The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy
|
|
|
- Vanessa Sherman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy Overview In this lesson, students will gain an overview of the Federal Reserve and monetary policy. Students will learn how the FED manipulates the money supply through open market operations, changing the discount rate and changing the reserve requirements. Students will first acquire knowledge about monetary policy from a comic book and video. The students will then take on the role of the Federal Reserve Chairperson in an online monetary policy interactive simulation. Grade 10 NC Essential Standards for Civics & Economics (to be implemented in the school year) CE.E.3.2- Explain how fiscal policy and the monetary policy influence overall levels of employment, interest rates, production, price level and economic growth CE.E.3.3- Analyze organizations in terms of their roles and functions in the United States economy Essential Questions What is the role of the Federal Reserve in regulating the United States Economy? What is monetary policy? What are the tools of monetary policy? What is the appropriate response by the Federal Reserve to combat inflation or recession? Materials The Story of Monetary Policy comic book o Comic books are available as a free, printable.pdf at ary.pdf. The Story of Monetary Policy Guided reading questions (Handout 1), attached In Plain English: Making Sense of the Federal Reserve DVD o A free copy of the DVD can be obtained at and will take approximately two-three weeks to arrive DVD Player In Plain English: Making Sense of the Federal Reserve Viewer Questions, attached Computers with internet access (one-two students per computer) Interactive Simulation questions (Handout 2), attached Create a comic book assignment and Rubric (Handout 3), attached Sample EOC Questions and Answer Key, attached Duration block period(s) NC Civic Education Consortium 1
2 Preparation Students should have a basic knowledge of the definition and functions of money and the structure and operations of the banking system. Students should also have been introduced to how banks create money through loans, the structure of the Federal Reserve, as well as the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation. For lessons on these topics, see the Consortium s Database of Civic Resources at Procedure Warm Up: Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy 1. As a warm up, ask students to following questions: When there is a fire, what government officials/agencies might show up to help affected citizens? What do these individuals do to help put out the fire? When there is a hurricane, what government officials/agencies might show up to help affected citizens? What do these individuals do to help with the disaster relief? What if another country tried to invade the US, what government officials/agencies could help defend citizens? What would the individuals do to stop the invasion? What are some disasters that could occur with the economy? How are people affected by economic disasters as compared to the ways people are affected by the disasters discussed above? What government agencies help with these economic disasters? 2. Tell students that they will be learning about how the Federal Reserve deals with economic disasters such as a recession or high inflation. Ask the class to share what they already know regarding the Federal Reserve System (ideally from a previous lesson). Students should recall the four parts of the Federal Reserve System: the Board of Governors, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), the Federal Reserve banks, and the member banks. Project the definition of Monetary Policy : Monetary Policy is the process by which the government, central bank, or monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, availability of money, and rate of interest. The goal of monetary policy is either to encourage the growth of an economy or ensure stability in the value of a nation s money. 3. Pass out copies of The Story of Monetary Policy comic book and guided reading questions (Handout 1). Have students read the comic book and complete guided reading questions. Once students have completed the reading and questions, discuss answers as a class. Viewing In Plain English 4. Students will view the short film In Plain English: Making Sense of the Federal Reserve. The movie lasts approximately 15 minutes. Instruct students to take notes during the video. After viewing the film, host a class discussion regarding the structure of the Federal Reserve System and the Federal Open Market Committee using the questions below. (Teachers can either have the questions on the board, print student copies, or just verbally present the questions after the video has concluded. Much of the information will be a review from previous lesson and comic book.) What are the three parts of the Federal Reserve System? NC Civic Education Consortium 2
3 Which part of the Federal Reserve System constitutes the centralized national authority? Which part of the Federal Reserve System represents regional independence? Which part of the Federal Reserve System sets monetary policy? How does each meeting of the FOMC meeting end? How many districts are there in the Federal Reserve System? What is the official economic term for managing the nation s money supply? What is one long-term goal of the Fed? Preparing for and Conducting the Interactive Simulation 5. Next, lead students in an interactive simulation of monetary policy in which students take on the role of the Federal Reserve chairperson and alter the Federal Funds rate to appropriately address unemployment and inflation. The simulation is available at: Once there, scroll down to Fed Chairman Game. Click on this link and follow directions on the green screen to begin. Game directions will be on the left-hand side of the screen. Instructor should prompt students to do the following: Increase the Federal Funds rate in response to higher inflation. Decrease the Federal Funds rate in response to higher unemployment. If both inflation and unemployment are rising, student will have to choose between trade-off of economic growth and price stability. Review your expectations for appropriate use of technology and behavior in the computer lab. Remind students to try their best and take the simulation seriously. Circulate around the room to assist and regulate student activities while using the internet. Students should complete the reflection questions from Handout 2 (attached) while they play. As the Handout directs, students should play 3 separate rounds. Note: The teacher may choose to have students share computers during the simulation and work as partners in deciding appropriate monetary policy measures, Debriefing the Interactive Simulation 6. After the simulation has ended, have students applaud themselves for their hard work and debrief using their responses from Handout 2. What was your experience like when assuming the role of Chairman of the Federal Reserve? At what points do you feel you were successful at the game and why? When were you unsuccessful and why? What factors made some students more successful than others? What happened to inflation when you increased the Federal Funds rate? Decreased? What happened to unemployment when you increased the Federal Funds rate? Decreased? In your opinion, is it more important for the Federal Reserve to try to prevent inflation or unemployment? Explain What skills/knowledge/abilities do you think it would be important for the Chairman of the Federal Reserve to have? In what ways was the interactive simulation realistic? In what ways was the interactive simulation unrealistic? NC Civic Education Consortium 3
