FINANCIAL RISK TRANSFER MECHANISMS OVERVIEW
|
|
|
- Piers Reynold Caldwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Second Meeting of the Regional Platform for Financial Risk Transfer Mechanisms Mauritius, 26 th September 2012 FINANCIAL RISK TRANSFER MECHANISMS OVERVIEW â Luc Malâtre, Consultant to the COI
2 FINANCIAL RISK TRANSFER MECHANISMS OVERVIEW : CONTENTS Characteristics of financial risk transfer mechanisms for natural disasters The risks to be covered for the Islands project Review of the perils affecting the region Analysis of past events and their consequences Existing and required data Existing mechanisms in the Islands and other states The French CATNAT scheme The Mauritius Sugar Insurance Fund Board National contingency funds : Madagascar and Seychelles Parametric schemes : Malawi, Central America, the Caribbean The African Risk Capacity project Lessons to be drawn for the Islands project Which risks can be transferred, who buys coverage, what type of coverage Technical requirements Strategic decisions and action plan 2
3 CHARACTERISTICS OF FINANCIAL RISK TRANSFER MECHANISMS FOR NATURAL DISASTERS What are the risks covered and their characteristics? Perils : cyclones, floods, earthquakes, droughts,... History and data on events : dates, strengths, duration Physical damage and economic losses Who is covered = who purchases coverage and is indemnified? Individuals companies local authorities states Who provides coverage? Insurers Reinsurers Banks and Financial markets States Multilateral institutions How is compensation calculated? Actual damage and losses Parametric / index based calculations Deductibles / attachment points, limits / aggregates The sums insured and premiums will depend heavily on : Is coverage optional or general? What are the capacity for risk retention and risk pooling / mutualisation? What level of reinsurance protection? 3
4 FINANCIAL RISK TRANSFER MECHANISMS OVERVIEW : CONTENTS Characteristics of financial risk transfer mechanisms for natural disasters The risks to be covered for the Islands project Review of the perils affecting the region Analysis of past events and their consequences Existing and required data Existing mechanisms in the Islands and other states The French CATNAT scheme The Mauritius Sugar Insurance Fund Board National contingency funds : Madagascar and Seychelles Parametric schemes : Malawi, Central America, the Caribbean The African Risk Capacity project Lessons to be drawn for the Islands project Which risks can be transferred, who buys coverage, what type of coverage Technical requirements Strategic decisions and action plan 4
5 REVIEW OF THE PERILS AFFECTING THE REGION perils Comoros Madagascar Mauritius La Réunion Tropical Less than More than Less than Less than cyclones yearly y yearly y yearly y yearly y Storm Surges Seychel les Very rare Zanziba r Very rare Unfrequent Frequent Unfrequent Frequent Rare Not reported Floods Unfrequent Less than yearly Less than yearly Frequent Droughts Unfrequent Unfrequent Unfrequent Unfrequent Rare Unknow n Volcanic eruptions Earthqua kes Rare but strong impact Linked to eruptions Not exposed Not exposed Frequent but no impact rare rare Linked to eruptions Rare Not exposed Not exposed Not exposed Rare Tropical cyclones and associated floods or storm surges are the shared risks Drought and severe floods outside cyclonic conditions possible during ENSO oscillations Drought is under represented (or reported) but is increasing in all territories Geophysical phenomenon are less shared, except tsunamis Tsunamis 1 event in event in event in event in event in event in
6 REVIEW OF THE PERILS AFFECTING THE REGION / SOCIO-ECONOMIC DATA 2010 Madagascar Mauritius Comoros Seychelles Zanzibar La Réunion GDP million US $ Population 000s GNI per capita US $ Surface Km Population living below 5m elevation above sea level 2% 6% 14% 42% 7% Population living within less than 100km from the sea 50% 100% 100% 100% 100% 100% 6
7 ANALYSIS OF PAST EVENTS AND THEIR CONSEQUENCES (1/2) The most damaging g events by country from 1975 to 2010 (source EM-DAT) Comoros Madagascar Mauritius Disaster Date Damage Damage Damage Disaster Date Disaster Date (K US$) (K US$) (K US$) Storm 10/01/ Storm 01/02/ Storm 06/02/ Storm 03/01/ Storm 20/12/ Storm 22/12/ Storm 14/02/ Storm 24/03/ Drought Jan Storm 24/01/ Storm 09/04/ Storm 09/02/ Storm 07/03/ Storm 29/01/ Storm 15/03/ Storm 22/01/ Storm 15/03/ Storm 16/01/ Flood 18/01/ Storm Feb Storm 17/02/ Storm 24/01/ La Réunion (Météo-France) Seychelles Zanzibar Disaster Date Damage Damage Disaster Date (K US$) (K US$) Disaster Storm Earthquake/ tsunami Storm Flood 13/08/ Storm Date Damage (K US$) 26/12/ Flood 2005? 7
8 ANALYSIS OF PAST EVENTS AND THEIR CONSEQUENCES (2/2) Total costs of disasters for the last 30 years and 2010 GPD in million US$ 8
9 EXISTING AND REQUIRED DATA Available data of damage and loss estimates The EM-DAT database permits comparisons between territories but is incomplete, especially for events prior to the 80 s. Other sources are mostly derived from EM-DAT There are numerous national or international reports and documents from international organizations and NGO s, but they need to be centralized and made consistent The Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre is located in La Réunion and operated by METEO FRANCE; it monitors cyclones and records their characteristics. Missing and required Characteristics of droughts and floods Standardized assessment of damage and losses Consistent approach to evaluate economic losses Models including damage functions 9
10 EXISTING AND REQUIRED DATA : NEXT STEPS Data acquisition Complement the data for territories with a standardized approach (PDNA, DALA or other internationally adopted method for damage estimates) Take examples of practices from IOC members, know-how transfer is possible Use regional resources (RSMC for cyclones) and international databases to create an IOC database on hazards, vulnerabilities, exposures and costs of past events Modelling Existing data and capacities sufficient to model the main risks (cyclones, drought) Flood hazard still to be mapped in details Damage functions can be created from existing data for risk modelling Maximum height of sea level rise due to storm surge simulated with the Meteo-France storm surge model for La Réunion (figures in cm) 10
11 FINANCIAL RISK TRANSFER MECHANISMS OVERVIEW : CONTENTS Characteristics of financial risk transfer mechanisms for natural disasters The risks to be covered for the Islands project Review of the perils affecting the region Analysis of past events and their consequences Existing and required data Existing mechanisms in the Islands and other states The French CATNAT scheme The Mauritius Sugar Insurance Fund Board National contingency funds : Madagascar and Seychelles Parametric schemes : Malawi, Central America, the Caribbean The African Risk Capacity project Lessons to be drawn for the Islands project Which risks can be transferred, who buys coverage, what type of coverage Technical requirements Strategic decisions and action plan 11
12 TRADITIONAL INSURANCE MECHANISMS : The French CATNAT insurance scheme Since 1982, natural disasters have been fully insured under all policies covering property in France, today 40 millions policies (99% of individuals and companies are covered in mainland France) The French State plays a major role in this compensation scheme : Coverage is defined by Law Premium rates and deductibles are set by the State (deductibles increased if repeated losses) For coverage to apply an inter-ministerial commission must declare a natural disaster situation When a natural catastrophe situation is officially declared, insurers organize the usual loss surveys where necessary, and pay compensation for the losses assessed according to policy provisions. The cost of this coverage is a flat 12% additional premium on all Property policies (6% on vehicles). Total CATNAT premiums collected by insurers appr. 1,3 Bn per annum, losses average 900M. In practice, the costliest events have been floods (57%) and subsidence (37%), as well as cyclones in overseas departments - in mainland France, storms are covered outside of the CATNAT scheme. Subsidence losses in 2003, resulting from drought in mainland France, amounted to 1,4 Bn. In La Reunion, where 60% of households and most companies are insured, Dina (2002) cost 95 M. A major flood (in Paris) or earthquake (Southern France) would cost over 10 Bn. The French State gives its guarantee to the Caisse Centrale de Réassurance (CCR, state-owned) which provides insurers with unlimited reinsurance protection : most insurers buy it. 12
