unit VI Unit VII L L L L L L L Introduction Economics scope subject matter. Distinction between Economics Business Economics. Tools required Functional relationships, schedules, graphs, concept of slope its measurement- etc. Resources-scarcity efficiency - Production Possibility Frontier-it s shifting. 2 Basics of Dem Supply The concept of dem dem function - Derivation of Individual dem curve Market dem curve Shifting of the dem curve The supply function the supply curve Derivation of individual supply curve market supply curve Shifting of the supply curve- Determination of equilibrium price. 3 Theory of Consumer Behaviour: Cardinal analysis Law of diminishing marginal utility consumer surplus Ordinal approach Indifference curve analysis Budget line Consumer Equilibrium Income consumption curve Price consumption curve Hicksian decomposition of price effect into substitution effect Theory of Production Production Function The Law of variable proportions Relationships among TP, AP, MP. Concept of Isoquant Isocost Finding the optimal employment of inputs Ridge lines: the economic region of production Output expansion path homogeneous production function. 6 Theory of Cost Cost analysis Different concepts Accounting Economic costs, Opportunity cost, Private social costs; Short run long run costs 6 Market for Commodities Revenue concepts under different market conditions: TR, AR, MR relationship among AR, MR elasticity of dem. Perfect competition Short run long run equilibrium Supply curve in the short run (shutdown breakeven point concepts). Monopoly Short run long run equilibrium Concept of 12 Factor Price Determination Theory of Wage Determination - Backward Bending Supply curve of labour; Determination of Rent, Profit Interest rate. 11
10 income effect Dem curve for Normal, inferior Giffen goods Concept of Elasticities of dem Measurement pf various elasticities of dem Distinction between slope of a dem curve the elasticity of dem Elasticity of supply Measurement Price discrimination. Monopolistic competition, Oligopoly Market Short run long run equilibrium.
11 Module- II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Indian Business Environment Concepts: Economic Growth Development; Meaning of Underdeveloped Economy; Basic Characteristics of Indian economy. 4 Overview of Indian Economic Trends National Income: Concept - Methods of measurement of national income in Indian economy Trend of National Income & per capita income trend in structural composition of national income. Trend in occupational structure. Trends in Saving Investment in Indian economy. Issues in Indian Economy Problems of Growth: Unemployment, Poverty, Inequality in Income distribution, Inflation, Concept of Parallel economy Problems Policies of Indian Economy (A) Basic features of Indian agriculture: Low productivity; L reform; Green Revolution; Rural Credit; Agricultural Marketing; Impact of New Agricultural Policy (NEP) on Indian Agriculture with special reference to Food Security. 16 (B) Industrial development during plan period; Industrial sickness; Industrial policies in the Pre-reform Post-reform period in (C) Globalization the Policies of the Indian Economy under WTO Regime. 16 Indian Economic Planning Concepts of Economic Planning; Objective achievements of Indian Five-year Plans (Plan period I to XI). Import Substitution vs. Export Promotion Strategy.
12 BUSINESS MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Module I Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Unit VI Unit VII Unit VIII Unit IX Unit X Introduction:- Definition of Statistics; Importance scope of Mathematics Statistics in business decisions; Limitations 2 Permutations Definition, Factorial notation; Theorems on permutation, permutations with repetitions; Restricted permutations. 4 Combinations Definition; Theorems on combination; Basic identities; Restricted combinations. 4 Set Theory:- Definition of Set ; Presentation of Sets; Different types of Sets- Null Set, Finite Infinite Sets, Universal Set, Subset, Power Set etc.; Set operations ; Laws of algebra of Sets. 6 Logarithm Definition, Base index of logarithm, general properties of logarithm, Common problems. 4 Binomial Theorem Statement of the theorem for positive integral index, General term, Middle term, Equidistant terms, Simple properties of binomial coefficient. 4 Compound Interest Annuities: Different types of interest rates; Concept of Present value amount of sum; Types of annuities; Present value amount of an annuity; including the case of continuous compounding; Valuation of simple loans debentures; Problems relating to sinking funds. 8 Collection, Classification Presentation of Statistical Data Primary Secondary data; Methods of data collection; Tabulation of data; Graphs charts; Frequency distributions; Diagrammatic presentation of frequency distributions 8 Measures of Central Tendency Common measures of central tendency mean, median mode; Partition values quartiles, deciles, percentiles. 6 Measures of Dispersion Common measures of dispersion range, quartile deviation, mean deviation stard deviation; Measures of relative dispersion 4
13 BUSINESS MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Module II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Unit VI Moments, Skewness Kurtosis Different types of moments their relationships; Meaning of skewness kurtosis; Different measures of Skewness Kurtosis. 6 Correlation Regression Scatter diagram; Simple correlation coefficient; Simple regression lines; Spearman s rank correlation ; Measures of association of attributes. 8 Probability Theory Meaning of probability; Different definitions of probability; Conditional probability; Compound probability; Independent events; (excluding Bayes Theorem). Interpolation:- Finite differences; Newton s forward backward interpolation formula; Lagrange s interpolation formula. 6 Index Numbers:- Means types of index numbers ; Problems in construction of index numbers; Methods of construction of price quantity indices; Tests of adequacy; errors in index numbers; Chain-base index numbers; Base shifting, splicing, deflating; Consumer price index its uses. Time Series Analysis:- Causes of variation in time series data; Components of time series ; Additive multiplicative models; Determination of trend by semi average, moving average least squares(linear, second degree exponential) methods; Computation of seasonal indices by simple average, ratio-to-moving average, ratio-to trend link relative methods; Simple forecasting through time series data.
14 Communicative English Module II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Unit VI Listening & Understing Lessons 8 Reading Skill: Intensive Extensive Reading, Skimming Scanning 6 Communication Skill: Conversation Practice, Debates, Colloquium 5 Writing Skill: Basic Rules, Introductory Grammar, Common Errors Writing CVs, Official Correspondence, Letter for approval of the authority, Circular, Agenda, Notice, Press Release, Report writing about the proceedings of any seminar, Preparation of official reports, etc. 15 Business Communication: Letter to Vendorquotation, Query for details of any item, Reminder letter, Newsletters, Newspaper Reports, Advertisement, etc. Personality Grooming: Mock Interview, Group Discussions Seminar Presentations. 6
15 B.Com.(H) 2 nd year In Accounting & Finance INFORMATION TECHLOGY AND ITS APPLICATION IN BUSINESS MODULE I Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Unit VI Unit VII Information Technology Business An Overview Concepts of data, information computer based information system. impact of information technology on business (business data processing, intraorganisational interorganisational communication by using network technology, business process knowledge process outsourcing). Types of Information System - Transaction Processing System (TPS), Management Information System (MIS), 8 Number System Representation of Data in Computing System. Data representation bits, bytes, KB, MB, GB, TB. Concept of Number systems [Decimal, Binary, Octal Hexadecimal], Binary arithmetic [addition, subtraction using 1 s & 2 s complement method], Computer Codes BCD, EBCDIC, ASCII. 5 Fundamentals of Computer:- Components of digital computer their functions (input unit, processing unit, output unit storage unit). Basic concepts of hardware & software. Relationship between hardware software. Types of software: System software Operating systems [characteristics & functions, uses of GUI based O.S. LINUX AND WINDOWS], Programming Languages Translator Assembler, Compiler 8 4.Data organization Data Base Management System:- (a) Data organization: Character, field, record, file database. Types of Data Processing Systems [Serial, Batch, Realtime, Online, Centralized, Distributed], File 19 Organizations [Sequential, Direct, Indexed- Sequential, Relative], Traditional file organization Vs. Database File organization. (b) Data Base Management System: Concept of Data Base Data Communication Computer Network (a) Data Communication: Concept of Data communications, Transmission Modes [Simplex, Half-Duplex, Full Duplex, Serial, Parallel, Synchronous, Asynchronous], Communication Media. Wireless satellite communication, Wireless Broadb, WAP, Network components Bridge, Switch, Router, Gateway (b) Computer Networks: Network Concept, Types: LAN, WAN, MAN, VAN, SAN. 8 Introduction to Internet Meaning of Internet. Concepts of Internet Intranet Extranet, IP Address (IPv4, IPv6), URL, Domain name System. Internet Protocols - TCP/IP, UDP, FTP, TELNET,(brief ideas only). HTML, DHTML AND XML. (concepts only). 5 Security Issues Security threats - Virus, Trozan, Hacking, Spam. Security Measures - Firewall, Antivirus software, Digital Signature. Concept of data Encryption & Decryption. Symmetric asymmetric encryption. Digital envelope. 6
16 Decision Support System (DSS), Knowledge Management System (KMS) - their implementation at managerial levels(operational, tactical strategic). Recent trends in information technology (brief ideas) Enterprise computing, mobile communication, smart card Interpreter, Utilities. Application software (basic ideas examples). Management System, Important terms of Database [including Entity, Attribute, Primary Key, Foreign Key, Cidate Key, Referential integrity, Table, Views, Data Dictionary]. Types of database [hierarchical, network relational]. Basic ideas of Data Warehouse Data mining. Various Topologies: Bus, Star, Ring, Mesh, Tree.