4 Why is it important for the Chairperson to make the correct decision regarding monetary policy? What groups of people would benefit from lower interest rates? What groups of people would be hurt by lower interest rates? What groups of people would benefit from higher interest rates? What groups of people would be hurt by higher interest rates? What types of jobs would most likely be lost during a recession? Why does the government try to prevent unemployment from increasing? 7. As a culminating activity, have the students create their own comic book detailing what they have learned about the Federal Reserve System. See the attached Handout 3 for directions and a grading rubric. Additional Activities Have the students visit for detailed descriptions of monetary policy and the 3 instruments of monetary policy. Differentiation Students with Special Needs Decrease the number of pages from the comic book that students are required to read and allow students more time to read. Provide students with a graphic organizer rather than Guided Reading questions, such as the one at the following site: Allow students to work as partners during the interactive simulation. AIG To improve note taking and summarizing ability, do not provide students with Handout 1. Instead, have students read comic book and choose which topics they think are essential to understanding the Federal Reserve System and monetary policy. Have students create a non-linguistic representation while reading from The Story of Monetary Policy. They should create a graphic organizer that represents the essential topics from the reading. Allow time for the students to share how they organized the information. Have the students research FOMC meetings from the past year and write short reports about the decisions of the FOMC regarding the federal funds rate. Students should explain why the FOMC decided to increase, decrease, or leave the federal funds rate constant. NC Civic Education Consortium 4
5 Handout 1: The Story of Monetary Policy Guided Reading Questions While reading The Story of Monetary Policy, answer the following questions: 1. What is real GDP per capita (Examine all three parts: 1) real, 2) GDP, 3) per capita)? 2. What is monetary policy? What is money? 3. Why do we want the economy to grow? (2 reasons) 4. Who choose the members of the Board of Governors? 5. What is inflation? What groups are hurt by inflation? 6. What can cause inflation? What is hyperinflation? 7. What is a recession? How can slow money growth and tight credit lead to a recession? 8. What happens if the money supply grows too rapidly? 9. Describe the two main part of the Federal Reserve System: the Board of Governors and the district banks. 10. Why are Federal Reserve member chosen for 14 years? 11. How does a central bank s independence from political pressure affect its success at fighting inflation? 12. Who are the voting members of the FOMC 13. What is the job of the FOMC? What are open market operations? 14. What is the Federal Funds rate? Who is responsible for executing the FOMC s monetary policy? 15. What other tools can the Federal Reserve use to change the money supply? Describe each. NC Civic Education Consortium 5
6 Handout 1: The Story of Monetary Policy Guided Reading Questions- ANSWER KEY 1. What is real GDP per capita (Examine all three parts: 1) real, 2) GDP, 3) per capita)? Real means without inflation. GDP stands for gross domestic product, a measure of the size of an economy. Per capita means per person. 2. What is monetary policy? What is money? Monetary Policy is the process by which the government, central bank, or monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, availability of money, and rate of interest. 3. Why do we want the economy to grow? (2 reasons) Increases standard of living for citizens living in a nations; Allows more people to find employment. 4. Who choose the members of the Board of Governors? The US president. 5. What is inflation? What groups are hurt by inflation? Inflation is an overall increase in the average price level. People on fixed incomes and people that have saved money are hurt by inflation. 6. What can cause inflation? What is hyperinflation? An increase in the cost of resources or an increase in the demand for goods can cause inflation. Hyperinflation is inflation that is occurring at a very rapid rate. 7. What is a recession? How can slow money growth and tight credit lead to a recession? A recession is a period of at least six months of decreasing real GDP. People will reduce spending if there is less money moving through the economy. 8. What happens if the money supply grows too rapidly? Inflation can occur. 9. Describe the two main part of the Federal Reserve System: the Board of Governors and the district banks. The Board of Governors is the central authority of the Federal Reserve System that meets in Washington, DC. The District Banks are the regional authorities responsible for regulating and supervising member banks. 10. Why are Federal Reserve member chosen for 14 years? Board members have long term lengths to give them independence from political pressure. 11. How does a central bank s independence from political pressure affect its success at fighting inflation? The more independent a central bank is, the more effective it is in carrying on monetary policy. 12. Who are the voting members of the FOMC The Board of Governors and a rotating group of district bank presidents. 13. What is the job of the FOMC? What are open market operations? The FOMC sets monetary policy. Open market operations are the buying and selling of government securities to increase or decrease the money supply. 14. What is the Federal Funds rate? Who is responsible for executing the FOMC s monetary policy? The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate at which banks charge each other for short-term overnight loans. The trading desk at the New York Federal Reserve Banks. 15. What other tools can the Federal Reserve use to change the money supply? Describe each. Discount window: interest rate the Federal Reserve charges member banks for overnight loans Reserve requirement: percentage of deposit that member banks must keep in reserve. The rest of a deposit may be then loaned out. NC Civic Education Consortium 6
7 Handout 2: Federal Reserve Interactive Simulation A. After playing once, answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What is the federal funds rate? 2. How does the FOMC change the federal funds rate? 3. When did you decide to raise rates? Why? What was the result? 4. When did you decide to lower rates? Why? What was the result? 5. What was the federal funds rate when the game began? What was the highest it reached? What was it at the end of the game? 6. How did you do as the chairman of the Fed? B. Play the game again and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What happened differently this time? 2. When did you decide to raise rates? Why? What was the result? 3. When did you decide to lower rates? Why? What was the result? 4. How did you do as the chairman of the Fed this time? C. Play the game once more and answer the following questions in complete sentences: 1. What happened differently this time? 2. When did you decide to raise rates? Why? What was the result? 3. When did you decide to lower rates? Why? What was the result? 4. How did you do as the chairman of the Fed this time? NC Civic Education Consortium 7