13 TRADITIONAL MECHANISMS : The Mauritius Sugar Insurance Fund Board (SIFB) Sugar cane dominates the economy in terms of cultivated land (90% of arable lands) and foreign currency earnings (25% of export earnings in 2008). Insurance has been compulsory since 1946 for all cane planters and millers, and provided by SIFB, a non-profit Statutory Body. It covers losses arising from cyclones, drought, excessive rainfall and fire. To ensure that losses are not due to cane fields deliberately neglected, abandoned, or to diseases, pest, the Fund undertakes at least 3 annual inspections of cane cultivations. The premium, collected from the proceeds of the harvest, is a percentage of the value of the total insurable sugar (TIS) of each insured farmer or miller : TIS is the weighted average sugar yield per ha of the 3 best years out of the 8 preceding years * number of ha on which canes have been cut down and sent to mill Premium rates, between 5.5% and 8.8%, depend for each insured on past compensation received and premiums paid, and can be upgraded thanks to prevention actions. These rates have been reduced by 50% in In case of a natural disaster, an Event Year may be declared by the SIFB, no later than 31 st January. This opens the process towards compensation : The sugar accrued to each Insured is calculated : amount of cane supplied * extraction rate The sugar accrued is then compared to TIS to assess loss payable around the end of February 1999 was the worst year with compensation of MUR 2,3 Bn versus premiums of MUR 0,7 Bn ; reinsurers paid MUR 1,3 Bn. From 2005 to 2010 total compensation was MUR 2,6 Bn, premiums MUR 4 Bn, ofwhich 10% was ceded for reinsurance. In 2012 the SIFB having $170M in reserves ceased buying reinsurance. 13
14 NATIONAL CONTINGENCY FUNDS : Madagascar and Seychelles Madagascar has suffered 46 natural disasters (cyclones, droughts, epidemics, floods ) cumulatively affecting more than 11 million people in the past 35 years, causing $ billions in damage and losses. The Madagascar authorities have therefore decided in 2008 to set up anationalcontingency Fund to cope with the difficulties raised by these major events : The initial amount was 1 Billion Ariary (US$ ), e.g. around 0.1% of 2008 current expenditures (0.01% of GDP) The fund consists in a State Treasury deposit account, to be fed annually by an amount defined in the frame of the Finance Law The government shall decide how to use the amounts available on the contingency fund, in order to answer critical situations caused by a natural disaster Seychelles lies outside the tropical cyclone belt, but its islands are indirectly affected by atmospheric disturbances and are likely to be affected by global warming and associated climate changes. Seychelles State set up 3 financial mechanisms to reduce underlying risk factors of national disasters: Annual budget allocations (Ministries, Agencies, etc.), a Natural Disaster Fund (established in 2012 Sr10M or US$ 0.8M), and a National Contingency Fund : Initial amount is Sr75M (US$ 6M) or 0.6% of GDP This Contingency Fund is designed to cover expenses triggered by any substantial increase in the price of fuel products and food, natural calamities or costs related to piracy The Fund is replenished annually. If money is withdrawn, the Minister of Finance must explain to Parliament what it is spent on 14
15 PARAMETRIC MECHANISMS : Weather index-based insurance against Drought in Malawi (1/2) Agriculture represents 38% of the country s GDP but its performance has been weak and erratic mainly due to the impact of drought; this has constrained the country s growth. 2 risk transfer mechanisms have been set up: 1) On a micro level Banks in Malawi are unwilling to lend to small farmers, primarily because of the risk of insolvency in case of drought : without access to loans farmers cannot purchase quality seeds that would increase productivity and raise their living standards. The World Bank, in collaboration with Malawi s National Association of Small Farmers, developed a weather index-based crop insurance contract, sold to individual farmers, to increase their access to finance and protect them and their banks from weather risk. The contract is designed to provide compensation when rainfall during a crop growing g cycle is insufficient for farmers to grow and to optimize their yields : A weather insurance index measures changes in rainfall, thanks to 23 local meteorological stations, In case of severe drought, it is assumed that all farmers within a kilometre radius will be similarly affected. The insurance contract is bundled with bank loans to farmers : the insurance pays off part or all of the entire loan directly to the bank if the index hits the specified contract threshold. In 2011, the number of farmers covered was 10,500 for an amount insured of US$ 4.5 million: a relatively low take-up because the scheme is not compulsory and consequently expensive. 15
16 PARAMETRIC MECHANISMS : Weather index-based insurance against Drought in Malawi (2/2) 2) On a macro level In addition to economic losses for the Nation as a whole, Malawi s government finance are highly vulnerable to adverse weather shocks due to the unanticipated need for emergency interventions. A pilot was launched in 2008, in partnership with The World Bank, to provide Malawi with contingency funding in the event of extreme drought during the 2008/2009 agricultural season. The contract was structured as a derivative based on a rainfall index. The index links rainfall and maize production so that, if precipitation falls below a certain level, the index will reflect the projected loss in maize production : The level of rainfall is the only variable in the index The index is based on a model used by government since 1992, thanks to23 weather stations Under the contract, if the maize production in the country, as estimated by the rainfall index, drops below the historical average, Malawi will receive a payout from the World Bank of up to a maximum of $5 million (corresponding to a 10% drop). The World Bank transferred the risk through a mirroring agreement with a reinsurer. 16
17 PARAMETRIC MECHANISMS : The Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility (CCRIF) Following the huge losses caused by Hurricane Ivan in 2004, the Caribbean Community Heads of Government, with the help of the World Bank, decided to implement a risk transfer program for member countries. Started in 2007, CCRIF insures 16 countries against earthquakes, hurricanes and excess rainfall. Country risk profiles were created based on historical data to determine each country s premium. Annual premiums vary from $ 200,000 to 3,000,000 per country. Once a predefined level of earthquake, wind speed or amount of rain is reached, payout occurs within 14 days. The total coverage is limited to $ 100 million. So far there have been 8 payouts to 7 governments for events in 2007 (1M), 2008 ($6,3M), 2010 ($24,75M). This scheme allows Caribbean governments to be insured at a much lower cost than the usual market price, and to receive fast payments because under a parametric, index-based scheme there is no assessment of actual losses since indemnities are only based on the index. Reinsurers accept to protect this scheme, although they have many other opportunities to reinsure other risks in the region at higher prices. 17
18 PARAMETRIC MECHANISMS : The Regional Insurance Facility for Central America (RIFCA) Since 1975, disasters in Central America & the Caribbean have on average affected 4,7 million people annually, causing some 5,300 deaths and US$3.3 billion in physical losses per year (source EM-DAT) Inter-American Development Bank partnered with a reinsurer in 2010 to develop an insurance mechanism for countries in Central America and the Dominican Republic. Under the facility each government has established a captive insurance company, itself supported by the international reinsurance and capital markets : Each captive issues to its national government a single parametric natural catastrophe cover, usually for earthquakes and hurricanes The government pays a premium for this coverage, typically $2,5M for a $50M limit The scheme will pay in case of natural disaster affecting > 5% of the population RIFCA is based on parametric modelling of exposed population, as opposed to classical indemnitybased solutions : The use of physical intensity parameters enhances calculation of the effectively exposed population and payouts to the countries This Insurance facility will provide participating governments with quick access to insurance proceeds following a disaster. This approach allows them to plan more effectively and reduces the need for costly post-disaster debt financing. At the moment, the scheme has started in 2011 with the Dominican Republic. 18