17 INFORMATION TECHLOGY AND ITS APPLICATION IN BUSINESS MODULE II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Introduction to GUI based operating system WINDOWS/LINUX 2 Word Processor [2 Classes/ 5 marks] Features of Word Processor. Formatting- Font, Paragraph, Page. Tables, Columns, Dropcap. Tools-Language Checking Tools, Mail Merge, Autocorrect. 2 Electronic Spreadsheet [3 Classes/ 8 marks] Numerical Data Representation using formatting features for cell, Font, Column, Row, Work Sheet. FUNCTIONS- Mathematical, Logical, Financial. GRAPHS-LINE, BAR, AREA, PIE etc. Linking data using Cell References. Sheet Reference. Goal Seek Scenario. 14 Data Base Management System Creation of Tables, Defining Primary key. Multiple Table Hling Defining Relationship, Foreign Key. Generating simple Conditional Queries. Types of queries [Update, Delete, Append] Designing Forms Reports. 12 Financial Accounting Package its Implementation (TALLY / ACE) 9
18 Principles of Marketing & e-commerce Principles of Marketing (Module I) Unit 1 Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Unit VI Marketing: meaning, importance, marketing concepts traditional vs. modern; analysis of marketing environment demographic, political, economic, socio-cultural, natural, technological, legal; growing relevance of marketing in India; impact of global marketing Market Segmentation: concept, target market, bases of market segmentation - factors influencing choice of bases, ideas about customer base, market share, niche market 8 Marketing Mix: concept; 4 Ps vs. 4 Cs Product: meaning, product planning, product mix, product policy, product line decisions, product differentiation; bring; packaging; labelling; product life cycle; new product development process 8 Pricing: importance; factors influencing pricing; pricing policies strategies; service product pricing Promotion: elements of promotion mix; roles of advertising; personal selling; sales promotion; public relations 8 Marketing Channels: types; channel design decisions Logistics Management: objectives; decisions Marketing Information System (MIS): concept, components Marketing Research: meaning, techniques 8 Retail Management: meaning, functions, types, identifying consumers, developing merchise plans; pricing promotional strategies; retailing in India; trends in international retailing 8
19 E-Commerce Module II Unit 1 Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Unit VI Overview of E- Commerce Meaning. Importance in the context of today s business. Advantages of e- commerce (as compared with traditional system of commerce). E- commerce e- business. Internet its relation to e- business. Mobile Commerce-Basic Idea. 5 Categories of E- Commerce (Models) Business to Consumer (B to C) model Basic idea, major activities, major challenges. Models of B to C [portals, e-tailer, content provider, transaction broker] Business to Business (B to B) model Basic idea, major activities, types of B to B market [independent, buyer oriented, supplier oriented, vertical horizontal e- market place]. Other models Business to Government (B to G), Consumer to Consumer (C to C), Consumer to Business (C to B). 8 E-CRM Concept & definition, features, Goals of E-CRM business framework, Three phases of ECRM, Types of E-CRM 5 E-Payment Types of E- Payment Payment card [credit card debit card], Electronic or digital cash. Electronic or digital wallet. Stored value card [smart card]. Basic idea of online banking [core banking solution or CBS] 4 Introduction to ERP: Concept & definition, features, major characteristics, levels of ERP, Benefits of ERP, Enterprise potentials of ERP, Modules of ERP, Phases of ERP implementation, Limitations of ERP. 6 Supply Chain Management: Concept & definition, features, Types of supply chain, E-Supply chain planning (Components), E- supply chain fusion (Process). 6
20 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING II Module I Unit - I Unit - II Unit - III Unit - IV Unit - V Partnership accounts-ii Accounting for dissolution of firm insolvency of one or more partner, consideration of private estate private liabilities. Piecemeal distribution surplus capital basis; maximum possible loss basis. 15 Branch accounting Concept of Branch; different types of Branches. Synthetic method preparation of Branch account. Preparation of Branch Trading P/L account. ( at cost & at IP ) normal abnormal losses. Analytical method preparation of Branch Stock, Adjustment etc A/C (at cost & at IP ) normal & abnormal losses Independent branch concept of wholesale profit basic idea of incorporation Hire purchase Instalment payment System Meaning; difference with Installment payment system; Recording of transaction in the books of buyer allocation of interest use of Interest Suspense a/c partial complete repossession Books of Seller Stock Debtors A/C ( with repossession) Books of Seller H.P. Trading A/C ( with repossession) Concept of operating financial lease basic concept only Departmental Accounts Concept, difference with Branch, objective of preparation of departmental accounts apportionment of common cost; Preparation of Departmental Trading P/L account, Consolidated Trading P/L account; inter departmental transfer of goods at cost, cost plus at selling price elimination of unrealized profit. Introduction to Accounting Stard Financial accounting stards: concept, benefits, procedure for issuing accounting stards in India. Salient features of Accounting Stard (AS): 1 (ICAI). Need for a global stard, IFRS (concept only). 5
21 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING II Module II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Company Introduction And Accounting for Shares & debentures Meaning of Company; Maintenance of Books of Accounts; Statutory Books; Annual Return Issue of Shares issue, forfeiture, reissue, issue other than in cash consideration issue to the promoters; Pro-rata issue of shares. Issue of debentures. Sweat equity. Right Bonus Share Rules, Accounting Alteration of Share Capital; Conversion of fully paid shares into stock; Equity Shares with different rights. Underwriting of shares debentures: Rules; Determination of Underwriters Liability with marked, unmarked & firm underwriting; Accounting. Employee Stock Option Plan meaning; rules; Vesting Period; Exercise Period. Accounting for ESOP. Meaning Accounting of ESPS. 30 Buy back Redemption of preference shares Buy Back of Securities meaning, rules Accounting. Redemption of Preference Shares Rules Accounting (with without Bonus Shares) 30 Redemption of debenture Redemption of Debenture Important Provisions, Accounting for Redemption: by conversion, by lot, by purchase in the open market (cum ex-interest), held as Investment Use of Sinking Fund Company Final Accounts Redemption of Debenture Important Provisions, Accounting for Redemption: by conversion, by lot, by purchase in the open market (cum ex-interest), held as Investment Use of Sinking Fund 15
22 DIRECT & INDIRECT TAXATION MODULE-1 Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V a) Basic Concepts Definitions under IT Act Assessee, Previous year, Assessment year, Sources of income, Heads of income, Gross total income, Total income, Tax Evasion, Tax avoidance, Tax planning b) Residential Status Incidence of Tax Residential status of all persons except company c) Incomes which do not form part of Total Income Except sections A, AA, B, BA d) Agricultural Income Definition, determination of agricultural nonagricultural Income, assessment of tax liability when there are both Agricultural Nonagricultural income 7 Heads of Income Provisions governing Heads of Income Salaries, Income from House property Heads of Income Provisions governing Heads of Income a) Profits Gains from Business Profession Special emphasis on sec 32, 35, 35D, 36, 37, 40A(2), 40A(3), 43B (Excluding presumptive taxation) b) Capital Gain Meaning types of capital assets, basic concept of transfer, cost of Acquisition, cost of improvement indexation, computation of STCG LTCG, exemptions u/s 54 54F, taxability of STCG LTCG c) Income from Other Sources Basic concepts excluding deemed dividend a) Income of other Persons included in Assessee s Total Income Remuneration of spouse, income from assets transferred to spouse Son s wife, income of minor b) Set off Carry Forward of Losses Mode of set off carry forward, inter source inter head set off, Carry forward set off of losses u/s 71B, 72, 73, 74, 74A c) Dedictopms from Gross Total Income Basic concepts, deductions u/s 80C, 80CCC, 80CCD, 80CCE, 80CCF, 80D, 80DD, 80DDB, 80E, 80G, 80GG, 80GGA, 80GGC, 80U 9 Computation of Total Income Tax Payable a) Rate of tax applicable to different assesses (except corporate assessee) b) Computation of tax liability of an individual firm 5
23 DIRECT & INDIRECT TAXATION MODULE-II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V TAX MANAGEMENT a) Provision for Filing of Return Date of filing of return, relevant forms of return, different types of returns, return by whom to be signed, PAN, TAN b) Assessment of Return Self assessment, summary assessment u/s 143(1), scrutiny assessment u/s 143(3) best judgment assessment u/s 144 c) Advance Tax When liable to pay, due dates computation of advance tax (excluding Corporate assesses) d) Interest Interest u/s 234A, 234B, 234C, (simple problems on interest) e) TDS TDS from salary, lottery, horse racing, interest on securities WEALTH TAX Definitions, incidence of tax, basic concepts of assets, exempted assets, deemed assets debt owed, computation of net wealth tax payable (simple problem) CENTRAL SALES TAX, 1956 Definitions, incidence levy of tax, exemption exclusion, determination of turnover tax payable, registration of dealer, forms under CST WB VAT ACT, 2003 Basic concepts, features, advantages disadvantages of vat, rate of tax, definitions, input tax, output tax, input tax credit, incidence levy of tax, determination of tax payable, registration of dealer CENTRAL EXCISE ACT, 1944 Basic concepts, conditions of excise liability, taxable event of excise duty, definitions of goods, manufacture, excisable goods, factory, broker or commission agent, wholesale dealer, sale or purchase 3
24 COST & MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Module I Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV 15 Introduction: Definition of Costing, Cost Accounting Management Accounting. Objectives of Cost Accounting; Importance of Cost Accounting to Business Concern. Relationship between Cost Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting Financial Management; Advantages of a Cost Accounting system, Installing a Cost Accounting System, Essentials of a good Cost Accounting System. Cost concepts, terms classification of costs: Cost, Cost object, Cost units Cost Centres, Types of costs, classification of costs, cost sheet (introduction only), total costs unit costs. Costing Methods Techniques (introduction only). 8 Material Costs a. Purchase of materials: Purchasing needs organisation, purchase procedure, documentation, material costs (direct indirect). b. Storage of materials: Need for storage, location types, functions of a storekeeper, requisition, receipt, issue transfer of materials, storage record, accounting for materials cost. c. Materials control: Organisation; Tools: Just-in-Time Purchase; various stock levels, Economic Ordering Quantity ABC Analysis; Periodic Inventory, Perpetual Inventory, Physical verification; Discrepancies in stock their treatment. d. Methods of Pricing Material Issues Various methods of pricing materials issues; Advantages disadvantages of each method; Comparative analysis; Stock Valuation for Balance Sheet. Treatment of Normal Abnormal Loss of Materials; Accounting control of Waste, Scrap, Spoilage Defectives. Employee Cost- Introduction, Recording labour cost: Attendance payroll procedures (Time-keeping, Time- Booking, Payroll procedure, Payment of wages, Overview of statutory requirements), Idle time (causes treatment in Cost Accounting), Overtime (its effect treatment in Cost Accounting), Labour turnover-causes methods of calculating labour turnover; cost of labour turnover. Incentive Systems Main Principles for sound system of wage incentive schemes; labour utilisation; Distinction between direct indirect labour cost; System of Wage Payment Incentives; System of Incentive Schemes for Indirect Workers; Component of wages cost for costing purpose; Absorption of wages; Efficiency rating procedures. 15 Overhead (a) Introduction Definition, Classification of Overhead- Element-wise, Functional Behavioural; Need for of classifying overhead into fixed variable; various types of overheads. (b) Manufacturing Overheads: Allocation apportionment of Overhead; Absorption of Overhead: various methods their application; Treatment of under absorption/over absorption of overheads; Basic concepts of different Capacities. (c) Activity Based Costing: Problems of traditional costing; meaning of Activity Based Costing; cost analysis under ABC; advantages disadvantages; factors influencing application of ABC; installation of ABC. (d) Preparation of Cost Sheet (advanced level) 20