8 Handout 3: Comic Book Assignment Assignment: You will create a comic book about the Federal Reserve System and monetary policy. The comic book should display a coherent story with complimentary illustrations. You will integrate six (6) vocabulary words with their correct definitions from today s lesson. The vocabulary words you can choose from are: Federal Reserve System Discount rate Board of Governors Expansionary monetary policy (Easymoney) Federal Reserve Banks FOMC Contractionary monetary policy (Tightmoney) Fractional Reserve Banking Monetary Policy Recession Open-market operations Inflation Reserve requirement Rubric for Comic Book Assignment CATEGORY Organization Grammar Content - Accuracy Attractiveness & Organization Graphics/ Pictures Vocabulary The comic is wellorganized with a coherent story line. There is a clear beginning, middle, and end. There are no grammatical mistakes in the comic book. All facts in the comic book are accurate. The comic has exceptionally attractive formatting and wellorganized information. Graphics go well with the text and there is a good mix of text and graphics. The author correctly uses 6 vocabulary words. The comic book is organized with a story line. There is a beginning, middle and end. There are few grammatical mistakes in the comic book. Most of the facts in the comic book are accurate. The comic book has attractive formatting and well-organized information. Graphics go well with the text, but there are so many that they distract from the text. The author correctly used 4-5 vocabulary words. The comic book is not organized and has very little story. There is no clear beginning, middle, and end. There are multiple grammatical mistakes in the comic book. Some of the facts in the comic book are accurate. The comic book has well-organized information. Graphics go well with the text, but there are too few and the comic book seems "text-heavy". The author correctly used 2-3 vocabulary words. The comic has no organization or story line. There are many grammatical mistakes in the comic book. None of the facts in the comic book are accurate. The comic book 's formatting and organization of material are confusing to the reader. Graphics do not go with the accompanying text or appear to be randomly chosen. The author correctly used less than 2 vocabulary words. NC Civic Education Consortium 8
9 Practice EOC Multiple Choice Questions 1. Monetary policy in the United States is the responsibility which government institution? A) U.S. Treasury. B) Federal Reserve. C) Internal Revenue Service. D) Office of Management and Budget. 2. Which best describes the fundamental objective of monetary policy? A) a rapid pace of economic growth. B) a money supply which is based on the gold standard. C) a full-employment, noninflationary level of total output. D) a balanced-budget consistent with full-employment. 3. Which best explains how the Federal Reserve alters the amount of the nation's money supply? A) reducing the liabilities of the banking system. B) controlling the assets of the nation's largest banks. C) minting coins and printing currency that is distributed to banks. D) manipulating the size of excess reserves held by commercial banks 4. Which statement most accurately explains the role of the Open Market Committee of the Federal Reserve System (FED)? A) provides advice on banking policy to the FED. B) monitors regulatory banking laws for member banks. C) sets policy on the sale and purchase of government bonds by the FED. D) follows the actions and operations of financial markets to keep them open and competitive. 5. Which action would most likely increase the excess reserves of commercial banks? A) The central banks sell bonds to the public. B) The central banks sell bonds to commercial banks. C) The central banks buy bonds from commercial banks. D) The Board of Governors increases the discount rate. 6. The economy is experiencing high unemployment and a low rate of economic growth and the Fed decides to pursue an easy money policy. Which action by the Fed would be most consistent with this policy? A) buying government securities B) selling government securities C) raising the reserve ratio D) raising the discount rate 7. What consumer behavior is the Federal Reserve Board trying to encourage when it implements a loose monetary policy? A) increased saving and reduced spending B) decreased saving and increased spending C) increased saving and spending D) decreased saving and spending NC Civic Education Consortium 9
10 8. Which of the following are true statements about the federal funds rate? I. It is the same thing as the discount rate. II. It is the interest rate that banks charge each other for short-term loans. III. It is influenced by open market operations. A) I only B) II only C) III only D) I and II only E) II and III only 9. Which of the following does the Federal Reserve use most often to combat recession? A) Selling securities B) Buying securities C) Reducing the reserve requirement D) Increasing the discount rate E) Increasing the federal funds rate NC Civic Education Consortium 10
11 Practice EOC Multiple Choice Questions- ANSWER KEY 1. B) Federal Reserve. 2. C) a full-employment, noninflationary level of total output. 3. D) manipulating the size of excess reserves held by commercial banks 4. C) sets policy on the sale and purchase of government bonds by the FED. 5. C) The central banks buy bonds from commercial banks. 6. A) buying government securities 7. B) decreased saving and increased spending 8. E) II and III only 9. B) Buying securities NC Civic Education Consortium 11
GDP and Fiscal Policy Monopoly
 GDP and Fiscal Policy Monopoly Overview In this lesson, students will gain an understanding of the economic measure of gross domestic product (GDP) and fiscal policy by playing the board game Monopoly
GDP and Fiscal Policy Monopoly Overview In this lesson, students will gain an understanding of the economic measure of gross domestic product (GDP) and fiscal policy by playing the board game Monopoly
Exercise Chap 34. Student:
 Exercise Chap 34 Student: 1. A decrease in the interest rate will cause a(n): A. Increase in the transactions demand for money B. Decrease in the transactions demand for money C. Decrease in the amount
Exercise Chap 34 Student: 1. A decrease in the interest rate will cause a(n): A. Increase in the transactions demand for money B. Decrease in the transactions demand for money C. Decrease in the amount
Monetary Policy Assignment #15
 Monetary Policy Assignment #15 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=raeibejt5hy Monetary Policy & the FED- EconMovies #9: Despicable Me (5:00) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1dq7mmort9o&index=10&list=pl8dpuualjxtpnzwz5_o_5uirj8gqxnheo
Monetary Policy Assignment #15 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=raeibejt5hy Monetary Policy & the FED- EconMovies #9: Despicable Me (5:00) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1dq7mmort9o&index=10&list=pl8dpuualjxtpnzwz5_o_5uirj8gqxnheo
Economics Unit 3. The Last Unit!!
