and Conventions (iii) Accounting Standards concepts, objectives, benefits
|
|
|
- Clement Francis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Changes made in the Syllabus of CA Foundation Paper 1: Principles and Practices of Accounting (proposed) vis-a-vis CPT Section A :Fundamentals of Accounting (existing) Fundamentals of Accounting (60 Marks) as per the existing syllabus Principles and Practices of Accounting (100 Marks) as per the proposed syllabus 1. Theoretical Framework 1. Theoretical Framework (i) Meaning and Scope of accounting (ii) Accounting Concepts, Principles and Conventions (iii) Accounting Standards concepts, objectives, benefits (iv) Accounting Policies (v) Accounting as a measurement discipline valuation principles, accounting estimates 2. Accounting Process Books of Accounts leading to the preparation of Trial Balance, Capital and revenue expenditures, Capital and revenue receipts, Contingent assets and contingent liabilities, Fundamental errors including rectifications thereof. (i) Meaning and Scope of accounting (ii) Accounting Concepts, Principles and Conventions (iii) Accounting Standards concepts, objectives, benefits (iv) Accounting Policies (v) Accounting as a measurement discipline valuation principles, accounting estimates 2. Accounting Process Books of Accounts leading to the preparation of Trial Balance, Capital and revenue expenditures, Capital and revenue receipts, Contingent assets and contingent liabilities, Fundamental errors including rectifications thereof. 3. Bank Reconciliation Statement 3. Bank Reconciliation Statement 4. Inventories Basis of inventory valuation and record keeping. 4. Inventories Basis of inventory valuation and record keeping. Changes (Addition/ Deletion) Reasons for changes
2 5. Depreciation accounting Methods, computation and accounting treatment of depreciation, Change in depreciation methods. 6. Preparation of Final Accounts for SoleProprietors 5. Depreciation accounting Methods, computation and accounting treatment of depreciation, Change in depreciation methods. 6. Preparation of Final Accounts for SoleProprietors 7. Simple problems on Financial Statements of Not-for-Profit Organisations 8. Accounts from Incomplete Records 9. Average Due Date and Account Current Addition Addition Addition In the existing curriculum, this topic is covered at Intermediate (IPC) level Paper 1: Accounting. The underlying concepts of this topic is similar to the principles applied for preparation of final accounts. Hence, the basic of preparation of financial statements of Not-for-Profit Organisations has been covered at Foundation level and advanced problems on this topic dealing with sector wise accounting is proposed to be covered at Intermediate level in Paper 1 : Accounting. In the existing curriculum, this topic is covered at Intermediate (IPC) levelpaper 1: Accounting. The underlying concepts of this topic is also similar to the principles applied for preparation of final accounts. Hence, this topic has also been proposed to be shifted here at Foundation level. In the existing curriculum, this topic is covered at Intermediate (IPC) level Paper 1: Accounting. The technique of average due date is useful for calculating interest on transactions made by the proprietors or partners of a business firm at several points of time. Account current is very useful when frequent transactions take place between the two parties in settlement of their accounts.the underlying concepts of this topic is
3 7. Accounting for Special Transactions (a) Consignments (b) Joint Ventures (c) Bills of exchange and promissory notes (d) Sale of goods on approval or return basis. 8. Partnership Accounts Final accounts of partnership firms Basic concepts of admission, retirement and death of a partner including treatment of goodwill. 9. Introduction to Company Accounts Issue of shares and debentures, forfeiture of shares, re-issue of forfeited shares, redemption of preference shares. 10. Accounting for Special Transactions (a) Consignments (b) Joint Ventures (c) Bills of exchange and promissory notes (d) Sale of goods on approval or return basis applied in other topics of Foundation like bills of exchange and partnership for calculation of interest on capital and drawings. (e) Departmental accounts. Addition The concepts used in this topic are the basic principles applied for preparation of departmental accounts. Hence the topic has been shifted here from Intermediate (IPC) Paper 5 Advanced Accounting. 11. Partnership Accounts Final accounts of partnership firms Basic concepts of admission, retirement and death of a partner including treatment of goodwill. 12. Introduction to Company Accounts Issue of shares and debentures, forfeiture of shares, re-issue of forfeited shares, redemption of preference shares.
4 Changes made in the Syllabus of CA Foundation paper 2 (part I): Mercantile Laws (proposed) vis-a-vis Section B: Mercantile Laws (existing). Mercantile Laws (40 Marks) Mercantile Laws (60 Marks) Changes (Addition/ Deletion) 1. The Indian Contract Act, 1872: An overview of Sections 1 to 75 covering the general nature of contract, consideration, other essential elements of a valid contract, performance of contract and breach of contract. 1. The Indian Contract Act, 1872: An overview of Sections 1 to 75 covering the general nature of contract, consideration, other essential elements of a valid contract, performance of contract and breach of contract. - - Reasons for changes 2. The Sale of Goods Act, 1930: Formation of the contract of sale, Conditions and Warranties, Transfer of ownership and delivery of goods, Unpaid seller and his rights. 3. The Indian Partnership Act, 1932: General Nature of Partnership, Rights and duties of partners, Registration and dissolution of a firm. 2. The Sale of Goods Act, 1930: Formation of the contract of sale, Conditions and Warranties, Transfer of ownership and delivery of goods, Unpaid seller and his rights. 3. The Indian Partnership Act, 1932: General Nature of Partnership, Rights and duties of partners, Registration and dissolution of a firm The Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008: Introduction- covering nature and scope, Essential features, characteristics of LLP, Incorporation and differences with other forms of organizations. New addition LLP is a new corporate structure that combines the flexibility of a partnership and the advantages of limited liability of a company at a low compliance cost. With the increasing importance of the LLP in today s
5 - 5. The Companies Act, 2013 [section 1 to 22]: Important definitions, Introduction of company & corporate veil theory, Classes of companies, Conversion of company, Incorporation of company, Memorandum of Association, Articles of Association, Alteration of Memorandum and Articles, Doctrine of Indoor Management, Conversion of companies already registered, Promoters, Service of documents. Note 1: Here, chapters 1 to 4 carries 45 marks and chapter 5 carries 15 marks New addition [Section 1 to 22 of the Companies Act, 2013 has been shifted from Intermediate (IPC) Paper 2, Business Ethics and Communication, Existing syllabus business scenario, the knowledge of LLP is the requirement of the CA Profession. Company law is one of the most significant and pervasive statute among the various Corporate legislations and so form an important subject of the chartered accountancy course. The Companies Act, 2013 deals with the law and regulations for the formation and effective working of the corporate entity and to deal with the complexities in the business and corporate world. Note 2: If new legislations are enacted in place of the existing legislations, the syllabus would include the corresponding provisions of such new legislations with effect from dates notified by the Institute.
6 Changes made in the Syllabus of CA Foundation Paper 2 Part-II General English (proposed) Existing Syllabus General English (40-Marks) as per the proposed syllabus Changes (Addition/ Deletion) No existing Curriculum Section A Topic :Comprehension Passages and Note Making Subtopic : Comprehension Passages Introduction to Comprehension Passages Kind of Questions asked Multiple Choice questions Questions requiring short answers o Central theme o Inference/Conclusion Questions based on Vocabulary Steps to comprehend the text Helpful Hints to answer questions Points to Ponder Sample Passages with answers Exercises with answers Subtopic: Note Making Introduction to Note Making Significance of Note Making for students Detailed Format Heading(Title) New Paper Curriculum has been designed afresh Reasons for changes Not Applicable
7 Sub-heading Indentation Points Use of abbreviations Summary Content Expression Steps to Comprehend text Helpful Hints Points to Ponder Sample Passages with Notes Exercises with answers Section B Developing Writing Skills Subtopic: Article Writing Format Title Writer s Name Content (Value points related to the topic) 3-4 Paragraph Para 1 : Brief Introduction of the status of the issue Para 2 : Analysis of the topic in terms of o Types o Consequences o Causes o Good/bad aspects o related information Para 3: Implications social / environmental/psychological/health related. Para 4: Concluding Para-Suggestions / reminders.