25 COST & MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING Module II Unit 5 Unit6 Unit7 Unit8 Unit9 14 Cost Book-keeping (1) Non-Integrated System Meaning & Features; Ledgers Maintained; Accounts prepared; General/Cost Ledger Adjustment Account; Meaning of Closing Balance in Various Accounts; Disadvantages. (2) Integrated System Meaning, Features Advantages. (3) Reconciliation 30 Need for reconciliation (only under Non integrated System); Items causing differences between Cost Financial Profits; Memorum Reconciliation Statement / Account Job Costing (Job cost cards databases, Collecting direct costs of each job, Attributing overhead costs to jobs, Applications of job costing). Batch Costing Contract Costing - Progress payments, Retention money, Escalation clause, Contract accounts, Accounting for material, Accounting for plant used in a contract, Contract Profit Balance sheet entries. Service Costing Output Costing- Introduction; Motor Transport Costing, Hotel Costing (Staff Canteen Costing, Hospital Costing, Boiler House Costing brief idea only). Single or Output] Costing Process Costing : Meaning, Features, Process vs Job Costing, Principles of cost ascertainment for Materials, Labour & Overhead; Normal loss, Abnormal loss gain preparation of process accounts. Need for Valuation of WIP, Equivalent Production (units) preparation of process other relevant accounts valuing WIP under average method FIFO method (simple cases). Inter-process profit (simple cases)- Meaning, Advantages Disadvantages determination of stock value for the purpose of balance sheet CVP Analysis Introduction; CVP Assumptions Uses; Break-Even Analysis: BE Point Margin of Safety; Graphical presentation of CVP Relationship; Profit Graph Marginal Costing Management Decisions Marginal Costing visà-vis Absorption Costing; Marginal Costing Techniques; Marginal Cost Product Pricing; Product Mix Make or Buy Decisions, Shut Down Decisions (with simple type of problems on different areas of decision making) Budgetary Control: Budget Budgetary Control; The budget manual, principal budget factor, preparation monitoring procedures, preparation of functional budgets (Production, Sales, Materials), cash budget, (idea of master budget), flexible budget. Stard Costing. Stard Costs Stard Costing; Uses, & Importance. Differences with Budgetary Control, Preliminary Steps. Classification of Stards. Analysis computation of Materials, Labour Overhead Costs Variances (elementary level). 16
26 AUDITING MODULE I Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Introduction Definition-Nature- Scope Objectives of Independent Financial Audit- Limitation. Basic Principles Governing an Audit-Relation between Accounting Auditing. Errors Fraud-Concepts, Means of doing Fraud, Purpose- Conditions which increase the Risk of Fraud Error- Auditor s responsibility towards detection reporting. Classification-Objective wise(internal Independent Financial audit), Periodicity wise (Periodical, Continuous, Interim, Final, Limited Review) Technique wise (Balance sheet, Stard, Systems, EDP), Coverage wise (Complete, Partial), Organization structure wise (Statutory, Non- statutory), Specific Matter Wise (Cost, Management, Secretarial, Tax, Environment, Human Resource, Social, Operational, Propriety, Stock, Public Deposit, Corporate Governance, Cash Flow, Compliance, Performance etc.). 12 Auditing Procedures Techniques Auditing Engagement- Audit Planning- Audit Programme. 34 Documentation- Audit Working Papers, Ownership Custody of Working Papers- Audit File( Permanent, Current) Audit note Book- Audit Memorum. Audit Evidence- Concept, Need, Procedure to obtain Audit Evidence, Sources Reliability, Methods. Preparation Before Commencement of a New Audit. Internal Control Internal Audit Internal Check- Definition, Objective, Preparation of check-lists. Internal Control- Definition, Objectives, Evaluation, Internal control in Computerized Environment, ICQ its Preparation, Comparison with Internal Check. Internal audit- Definition, Objectives, Regulatory Requirements(Com panies Act), Reliance by Statutory Auditor on Internal Auditor s Work. Audit Risk- Concept, Types their Assessment Procedure. Audit Sampling Analytical Procedure (Classes-8 / Marks) Concept, Need, Types of Sampling- Sampling Risk- Stages in Audit Sampling. Test Checking- Auditing in Depth Cut-Off checking. Analytical Procedure- Nature Application of Analytical Procedure- Tools Techniques of Analytical Procedure- Extent of Reliance on Analytical Procedure- Use of analytical procedure for Substantive Testing. Audit (Vouching Verification) of Different Items Vouching- Meaning, Objectives-Vouching of Different Items (Receipts o Payments Related). Verification Concept, Objectives Audit of Share Capital, Loans(Secured Unsecured), Fixed assets (Building, Plant Machinery, Loans Advances, Investment, Goodwill, Copy Right, Patent Right Inventories, Debtors), Creditors, Subsequent Events, Preliminary Expenditures, Directors Remuneration etc.
27 AUDITING MODULE II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Company Audit Qualification, Disqualification, Appointment, Removal, Remuneration of Auditors. Audit Ceiling-Status, Power, Duties Liabilities of auditors. Branch Audit-Joint Audit- Special Audit. Maintenance of Books of Account Related Party Disclosures- Segment Reporting. Divisible Profit, Dividend Depreciation (Companies Act, Stards on Accounting, Legal Decisions Auditor s Responsibility). Representations by Management-Contents of Annual Report( A Brief Idea). 12 Audit Report Certificate Definition- Distinction between Report Certificate- Types of Reports/Opinion 35 (Clean, Qualified, Disclaimer, Negative Piecemeal) Contents of Audit Report(As per Companies Act Stards on auditing). True Fair View (Concept Guiding Factors)- Materiality(Conce pts Relevance)- Limited Review- Disclosures. Certificate on Corporate Governance- Cash Flow Statement Reporting. Audit of Different Institutions Banks- Legislation Relevant to Audit Of Banks, Approach to Bank Audit, Internal Control Evaluation, Non- Performance Assets( Concept, Provisions), Long Form Audit Report. Insurance Companies- Legislation Relevant to Audit of Insurance companies( Life And General Insurance), Review of Internal Control, Audit Report( Matters as per IRDA). Educational Institutions Hospital Features Basic Principles of Government Audit-Local Bodies Non- Profit Seeking Organizations( including NGOs). Comptroller Auditor General its Constitutional Role. Investigation Meaning, Purpose- Distinction between Investigation Auditing Approach to Investigation- Types of Investigations. Assessing a Business ( Due Diligence Review, Valuation). Investigations to Detect Fraud, Misappropriations Defalcations- Investigations with respect to Business Combinations. 6 Other Thrust Areas (Classes 12 / Marks ) Cost Audit- Concepts, Objectives, Advantages, Relevant Provisions of Comp. Act. Management Audit- Tax Audit- Systems Audit- Social Audit- Environment Audit Energy Audit- Forensic Audit-Peer review ( Concepts, Objectives Regulatory Requirements). Ethics in Auditing Auditor s Independence. Auditing in CIS Environment. Stards on Auditing (Concepts, Purpose Present Position as to Number Title as issued by ICAI). 12
28 B.Com.(H) 3 rd year In Accounting & Finance FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING III MODULE-I Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Investment Accounts Maintenance of Investment Ledger; Preparation of Investment Account (transaction with brokerage, STT, cum & ex-interest), Valuation of Investment under FIFO Average method; Investment Account for Shares (with Right Shares, Bonus Shares Sale of Right). Relevant Accounting Stard. 8 Business Acquisition Conversion of partnership into limited company Profit/ loss prior to incorporation; Accounting for Acquisition of business. Conversion of Partnership into Limited Company with without same set of books Amalgamation of firms, accounting in the books transferor transferee firm. 8 Company Merger And Reconstruction Amalgamation, Absorption Reconstruction Meaning; relevant stard meaning of different terms, Accounting in the books of Transferor Company. Accounting in the books of Transferee (both for amalgamation in the nature of Merger of Purchase); inter-company transactions (including inter-company share holding). Internal reconstruction meaning, provisions Accounting, Surrender of Shares for redistribution; preparation of Balance Sheet after reconstruction 18 Valuation Goodwill valuation using different methods,i.e., Average Profit, Super Profit, Capitalisation Annuity. Shares Valuation using different methods: Intrinsic, Earnings, Dividend Yield, Earnings-Price, Cum-div Ex-div, Majority Minority view Fair Value Holding Company Meaning of Holding Company & Subsidiary Company; relevant stard; Consolidation of Balance Sheets of Parent & Subsidiary (only one); Minority Interest Basic principles preparation of CBS; CBS with loss balance of Subsidiary Treatment for: Revaluation of Assets of Subsidiary, Intragroup Transactions, Holding of different securities. Consideration of dividend paid or proposed by Subsidiary in CBS; Bonus Shares issued or proposed to be issued by Subsidiary (excluding shares acquired on different dates by the Parent company, chain cross holding) 16
29 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING III MODULE-II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Fund Flow Statement Cash Flow Statement Introduction to Accounting Theory Concept of accounting theory; relation with practice; GAAP; Capital capital maintenance concepts, relation with income; Limitations of Historic Cost accounting; Introduction to Fair Value accounting Introduction to Financial Statements Nature Component of Financial Statement; Meaning Need for FSA, Traditional & Modern approaches to FSA, Parties interested in FSA. Comparative Statement meaning, preparation, uses, merits demerits Common-size Statement - meaning, preparation, uses, merits demerits Trend Analysis - meaning, determination, uses, merits demerits Accounting Ratios for FSA Meaning, objective, Classification of Accounting Ratios, Advantages & Limitations Preparation of Financial Statement Statement of Proprietor s Fund from the given Ratios. Computation, Analysis Interpretation of important ratios for measuring Liquidity, Solvency, Capital Structure, Profitability Managerial Effectiveness Concept of fund, meaning, nature, various sources, advantages & limitations of Fund Flow Statement its preparation. Meaning, objectives, difference with Fund Flow Statement; activity classification preparation presentation as per AS-3