 Economics Unit 3 The Last Unit!! Objective 3.01: Identify phases of the business cycle and the economic indicators used to measure economic activities and trends. Measuring the Economy GDP Gross Domestic
Economics Unit 3 The Last Unit!! Objective 3.01: Identify phases of the business cycle and the economic indicators used to measure economic activities and trends. Measuring the Economy GDP Gross Domestic
The Federal Reserve System the Fed
 The Federal Reserve System the Fed 12 Federal Reserve Districts Commercial banks banker Board of Governors Board of Governors 7 members appointed by president approved by Senate 14 yr. term chairman Janet
The Federal Reserve System the Fed 12 Federal Reserve Districts Commercial banks banker Board of Governors Board of Governors 7 members appointed by president approved by Senate 14 yr. term chairman Janet
SESSION 5: The Federal Reserve System
 SESSION 5: The Federal Reserve System Session Description Students will learn about the Federal Reserve System and its role in the economy. Talking Points 1. The Federal Reserve System (often referred
SESSION 5: The Federal Reserve System Session Description Students will learn about the Federal Reserve System and its role in the economy. Talking Points 1. The Federal Reserve System (often referred
Dr. Mary J. McGlasson Video #32 on Monetary Policy
 Monetary Policy Assignment #14 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1dq7mmort9o&index=10&list=pl8dpuualjxtpnzwz5_o_5uirj8gqxnheo Monetary Policy and the Federal Reserve: Crash Course Economics #10 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hdznoqp4smu&index=32&list=plf2a3693d8481f442
Monetary Policy Assignment #14 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1dq7mmort9o&index=10&list=pl8dpuualjxtpnzwz5_o_5uirj8gqxnheo Monetary Policy and the Federal Reserve: Crash Course Economics #10 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hdznoqp4smu&index=32&list=plf2a3693d8481f442
Economics-in-Marketing CTE Lesson Plan
 Economics-in-Marketing CTE Lesson Plan Lesson Title Lesson Objective At the completion of this lesson, students will be able to identify fiscal policy and the consequences associated to the macroeconomic
Economics-in-Marketing CTE Lesson Plan Lesson Title Lesson Objective At the completion of this lesson, students will be able to identify fiscal policy and the consequences associated to the macroeconomic
Macro Graphs: Using Manipulatives and Technology to Review Macro Models
 Macro Graphs: Using Manipulatives and Technology to Review Macro Models Lesson by Sherilyn Narker, senior education program manager, Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Lesson description This lesson provides
Macro Graphs: Using Manipulatives and Technology to Review Macro Models Lesson by Sherilyn Narker, senior education program manager, Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Lesson description This lesson provides
High School Lesson Plan
 Standards New York 12.G5b. On various issues, certain governmental branches and agencies are responsible for determining policy. Those who create public policies attempt to balance regional and national
Standards New York 12.G5b. On various issues, certain governmental branches and agencies are responsible for determining policy. Those who create public policies attempt to balance regional and national
Discussion Guide for. Organizing Questions. Introduction. Objectives. Materials
 Discussion Guide for Japan s Insufficient Demand Problem a discussion with Professor Kyoji Fukao Organizing Questions Introduction What does it mean for an economy to grow? What factors determine how quickly
Discussion Guide for Japan s Insufficient Demand Problem a discussion with Professor Kyoji Fukao Organizing Questions Introduction What does it mean for an economy to grow? What factors determine how quickly
Money, Banking and the Federal Reserve
 Money, Banking and the Federal Reserve What Is Money? Money is any asset that can easily be used to purchase goods and services. Fiat money : Money, such as paper currency, that is authorized by a central
Money, Banking and the Federal Reserve What Is Money? Money is any asset that can easily be used to purchase goods and services. Fiat money : Money, such as paper currency, that is authorized by a central
Unit 7 Measuring the Economy
 Unit 7 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Unit 7 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Take a Seat at the Table: An FOMC Simulation
 Take a Seat at the Table: An FOMC Simulation Lesson Description In this lesson, students are given the opportunity to play the role of a Federal Reserve Bank president in two aspects of a Federal Open
Take a Seat at the Table: An FOMC Simulation Lesson Description In this lesson, students are given the opportunity to play the role of a Federal Reserve Bank president in two aspects of a Federal Open
MONEY. Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout
 MONEY Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout Barter Economy A barter economy is an economy with no money. The only way you can get what you want in a barter economy is to trade something
MONEY Economics Unit 4 Macroeconomics Just the Facts Handout Barter Economy A barter economy is an economy with no money. The only way you can get what you want in a barter economy is to trade something
Key Council on Economic Education & Federal Reserve Education A.P. Resources
 Key Council on Economic Education & Federal Reserve Education A.P. Resources Today s Conductor : Karen O. Kokernak, MBA Courtesy of the Maryland Council on Economic Education Featuring the Maestro of Maryland
Key Council on Economic Education & Federal Reserve Education A.P. Resources Today s Conductor : Karen O. Kokernak, MBA Courtesy of the Maryland Council on Economic Education Featuring the Maestro of Maryland
Economics Unit 14. The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy
 Economics Unit 14 The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy These documents are being distributed for educational discussion purposes only. They do not reflect any attempt by the North East Independent School
Economics Unit 14 The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy These documents are being distributed for educational discussion purposes only. They do not reflect any attempt by the North East Independent School
HOW SHOULD GOVERNMENTS STRUCTURE THE TAX SYSTEM?