19 A PARAMETRIC PAN-AFRICAN PROJECT : The African Risk Capacity project (ARC) As viewed previously quick-disbursing funding helps protect livelihoods of the vulnerable, lowers the total assistance cost and protects development gains, when coupled with adequate contingency plans : a contingency fund of US$250 M could save African countries and donors nearly US$1 Bn in cash over 20 years (WFP estimate). In 2010, the AU initiated the ARC Project, envisaged as an African-owned financial entity providing governments with quick funds in the event of a severe drought by pooling risk across the continent : Pay-outy would be based on pre-defined rainfall trigger specified by each country, Initial scheme would cover severe drought, but shall later expand to other risks, such as flood. African governments joining the ARC will pool risks across the continent, thereby reducing costs: preliminary findings indicate a 50% reduction in the contingent funds needed if the risk is pooled among nations and managed as a group. The ARC risk evaluation for each country will rely on the Africa RiskView model, thatestimatesboth how many people may be affected by different drought severities and the required response costs. Each country will customize 3 parameters which will determine its premium: the deductible, the ceded percentage and the maximum payout Preliminary analysis shows that with 9 dispersed countries and a max. payout of US$30 M per country, ARC would require an initial capital of ca. US$175 M to remain solvent over several years. 19
20 FINANCIAL RISK TRANSFER MECHANISMS OVERVIEW : CONTENTS Characteristics of financial risk transfer mechanisms for natural disasters The risks to be covered for the Islands project Review of the perils affecting the region Analysis of past events and their consequences Existing and required data Existing mechanisms in the Islands and other states The French CATNAT scheme The Mauritius Sugar Insurance Fund Board National contingency funds : Madagascar and Seychelles Parametric schemes : Malawi, Central America, the Caribbean The African Risk Capacity project Lessons to be drawn for the Islands project Which risks can be transferred, who buys coverage, what type of coverage Technical requirements Strategic decisions and action plan 20
21 LESSONS TO BE DRAWN FOR THE ISLANDS PROJECT : Transferrable risks, who buys coverage, what type of coverage Transferrable risks Cyclones are documented, including related floods, rainfalls and storm surges Tsunamis are the result of seismic activities Droughts can be measured through rainfall levels Who buys coverage is it compulsory or facultative Individuals, Farms, Companies, Local authorities, Governments What type of coverage Indemnity i.e. French CatNat or Mauritius SIFB National contingency funds i.e. Madagascar or Seychelles Parametric i.e. CCRIF, RIFCA, Malawi or ARC 21
22 LESSONS TO BE DRAWN FOR THE ISLANDS PROJECT : Technical requirements Necessity to build probabilistic models Based on historic data of events, as well as evaluation of vulnerabilities, they enable to link the intensity of the peril (e.g. wind speed or rainfall) to a return period and to financial costs History of events characteristics (wind speeds, sea rises, rainfalls, ) duration and frequencies Vulnerabilties Property at risk, Damage function Costs Direct damage (reconstruction) Consecutive economic losses An opportunity : the CCR initiative in La Réunion In its role as reinsurer, CCR has hired a modelling agency to develop a probabilistic model of cyclone risks (including related floods and storm surges). Using data from METEO-FRANCE on past events, it will relate wind speeds to return periods and expected damage. This will permit to quantify return period losses. We suggest exploring the feasibility of extending this project to the whole COI Region. 22
23 LESSONS TO BE DRAWN FOR THE ISLANDS PROJECT : Strategic decisions and action plan Decide what risks can be shared / mutualised Decide who will be insured Decide on type of coverage Decide how to measure damage and losses Build probabilistic model(s) with the help of meteorological authorities and modelling agencies Decide structure insurance and reinsurance, location, administration, staffing, Seek international support 23
24 FINANCIAL RISK TRANSFER MECHANISMS OVERVIEW THANK YOU 24
French Protection Covers Against Natural Disasters. P. Tinard Sr. Cat Modeler R&D Technical Studies Public Reinsurance
 French Protection Covers Against Natural Disasters P. Tinard Sr. Cat Modeler R&D Technical Studies Public Reinsurance Agenda - Highlights on the French context - Main characteristics of the Nat Cat compensation
French Protection Covers Against Natural Disasters P. Tinard Sr. Cat Modeler R&D Technical Studies Public Reinsurance Agenda - Highlights on the French context - Main characteristics of the Nat Cat compensation
TERMINOLOGY. What is Climate risk insurance? What is Disaster risk insurance?
 TERMINOLOGY What is Climate risk insurance? Climate risk insurance describes a suite of instruments for financial risk transfer that provides protection against risks arising from extreme weather events
TERMINOLOGY What is Climate risk insurance? Climate risk insurance describes a suite of instruments for financial risk transfer that provides protection against risks arising from extreme weather events
INDEX BASED RISK TRANSFER AND INSURANCE MECHANISMS FOR ADAPTATION. Abedalrazq Khalil, PhD Water Resources Specialist, World Bank
 INDEX BASED RISK TRANSFER AND INSURANCE MECHANISMS FOR ADAPTATION Abedalrazq Khalil, PhD Water Resources Specialist, World Bank Outline Introduction: Climate Change and Extremes Index Based Risk Transfer:
INDEX BASED RISK TRANSFER AND INSURANCE MECHANISMS FOR ADAPTATION Abedalrazq Khalil, PhD Water Resources Specialist, World Bank Outline Introduction: Climate Change and Extremes Index Based Risk Transfer:
From managing crises to managing risks: The African Risk Capacity (ARC)
 Page 1 of 7 Home > Topics > Risk Dialogue Magazine > Strengthening food security > From managing crises to managing risks: The African Risk Capacity (ARC) From managing crises to managing risks: The African
Page 1 of 7 Home > Topics > Risk Dialogue Magazine > Strengthening food security > From managing crises to managing risks: The African Risk Capacity (ARC) From managing crises to managing risks: The African
CARIBBEAN AND CENTRAL AMERICAN PARTNERSHIP FOR CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE POOLING RISK TO SAFEGUARD AGAINST CATASTROPHES GENERATED BY NATURAL EVENTS
 CARIBBEAN AND CENTRAL AMERICAN PARTNERSHIP FOR CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE POOLING RISK TO SAFEGUARD AGAINST CATASTROPHES GENERATED BY NATURAL EVENTS May 2014 NINE COUNTRIES IN THE CARIBBEAN AND CENTRAL
CARIBBEAN AND CENTRAL AMERICAN PARTNERSHIP FOR CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE POOLING RISK TO SAFEGUARD AGAINST CATASTROPHES GENERATED BY NATURAL EVENTS May 2014 NINE COUNTRIES IN THE CARIBBEAN AND CENTRAL
Catastrophe Risk Financing Instruments. Abhas K. Jha Regional Coordinator, Disaster Risk Management East Asia and the Pacific
 Catastrophe Risk Financing Instruments Abhas K. Jha Regional Coordinator, Disaster Risk Management East Asia and the Pacific Structure of Presentation Impact of Disasters in developing Countries The Need
Catastrophe Risk Financing Instruments Abhas K. Jha Regional Coordinator, Disaster Risk Management East Asia and the Pacific Structure of Presentation Impact of Disasters in developing Countries The Need
France s Funds and Insurance Schemes for Natural Disasters. Update
 France s Funds and Insurance Schemes for Natural Disasters Update 1 Mandatory cover of losses arising from Natural Catastrophes in: all Physical Damage (a.k.a. Fire ) insurance policies covering risks
France s Funds and Insurance Schemes for Natural Disasters Update 1 Mandatory cover of losses arising from Natural Catastrophes in: all Physical Damage (a.k.a. Fire ) insurance policies covering risks
Insurance as a Risk Reduction Tool: Role of Parametric and Traditional Insurance
 Insurance as a Risk Reduction Tool: Role of Parametric and Traditional Insurance Saundra Bailey Group Managing Director Caribbean Emergency Legislation Project (CELP) 25 March 2010 The Caribbean context
Insurance as a Risk Reduction Tool: Role of Parametric and Traditional Insurance Saundra Bailey Group Managing Director Caribbean Emergency Legislation Project (CELP) 25 March 2010 The Caribbean context
Adaptation Committee: Workshop on the means of implementation for enhanced adaptation action. 2-4 March 2015 Wissenschaftszentrum, Bonn
 Adaptation Committee: Workshop on the means of implementation for enhanced adaptation action 2-4 March 2015 Wissenschaftszentrum, Bonn The way disaster response in Africa has worked for over 60 years Household
Adaptation Committee: Workshop on the means of implementation for enhanced adaptation action 2-4 March 2015 Wissenschaftszentrum, Bonn The way disaster response in Africa has worked for over 60 years Household
CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK SUPPORT FOR HAITI TO MEET COMMITMENT TO CARIBBEAN CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE FACILITY FOR THE HURRICANE SEASON
 PUBLIC DISCLOSURE AUTHORISED CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK SUPPORT FOR HAITI TO MEET COMMITMENT TO CARIBBEAN CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE FACILITY FOR THE 2017-2018 HURRICANE SEASON This Document is being made
PUBLIC DISCLOSURE AUTHORISED CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK SUPPORT FOR HAITI TO MEET COMMITMENT TO CARIBBEAN CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE FACILITY FOR THE 2017-2018 HURRICANE SEASON This Document is being made
Africa RiskView Customisation Review. Terms of Reference of the Customisation Review Committee & Customisation Review Process
 Africa RiskView Customisation Review Terms of Reference of the Customisation Review Committee & Customisation Review Process April 2018 1 I. Introduction a. Background African Risk Capacity Agency (ARC
Africa RiskView Customisation Review Terms of Reference of the Customisation Review Committee & Customisation Review Process April 2018 1 I. Introduction a. Background African Risk Capacity Agency (ARC
RISK TRANSFER AND FINANCE EXPERIENCE IN THE CARIBBEAN. Orville Grey March 2016
 RISK TRANSFER AND FINANCE EXPERIENCE IN THE CARIBBEAN Orville Grey March 2016 WHO WE ARE? WHER E WE ARE? WEATHER-RELATED LOSS & DAMAGE RISING Caribbean is vulnerable to weather related hazards e.g. drought,
RISK TRANSFER AND FINANCE EXPERIENCE IN THE CARIBBEAN Orville Grey March 2016 WHO WE ARE? WHER E WE ARE? WEATHER-RELATED LOSS & DAMAGE RISING Caribbean is vulnerable to weather related hazards e.g. drought,
Disaster Management The
 Disaster Management The UKRAINIAN Agricultural AGRICULTURAL Dimension WEATHER Global Facility for RISK Disaster MANAGEMENT Recovery and Reduction Seminar Series February 20, 2007 WORLD BANK COMMODITY RISK
Disaster Management The UKRAINIAN Agricultural AGRICULTURAL Dimension WEATHER Global Facility for RISK Disaster MANAGEMENT Recovery and Reduction Seminar Series February 20, 2007 WORLD BANK COMMODITY RISK
WAYS AND BENEFITS OF PRODUCING AND USING RISK INFORMATION
 WAYS AND BENEFITS OF PRODUCING AND USING RISK INFORMATION HISTORY OF NATURAL DISASTER IN SEYCHELLES Geographically, Seychelles is exposed to major natural hazard such as landslide, floods, storm surge,
WAYS AND BENEFITS OF PRODUCING AND USING RISK INFORMATION HISTORY OF NATURAL DISASTER IN SEYCHELLES Geographically, Seychelles is exposed to major natural hazard such as landslide, floods, storm surge,
Loss and Damage Associated with Climate Change Impacts The (possible) role of Disaster Risk Financing and Insurance
 UNFCC regional expert meeting on loss and damage August 27 29, 2012 Bangkok, Thailand Loss and Damage Associated with Climate Change Impacts The (possible) role of Disaster Risk Financing and Insurance
UNFCC regional expert meeting on loss and damage August 27 29, 2012 Bangkok, Thailand Loss and Damage Associated with Climate Change Impacts The (possible) role of Disaster Risk Financing and Insurance
Risk Transfer Schemes the Example of CCRIF SPC
 Risk Transfer Schemes the Example of CCRIF SPC Isaac Anthony Chief Executive Officer CCRIF SPC Fourth Forum of the Standing Committee on Finance Financial instruments that address the risks of loss and
Risk Transfer Schemes the Example of CCRIF SPC Isaac Anthony Chief Executive Officer CCRIF SPC Fourth Forum of the Standing Committee on Finance Financial instruments that address the risks of loss and
GOVERNMENTS IN THE LEAD ON FINANCIAL PREPAREDNESS
 GOVERNMENTS IN THE LEAD ON FINANCIAL PREPAREDNESS Lessons learned from around the world Wednesday, November 18, 2015 African Union Addis Ababa, Ethiopia GOVERNMENTS IN THE LEAD ON FINANCIAL PREPAREDNESS
GOVERNMENTS IN THE LEAD ON FINANCIAL PREPAREDNESS Lessons learned from around the world Wednesday, November 18, 2015 African Union Addis Ababa, Ethiopia GOVERNMENTS IN THE LEAD ON FINANCIAL PREPAREDNESS
Understanding CCRIF s Hurricane, Earthquake and Excess Rainfall Policies
 Understanding CCRIF s Hurricane, Earthquake and Excess Rainfall Policies Technical Paper Series # 1 Revised March 2015 Background and Introduction G overnments are often challenged with the significant
Understanding CCRIF s Hurricane, Earthquake and Excess Rainfall Policies Technical Paper Series # 1 Revised March 2015 Background and Introduction G overnments are often challenged with the significant
THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE
 THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE InsuResilience at a glance The InsuResilience Climate Risk Insurance Initiative was adopted by the G7 partner countries Germany, France, Italy, Japan, Canada, the
THE CLIMATE RISK INSURANCE INITIATIVE InsuResilience at a glance The InsuResilience Climate Risk Insurance Initiative was adopted by the G7 partner countries Germany, France, Italy, Japan, Canada, the
Ex Ante Financing for Disaster Risk Management and Adaptation
 Ex Ante Financing for Disaster Risk Management and Adaptation A Public Policy Perspective Dr. Jerry Skees H.B. Price Professor, University of Kentucky, and President, GlobalAgRisk, Inc. Piura, Peru November
Ex Ante Financing for Disaster Risk Management and Adaptation A Public Policy Perspective Dr. Jerry Skees H.B. Price Professor, University of Kentucky, and President, GlobalAgRisk, Inc. Piura, Peru November
Small States Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility
 Small 2005 States Forum 2005 Annual Meetings World Bank Group/International Monetary Fund Washington, DC DRAFT September 24, 2005 www.worldbank.org/smallstates Small States Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility
Small 2005 States Forum 2005 Annual Meetings World Bank Group/International Monetary Fund Washington, DC DRAFT September 24, 2005 www.worldbank.org/smallstates Small States Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility
French Protection Covers Against Natural Disasters
 French Protection Covers Against Natural Disasters Summary 1. French exposure 2. Nat Cat insurance penetration 3. French Protection Covers Against Natural Disasters 4. The French National Disaster Compensation
French Protection Covers Against Natural Disasters Summary 1. French exposure 2. Nat Cat insurance penetration 3. French Protection Covers Against Natural Disasters 4. The French National Disaster Compensation
Terms of Reference. 1. Background
 Terms of Reference Peer Review of the Actuarial Soundness of CCRIF SPC s Loss Assessment Models for Central America and the Caribbean (i) Earthquake and Tropical Cyclone Loss Assessment Model (SPHERA)
Terms of Reference Peer Review of the Actuarial Soundness of CCRIF SPC s Loss Assessment Models for Central America and the Caribbean (i) Earthquake and Tropical Cyclone Loss Assessment Model (SPHERA)
PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) ADDITIONAL FINANCING Report No.: PIDA5305. Project Name. Parent Project Name. Region Country Sector(s) Theme(s)
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Project Name Parent Project Name Region Country Sector(s) Theme(s) Lending Instrument
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Project Name Parent Project Name Region Country Sector(s) Theme(s) Lending Instrument
Disaster Risk Reduction and Financing in the Pacific A Catastrophe Risk Information Platform Improves Planning and Preparedness
 Disaster Risk Reduction and Financing in the Pacific A Catastrophe Risk Information Platform Improves Planning and Preparedness Synopsis The Pacific Islands Countries (PICs) 1, with a combined population
Disaster Risk Reduction and Financing in the Pacific A Catastrophe Risk Information Platform Improves Planning and Preparedness Synopsis The Pacific Islands Countries (PICs) 1, with a combined population
Weathering Climate Change through Climate Risk Transfer Solutions
 The G20's role on climate risk insurance & pooling: Weathering Climate Change through Climate Risk Transfer Solutions With this document, the Munich Climate Insurance Initiative (MCII) provides suggestions
The G20's role on climate risk insurance & pooling: Weathering Climate Change through Climate Risk Transfer Solutions With this document, the Munich Climate Insurance Initiative (MCII) provides suggestions
RTD on Climate Change Policy Reforms May 14, 2014
 RTD on Climate Change Policy Reforms May 14, 2014 William H. Martirez, Country Manager What is MicroEnsure? Micro Ensure is a global insurance intermediary dedicated to serving poor households and the
RTD on Climate Change Policy Reforms May 14, 2014 William H. Martirez, Country Manager What is MicroEnsure? Micro Ensure is a global insurance intermediary dedicated to serving poor households and the
Climate Insurance Fund