8 Expression Grammatical accuracy, spellings, coherence, relevance of ideas and style. Steps to write an article Ideas associated with the topic Structuring the ideas in a logical progression. Quick Review Subtopic: Report Writing What is a Report Essential elements of Report Writing Kinds of Reports Reporting for a Meeting/Assembly Reporting for a Newspaper Reporting for a Magazine Detailed Format (for each) Title By- Writer s Name Place, Date Body o What o When o Where o Who o How Tips and Conventions of Report Writing Sample Reports Exercises with Answer hints
9 Subtopic : Writing Formal Letters Detailed format Date Salutation Subject Body of the letter o First paragraph o Second paragraph Complimentary Closing Points to Remember Subtopic : Writing Formal Mails How to Write a Formal Mail Writing Effective Mails Essential elements of Mails Subject line Formal Greetings Target Audience(Reader) Clarity and Conciseness Formal Closing Proof read Feedback Tips and Conventions of Mails Sample Mails Exercises with answer hints Subtopic : Resume Writing Essential Elements of Resume Name and contact details Objective Summary
10 Academic Qualifications and Achievements Co-curricular Achievements Training Programs attended/completed Strengths Interests/Hobbies Declaration Signature Resume Writing Tips and Conventions Do s and Don ts of Resume Writing Sample Resumes Exercises with answer hints Section C: Grammar Subtopic: Introduction to Basic Writing Introduction Process of writing Styles of Writing Significance of writing skills for students Writing Conventions Characteristics of good writing How to make writing effective Do s and Don ts of good writing Subtopic: Basic English Grammar(Nouns, Pronouns and Verbs) Nouns: Definition, Examples Different types and categories of nouns(classification with examples) o Common and Proper Noun o Abstract and Concrete Noun
11 o Countable and Uncountable Noun o Compound Noun o Collective Noun o Verbal Noun and Gerunds Pronouns: Definition, Examples Different categories of Pronouns(Classification with examples) o Subject Pronoun o Object Pronoun o Possessive Adjectives/Determiners o Possessive Pronouns o Reflexive Pronouns o Intensive Pronouns o Indefinite Pronouns o Demonstrative Pronoun o Relative Pronoun o Interrogative Pronoun o Reciprocal Pronoun Verbs: Definition, Examples Different categories of Verbs(Classification with examples) o Action and Stative Verbs o Transitive and Intransitive Verbs o Auxiliary and Modal Verbs o Irregular Verbs o Phrasal Verbs Different Verb Forms
12 Simple Continuous Perfect Perfect Continuous Simple Present Simple Past Simple Future Present Continuous Past Continuous Future Continuous Present Perfect Past Perfect Future Perfect Present Perfect Continuous Past Perfect Continuous Future Perfect Continuous Subtopic: Articles, Adjectives and Adverbs Articles: Definition, Examples Types of Articles(classification with examples) o Definite Article o Indefinite Articles Difference in usage of a and an Difference in usage of a and the Usage of the When to use and when not to use Articles Adjectives: Definition, Examples Classification of Adjectives(with examples) o Adjectives of quality o Adjectives of quantity o Adjectives of Number o Demonstrative Adjectives o Interrogative Adjectives o Coordinate Adjectives o Non-coordinate adjectives Order of placement of different kinds of adjectives in a
13 sentence Adverbs: Definition, Examples Usage of adverbs Adverb basics Forming adverbs form adjectives Classification of Adverbs(with examples) o Comparative Adverbs o Superlative Adverbs o Adverbs of place(location and prepositions) o Adverbs of movement o Adverbs of time(specific time, time period, periodicity) o Adverbs of manner o Adverbs of degree o Adverbs of certainty Subtopic: Prepositions, Conjunctions and Interjections Prepositions: Definition, Examples Simple Prepositions, Double Prepositions Compound Prepositions Participle Prepositions Phrase Prepositions Prepositions of time Prepositions of place Prepositions of movement. Conjunctions: Definition, Examples Classification of Conjunctions(with examples) Coordinating Conjunctions
14 Subordinating Conjunctions o Subordinating conjunctions of time o Subordinating conjunctions of place o Subordinating conjunctions of reason o Subordinating conjunctions of purpose o Subordinating conjunctions of condition o Subordinating conjunctions of comparison Correlative Conjunctions Compound Conjunctions Interjection: Definition,Examples Classification of Interjections(with examples) Mild Interjection Strong Interjection Subtopic: Sentence Types, Direct-Indirect, Active -Passive Speech Sentence: Definition Classification of sentence based on connotation Assertive sentences Interrogative sentences Imperative sentences Exclamatory sentences Optative sentences Sentence Structure Subject and Predicate Verb (Auxiliary, Finite) Object (Direct, Indirect) Complement Adjunct or Adverbial
15 Sentence Clause Structure Types of Clauses Independent clauses Dependent clauses Relative or noun clauses Types of sentences Simple sentence Compound sentence Complex sentence Compound-complex sentence Direct-Indirect Speech: Introduction Procedure for converting Direct speech into Indirect speech Rules for converting Direct speech into Indirect speech Change in pronouns Change in tenses Change in modals Changes for Imperative sentences Changes for Exclamatory sentences Changes for Interrogative sentences Punctuation in Direct speech Procedure for converting Indirect speech into Direct speech Rules for converting Indirect speech into Direct speech Active Passive Voice: Introduction Usage Active Vs passive voice
16 Reasons for using Passive voice Changing Passive voice to Active voice Changing Active voice to Passive voice Suggestions for using Active and Passive voice Verbs Voice Active or passive Verbs Mood Indicative Imperative Subjunctive Subtopic : Vocabulary Root Words, Synonyms, Antonyms, Prefixes, Suffixes), Phrasal verbs, Collocations and Idioms. Introduction Types of Vocabulary Significance of improving vocabulary How to improve vocabulary List of commonly used words with usage Root words Synonyms and Antonyms Words formed by using Prefixes Words formed by using Suffixes Phrasal verbs Collocations Idioms Exercises with answers
17 Reason for Addition / Deletion of the topics: Foundation Course Paper 3-Business Mathematics Logical Reasoning and Statistics (100 Marks) S.No CPT- Quantitative Aptitude (50 Marks) Foundation Course -Business Mathematics Logical Reasoning and Statistics (100 Marks) A. Business Mathematics and Logical Reasoning (60 Marks A. Mathematics (25 marks) Business Mathematics and Logical Reasoning (40 Marks ) 1 Ratio and Proportion and Indices and Logarithms. Numbers, Laws of Indices, Exponents and Logarithms and Anti Logarithms Ratio and proportion and Time and work related problems. Adding/ Deletion same topic in CPT Reason Chapter one deals with applications of basic fundamental tools for all calculations in Business and Finance. Ratio and proportion are very useful business applications. 2 Equations: Linear Simultaneous linear equations up to three variables, Quadratic and Cubic equations in one variable. Equations of Straight line, Intersection of Straight lines Equations: Linear Simultaneous linear equations up to three variables, Quadratic and Cubic equations in one variable. Algebra of Matrices, Inverse of a Matrix and determinants, solving system of equations using matrix method (Cramer s rule) involving not more than three variables. The topics related Coordinate Geometry deleted. (Rest of the topic in CPT) and Matrices is a new topic in this chapter Coordinate Geometry applications are too mathematical and the objective in this chapter to find out the unknown variables similar method we are used using the solving equations. Matrices helps to find the unknown variables. Which helps formation of linear programming problems in maximization and minimization problems.
18 3 Inequalities: Linear Inequalities in one variable and the solution space 4 Simple Interest And Compound interest including annuity applications 5 Basic Concepts of Permutations and Combinations 6 Introduction Sequences, Series, Arithmetic and Geometric progression Inequalities: Linear Inequalities in one variable and the solution space Time value of Money Simple Interest Compound interest Effective Rate of Interest Present Value Net Present Value Future Value Perpetuity Annuities Sinking Funds Calculating of EMI Calculations of Returns: Nominal Rate of Return Compound Annual growth rate (CAGR) Basic concepts of Permutations and combinations: Introduction, the factorial, permutations, results, circular permutations, permutations with restrictions, Combinations with standard results. Introduction Sequences, Series, Arithmetic and Geometric progression same topic in CPT Helps to formation of linear programming problems in maximization and minimization problems. Same topic in CPT (Removed from FM in IPCC and shifted here) This is a new topic Time value of money Interest rates and Annuity applications are very useful for Chartered accountant students. This topics are useful in Financials and to calculate interests Same topic in CPT Permutation and combination applications are useful in Finance applications and Risk Management also. Same topic in CPT Arithmetic and geometric series applications are used in the area of Finance. 7 Sets,Functions and Relations Sets,Functions and Relations Same topic in CPT Sets, Functions are very important to understand relation in Economic and Business Functions.
19 8 Limits and Continuity intuitive approach 9 Basic applications of Differential and Integral calculus (Excluding the trigonometric applications) Limits and Continuity intuitive approach (Deleted) Basic applications of Differential and Integral calculus (Excluding the trigonometric applications) Deleted Same topic in CPT Limits and continuity functions are not much useful for CA students and they are too mathematical also. Differential calculus is used to find the Marginal concepts with respect to linear or non-linear change of functions. With the help of Integral Cal calculus we can find the total cost,total Revenues When Marginal Cost and Marginal Revenues are known Logical Reasoning (20 Marks) 10 Number series coding and Decoding and All the topics of odd man out. Logical reasoning 11 Blood Relations, topics are new.since this subject To test the analytical ability of the 12 Seating Arrangements, has been students 13 Direction Tests introduced in the 14 Syllogism. proposed scheme. B. Statistics (25 Marks) B. Business Statistics (40 Marks) Addition /deletion Reason 15 Statistical Representation of Data, Statistical Representation of Data, Same topic in CPT It s used to understand the data Diagrammatic representation of Diagrammatic representation of data, collections of sampling and pictorial data, Frequency distribution, Frequency distribution, Graphical representation of data Graphical representation of representation of Frequency Distribution Frequency Distribution Histogram, Frequency Polygon, Ogive, Piechart. Histogram, Frequency Polygon, Ogive, Pie-chart.
20 16 Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion: Mean Median, Mode, Mean Deviation, Quartiles and Quartile Deviation, Standard Deviation, Co-efficient of Variation, Coefficient of Quartile Deviation. Measures of Central Tendency and Dispersion: Mean Median, Mode, Mean Deviation, Quartiles and Quartile Deviation, Standard Deviation, Co-efficient of Variation, Coefficient of Quartile Deviation Same topic in CPT The statistical tools like Mean,Standard Deviation and Variance are very useful for CA 17 Correlation and Regression: Scatter diagram, Karl Pearson s Coefficient of Correlation Rank Correlation, Regression lines, Regression equations, Regression coefficients Correlation and Regression: Scatter diagram, Karl Pearson s Coefficient of Correlation Rank Correlation, Regression lines, Regression equations, Regression coefficients Same topic in CPT With the help of the correlation and regression can understand the relation between variables 18 Probability and Expected value by Mathematical Expectation Probability and Expected value by Mathematical Expectation Same topic in CPT Probability applications are used in Finance and Risk Management.
21 19 Theoretical Distribution: Binomial Distribution, Poisson distribution basic application and Normal Distribution basic applications. Theoretical Distribution: Binomial Distribution, Poisson distribution basic application and Normal Distribution basic applications Same topic in CPT Theoretical distributions are useful in Finance and Cost Management applications 20 Sampling Theory : Basic Principles of Sample survey, Comparison between sample survey and enumeration, errors in Sample survey, some important terms associated with sampling, types of sampling 21 Index Numbers and Time series Uses of Index Numbers, Problems involved in construction of Index Numbers, Methods of construction of Index Numbers. Sampling Theory and testing of hypothesis (a) Basic Principles of Sample survey, Comparison between sample survey and enumeration, errors in Sample survey, some important terms associated with sampling, types of sampling. (b) Testing of Hypothesis, Large sample tests (Test for means, test for proportions and test for Standard deviations) and sample tests applications of t, F-distribution (Variance ratio test) and Chi-square test. Index Numbers and Time series Uses of Index Numbers, Problems involved in construction of Index Numbers, Methods of construction of Index Numbers. Time Series Analysis basic application including Moving Average, Moving Average Method, and Method of Least Squares. Same topic of sampling theory Testing hypothesis added of is Same topic in CPT Time Series part added Sampling techniques are very useful in auditing also. Testing of Hypothesis tools provides a basis for taking ideas or theories someone initially develops the economy or investing markets, and then deciding whether these ideas or true or false.testing of hypothesis tools helps to decide whether the tested ideas are probably true or false with the help of this tools can analyses the results Index numbers and Time series analysis are very useful for framing the suitable business and economic policies, useful deflating and adjusting data. Useful for calculating changes in wages in inflationary conditions and useful Cost of Living index numbers.
22 Section C: General Economics (50 marks) Paper 4*: Business Economics & Business and Commercial Knowledge (100 Marks) Changes (Addition/ Deletion) (I) Micro Economics Part I: Business Economics (60 Marks) Additions 1. Introduction to Micro Economics 1. Introduction to Business Economics Introduction to Business (a) Definition, scope and nature (a) Meaning of Business Economics Economics of Economics (b) Objectives of Business Firm- Profit (a) Meaning of Business (b) Methods of economic study Maximization, Sales Maximization, Growth Economics (c) Central problems of an Maximization. (b) Objectives of Business economy and Production Firm- Profit Maximization, possibilities curve. Sales Maximization, Growth Maximization. 2. Theory of Demand and Supply 2. Theory of Demand and Supply Demand Forecasting (a) Meaning and determinants of (a) Meaning and determinants of demand, Law of demand, Law of demand and demand and Elasticity of demand Price, Elasticity of demand Price, income and cross elasticity income and cross elasticity (b) Theory of consumer s behaviour Marshallian (b) Theory of consumer s approach and Indifference curve approach behavior Marshallian (c) Meaning and determinants of supply, Law of approach and Indifference supply and Elasticity of supply. curve approach (d) Demand Forecasting (c) Meaning and determinants of supply, Law of supply and Elasticity of supply. 3. Theory of Production and Cost (a) Meaning and Factors of production (b) Laws of Production The Law of variable proportions and Laws of returns to scale (c) Concepts of Costs Short 3. Theory of Production and Cost (a) Meaning and Factors of production (b) Laws of Production The Law of Variable proportions and Laws of Returns to Scale, Producer s equilibrium (c) Concepts of Costs Short-run and long-run costs, Average and marginal costs, Total, fixed Reasons for changes These are added as the name of the subject has been changed from General Economics to Business Economics and it is desirable to introduce the new subject including its meaning, nature and subject matter to students. Forecasting of demand, which is the art of predicting demand for a product or a service at some future date on the basis of certain present and past behaviour patterns of some related events, is being taught here as the survival of businesses today, to a great extent, depends upon the extent to which they can predict the demand for their products and services in future accurately. The students should be aware of various techniques of demand forecasting, it is felt.
