PAKISTAN MICROFINANCE REVIEW 2014 ANNUAL ASSESSMENT OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY FINANCIAL SERVICES FOR ALL
|
|
|
- Joy Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AKISTAN MICROFINANCE REVIEW 2014 ANNUAL ASSESSMENT OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY FINANCIAL SERVICES FOR ALL
2
3
4 roduced by akistan Microfinance Network Design and Layout by O3 Interfaces
5 akistan Microfinance Review 2014 Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry
6 akistan Microfinance Review 2014 Financial Services for all Editorial Board Mr. Ghalib Nishtar Chairperson Editorial Board resident, Khushhali Bank Limited (KBL) Dr. Saeed Ahmed Director, Agriculture Credit and Microfinance Department, State Bank of akistan (SB) Mr. Blain Stephens COO and Director of Analysis Microfinance Information exchange, Inc. (MIX) Mr. Yasir Ashfaq Group Head, Financial Services Group, akistan overty Alleviation Fund (AF) Mr. Raza Khan Statistics & Results Adviser, Results & Evaluation Team- Economic Growth Group, Department for International Development (UK) Mr. Abrar Mir SEV & Group Executive Banking roducts Group, United Bank Limited (UBL) Mr. Masood Safdar Gill Director rogram, Urban overty Alleviation rogram, National Rural Support rogramme (NRS) i
7 Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry Financial Services for all MR Team Mr. Ali Basharat Author and Managing Editor Mr. Ammar Arshad Co Author and Data Collection Ms. Khadija Ali Co Author and Data Collection ii
8 Financial Services for all Acronyms and Abbreviations akistan Microfinance Review 2014 AC &MFD ADB AMRDO AML BS CAR CIB CDD CGA CNIC C CI CC DFI DFID DF ECA ESM EUR FATF FI FMFB FSS FY G2 GB GD GL GNI Go IAFSF IFAD IFC JIWS KBL KF Agriculture and Microfinance Division Asian Development Bank Al-Mehran Rural Development Organization Anti-Money Laundering Basis oints Capital Adequacy Ratio Credit Information Bureau Customer Due Diligence Consultative Group to Assist the oor Computerized National Identity Card Client rotection rinciples Consumer rice Index Consumer rotection Code Development Financial Institution Department for International Development, UK Depositor s rotection Fund Eastern and Central Europe Environment and Social Management Euro Financial Action Task Force Financial Inclusion rogram The First Microfinance Bank Ltd. Financial Self Sufficiency Financial Year Government to erson Great Britain ound Gross Domestic roduct Gross Loan ortfolio Gross National Income Government of akistan Improving Access to Financial Services Support Fund International Fund for Agricultural Development International Finance Corporation Jinnah Welfare Society Khushhali Bank Ltd. Kashf Foundation iii
9 Acronyms and Abbreviations Financial Services for all KIBOR KMFBL K MCGF MCR MENA MFB MFCG MF-CIB MF MFI MIS MSME MIV MO NADRA NGO NFL NMFB NLs NRD NRS OD OSS 2 AR BA KR MN O AF RISM RS TA ROA ROE RS SB SC SDS SEC STF SME SRSO SRDO SVD Karachi Inter-Bank Offering Rate Kashf Microfinance Bank Ltd. Khyber akhtunkhwa Microfinance Credit Guarantee Facility Minimum Capital Requirement Middle East and North Africa Microfinance Bank Microfinance Consultative Group Microfinance Credit Information Bureau Microfinance roviders Microfinance Institution Management Information System Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Microfinance Investment Vehicle Micro-Options National Database and Registration Authority Non-Governmental Organization National Financial Literacy rogram Network Microfinance Bank Limited Non-erforming Loans National Rural Development rogram National Rural Support rogramme Organization for articipatory Development Operational Self Sufficiency erson to erson ortfolio at Risk akistan Banks Association akistan Rupee akistan Microfinance Network artner Organization akistan overty Alleviation Fund rogramme for Increasing Sustainable Microfinance unjab Rural Support rogram akistan Telecom Authority Return on Assets Return on Equity Rural Support rogramme State Bank of akistan The Smart Campaign SAATH Development Society Securities and Exchange Commission of akistan Social erformance Task Force Small and Medium Enterprise Sindh Rural Support Organization Shadab Rural Development Organization Soon Valley Development rogram Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry iv
10 Financial Services for all TMFB UBL USD USSM VDO WI Tameer Microfinance Bank Ltd United Bank Limited United State Dollar Universal Standards for Social erformance Management Village Development Organization Wholesale rice Index akistan Microfinance Review 2014 v
11 Did you know? akistan Microfinance Industry has a dedicated and robust Credit Information Bureau (MF-CIB) MN VISION Frontiers of Formal Financial Services reach out to all MISSION akistan is ranked among the top 10 countries to have an enabling environment for financial inclusion by the Economist Intelligence Unit s Global Microscope report Support the financial sector, especially retail financial service providers, to enhance their scale, quality, diversity and sustainability in order to achieve inclusive financial services
12 Did you know? akistan has been called the Laboratory of Innovation in Branchless Banking by CGA Core Values Collaboration Innovation Diversity Empowerment Transparency akistan Microfinance industry now has assets over KR 100 billion
13 MACRO-ECONOMY USD Billions of GL ercentage Number of Active Borrowers 6 Months KIBOR Discount Rate Consumer rice Inflation (Avergae) Active borrowers in millions > 3 MILLION active borrowers 3x projected growth Turnaround Time Access to Clearing House Historical and rojected Growth of Active Borrowers Amount in Millions Retails Deposits Confidence of Regulator Availability of Funds for Mid-Sized MFs Microfinance Credit Guarantee Facility 7.87 Yr Yr 2019 Increase in Growth Investor Confidence Draft NBMFI Regulations Mitigate External Interference Mainstreaming Non-Bank MFs olicy & Regulatory Achievements 3.14 Yr Yr Yr Yr Yr Yr Yr Yr 2017
14 CLIENT ROTECTION 100% Appropriate roduct Design & Delivery Channels 100 Mechanism for Complaint Resolution 80% 60% revention of Over-Indebtedness 5.3 Million Depositors in 2014 CAITAL STRUCTURE Debt 33% % Deposits rivacy of Client Data Fair & Respectful Treatment of Clients 40% 20% 0% Responsible ricing Transparency 20 % of indicators that are not met 0 23% Equity % of indicators that are partially met % of indicators that are fully met ACTIVE BORROWERS BY URBAN/RURAL AREAS Rural Urban Center of Excellence Funding 58% female borrowers 42% male borrowers Regulatory framework for NBMFIs Disaster Risk Management
15
16 akistan Microfinance Review 2014 Financial Services for all Highlights Year Active Borrowers (in millions) Gross Loan ortfolio (KR billions) KR 20.2 KR 24.8 KR 33.1 KR 46.6 KR Active Women Borrowers (in millions) Branches Total Staff ,405 1,550 1,460 1,606 1,747 12,005 14,202 14,648 17,456 19,881 Total Assets (KR billions) Deposits (KR billions) Total Debt (KR billions) Total Revenue (KR billions) OSS (percentage) FSS (percentage) AR > 30 (percentage) xi
17 Financial Services for all Contents THE YEAR IN REVIEW INDUSTRY ERFORMANCE Macro-economy and Microfinance Industry 01 olicy and Regulatory Environment 02 Microfinance Industry Initiatives 04 Conclusion 07 Section 2A: Industry erformance 11 Section 2B: Social erformance THE WAY FORWARD ANNEXURES Inclusive Finance and Microfinance Industry 41 Towards Accelerated Growth 42 Adapting Government Credit Schemes 42 Impact Investment 43 Diversifying Funding Sources 43 Capacity Building rogram 44 Micro, Small & Medium Enterprise (MSME) 45 Lending Anti-Money Laundering (AML), Customer 46 Due Diligence (CDD) and Terrorist Financing Agriculture Value Chains 46 erformance indicators of industry 51 erformance indicators of individual MFs 59 Social erformance Indicators of Individual 103 MFs Regional Benchmarks 140 Sources of Data 141 Adjustment to Financial Data 152 Terms and Definitions 155 Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry xii
18
19 Section 1 The Year in Review
20 Financial Services for all Section 1 The Year in Review The year 2014 saw the industry achieve a major milestone by crossing the 3 million active borrowers mark for the first time. Overall, the industry witnessed double digit growth in not only credit but also in savings and insurance. Although the national economy grew at a modest rate, the macroeconomic stability ensured a favorable environment for the players. Despite the persistent energy crisis and security challenges, positive economic indicators like lower inflation, falling interest rates and uptake on private credit led to a positive impact on the sector in terms of growth and sustainability. On the policy and regulatory side, the microfinance banks (MFBs) have been allowed to become members of the national clearing house which will greatly enhance their ability to mobilize their retail deposits. In addition, to facilitate mid-tier players to raise funds from commercial sources, risk coverage under the Microfinance Credit Guarantee Fund (MCGF) was enhanced to 60 percent by the State Bank of akistan (SB). One of key challenge facing the industry has been the lack of a regulatory umbrella for the nonbank microfinance providers (MFs). In this regard, the last year saw the Securities and Exchange Commission of akistan (SEC) sharing a draft of proposed regulations with players for comments. Among other major developments in the sector last year an industry risk register is being developed by the akistan Microfinance Network (MN). In addition, branchless banking continues to witness growth and the Microfinance Credit Information Bureau (MF- CIB) is fully operational with most of the MFs generating enquiries. The M Interest Free Loan Scheme announced in 2013 was formally launched last year through the akistan overty Alleviation Fund (AF), with an aim of reaching out to 1 million clients in the next three years. As part of the responsible finance initiative, client protection assessments were carried out under the SMART campaign. Macro-economy and the Microfinance Industry akistan Microfinance Review 2014 The year 2014 was a better year for akistan s economy as it witnessed lower than expected inflation, reduction in fiscal deficit and improvement in private sector credit. In addition, the overall economy grew by 4.1 percent compared to the 3.7 percent in However, this was less than the target of 4.4 percent for the year Inflation for the year clocked at 8.6 percent - higher than the previous year s 7.4%, but lower than the expected rate of percent. However, despite the lower inflation, the central bank took a cautious approach to monetary policy with the policy rate remaining constant for the better part of the year. The end of the year saw the policy rate cut by 50 bps taking it from 10 percent to 9.5 percent as shown in Exhibit 1.1. This trend which continued in early 2015, would likely result in the lowering of borrowing costs of Microfinance roviders (MFs). Another positive for the year was the uptake in private sector credit growth which registered a double digit growth of 11.4 percent. This increase which was the highest in the last six years came on the back of an increased supply of loanable funds, improvement in business confidence and lower effective cost of borrowing. This augurs well for MFs which are witnessing increased dependence upon commercial borrowing to meet their funding needs. 1