 Climate Insurance Fund An innovative approach to safeguard against extreme weather events in developing countries Frankfurt, 5 th July, 2013 Monika Beck Director Competence Center Financial Sector Development
Climate Insurance Fund An innovative approach to safeguard against extreme weather events in developing countries Frankfurt, 5 th July, 2013 Monika Beck Director Competence Center Financial Sector Development
Catastrophe Insurance System in France
 The Geneva Papers on Risk and Insurance, 20 (No. 77 October 1995) 474-480 Catastrophe Insurance System in France by Serge Magnan * 1. Introduction Since the beginning of the fifties, French insurance companies
The Geneva Papers on Risk and Insurance, 20 (No. 77 October 1995) 474-480 Catastrophe Insurance System in France by Serge Magnan * 1. Introduction Since the beginning of the fifties, French insurance companies
Weathering the Risks: Scalable Weather Index Insurance in East Africa
 Weathering the Risks: Scalable Weather Index Insurance in East Africa Having enough food in East Africa depends largely on the productivity of smallholder farms, which in turn depends on farmers ability
Weathering the Risks: Scalable Weather Index Insurance in East Africa Having enough food in East Africa depends largely on the productivity of smallholder farms, which in turn depends on farmers ability
WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE,
 WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE, DURBAN 2011 ELECTRONIC PRESS FOLDER Status: 25.11.2011 Contents 1. Current meteorological knowledge 2. Extreme weather events 3. Political action required 4. Insurance
WEATHER EXTREMES, CLIMATE CHANGE, DURBAN 2011 ELECTRONIC PRESS FOLDER Status: 25.11.2011 Contents 1. Current meteorological knowledge 2. Extreme weather events 3. Political action required 4. Insurance
African Risk Capacity. Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions A Project of the African Union
 African Risk Capacity Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions A Project of the African Union The Way Disaster Assistance Works Now EVENT ASSESS APPEAL FUNDING RESPONSE CNN EFFECT time The Way Disaster Assistance
African Risk Capacity Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions A Project of the African Union The Way Disaster Assistance Works Now EVENT ASSESS APPEAL FUNDING RESPONSE CNN EFFECT time The Way Disaster Assistance
African Risk Capacity. Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions A Project of the African Union
 African Risk Capacity Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions A Project of the African Union The Way Disaster Assistance Works Now EVENT ASSESS APPEAL FUNDING RESPONSE CNN EFFECT time The Way Disaster Assistance
African Risk Capacity Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions A Project of the African Union The Way Disaster Assistance Works Now EVENT ASSESS APPEAL FUNDING RESPONSE CNN EFFECT time The Way Disaster Assistance
African Risk Capacity (ARC): Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions
 African Risk Capacity (ARC): Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions Protecting Livelihoods & Development Gains Cost-effective contingency funding protects livelihoods and development gains 1 A Household Coping
African Risk Capacity (ARC): Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions Protecting Livelihoods & Development Gains Cost-effective contingency funding protects livelihoods and development gains 1 A Household Coping
DEFINING THE PROTECTION GAP. 1: Decide who /what should be protected:
 DEFINING THE PROTECTION GAP Introduction In recent years, we ve seen a considerable increase in disasters, both in their frequency and severity. Overall economic losses from such disasters currently average
DEFINING THE PROTECTION GAP Introduction In recent years, we ve seen a considerable increase in disasters, both in their frequency and severity. Overall economic losses from such disasters currently average
Caribbean and Central American Partnership for Catastrophe Risk Insurance
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Caribbean and Central American Partnership for Catastrophe Risk Insurance Pooling Risk
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Caribbean and Central American Partnership for Catastrophe Risk Insurance Pooling Risk
PCDIP. Philippine City Disaster Insurance Pool
 PCDIP Philippine City Disaster Insurance Pool Disaster Risk The Philippines is located in one of the world s most disaster-prone regions. Positioned on the Pacific Ring of Fire and within the Western North
PCDIP Philippine City Disaster Insurance Pool Disaster Risk The Philippines is located in one of the world s most disaster-prone regions. Positioned on the Pacific Ring of Fire and within the Western North
PUBLIC DISCLOSURE AUTHORISED
 PUBLIC DISCLOSURE AUTHORISED CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK SUPPORT FOR HAITI TO MEET COMMITMENT TO CARIBBEAN CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE FACILITY FOR THE 2013-2014 HURRICANE SEASON This Document is being made
PUBLIC DISCLOSURE AUTHORISED CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK SUPPORT FOR HAITI TO MEET COMMITMENT TO CARIBBEAN CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE FACILITY FOR THE 2013-2014 HURRICANE SEASON This Document is being made
Resilience in Florida
 Resilience in Florida Parametric Insurance as a Solution to Protection Gaps in Insurance Coverage Instructor: Alok Jha Instructor ID: 1339258 (ID provided by Florida Department of Financial Services) Course
Resilience in Florida Parametric Insurance as a Solution to Protection Gaps in Insurance Coverage Instructor: Alok Jha Instructor ID: 1339258 (ID provided by Florida Department of Financial Services) Course
1. Background. CCRIF SPC s sustainability relies on certain key factors:
 Terms of Reference Peer Review of the Financial Module of the Earthquake and Tropical Cyclone Loss Assessment Model (SPHERA) for Central America and the Caribbean 1. Background In 2007, the Caribbean Catastrophe
Terms of Reference Peer Review of the Financial Module of the Earthquake and Tropical Cyclone Loss Assessment Model (SPHERA) for Central America and the Caribbean 1. Background In 2007, the Caribbean Catastrophe
World Meteorological Organization Role of WMO and National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in Disaster Risk Reduction
 World Meteorological Organization Role of WMO and National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in Disaster Risk Reduction By Maryam Golnaraghi, Ph.D. Chief of Disaster Risk Reduction Programme Extreme
World Meteorological Organization Role of WMO and National Meteorological and Hydrological Services in Disaster Risk Reduction By Maryam Golnaraghi, Ph.D. Chief of Disaster Risk Reduction Programme Extreme
Boosting Financial Resilience to Disaster Shocks
 Boosting Financial Resilience to Disaster Shocks Good Practices and New Frontiers World Bank Technical Contribution to the 2019 G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors Process January 16, 2019.
Boosting Financial Resilience to Disaster Shocks Good Practices and New Frontiers World Bank Technical Contribution to the 2019 G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors Process January 16, 2019.
Resilience and the Economics of Risk. NACo s Resilient Counties Advisory Board February 2016
 Resilience and the Economics of Risk NACo s Resilient Counties Advisory Board February 2016 The growing burden of uninsured losses Natural catastrophe losses 1970 2014 (in 2014 USD) 450 400 350 300 Uninsured
Resilience and the Economics of Risk NACo s Resilient Counties Advisory Board February 2016 The growing burden of uninsured losses Natural catastrophe losses 1970 2014 (in 2014 USD) 450 400 350 300 Uninsured
Economic Risk and Potential of Climate Change
 Economic Risk and Potential of Climate Change Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe; Dr. Ernst Rauch This document appeared in Detlef Stolten, Bernd Emonts (Eds.): 18th World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2010 - WHEC 2010
Economic Risk and Potential of Climate Change Prof. Dr. Peter Hoeppe; Dr. Ernst Rauch This document appeared in Detlef Stolten, Bernd Emonts (Eds.): 18th World Hydrogen Energy Conference 2010 - WHEC 2010
DOCUMENT OF THE WORLD BANK RESTRUCTURING PAPER ON A PROPOSED PROJECT RESTRUCTURING HONDURAS AND NICARAGUA CATASTROPHE RISK INSURANCE PROJECT
 Public Disclosure Authorized The World Bank DOCUMENT OF THE WORLD BANK REPORT NO.: RES24760 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized RESTRUCTURING PAPER ON A PROPOSED PROJECT RESTRUCTURING
Public Disclosure Authorized The World Bank DOCUMENT OF THE WORLD BANK REPORT NO.: RES24760 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized RESTRUCTURING PAPER ON A PROPOSED PROJECT RESTRUCTURING