23 run and long run costs, Average and marginal costs, Total, fixed and variable costs. and variable costs. 4. Price Determination in Different Markets (a) Various forms of markets Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly (b) Price determination in these markets. (II) Indian Economic Development 5. Indian Economy A Profile 6. Select Aspects of Indian Economy 7. Economic Reforms in India 8. Money and Banking 4. Price Determination in Different Markets (a) Various forms of markets Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly (b) Price determination in these markets. 5. Business Cycles Meaning of Business Cycles Phases of Business Cycles Features of Business Cycles. Causes behind these Cycles. Addition Business Cycles Dealt in Intermediate in the paper on business economic environment Every business undergoes phases of ups and downs during its lifetime. These phases in economic activity may be of short duration or long duration and these are called business cycles. A knowledge of the concept of Business Cycles is important for students as it helps them to understand the various economic events taking place in the real world- like great depression, financial crisis, booms etc.
24 Changes made in the Syllabus of CA Foundation Paper 4 Part-II Business and Commercial Knowledge (proposed) Existing Syllabus Business and Commercial Knowledge (40-Marks) as per the proposed syllabus Changes (Addition/ Deletion) Reasons for changes None No existing Curriculum 1. Introduction to Business Nature of Business, Profession and Employment. Objectives of Business. Business and Commercial Knowledge. Economic and Non-Economic Activities. 2. Business Environment Micro and Macro Environment, Elements of Micro Environment Consumers/Customers, Competitors, Organization, Market, suppliers, Intermediaries, Elements of Macro Environment Demographic, Economic, Politicallegal, Socio-cultural, Technological, Global Environment. 3. Business organizations Top Indian and Global Companies. 4. Government Policies for Business Growth Policies creating conducive business environment Startups,E-commerce. Liberalization, Privatization, Foreign Direct Investment. 5. Organizations facilitating Business Indian regulatory bodies - SEBI, RBI, IRDA, CCI, FMC, CBDT, CBEC Indian Development Banks IFCI, IDBI, SIDBI, EXIM Bank,NABARD Global organizations and world trade bodies IMF, ADB, WTO, OECD, SAARC, ASEAN, OPEC. Accounting Bodies IFAC,IASB, IESB, CAPA, SAFA, New Paper. Curriculum has been designed afresh.
25 AOSSG. 6. Common Business and Commercial Terminologies Finance, Marketing and other business terms. Stock Market Terminology.
26 Changes made in the Syllabus of CA Intermediate Paper 1: Accounting (proposed) vis-a-vis Intermediate (IPC) Paper 1 : Accounting (existing) Accounting as per the existing syllabus Accounting as per the proposed syllabus 1. A General Knowledge of the framing of the accounting standards, national and international accounting authorities, adoption of international financial reporting standards 2. Accounting Standards - Working knowledge of: AS 1 : Disclosure of Accounting Policies 1. Process of formulation of Accounting Standards including Ind ASs and their convergence with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRSs) and various other International accounting standard setting bodies. 2. Framework for Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statements (as per Accounting Standard) 3. Accounting Standards: AS 1 : Disclosure of Accounting Policies AS 2 : Valuation of Inventories AS 2 : Valuation of Inventories Changes (Addition/ Deletion) Modification Addition Reasons for changes At Final level, it is proposed to discuss all Ind AS at length.accordingly, it was felt necessary to introduce Ind AS at Intermediate level by including the formulation of Ind AS and briefing theknowledge regarding various international accounting standard setting bodies, before studying the same in detail at Final level. Framework sets out the concepts that underlie the preparation and presentation of financial statements for external users. It assist preparers of financial statements in applying AS and in dealing with topics that have yet to form the subject of AS. Hence, it was decided to include this topic here only before teaching the basic AS.
27 AS 3 : Cash Flow Statements AS 3 : Cash Flow Statements AS 4 : Contingencies and Events occurring after the Balance Sheet Date AS 5 : Net Profit or Loss for the Period, Prior Period Items and Changes in Accounting Policies AS 6 : Depreciation Accounting AS 6 : Depreciation Accounting AS 7 : Construction Contracts (Revised 2002) AS 7 : Construction Contracts (Revised 2002) AS 9 : Revenue Recognition AS 9 : Revenue Recognition AS 10 : Accounting for Fixed Assets AS 10 : Accounting for Fixed Assets AS 11 : The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange Rates (Revised 2003) AS 12 : Accounting for Government Grants Addition Addition Addition Addition Earlier only 18 standards were covered at Intermediate level i.e. 9 AS in Paper 1 : Accounting and 9 AS in Paper 5 : Advanced Accounting. After inclusion of Ind AS and AS at Final level, it was felt that the content of the paper will not commensurate with 100 marks. So all the standards has been shifted at Intermediate level i.e. 13 AS in Paper 1 and 15 AS in Paper 5. To accommodate 13 AS in Paper 1 Accounting, above AS which are covered in the existing syllabus in Paper 5 : Advanced Accounting have been shifted herebased on the intricacies involved in each of the standard. Earlier only 18 standards were covered at Intermediate level i.e. 9 AS in Paper 1 : Accounting and 9 AS in Paper 5 : Advanced Accounting. After inclusion of Ind AS and AS at Final level, it was felt that the content of the paper will not commensurate with 100 marks. So all
28 AS 13 : Accounting for Investments AS 14 : Accounting for Amalgamations AS 13 : Accounting for Investments Deletion the standards has been shifted at Intermediate level i.e. 13 AS in Paper 1 and 15 AS in Paper 5. To accommodate 13 AS in Paper 1 Accounting, above AS which are covered in the existing syllabus in Paper 5 : Advanced Accounting have been shifted herebased on the intricacies involved in each of the standard. In the existing curriculum, the topic of Accounting for Amalgamation is also covered at Intermediate (IPC) level in Paper 5. In the new proposed syllabus, repetition has been avoided and this standard is now shifted at Paper 5 of Intermediate level alongwith the respective topic. AS 16 : Borrowing Costs Addition Earlier only 18 standards were covered at Intermediate level i.e. 9 AS in Paper 1 : Accounting and 9 AS in Paper 5 : Advanced Accounting. After inclusion of Ind AS and AS at Final level, it was felt that the content of the paper will not commensurate with 100 marks. So all the standards has been shifted at Intermediate level i.e. 13 AS in Paper 1 and 15 AS in Paper 5. To accommodate 13 AS in Paper 1 Accounting, above AS which are
29 3. Company Accounts 4. Company Accounts (a) Preparation of financial statements Profit and Loss Account, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement, Statement of changes in Equity and Explanatory Notes. (b) Profit (Loss) prior to incorporation (c) Alteration of share capital, Conversion of fully paid shares into stock and stock into shares, Accounting for bonus issue (d) Simple problems on Accounting for business acquisition, Amalgamation and reconstruction (excluding problems of amalgamation on inter-company holding) (a) Preparation of financial statements Statement of Profit and Loss, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement, Statement of changes in Equity and Explanatory Notes; (b) Profit (Loss) prior to incorporation; (c) Alteration of share capital, Accounting for bonus issue. Partial Deletion Deletion covered in the existing syllabus in Paper 5 : Advanced Accounting have been shifted herebased on the intricacies involved in each of the standard. Specific mention to this topic Conversion of fully paid shares into stock and stock into shares has been removed. However, it will be covered under the topic Alteration of share capital In the existing curriculum, this topic is also covered at Intermediate (IPC) level in Paper 5. In the new proposed syllabus, repetition has been avoided and this topic is now shifted at Paper 5 of Intermediate level alongwith the respective AS. 5. Cash flow Analysis. Addition In the existing curriculum, this topic forms part of Financial Management. However, AS 3 deals with Cash flow statement, hence, analysis of cash flow statement is proposed to be shifted
30 here. 4. Average Due Date, Account Current, Self-Balancing Ledgers 5. Financial Statements of Not-for- Profit Organisations 8. Advanced Problems on Financial Statements of Not-for-Profit Organisations. Deletion Modification The concepts underlying in the topics of Average due date and account current are basic in nature. Also The underlying concepts of these topics are applied in other topics of Foundation like bills of exchange and partnership for calculation of interest on capital and drawings. Hence these topics are shifted at Foundation level. However, after computerization of accounting and development of various accounting softwares, the relevance of self balancing ledgers has been reduced. Therefore, most of the organizations have stopped following this system and hence the topic on self balancing has been removed from the syllabus. In the existing curriculum, this topic is covered at Intermediate (IPC) level. The underlying concepts of this topic is similar to the principles applied for preparation of final accounts. Hence, the basic of preparation of financial statements of Not-for-Profit Organisations has been covered at Foundation level and advanced problems on this topic dealing with sector wise accounting is proposed to be covered at Intermediate level in Paper 1 : Accounting.
31 6. Accounts from Incomplete Records 7. Accounting for Special Transactions (a) Hire purchase and instalment sale transactions 6. Accounting for Special Transactions: (b) Investment accounts (a) Investment Accounting and (c) Insurance claims for loss of stock and loss of profit. (b) Insurance claims for loss of stock and loss of profit. (c) Branch accounts including foreign branches. 8. Issues in Partnership Accounts 7. Advanced Issues in Partnership Accounts in respect of Final accounts of partnership firms Admission, retirement and death of a partner including treatment of goodwill. Admission, Retirement and Death of a Partner including treatment of goodwill, Dissolution of partnership firms including piecemeal distribution of assets; Deletion The underlying concepts of this topic is also similar to the principles applied for preparation of final accounts. Hence, this topic has also been proposed to be shifted here at Foundation level. Deletion This topic uses the concept of AS 19 which is proposed in the syllabus of Paper 5 Advanced Accounting. Therefore, the topic is also shifted to that paper. Addition Addition In the existing curriculum, this topic is covered at Intermediate (IPC) level in Paper 5. In the new proposed syllabus, since AS 11 has been included in this paper, the topic related to it i.e. Branch accounts including foreign branches is now shifted here. In the existing curriculum, this topic is covered at Intermediate (IPC) level in
32 Amalgamation of partnership firms; Conversion into a company and Sale to a company; Issues related to accounting in Limited Liability Partnerships. Paper 5. In order to bring all the sub topics of partnership at one place, this topic has been shifted here. 9. Accounting in Computerised Environment An overview of computerized accounting system Salient features and significance, Concept of grouping of accounts, Codification of accounts, Maintaining the hierarchy of ledger, Accounting packages and consideration for their selection, Generating Accounting Reports. Note : If either old Accounting Standards (ASs), Announcements and Limited Revisions to ASs are withdrawn or new ASs, Announcements and Limited Revisions to ASs are issued by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India in place of existing ASs, Announcements and Limited Revisions to ASs, the syllabus will accordingly exclude/include such new developments in place of the existing ones with effect from the date to be notified by the Institute. Note : If either a new Accounting Standards (ASs), Announcements and Limited Revisions to ASs are issued or the earlier one are withdrawn or new ASs, Announcements and Limited Revisions to ASs are issued in place of existing ASs, Announcements and Limited Revisions to AS, the syllabus will accordingly include / exclude such new developments in the place of the existing ones with effect from the date to be notified. Deletion This topic has been proposed to be shifted in the Intermediate paper of Information Technology and is proposed to be covered there under the heading Accounting Information System. The practical aspects of the same is also covered in the 100 hours ITT.