21 The Year in Review Financial Services for all Discount Rate 6 -Months KIBOR Consumer rice Inflation (Average) ercentage Exhibit 1.1: olicy Rate, 6-Month KIBOR and CI olicy and Regulatory Environment akistan s regulatory environment for microfinance continues to be ranked among the best in the world. Microfinance Banks (MFBs) established under the MFI Ordinance 2001 and regulated by the State Bank of akistan (SB) currently account for 70 percent of the asset base of the microfinance industry and have witnessed huge investor interest as evident from the series of acquisitions that have taken place over the last few years. In order to create a level playing field for the industry, non-bank microfinance providers are also being brought under the regulatory umbrella. This would allow non-bank MFs to grow, transform into stronger institutes and attract investments for further expansion. The details of these proposed regulations are discussed in a subsequent section. SB is among the pioneer regulators who rolled out regulations for branchless banking in These regulations spurred a growth in the branchless banking arena. Over eight branchless banking systems are in operation in the country which are providing a wide array of services including savings, Government to erson and erson to erson payments leading to akistan being called the Laboratory for Innovation in Branchless Banking. The key developments on the policy and regulatory environment for the year 2014 are as follow: Clearing House Membership A key challenge faced by the MFBs in mobilizing deposits has been the absence of membership of the national clearing house. Lack of membership of the clearing house meant that MFBs had to rely on commercial banks for clearance of their payments which led to increased turnaround time. This had badly affected the practitioners ability to mobilize retail deposits and forced them to rely on expensive and volatile fixed deposits acquired at above market rates. Clearing house membership has been on the agenda of policy makers for a while and early this year, MFBs have been allowed to become part of the clearing house under a special category by the central bank. This will enable MFBs to reduce the processing time for payments and be able to attract retail deposits in an effective manner. Moreover, it would lead to growth in deposits and reduce reliance of MFBs on expensive fixed deposits resulting in reduction in cost of funds. Non-Bank MF Regulations A key challenge facing the microfinance industry in akistan has been the absence of regulatory and legal cover for the non-bank MFs. Though these organizations are among the pioneers of microfinance in the country they have witnessed their market share shrink over the years. One of the main reasons for Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 2
22 Financial Services for all Section 1 akistan Microfinance Review 2014 this has been lack of regulatory umbrella. Due to this non-bank MFs have found it difficult to attract commercial financing. Moreover, this has resulted in a lack of recourse mechanism for clients and practitioners and the non-bank MFs have remained vulnerable to the risk of external interference. Keeping in view the above, a steering committee was formed in 2012 chaired by Chairman Securities and Exchange Commission of akistan (SEC) that included all key stakeholders of the industry like SB, akistan overty Alleviation Fund (AF), MN and key MFs to extend legal and regulatory cover for the non-bank MFs. Last year a draft of proposed regulations were shared with the players for their feedback. A summary of the main points raised by the players and MN is as follows: It is hoped that SEC shall play a stewardship role post-regulations similar to that of SB in case of MFBs. A liberal interest rate regime for non-bank MFs should be followed that focuses on market instruments of competition and full disclosures as followed by SB. The current and proposed Non-Bank Financial Companies (NBFC) laws do not adequately cater to the microfinance sector as they do not provide for micro-financing as a distinct form of business carried out by NBFCs. Certain conditions and requirements of the NBFC Laws are not realistic when taken in the context of the working microfinance industry in akistan; thus, there is a need for microfinance to be treated as a distinct class of NBFCs and specific regulations applicable upon them are required. With the exception of one non-bank MF, all others are not for profit entities and many of them would like to continue as non-profit under the proposed regulatory framework. Therefore the proposed regulatory framework, in addition to designating NBMFIs as a specific class of NBFCs, should allow for the creation of a further distinction in the NBFC Laws between for profit non-bank MF and not for profit non-bank MFs. Since the proposed regulations cater for the establishment of a consultative group with representatives of the sector to review the regulations and restrictions, limits, requirements, criterion, etc. it has been proposed that the consultative group meet with SEC every six months to bring the regulator and the industry on the same page and to revise the regulations as the industry evolves. It is hoped that regulations will come into effect by the end of 2015 with adequate time being provided for non-bank MFs to conform to their requirements. These regulations will play a role of catalyst for this segment of the microfinance industry to attract both debt and equity capital from the private sector and be recognized as a mainstream part of the financial landscape in akistan. Amendments in Microfinance Credit Guarantee Facility (MCGF) MCGF was launched in 2009 under the auspices of the Financial Inclusion rogram (FI) with the aim of boosting commercial funding to the industry by offering partial risk coverage to lenders. In order for the sector to become sustainable and grow into a viable part of the financial industry, commercial funding is undeniably important. Initially MFBs and later, MFIs and RSs were allowed to utilize the facility to obtain loans from commercial banks and also issue redeemable capital. However, the uptake of the facility among small and mid-sized MFBs was low as many had riskier profiles compared to their larger, more established peers. SB recently revised guidelines regarding the MCGF in order to facilitate and promote lending from commercial financial institutions for small to mid-sized MFs. In this regard, a tiering criterion has been developed and the risk coverage for the lender has been enhanced. Initially under the MCGF, 25 percent first loss guarantee or 40 percent partial guarantee was provided in case of bilateral loans or redeemable capital to the lenders. However, now in the case of bilateral loans to Tier 2 MFs, 60 percent partial guarantee is now being provided. Tier 2 MFs are defined as those entities that have been in business for 3 years instead of 5 years which is a criterion for Tier 1 MFs and have a GL above KR 500 million as compared to KR 3 billion for Tier 1. Among other conditions, the Tier 2 MF needs to have an improving trend in its return on assets (ROA) for the past three years and for last year the ROA needs to be greater than -10 percent. In addition, the ortfolio at Risk (AR) > 30 days also needs to below 10 percent. These amendments will likely lead to enhancement in lending to small and mid-sized MFs which are largely reliant on funding from the national apex and 3
23 The Year in Review Financial Services for all have yet to initiate commercial borrowing relationships. This would allow them to not only enhance but also diversify their funding sources leading to increase in outreach and upscaling of loan sizes. Microfinance Industry Initiatives Risk Register Risk taking is an inherent element of financial services, and like all financial institutions, microfinance providers (MFs) face risks that they must manage effectively to achieve their financial and social objectives. oorly managed risks can lead to losses endangering the safety and soundness of microfinance institutions. Hence, it is imperative for microfinance providers to have a formal risk management structure in place to counter potential threats. As part of MN s long term strategy to achieve sustainable growth in the akistan microfinance sector, the Network is taking constructive steps to promote sound risk management practices among microfinance practitioners. One initiative MN has underway is the development of a comprehensive risk register for the microfinance sector in akistan. A risk register is a tool widely used by organizations for the identification and assessment of risks. The tool is considered a vital component of the risk management process which serves as a central source for the organization s risk information and acts as a risk directory. The tool is used by organizations to list various risks, highlighting their probability and severity of impact, along with possible risk mitigation steps and strategies. MN is of the opinion that such a tool will enable MFs (especially those with no existing risk management structures in place) to understand the nature of risks faced by the institutes at the departmental and strategic level. The risk register will provide management and key stakeholders with significant information on various threats, which can be utilized to design risk management strategies to mitigate potential threats. rime Minister Interest Free Loan Scheme The Government of akistan (Go) launched an interest-free microloan scheme last year to address the issues of poverty and rising unemployment in the country. Under the scheme, KR 3.5 billion were earmarked for the poor and destitute segments of the population. Initially, the industry stakeholders were apprehensive about the scheme as it could have distorted the market for conventional microfinance. However, in order to safeguard the interest of the MFs it was decided that the funds for the scheme would be routed through the national apex, AF and loans will be extended to those individual who fall below 40 on the poverty scorecard. In order to mitigate the overlap between interest free loans and conventional microloans, the loans under this scheme would only be extended in Union Councils that have low or no penetration of conventional microfinance. Currently, 24 MFs have partnered with AF in extending interest free loans under this scheme. It is hoped that the scheme would lead to over 1 million additional active borrowers over the next three years. Since this scheme is targeted toward those areas where conventional microfinance has little or no penetration, it provides MFs an opportunity to expand outreach in newer geographic markets. Moreover, it has the potential to allow for borrowers of interest free loans to graduate to conventional microfinance. This is ensured as the interest free loan would be provided only once to an individual and after the completion of the first cycle he/she would be eligible only for a conventional microfinance loan. Lastly in an industry that views funding as one of the key constraints to growth, it is felt that despite the skepticism, this scheme can be useful for the industry with change in design and understanding that the interest free loan program can help in graduation of clients to the next level and mainstreaming them into the microfinance segment. Client rotection Assessments in collaboration with the SMART Campaign Third-party client protection assessments using the SMART Campaign s Smart Assessment Tool were conducted for six MFs during the year in review. In total, 18 assessments have been conducted since the inception of the Client rotection Initiative (CI), cov- Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 4