30 ECOMICS II Module I Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Macroeconomics scope basic concepts. 2 National Income Accounting - Concepts measurement of GDP, GNP, NNP, NI DPI - Circular flow of income Real Nominal GDP Implicit deflator. 8 Theory of Equilibrium Income Determination: Simple Keynesian Model; Consumption, saving investment functions National income determination; Investment Government expenditure multipliers 12 Commodity market Money market equilibrium; Derivation of IS LM curves Shifts of IS LM curvesequilibrium in IS-LM model Effectiveness of monetary fiscal policies 12 Money inflation Concept of dem for supply of money. Quantity theory of money Keynesian theory of dem for money. Measures of money supply High powered money Money multiplier. Concept of Inflation Dempull cost-push theories of inflation Monetary fiscal policies to control inflation Instruments, objectives limitations. 16
31 Advanced Business Mathematics Module II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Unit VI Unit VII Functions: Definition of functions; Classification of functions; Different types of functions(excluding Trigonometrical functions); Bounded functions; Monotonic functions; Even odd functions; Parametric form of a function; Composite functions; Graphical representation of functions 6 Limit Continuty : Elementary ideas of limit continuity through the use of simple algebric functions. 6 Differentiation: Derivative its meaning; Rules of differentiation; Geometrical interpretation; Significance of derivative as rate measure; Second higher order derivatives; Partial derivatives up to second order; Homogeneity of function Euler s theorem; Total differentials; Differentiation of implicit function with the help of total differentials. 8 Applications of Derivative: Maximum minimum values ; Cost function ; Dem function ; Profit function;increasing decreasing functions ; Rate measure Applied problems on Average cost (AC), Average variable cost (AVC), Marginal cost (MC), Marginal revenue (MR). 8 Integration: Integration as anti-derivative process; Stard forms; Integration by substitution, by parts by use of partial functions; Definite integral; Finding areas in simple cases; consumers producers surplus; Nature of commodities learning curve. 8 Determinants: Determinants of a square matrix up to third order ; Elementary properties of determinants ; Minors Cofactors ; Adjoint of a determinant ; Cramer's Rule (not more than three variables). 6 Matrix: Definition of matrix ; Types of matrices ; Operations on matrices (addition, subtraction, multiplication); Adjoint of a matrix; Inverse of a matrix ; Solution of a system of linear equations by matrix inversion method (not more than three variables). 8
32 Indian Financial System Financial Market MODULE 1 Indian Financial System Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Financial System Meaning significance; Role of finance in an economy, Components (instruments, markets, etc.); kinds of finance Rudimentary finance, Direct Indirect finance; Role of financial intermediaries. The structure of Indian Financial System 5 Money Indian Banking System Functions; Alternative measures to money supply in India Their different components; Commercial Banks Importance functions; Structure of Commercial banking system in India; Distinction between Commercial Central bank; Credit Creation Process of Commercial banks; High powered money meaning uses Concept of Money Multiplier. The Reserve Bank of India: Functions; Instruments of Monetary Credit control, Main features of Monetary Policy since independence. 15 Development Banks Concept of Development bank their needs in Indian financial system Difference with Commercial banks Major Development banks their functions (IFCI, IDBI, ICICI, EXIM Bank, SIDBI, SFCs, NABARD) Financial Institutions Commodity market Money market equilibrium; Derivation of IS LM curves Shifts of IS LM curvesequilibrium in IS-LM model Effectiveness of monetary fiscal policies Interest Rate Structure Meaning Gross Net interest rate their difference, Nominal Real interest rate their difference, Differential interest rate, Causes of variation of interest rate, relationship between interest rate economic progress, Administered Market determined interest rate. Recent changes in interest structure in India.
33 FINANCIAL MARKET Module II Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V An overview of financial markets in India 3 Money Market: Concept, Structure of Indian Money Market, Acceptance Houses, Discount Houses, Call money market, Recent trends of Indian money markets Capital Market Concept, Security market, Primary & Secondary markets- Functions & Role, Functionaries of stock exchanges-brokers, Sub- Brokers, Jobbers, Consultants, Institutional Investors & NRIs 17 Investors Protection Grievances concerning Stock Exchange dealings & their removal, Grievance Redressal Cell in Stock Exchanges, Role of The SEBI, Company Law Board, Judiciary & Media Financial Services Merchant Banking- Functions & Roles, SEBI guidelines, Credit ratingconcept & types, Functions & limitations, Profile of Indian Rating Agencies 19
34 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Module I Unit I Unit II Unit III Unit IV Unit V Introduction Important functions of Financial Management Objectives of the firm: Profit maximisation vs. value maximisation Role of Chief Financial Officer. Basic Concepts Time Value of Money: Compounding Discounting techniques- Concepts of Annuity Perpetuity. Risk-return relationship Financial environment in which a firm has to operate Sources of Finance Cost of Capital Different sources of finance; long term short term sources 38 Cost of capital: concept, relevance of cost of capital, specific costs weighted average cost, rationale of after tax weighted average cost of capital, marginal cost of capital Leverage Capital Structure Theories Leverage- Business Risk Financial Risk - Operating financial leverage, Trading on Equity Capital Structure decisions - Capital structure patterns, Designing optimum capital structure, Constraints, Various capital structure theories Working Capital Management (1) Introduction; Meaning Concept of Working Capital; Management of Working Capital Issues in Working Capital; Estimating Working Capital Needs; Operating or Working Capital Cycle.
LESSON PLAN ( ) Part-III: B.Com.(Hons)
 Paper 3.1 HA MODULE-I FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING III LEON PLAN (2017-18) Part-III: B.Com.(Hons) Full Marks : 50 Total Lectures : 60 1 Investment Accounts - Maintenance of Investment Ledger; Preparation of Investment
Paper 3.1 HA MODULE-I FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING III LEON PLAN (2017-18) Part-III: B.Com.(Hons) Full Marks : 50 Total Lectures : 60 1 Investment Accounts - Maintenance of Investment Ledger; Preparation of Investment
LESSON PLAN ( ) Ist Semester B.Com.(Hons & Gen)
 LEON PLAN (207-8) Ist Semester B.Com.(Hons & Gen) GE. Chg Microeconomics I & Statistics (50+50) Module I: Microeconomics I UNIT TOPIC TEACHER Demand and Consumer Behaviour (5 marks) Concept of Demand,
LEON PLAN (207-8) Ist Semester B.Com.(Hons & Gen) GE. Chg Microeconomics I & Statistics (50+50) Module I: Microeconomics I UNIT TOPIC TEACHER Demand and Consumer Behaviour (5 marks) Concept of Demand,
Syllabus for Common Entrance Test (2017): M. Com.
 Syllabus for Common Entrance Test (2017): M. Com. A. Subject Related 75 Questions all over the Syllabus: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Financial accounting: concept, need, objectives & scope; accounting principles-
Syllabus for Common Entrance Test (2017): M. Com. A. Subject Related 75 Questions all over the Syllabus: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Financial accounting: concept, need, objectives & scope; accounting principles-
ANUPGCET 2018 :: 113-COMMERCE (SYLLABUS)
 ANUPGCET 2018 :: 113-COMMERCE (SYLLABUS) Max. Marks: 100 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING: Introduction to Accounting Need for Accounting definition, features, objectives, functions, systems and bases and scope of
ANUPGCET 2018 :: 113-COMMERCE (SYLLABUS) Max. Marks: 100 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING: Introduction to Accounting Need for Accounting definition, features, objectives, functions, systems and bases and scope of
MODULAR SYLLABUS: B.COM (HONS & GEN)
 MODULAR SYLLABUS: 2016-17 B.COM ( & ) 1 ST NAME/ PAPER FA/1.2c g MODULE UNIT TOPIC TEACHER MONTH I 1 Introduction-Nature of accounting-double entry book keeping system-bases of accounting-basic concepts
MODULAR SYLLABUS: 2016-17 B.COM ( & ) 1 ST NAME/ PAPER FA/1.2c g MODULE UNIT TOPIC TEACHER MONTH I 1 Introduction-Nature of accounting-double entry book keeping system-bases of accounting-basic concepts
Financial Accounting and Auditing Paper-V: Financial Accounting
 Allocation of the Syllabus and Question Paper Pattern of Courses of B.Com. Programme at T.Y.B.Com. Semester V with Effect from the Academic Year 2013-2014 Financial Accounting and Auditing Paper-V: Financial
Allocation of the Syllabus and Question Paper Pattern of Courses of B.Com. Programme at T.Y.B.Com. Semester V with Effect from the Academic Year 2013-2014 Financial Accounting and Auditing Paper-V: Financial
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU
 UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU NET SYLLABUS Subject: Commerce Code No. : 08 Unit 1: Business Environment and International Business Unit 2: Accounting and Auditing Unit 3: Business Economics Unit
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU NET SYLLABUS Subject: Commerce Code No. : 08 Unit 1: Business Environment and International Business Unit 2: Accounting and Auditing Unit 3: Business Economics Unit
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU
 UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU NET SYLLABUS Subject: Commerce Code No. : 08 Unit 1: Business Environment and International Business Unit 2: Accounting and Auditing Unit 3: Business Economics Unit
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU NET SYLLABUS Subject: Commerce Code No. : 08 Unit 1: Business Environment and International Business Unit 2: Accounting and Auditing Unit 3: Business Economics Unit
4. Negotiable Instrument Act, The Consumer Protection Act, Foreign Exchange Management Act, 2000
 REVISED SYLLLABUS FYBAF SEM. II BUSINESS LAW PAPER -1: Business Regulatory Framework Topics for Study 1. Law of contract 1872 2. Special Contracts 3. Sales of Goods Act 1930 4. Negotiable Instrument Act
REVISED SYLLLABUS FYBAF SEM. II BUSINESS LAW PAPER -1: Business Regulatory Framework Topics for Study 1. Law of contract 1872 2. Special Contracts 3. Sales of Goods Act 1930 4. Negotiable Instrument Act
ACCOUNTS (858) CLASS XI
 ACCOUNTS (858) Aims: 1. To provide an understanding of the principles of accounts and practice in recording transactions and interpreting individual as well as company accounts. 2. To develop an understanding
ACCOUNTS (858) Aims: 1. To provide an understanding of the principles of accounts and practice in recording transactions and interpreting individual as well as company accounts. 2. To develop an understanding
SYLLABUS COMMON PROFICIENCY TEST
 SYLLABUS COMMON PROFICIENCY TEST Session I Section A Fundamentals of Accounting 60 Marks Section B Mercantile Law 40 Marks Session II Section C General Economics 50 Marks Section D Quantitative Aptitude
SYLLABUS COMMON PROFICIENCY TEST Session I Section A Fundamentals of Accounting 60 Marks Section B Mercantile Law 40 Marks Session II Section C General Economics 50 Marks Section D Quantitative Aptitude
INTERMEDIATE COURSE. ICWAI Syllabus GROUP -I. Paper 5 : Financial Accounting (One Paper: 3 hours:100 marks)
 INTERMEDIATE COURSE GROUP -I Paper 5 : Financial Accounting (One Paper: 3 hours:100 marks) Objectives To have working knowledge of accounting concepts, detailed procedures and documentation involved in
INTERMEDIATE COURSE GROUP -I Paper 5 : Financial Accounting (One Paper: 3 hours:100 marks) Objectives To have working knowledge of accounting concepts, detailed procedures and documentation involved in
Chapter 6 Simple Correlation and
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics Meaning of Statistics... 1 Definition of Statistics... 2 Importance and Scope of Statistics... 2 Application of Statistics... 3 Characteristics of Statistics...