 LESSON 11 HOW SHOULD GOVERNMENTS STRUCTURE THE TAX SYSTEM? 143 LESSON 11 HOW SHOULD GOVERNMENTS STRUCTURE THE TAX SYSTEM? INTRODUCTION Collecting revenue through taxation creates complicated and controversial
LESSON 11 HOW SHOULD GOVERNMENTS STRUCTURE THE TAX SYSTEM? 143 LESSON 11 HOW SHOULD GOVERNMENTS STRUCTURE THE TAX SYSTEM? INTRODUCTION Collecting revenue through taxation creates complicated and controversial
UNITS 12-13: FIXING AN ECONOMY: FISCAL & MONETARY POLICY WORKSHEET USE THE LECTURE NOTES TO ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS (10 pts each)
 DUE DATE: NAME: UNITS 12-13: FIXING AN ECONOMY: FISCAL & MONETARY POLICY WORKSHEET USE THE LECTURE NOTES TO ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS (10 pts each) 1. John Keynes suggested that government should
DUE DATE: NAME: UNITS 12-13: FIXING AN ECONOMY: FISCAL & MONETARY POLICY WORKSHEET USE THE LECTURE NOTES TO ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS (10 pts each) 1. John Keynes suggested that government should
LESSON 2 -- BUILDING A BETTER BUDGET
 LESSON 2 -- BUILDING A BETTER BUDGET LESSON DESCRIPTION AND BACKGROUND This lesson uses the Better Money Habits (www.bettermoneyhabits.com) video How to Set a Budget and Stick to It to reinforce the concepts
LESSON 2 -- BUILDING A BETTER BUDGET LESSON DESCRIPTION AND BACKGROUND This lesson uses the Better Money Habits (www.bettermoneyhabits.com) video How to Set a Budget and Stick to It to reinforce the concepts
Student Name: Financial Services Types of financial institutions Bank Owned by Profits go to investors. Credit Union Owned by Non-profit entity
 Student Name: Financial Services Types of financial institutions Bank Owned by Profits go to investors Credit Union Owned by Non-profit entity Features when comparing checking accounts electronic banking
Student Name: Financial Services Types of financial institutions Bank Owned by Profits go to investors Credit Union Owned by Non-profit entity Features when comparing checking accounts electronic banking
Today s compelling question
 Today s compelling question What tools does the Federal Reserve System have at its disposal? 24-1 Objectives: Students will be able to --Identify monetary policy tools available to the Fed. --Describe
Today s compelling question What tools does the Federal Reserve System have at its disposal? 24-1 Objectives: Students will be able to --Identify monetary policy tools available to the Fed. --Describe
Economics Chapter 13: FISCAL AND MONETARY POLICY
 Economics Chapter 13: FISCAL AND MONETARY POLICY SECTION 1 Fiscal Policy Two Types of Fiscal Policy Fiscal policy deals with the government makes in spending or taxation to achieve particular economic.
Economics Chapter 13: FISCAL AND MONETARY POLICY SECTION 1 Fiscal Policy Two Types of Fiscal Policy Fiscal policy deals with the government makes in spending or taxation to achieve particular economic.
Marketplaces Investing Basics
 Marketplaces Investing Basics Curriculum Guide Recommended Grade Level 9-12 Subject Fit Business, Economics, Social Studies, and CTE Total Time 5 modules, 10-20 minutes each Standards Alignment Jump$tart
Marketplaces Investing Basics Curriculum Guide Recommended Grade Level 9-12 Subject Fit Business, Economics, Social Studies, and CTE Total Time 5 modules, 10-20 minutes each Standards Alignment Jump$tart
A warm up to review identifying proportional and non-proportional relationships from tables and graphs would give students entry to the activity.