33 Changes made in the Syllabus of CA Intermediate (IPC) paper 2: Corporate and Other Laws (proposed) vis-a-vis Paper 2: Business Laws, Ethics and Communication (existing). Business Laws, Ethics and Communication (100 Marks) Corporate and Other Laws (100 Marks) Changes (Addition/ Deletion) Reasons for changes PART I- BUSINESS LAW (60 MARKS) Business Law (30 Marks) PART II- Other Laws (40 Marks) 1. The Indian Contract Act, 1872 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 (Specific contracts covered from section 76 onwards): Contract of Indemnity and Guarantee, Bailment, Pledge, Agency 2. The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 The Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881: Meaning of Negotiable Instruments Characteristics, Classification of Instruments, Different provisions relating to Negotiation, Negotiability, Assignability, Right and Obligation of parties, presentment of Instruments, Rules of Compensation 3. The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965 The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965: Applicability, Definitions, Entitlement of payment of bonus, Minimum and Maximum bonus, Calculation of bonus, Miscellaneous provisions 4. The Employees Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952 The Employees Provident Fund and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952: Introduction, Definition, Various Schemes and other provisions 5. The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972 The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972: Extent & Applicability, Definitions, Payment of Gratuity, Calculation, Nominations & Miscellaneous provisions Interpretation of statutes and Drafting of simple deeds and documents: Rules of Interpretation of statutes, Aids to interpretation, New topic added [shifted from Final This topic helps in the understanding of the law and
34 Company Law (30 Marks) Rules of Interpretation/construction of Deeds and Documents, Drafting of Resolution, Minutes, Notices and Reports. The Prevention of Money Laundering Act, Basic structure: Preliminary and Punishment for the Offence of Money laundering The Consumer Protection Act, 1986: Definitions and Application of the Act, Consumer Disputes Redressal agencies and Miscellaneous provisions. Tabular Format of major Labour Acts covering their name, preamble and basic comments PART I: Corporate law (60 Marks) paper 4: Corporate and Allied Laws, Existing syllabus] New Act added [shifted the basic structure from Final paper 4: Corporate and Allied Laws, Existing syllabus and advance portion of this Act will remain in the Final. New Act added Newly added improves writing skill as to drafting of simple deeds and documents. The students are required to have the knowledge of the same in order to point out the frauds committed by the corporates. Being student, knowledge is required to safeguard the interest being a consumer in one or the other through the redressal forums. To keep apprise the students regarding the major Labour Acts covering their name preamble and basic comments. The Companies Act, 2013 Sections 1 to 122 (a) Preliminary (b) Incorporation of Company and Matters Incidental thereto (c) Prospectus and Allotment of Securities (d) Share Capital and Debentures The Companies Act, 2013 Sections 1 to 122 (a) Preliminary (b) Incorporation of Company and Matters Incidental thereto (c) Prospectus and Allotment of Securities (d) Share Capital and Debentures e) Acceptance of Deposits by companies -
35 (e) Acceptance of Deposits by companies (f) Registration of Charges (g) Management and Administration (i) Company Law in a computerized Environment E-filing. (f) Registration of Charges (g) Management and Administration (i) Company Law in a computerized Environment E-filing. Part II ETHICS (20 Marks) - Deleted Covered in other CA papers 1. Introduction to Business Ethics 2. Environment issues 3. Ethics in Workplace 4. Ethics in Marketing and Consumer Protection 5. Ethics in Accounting and Finance Part III- COMMUNICATION (20 Marks) - Deleted Covered in other CA papers 1. Elements of Communication 2. Communication in Business Environment 3. Basic understanding of legal deeds and documents Note 1: The provisions of the Companies Act, 1956 which are still in force would form part of the syllabus till the time their corresponding or new provisions of the Companies Act, 2013 are enforced. Note 2: If new legislations are enacted in place of the existing legislations, the syllabus would include the corresponding provisions of such new legislations with effect from dates notified by the Institute. Similarly if any existing legislation ceases to have effect, the syllabus will accordingly exclude such legislation with effect from the date to be notified by the Institute.
36 Changes made in the Syllabus of CA Intermediate Paper 3: Cost and Management Accounting (proposed) vis-a-vis Paper 3: Cost Accounting (existing). Cost Accounting (50 Marks) Cost and Management Accounting (100 Marks) Changes (Addition/ Deletion) 1. Introduction to Cost Accounting A. Overview of Cost and Management Accounting (a) Objectives and scope of Cost Accounting (a) Introduction to Cost and Management Accounting (b) Cost centres and Cost units (i) Objectives and Scope of Cost and Management (c) Cost classification for stock valuation, Profit Accounting, measurement, Decision making and control (ii) The users of Cost and Management accounting (d) Coding systems information- Functions of management accounting. (e) Elements of Cost (iii) Role of cost accounting department in an (f) Cost behaviour pattern, Separating the organisation and its relation with other departments. components of semi-variable costs (iv) Installation of Costing System (g) Installation of a Costing system (v) Relationship of Cost Accounting, Financial Accounting, Management Accounting and Financial (h) Relationship of Cost Accounting, Financial Management. Accounting, Management Accounting and Financial (vi) Cost terms and Concepts Management. (vii) Cost Reduction and Cost Control (viii) Elements of Costs (ix) Cost behavior pattern, Separating the components of semi-variable costs, step costs. (x) Methods of Costing, Techniques of Costing. (xi) Coding Systems. (b) Elements of Cost and preparation of Cost Sheet (i) Functional classification and ascertainment of cost (ii) Preparation of Cost Sheet Additions: (b)elements of Cost and preparation of Cost Sheet (i) Functional classification and ascertainment of cost (ii) Preparation of Reasons for changes Topics have been elaborated and specified to cover basic cost concepts of cost and management accounting. Understanding of cost sheet is essential for the students to familiarize them with the basic cost concepts.
37 2. Cost Ascertainment (a) Material Cost (i) Procurement procedures Store procedures and documentation in respect of receipts and issue of stock, Stock verification (ii) Inventory control Techniques of fixing of minimum, maximum and reorder levels, Economic Order Quantity, ABC classification; Stocktaking and perpetual inventory (iii) Inventory accounting (iv) Consumption Identification with products of cost centres, Basis for consumption entries in financial accounts, Monitoring consumption. (b) (i) Employee Cost Attendance and payroll procedures, Overview of statutory requirements, Overtime, Idle time and Incentives (ii) Labour turnover (iii) Utilisation of labour, Direct and indirect labour, Charging of labour cost, Identifying labour hours with work orders or batches or capital jobs B. Ascertainment of Cost and Cost Accounting System (a) Material Cost (i) Procurement procedures- Store procedures and documentation in respect of receipts and issue of stock, Stock verification, (ii) Valuation of material receipts, (iii) Inventory control- - Techniques of fixing level of stocks- minimum, maximum, re-order point, safety stock, determination of optimum stock level, - Determination of Optimum Order quantity- Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), - Techniques of Inventory control- ABC Analysis, FSN, HML, VED, Just-in-Time (JIT)- Stock taking and perpetual inventory system, use of control ratios, (iv) Inventory Accounting (v) Consumption- Identification with products of cost centres, Basis for consumption entries in financial accounts, monitoring consumption. (b) Employee Cost (i) Attendance and Payroll procedures- - Elements of wages- Basic wages, Dearness Allowance, Overtime, Bonus, Holiday and leave wages, Allowances and perquisites. (ii) Labour Cost Control (iii) Labour Turnover- Methods of calculating labour turnover, causes of labour turnover, effects of labour turnover. (iv) Utilisation of labour, Direct and indirect labour, charging of labour cost, Identifying labour hours with Cost Sheet Topics have been elaborated and specified to cover specific aspects of Material cost. Topics have been elaborated and specified to cover specific aspects of Employee cost.
38 (iv) Efficiency rating procedures (v) Remuneration systems and incentive schemes. work orders or batches or capital jobs. (v) Remuneration systems and incentive schemes- -Time Rate System, Piece Rate System, Differential piece rate system, Calculation of wages, Effective Wages. (c) Direct Expenses Sub-contracting Control on material movements, Identification with the main product or service. (c) Direct Expenses (i) Direct expenses and Direct Material (ii) Nature of Direct or Chargeable expenses. (iii) Sub-contracting- Control on material movements, Identification with the main product or service. Topics have been elaborated. (d) Overheads (i) Functional analysis Factory, Administration, Selling, Distribution, Research and Development Behavioural analysis Fixed, Variable, Semi variable and Step cost (ii) Factory Overheads Primary distribution and secondary distribution, Criteria for choosing suitable basis for allotment, Capacity cost adjustments, Fixed absorption rates for absorbing overheads to products or services (iii) Administration overheads Method of allocation to cost centres or products (iv) Selling and distribution overheads Analysis and absorption of the expenses in products/customers, impact of marketing strategies, Cost effectiveness of various methods of sales promotion. (d) Overheads (i) Functional analysis- Factory, Administration, Selling, Distribution, Research and Development. (ii) Behavioral analysis- Fixed, Variable, Semi- Variable and Step cost. (iii) Allocation and Apportionment of overheads using Absorption Costing Method. (iv) Factory Overheads- Primary distribution and secondary distribution, (v) Administration Overheads- Method of allocation to cost centres or products, (vi) Selling & Distribution Overheads- Analysis and absorption of the expenses in products/ customers, impact of marketing strategies, cost effectiveness of various methods of sales promotion. (vii) Concepts of Activity Based Costing (ABC). Additions: Concepts of Activity Based Costing (ABC) Basic understanding of Activity Based Costing is essential at this level so that student are well versed with the concept of overhead. 3. Cost Book-keeping Cost Ledgers Non-integrated accounts, (e) Recording and Accounting of Costs (i) Non-integrated Accounting system- Ledger under
SYLLABUS COMMON PROFICIENCY TEST
 SYLLABUS COMMON PROFICIENCY TEST Session I Section A Fundamentals of Accounting 60 Marks Section B Mercantile Law 40 Marks Session II Section C General Economics 50 Marks Section D Quantitative Aptitude
SYLLABUS COMMON PROFICIENCY TEST Session I Section A Fundamentals of Accounting 60 Marks Section B Mercantile Law 40 Marks Session II Section C General Economics 50 Marks Section D Quantitative Aptitude
twitter.com/taxupindia facebook.com/taxupindia taxupindia.com Section wise Weightage for subjects under the Revised Scheme of Education and Training
 Section wise Weightage for subjects under the Revised Scheme of Education and Training Foundation Course Foundation Paper 1: Principles and Practice of Accounting (100 Marks) Sections Weightage Content
Section wise Weightage for subjects under the Revised Scheme of Education and Training Foundation Course Foundation Paper 1: Principles and Practice of Accounting (100 Marks) Sections Weightage Content
Syllabus for Common Entrance Test (2017): M. Com.