24 Financial Services for all Section 1 ering over 70 percent of the market in terms of overall outreach to active borrowers. These assessments were made possible with funding support from the SB through the DFID-sponsored FI. The assessments provide a unique opportunity for MN to observe the state of practice in client protection among member MFs; for some of the key findings see Box 1.1. For participating MFs, the assessments provide an opportunity to evaluate their practices in comparison with globally accepted standards of client protection, and seek recommendations for institutional improvements to better comply with the standards. They also indicate whether an institution is ready to pursue SMART Certification, a designation recognized across the global market that an institution successfully integrates Client rotection rinciples into their practices. After undergoing an assessment through the CI project and acting on its results, one MF became the first in akistan to achieve SMART Certification in Microfinance Credit Information Bureau (MF-CIB) The Microfinance Credit Information Bureau (MF-CIB) was launched nation-wide in 2012, with the support of SB, AF, Department for International Development (DFID) and International Finance Corporation (IFC). It was aimed at mitigating the various challenges faced by the microfinance sector ranging from information asymmetry, adverse selection, and moral hazard to over-indebtedness due to multiple borrowing. The delinquency crisis in India s Andhra radesh (2009) and akistan s unjab (2008-9) also served as stark reminders for the industry to institutionalize Box 1.1 State of ractice in Client rotection In 2014, MN conducted analysis of the state of sector in client protection. It is based first 10 third-party assessments of member MFs, out of which 5 were for MFIs and 5 were for MFBs. To arrive at this summary, an average was taken for scores against each client protection principle across these MFs. This first look at the state of the sector in client protection provides substantial evidence that clients are kept at the center of microfinance in akistan. At the broad level, the results indicate that MFs are performing well on the client protection principles of [1] appropriate product design and delivery, [2] prevention of over-indebtedness, [3] transparency, and [4] responsible pricing (see: graph below). At the same time, the results also reflect weakness in certain areas, particularly C principles of privacy of client data and mechanisms for complaints resolution. There are opportunities for improvement in these principles, as well as in certain indicators within the principle of fair and respectful treatment of clients. Appropriate roduct Design & Delivery Channels 100% Mechanism for Complaint Resolution 80% 60% 40% revention of Over-Indebtedness 20% akistan Microfinance Review 2014 rivacy of Client Data Fair & Respectful Treatment of Clients 0% Transparency Responsible ricing % of indicators that are fully met % of indicators that are partially met % of indicators that are not met 5
25 The Year in Review Financial Services for all the use of the Bureau as an integral part of the loan approval process in order to manage credit risk and assess credit worthiness. Over the past three years, the MF-CIB has gradually matured into a reliable risk mitigation tool and has been gradually integrated into the ecosystem of the sector. The enquiry numbers in the year 2014, barring a seasonal decline, showed an upward trend as shown in Exhibit 1.2. it allows for provision of financial services at lower costs than the traditional banking structures making it an ideal channel for reaching out to the unbanked. Branchless banking in akistan continued to expand in the year 2014 with over 60% increase in the value of transactions which reached KR billion as compared to KR billion in December, The number of transactions exhibited over 23% increase reaching to 66.8 million from 54.1 million in at the end of A 35.6% increase was also observed in 160 Enquries in Thousands Jan 14 Feb 14 Mar 14 Apr 14 May 14 Jun 14 Jul 14 Aug 14 Sep 14 Oct 14 Nov 14 Dec 14 Exhibit 1.2: Yearly trend in MF-CIB enquiries Currently, 70% of the organizations are actively generating enquiries (35 out of 50 members) and it is expected that enquiry numbers would grow even more after the complete rollout as some MFs are currently in a partial rollout state. Attention is also being paid to improve the governance structure of the Bureau and make it more inclusive and representative. The Credit Bureau Act, which is expected to be ratified by the arliament this year, will also result in increased transparency from the service provider s perspective. The pricing mechanism is being scrutinized and MN is working with the Bureau and MFs to create a framework for determining prices in future. MN is also conducting a financial literacy program aimed at raising awareness amongst the clients visà-vis the Bureau s importance and utilization. Moreover, a grievance addressing mechanism delineating the rights and obligations of MFs, Bureau and Clients is also being worked out. Branchless Banking Branchless banking is an important tool available to the microfinance industry to expand outreach by leveraging cellular technology infrastructure. Moreover, the number of m-wallet accounts which reached 4.7 million from 3.4 million in the same time period. akistan s branchless banking market is still in an evolutionary phase with eight players competing for market share of agents, number and value of transactions, etc. With the agent network currently standing at 186,000 agents exhibiting a 49% increase from 125,000 in the year, there are concerns about the quality of agents due to a widespread sharing phenomenon. At present, the market is focused on Over the Counter (OTC) transactions. This fuels a commission war to lure agents hence dictating the process of agent acquisition and a nominal addition of new access points which would be, in real terms, expansion of the agent network. A few players are, however, bringing innovation to build business cases around mobile wallets. The SB has continued to facilitate efforts for a broader vision financial inclusion through strengthening the ecosystem for digital transaction accounts. The SB signed an MOU with NADRA in November 2014 according to which, biometric verification cost has been brought down to KR 10 for each m-wallet account opening at the industry level. The placement of biometric verification apparatus across all telecom operators offices enables account opening within a Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 6
26 Financial Services for all Section 1 few seconds via fingerprint verification, and coupled with TA s directive of mandatory biometric mobile SIM verification, this will result in the country s mobile clientele ready to be inducted in the branchless banking arena. This has also proven to be a catalyst for the explosive growth of m-wallets since the beginning of Over 12 microfinance institutions are currently providing disbursement and recovery services to their clients through digital channels. Some players have also started extending insurance services to their clients through branchless banking channels. The industry is poised to witness accelerated growth in future in volume and variety of financial services. Branchless banking can serve as a growth driver owing to its capacity to increase outreach by lowering delivery cost and aiding profitability of institutions. Conclusion The microfinance industry in akistan having witnessed continuous growth over the last few years in not only credit but also savings, insurance and remittances, is ideally positioned to play an important role in the inclusive finance sphere. It can offer a wide variety of financial services to the unbanked particularly at the base of the pyramid. The current macroeconomic stability in the country provides an ideal environment for the sector to grow and expand. Falling interest rates on the back of lower inflation and uptake on private credit provides an opportunity for the microfinance sector to reduce costs and fund their expansion by borrowing from commercial sources. With major policy and regulatory initiatives like clearing house membership for MFBs and enhanced risk coverage for lenders to mid-tier MFs being taken, players are better poised to address funding challenges. Also, the launch of non-bank MFs regulatory framework will lead to strengthening of these institutes and provide them with an opportunity to expand. Branchless banking continues to gain popularity and provides opportunities to not only expand outreach and reduce costs but also expand the variety of financial services on offer. MF-CIB is fully operation with enquiries being generated by MFs and remains a key catalyst for future growth of the industry. In addition, significant steps towards ensuring responsible inclusive finance, by working towards global best practices in client protection have been taken. Establishment of an industry risk register will allow members to identify risks and take steps to mitigate their impact. akistan Microfinance Review
27 The Year in Review Financial Services for all Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 8
28 Financial Services for all Section 1 akistan Microfinance Review
29 Industry erformance Financial Services for all Section 2 Industry erformance Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 10
30 Financial Services for all Section 2 Industry erformance The section is divided into two parts. Section 2A covers the financial performance of the microfinance industry whereas Section 2B deals with the social performance of the industry. Section 2A: Industry erformance This section provides a detailed analysis of the financial performance of akistan s microfinance industry in erformance has been assessed on three levels: industry wise, across peer groups and institution wise. The analysis is backed by 88 financial indicators, calculated from the audited financial statements of the reporting organizations. These indicators have been compared across time and regions to develop a reliable and fair assessment of sector. Detailed financial information is provided in Annex A-I and A-II of the MR. Aggregate data has been reproduced for five years, whereas, the peer group and institution specific data has been made available only for the year A total of 42 MFs submitted their audited financial statements for MR During the period, five new respondents provided their dataset for the first time. For a complete list of reporting organizations refer to Annex B. Industry players are categorized into three groups for benchmarking and comparison purposes: Microfinance Banks (MFBs), Microfinance Institutions (MFIs) and Rural Support rogrammes (RSs). See Box 2A.1 for detailed definitions. Box 2A.1 eer Groups akistan Microfinance Review 2014 Microfinance Institution: A non-bank non-government organization (NGO) providing microfinance services. Organizations in this group are registered under a variety of regulations, including the Societies Act, Trust Act, and the Companies Ordinance. The MFI peer group includes local as well as multinational NGOs such as BRAC-akistan and ASA-akistan. Microfinance Bank: A commercial bank licensed and prudentially regulated by the SB to exclusively service the microfinance market. The first MFB was established in 2000 under a presidential decree. Since then, ten MFBs have been licensed under the Microfinance Institutions Ordinance, Eight of them are operating at national level, while two at the provincial level. MFBs are legally empowered to accept and intermediate deposits from the public. Rural Support rogramme: An NGO registered as a non-profit company under the Companies Ordinance. An RS is differentiated from the MFI peer group based on the purely rural focus of its credit operations. As a group, the RSs are registered with and supervised by the Securities and Exchange Commission of akistan (SEC). 11
31 Industry erformance Financial Services for all The distribution of respondents (number of reporting organizations) by peer group is given in Exhibit 2A.1. The MFI peer group comprises of the largest number of respondents followed by MFBs and then RSs. portfolio increased significantly by 31 percent from KR 46.6 billion to KR 61.1 billion (Exhibit 2A.2). Among the MFs, growth in active borrowers was led by National Rural Support rogram (NRS) which RS, 5% MFI, 27% MFB, 9% Exhibit 2A.1 Distribution of Respondents by eer Groups Scale and outreach This section focuses on outreach indicators to provide performance analysis of the industry in terms of credit growth and composition, deposit mobilization, depth of outreach and gender. Scale and Outreach: Breadth Outreach witnessed growth in all key indicators in added 101,000 borrowers to its portfolio in 2014 depicting an increase of 26 percent year-over-year. Khushhali Bank (KBL) and ASA akistan (ASA-) also witnessed significant growth, with borrowers increasing from 409,000 to 469,000 and 180,000 to 221,000 respectively. In the current year, Kashf Foundation (KF) saw a significant reduction in borrowers (by 26 percent) from 312,000 in 2013 to 230,000 in This reduction was primarily due to write-offs of non-performing loans. The industry in terms of outreach was dominated GL Active borrowers Active borrowers in millions active borrowers grew by 15 percent from 2.4 million to touch 2.8 million, whereas, the gross loan Exhibit 2A.2: Growth in Number of Active Borrowers and GL by nine MFs that accounted for 79 percent of the outreach as shown in Exhibit 2A.3. During the period, GL in KR Billions Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 12