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics Meaning of Statistics... 1 Definition of Statistics... 2 Importance and Scope of Statistics... 2 Application of Statistics... 3 Characteristics of Statistics...
Intermediate Course Paper 1: Accounting (100 Marks)
 Intermediate Course Intermediate Course Paper 1: Accounting (100 Marks) Sections Weightage Content Area I 20%-25% 1. Process of formulation of Accounting Standards including Ind AS (IFRS converged standards)
Intermediate Course Intermediate Course Paper 1: Accounting (100 Marks) Sections Weightage Content Area I 20%-25% 1. Process of formulation of Accounting Standards including Ind AS (IFRS converged standards)
For Information Only
 AC 29-5-15 Item No. 4.1 University of Mumbai Revised Syllabus and Question For Information Paper Pattern of Only Courses of B.Com. (Accounting and Finance) Programme at Third Year Semester V and VI Under
AC 29-5-15 Item No. 4.1 University of Mumbai Revised Syllabus and Question For Information Paper Pattern of Only Courses of B.Com. (Accounting and Finance) Programme at Third Year Semester V and VI Under
SENIOR SCHOOL CURRICULUM
 SENIOR SCHOOL CURRICULUM 2017-18 ACCOUNTANCY & TAXATION Introduction The course is designed to enable students to develop conceptual, skill and application skill in the commerce related field. The course
SENIOR SCHOOL CURRICULUM 2017-18 ACCOUNTANCY & TAXATION Introduction The course is designed to enable students to develop conceptual, skill and application skill in the commerce related field. The course
Semester I (June October)
 BAF Course Syllabus: Semester I (June October) Financial Accounting Paper I Introduction to Accounting Accounting Procedure Capital & Revenue Reconciliation & Rectification Depreciation provisions & Reserve
BAF Course Syllabus: Semester I (June October) Financial Accounting Paper I Introduction to Accounting Accounting Procedure Capital & Revenue Reconciliation & Rectification Depreciation provisions & Reserve
CONTENTS. 1. Meaning and Scope of Accounting
 CONTENTS 1. Meaning and Scope of Accounting Need for Accounting Development and Definition of Accounting Book Keeping and Accounting Persons interested in Accounting Branches of Accounting Financial Accounting
CONTENTS 1. Meaning and Scope of Accounting Need for Accounting Development and Definition of Accounting Book Keeping and Accounting Persons interested in Accounting Branches of Accounting Financial Accounting
COURSE OUTCOME. Class :- B.Com I. Subject :- PRINCIPLES OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT. Subject: - Financial Accounting
 COURSE OUTCOME Class :- B.Com I Subject :- PRINCIPLES OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT BUSINESS AND COMMERCE : AN INTRODUCTION MANAGEMENT :AN INTRODUCTION,MANAGEMENT AS SCIENCE, ART AND PROFESSION,APPROACHES TO
COURSE OUTCOME Class :- B.Com I Subject :- PRINCIPLES OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT BUSINESS AND COMMERCE : AN INTRODUCTION MANAGEMENT :AN INTRODUCTION,MANAGEMENT AS SCIENCE, ART AND PROFESSION,APPROACHES TO
Depository Act Depository process, De-mat, NSDL,SHCIL, Need for investor education
 COMMERCE UNIT I ACCOUNTING: UNIT II Financial Accounting: Accounting concepts and conventions, Preparation of Final Accounts (Sole trading concern and Partnership) with adjusting entries. Corporate Accounting:
COMMERCE UNIT I ACCOUNTING: UNIT II Financial Accounting: Accounting concepts and conventions, Preparation of Final Accounts (Sole trading concern and Partnership) with adjusting entries. Corporate Accounting:
Cost and Management Accounting
 Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus... Q&A-2.2 Bird's-Eye View... Q&A-2.5 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance Chapters... Q&A-2.7 Table Showing Importance of Chapter on the Basis of Marks...
Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus... Q&A-2.2 Bird's-Eye View... Q&A-2.5 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance Chapters... Q&A-2.7 Table Showing Importance of Chapter on the Basis of Marks...
ECONOMICS B.A. part 1 M.M.100 Paper I MICRO ECONOMICS Unit I 1.Consumer s Behaviour : The Neo Classical Marginal Utility approach and a study of
 ECONOMICS B.A. part 1 M.M.100 Paper I MICRO ECONOMICS 1.Consumer s Behaviour : The Neo Classical Marginal Utility approach and a study of consumer s equilibrium and derivation of law of demand. The Indifference
ECONOMICS B.A. part 1 M.M.100 Paper I MICRO ECONOMICS 1.Consumer s Behaviour : The Neo Classical Marginal Utility approach and a study of consumer s equilibrium and derivation of law of demand. The Indifference
PART I BUSINESS LAWS & COMPANY LAW
 Contents About the author I-5 Preface to fourth edition I-7 Syllabus I-19 CA - Intermediate (IPC) Nov. 2015 Examinations I-23 CA - Intermediate (IPC) May 2015 Examinations I-27 CA - Intermediate (IPC)
Contents About the author I-5 Preface to fourth edition I-7 Syllabus I-19 CA - Intermediate (IPC) Nov. 2015 Examinations I-23 CA - Intermediate (IPC) May 2015 Examinations I-27 CA - Intermediate (IPC)
CFA Level I - LOS Changes
 CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2018-2019 Topic LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) LOS Level I - 2019 (525 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics Ethics 1.1.b 1.1.c describe the role
CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2018-2019 Topic LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) LOS Level I - 2019 (525 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics Ethics 1.1.b 1.1.c describe the role
Cost and Management Accounting
 Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus......................................... 2.2 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance of Chapters...... 2.6 Table Showing Importance of Chapter on the Basis
Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus......................................... 2.2 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance of Chapters...... 2.6 Table Showing Importance of Chapter on the Basis
SYBAF / SEM. III / / Revised / Economics Paper II (Macro economics)
 SYBAF / SEM. III / / Revised / 2.3.4 Economics Paper II (Macro economics) National Income Money supply & banking Money Demand and Inflation Fiscal Operations Economics stabilization Balance of Payments
SYBAF / SEM. III / / Revised / 2.3.4 Economics Paper II (Macro economics) National Income Money supply & banking Money Demand and Inflation Fiscal Operations Economics stabilization Balance of Payments
Affiliated to UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the T.Y.B.COM. Program: COMMERCE Program Code: RJCUCOM (CBCS )
 Hindi Vidya Prachar Samiti s Ramniranjan Jhunjhunwala College of Arts, Science and Commerce (Autonomous College) Affiliated to UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the T.Y.B.COM. Program: COMMERCE Program
Hindi Vidya Prachar Samiti s Ramniranjan Jhunjhunwala College of Arts, Science and Commerce (Autonomous College) Affiliated to UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the T.Y.B.COM. Program: COMMERCE Program
CFA Level I - LOS Changes
 CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2017-2018 Topic LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics 1.1.b describe the role of a code of
CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2017-2018 Topic LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics 1.1.b describe the role of a code of
I B.Com PA [ ] Semester II Core: Management Accounting - 218A Multiple Choice Questions.