 Syllabus for Common Entrance Test (2017): M. Com. A. Subject Related 75 Questions all over the Syllabus: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Financial accounting: concept, need, objectives & scope; accounting principles-
Syllabus for Common Entrance Test (2017): M. Com. A. Subject Related 75 Questions all over the Syllabus: FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING Financial accounting: concept, need, objectives & scope; accounting principles-
Reserve Bank Of India (RBI) Syllabus
 RBI Officer Grade C Syllabus - General Awareness Indian History Indian Culture & Heritage Current Events National & International Indian Polity Indian Constitution Science & Technology Indian Geography
RBI Officer Grade C Syllabus - General Awareness Indian History Indian Culture & Heritage Current Events National & International Indian Polity Indian Constitution Science & Technology Indian Geography
Cost and Management Accounting
 Intermediate Course Study Material (Modules 1 to 2) Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting Module - 1 BOARD OF STUDIES THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA ii This Study Material has been prepared
Intermediate Course Study Material (Modules 1 to 2) Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting Module - 1 BOARD OF STUDIES THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA ii This Study Material has been prepared
COST ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
 STUDY MATERIAL Intermediate (IPC) Course PAPER : 3 COST ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Part 1 : Cost Accounting VOLUME I BOARD OF STUDIES THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA This study
STUDY MATERIAL Intermediate (IPC) Course PAPER : 3 COST ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Part 1 : Cost Accounting VOLUME I BOARD OF STUDIES THE INSTITUTE OF CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS OF INDIA This study
PAPER 1 ACCOUNTING. (One paper Three hours 100 Marks)
 Objectives: PAPER 1 ACCOUNTING (One paper Three hours 100 Marks) To acquire the ability to apply specific accounting standards and legislations to different transactions and events and in preparation and
Objectives: PAPER 1 ACCOUNTING (One paper Three hours 100 Marks) To acquire the ability to apply specific accounting standards and legislations to different transactions and events and in preparation and
STUDY MATERIAL BASED CONTENTS
 STUDY MATERIAL BASED CONTENTS Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus....................................... 3. Examination Trend Analysis........................ 3.7 Line Chart Showing Relative
STUDY MATERIAL BASED CONTENTS Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus....................................... 3. Examination Trend Analysis........................ 3.7 Line Chart Showing Relative
Intermediate Course Paper 1: Accounting (100 Marks)
 Intermediate Course Intermediate Course Paper 1: Accounting (100 Marks) Sections Weightage Content Area I 20%-25% 1. Process of formulation of Accounting Standards including Ind AS (IFRS converged standards)
Intermediate Course Intermediate Course Paper 1: Accounting (100 Marks) Sections Weightage Content Area I 20%-25% 1. Process of formulation of Accounting Standards including Ind AS (IFRS converged standards)
Group 1. Paper 1 Accounting 100 Marks. Paper 2 Corporate Laws and Other Laws 100 Marks. Part I: Corporate Laws (60 Marks)
 Group 1 Paper 1 Accounting 100 Marks Paper 2 Corporate Laws and Other Laws 100 Marks Part I: Corporate Laws (60 Marks) Part II: Other Laws (40 Marks) Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting 100 Marks Paper
Group 1 Paper 1 Accounting 100 Marks Paper 2 Corporate Laws and Other Laws 100 Marks Part I: Corporate Laws (60 Marks) Part II: Other Laws (40 Marks) Paper 3 Cost and Management Accounting 100 Marks Paper
CA INTERMEDIATE SYLLABUS
 CA INTERMEDIATE SYLLABUS In this article we are providing you the CA Intermediate syllabus applicable for the students registered with the revised scheme. Students can register for the CA Intermediate
CA INTERMEDIATE SYLLABUS In this article we are providing you the CA Intermediate syllabus applicable for the students registered with the revised scheme. Students can register for the CA Intermediate
ANUPGCET 2018 :: 113-COMMERCE (SYLLABUS)
 ANUPGCET 2018 :: 113-COMMERCE (SYLLABUS) Max. Marks: 100 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING: Introduction to Accounting Need for Accounting definition, features, objectives, functions, systems and bases and scope of
ANUPGCET 2018 :: 113-COMMERCE (SYLLABUS) Max. Marks: 100 FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING: Introduction to Accounting Need for Accounting definition, features, objectives, functions, systems and bases and scope of
4. Negotiable Instrument Act, The Consumer Protection Act, Foreign Exchange Management Act, 2000
 REVISED SYLLLABUS FYBAF SEM. II BUSINESS LAW PAPER -1: Business Regulatory Framework Topics for Study 1. Law of contract 1872 2. Special Contracts 3. Sales of Goods Act 1930 4. Negotiable Instrument Act
REVISED SYLLLABUS FYBAF SEM. II BUSINESS LAW PAPER -1: Business Regulatory Framework Topics for Study 1. Law of contract 1872 2. Special Contracts 3. Sales of Goods Act 1930 4. Negotiable Instrument Act
Chapter 6 Simple Correlation and
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics Meaning of Statistics... 1 Definition of Statistics... 2 Importance and Scope of Statistics... 2 Application of Statistics... 3 Characteristics of Statistics...
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction to Statistics Meaning of Statistics... 1 Definition of Statistics... 2 Importance and Scope of Statistics... 2 Application of Statistics... 3 Characteristics of Statistics...
SENIOR SCHOOL CURRICULUM
 SENIOR SCHOOL CURRICULUM 2017-18 ACCOUNTANCY & TAXATION Introduction The course is designed to enable students to develop conceptual, skill and application skill in the commerce related field. The course
SENIOR SCHOOL CURRICULUM 2017-18 ACCOUNTANCY & TAXATION Introduction The course is designed to enable students to develop conceptual, skill and application skill in the commerce related field. The course
MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION
 ZIMBABWE MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS FORMS 5-6 2015 2022 Curriculum Development Unit P.O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant Harare All rights reserved 2015 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The
ZIMBABWE MINISTRY OF PRIMARY AND SECONDARY EDUCATION ACCOUNTING SYLLABUS FORMS 5-6 2015 2022 Curriculum Development Unit P.O. Box MP 133 Mount Pleasant Harare All rights reserved 2015 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The
Semester I (June October)
 BAF Course Syllabus: Semester I (June October) Financial Accounting Paper I Introduction to Accounting Accounting Procedure Capital & Revenue Reconciliation & Rectification Depreciation provisions & Reserve
BAF Course Syllabus: Semester I (June October) Financial Accounting Paper I Introduction to Accounting Accounting Procedure Capital & Revenue Reconciliation & Rectification Depreciation provisions & Reserve
INTERMEDIATE COURSE. ICWAI Syllabus GROUP -I. Paper 5 : Financial Accounting (One Paper: 3 hours:100 marks)
 INTERMEDIATE COURSE GROUP -I Paper 5 : Financial Accounting (One Paper: 3 hours:100 marks) Objectives To have working knowledge of accounting concepts, detailed procedures and documentation involved in
INTERMEDIATE COURSE GROUP -I Paper 5 : Financial Accounting (One Paper: 3 hours:100 marks) Objectives To have working knowledge of accounting concepts, detailed procedures and documentation involved in
AM Syllabus ( ): Accounting AM SYLLABUS ( ) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS
 AM SYLLABUS (2008-2013) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM 01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus builds on the topics set for the SEC
AM SYLLABUS (2008-2013) ACCOUNTING AM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting AM 01 Syllabus (Available in September) Paper I (3 hrs) + Paper II (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus builds on the topics set for the SEC
LESSON PLAN ( ) Ist Semester B.Com.(Hons & Gen)
 LEON PLAN (207-8) Ist Semester B.Com.(Hons & Gen) GE. Chg Microeconomics I & Statistics (50+50) Module I: Microeconomics I UNIT TOPIC TEACHER Demand and Consumer Behaviour (5 marks) Concept of Demand,
LEON PLAN (207-8) Ist Semester B.Com.(Hons & Gen) GE. Chg Microeconomics I & Statistics (50+50) Module I: Microeconomics I UNIT TOPIC TEACHER Demand and Consumer Behaviour (5 marks) Concept of Demand,
Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019
 Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
Management Accounting (MA)/FMA September 2018 to August 2019 Guide to structure of the syllabus and Study guide This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended
BUSINESS LAWS, ETHICS AND COMMUNICATION
 INTERMEDIATE (IPC) COURSE STUDY MATERIAL MODULES 1 4 PAPER : 2 BUSINESS LAWS, ETHICS AND COMMUNICATION [Relevant for May, 2015 Examination and onwards] Module 1 Chapter 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872
INTERMEDIATE (IPC) COURSE STUDY MATERIAL MODULES 1 4 PAPER : 2 BUSINESS LAWS, ETHICS AND COMMUNICATION [Relevant for May, 2015 Examination and onwards] Module 1 Chapter 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872
(F2/FMA) December 2011
 Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016)
 Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016) This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide
Management Accounting (F2/FMA) September 2015 to August 2016 (for CBE exams up to 22 September 2016) This syllabus and study guide are designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide
(F2/FMA) December 2011
 Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
Manage ment Accounting (F2/FMA) December 2011 This syllabus and study guide is designed to help with teaching and learning and is intended to provide detailed information on what could be assessed in any
ACCOUNTS (858) CLASS XI
 ACCOUNTS (858) Aims: 1. To provide an understanding of the principles of accounts and practice in recording transactions and interpreting individual as well as company accounts. 2. To develop an understanding
ACCOUNTS (858) Aims: 1. To provide an understanding of the principles of accounts and practice in recording transactions and interpreting individual as well as company accounts. 2. To develop an understanding
Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII ( )
 Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII (2017-18) One Paper Theory: 80 Marks 3 Hours Units Periods Marks Part A Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies Unit 1. Accounting for Partnership Firms 90 35
Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII (2017-18) One Paper Theory: 80 Marks 3 Hours Units Periods Marks Part A Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies Unit 1. Accounting for Partnership Firms 90 35
Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII ( )
 Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII (2015-16) One Paper Theory: 80 Marks 3 Hours Units Periods Marks Part A Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies Unit 1. Accounting for Partnership Firms 90 35
Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII (2015-16) One Paper Theory: 80 Marks 3 Hours Units Periods Marks Part A Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies Unit 1. Accounting for Partnership Firms 90 35
Financial Accounting and Auditing Paper-V: Financial Accounting
 Allocation of the Syllabus and Question Paper Pattern of Courses of B.Com. Programme at T.Y.B.Com. Semester V with Effect from the Academic Year 2013-2014 Financial Accounting and Auditing Paper-V: Financial
Allocation of the Syllabus and Question Paper Pattern of Courses of B.Com. Programme at T.Y.B.Com. Semester V with Effect from the Academic Year 2013-2014 Financial Accounting and Auditing Paper-V: Financial
UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI
 Enclosure to Item No. 4.63 A.C. 25/05/2011 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the F.Y.B.Com. Program : B.Com Course : Mathematical & Statistical Techniques (Credit Based Semester and Grading System with
Enclosure to Item No. 4.63 A.C. 25/05/2011 UNIVERSITY OF MUMBAI Syllabus for the F.Y.B.Com. Program : B.Com Course : Mathematical & Statistical Techniques (Credit Based Semester and Grading System with
StudyCBSENotes.com 1
 StudyCBSENotes.com 1 StudyCBSENotes.com 2 Past adjustments (relating to interest on capital, interest on drawing, salary and profit sharing ratio). Goodwill: nature, factors affecting and methods of valuation
StudyCBSENotes.com 1 StudyCBSENotes.com 2 Past adjustments (relating to interest on capital, interest on drawing, salary and profit sharing ratio). Goodwill: nature, factors affecting and methods of valuation
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU
 UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU NET SYLLABUS Subject: Commerce Code No. : 08 Unit 1: Business Environment and International Business Unit 2: Accounting and Auditing Unit 3: Business Economics Unit
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU NET SYLLABUS Subject: Commerce Code No. : 08 Unit 1: Business Environment and International Business Unit 2: Accounting and Auditing Unit 3: Business Economics Unit
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU
 UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU NET SYLLABUS Subject: Commerce Code No. : 08 Unit 1: Business Environment and International Business Unit 2: Accounting and Auditing Unit 3: Business Economics Unit
UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION NET BUREAU NET SYLLABUS Subject: Commerce Code No. : 08 Unit 1: Business Environment and International Business Unit 2: Accounting and Auditing Unit 3: Business Economics Unit
32.S [F] SU 02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1
![32.S [F] SU 02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1 32.S [F] SU 02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1](/thumbs/87/96342483.jpg) 32.S [F] SU 02 June 2014 2015 All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1 32.S [F] SU 02 June 2014 2015 All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 2 32.S
32.S [F] SU 02 June 2014 2015 All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 1 32.S [F] SU 02 June 2014 2015 All Syllabus Science Faculty B.A. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] 2 32.S
34.S-[F] SU-02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.Sc. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] - 1 -
![34.S-[F] SU-02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.Sc. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] - 1 - 34.S-[F] SU-02 June All Syllabus Science Faculty B.Sc. I Yr. Stat. [Opt.] [Sem.I & II] - 1 -](/thumbs/87/96342487.jpg) [Sem.I & II] - 1 - [Sem.I & II] - 2 - [Sem.I & II] - 3 - Syllabus of B.Sc. First Year Statistics [Optional ] Sem. I & II effect for the academic year 2014 2015 [Sem.I & II] - 4 - SYLLABUS OF F.Y.B.Sc.