32 Financial Services for all Section FINCA TRD FMFB NRS Bank ASA- TMFB KF KBL NRS Exhibit 2A.3: Active Borrowers of Nine Largest MFs NRS surpassed KBL to become the largest provider of microcredit in terms of active borrowers. NRS s client base crossed 490,000 after witnessing a substantial growth of 26%. KF maintained its position as the third largest provider of microcredit, despite a reduction in active borrowers by 81,000. witnessed the largest increase in GL (by KR 8.7 billion) primarily on the back of KBL, FINCA and FMFB as their loan portfolios increased by KR 3.4 billion, KR 2.0 billion and KR 1.0 billion respectively. Moreover, the average loan size of MFBs remained the highest among peer group (KR 35,699), indicating a greater RS MFI MFB 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 35% 25% 28% 27% 25% 27% 28% 34% 35% 31% 30% 20% 10% 40% 44% 39% 40% 42% Exhibit 2A.4: ercentage Share in Active Borrowers by eer Group akistan Microfinance Review Among the peer groups, MFBs continue to dominate the sector by holding 42 percent of the total market share followed by RSs (35 percent) and MFIs (31 percent) as shown in Exhibit 2A.4. The market share of MFBs and RSs increased by 2 percent in 2014, whereas in the same period, the share of MFIs decreased from 35 percent to 31 percent. The increase in share of RSs can be attributed to the increase in borrowers by NRS and TRD (both RSs collectively added 140,000 microcredit clients) non-inclusion of Akhuwat in the dataset. In terms of GL, MFBs account for 60 percent of the total GL, followed by MFIs with a share of 21 percent and RSs with a share of 19 percent. The overall GL of the sector has increased by KR 14.5 billion to touch KR 61.1 billion in 2014 (Exhibit 2A.5). MFBs GL. The share of RSs in the overall gross loan portfolio has increased from 18% to 19% - this too was on the back of NRS which contributed KR 2.1 billion worth of loan portfolio. Furthermore, approximately 82 percent of the industry s GL is accounted for by nine MFs (Exhibit 2A.6). KBL continues to dominate the market in terms of portfolio size by having a GL of KR 12.2 billion depicting an increase of 38 percent compared to the previous year. This is reflective of the active borrowers of KBL (second highest in the sector) coupled with a shift towards higher average loan size (KR 21,600 in 2013 to KR 26,100). During the year, FINCA Microfinance Bank saw the greatest percentage increase in GL (by a remarkable 98%) from KR 2.0 billion to KR 4.0 billion. The growth in portfolio was mainly
33 Industry erformance Financial Services for all RS MFI MFB 70 KR in Billions Exhibit 2A.5: GL (KR billions) by eer Group supported by a large deposit base of the bank. TMFB, backed by its above average loans sizes, remained the second largest player in terms of portfolio size with a GL of KR 9.0 billion. growth in depositors can be attributed to the surge in branchless banking activities, especially the opening of m-wallet accounts, along with increasing government disbursements for safety net programs such as the Benazir Income Support rogram (BIS). TMFB was followed by KBL and NRS Bank which contributed 226,000 and 219,000 depositors respectively in the reporting year. In terms of growth in value of deposits, FINCA was the largest contributor to the value of deposits; by adding KR 1.9 billion worth of deposits to increase SRSO ASA- KF FINCA FMFB NRS Bank NRS TMFB KBL In the year under review, the sector witnessed a staggering rise in the number of depositors (by 150 percent) from 2.2 million in 2013 to 5.7 million in Similarly, the value of deposits grew by 30 percent in the same year, from KR 32.9 billion to KR 42.7 billion (Exhibit 2A.7). Resultantly, deposits now represent 78 percent of the total liabilities of the MFB peer group an increase from 72 percent in the previous year. Moreover, deposits continue to outgrow the loan portfolio of MFBs, as is evident from the deposits-to-gross loan portfolio ratio which currently stands at 116.1%. The largest increase in the number of depositors came from TMFB which added 2.65 million new depositors (an increase of over 300 percent). The hefty Exhibit 2A.6: GL of Nine Largest MFs 12.2 its deposit base from KR from KR 2.7 billion in 2013 to KR 4.7 billion in 2014 (Exhibit 2A.8). FINCA was followed by TMFB whose deposits grew by KR 1.6 billion to close its balance sheet at KR 12.3 billion deposits. The Deposit-to-GL ratio for MFBs remained stagnant in the current year; the ratio decreased by 1 percent from 117 percent in 2013 to 116 percent in 2014 Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 14
34 Financial Services for all Section 2 Deposits Outstanding Depositors 6, Depositors in thousands 5,000 4,000 3,000 2, Deposits outstanding in billions 1, Exhibit 2A.7: Growth in Deposits and Number of Depositors OMFB Ubank WMFB AMFB FINCA NRS-B KBL FMFB TMFB Exhibit 2A.8: Deposit Growth by MFB (Exhibit 2A.9). The current ratio depicts MFBs heavy reliance on deposits as a primary source of financing as it keeps their cost funding at reasonably low levels. During the year, the cost of funds of MFBs stood at 6.7 percent as compared to an average of 8.9 percent of non-bank MFIs. The liquidity position of MFBs can also be determined by the deposit-to-gl ratio; a high ratio implies that MFBs have excess funds at hand and are adequately liquid. Moreover, the cost of funds has remained in single digits despite mobilizing deposits at above market rates. Deposit-to-GL Deposits GL % akistan Microfinance Review 2014 In KR Billions Feb % 100% 80% 60% 40% 20% Deposit-to-GL Ratio Exhibit 2A.9: Deposit-To-GL Relation for MFBs 15
35 Industry erformance Financial Services for all Sum Insured olicy Holders olicy Holders in millions Sum Insured in KR Billions Exhibit 2A.10: Growth in Number of olicy Holders and Sum Insured Micro-insurance indicators number of policy holders and sum insured both showed a significant improvement in the year The number of policy holders grew by 23.8 percent over the year, rising from 3.0 million to 3.8 million, while the sum insured increased by 50.0 percent from KR 40.3 billion to KR 60.4 billion (see Exhibit 2A.10). Scale and Outreach: Depth The depth of outreach in microcredit operations is measured by a proxy indicator: average loan balance per borrower in proportion to per capita Gross National Income (GNI). A value below 20 percent is assumed to mean that the MF is poverty focused. Except for KBL and NRS Bank, all of the other MFBs fall above this benchmark (Exhibit 2A.11). Comparison across peer groups shows that the ratio of average loan balance to per capita GNI for MFBs has been on the rise Cut-off Industry RS MFI MFB 25% Average Loan Balance er GD 20% 15% 10% 5% The greatest increase in micro-insurance came from the MFB peer group whose policy holders and sum insured increased by 46 percent and 80 percent respectively. During the year, MFBs enhanced the coverage of their insurance products by securing more credit clients, along with their spouses. However, among individual institutes, NRS remained the largest providers of micro-insurance; holding a market share of 22 percent and 24 percent in terms of policy holders and total sum insured, respectively. Among the types of insurance policies, health insurance constituted almost 51 percent of total insurance policies followed by credit life at 49 percent. Exhibit 2A.11: Depth of Outreach by eer Groups for the past four years. MFBs tend to target the upper end of the market through relatively larger loan sizes, and hence have a ratio of 20 percent compared to MFIs and RSs which have a ratio of 10 percent each. The ratio of average loan balance to per capita GNI witnessed a modest increase for MFBs (by 2 percent) and MFIs (by 1 percent), while the ratio for RSs remained stagnant at 10.0 percent. This could be interpreted as the sector continuing to target the poor but also has implications for appropriate loan sizes in the Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 16
36 Financial Services for all Section 2 context of akistan s inflationary environment. Erosion in the value of money means that a loan worth KR 30,000 in one year would be considerably lower in value in the following year. Lending Methodology In the akistan microfinance sector, majority of MFs follow the group lending methodology in 2014, 68 percent of the active borrowers represented group were the main drivers for the increase in the share of individual borrowing from 24 percent in 2013 to 27 percent in Gender Distribution The proportion of women borrowers depicted a downward movement in the current year, decreasing from 60.3 percent in 2013 to 58.0 percent in 2014 (Exhibit 2A.13). The proportion of women borrowers Group Borrowing Individual Borrowing 3,500 Active Borrowers in Thousands 3,000 2,500 2,000 1,500 1,000 90% 88% 78% 76% 73% % 12% 22% 24% 27% Exhibit 2A.12: Lending Methodology lending (see Exhibit 2A.12). However, over the past four years, the share of individual lending has been increasing gradually, as many MFs which were following the group lending methodology, also started focusing on Individual lending methodology. In the for MFBs and MFIs increased slightly by 1 percent, whereas, the proportion of women borrowers for RSs remained unchanged. Out of the three peer groups, the client base of MFBs is mostly composed of male borrowers, while MFIs and RSs are more Female Borrowers Male Borrowers 100% akistan Microfinance Review % 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 25% 75% 89% 11% MFB MFI RS Total period under review, individual lending showed an increse of 8 percent, whereas, group lending has decreased from 76 percent to 68 percent. During the reporting year, FINCA, Kashf Foundation and TMFB 74% 26% Exhibit 2A.13: Gender Distribution of Credit Outreach by eer Groups 58% 42% oriented towards women borrowers. Women borrowers remain an integral part of the akistan microfinance sector and lending to women 17
37 Industry erformance Financial Services for all Manufacturing/roduction Services Trade Livestock/oultry Agriculture Housing Other 100% 90% 80% 70% 08% 0% 07% 11% 08% 0% 09% 07% 09% 0% 09% 09% 15% 0% 09% 08% 15% 0% 09% 08% 60% 50% 36% 38% 35% 30% 29% 40% 30% 14% 15% 16% 16% 16% 20% 10% 23% 23% 22% 22% 23% Exhibit 2A.14: Active borrowers by sector has been encouraged by various donor and regulatory bodies. The national apex AF provides funding to MFs based on a commitment that at least 40 percent of the borrowers will be women. Large players such as NRS, ASA akistan, and SRSO have portfolios that mostly constitute of women borrowers, whereas, Kashf Foundation only lends to women borrowers. ortfolio Distribution by Sector The credit portfolio distribution showed insignificant change as compared to the previous year (Exhibit 2A.14). The share of trading sector declined by 1 percent in 2014 but continued to dominate the sector-wise distribution of microcredit with an overall agriculture sector which made up 23 percent of the borrowers, while the livestock sector continued to be a distant third accounting for only 16 percent of the borrowers. Rural- Urban Lending The share of rural borrowers continued to dominate the sector; out of total borrowers, 57 percent belong to rural areas while 43 percent belong to urban areas (Exhibit 2A.15). Majority of the borrowers of the two dominant players (NRS and KBL) belong to the rural segment of the population. However, in the year under review, the share of urban borrowers saw a modest increase of 1 percent. This increase can be attributed to growth seen by FINCA, TMFB and ASA Rural Urban 100% 90% 80% 70% 52% 46% 56% 58% 57% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 48% 54% share of 29 percent. The trade sector primarily comprises of general stores, karyana shops, stall hawkers, fruit vendors, etc. Trade was followed by the 44% 42% Exhibit 2A.15: Active Borrowers by Urban/Rural Areas 43% akistan, as more than 50 percent borrowers of these institutes belong to urban regions. Annual Assessment of the Microfinance Industry 18
ANNUAL ASSESSMENT OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY FINANCIAL SERVICES FOR ALL