ENSO Impact regions 10/21/12. ENSO Prediction and Policy. Index Insurance for Drought in Africa. Making the world a better place with science
 ENSO Prediction and Policy Making the world a better place with science Index Insurance for Drought in Africa Science in service of humanity Dan Osgoode & Eric Holthaus International Research Institute
ENSO Prediction and Policy Making the world a better place with science Index Insurance for Drought in Africa Science in service of humanity Dan Osgoode & Eric Holthaus International Research Institute
DISASTER RISK FINANCING STRATEGIES AND ITS COMPONENTS
 DISASTER RISK FINANCING STRATEGIES AND ITS COMPONENTS Mamiko Yokoi-Arai, Principal Administrator, Insurance and Private Pensions, OECD Joint DAC-EPOC Task Team on Climate Change and Development Co-operation
DISASTER RISK FINANCING STRATEGIES AND ITS COMPONENTS Mamiko Yokoi-Arai, Principal Administrator, Insurance and Private Pensions, OECD Joint DAC-EPOC Task Team on Climate Change and Development Co-operation
CDEMA Symposium to Commemorate the 10th Anniversary of Hurricane Ivan Exploring Response and Recovery, Embracing Resilience
 CDEMA Symposium to Commemorate the 10th Anniversary of Hurricane Ivan Exploring Response and Recovery, Embracing Resilience Radisson Grenada Beach Resort, Grand Anse, Grenada 1st 3rd December, 2014 CCRIF
CDEMA Symposium to Commemorate the 10th Anniversary of Hurricane Ivan Exploring Response and Recovery, Embracing Resilience Radisson Grenada Beach Resort, Grand Anse, Grenada 1st 3rd December, 2014 CCRIF
Agricultural Risk Management in the Caribbean
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Table of Contents Agricultural Risk Management in the Caribbean Lessons and Experiences
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Table of Contents Agricultural Risk Management in the Caribbean Lessons and Experiences
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Pool Initiative Concept Presentation
 Pacific Catastrophe Risk Pool Initiative Concept Presentation Nigel Roberts Country Director, Pacific Islands, PNG and Timor Leste Small States Forum Washington DC, October 21, 2007 In the aftermath of
Pacific Catastrophe Risk Pool Initiative Concept Presentation Nigel Roberts Country Director, Pacific Islands, PNG and Timor Leste Small States Forum Washington DC, October 21, 2007 In the aftermath of
The Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility. Excess Rainfall Coverage
 The Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility Excess Rainfall Coverage Dr. Simon Young CEO, Caribbean Risk Managers Ltd. CCRIF Facility Supervisor March 2013 Rationale for Excess Rainfall Coverage
The Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance Facility Excess Rainfall Coverage Dr. Simon Young CEO, Caribbean Risk Managers Ltd. CCRIF Facility Supervisor March 2013 Rationale for Excess Rainfall Coverage
Southeast Asia Disaster Risk Insurance Facility
 Southeast Asia Disaster Risk Insurance Facility PROTECT THE GREATEST HOME OF ALL: OUR COUNTRIES SEADRIF is a regional platform to provide ASEAN countries with financial solutions and technical advice to
Southeast Asia Disaster Risk Insurance Facility PROTECT THE GREATEST HOME OF ALL: OUR COUNTRIES SEADRIF is a regional platform to provide ASEAN countries with financial solutions and technical advice to
Workshop Climate Change Adaptation (CCA)
 Workshop Climate Change Adaptation (CCA) March 24th 27th, 2014 Manila, Philippines Tuesday, March 25th, 2014 09.00h 09.30h: Exchange of Experiences and Key Learning Points Resty Lou Talamayan (PRC) Session
Workshop Climate Change Adaptation (CCA) March 24th 27th, 2014 Manila, Philippines Tuesday, March 25th, 2014 09.00h 09.30h: Exchange of Experiences and Key Learning Points Resty Lou Talamayan (PRC) Session
Disaster Risk Management in the Caribbean Case Study: Rapid Damage and Loss Assessment following the 2013 Disaster
 Belize benefits from knowledge and experiences from the PPCR Disaster Risk Management in the Caribbean Case Study: Rapid Damage and Loss Assessment following the 2013 Disaster Photo Credit: http://gov.vc
Belize benefits from knowledge and experiences from the PPCR Disaster Risk Management in the Caribbean Case Study: Rapid Damage and Loss Assessment following the 2013 Disaster Photo Credit: http://gov.vc
EXPERIENCES IN ECONOMIC ASSESSSMET OF DISASTERS IMPACT
 EXPERIENCES IN ECONOMIC ASSESSSMET OF DISASTERS IMPACT AS A TOOL FOR RISK REDUCTION AND MAINSTREAMING DISASTER REDUCTION IN DEVELOPMENT POLICY Ricardo Zapata-Marti, Focal Point for Disaster Evaluation
EXPERIENCES IN ECONOMIC ASSESSSMET OF DISASTERS IMPACT AS A TOOL FOR RISK REDUCTION AND MAINSTREAMING DISASTER REDUCTION IN DEVELOPMENT POLICY Ricardo Zapata-Marti, Focal Point for Disaster Evaluation
Philippine City Disaster Insurance Pool (PCDIP)
 Philippine City Disaster Insurance Pool (PCDIP) Strengthening the Enabling Environment for Disaster Risk Financing: Options for Enhancing Financial Resilience Benita Ainabe Financial Sector Specialist
Philippine City Disaster Insurance Pool (PCDIP) Strengthening the Enabling Environment for Disaster Risk Financing: Options for Enhancing Financial Resilience Benita Ainabe Financial Sector Specialist
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT) 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
 National Disaster Risk Management Fund (RRP PAK 50316) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT) A. Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities a. Performance
National Disaster Risk Management Fund (RRP PAK 50316) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (DISASTER RISK MANAGEMENT) A. Sector Road Map 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities a. Performance
International Agricultural and Natural Catastrophe Insurance Forum. Experience by GIZ Matthias Range
 International Agricultural and Natural Catastrophe Insurance Forum Experience by GIZ Rüschlikon, Switzerland, October 2016 Seite 1 Agenda GIZ GIZ and Financial Systems Development GIZ and Agricultural
International Agricultural and Natural Catastrophe Insurance Forum Experience by GIZ Rüschlikon, Switzerland, October 2016 Seite 1 Agenda GIZ GIZ and Financial Systems Development GIZ and Agricultural
CATASTROPHIC RISK AND INSURANCE Hurricane and Hydro meteorological Risks
 CATASTROPHIC RISK AND INSURANCE Hurricane and Hydro meteorological Risks INTRODUCTORY REMARKS OECD IAIS ASSAL VII Conference on Insurance Regulation and Supervision in Latin America Lisboa, 24-28 April
CATASTROPHIC RISK AND INSURANCE Hurricane and Hydro meteorological Risks INTRODUCTORY REMARKS OECD IAIS ASSAL VII Conference on Insurance Regulation and Supervision in Latin America Lisboa, 24-28 April
OVERVIEW. Linking disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation. Disaster reduction - trends Trends in economic impact of disasters
 Linking disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation Inter-Agency Secretariat for the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR) A. Trends OVERVIEW B. Disaster reduction a tool for
Linking disaster risk reduction and climate change adaptation Inter-Agency Secretariat for the International Strategy for Disaster Reduction (UNISDR) A. Trends OVERVIEW B. Disaster reduction a tool for
Evaluating Sovereign Disaster Risk Finance Strategies: Case Studies and Guidance
 Public Disclosure Authorized Evaluating Sovereign Disaster Risk Finance Strategies: Case Studies and Guidance October 2016 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized
Public Disclosure Authorized Evaluating Sovereign Disaster Risk Finance Strategies: Case Studies and Guidance October 2016 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized
Time for action in developing countries. How Insurance can serve the poor COP 12 UNFCCC climate talk. Thomas Loster
 Time for action in developing countries How Insurance can serve the poor COP 12 UNFCCC climate talk Thomas Loster November 2006 The Munich Re Foundation Focus humans at risk Water: Resource and risk factor
Time for action in developing countries How Insurance can serve the poor COP 12 UNFCCC climate talk Thomas Loster November 2006 The Munich Re Foundation Focus humans at risk Water: Resource and risk factor
InsuResilience Solutions Fund (ISF) Transforming concepts into products
 InsuResilience Solutions Fund (ISF) Transforming concepts into products The need for climate risk insurance solutions Increasing risks of natural disasters Increasing intensity and frequency of extreme
InsuResilience Solutions Fund (ISF) Transforming concepts into products The need for climate risk insurance solutions Increasing risks of natural disasters Increasing intensity and frequency of extreme
Disaster Risk. Management. Niels Holm-Nielsen. Lead Specialist Disaster Risk Management