 1 Interpreting Slopes and Y-Intercepts of Proportional and Non-Proportional Relationships Task 1: Investigating Proportional and Non-Proportional Relationships Framework Cluster Standard(s) Materials/Links
1 Interpreting Slopes and Y-Intercepts of Proportional and Non-Proportional Relationships Task 1: Investigating Proportional and Non-Proportional Relationships Framework Cluster Standard(s) Materials/Links
Things you should know about inflation
 Things you should know about inflation February 23, 2015 Inflation is a general increase in prices. Equivalently, it is a fall in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of inflation is deflation a
Things you should know about inflation February 23, 2015 Inflation is a general increase in prices. Equivalently, it is a fall in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of inflation is deflation a
Unit 6 Measuring the Economy
 Unit 6 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
Unit 6 Measuring the Economy - Study Guide - Answer, Explain and define the following: 1) GNP 2) GDP 3) Dept. of Commerce 4) Intermediate goods 5) Disposable personal income 6) Contraction 7) Recession
The Structure of the Federal Reserve System
 What Tools Does Monetary Policy Use to Stabilize the Economy? (EA) Monetary policy consists of decisions made by a central bank about the amount of money in circulation and interest rates. In the United
What Tools Does Monetary Policy Use to Stabilize the Economy? (EA) Monetary policy consists of decisions made by a central bank about the amount of money in circulation and interest rates. In the United
The Business Cycle. jobs and spending. How do we know if the economy is prosperous or in a depression?
 The Business Cycle Consumers spend their money to buy products then production increases How do we know if the economy is prosperous or in a depression? Lots of jobs and money Spending slows and jobs begin
The Business Cycle Consumers spend their money to buy products then production increases How do we know if the economy is prosperous or in a depression? Lots of jobs and money Spending slows and jobs begin
Chapter 14 Monetary Policy
 Chapter Overview Chapter 14 Monetary Policy The objectives and the mechanics of monetary policy are covered in this chapter. It is organized around seven major topics: (1) interest rate determination;
Chapter Overview Chapter 14 Monetary Policy The objectives and the mechanics of monetary policy are covered in this chapter. It is organized around seven major topics: (1) interest rate determination;
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices
 SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
SSEMA1 The student will illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. a. Explain that overall levels of income, employment, and prices are determined by the spending and production decisions
Basic Finance. The Federal Reserve. An introduction to financial institutions, investments & Management Eleventh Edition.
 Basic Finance The Federal Reserve 5 An introduction to financial institutions, investments & Management Eleventh Edition 1 U.S. Treasury Federal Reserve 2 Economy 3 U.S. Treasury Prints money IRS...collects
Basic Finance The Federal Reserve 5 An introduction to financial institutions, investments & Management Eleventh Edition 1 U.S. Treasury Federal Reserve 2 Economy 3 U.S. Treasury Prints money IRS...collects
Deciding which car and car loan you can afford
 car loan you can afford In this simulation activity, students calculate monthly installment loan payments and total costs for three different cars to apply a common strategy for purchasing big-ticket items.
car loan you can afford In this simulation activity, students calculate monthly installment loan payments and total costs for three different cars to apply a common strategy for purchasing big-ticket items.
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 16 review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why does the Federal Reserve alter monetary policy? a. to regulate the
Chapter 16 review Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Why does the Federal Reserve alter monetary policy? a. to regulate the
16 SECTION 1 The Federal Reserve System
 CHAPTER 16 The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy SECTION 1 The Federal Reserve System SECTION 2 Functions of the Federal Reserve SECTION 3 Monetary Policy SECTION 4 Applying Monetary and Fiscal Policy
CHAPTER 16 The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy SECTION 1 The Federal Reserve System SECTION 2 Functions of the Federal Reserve SECTION 3 Monetary Policy SECTION 4 Applying Monetary and Fiscal Policy
Every Breath You Take
 Every Breath You Take Every Breath You Take Monetary and Fiscal Policy Chapters 10, 13, and 14! Stabilizing the Economy Controlling unemployment and inflation (Dual Mandate)! Demand Side Policies Keynesian
Every Breath You Take Every Breath You Take Monetary and Fiscal Policy Chapters 10, 13, and 14! Stabilizing the Economy Controlling unemployment and inflation (Dual Mandate)! Demand Side Policies Keynesian
Lesson Plan. Preparation
 Financial Institutions Banking and Financial Services Finance Lesson Plan Performance Objective Students will understand the purposes, similarities, and differences among types of financial institutions.
Financial Institutions Banking and Financial Services Finance Lesson Plan Performance Objective Students will understand the purposes, similarities, and differences among types of financial institutions.