![I B.Com PA [ ] Semester II Core: Management Accounting - 218A Multiple Choice Questions. I B.Com PA [ ] Semester II Core: Management Accounting - 218A Multiple Choice Questions.](/thumbs/80/82536614.jpg) 1 of 23 1/27/2018, 11:53 AM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
1 of 23 1/27/2018, 11:53 AM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
Cost and Management Accounting
 Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus................................................ 2.2 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance of Chapters............ 2.5 Table Showing Importance of Chapter
Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus................................................ 2.2 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance of Chapters............ 2.5 Table Showing Importance of Chapter
6.1 BUSINESS REGULATIONS
 6.1 BUSINESS REGULATIONS OBJECTIVE: To introduce the students to various Business Regulations and familiarize them with common issues of relevance. UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS LAWS Introduction, Nature
6.1 BUSINESS REGULATIONS OBJECTIVE: To introduce the students to various Business Regulations and familiarize them with common issues of relevance. UNIT 1: INTRODUCTION TO BUSINESS LAWS Introduction, Nature
COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND SOCIAL SCIENCES
 COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND SOCIAL SCIENCES 1. DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES (a) Curriculum for B.Sc. Degree in Accounting 100 Level Harmattan Semester Course Code Course Title Pre-requisite
COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND SOCIAL SCIENCES 1. DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES (a) Curriculum for B.Sc. Degree in Accounting 100 Level Harmattan Semester Course Code Course Title Pre-requisite
PAPER 1 ACCOUNTING. (One paper Three hours 100 Marks)
 Objectives: PAPER 1 ACCOUNTING (One paper Three hours 100 Marks) To acquire the ability to apply specific accounting standards and legislations to different transactions and events and in preparation and
Objectives: PAPER 1 ACCOUNTING (One paper Three hours 100 Marks) To acquire the ability to apply specific accounting standards and legislations to different transactions and events and in preparation and
Group 1. Paper 1 Accounting 100 Marks. Paper 2 Corporate Laws and Other Laws 100 Marks. Part I: Corporate Laws (60 Marks)
 Group 1 Paper 1 Accounting 100 Marks Paper 2 Corporate Laws and Other Laws 100 Marks Part I: Corporate Laws (60 Marks) Part II: Other Laws (40 Marks) Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting 100 Marks Paper
Group 1 Paper 1 Accounting 100 Marks Paper 2 Corporate Laws and Other Laws 100 Marks Part I: Corporate Laws (60 Marks) Part II: Other Laws (40 Marks) Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting 100 Marks Paper
ECONOMICS EXAMINATION OBJECTIVES
 ECONOMICS EXAMINATION OBJECTIVES The following objectives of the examination are to test whether the candidates have acquired a basic understanding of economics with special emphasis on Hong Kong conditions
ECONOMICS EXAMINATION OBJECTIVES The following objectives of the examination are to test whether the candidates have acquired a basic understanding of economics with special emphasis on Hong Kong conditions
Contents. An Overview of Statistical Applications CHAPTER 1. Contents (ix) Preface... (vii)
 Contents (ix) Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Statistical Applications 1.1 Introduction... 1 1. Probability Functions and Statistics... 1..1 Discrete versus Continuous Functions... 1..
Contents (ix) Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Statistical Applications 1.1 Introduction... 1 1. Probability Functions and Statistics... 1..1 Discrete versus Continuous Functions... 1..
Faculty of Commerce. Karim City College, Jamshedpur. Syllabus Distribution
 Faculty of Commerce Karim City College, Jamshedpur Syllabus Distribution Teacher Wise Allocation of Topics/Portions for 2016-17 B.Com Honours Part 1 Account Group Subject: Financial Accounting ( Honours
Faculty of Commerce Karim City College, Jamshedpur Syllabus Distribution Teacher Wise Allocation of Topics/Portions for 2016-17 B.Com Honours Part 1 Account Group Subject: Financial Accounting ( Honours
Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019
 Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
COURSES OF STUDY FOR B.
 PATNA UNIVERSITY COURSES OF STUDY FOR B. Com. Examination (2015-18) Three Year Degree Course Part III 1 PATNA UNIVERSITY COURSES OF STUDY For 2015-2018 (Three Year Degree Course) B. Com. (Honours) Course
PATNA UNIVERSITY COURSES OF STUDY FOR B. Com. Examination (2015-18) Three Year Degree Course Part III 1 PATNA UNIVERSITY COURSES OF STUDY For 2015-2018 (Three Year Degree Course) B. Com. (Honours) Course
Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016)
 Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016) This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide
Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016) This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide
MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION
 ZIMBABWE MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS FORMS 5-6 2015 2022 Curriculum Development Unit P.O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant Harare All rights reserved 2015 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The
ZIMBABWE MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS FORMS 5-6 2015 2022 Curriculum Development Unit P.O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant Harare All rights reserved 2015 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The
B.A. SOCIAL SCIENCE - ECONOMICS. Semester - I. Title of The Paper - MICRO ECONOMICS
 B.A. SOCIAL SCIENCE - ECONOMICS Semester - I Title of The Paper - MICRO ECONOMICS Unit-I Definition, Evolution, Scope & Nature of Economics, Methods of Economic Analysis Inductive & Deductive Methods.
B.A. SOCIAL SCIENCE - ECONOMICS Semester - I Title of The Paper - MICRO ECONOMICS Unit-I Definition, Evolution, Scope & Nature of Economics, Methods of Economic Analysis Inductive & Deductive Methods.
Bachelor of Science in Accounting
 Bachelor of Science in Accounting 2018 DANESHPAJOOHAN PISHRO HIGHER EDUCATION INSTITUTE COURSE CHART SYLLABUS SEMESTER CHART Accounting Undergraduate Chart General s 61-11-004 Islamic Thoughts-I 2 2 0
Bachelor of Science in Accounting 2018 DANESHPAJOOHAN PISHRO HIGHER EDUCATION INSTITUTE COURSE CHART SYLLABUS SEMESTER CHART Accounting Undergraduate Chart General s 61-11-004 Islamic Thoughts-I 2 2 0
COMMERCE (857) CLASS XI
 COMMERCE (857) Aims: 1. To develop an interest in the theory and practice of business, trade and industry. 2. To familiarise candidates with theoretical foundations, organising, managing and handling operations
COMMERCE (857) Aims: 1. To develop an interest in the theory and practice of business, trade and industry. 2. To familiarise candidates with theoretical foundations, organising, managing and handling operations
BHARATI VIDYAPEETH UNIVERSITY, PUNE SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION. Home Assignments. T. Y. B. Com. Subject: Corporate Accounting II
 BHARATI VIDYAPEETH UNIVERSITY, PUNE SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION Home Assignments T. Y. B. Com Subject: Corporate Accounting II N.B.: Attempt ANY TWO ASSIGNMENTS of the following: Assignment I Q.1 Attempt
BHARATI VIDYAPEETH UNIVERSITY, PUNE SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION Home Assignments T. Y. B. Com Subject: Corporate Accounting II N.B.: Attempt ANY TWO ASSIGNMENTS of the following: Assignment I Q.1 Attempt
(F2/FMA) December 2011
 Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Cost and Management Accounting
 Intermediate Course Study Material (Modules 1 to 2) Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting Module - 1 BOARD OF STUDIES THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA ii This Study Material has been prepared
Intermediate Course Study Material (Modules 1 to 2) Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting Module - 1 BOARD OF STUDIES THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA ii This Study Material has been prepared
Topic:- DU_J18_MCOM_Topic01
 DU MCom Topic:- DU_J18_MCOM_Topic01 1) If the probability of A is 0.5 and the probability of B is 0.2 and the probability of the union of A and B is 0.7, then : [Question ID = 30693] 1. A and B are dependent
DU MCom Topic:- DU_J18_MCOM_Topic01 1) If the probability of A is 0.5 and the probability of B is 0.2 and the probability of the union of A and B is 0.7, then : [Question ID = 30693] 1. A and B are dependent
1) If the probability of A is 0.5 and the probability of B is 0.2 and the probability of the union of A and B is 0.7, then : [Question ID = 30693]
![1) If the probability of A is 0.5 and the probability of B is 0.2 and the probability of the union of A and B is 0.7, then : [Question ID = 30693] 1) If the probability of A is 0.5 and the probability of B is 0.2 and the probability of the union of A and B is 0.7, then : [Question ID = 30693]](/thumbs/95/125321731.jpg) DU MCom Topic:- DU_J18_MCOM_Topic01 1) If the probability of A is 0.5 and the probability of B is 0.2 and the probability of the union of A and B is 0.7, then : [Question ID = 30693] 1. A and B are dependent
DU MCom Topic:- DU_J18_MCOM_Topic01 1) If the probability of A is 0.5 and the probability of B is 0.2 and the probability of the union of A and B is 0.7, then : [Question ID = 30693] 1. A and B are dependent
100 Accounting Interview Questions and Answers
 100 Accounting Interview Questions and Answers 1) Why did you select accounting as your profession? Well, I was quite good in accounting throughout but in my masters, when I got distinction I decided to
100 Accounting Interview Questions and Answers 1) Why did you select accounting as your profession? Well, I was quite good in accounting throughout but in my masters, when I got distinction I decided to
Answer to MTP_Intermediate_Syllabus2016_June2018_Set 2 Paper 5- Financial Accounting
 Paper 5- Financial Accounting Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 5- Financial Accounting Full Marks : 100 Time allowed:
Paper 5- Financial Accounting Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 5- Financial Accounting Full Marks : 100 Time allowed:
Course : B.Com. Semester 1. Module 1 - Accounting Concepts and Conventions
 Course : B.Com Semester 1 Module 1 - Accounting Concepts and Conventions Accounting conventions and their importance Generally accepted accounting principles Purpose of financial statements, underlying
Course : B.Com Semester 1 Module 1 - Accounting Concepts and Conventions Accounting conventions and their importance Generally accepted accounting principles Purpose of financial statements, underlying
CA INTERMEDIATE SYLLABUS
 CA INTERMEDIATE SYLLABUS In this article we are providing you the CA Intermediate syllabus applicable for the students registered with the revised scheme. Students can register for the CA Intermediate
CA INTERMEDIATE SYLLABUS In this article we are providing you the CA Intermediate syllabus applicable for the students registered with the revised scheme. Students can register for the CA Intermediate
STUDY MATERIAL BASED CONTENTS
 STUDY MATERIAL BASED CONTENTS Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus....................................... 3. Examination Trend Analysis........................ 3.7 Line Chart Showing Relative
STUDY MATERIAL BASED CONTENTS Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus....................................... 3. Examination Trend Analysis........................ 3.7 Line Chart Showing Relative
(F2/FMA) December 2011
 Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
METHODS OF CALCULATING NATIONAL INCOME
 1) What is meant by circular flow of income? 1 2) What are the two types of circular flow of income? 1 3) What do you mean by real flow? 1 4) What do you mean by money flow? 1 5) Differentiate between
1) What is meant by circular flow of income? 1 2) What are the two types of circular flow of income? 1 3) What do you mean by real flow? 1 4) What do you mean by money flow? 1 5) Differentiate between
BPC6C Cost and Management Accounting. Unit : I to V
 BPC6C Cost and Management Accounting Unit : I to V UNIT -1 FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING Nature and scope of Cost Accounting, Distinction between cost and financial accounting, Cost sheet, tenders Characteristics
BPC6C Cost and Management Accounting Unit : I to V UNIT -1 FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING Nature and scope of Cost Accounting, Distinction between cost and financial accounting, Cost sheet, tenders Characteristics
Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting
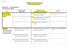 Suggested Revised BAFS Curriculum Draft as at 30 January 2013 Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting Topic Books of Original Entry and Types of Ledgers Explanatory Notes (original
Suggested Revised BAFS Curriculum Draft as at 30 January 2013 Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting Topic Books of Original Entry and Types of Ledgers Explanatory Notes (original
CA IPCC (New) SUPERIOR
 Accounts 1) Introduction to Accounting Standards 2) Framework for Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statement 3) Accounting Standards ( 1,2,3,4,5,10) 4) Accounting Standards (11,12,13,16,17,22)
Accounts 1) Introduction to Accounting Standards 2) Framework for Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statement 3) Accounting Standards ( 1,2,3,4,5,10) 4) Accounting Standards (11,12,13,16,17,22)
CFA Level 1 - LOS Changes
 CFA Level 1 - LOS s 2015-2016 Ethics Ethics Ethics 1.1.a 1.1.b 1.1.c describe the structure of the CFA Institute Professional Conduct Program and the process for the enforcement of the Code and Standards
CFA Level 1 - LOS s 2015-2016 Ethics Ethics Ethics 1.1.a 1.1.b 1.1.c describe the structure of the CFA Institute Professional Conduct Program and the process for the enforcement of the Code and Standards
P.G. Diploma in Financial Services (Semester I) Examination, : FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern)
 *3985101* [3985] 101 P.G. Diploma in Financial Services (Semester I) Examination, 2011 101 : FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70 Instructions : 1) Q. 1 and Q.2 are
*3985101* [3985] 101 P.G. Diploma in Financial Services (Semester I) Examination, 2011 101 : FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70 Instructions : 1) Q. 1 and Q.2 are
FOUNDATION EXAMINATION
 FOUNDATION EXAMINATION (SYLLABUS 2008) SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS JUNE 2012 Paper-2 : ACCOUNTING Time Allowed : 3 Hours Full Marks : 100 The figures in the margin on the right side indicate full marks.