 Disaster Risk Management Niels Holm-Nielsen Lead Specialist Disaster Risk Management 1 Who Cares? 1 tropical storm was the likely cause of 20% of the increase in poverty in Guatemala between 2006 and 2011
Disaster Risk Management Niels Holm-Nielsen Lead Specialist Disaster Risk Management 1 Who Cares? 1 tropical storm was the likely cause of 20% of the increase in poverty in Guatemala between 2006 and 2011
Terms of Reference GIS Review of the Earthquake and Tropical Cyclone Loss Assessment Model (SPHERA) for Central America and the Caribbean
 Terms of Reference GIS Review of the Earthquake and Tropical Cyclone Loss Assessment Model (SPHERA) for Central America and the Caribbean 1. Background In 2007, the Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance
Terms of Reference GIS Review of the Earthquake and Tropical Cyclone Loss Assessment Model (SPHERA) for Central America and the Caribbean 1. Background In 2007, the Caribbean Catastrophe Risk Insurance
How insurance can support climate resilience
 Accepted manuscript - 1 Embargoed till 24 March at 9am GMT (10:00 CET) How insurance can support climate resilience Swenja Surminski (Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at
Accepted manuscript - 1 Embargoed till 24 March at 9am GMT (10:00 CET) How insurance can support climate resilience Swenja Surminski (Grantham Research Institute on Climate Change and the Environment at
Measuring and Mapping the Welfare Effects of Natural Disasters A Pilot
 Measuring and Mapping the Welfare Effects of Natural Disasters A Pilot Luc Christiaensen,, World Bank, presentation at the Managing Vulnerability in East Asia workshop, Bangkok, June 25-26, 26, 2008 Key
Measuring and Mapping the Welfare Effects of Natural Disasters A Pilot Luc Christiaensen,, World Bank, presentation at the Managing Vulnerability in East Asia workshop, Bangkok, June 25-26, 26, 2008 Key
PARAMETRIC INSURANCE COVER FOR NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISKS. Serghei Mărgulescu 1 Elena Mărgulescu 2
 PARAMETRIC INSURANCE COVER FOR NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISKS Serghei Mărgulescu 1 Elena Mărgulescu 2 Abstract With economic losses of over USD 370 bn caused by 325 catastrophic events, 2011 ranks as the worst
PARAMETRIC INSURANCE COVER FOR NATURAL CATASTROPHE RISKS Serghei Mărgulescu 1 Elena Mărgulescu 2 Abstract With economic losses of over USD 370 bn caused by 325 catastrophic events, 2011 ranks as the worst
Index Based Crop Insurance Initiative Kenya April 2012
 Index Based Crop Insurance Initiative Kenya April 2012 Presentation Outline 1. What is Index Insurance? 2. Why do farmers need insurance? 3. What is Kilimo Salama? 4. How does Kilimo Salama work? 5. Key
Index Based Crop Insurance Initiative Kenya April 2012 Presentation Outline 1. What is Index Insurance? 2. Why do farmers need insurance? 3. What is Kilimo Salama? 4. How does Kilimo Salama work? 5. Key
UNEP FI Adaption How Insurance can serve the poor. Thomas Loster
 UNEP FI Adaption How Insurance can serve the poor Thomas Loster November 2006 The Munich Re Foundation Focus humans at risk Water: Resource and risk factor Population development Environmental and climate
UNEP FI Adaption How Insurance can serve the poor Thomas Loster November 2006 The Munich Re Foundation Focus humans at risk Water: Resource and risk factor Population development Environmental and climate
The Lessons of 2017 Perspective from the World Bank Group
 The Lessons of 2017 Perspective from the World Bank Group Barbuda Dominica Hurricane Irma Hurricane Maria Rebuild, Rethink, Resilience: Lessons for economic and security partnerships following after the
The Lessons of 2017 Perspective from the World Bank Group Barbuda Dominica Hurricane Irma Hurricane Maria Rebuild, Rethink, Resilience: Lessons for economic and security partnerships following after the
LESSONS LEARNED IMPLEMENTATION OF A SOVEREIGN RISK MANAGEMENT AND INSURANCE MECHANISM
 Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions A Specialized Agency of the African Union LESSONS LEARNED IMPLEMENTATION OF A SOVEREIGN RISK MANAGEMENT AND INSURANCE MECHANISM September 2017 www.africanriskcapacity.org
Sovereign Disaster Risk Solutions A Specialized Agency of the African Union LESSONS LEARNED IMPLEMENTATION OF A SOVEREIGN RISK MANAGEMENT AND INSURANCE MECHANISM September 2017 www.africanriskcapacity.org
DISASTER RISK FINANCING ADB Operational Innovations in South Asia
 DISASTER RISK FINANCING ADB Operational Innovations in South Asia Erik Kjaergaard, Disaster Risk Management Specialist South Asia Department with input from Mayumi Ozaki, Senior Portfolio Management Specialist
DISASTER RISK FINANCING ADB Operational Innovations in South Asia Erik Kjaergaard, Disaster Risk Management Specialist South Asia Department with input from Mayumi Ozaki, Senior Portfolio Management Specialist
VIETNAM CATASTROPHE RISK Country risk profile and methodology. NGO VIET TRUNG Deputy Director General Insurance Supervisory Authority 1
 VIETNAM CATASTROPHE RISK Country risk profile and methodology NGO VIET TRUNG Deputy Director General Insurance Supervisory Authority 1 NATURAL HAZARD PROFILE One of the world s most exposed countries to
VIETNAM CATASTROPHE RISK Country risk profile and methodology NGO VIET TRUNG Deputy Director General Insurance Supervisory Authority 1 NATURAL HAZARD PROFILE One of the world s most exposed countries to
Financial Protection of the State against Natural Disasters. Summary. Introduction
 Financial Protection of the State against Natural Disasters Francis Ghesquiere, Lead Disaster Risk Management Specialist, World Bank Olivier Mahul, Program Coordinator, Insurance for the Poor & Disaster
Financial Protection of the State against Natural Disasters Francis Ghesquiere, Lead Disaster Risk Management Specialist, World Bank Olivier Mahul, Program Coordinator, Insurance for the Poor & Disaster
I n v i r t i e n d o p a r a l a R e s i l i e n c i a. I n v i r t i e n d o p a r a l a R e s i l i e n c i a
 I n v i r t i e n d o p a r a l a R e s i l i e n c i a Disaster Risk Financing: I n v i r t i e n d o p a r a l a R e s i l i e n c i a The Evolving Role of (Re)Insurance and Financial Markets Claudia
I n v i r t i e n d o p a r a l a R e s i l i e n c i a Disaster Risk Financing: I n v i r t i e n d o p a r a l a R e s i l i e n c i a The Evolving Role of (Re)Insurance and Financial Markets Claudia
African Risk Capacity (ARC) Risk Management In Agriculture
 African Risk Capacity (ARC) Risk Management In Agriculture November 2016 Disaster Management Response ARC aims to provide cost-effective contingency funding to protect livelihoods and development gains
African Risk Capacity (ARC) Risk Management In Agriculture November 2016 Disaster Management Response ARC aims to provide cost-effective contingency funding to protect livelihoods and development gains
REPUBLIC OF KENYA THE NATIONAL TREASURY AND MINISTRY OF PLANNING
 REPUBLIC OF KENYA THE NATIONAL TREASURY AND MINISTRY OF PLANNING DISASTER RISK FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS IN KENYA EXECUTIVE SEMINAR ON INDEX BASED LIVESTOCK INSURANCE SAROVA WHITESANDS HOTEL 19 TH -20 TH APRIL,
REPUBLIC OF KENYA THE NATIONAL TREASURY AND MINISTRY OF PLANNING DISASTER RISK FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS IN KENYA EXECUTIVE SEMINAR ON INDEX BASED LIVESTOCK INSURANCE SAROVA WHITESANDS HOTEL 19 TH -20 TH APRIL,
Knowledge FOr Resilient
 Date: 14 December 2017 Place: Novi Sad Knowledge FOr Resilient society FINANCIAL RESILIENCE TO HAZARDS AND CLIMATE FINANCE: A COMPREHENSIVE APPROACH OF TOOLS AND METHODS FOR DISASTER RISK FINANCE Outline
Date: 14 December 2017 Place: Novi Sad Knowledge FOr Resilient society FINANCIAL RESILIENCE TO HAZARDS AND CLIMATE FINANCE: A COMPREHENSIVE APPROACH OF TOOLS AND METHODS FOR DISASTER RISK FINANCE Outline
Quantifying Disaster Risk: measuring progress in the path towards resilience
 Quantifying Disaster Risk: measuring progress in the path towards resilience Sujit Mohanty UNISDR -ROAP Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on Improving Disaster Data to Build Resilience in Asia and the Pacific,
Quantifying Disaster Risk: measuring progress in the path towards resilience Sujit Mohanty UNISDR -ROAP Expert Group Meeting (EGM) on Improving Disaster Data to Build Resilience in Asia and the Pacific,
An Operational Framework for Disaster Risk Financing and Insurance
 Financial Protection Against Natural Disasters An Operational Framework for Disaster Risk Financing and Insurance This part seeks to tie together the experience and collected knowledge from partners in
Financial Protection Against Natural Disasters An Operational Framework for Disaster Risk Financing and Insurance This part seeks to tie together the experience and collected knowledge from partners in
Current Approaches to Drought Vulnerability and Impact assessment