CURRICULUM MAP. Course /Subject: Finance and Investment Grade: 9, 10, 11, 12
 Enduring Understanding Individuals must be responsible for creating and protecting their own wealth. The government and companies will not do it for you. A person s standard of living is determined by
Enduring Understanding Individuals must be responsible for creating and protecting their own wealth. The government and companies will not do it for you. A person s standard of living is determined by
The Federal Reserve In Action
 The Federal Reserve In Action What is the Fed? Central bank of the United States Established in 1913 Purpose is to ensure a stable economy for the nation Roles & Responsibilities Conduct the nation s monetary
The Federal Reserve In Action What is the Fed? Central bank of the United States Established in 1913 Purpose is to ensure a stable economy for the nation Roles & Responsibilities Conduct the nation s monetary
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro
 Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro Concept / Topic To Teach: Unit 4 MODULE 22: SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL Specific Objectives: ELD Standards SYSTEM Week
Shanghai Livingston American School Quarterly / Trimester Plan 3 AP Macro Concept / Topic To Teach: Unit 4 MODULE 22: SAVING, INVESTMENT, AND THE FINANCIAL Specific Objectives: ELD Standards SYSTEM Week
Middle School Lesson Plan
 Standards New York 8.2e Progressive reformers sought to address political and social issues at the local, state, and federal levels of government between 1890 and 1920. New Jersey 6.1.8.A.2.b Explain how
Standards New York 8.2e Progressive reformers sought to address political and social issues at the local, state, and federal levels of government between 1890 and 1920. New Jersey 6.1.8.A.2.b Explain how
Chapter 16: The Federal Reserve and Monetary Policy
 SCHS SOCIAL STUDIES What you need to know UNIT 6 1. Describe the structure of today s Federal Reserve System 2. Describe how the Federal Reserve serves the federal government 3. Understand why some monetary
SCHS SOCIAL STUDIES What you need to know UNIT 6 1. Describe the structure of today s Federal Reserve System 2. Describe how the Federal Reserve serves the federal government 3. Understand why some monetary
Unemployment that occurs at the natural rate of output is called:
 ECON 1A Macroeconomics Lecture Notes: Chapter 11 - Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply in the Short Run AS - relationship between the economy s price level and Assuming: Technology is fixed. Labor & AS:
ECON 1A Macroeconomics Lecture Notes: Chapter 11 - Aggregate Supply Aggregate Supply in the Short Run AS - relationship between the economy s price level and Assuming: Technology is fixed. Labor & AS:
???????????????????????????????? Where does Government get their money?
 Fiscal policy Taxing and spending BUDGET Proposed by the president Approved by congress What do you think the largest expenditure is for the US Government? ???????????????????????????????? Where does
Fiscal policy Taxing and spending BUDGET Proposed by the president Approved by congress What do you think the largest expenditure is for the US Government? ???????????????????????????????? Where does
Unemployment Role Play Activity
 FEDERAL RESERVE BANK OF ST. LOUIS ECONOMIC EDUCATION Standards and Benchmarks (see page 14) Activity Description This activity is designed to demonstrate the impact that unemployment and reduced consumer
FEDERAL RESERVE BANK OF ST. LOUIS ECONOMIC EDUCATION Standards and Benchmarks (see page 14) Activity Description This activity is designed to demonstrate the impact that unemployment and reduced consumer
Macro Problem Set 3 Fall 2015
 Macro Problem Set 3 Fall 2015 Directions: The True/False and Multiple Choice questions do not have to be turned in for credit. It would be foolish, however, not to spend a great deal of time working on
Macro Problem Set 3 Fall 2015 Directions: The True/False and Multiple Choice questions do not have to be turned in for credit. It would be foolish, however, not to spend a great deal of time working on
Unit: Monetary Policy
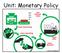 Unit: Monetary Policy 2 3 Showing the Effects of Monetary Policy Graphically Three Related Graphs: Ø Money Market Ø Investment Demand Ø AD/AS Interest Rate (i) S&D of Money S M S M1 Interest Rate (i) Investment
Unit: Monetary Policy 2 3 Showing the Effects of Monetary Policy Graphically Three Related Graphs: Ø Money Market Ø Investment Demand Ø AD/AS Interest Rate (i) S&D of Money S M S M1 Interest Rate (i) Investment
Monetary Policy Tools 16.3
 Monetary Policy Tools 16.3 What is the process of money creation? What three tools does the Federal Reserve use to change the money supply? Why are some tools of monetary policy favored over others? Money
Monetary Policy Tools 16.3 What is the process of money creation? What three tools does the Federal Reserve use to change the money supply? Why are some tools of monetary policy favored over others? Money
Determining how down payments affect loans
 payments affect loans Students calculate how monthly payments for installment loans change based on the size of the down payment. Learning goals Big idea Installment loans can help people purchase big-ticket
payments affect loans Students calculate how monthly payments for installment loans change based on the size of the down payment. Learning goals Big idea Installment loans can help people purchase big-ticket
Credit Cards Friend or Foe? An exploration of credit cards and debit cards utilizing Internet resources and spreadsheets.
 Credit Cards Friend or Foe? An exploration of credit cards and debit cards utilizing Internet resources and spreadsheets. Day One Investigating Credit Cards and Debit Cards The students will need access
Credit Cards Friend or Foe? An exploration of credit cards and debit cards utilizing Internet resources and spreadsheets. Day One Investigating Credit Cards and Debit Cards The students will need access
Personal Finance and Budget
 Teacher Notes Activity at a Glance Subject: Social Studies Subject Area: Economics Category: Personal Finance Topic: Personal Budget Personal Finance and Budget Activity 2 Personal Budget Grade Level:
Teacher Notes Activity at a Glance Subject: Social Studies Subject Area: Economics Category: Personal Finance Topic: Personal Budget Personal Finance and Budget Activity 2 Personal Budget Grade Level:
Fiscal and Monetary Policy
 Fiscal and Monetary Policy Chapter 13 Part 4 of the Final Exam Review should be put in the basket on the projector cart at the beginning of class. The answer key for Part 3 is posted around the room. When
Fiscal and Monetary Policy Chapter 13 Part 4 of the Final Exam Review should be put in the basket on the projector cart at the beginning of class. The answer key for Part 3 is posted around the room. When
AP Macroeconomics. Monetary Policy
 AP Macroeconomics Monetary Policy Monetary Policy Central bank (The Fed, Bank of Japan, ECB, Bank of England ) efforts to promote full employment, maintain price stability, and encourage long-run economic
AP Macroeconomics Monetary Policy Monetary Policy Central bank (The Fed, Bank of Japan, ECB, Bank of England ) efforts to promote full employment, maintain price stability, and encourage long-run economic
Focus Question: To what extent should businesses be concerned about actions taken by the Federal Reserve?