FOUNDATION EXAMINATION (SYLLABUS 2008) SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS JUNE 2012 Paper-2 : ACCOUNTING Time Allowed : 3 Hours Full Marks : 100 The figures in the margin on the right side indicate full marks.
B COM 01 (Business Organisation) Basic Concepts and Forms of Business Organization
 B COM 01 (Business Organisation) BLOCK-I Basic Concepts and Forms of Business Organization UNIT-01: Nature and Scope of Business Human activities, business, essential features of business, objectives of
B COM 01 (Business Organisation) BLOCK-I Basic Concepts and Forms of Business Organization UNIT-01: Nature and Scope of Business Human activities, business, essential features of business, objectives of
SYLLABUS (CPA AUSTRALIA)
 SYLLABUS (CPA AUSTRALIA) PAPER - 1: CORPORATE AND ALLIED LAWS (One paper - Three hours - 100 marks) Objective: SECTION A : COMPANY LAW (70 MARKS) To be able to analyze and apply various provisions of the
SYLLABUS (CPA AUSTRALIA) PAPER - 1: CORPORATE AND ALLIED LAWS (One paper - Three hours - 100 marks) Objective: SECTION A : COMPANY LAW (70 MARKS) To be able to analyze and apply various provisions of the
ACCOUNTING INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
 www.globalcma.in Learning Platform for Cost Accountants (CMA) 1) Why did you select accounting as your profession? Well, I was quite good in accounting throughout but in my masters, when I got distinction
www.globalcma.in Learning Platform for Cost Accountants (CMA) 1) Why did you select accounting as your profession? Well, I was quite good in accounting throughout but in my masters, when I got distinction
OUTLINE ANSWERS TO EXERCISES
 OUTLINE ANSWERS TO EXERCISES 437 2.1 Cash account balance carried forward 1,680 2.2 Rent account Credit balance carried forward 300 Profit and loss charge 1,050 Rates account Debit balance carried forward
OUTLINE ANSWERS TO EXERCISES 437 2.1 Cash account balance carried forward 1,680 2.2 Rent account Credit balance carried forward 300 Profit and loss charge 1,050 Rates account Debit balance carried forward
SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION :: ANDHRA UNIVERSITY 3-YEAR MBA I YEAR ASSIGNMENTS FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR MANAGEMENT PROCESS AND BEHAVIOUR
 MANAGEMENT PROCESS AND BEHAVIOUR 1. a) Differences between leaders and managers b) Corporate Governance 2. a) Planning Premises b) Decision Tree Analysis 3. a) Theory X, Theory Y and Theory Z b) Leadership
MANAGEMENT PROCESS AND BEHAVIOUR 1. a) Differences between leaders and managers b) Corporate Governance 2. a) Planning Premises b) Decision Tree Analysis 3. a) Theory X, Theory Y and Theory Z b) Leadership
AM Syllabus ( ): Accounting AM SYLLABUS ( ) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS
 AM SYLLABUS (2008-2013) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM 01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus builds on the topics set for the SEC
AM SYLLABUS (2008-2013) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM 01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus builds on the topics set for the SEC
B.Com II Cost Accounting
 B.Com II Cost Accounting Chapter - 1 Cost Accounting: An Overview of Fundamental Aspects 2009 (1) Discuss the objectives of Cost Accounting. 2011 (1) Discuss importance of cost accounting. 2012 (1) What
B.Com II Cost Accounting Chapter - 1 Cost Accounting: An Overview of Fundamental Aspects 2009 (1) Discuss the objectives of Cost Accounting. 2011 (1) Discuss importance of cost accounting. 2012 (1) What
West Bengal State University. Syllabus. For. Three Year B.A/B.SC General in ECONOMICS
 West Bengal State University Syllabus For Three Year B.A/B.SC General in ECONOMICS PART-I PAPER I: Microeconomics (100) 1. Basic Concepts: Concept of Market, Demand & Supply, Price & Value, Personal Income
West Bengal State University Syllabus For Three Year B.A/B.SC General in ECONOMICS PART-I PAPER I: Microeconomics (100) 1. Basic Concepts: Concept of Market, Demand & Supply, Price & Value, Personal Income
PG Diploma in Industrial and Company Law Non- Semester (With Effect from the Academic Year )
 PG Diploma in Industrial and Company Law Non- Semester (With Effect from the Academic Year 2013-14) Eligibility for the course : A Pass in any Undergraduate degree Duration of the course : 1 Year Examination:
PG Diploma in Industrial and Company Law Non- Semester (With Effect from the Academic Year 2013-14) Eligibility for the course : A Pass in any Undergraduate degree Duration of the course : 1 Year Examination:
Roll No : 1 : Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100. Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 11
 Roll No : 1 : Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 11 NOTE : All working notes should be shown distinctly. PART A (Answer Question No.1
Roll No : 1 : Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 11 NOTE : All working notes should be shown distinctly. PART A (Answer Question No.1
Free of Cost ISBN : Appendix. CMA (CWA) Inter Gr. II (Solution upto Dec & Questions of June 2013 included)
 Free of Cost ISBN : 978-93-5034-631-0 Appendix CMA (CWA) Inter Gr. II (Solution upto Dec. 2012 & Questions of June 2013 included) Paper - 8 : Cost and Management Accounting Chapter - 3 : Labour Accounting
Free of Cost ISBN : 978-93-5034-631-0 Appendix CMA (CWA) Inter Gr. II (Solution upto Dec. 2012 & Questions of June 2013 included) Paper - 8 : Cost and Management Accounting Chapter - 3 : Labour Accounting
DISCLAIMER. The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 DISCLAIMER The Suggested Answers hosted in the website do not constitute the basis for evaluation of the students answers in the examination. The answers are prepared by the Faculty of the Board of Studies
DISCLAIMER The Suggested Answers hosted in the website do not constitute the basis for evaluation of the students answers in the examination. The answers are prepared by the Faculty of the Board of Studies
Accounting And Finance For Bankers - JAIIB
 Timing: 3 Hours Question : 100 1. When simple rate of interest is calculated, the interest rate % age is expresses as: a. Rate/100 b. Rate*100 c. 100/Rate d. 1+rate/100 2. Identify a personal account out
Timing: 3 Hours Question : 100 1. When simple rate of interest is calculated, the interest rate % age is expresses as: a. Rate/100 b. Rate*100 c. 100/Rate d. 1+rate/100 2. Identify a personal account out
B.A.F. / THIRD YEAR - VTH SEMESTER (REVISED)
 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING PAPER VI Topics 1. AS- 14 Amalgamation, Absorption & External Reconstruction (excluding inter - company holding) 1. In the nature of purchase with corresponding accounting treatments
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING PAPER VI Topics 1. AS- 14 Amalgamation, Absorption & External Reconstruction (excluding inter - company holding) 1. In the nature of purchase with corresponding accounting treatments
Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting
 Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FA2-MA2.X Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Intermediate course orientation
Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FA2-MA2.X Intermediate Financial and Management Accounting Intermediate course orientation
Syllabus for foundation course I at the F.Y.B.Com course
 Syllabus for foundation course I at the F.Y.B.Com course Foundation course I Syllabus II nd term C. Globalization and Indian Society: Emerging Issues 1. Concepts of liberalization, Privatization and globalization;
Syllabus for foundation course I at the F.Y.B.Com course Foundation course I Syllabus II nd term C. Globalization and Indian Society: Emerging Issues 1. Concepts of liberalization, Privatization and globalization;
Contents. Preface to the eighth edition... Preface to the seventh edition... Foreword... CHAPTER 1 The context of costing... 1
 Contents Preface to the eighth edition... Preface to the seventh edition... Foreword... Page v vii ix CHAPTER 1 The context of costing... 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES... 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE... 1 THE NEED FOR RELEVANT
Contents Preface to the eighth edition... Preface to the seventh edition... Foreword... Page v vii ix CHAPTER 1 The context of costing... 1 LEARNING OUTCOMES... 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE... 1 THE NEED FOR RELEVANT
(Assignment)
 (Assignment) 2017-2018 Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com) Subject : Commerce Subject Code : B.Com Subject Title : Business ganization Course Code : B.Com -01 (N) B.Com -01 (O) Maximum Marks: 30 Note: Long Answer
(Assignment) 2017-2018 Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com) Subject : Commerce Subject Code : B.Com Subject Title : Business ganization Course Code : B.Com -01 (N) B.Com -01 (O) Maximum Marks: 30 Note: Long Answer
Answer to MTP_ Intermediate_Syllabus2016_Jun 2017_Set 2 Paper 12- Company Accounts & Audit
 Paper 12- Company Accounts & Audit Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 12- Company Accounts & Audit Full Marks: 100