 Current Approaches to Drought Vulnerability and Impact assessment Experiences from risk monitoring work (GAR) and reviews of progress against the Hyogo Framework for Action John A. Harding UN Relations
Current Approaches to Drought Vulnerability and Impact assessment Experiences from risk monitoring work (GAR) and reviews of progress against the Hyogo Framework for Action John A. Harding UN Relations
DISASTER RISK FINANCING AND INSURANCE PROGRAM
 DISASTER RISK FINANCING AND INSURANCE PROGRAM Strengthening Financial Resilience to Disasters What We Do DRFIP helps developing countries manage the cost of disaster and climate shocks. The initiative
DISASTER RISK FINANCING AND INSURANCE PROGRAM Strengthening Financial Resilience to Disasters What We Do DRFIP helps developing countries manage the cost of disaster and climate shocks. The initiative
Response of Caisse Centrale de Réassurance (CCR) to the European Commission's Green Paper on natural and man-made disasters
 Response of Caisse Centrale de Réassurance (CCR) to the European Commission's Green Paper on natural and man-made disasters Preamble: At present, there are marked differences in disaster risk cover in
Response of Caisse Centrale de Réassurance (CCR) to the European Commission's Green Paper on natural and man-made disasters Preamble: At present, there are marked differences in disaster risk cover in
RUTH VARGAS HILL MAY 2012 INTRODUCTION
 COST BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF THE AFRICAN RISK CAPACITY FACILITY: ETHIOPIA COUNTRY CASE STUDY RUTH VARGAS HILL MAY 2012 INTRODUCTION The biggest source of risk to household welfare in rural areas of Ethiopia
COST BENEFIT ANALYSIS OF THE AFRICAN RISK CAPACITY FACILITY: ETHIOPIA COUNTRY CASE STUDY RUTH VARGAS HILL MAY 2012 INTRODUCTION The biggest source of risk to household welfare in rural areas of Ethiopia
The AIR Typhoon Model for South Korea
 The AIR Typhoon Model for South Korea Every year about 30 tropical cyclones develop in the Northwest Pacific Basin. On average, at least one makes landfall in South Korea. Others pass close enough offshore
The AIR Typhoon Model for South Korea Every year about 30 tropical cyclones develop in the Northwest Pacific Basin. On average, at least one makes landfall in South Korea. Others pass close enough offshore
PROGRAM INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: Second Disaster Risk Management Development Policy Loan with a CAT-DDO Region
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROGRAM INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: Operation Name Second Disaster
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROGRAM INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: Operation Name Second Disaster
3 RD MARCH 2009, KAMPALA, UGANDA
 INNOVATIVE NEW PRODUCTS WEATHER INDEX INSURANCE IN MALAWI SHADRECK MAPFUMO VICE PRESIDENT, AGRICULTURE INSURANCE 3 RD MARCH 2009, KAMPALA, UGANDA Acknowledgements The Commodity Risk Management Group at
INNOVATIVE NEW PRODUCTS WEATHER INDEX INSURANCE IN MALAWI SHADRECK MAPFUMO VICE PRESIDENT, AGRICULTURE INSURANCE 3 RD MARCH 2009, KAMPALA, UGANDA Acknowledgements The Commodity Risk Management Group at
Agricultural Insurance for Developing Countries The Role of Governments
 FARM - Pluriagri conference on Insuring Agricultural Production Paris, France December 18, 2012 Agricultural Insurance for Developing Countries The Role of Governments Olivier Mahul Program Coordinator,
FARM - Pluriagri conference on Insuring Agricultural Production Paris, France December 18, 2012 Agricultural Insurance for Developing Countries The Role of Governments Olivier Mahul Program Coordinator,
Background Paper. Market Risk Transfer. Phillippe R. D. Anderson The World Bank
 Background Paper Market Risk Transfer Phillippe R. D. Anderson The World Bank Market Risk Transfer Background Paper for the World Development Report 2014 on Opportunity and Risk: Managing Risk for Development
Background Paper Market Risk Transfer Phillippe R. D. Anderson The World Bank Market Risk Transfer Background Paper for the World Development Report 2014 on Opportunity and Risk: Managing Risk for Development
Climate Insurance Fund (CIF) Luxembourg, June 2017
 Climate Insurance Fund (CIF) Luxembourg, June 2017 KfW Development Bank s Role in Insurance Our Mandate As the German development bank, our objectives is help our partners to fight poverty, maintain peace,
Climate Insurance Fund (CIF) Luxembourg, June 2017 KfW Development Bank s Role in Insurance Our Mandate As the German development bank, our objectives is help our partners to fight poverty, maintain peace,
RESILIENCE Provisional copy
 RESILIENCE Promoting Disaster and Climate Risk Resilience Through Regional Programmatic and Risk Financing Mechanisms Action Statement and Action Plan Provisional copy Overview and Context Climate change
RESILIENCE Promoting Disaster and Climate Risk Resilience Through Regional Programmatic and Risk Financing Mechanisms Action Statement and Action Plan Provisional copy Overview and Context Climate change
Source: NOAA 2011 NATURAL CATASTROPHE YEAR IN REVIEW
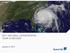 Source: NOAA 2011 NATURAL CATASTROPHE YEAR IN REVIEW January 4, 4 2012 U.S. NATURAL CATASTROPHE UPDATE Carl Hedde, SVP, Head of Risk Accumulation Munich Reinsurance America, Inc. MR NatCatSERVICE One of
Source: NOAA 2011 NATURAL CATASTROPHE YEAR IN REVIEW January 4, 4 2012 U.S. NATURAL CATASTROPHE UPDATE Carl Hedde, SVP, Head of Risk Accumulation Munich Reinsurance America, Inc. MR NatCatSERVICE One of
Global Resilience Risk
 Global Resilience Risk An Insurers Perspective WEC Energy Summit 16 March 2016 Jamie Summons, Head of Weather Solutions, Asia Pacific Swiss Re Weather Market Capability Global presence, market leadership
Global Resilience Risk An Insurers Perspective WEC Energy Summit 16 March 2016 Jamie Summons, Head of Weather Solutions, Asia Pacific Swiss Re Weather Market Capability Global presence, market leadership
Policy Implementation for Enhancing Community. Resilience in Malawi
 Volume 10 Issue 1 May 2014 Status of Policy Implementation for Enhancing Community Resilience in Malawi Policy Brief ECRP and DISCOVER Disclaimer This policy brief has been financed by United Kingdom (UK)
Volume 10 Issue 1 May 2014 Status of Policy Implementation for Enhancing Community Resilience in Malawi Policy Brief ECRP and DISCOVER Disclaimer This policy brief has been financed by United Kingdom (UK)
Fatou Assah. The World Bank. April 2012
 Fatou Assah Senior Financial Sector specialist The World Bank April 2012 1 Contents 2 Disaster Risk Management Framework Disaster Risk Financing & Insurance Program Mainstream disaster risk financing and
Fatou Assah Senior Financial Sector specialist The World Bank April 2012 1 Contents 2 Disaster Risk Management Framework Disaster Risk Financing & Insurance Program Mainstream disaster risk financing and
Francesco Rispoli, IFAD, Italy
 Scaling up insurance as a disaster resilience strategy for smallholder farmers in Latin America 11 th Consultative Forum on microinsurance regulation for insurance supervisory authorities, insurance practitioners
Scaling up insurance as a disaster resilience strategy for smallholder farmers in Latin America 11 th Consultative Forum on microinsurance regulation for insurance supervisory authorities, insurance practitioners
Key Messages. Dealing with Natural Disaster Risks Institutions & Products
 Workshop on Insurance and Risk Assessment Key Messages Dealing with Natural Disaster Risks Institutions & Products Vijay Kalavakonda Insurance Specialist email: vkalavak@worldbank.org World Bank Insurance
Workshop on Insurance and Risk Assessment Key Messages Dealing with Natural Disaster Risks Institutions & Products Vijay Kalavakonda Insurance Specialist email: vkalavak@worldbank.org World Bank Insurance
THE SPANISH AGRICULTURAL INSURANCE SYSTEM WORKSHOP ON RISK MANAGEMENT MAY 2017
 THE SPANISH AGRICULTURAL INSURANCE SYSTEM WORKSHOP ON RISK MANAGEMENT 18-19 MAY 2017 1. General features of the AIS. Agricultural Insurance System (AIS) is almost 40 years old. Risks covered are the damages
THE SPANISH AGRICULTURAL INSURANCE SYSTEM WORKSHOP ON RISK MANAGEMENT 18-19 MAY 2017 1. General features of the AIS. Agricultural Insurance System (AIS) is almost 40 years old. Risks covered are the damages
Disaster risk management for climate change adaptation: Experiences from German development cooperation
 Disaster risk management for climate change adaptation: Experiences from German development cooperation Britta Heine 1, Jens Etter 2 1 Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Postfach
Disaster risk management for climate change adaptation: Experiences from German development cooperation Britta Heine 1, Jens Etter 2 1 Deutsche Gesellschaft für Technische Zusammenarbeit (GTZ) GmbH, Postfach