 ANNUAL ASSESSMENT OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY FINANCIAL SERVICES FOR ALL roduced by akistan Microfinance Network Design and Layout by O3 Interfaces www.o3interfaces.com ANNUAL ASSESSMENT OF THE MICROFINANCE
ANNUAL ASSESSMENT OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY FINANCIAL SERVICES FOR ALL roduced by akistan Microfinance Network Design and Layout by O3 Interfaces www.o3interfaces.com ANNUAL ASSESSMENT OF THE MICROFINANCE
State Bank of Pakistan
 Performance Review of Deposit Mobilization Assessing structure and stability of MFBs deposits (Dec 31, 2013) State Bank of Pakistan Agricultural Credit & Microfinance Department (Development Finance Group)
Performance Review of Deposit Mobilization Assessing structure and stability of MFBs deposits (Dec 31, 2013) State Bank of Pakistan Agricultural Credit & Microfinance Department (Development Finance Group)
MICROFINANCE BANKS AN OVERVIEW. My greatest challenge has been to change the mindset of people. Muhammad Yunus
 MICROFINANCE BANKS AN OVERVIEW My greatest challenge has been to change the mindset of people. Muhammad Yunus March 2015 ABSTRACT Pakistan s Microfinance Sector comprises 45 Microfinance Providers (MFPs)
MICROFINANCE BANKS AN OVERVIEW My greatest challenge has been to change the mindset of people. Muhammad Yunus March 2015 ABSTRACT Pakistan s Microfinance Sector comprises 45 Microfinance Providers (MFPs)
BRAC BANK LTD (BRACBANK)
 BDT : 980.00 Tk. 1,600 1,400 1,200 1,000 800 600 400 200 0 31-Jan-07 3-Mar-07 BRAC Bank Adjusted Price-Volume Graph Volume Price 3-Apr-07 3-May-07 3-Jun-07 3-Jul-07 3-Aug-07 Farzana Hoque farzana@lbsbd.com
BDT : 980.00 Tk. 1,600 1,400 1,200 1,000 800 600 400 200 0 31-Jan-07 3-Mar-07 BRAC Bank Adjusted Price-Volume Graph Volume Price 3-Apr-07 3-May-07 3-Jun-07 3-Jul-07 3-Aug-07 Farzana Hoque farzana@lbsbd.com
COMPANY PROFILE. Passion. Progress. for
 COMPANY PROFILE Passion for Progress COMPANY OVERVIEW Pakistan Microfinance Investment Company Limited (PMIC) is a national-level apex institution for microfinance providers in the country. PMIC was established
COMPANY PROFILE Passion for Progress COMPANY OVERVIEW Pakistan Microfinance Investment Company Limited (PMIC) is a national-level apex institution for microfinance providers in the country. PMIC was established
PROGRAM-FOR-RESULTS INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.:
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROGRAM-FOR-RESULTS INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: 113653 Program
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized PROGRAM-FOR-RESULTS INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) CONCEPT STAGE Report No.: 113653 Program
Session on Branchless Banking and Savings 17 March 2012, Marriott, Karachi
 Session on Branchless Banking and Savings 17 March 2012, Marriott, Karachi Pakistan Poverty Alleviation Fund (PPAF) recently completed two pilots on branchless banking with Tameer Microfinance Bank s (TMFB)
Session on Branchless Banking and Savings 17 March 2012, Marriott, Karachi Pakistan Poverty Alleviation Fund (PPAF) recently completed two pilots on branchless banking with Tameer Microfinance Bank s (TMFB)
Identification & Assessment of Risks Authors: Ali Basharat & Zeenoor Sohail Sheikh
 Identification & Assessment of Risks 2018 Authors: Ali Basharat & Zeenoor Sohail Sheikh Risk Management for the Microfinance Sector (2018) Identification & Assessment of Risks 1) Risk Register Tool An
Identification & Assessment of Risks 2018 Authors: Ali Basharat & Zeenoor Sohail Sheikh Risk Management for the Microfinance Sector (2018) Identification & Assessment of Risks 1) Risk Register Tool An
BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY REPORT FOR QUARTER ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2018
 BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY REPORT FOR QUARTER ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2018 MARCH 2019 Table of Contents 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 2. ARCHITECTURE OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY... 4 3. PERFORMANCE
BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY REPORT FOR QUARTER ENDED 31 DECEMBER 2018 MARCH 2019 Table of Contents 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 2. ARCHITECTURE OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY... 4 3. PERFORMANCE
The First MicroFinanceBank Limited (FMFB)
 Rating Report RATING REPORT REPORT DATE: May 07, 2018 RATING ANALYSTS: Maimoon Rasheed maimoon@jcrvis.com.pk Maham Qasim maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating Previous Rating Rating Category
Rating Report RATING REPORT REPORT DATE: May 07, 2018 RATING ANALYSTS: Maimoon Rasheed maimoon@jcrvis.com.pk Maham Qasim maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating Previous Rating Rating Category
Financial Deepening & Development
 Financial Deepening & Development Pakistan Development Forum April 26, 2007 Zubyr Soomro Country Officer & MD, Citibank N.A., Pakistan Case Study- Anopo from Thar 3 micro loans taken over 3 years helped
Financial Deepening & Development Pakistan Development Forum April 26, 2007 Zubyr Soomro Country Officer & MD, Citibank N.A., Pakistan Case Study- Anopo from Thar 3 micro loans taken over 3 years helped
KASHF FOUNDATION (KF)
 Rating Report RATING REPORT KASHF FOUNDATION (KF) REPORT DATE: April 5, 2017 RATING ANALYSTS: Maimoon Rasheed maimoon@jcrvis.com.pk Muneeba Alam muneeba.alam@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating
Rating Report RATING REPORT KASHF FOUNDATION (KF) REPORT DATE: April 5, 2017 RATING ANALYSTS: Maimoon Rasheed maimoon@jcrvis.com.pk Muneeba Alam muneeba.alam@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating
M2i s Experience in Microfinance
 M2i s Experience in Microfinance Title Duration Client Page Implementation of Risk Management International Finance June 2012-May 2015 Framework in 5 MFIs Corporation 3 Adaptation of Global Risk International
M2i s Experience in Microfinance Title Duration Client Page Implementation of Risk Management International Finance June 2012-May 2015 Framework in 5 MFIs Corporation 3 Adaptation of Global Risk International
Gearing Towards Microenterprise Lending
 Gearing Towards Microenterprise Lending By Ali Basharat & Zeenoor Sohail Sheikh No. 38 December 2018 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Microenterprise lending in Pakistan has been low when compared to the total microcredit
Gearing Towards Microenterprise Lending By Ali Basharat & Zeenoor Sohail Sheikh No. 38 December 2018 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Microenterprise lending in Pakistan has been low when compared to the total microcredit
BSE: NSE: SATIN CSE: Corporate Identity No. L65991DL1990PLC Familiarization Programme for Independent Directors
 BSE: 539404 NSE: SATIN CSE: 30024 Corporate Identity No. L65991DL1990PLC041796 Familiarization Programme for Independent Directors Microfinance Through Window of Relevance Micro-finance is defined as financial
BSE: 539404 NSE: SATIN CSE: 30024 Corporate Identity No. L65991DL1990PLC041796 Familiarization Programme for Independent Directors Microfinance Through Window of Relevance Micro-finance is defined as financial
Overview. Financial Systems approach to microfinance Basic roles and functions of government and donors at various points within the financial sector
 Overview Financial Systems approach to microfinance Basic roles and functions of government and donors at various points within the financial sector The Borders of Microfinance are Blurring Khan bank serving
Overview Financial Systems approach to microfinance Basic roles and functions of government and donors at various points within the financial sector The Borders of Microfinance are Blurring Khan bank serving
MICROFINANCE QUARTERLY REPORT 30 JUNE 2017
 MICROFINANCE QUARTERLY REPORT 30 JUNE 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY...3 2 ARCHITECTURE OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY...3 Branch Network and Outreach...4 Microfinance Active Clients...6 3 PERFORMANCE
MICROFINANCE QUARTERLY REPORT 30 JUNE 2017 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY...3 2 ARCHITECTURE OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY...3 Branch Network and Outreach...4 Microfinance Active Clients...6 3 PERFORMANCE
MICROFINANCE Forum 2015
 SHAMROCK CONFERENCES INTERNATIONAL www.shamrockconferences.net PAKISTAN MICROFINANCE Forum 2015 9 TH ANNUAL ASSEMBLY OF MICROFINANCE STAKEHOLDERS 26 November 2015, Ramada Hotel, Islamabad Theme Time to
SHAMROCK CONFERENCES INTERNATIONAL www.shamrockconferences.net PAKISTAN MICROFINANCE Forum 2015 9 TH ANNUAL ASSEMBLY OF MICROFINANCE STAKEHOLDERS 26 November 2015, Ramada Hotel, Islamabad Theme Time to
Produced by Central Africana Limited, Blantyre, Malawi
 Produced by Central Africana Limited, Blantyre, Malawi centralafricana@africa-online.net www.centralafricana.com RESERVE BANK OF MALAWI FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS SUPERVISION ANNUAL REPORT 2015 RESERVE BANK
Produced by Central Africana Limited, Blantyre, Malawi centralafricana@africa-online.net www.centralafricana.com RESERVE BANK OF MALAWI FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS SUPERVISION ANNUAL REPORT 2015 RESERVE BANK
Viet Nam: Microfinance Development Program (Subprograms 1 and 2)
 Validation Report Reference Number: PVR-478 Project Numbers: 42235-013 and 42235-023 Loan Numbers: 2877 and 3213 December 2016 Viet Nam: Microfinance Development Program (Subprograms 1 and 2) Independent
Validation Report Reference Number: PVR-478 Project Numbers: 42235-013 and 42235-023 Loan Numbers: 2877 and 3213 December 2016 Viet Nam: Microfinance Development Program (Subprograms 1 and 2) Independent
Supply of and Demand for Financial Products
 Chapter 2 Supply of and Demand for Financial Products 2.1 Payment and Transaction Products Payment and transaction products play key roles in smoothing retail banking and settling payment obligations in
Chapter 2 Supply of and Demand for Financial Products 2.1 Payment and Transaction Products Payment and transaction products play key roles in smoothing retail banking and settling payment obligations in
HM Queen Maxima UNSGSA on Inclusive Finance for Development visit to Pakistan
 HM Queen Maxima UNSGSA on Inclusive Finance for Development visit to Pakistan February 9th 11th, 2016 Islamabad-Pakistan State Bank of Pakistan Executive Summary/ Visit Context Financial Inclusion plays
HM Queen Maxima UNSGSA on Inclusive Finance for Development visit to Pakistan February 9th 11th, 2016 Islamabad-Pakistan State Bank of Pakistan Executive Summary/ Visit Context Financial Inclusion plays
Micro Finance in the World and in India: Status, Problems and Prospects
 Micro Finance in the World and in India: Status, Problems and Prospects By Vijay Mahajan Chair, CGAP ExCom Founder and CEO, BASIX Social Enterprise Group, India President, MFIN (MFI Network of India) March
Micro Finance in the World and in India: Status, Problems and Prospects By Vijay Mahajan Chair, CGAP ExCom Founder and CEO, BASIX Social Enterprise Group, India President, MFIN (MFI Network of India) March
E- ISSN X ISSN MICRO FINANCE-AN IMPERATIVE FOR FINANCIAL INCLUSION IN INDIA
 MICRO FINANCE-AN IMPERATIVE FOR FINANCIAL INCLUSION IN INDIA Dr.K.Jayalakshmi PDF(ICSSR),Dept. of Commerce,S.K.University, Anantapur. Andhra Pradesh. Abstract Financial inclusion is a flagship programme
MICRO FINANCE-AN IMPERATIVE FOR FINANCIAL INCLUSION IN INDIA Dr.K.Jayalakshmi PDF(ICSSR),Dept. of Commerce,S.K.University, Anantapur. Andhra Pradesh. Abstract Financial inclusion is a flagship programme
QUARTERLY PERFORMANCE REPORT OF THE MICROFINANCE SECTOR. as at 31 March 2017 ZAMFI CREDIT ONLY MFI MEMBERS
 Zimbabwe Association of Microfinance Institutions creating sustainable microfinance QUARTERLY PERFORMANCE REPORT OF THE MICROFINANCE SECTOR as at 31 March 2017 ZAMFI CREDIT ONLY MFI MEMBERS 1 PERFORMANCE
Zimbabwe Association of Microfinance Institutions creating sustainable microfinance QUARTERLY PERFORMANCE REPORT OF THE MICROFINANCE SECTOR as at 31 March 2017 ZAMFI CREDIT ONLY MFI MEMBERS 1 PERFORMANCE
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISES FINANCING) 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities
 Additional Financing of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Line of Credit Project (RRP SRI 49273-002) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISES FINANCING) 1. Sector Performance,
Additional Financing of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Line of Credit Project (RRP SRI 49273-002) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE (SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISES FINANCING) 1. Sector Performance,
BRINGING THE "FORGOTTEN HALF" OF MICROFINANCE INTO FOCUS: Analysis of Recent. By SHAHBANO HAMEED and ALI BASHARAT INTRODUCTION
 No: 19 December 2013 MicroNOTE BRINGING THE "FORGOTTEN HALF" OF MICROFINANCE INTO FOCUS: Analysis of Recent Trends and Issues in Mobilization by Microfinance Banks in Pakistan By SHAHBANO HAMEED and ALI
No: 19 December 2013 MicroNOTE BRINGING THE "FORGOTTEN HALF" OF MICROFINANCE INTO FOCUS: Analysis of Recent Trends and Issues in Mobilization by Microfinance Banks in Pakistan By SHAHBANO HAMEED and ALI
The Pakistan Credit Rating Agency Limited. Stable Initial 24 th October, 2017
 The Pakistan Credit Rating Agency Limited ENTITY RATINGS REPORT PAKISTAN MICROFINANCE INVESTMENT COMPANY LIMITED ENTITY RATING OUTLOOK ACTION DATE Pakistan Microfinance Investment Company Limited (PMIC)
The Pakistan Credit Rating Agency Limited ENTITY RATINGS REPORT PAKISTAN MICROFINANCE INVESTMENT COMPANY LIMITED ENTITY RATING OUTLOOK ACTION DATE Pakistan Microfinance Investment Company Limited (PMIC)
The Strategy for Development of the. Microfinance Sector in Sudan. A Central Bank Initiative
 The Strategy for Development of the Microfinance Sector in Sudan A Central Bank Initiative Abda Y. El-Mahdi Managing Director Unicons Consultancy Ltd. The Status of the Microfinance Sector in Sudan A growing
The Strategy for Development of the Microfinance Sector in Sudan A Central Bank Initiative Abda Y. El-Mahdi Managing Director Unicons Consultancy Ltd. The Status of the Microfinance Sector in Sudan A growing
NRSP Microfinance Bank Limited
 JCR-VIS Credit Rating Company Limited Technical Partner IIRA, Bahrain JV Partner CRISL, Bangladesh Rating Report RATING REPORT REPORT DATE: May 03, 2018 RATING ANALYSTS: Maimoon Rasheed Maimoon@jcrvis.com.pk
JCR-VIS Credit Rating Company Limited Technical Partner IIRA, Bahrain JV Partner CRISL, Bangladesh Rating Report RATING REPORT REPORT DATE: May 03, 2018 RATING ANALYSTS: Maimoon Rasheed Maimoon@jcrvis.com.pk
Policy, Regulatory and Supervisory Environment for Microfinance in Tanzania
 ESSAYS ON REGULATION AND SUPERVISION Policy, Regulatory and Supervisory Environment for Microfinance in Tanzania G.C. RUBAMBEY BANK OF TANZANIA December 2005 ESSAYS ON REGULATION AND SUPERVISION No.15
ESSAYS ON REGULATION AND SUPERVISION Policy, Regulatory and Supervisory Environment for Microfinance in Tanzania G.C. RUBAMBEY BANK OF TANZANIA December 2005 ESSAYS ON REGULATION AND SUPERVISION No.15
Khushhali Microfinance Bank Limited
 Rating Report RATING REPORT Khushhali Microfinance Bank Limited REPORT DATE: May 04, 2018 RATING ANALYSTS: Maimoon Rasheed maimoon @jcrvis.com.pk Maham Qasim maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest
Rating Report RATING REPORT Khushhali Microfinance Bank Limited REPORT DATE: May 04, 2018 RATING ANALYSTS: Maimoon Rasheed maimoon @jcrvis.com.pk Maham Qasim maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest
MICROFINANCE QUARTERLY REPORT
 MICROFINANCE QUARTERLY REPORT 31 MARCH 2017 Table of Contents Table of Figures... 2 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 ARCHITECTURE OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY.....3 Branch Network and Outreach... 4 Microfinance
MICROFINANCE QUARTERLY REPORT 31 MARCH 2017 Table of Contents Table of Figures... 2 1 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 ARCHITECTURE OF THE MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY.....3 Branch Network and Outreach... 4 Microfinance
Community level impacts of financial inclusion in Kenya with particular focus on poverty eradication and employment creation
 Community level impacts of financial inclusion in Kenya with particular focus on poverty eradication and employment creation By Matu Mugo Central Bank of Kenya UN Expert Group Meeting 8 th to 11 th May
Community level impacts of financial inclusion in Kenya with particular focus on poverty eradication and employment creation By Matu Mugo Central Bank of Kenya UN Expert Group Meeting 8 th to 11 th May
INDONESIA RISING. Policy Priorities for 2010 and Beyond
 INDONESIA RISING. Policy Priorities for 2010 and Beyond Towards a Stable, Efficient, and Accessible Financial Sector Key Messages 1. The government s focus on maintaining and strengthening the stability
INDONESIA RISING. Policy Priorities for 2010 and Beyond Towards a Stable, Efficient, and Accessible Financial Sector Key Messages 1. The government s focus on maintaining and strengthening the stability
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE 1
 Country Partnership Strategy: Pakistan, 2015 2019 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE 1 1. Sector Performance, Issues and Opportunities 1. Financial sector participants. Pakistan s financial sector is
Country Partnership Strategy: Pakistan, 2015 2019 SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE 1 1. Sector Performance, Issues and Opportunities 1. Financial sector participants. Pakistan s financial sector is
Financial Access and Financial Regulation and Supervision Issues and Practices
 Financial Access and Financial Regulation and Supervision Issues and Practices Seminar for Senior Bank Supervisors Federal Reserve and the World Bank October 18, 2006 Presented by: Anjali Kumar World Bank
Financial Access and Financial Regulation and Supervision Issues and Practices Seminar for Senior Bank Supervisors Federal Reserve and the World Bank October 18, 2006 Presented by: Anjali Kumar World Bank
Ex post evaluation Pakistan
 Ex post evaluation Pakistan Sector: Informal/semi-formal financial intermediaries (CRS 24040) Project: A. Microfinancing programme (THB) (BMZ No. 2008 66 541)* B. Microfinancing programme (THB subordinated
Ex post evaluation Pakistan Sector: Informal/semi-formal financial intermediaries (CRS 24040) Project: A. Microfinancing programme (THB) (BMZ No. 2008 66 541)* B. Microfinancing programme (THB subordinated
2018/SMEWG/DIA/008 National Financial Inclusion Strategy
 2018/SMEWG/DIA/008 National Financial Inclusion Strategy 2016-2020 Submitted by: Centre for Excellence in Financial Inclusion Policy Dialogue on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Internationalization
2018/SMEWG/DIA/008 National Financial Inclusion Strategy 2016-2020 Submitted by: Centre for Excellence in Financial Inclusion Policy Dialogue on Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Internationalization
Statement by the IMF Managing Director on The Role of the Fund in Low-Income Countries October 2, 2008
 Statement by the IMF Managing Director on The Role of the Fund in Low-Income Countries October 2, 2008 1. Progress in recent years but challenges remain. In my first year as Managing Director, I have been
Statement by the IMF Managing Director on The Role of the Fund in Low-Income Countries October 2, 2008 1. Progress in recent years but challenges remain. In my first year as Managing Director, I have been
Agenda item 12: Consideration of accreditation proposals
 Page 5 (h) (j) (k) (l) (m) (n) Also requests the Appointment Committee to provide additional recommendations on the salary levels for consideration by the Board at its eleventh meeting; Decides that the
Page 5 (h) (j) (k) (l) (m) (n) Also requests the Appointment Committee to provide additional recommendations on the salary levels for consideration by the Board at its eleventh meeting; Decides that the
ANNUAL REPORT Annual REPORT
 ANNUAL REPORT 2017 Annual REPORT 2017 1 OPERATIONAL STATISTICS 2017 2016 INDEX Number of loan clients 43,070 37,428 115% Number of savings clients 41,255 38,175 108% Number of staff 338 312 108% Average
ANNUAL REPORT 2017 Annual REPORT 2017 1 OPERATIONAL STATISTICS 2017 2016 INDEX Number of loan clients 43,070 37,428 115% Number of savings clients 41,255 38,175 108% Number of staff 338 312 108% Average
Monetary Policy Implementation and Banking Sector Development in Cambodia
 Presentation at Sophia University November 13 th, 2017, Tokyo Monetary Policy Implementation and Banking Sector Development in Cambodia Mr. Duong Sophak, Division Chief and Mr. You Vithyea, Section Chief
Presentation at Sophia University November 13 th, 2017, Tokyo Monetary Policy Implementation and Banking Sector Development in Cambodia Mr. Duong Sophak, Division Chief and Mr. You Vithyea, Section Chief
Benchmarking Microfinance in Romania
 Benchmarking Microfinance in Romania 2006-2007 A report from Eurom Consultancy and Studies SRL for European Microfinance Network s Micro finance Conference Nice, France 2008 Bucharest Romania www.eurom-consultancy.ro
Benchmarking Microfinance in Romania 2006-2007 A report from Eurom Consultancy and Studies SRL for European Microfinance Network s Micro finance Conference Nice, France 2008 Bucharest Romania www.eurom-consultancy.ro
AMFI SECTOR REPORT DECEMBER 2017
 AMFI SECTOR REPORT DECEMBER 2017 1.1.0: INTRODUCTION 1.1.1: BACKGROUND INFORMATION The Association for Microfinance Institutions (AMFI) is a member-based organization that was established and registered
AMFI SECTOR REPORT DECEMBER 2017 1.1.0: INTRODUCTION 1.1.1: BACKGROUND INFORMATION The Association for Microfinance Institutions (AMFI) is a member-based organization that was established and registered
KASHF FOUNDATION (KF)
 RATING REPORT KASHF FOUNDATION (KF) REPORT DATE: April 01, 2016 RATING ANALYSTS: Waqas Munir, FRM waqas.munir@jcrvis.com.pk Maham Qasim maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating Previous Rating
RATING REPORT KASHF FOUNDATION (KF) REPORT DATE: April 01, 2016 RATING ANALYSTS: Waqas Munir, FRM waqas.munir@jcrvis.com.pk Maham Qasim maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating Previous Rating
ARIES. FINCA Program Brief No. 4 AFGHANISTAN. Agriculture, Rural Investment and Enterprise Strengthening Program in Afghanistan
 ARIES Agriculture, Rural Investment and Enterprise Strengthening Program in Afghanistan FINCA Program Brief No. 4 AFGHANISTAN The Financial Integration, Economic Leveraging, Broad-Based Dissemination Leader
ARIES Agriculture, Rural Investment and Enterprise Strengthening Program in Afghanistan FINCA Program Brief No. 4 AFGHANISTAN The Financial Integration, Economic Leveraging, Broad-Based Dissemination Leader
Figure 5.1: 6-month Yields Auction cut-off Repo rate percent Sep-03
 5 Money Market Third Quarterly Report for FY4 After the reversal of the December 23 upsurge in short-term rates, the market entered a period of relative stability. While it continued to expect a modest
5 Money Market Third Quarterly Report for FY4 After the reversal of the December 23 upsurge in short-term rates, the market entered a period of relative stability. While it continued to expect a modest
Financial Sector Performance Review Report. March 2018
 Financial Sector Performance Review Report March 2018 This report presents the performance of the Bhutanese financial sector on peer group basis (excluding NPPF) for the period ended Q1FY 18 in comparison
Financial Sector Performance Review Report March 2018 This report presents the performance of the Bhutanese financial sector on peer group basis (excluding NPPF) for the period ended Q1FY 18 in comparison
NRSP Microfinance Bank Limited
 Rating Report RATING REPORT REPORT DATE: May 3, 2017 RATING ANALYSTS: Jazib Ahmed, CFA jazib.ahmed@jcrvis.com.pk Narendar Shankar Lal narendar.shankar@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating Previous
Rating Report RATING REPORT REPORT DATE: May 3, 2017 RATING ANALYSTS: Jazib Ahmed, CFA jazib.ahmed@jcrvis.com.pk Narendar Shankar Lal narendar.shankar@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating Previous
Identification & Assessment of Risks
 RISK MANAGEMENT Identification & Assessment of s FOR THE MICROFINANCE SECTOR All rights reserved. The data in this report have been carefully compiled and are believed to be accurate. Such accuracy is