Paper 12- Company Accounts & Audit Academics Department, The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (Statutory Body under an Act of Parliament) Page 1 Paper 12- Company Accounts & Audit Full Marks: 100
CFA Program Financial Accounting (Text Book) - Study Plan
 CFA Program Financial Accounting (Text Book) - Study Plan S.No 1. Introduction to Accounting and Financial Statements The meaning of Accounting Attributes of Accounting Output of accounting process Use
CFA Program Financial Accounting (Text Book) - Study Plan S.No 1. Introduction to Accounting and Financial Statements The meaning of Accounting Attributes of Accounting Output of accounting process Use
Downloaded from
 XII ECONOMICS SURE SHOT SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS MICROECONOMICS UNIT - INTRODUCTION Q. Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. 3 Q.2 Discuss the central problems of an economy. Why do they
XII ECONOMICS SURE SHOT SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS MICROECONOMICS UNIT - INTRODUCTION Q. Distinguish between microeconomics and macroeconomics. 3 Q.2 Discuss the central problems of an economy. Why do they
Economics. Model Question Paper - 1 Time : 2.30 Hours MARKS : 90. Part - I. c) Deciding the Location of the Production Unit d) None
 Higher Secondary Second year Economics Model Question Paper - 1 Time : 2.30 Hours MARKS : 90 Part - I I Choose the correct answer 20 X 1 = 20 1. The author of wealth definition is a) Alfred Marshall b)
Higher Secondary Second year Economics Model Question Paper - 1 Time : 2.30 Hours MARKS : 90 Part - I I Choose the correct answer 20 X 1 = 20 1. The author of wealth definition is a) Alfred Marshall b)
GUJARAT STATE LEVEL ELIGIBILITY TEST
 GUJARAT STATE LEVEL ELIGIBILITY TEST Code No. : 17 Subject : COMMERCE SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS Note : There will be two question papers, Paper II and Paper III. Paper II will cover 50 Objective Type
GUJARAT STATE LEVEL ELIGIBILITY TEST Code No. : 17 Subject : COMMERCE SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS Note : There will be two question papers, Paper II and Paper III. Paper II will cover 50 Objective Type
Department of Economics, IUST-Awantipora Syllabus for Ph. D Entrance Test (ECONOMICS)
 Department of Economics, IUST-Awantipora Syllabus for Ph. D Entrance Test (ECONOMICS) Part-I: Core Economics Module I: Micro Economic Analysis Module II: Macro Economics Module III: Money, Banking and
Department of Economics, IUST-Awantipora Syllabus for Ph. D Entrance Test (ECONOMICS) Part-I: Core Economics Module I: Micro Economic Analysis Module II: Macro Economics Module III: Money, Banking and
December CS Executive Programme Module - I Paper - 2
 December - 2015 CS Executive Programme Module - I Paper - 2 (New Syllabus) Cost and Management Accounting Total number of questions: 100 Maximum marks: 100 Assertion A: 1. In management accounting, firm
December - 2015 CS Executive Programme Module - I Paper - 2 (New Syllabus) Cost and Management Accounting Total number of questions: 100 Maximum marks: 100 Assertion A: 1. In management accounting, firm
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Introduction course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: What, when and why? Lesson
Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Introduction course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: What, when and why? Lesson
( PART : B DESCRIPTIVE )
 BCOM/III/CC/08 ( 2 ) 2 0 1 7 ( CBCS ) ( 3rd Semester ) COMMERCE ( Indian Economy ) Full Marks : 75 Time : 3 hours ( PART : B DESCRIPTIVE ) ( Marks : 50 ) The figures in the margin indicate full marks for
BCOM/III/CC/08 ( 2 ) 2 0 1 7 ( CBCS ) ( 3rd Semester ) COMMERCE ( Indian Economy ) Full Marks : 75 Time : 3 hours ( PART : B DESCRIPTIVE ) ( Marks : 50 ) The figures in the margin indicate full marks for
Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (IAS) Effective for examinations to be held after January 2008
 LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (IAS) Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after January 2008 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909
LCCI International Qualifications Level 3 Certificate in Accounting (IAS) Syllabus Effective for examinations to be held after January 2008 For further information contact us: Tel. +44 (0) 8707 202909
Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 PAPER 3 : ADVANCED AUDITING Answer all questions. Question 1 As an auditor how would you deal with the following? (a) There is a sales-tax demand of Rs. 3 crores against X Ltd. relating to prior years
PAPER 3 : ADVANCED AUDITING Answer all questions. Question 1 As an auditor how would you deal with the following? (a) There is a sales-tax demand of Rs. 3 crores against X Ltd. relating to prior years
KDF1D Advanced Corporate Accounting and. Accounting Standards Unit : 1-5
 KDF1D Advanced Corporate Accounting and Accounting Standards Unit : 1-5 UNIT-1 (SYLLABUS) Advanced problems in share capital Debenture transactions including underwriting Valuation of goodwill and shares
KDF1D Advanced Corporate Accounting and Accounting Standards Unit : 1-5 UNIT-1 (SYLLABUS) Advanced problems in share capital Debenture transactions including underwriting Valuation of goodwill and shares
01 & & 211 PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS INTERNATIONAL MONETARY INSTITUTIONS ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT &
 (CORE & ELECTIVE) NEW SYLLABUS IN FORCE FROM THE NEW ACADEMIC YEAR 2017-2018 NO SEMESTER PAPER NO NAME OF THE PAPER FACULTY 101 & 111 ELEMENTARY ECONOMICS- ARTS 01 & 02 1 01 &02 (CORE & ELECTIVE) UG 2
(CORE & ELECTIVE) NEW SYLLABUS IN FORCE FROM THE NEW ACADEMIC YEAR 2017-2018 NO SEMESTER PAPER NO NAME OF THE PAPER FACULTY 101 & 111 ELEMENTARY ECONOMICS- ARTS 01 & 02 1 01 &02 (CORE & ELECTIVE) UG 2
FUNDAMENTALS OF BUSINESS ECONOMICS 2 (MACRO ECONOMICS)
 FUNDAMENTALS OF BUSINESS ECONOMICS 2 (MACRO ECONOMICS) Course Content: Unit No. UNIT -I UNIT - THE LEVEL OF OVERALL ECONOMIC ACTITY 1.1. Economic activity: the circular flow of income model, Measures of
FUNDAMENTALS OF BUSINESS ECONOMICS 2 (MACRO ECONOMICS) Course Content: Unit No. UNIT -I UNIT - THE LEVEL OF OVERALL ECONOMIC ACTITY 1.1. Economic activity: the circular flow of income model, Measures of
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. Duration 10 weeks ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Course orientation Start of course survey Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2:
Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. Duration 10 weeks ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Course orientation Start of course survey Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2:
M. COM.: New optional (elective)
 M. COM.: New optional (elective) Advanced Accounting and Auditing [Code: COM EE] Semester II: Com EA/EE 410 Financial Accounting and Auditing 1 Com EA/EE 411 Cost Accounting 1 Com 412 EE Cost Accounting
M. COM.: New optional (elective) Advanced Accounting and Auditing [Code: COM EE] Semester II: Com EA/EE 410 Financial Accounting and Auditing 1 Com EA/EE 411 Cost Accounting 1 Com 412 EE Cost Accounting
INTERMEDIATE EXAMINATION GROUP - I (SYLLABUS 2016)
 INTERMEDIATE EXAMINATION GROUP - I (SYLLABUS 2016) SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS JUNE - 2017 Paper - 5 : FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Time Allowed : 3 Hours Full Marks : 100 The figures in the margin on the right
INTERMEDIATE EXAMINATION GROUP - I (SYLLABUS 2016) SUGGESTED ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS JUNE - 2017 Paper - 5 : FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Time Allowed : 3 Hours Full Marks : 100 The figures in the margin on the right
Class: XI Subject: ACCOUNTANCY. NO OF PERIOD Unit-1 (25 periods) LEARNING OUTCOMES
 Unit-1 (25 CH-1. Introduction to Accounting - Project on Accounting: objectives, advantages and International limitations, types of accounting information; Accounting users of accounting information and
Unit-1 (25 CH-1. Introduction to Accounting - Project on Accounting: objectives, advantages and International limitations, types of accounting information; Accounting users of accounting information and
Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101
![Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101 Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101](/thumbs/96/128932629.jpg) Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101 P. G. D. F. S. (Semester - I) Examination - 2010 FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 70 (1)
Total No. of Questions : 7] [Total No. of Printed Pages : 2 [3885]-101 P. G. D. F. S. (Semester - I) Examination - 2010 FINANCIAL AND COST ACCOUNTING (2008 Pattern) Time : 3 Hours] [Max. Marks : 70 (1)
REVALIDATION TEST PAPERS
 REVALIDATION TEST PAPERS INTERMEDIATE Group II REVISED SYLLABUS 2008 THE INSTITUTE OF COST ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA DIRECTORATE OF STUDIES Copyright Reserved by the Institute of Cost Accountants of India 2
REVALIDATION TEST PAPERS INTERMEDIATE Group II REVISED SYLLABUS 2008 THE INSTITUTE OF COST ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA DIRECTORATE OF STUDIES Copyright Reserved by the Institute of Cost Accountants of India 2