[Sem.I & II] - 1 - [Sem.I & II] - 2 - [Sem.I & II] - 3 - Syllabus of B.Sc. First Year Statistics [Optional ] Sem. I & II effect for the academic year 2014 2015 [Sem.I & II] - 4 - SYLLABUS OF F.Y.B.Sc.
CA IPCC (New) SUPERIOR
 Accounts 1) Introduction to Accounting Standards 2) Framework for Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statement 3) Accounting Standards ( 1,2,3,4,5,10) 4) Accounting Standards (11,12,13,16,17,22)
Accounts 1) Introduction to Accounting Standards 2) Framework for Preparation and Presentation of Financial Statement 3) Accounting Standards ( 1,2,3,4,5,10) 4) Accounting Standards (11,12,13,16,17,22)
Depository Act Depository process, De-mat, NSDL,SHCIL, Need for investor education
 COMMERCE UNIT I ACCOUNTING: UNIT II Financial Accounting: Accounting concepts and conventions, Preparation of Final Accounts (Sole trading concern and Partnership) with adjusting entries. Corporate Accounting:
COMMERCE UNIT I ACCOUNTING: UNIT II Financial Accounting: Accounting concepts and conventions, Preparation of Final Accounts (Sole trading concern and Partnership) with adjusting entries. Corporate Accounting:
GUJARAT STATE LEVEL ELIGIBILITY TEST
 GUJARAT STATE LEVEL ELIGIBILITY TEST Code No. : 17 Subject : COMMERCE SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS Note : There will be two question papers, Paper II and Paper III. Paper II will cover 50 Objective Type
GUJARAT STATE LEVEL ELIGIBILITY TEST Code No. : 17 Subject : COMMERCE SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS Note : There will be two question papers, Paper II and Paper III. Paper II will cover 50 Objective Type
Department of Economics, IUST-Awantipora Syllabus for Ph. D Entrance Test (ECONOMICS)
 Department of Economics, IUST-Awantipora Syllabus for Ph. D Entrance Test (ECONOMICS) Part-I: Core Economics Module I: Micro Economic Analysis Module II: Macro Economics Module III: Money, Banking and
Department of Economics, IUST-Awantipora Syllabus for Ph. D Entrance Test (ECONOMICS) Part-I: Core Economics Module I: Micro Economic Analysis Module II: Macro Economics Module III: Money, Banking and
Strictly Based on the Latest Syllabus issued by CBSE Board for 2015 Examination QUESTION BANK. Chapter-Wise Solutions. Accountancy
 Strictly Based on the Latest Syllabus issued by CBSE Board for 2015 Examination QUESTION BANK Chapter-Wise Solutions Accountancy Includes Compartment (Solved) Paper - 2014 Published by : OSWAAL BOOKS Oswaal
Strictly Based on the Latest Syllabus issued by CBSE Board for 2015 Examination QUESTION BANK Chapter-Wise Solutions Accountancy Includes Compartment (Solved) Paper - 2014 Published by : OSWAAL BOOKS Oswaal
RELATIONAL DIAGRAM OF MAIN CAPABILITIES
 Syllabus MAIN CAPABILITIES APM (P5) On successful completion of this paper, candidates should be able to: A Explain the nature and purpose of cost and management accounting PM (F5) FM (F9) B Describe costs
Syllabus MAIN CAPABILITIES APM (P5) On successful completion of this paper, candidates should be able to: A Explain the nature and purpose of cost and management accounting PM (F5) FM (F9) B Describe costs
Dip. in Accountancy & Tally (Comm. Coll.) Page 1 of 6 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTANCY & TALLY
 Dip. in Accountancy & Tally (Comm. Coll.) 2012-13 Page 1 of 6 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTANCY & TALLY PAPER NO TITLE OF THE PAPER MARKS I. Principle of Accountancy 100 II. Advanced Accountancy 100 III. Communicative
Dip. in Accountancy & Tally (Comm. Coll.) 2012-13 Page 1 of 6 DIPLOMA IN ACCOUNTANCY & TALLY PAPER NO TITLE OF THE PAPER MARKS I. Principle of Accountancy 100 II. Advanced Accountancy 100 III. Communicative
I B.Com PA [ ] Semester II Core: Management Accounting - 218A Multiple Choice Questions.
![I B.Com PA [ ] Semester II Core: Management Accounting - 218A Multiple Choice Questions. I B.Com PA [ ] Semester II Core: Management Accounting - 218A Multiple Choice Questions.](/thumbs/80/82536614.jpg) 1 of 23 1/27/2018, 11:53 AM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
1 of 23 1/27/2018, 11:53 AM Dr.G.R.Damodaran College of Science (Autonomous, affiliated to the Bharathiar University, recognized by the UGC)Reaccredited at the 'A' Grade Level by the NAAC and ISO 9001:2008
MODULAR SYLLABUS: B.COM (HONS & GEN)
 MODULAR SYLLABUS: 2016-17 B.COM ( & ) 1 ST NAME/ PAPER FA/1.2c g MODULE UNIT TOPIC TEACHER MONTH I 1 Introduction-Nature of accounting-double entry book keeping system-bases of accounting-basic concepts
MODULAR SYLLABUS: 2016-17 B.COM ( & ) 1 ST NAME/ PAPER FA/1.2c g MODULE UNIT TOPIC TEACHER MONTH I 1 Introduction-Nature of accounting-double entry book keeping system-bases of accounting-basic concepts
COURSES OF STUDY FOR B.
 PATNA UNIVERSITY COURSES OF STUDY FOR B. Com. Examination (2015-18) Three Year Degree Course Part III 1 PATNA UNIVERSITY COURSES OF STUDY For 2015-2018 (Three Year Degree Course) B. Com. (Honours) Course
PATNA UNIVERSITY COURSES OF STUDY FOR B. Com. Examination (2015-18) Three Year Degree Course Part III 1 PATNA UNIVERSITY COURSES OF STUDY For 2015-2018 (Three Year Degree Course) B. Com. (Honours) Course
LESSON PLAN ( ) Part-III: B.Com.(Hons)
 Paper 3.1 HA MODULE-I FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING III LEON PLAN (2017-18) Part-III: B.Com.(Hons) Full Marks : 50 Total Lectures : 60 1 Investment Accounts - Maintenance of Investment Ledger; Preparation of Investment
Paper 3.1 HA MODULE-I FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING III LEON PLAN (2017-18) Part-III: B.Com.(Hons) Full Marks : 50 Total Lectures : 60 1 Investment Accounts - Maintenance of Investment Ledger; Preparation of Investment
Open University of Mauritius. M.Sc. Financial Management and Taxation -OUpm002
 Open University of Mauritius 1. M.Sc. Financial Management and Taxation -OUpm002 This course is an excellent preparation for a financial career in a diverse range of business organisations. Designed for
Open University of Mauritius 1. M.Sc. Financial Management and Taxation -OUpm002 This course is an excellent preparation for a financial career in a diverse range of business organisations. Designed for
B.A. SOCIAL SCIENCE - ECONOMICS. Semester - I. Title of The Paper - MICRO ECONOMICS
 B.A. SOCIAL SCIENCE - ECONOMICS Semester - I Title of The Paper - MICRO ECONOMICS Unit-I Definition, Evolution, Scope & Nature of Economics, Methods of Economic Analysis Inductive & Deductive Methods.
B.A. SOCIAL SCIENCE - ECONOMICS Semester - I Title of The Paper - MICRO ECONOMICS Unit-I Definition, Evolution, Scope & Nature of Economics, Methods of Economic Analysis Inductive & Deductive Methods.
Contents. An Overview of Statistical Applications CHAPTER 1. Contents (ix) Preface... (vii)
 Contents (ix) Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Statistical Applications 1.1 Introduction... 1 1. Probability Functions and Statistics... 1..1 Discrete versus Continuous Functions... 1..
Contents (ix) Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 An Overview of Statistical Applications 1.1 Introduction... 1 1. Probability Functions and Statistics... 1..1 Discrete versus Continuous Functions... 1..
Cost and Management Accounting
 Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus... Q&A-2.2 Bird's-Eye View... Q&A-2.5 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance Chapters... Q&A-2.7 Table Showing Importance of Chapter on the Basis of Marks...
Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus... Q&A-2.2 Bird's-Eye View... Q&A-2.5 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance Chapters... Q&A-2.7 Table Showing Importance of Chapter on the Basis of Marks...
Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting
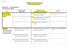 Suggested Revised BAFS Curriculum Draft as at 30 January 2013 Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting Topic Books of Original Entry and Types of Ledgers Explanatory Notes (original
Suggested Revised BAFS Curriculum Draft as at 30 January 2013 Elective Part -- Accounting Module 2(a) Financial Accounting Topic Books of Original Entry and Types of Ledgers Explanatory Notes (original
Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII ( ) Units Periods Marks
 One Paper Theory: 80 Marks 3 Hours Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII (2015-16) Units Periods Marks Part A Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies Unit 1. Accounting for Partnership Firms 90 35
One Paper Theory: 80 Marks 3 Hours Accountancy (Code No. 055) Class-XII (2015-16) Units Periods Marks Part A Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies Unit 1. Accounting for Partnership Firms 90 35
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Introduction course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: What, when and why? Lesson
Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Introduction course orientation Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2: What, when and why? Lesson
Maharashtra State Eligibility Test for Lectureship SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS. Conducted by University of Pune
 Maharashtra State Eligibility Test for Lectureship _hmamï > amá` ì`m»`mvmnxmgmr>r amá`ñvar` nmìvm MmMUr (goq>) narjm Conducted by University of Pune (AS THE STATE AGENCY) SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS
Maharashtra State Eligibility Test for Lectureship _hmamï > amá` ì`m»`mvmnxmgmr>r amá`ñvar` nmìvm MmMUr (goq>) narjm Conducted by University of Pune (AS THE STATE AGENCY) SYLLABUS AND SAMPLE QUESTIONS
Resonance Eduventures Ltd. Commerce & Law Program Division Academic Session: ALL INDIA Test Series for CA-IPCC Nov-2017
 Commerce & Program Division Academic Session: 2017-18 ALL INDIA Test Series for CA-IPCC Nov-2017 Resonance Test Series provide students an innovative test preparation framework to prepare for CA-IPCC examination
Commerce & Program Division Academic Session: 2017-18 ALL INDIA Test Series for CA-IPCC Nov-2017 Resonance Test Series provide students an innovative test preparation framework to prepare for CA-IPCC examination
B.Com II Cost Accounting
 B.Com II Cost Accounting Chapter - 1 Cost Accounting: An Overview of Fundamental Aspects 2009 (1) Discuss the objectives of Cost Accounting. 2011 (1) Discuss importance of cost accounting. 2012 (1) What
B.Com II Cost Accounting Chapter - 1 Cost Accounting: An Overview of Fundamental Aspects 2009 (1) Discuss the objectives of Cost Accounting. 2011 (1) Discuss importance of cost accounting. 2012 (1) What
Cost and Management Accounting
 Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus......................................... 2.2 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance of Chapters...... 2.6 Table Showing Importance of Chapter on the Basis
Paper 2 Cost and Management Accounting Syllabus......................................... 2.2 Line Chart Showing Relative Importance of Chapters...... 2.6 Table Showing Importance of Chapter on the Basis
Management Accounting
 Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. Duration 10 weeks ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Course orientation Start of course survey Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2:
Management Accounting Course map This document outlines the course structure. Duration 10 weeks ACCA: FMA-F2.x Management Accounting Course orientation Start of course survey Lesson 1: Welcome Lesson 2:
Bachelor of Science in Accounting
 Bachelor of Science in Accounting 2018 DANESHPAJOOHAN PISHRO HIGHER EDUCATION INSTITUTE COURSE CHART SYLLABUS SEMESTER CHART Accounting Undergraduate Chart General s 61-11-004 Islamic Thoughts-I 2 2 0
Bachelor of Science in Accounting 2018 DANESHPAJOOHAN PISHRO HIGHER EDUCATION INSTITUTE COURSE CHART SYLLABUS SEMESTER CHART Accounting Undergraduate Chart General s 61-11-004 Islamic Thoughts-I 2 2 0
Contents Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework Population, Sample, and Observations Variables Quali
 Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework... 3 1.1 Population, Sample, and Observations... 3 1.2 Variables.... 4 1.2.1 Qualitative and Quantitative Variables.... 5 1.2.2 Discrete and Continuous
Part I Descriptive Statistics 1 Introduction and Framework... 3 1.1 Population, Sample, and Observations... 3 1.2 Variables.... 4 1.2.1 Qualitative and Quantitative Variables.... 5 1.2.2 Discrete and Continuous
SYLLABUS ACCOUNTANCY (055) CLASS XII ( )
 SYLLABUS ACCOUNTANCY (055) Annexure J learncbse.in CLASS XII (2012-13) One Paper 3 Hours 80 Marks Unit Periods Marks Part A : Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies 1. Accounting for Partnership
SYLLABUS ACCOUNTANCY (055) Annexure J learncbse.in CLASS XII (2012-13) One Paper 3 Hours 80 Marks Unit Periods Marks Part A : Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies 1. Accounting for Partnership
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DELHI REGION SPLIT UP SYLLABUS Class--xi Subject --Economics
 S. No Month Expected No.of working Days Branch of Subject KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DELHI REGION SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2016-17 Class--xi Subject --Economics Chapter No & Chapter Detailed Split-up Periods
S. No Month Expected No.of working Days Branch of Subject KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN DELHI REGION SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2016-17 Class--xi Subject --Economics Chapter No & Chapter Detailed Split-up Periods
IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS
 IM Syllabus (2020): Accounting IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial
IM Syllabus (2020): Accounting IM SYLLABUS (2020) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial
SYLLABUS ACCOUNTANCY (055) CLASS XII (March-2014) Period Marks
 Annexure 'J' SYLLABUS ACCOUNTANCY (055) CLASS XII (March-2014) 3 Hours One Paper Unit 80 Marks +20 Marks Period Marks Part A: Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies 1. Accounting for Partnership
Annexure 'J' SYLLABUS ACCOUNTANCY (055) CLASS XII (March-2014) 3 Hours One Paper Unit 80 Marks +20 Marks Period Marks Part A: Accounting for Partnership Firms and Companies 1. Accounting for Partnership
ECONOMICS B.A. part 1 M.M.100 Paper I MICRO ECONOMICS Unit I 1.Consumer s Behaviour : The Neo Classical Marginal Utility approach and a study of
 ECONOMICS B.A. part 1 M.M.100 Paper I MICRO ECONOMICS 1.Consumer s Behaviour : The Neo Classical Marginal Utility approach and a study of consumer s equilibrium and derivation of law of demand. The Indifference
ECONOMICS B.A. part 1 M.M.100 Paper I MICRO ECONOMICS 1.Consumer s Behaviour : The Neo Classical Marginal Utility approach and a study of consumer s equilibrium and derivation of law of demand. The Indifference
Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011
 www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011 Note for Exams Officers: Before making Final Entries, please check
www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus Cambridge International A & AS Level Accounting Syllabus code 9706 For examination in June and November 2011 Note for Exams Officers: Before making Final Entries, please check
COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND SOCIAL SCIENCES
 COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND SOCIAL SCIENCES 1. DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES (a) Curriculum for B.Sc. Degree in Accounting 100 Level Harmattan Semester Course Code Course Title Pre-requisite
COLLEGE OF MANAGEMENT AND SOCIAL SCIENCES 1. DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT SCIENCES (a) Curriculum for B.Sc. Degree in Accounting 100 Level Harmattan Semester Course Code Course Title Pre-requisite
SUGGESTED SOLUTIONS. KE2 Management Accounting Information. March All Rights Reserved
 SUGGESTED SOLUTIONS KE2 Management Accounting Information March 2017 All Rights Reserved Answer 01 SECTION 01 1.1 Relevant Learning outcome : 1.1.2 Explain the nature, scope and purpose of cost classifications
SUGGESTED SOLUTIONS KE2 Management Accounting Information March 2017 All Rights Reserved Answer 01 SECTION 01 1.1 Relevant Learning outcome : 1.1.2 Explain the nature, scope and purpose of cost classifications
Content Added to the Updated IAA Education Syllabus
 IAA EDUCATION COMMITTEE Content Added to the Updated IAA Education Syllabus Prepared by the Syllabus Review Taskforce Paul King 8 July 2015 This proposed updated Education Syllabus has been drafted by
IAA EDUCATION COMMITTEE Content Added to the Updated IAA Education Syllabus Prepared by the Syllabus Review Taskforce Paul King 8 July 2015 This proposed updated Education Syllabus has been drafted by
SYLLABUS PAPERS & CONTENTS
 SYLLABUS - 2016 PAPERS & Syllabus 2016 Foundation Course: Paper 1 Paper 2 Paper 3 Paper 4 Fundamentals of Economics and Management Fundamentals of Accounting Fundamentals of Laws and Ethics Fundamentals
SYLLABUS - 2016 PAPERS & Syllabus 2016 Foundation Course: Paper 1 Paper 2 Paper 3 Paper 4 Fundamentals of Economics and Management Fundamentals of Accounting Fundamentals of Laws and Ethics Fundamentals
International Certificate in Wealth and Investment Management
 International Certificate in Wealth and Investment Management Effective from 21 May 2017 Chartered Institute for Securities & Investment Objective of the examination The objective of the examination is
International Certificate in Wealth and Investment Management Effective from 21 May 2017 Chartered Institute for Securities & Investment Objective of the examination The objective of the examination is
SCHOOL OF DISTANCE EDUCATION :: ANDHRA UNIVERSITY 3-YEAR MBA I YEAR ASSIGNMENTS FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR MANAGEMENT PROCESS AND BEHAVIOUR
 MANAGEMENT PROCESS AND BEHAVIOUR 1. a) Differences between leaders and managers b) Corporate Governance 2. a) Planning Premises b) Decision Tree Analysis 3. a) Theory X, Theory Y and Theory Z b) Leadership
MANAGEMENT PROCESS AND BEHAVIOUR 1. a) Differences between leaders and managers b) Corporate Governance 2. a) Planning Premises b) Decision Tree Analysis 3. a) Theory X, Theory Y and Theory Z b) Leadership
BPC6C Cost and Management Accounting. Unit : I to V
 BPC6C Cost and Management Accounting Unit : I to V UNIT -1 FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING Nature and scope of Cost Accounting, Distinction between cost and financial accounting, Cost sheet, tenders Characteristics
BPC6C Cost and Management Accounting Unit : I to V UNIT -1 FUNDAMENTALS OF COST ACCOUNTING Nature and scope of Cost Accounting, Distinction between cost and financial accounting, Cost sheet, tenders Characteristics
PAPER C01 Fundamentals of Management Accounting Acorn chapters
 PAPER C01 Fundamentals of Management Accounting Acorn chapters 1 Classification of costs 2 The context of management accounting 3 Absorbing fixed production overhead 4 Absorption and marginal costing 5
PAPER C01 Fundamentals of Management Accounting Acorn chapters 1 Classification of costs 2 The context of management accounting 3 Absorbing fixed production overhead 4 Absorption and marginal costing 5
PART I BUSINESS LAWS & COMPANY LAW
 Contents About the author I-5 Preface to fourth edition I-7 Syllabus I-19 CA - Intermediate (IPC) Nov. 2015 Examinations I-23 CA - Intermediate (IPC) May 2015 Examinations I-27 CA - Intermediate (IPC)