RISK MANAGEMENT Identification & Assessment of s FOR THE MICROFINANCE SECTOR All rights reserved. The data in this report have been carefully compiled and are believed to be accurate. Such accuracy is
Microfinance Demonstration of at the bottom of pyramid theory Dipti Kamble
 Microfinance Demonstration of at the bottom of pyramid theory Dipti Kamble MBA - I, Finance What is Microfinance? Microfinance is the supply of loans, savings, and other basic financial services to the
Microfinance Demonstration of at the bottom of pyramid theory Dipti Kamble MBA - I, Finance What is Microfinance? Microfinance is the supply of loans, savings, and other basic financial services to the
HDFC Bank Ltd. BUY. Investment Rationale. July 2, Volume No.. 1 Issue No. 28
 Jun-14 Jul-14 Aug-14 Sep-14 Oct-14 Nov-14 Dec-14 Jan-15 Feb-15 Mar-15 Apr-15 May-15 Jun-15. Volume No.. 1 Issue No. 28 HDFC Bank Ltd. July 2, 2015 BSE Code: 500180 NSE Code: HDFCBANK Reuters Code: HDBK.BO
Jun-14 Jul-14 Aug-14 Sep-14 Oct-14 Nov-14 Dec-14 Jan-15 Feb-15 Mar-15 Apr-15 May-15 Jun-15. Volume No.. 1 Issue No. 28 HDFC Bank Ltd. July 2, 2015 BSE Code: 500180 NSE Code: HDFCBANK Reuters Code: HDBK.BO
Funding Housing in the Bond Market. September 2016
 Funding Housing in the Bond Market September 2016 Overview: ALCB Fund PART 1 Overview of ALCB Fund Target Impact: Capital Market Development Increased primary issuance and capacity Issuer Balance Sheet
Funding Housing in the Bond Market September 2016 Overview: ALCB Fund PART 1 Overview of ALCB Fund Target Impact: Capital Market Development Increased primary issuance and capacity Issuer Balance Sheet
BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION MICROFINANCE SECTOR REPORT FOR QUARTER ENDED 30 SEPTEMBER 2018
 BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION MICROFINANCE SECTOR REPORT FOR QUARTER ENDED 30 SEPTEMBER 2018 NOVEMBER 2018 Table of Contents 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 2. ARCHITECTURE OF THE MICROFINANCE SECTOR... 4 3. PERFORMANCE
BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION MICROFINANCE SECTOR REPORT FOR QUARTER ENDED 30 SEPTEMBER 2018 NOVEMBER 2018 Table of Contents 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 3 2. ARCHITECTURE OF THE MICROFINANCE SECTOR... 4 3. PERFORMANCE
OJK INTERNATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR MICROFINANCE AND INCLUSION OJK - PUSAT KEUANGAN MIKRO DAN INKLUSI (OJK- PROKSI)
 OJK INTERNATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR MICROFINANCE AND INCLUSION OJK - PUSAT KEUANGAN MIKRO DAN INKLUSI (OJK- PROKSI) Microfinance Sub Sectors in Indonesia Micro- Credit Very small loan No Collateral
OJK INTERNATIONAL CENTER OF EXCELLENCE FOR MICROFINANCE AND INCLUSION OJK - PUSAT KEUANGAN MIKRO DAN INKLUSI (OJK- PROKSI) Microfinance Sub Sectors in Indonesia Micro- Credit Very small loan No Collateral
Annual Report 2012/13
 Annual Report 2012/13 i Working towards a World-Class Commercial Bank ii Contents Key figures (in Millions of Birr)... 6 Message of the President... 8 1. Macroeconomic Highlights... 10 1.1. Global Economy...10
Annual Report 2012/13 i Working towards a World-Class Commercial Bank ii Contents Key figures (in Millions of Birr)... 6 Message of the President... 8 1. Macroeconomic Highlights... 10 1.1. Global Economy...10
1. Key development issues and rationale for Bank involvement
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized DRAFT PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) APPRAISAL STAGE Report No.: AB5278 Project Name
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized DRAFT PROJECT INFORMATION DOCUMENT (PID) APPRAISAL STAGE Report No.: AB5278 Project Name
Ujjivan Leading the Expansion of Gendered Individual Lending in India
 SCBF 2012-09 June 2014 Ujjivan Leading the Expansion of Gendered Individual Lending in India 1. Development relevance Economic and Poverty Context: i With 1,2 billion people and the world s fourth-largest
SCBF 2012-09 June 2014 Ujjivan Leading the Expansion of Gendered Individual Lending in India 1. Development relevance Economic and Poverty Context: i With 1,2 billion people and the world s fourth-largest
NRSP Microfinance Bank Limited
 RATING REPORT REPORT DATE: May 02, 2016 RATING ANALYSTS: Waqas Munir, FRM waqas.munir@jcrvis.com. pk Maham Qasim Maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating Previous Rating Rating Category Longterm
RATING REPORT REPORT DATE: May 02, 2016 RATING ANALYSTS: Waqas Munir, FRM waqas.munir@jcrvis.com. pk Maham Qasim Maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest Rating Previous Rating Rating Category Longterm
Report and Recommendation of the President to the Board of Directors
 Report and Recommendation of the President to the Board of Directors Project Number: 49207-001 November 2015 Proposed Equity Investment and Loan RBL Bank Supporting Financial Inclusion Project (India)
Report and Recommendation of the President to the Board of Directors Project Number: 49207-001 November 2015 Proposed Equity Investment and Loan RBL Bank Supporting Financial Inclusion Project (India)
September. EMN POLICY NOTE on the EMN Overview of the Microcredit Sector in the European Union
 September 2014 EMN POLICY NOTE on the EMN Overview of the Microcredit Sector in the European Union 2012-13 EMN POLICY NOTE Steady growth of microcredit provision in value and number of microloans surveyed
September 2014 EMN POLICY NOTE on the EMN Overview of the Microcredit Sector in the European Union 2012-13 EMN POLICY NOTE Steady growth of microcredit provision in value and number of microloans surveyed
Monitoring the progress of graduated countries Cape Verde
 CDP/RM Committee for Development Policy Expert Group Meeting Review of the list of Least Developed Countries New York, 16-17 January 2011 Monitoring the progress of graduated countries Cape Verde Background
CDP/RM Committee for Development Policy Expert Group Meeting Review of the list of Least Developed Countries New York, 16-17 January 2011 Monitoring the progress of graduated countries Cape Verde Background
Credit Information Sharing. Recent Developments: Credit Reporting Standards G20 SME Finance Initiative. Hong Kong, 24 th March 2011
 Credit Information Sharing Recent Developments: Credit Reporting Standards G20 SME Finance Initiative Hong Kong, 24 th March 2011 Tony Lythgoe Head, Financial Infrastructure, Global Credit Bureau Program
Credit Information Sharing Recent Developments: Credit Reporting Standards G20 SME Finance Initiative Hong Kong, 24 th March 2011 Tony Lythgoe Head, Financial Infrastructure, Global Credit Bureau Program
The goals to Access / Financial Inclusion 2020 Briefing for World Bank Group President Dr. Jim Yong Kim Terence Gallagher Senior Specialist in Micro
 The goals to Access / Financial Inclusion 2020 Briefing for World Bank Group President Dr. Jim Yong Kim Terence Gallagher Senior Specialist in Micro and Small Enterprise Finance Financial Institutions
The goals to Access / Financial Inclusion 2020 Briefing for World Bank Group President Dr. Jim Yong Kim Terence Gallagher Senior Specialist in Micro and Small Enterprise Finance Financial Institutions
The global enabling environment for microfinance: the G20, the Financial Action Task Force, the Basel Committee and the other standard setting bodies
 The global enabling environment for microfinance: the G20, the Financial Action Task Force, the Basel Committee and the other standard setting bodies UNCITRAL International Colloquium on Microfinance Vienna,
The global enabling environment for microfinance: the G20, the Financial Action Task Force, the Basel Committee and the other standard setting bodies UNCITRAL International Colloquium on Microfinance Vienna,
MICROFINANCE SECTOR AN OVERVIEW
 MICROFINANCE SECTOR AN OVERVIEW March 2013 WHAT WHY WHO of micro-finance Means of providing financial services to poor Average transaction size is very small Services offered by profit and non-profit organizations
MICROFINANCE SECTOR AN OVERVIEW March 2013 WHAT WHY WHO of micro-finance Means of providing financial services to poor Average transaction size is very small Services offered by profit and non-profit organizations
MicroWATCH A QUARTERLY UPDATE ON MICROFINANCE OUTREACH IN PAKISTAN. ISSUE 29: QUARTER 3 (Jul-Sep 2013)
 MicroWATCH A QUARTERLY UPDATE ON MICROFINANCE OUTREACH IN PAKISTAN ISSUE 29: QUARTER 3 (Jul-Sep 213) T Change Q3 Q2 Units % Number of Branches/Units 1,984 1,932 52 2.69 Number of Districts Covered 93 94-1
MicroWATCH A QUARTERLY UPDATE ON MICROFINANCE OUTREACH IN PAKISTAN ISSUE 29: QUARTER 3 (Jul-Sep 213) T Change Q3 Q2 Units % Number of Branches/Units 1,984 1,932 52 2.69 Number of Districts Covered 93 94-1
Overview of Microfinance Markets and Investment Opportunities in Russia and China
 November 3, 2011 After Hours Seminar microlinks.kdid.org/afterhours Overview of Microfinance Markets and Investment Opportunities in Russia and China Participate during the seminar Mikhail Mamuta Russian
November 3, 2011 After Hours Seminar microlinks.kdid.org/afterhours Overview of Microfinance Markets and Investment Opportunities in Russia and China Participate during the seminar Mikhail Mamuta Russian
Jordan Country Brief 2011
 Jordan Country Brief 2011 CONTEXT The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan is an upper middle income country with a population of 6 million and a per-capita GNI of US $4,390. Jordan s natural resources are potash
Jordan Country Brief 2011 CONTEXT The Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan is an upper middle income country with a population of 6 million and a per-capita GNI of US $4,390. Jordan s natural resources are potash
PORTFOLIO COMMITTEE ON TRADE AND INDUSTRY. Mr. Sithembele Mase. CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER: samaf. CONTACT : (Marketing Manager)
 PORTFOLIO COMMITTEE ON TRADE AND INDUSTRY Mr. Sithembele Mase CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER: samaf CONTACT : 012 394 1805 (Marketing Manager) 012 394 1722 (PA Line) 012 394 1116 (Direct Line) 1 CONTENT 1. Rationale
PORTFOLIO COMMITTEE ON TRADE AND INDUSTRY Mr. Sithembele Mase CHIEF EXECUTIVE OFFICER: samaf CONTACT : 012 394 1805 (Marketing Manager) 012 394 1722 (PA Line) 012 394 1116 (Direct Line) 1 CONTENT 1. Rationale
Monetary Policy Reforms Since Early 2005 Adib Mayaleh Governor of the Central Bank of Syria Governor London 7 Nov 2007
 Monetary Policy Reforms Since Early 2005 Adib Mayaleh Governor of the Central Bank of Syria London 7 Nov 2007 I would first of all like to express, on behalf of my country Syria and on my own behalf, our
Monetary Policy Reforms Since Early 2005 Adib Mayaleh Governor of the Central Bank of Syria London 7 Nov 2007 I would first of all like to express, on behalf of my country Syria and on my own behalf, our
MICROFINANCE: Enabling The Power of Ideas & Entrepreneurial Energy for the Other Half. Vinod Khosla May 2004
 MICROFINANCE: Enabling The Power of Ideas & Entrepreneurial Energy for the Other Half Vinod Khosla May 2004 Story: 1994 First Inspiration SHARE: History 1998-99 Active Clients 1999-2000 2000-2001 2001-02
MICROFINANCE: Enabling The Power of Ideas & Entrepreneurial Energy for the Other Half Vinod Khosla May 2004 Story: 1994 First Inspiration SHARE: History 1998-99 Active Clients 1999-2000 2000-2001 2001-02
Ex Post-Evaluation Brief Democratic Republic of the Congo: ProCredit Bank Congo (Fiduciary Holding)
 Ex Post-Evaluation Brief Democratic Republic of the Congo: ProCredit Bank Congo (Fiduciary Holding) Programme/Client ProCredit Bank Congo (Fiduciary Holding) 2005 65 911 Programme executing agency ProCredit
Ex Post-Evaluation Brief Democratic Republic of the Congo: ProCredit Bank Congo (Fiduciary Holding) Programme/Client ProCredit Bank Congo (Fiduciary Holding) 2005 65 911 Programme executing agency ProCredit
MICROFINANCE BANKS AN OVERVIEW
 MICROFINANCE BANKS AN OVERVIEW February 2017 MFPS SECTOR SNAPSHOT *Others include organizations running microfinance ops as part of various other services Gross Loan Portfolio (PKRmln) Number Sep-16 Dec-15
MICROFINANCE BANKS AN OVERVIEW February 2017 MFPS SECTOR SNAPSHOT *Others include organizations running microfinance ops as part of various other services Gross Loan Portfolio (PKRmln) Number Sep-16 Dec-15
BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION
 MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY QUARTERLY REPORT 31 DECEMBER2015 BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION 1. Executive Summary 1.1. The microfinance sector which by its nature targets the low income households and micro, small
MICROFINANCE INDUSTRY QUARTERLY REPORT 31 DECEMBER2015 BANK SUPERVISION DIVISION 1. Executive Summary 1.1. The microfinance sector which by its nature targets the low income households and micro, small
Unique mobile subscribership 3 44 %
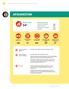 1 AFGHANISTAN 54 % Country commitment 44% Mobile capacity 83% Regulatory environment 72% Adoption 36% $20 17 44 % 10 % 4 % Committed to the Alliance for Financial Inclusion in 2009 Joined the Better Than
1 AFGHANISTAN 54 % Country commitment 44% Mobile capacity 83% Regulatory environment 72% Adoption 36% $20 17 44 % 10 % 4 % Committed to the Alliance for Financial Inclusion in 2009 Joined the Better Than
Microfinance Investment Vehicles An Emerging Asset Class
 The Rating Agency for Microfinance MFInsights Microfinance Investment Vehicles An Emerging Asset Class November 26 MICROFINANCE INVESTMENT VEHICLES A REVIEW BACKGROUND The Emerging Microfinance Investment
The Rating Agency for Microfinance MFInsights Microfinance Investment Vehicles An Emerging Asset Class November 26 MICROFINANCE INVESTMENT VEHICLES A REVIEW BACKGROUND The Emerging Microfinance Investment
Technical Cooperation s Contribution to Transition in Early Transition Countries: Evidence from Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Lending 1
 WORKING DRAFT Technical Cooperation s Contribution to Transition in Early Transition Countries: Evidence from Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Lending 1 Office of Chief Economist, the European Bank
WORKING DRAFT Technical Cooperation s Contribution to Transition in Early Transition Countries: Evidence from Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Lending 1 Office of Chief Economist, the European Bank
The First MicroFinance Bank Limited (FMFB)
 RATING REPORT The First MicroFinance Bank Limited (FMFB) REPORT DATE: May 2, 2016 RATING ANALYSTS: Waqas Munir, FRM waqas.munir@jcrvis.com.pk Maham Qasim maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest
RATING REPORT The First MicroFinance Bank Limited (FMFB) REPORT DATE: May 2, 2016 RATING ANALYSTS: Waqas Munir, FRM waqas.munir@jcrvis.com.pk Maham Qasim maham.qasim@jcrvis.com.pk RATING DETAILS Latest
RURAL ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT SECTOR
 RURAL ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT SECTOR Final Documentation Report People Women Empowerment Program Report Generated by: Monitoring Evaluation & Research Section Rural Credit Enterprise Development Sector
RURAL ENTERPRISE DEVELOPMENT SECTOR Final Documentation Report People Women Empowerment Program Report Generated by: Monitoring Evaluation & Research Section Rural Credit Enterprise Development Sector
PMN Governance and Membership Structure. Figure 1: PMN Governance and Membership Pyramid. Board of Directors. Members of the General Body
 PMN Governance and Membership Structure The revised governance and membership structure of Pakistan Microfinance Network (PMN) was approved by the Network s board of directors in June 2008 and came into
PMN Governance and Membership Structure The revised governance and membership structure of Pakistan Microfinance Network (PMN) was approved by the Network s board of directors in June 2008 and came into
2018 SYMBIOTICS MIV SURVEY Market Data & Peer Group Analysis. 12 th edition September 2018
 2018 SYMBIOTICS MIV SURVEY Market Data & Peer Group Analysis 12 th edition September 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. About the Symbiotics MIV Survey... 3 1.1 About the Symbiotics MIV Survey: Overview... 4 1.2
2018 SYMBIOTICS MIV SURVEY Market Data & Peer Group Analysis 12 th edition September 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. About the Symbiotics MIV Survey... 3 1.1 About the Symbiotics MIV Survey: Overview... 4 1.2
Market Report (KOREA)
 Market Report (KOREA) Presented by Korea Financial Investment Association Macro-Economic Overview 2017-2018 Korea s per capita gross national income (GNI) registered USD 29,744 in 2017, up by 7.5% from
Market Report (KOREA) Presented by Korea Financial Investment Association Macro-Economic Overview 2017-2018 Korea s per capita gross national income (GNI) registered USD 29,744 in 2017, up by 7.5% from
FIDC Finance Industry Development Council
 Finance Industry Development Council Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs) - Contribution to the Economy & Way Forward Presented by: Raman Aggarwal Chairman 28 September, 2017 Page 1 NBFCs : Overview (As
Finance Industry Development Council Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs) - Contribution to the Economy & Way Forward Presented by: Raman Aggarwal Chairman 28 September, 2017 Page 1 NBFCs : Overview (As
Comments to be submitted by March 15, Consultative Paper on the Review of the Microfinance Legislations
 Consultative Paper on the Review of the Microfinance Legislations FEBRUARY 23 2018 CONSULTATIVE PAPER ON THE REVIEW OF THE MICROFINANCE LEGISLATIONS 1.0. Introduction The Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) is
Consultative Paper on the Review of the Microfinance Legislations FEBRUARY 23 2018 CONSULTATIVE PAPER ON THE REVIEW OF THE MICROFINANCE LEGISLATIONS 1.0. Introduction The Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) is
SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE
 Inclusive Financial Sector Development Program, Subprogram 1 (RRP CAM 44263 013) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities a. Sector Context and Performance
Inclusive Financial Sector Development Program, Subprogram 1 (RRP CAM 44263 013) SECTOR ASSESSMENT (SUMMARY): FINANCE 1. Sector Performance, Problems, and Opportunities a. Sector Context and Performance
FROM BILLIONS TO TRILLIONS: TRANSFORMING DEVELOPMENT FINANCE POST-2015 FINANCING FOR DEVELOPMENT: MULTILATERAL DEVELOPMENT FINANCE
 DEVELOPMENT COMMITTEE (Joint Ministerial Committee of the Boards of Governors of the Bank and the Fund on the Transfer of Real Resources to Developing Countries) DC2015-0002 April 2, 2015 FROM BILLIONS
DEVELOPMENT COMMITTEE (Joint Ministerial Committee of the Boards of Governors of the Bank and the Fund on the Transfer of Real Resources to Developing Countries) DC2015-0002 April 2, 2015 FROM BILLIONS
Market P/E (X) : Year Avg. Daily Turnover : USD Million Market Cap to GDP Ratio : 21%
 Market P/E (X) : 16.78 5 Year Avg. Daily Turnover : USD 68.26 Million Market Cap to GDP Ratio : 21% Bangladesh Capital Market Commentary: Bangladesh equities market continued to exhibit a resilient performance
Market P/E (X) : 16.78 5 Year Avg. Daily Turnover : USD 68.26 Million Market Cap to GDP Ratio : 21% Bangladesh Capital Market Commentary: Bangladesh equities market continued to exhibit a resilient performance
KASHF QUARTERLY REPORT
 KASHF QUARTERLY REPORT JULY-SEPTEMBER 2016 K A S H F : T H E L A RG E S T P ROV I D E R O F M I C RO I N S U R A N C E I N PA K I S TA N Kashf provides insurance to low-income households to create social
KASHF QUARTERLY REPORT JULY-SEPTEMBER 2016 K A S H F : T H E L A RG E S T P ROV I D E R O F M I C RO I N S U R A N C E I N PA K I S TA N Kashf provides insurance to low-income households to create social
MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT JULY-DECEMBER 2004
 MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT JULY-DECEMBER 2004 Monetary Policy Statement (July-December 2004) Monetary Policy Statement July-December, 2004 Macroeconomic Outlook and Monetary Policy Stance Recent global
MONETARY POLICY STATEMENT JULY-DECEMBER 2004 Monetary Policy Statement (July-December 2004) Monetary Policy Statement July-December, 2004 Macroeconomic Outlook and Monetary Policy Stance Recent global
Results presentation. For the year ended 31 March 2014
 Results presentation For the year ended 31 March 214 The year in review 2 Improving operating environment Results impacted by strength of sterling against other operating currencies Equity markets Interest
Results presentation For the year ended 31 March 214 The year in review 2 Improving operating environment Results impacted by strength of sterling against other operating currencies Equity markets Interest
Sterling Bank PLC H Investor/Creditor Presentation. July 2011
 Sterling Bank PLC H1 2011 Investor/Creditor Presentation July 2011 Important Information Investor Relations This presentation has been prepared by Sterling Bank PLC. It is intended for an audience of professional
Sterling Bank PLC H1 2011 Investor/Creditor Presentation July 2011 Important Information Investor Relations This presentation has been prepared by Sterling Bank PLC. It is intended for an audience of professional
Pakistan Microfinance Review. Mainstreaming Microfinance. Progress, Opportunities and Challenges
 Pakistan Microfinance Review 2008 Mainstreaming Microfinance Progress, Opportunities and Challenges Editorial Board Ghalib Nishtar Chairperson Editorial Board President,Khushhali Bank Ltd Dr Saeed Ahmed
Pakistan Microfinance Review 2008 Mainstreaming Microfinance Progress, Opportunities and Challenges Editorial Board Ghalib Nishtar Chairperson Editorial Board President,Khushhali Bank Ltd Dr Saeed Ahmed
FINCA Microfinance Bank Limited
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Rating Report Report Contents 1. Rating Analysis 2. Financial Information 3. Rating Scale 4. Regulatory and Supplementary Disclosure Rating History Dissemination Date Long
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Rating Report Report Contents 1. Rating Analysis 2. Financial Information 3. Rating Scale 4. Regulatory and Supplementary Disclosure Rating History Dissemination Date Long
Our Expertise. IFC blends investment with advice and resource mobilization to help the private sector advance development.
 Our Expertise IFC blends investment with advice and resource mobilization to help the private sector advance development. Where We Work As the largest global development institution focused on the private
Our Expertise IFC blends investment with advice and resource mobilization to help the private sector advance development. Where We Work As the largest global development institution focused on the private
Ghana : Financial services for women entrepreneurs in the informal sector
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized No. 136 June 1999 Findings occasionally reports on development initiatives not assisted
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized No. 136 June 1999 Findings occasionally reports on development initiatives not assisted
Banking and Finance Indian Microfinance Sector: Entering a phase of moderate credit risk, three years post AP crisis
 Indian Microfinance Sector: Entering a phase of moderate credit risk, three years post AP crisis March 7, 214 Summary Microfinance sector in India has gone through 3 broad risk phases in the past high
Indian Microfinance Sector: Entering a phase of moderate credit risk, three years post AP crisis March 7, 214 Summary Microfinance sector in India has gone through 3 broad risk phases in the past high
EGYPT Affordable Mortgage Finance Program Development Policy Loan (Loan No EG) Release of the Second Tranche Full Compliance
 Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized EGYPT Affordable Mortgage Finance Program Development Policy Loan (Loan No. 7747-EG)
Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized Public Disclosure Authorized EGYPT Affordable Mortgage Finance Program Development Policy Loan (Loan No. 7747-EG)
Community Managed Revolving Fund (Sustainable mechanism of microfinance practices to disadvantaged community)
 Community Managed Revolving Fund (Sustainable mechanism of microfinance practices to disadvantaged community) A paper presented in Micro Finance Summit 2008 New departure in expanding the outreach of Micro-finance
Community Managed Revolving Fund (Sustainable mechanism of microfinance practices to disadvantaged community) A paper presented in Micro Finance Summit 2008 New departure in expanding the outreach of Micro-finance