Contents About the author I-5 Preface to fourth edition I-7 Syllabus I-19 CA - Intermediate (IPC) Nov. 2015 Examinations I-23 CA - Intermediate (IPC) May 2015 Examinations I-27 CA - Intermediate (IPC)
UPDATED IAA EDUCATION SYLLABUS
 II. UPDATED IAA EDUCATION SYLLABUS A. Supporting Learning Areas 1. STATISTICS Aim: To enable students to apply core statistical techniques to actuarial applications in insurance, pensions and emerging
II. UPDATED IAA EDUCATION SYLLABUS A. Supporting Learning Areas 1. STATISTICS Aim: To enable students to apply core statistical techniques to actuarial applications in insurance, pensions and emerging
Syllabus for foundation course I at the F.Y.B.Com course
 Syllabus for foundation course I at the F.Y.B.Com course Foundation course I Syllabus II nd term C. Globalization and Indian Society: Emerging Issues 1. Concepts of liberalization, Privatization and globalization;
Syllabus for foundation course I at the F.Y.B.Com course Foundation course I Syllabus II nd term C. Globalization and Indian Society: Emerging Issues 1. Concepts of liberalization, Privatization and globalization;
Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100. Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 7 PART A
 : 1 : Roll No... Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 7 PART A (Answer Question No.1 which is compulsory and any two of the rest from
: 1 : Roll No... Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Total number of questions : 8 Total number of printed pages : 7 PART A (Answer Question No.1 which is compulsory and any two of the rest from
Syllabus. General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level ACCOUNTING 9706
 General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus ACCOUNTING 9706 For examination in June and November 2009 CIE provides syllabuses,
General Certificate of Education (International) Advanced Level and Advanced Subsidiary Level www.xtremepapers.com Syllabus ACCOUNTING 9706 For examination in June and November 2009 CIE provides syllabuses,
PG Diploma in Industrial and Company Law Non- Semester (With Effect from the Academic Year )
 PG Diploma in Industrial and Company Law Non- Semester (With Effect from the Academic Year 2013-14) Eligibility for the course : A Pass in any Undergraduate degree Duration of the course : 1 Year Examination:
PG Diploma in Industrial and Company Law Non- Semester (With Effect from the Academic Year 2013-14) Eligibility for the course : A Pass in any Undergraduate degree Duration of the course : 1 Year Examination:
IM SYLLABUS (2018) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS
 IM SYLLABUS (2018) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial literacy, and the presentation
IM SYLLABUS (2018) ACCOUNTING IM 01 SYLLABUS 1 Accounting IM01 Syllabus (Available in September) 1 Paper (3 hrs) Introduction The syllabus seeks to develop sound financial literacy, and the presentation
ENGAGEMENTS TO REVIEW FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Effective for reviews of financial statements for periods beginning on or after April 1, 2010)
 SRE 2400* ENGAGEMENTS TO REVIEW FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Effective for reviews of financial statements for periods beginning on or after April 1, 2010) Contents Paragraph(s) Introduction...1-2 Objective of
SRE 2400* ENGAGEMENTS TO REVIEW FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Effective for reviews of financial statements for periods beginning on or after April 1, 2010) Contents Paragraph(s) Introduction...1-2 Objective of
Free of Cost ISBN : Appendix. CMA (CWA) Inter Gr. II (Solution upto Dec & Questions of June 2013 included)
 Free of Cost ISBN : 978-93-5034-631-0 Appendix CMA (CWA) Inter Gr. II (Solution upto Dec. 2012 & Questions of June 2013 included) Paper - 8 : Cost and Management Accounting Chapter - 3 : Labour Accounting
Free of Cost ISBN : 978-93-5034-631-0 Appendix CMA (CWA) Inter Gr. II (Solution upto Dec. 2012 & Questions of June 2013 included) Paper - 8 : Cost and Management Accounting Chapter - 3 : Labour Accounting
SYLLABUS (CPA AUSTRALIA)
 SYLLABUS (CPA AUSTRALIA) PAPER - 1: CORPORATE AND ALLIED LAWS (One paper - Three hours - 100 marks) Objective: SECTION A : COMPANY LAW (70 MARKS) To be able to analyze and apply various provisions of the
SYLLABUS (CPA AUSTRALIA) PAPER - 1: CORPORATE AND ALLIED LAWS (One paper - Three hours - 100 marks) Objective: SECTION A : COMPANY LAW (70 MARKS) To be able to analyze and apply various provisions of the
CFA Level I - LOS Changes
 CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2018-2019 Topic LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) LOS Level I - 2019 (525 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics Ethics 1.1.b 1.1.c describe the role
CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2018-2019 Topic LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) LOS Level I - 2019 (525 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics Ethics 1.1.b 1.1.c describe the role
About the author I-5 Acknowledgement I-7 Preface I-9 Chapter-heads I-11
 CONTENTS About the author I-5 Acknowledgement I-7 Preface I-9 Chapter-heads I-11 1 INTRODUCTION u Cost 1 u Costing 2 u Cost accounting 2 u Cost accountancy 2 u Classification of costs 3 u Distinction between
CONTENTS About the author I-5 Acknowledgement I-7 Preface I-9 Chapter-heads I-11 1 INTRODUCTION u Cost 1 u Costing 2 u Cost accounting 2 u Cost accountancy 2 u Classification of costs 3 u Distinction between
OFFICE OF THE CONTROLLER GENERAL OF ACCOUNTS ISLAMABAD PIPFA SYLLABUS FOR CGA DEPARTMENT
 OFFICE OF THE CONTROLLER GENERAL OF ACCOUNTS ISLAMABAD PIPFA SYLLABUS FOR CGA DEPARTMENT Table of Contents Level -1... 2 1. Quantitative Methods... 3 2. Basic Accounting... 6 3. Business English and Behavioral
OFFICE OF THE CONTROLLER GENERAL OF ACCOUNTS ISLAMABAD PIPFA SYLLABUS FOR CGA DEPARTMENT Table of Contents Level -1... 2 1. Quantitative Methods... 3 2. Basic Accounting... 6 3. Business English and Behavioral
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS 2013-AL-P ACCT ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding
CS Executive Programme Module - I December Paper - 2 : Cost and Management Accounting
 ISBN : 978-93-5034-747-8 Solved Scanner Appendix CS Executive Programme Module - I December - 2013 Paper - 2 : Cost and Management Accounting Chapter - 1 : Introduction to Cost and Management Accounting
ISBN : 978-93-5034-747-8 Solved Scanner Appendix CS Executive Programme Module - I December - 2013 Paper - 2 : Cost and Management Accounting Chapter - 1 : Introduction to Cost and Management Accounting
Faculty of Commerce. Karim City College, Jamshedpur. Syllabus Distribution
 Faculty of Commerce Karim City College, Jamshedpur Syllabus Distribution Teacher Wise Allocation of Topics/Portions for 2016-17 B.Com Honours Part 1 Account Group Subject: Financial Accounting ( Honours
Faculty of Commerce Karim City College, Jamshedpur Syllabus Distribution Teacher Wise Allocation of Topics/Portions for 2016-17 B.Com Honours Part 1 Account Group Subject: Financial Accounting ( Honours
CFA Level I - LOS Changes
 CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2017-2018 Topic LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics 1.1.b describe the role of a code of
CFA Level I - LOS Changes 2017-2018 Topic LOS Level I - 2017 (534 LOS) LOS Level I - 2018 (529 LOS) Compared Ethics 1.1.a explain ethics 1.1.a explain ethics Ethics 1.1.b describe the role of a code of
Certified Cost Controller TM
 Certified Cost Controller TM Email: info@iabfm.org Web: www.iabfm.org Tel: + 852 685 40145/+86 756 2216205 5 Key Business Benefits 1. Control and manage ALL of your organisation s costs 2. Fully understand
Certified Cost Controller TM Email: info@iabfm.org Web: www.iabfm.org Tel: + 852 685 40145/+86 756 2216205 5 Key Business Benefits 1. Control and manage ALL of your organisation s costs 2. Fully understand
PRINCIPLES OF COST ACCOUNTING
 1. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES PRINCIPLES OF COST ACCOUNTING The aims of this examination are to test candidates ability to a) assemble, analyze and ascertain the cost of producing and procuring goods and services;
1. AIMS AND OBJECTIVES PRINCIPLES OF COST ACCOUNTING The aims of this examination are to test candidates ability to a) assemble, analyze and ascertain the cost of producing and procuring goods and services;
LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION
 LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Lesotho General Certificate of Secondary Education Syllabus Accounting 0187 For examination in November 2018 National Curriculum Development Centre in
LESOTHO GENERAL CERTIFICATE OF SECONDARY EDUCATION Lesotho General Certificate of Secondary Education Syllabus Accounting 0187 For examination in November 2018 National Curriculum Development Centre in
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF COMMERCE
 ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF COMMERCE (AUTONOMOUS) LESSON PLAN 207-208 EVEN SEMESTER B.Com - Travel and Tourism C2 5 MC 40 Cost Accounting TEACHING LESSON PLAN- B.Com (Travel and Tourism) 4 th Semester SUBJECT:
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF COMMERCE (AUTONOMOUS) LESSON PLAN 207-208 EVEN SEMESTER B.Com - Travel and Tourism C2 5 MC 40 Cost Accounting TEACHING LESSON PLAN- B.Com (Travel and Tourism) 4 th Semester SUBJECT:
Open University of Mauritius. BSc (Hons) Economics, Finance and Banking [OUbs018]
![Open University of Mauritius. BSc (Hons) Economics, Finance and Banking [OUbs018] Open University of Mauritius. BSc (Hons) Economics, Finance and Banking [OUbs018]](/thumbs/79/79150999.jpg) 1. Aim and rationale Open University of Mauritius BSc (Hons) Economics, Finance and Banking [OUbs018] The is a specifically designed 4-year programme intended for students who have a keen interest in the
1. Aim and rationale Open University of Mauritius BSc (Hons) Economics, Finance and Banking [OUbs018] The is a specifically designed 4-year programme intended for students who have a keen interest in the
December CS Executive Programme Module - I Paper - 2
 December - 2015 CS Executive Programme Module - I Paper - 2 (New Syllabus) Cost and Management Accounting Total number of questions: 100 Maximum marks: 100 Assertion A: 1. In management accounting, firm
December - 2015 CS Executive Programme Module - I Paper - 2 (New Syllabus) Cost and Management Accounting Total number of questions: 100 Maximum marks: 100 Assertion A: 1. In management accounting, firm
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS
 PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding of accounting
PRINCIPLES OF ACCOUNTS ADVANCED LEVEL OBJECTIVES The examination aims to test the candidates abilities to: 1. demonstrate knowledge of accounting procedures and practices and an understanding of accounting
Accounting & Finance for Managers
 Accounting & Finance for Managers SYLLABUS UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING * Introduction to Accounting * Meaning * Evolution of Accounting * Importance of Accounting * Users of financial statements
Accounting & Finance for Managers SYLLABUS UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING * Introduction to Accounting * Meaning * Evolution of Accounting * Importance of Accounting * Users of financial statements
322 Roll No : 1 : Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100
 2/2013/CMA (N/S) Roll No : 1 : Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Total number of questions : 6 Total number of printed pages : 7 NOTE : 1. Answer ALL Questions. 2. All working notes should be
2/2013/CMA (N/S) Roll No : 1 : Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum marks : 100 Total number of questions : 6 Total number of printed pages : 7 NOTE : 1. Answer ALL Questions. 2. All working notes should be