 LES S ON 12: T HE FE DE RAL RESE RVE Focus Question: To what extent should businesses be concerned about actions taken by the Federal Reserve? Objectives Students will be able to: Examine the goals of
LES S ON 12: T HE FE DE RAL RESE RVE Focus Question: To what extent should businesses be concerned about actions taken by the Federal Reserve? Objectives Students will be able to: Examine the goals of
Responses to Survey of Primary Dealers Markets Group, Federal Reserve Bank of New York April 2012
 Responses to Survey of Primary Dealers Markets Group, Federal Reserve Bank of New York April Responses to the Primary Dealer Policy Expectations Survey Distributed: 4/12/ Received by: 4/16/ For most questions,
Responses to Survey of Primary Dealers Markets Group, Federal Reserve Bank of New York April Responses to the Primary Dealer Policy Expectations Survey Distributed: 4/12/ Received by: 4/16/ For most questions,
PFIN 5: Banking Procedures 24
 PFIN 5: Banking Procedures 24 5 1 Checking Accounts OBJECTIVES Explain the purpose and use of a checking account. Prepare a checkbook register. Write a check and prepare a deposit slip. Prepare a bank
PFIN 5: Banking Procedures 24 5 1 Checking Accounts OBJECTIVES Explain the purpose and use of a checking account. Prepare a checkbook register. Write a check and prepare a deposit slip. Prepare a bank
Lesson Description. Concepts. Objectives. Content Standards. Cards, Cars and Currency Lesson 3: Banking on Debit Cards
 Lesson Description After discussing basic information about debit cards, students work in pairs to balance a bank account statement and calculate the costs of using a debit card irresponsibly. The students
Lesson Description After discussing basic information about debit cards, students work in pairs to balance a bank account statement and calculate the costs of using a debit card irresponsibly. The students
Economics Unit 3 Summary
 SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
SSEMA1 Illustrate the means by which economic activity is measured. Economic activity derives from the sectors of the economy explored in the fundamentals and microeconomics units. Individuals, businesses,
RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF
 RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF PRIMARY DEALERS Markets Group, Federal Reserve Bank of New York RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF a v JANUARY Distributed: 1/18/ Received by: 1/22/ The Survey of Primary Dealers is formulated
RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF PRIMARY DEALERS Markets Group, Federal Reserve Bank of New York RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF a v JANUARY Distributed: 1/18/ Received by: 1/22/ The Survey of Primary Dealers is formulated
Unit 5 Notes. National Economic Performance
 Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics
Unit 5 Notes National Economic Performance Economic Indicators Economic Indicators are statistics that economists use to determine the health of a nation s economy. We are going to focus on three statistics
McGraw-Hill/Irwin 2002 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights Reserved.
 The Business Cycle Macroeconomics The Great Depression was the springboard for modern macroeconomics. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of aggregate economic behavior, of the economy as a whole.
The Business Cycle Macroeconomics The Great Depression was the springboard for modern macroeconomics. Macroeconomics Macroeconomics is the study of aggregate economic behavior, of the economy as a whole.
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 2 Monetary Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does the government promote the economic goals of price stability, full employment, and economic growth? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary explicit openly
Lesson 2 Monetary Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does the government promote the economic goals of price stability, full employment, and economic growth? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary explicit openly
Remarks of Dr. N. Gregory Mankiw Chairman Council of Economic Advisers at the 21 st Annual Minority Enterprise Development Week Washington, D.C.
 Remarks of Dr. N. Gregory Mankiw Chairman Council of Economic Advisers at the 21 st Annual Minority Enterprise Development Week Washington, D.C. Monday, September 29, 2003 I am delighted to be here. Thank
Remarks of Dr. N. Gregory Mankiw Chairman Council of Economic Advisers at the 21 st Annual Minority Enterprise Development Week Washington, D.C. Monday, September 29, 2003 I am delighted to be here. Thank
Subject: Personal Finance Grade: 12th Mr. Holmes Unit Lesson Layer Duration "Take Charge of Your TYPES OF INSURANCE Applied (do) 2/4/13-2/15/13
 Subject: Personal Finance Grade: 12th Mr. Holmes Unit Lesson Layer Duration "Take Charge of Your TYPES OF INSURANCE Applied (do) 2/4/13-2/15/13 Finances" Advanced Level Essential Questions What do you
Subject: Personal Finance Grade: 12th Mr. Holmes Unit Lesson Layer Duration "Take Charge of Your TYPES OF INSURANCE Applied (do) 2/4/13-2/15/13 Finances" Advanced Level Essential Questions What do you
This page intentionally left blank
 This page intentionally left blank This page intentionally left blank. Table of Contents CreditSmart Module 2: Managing Your Money Welcome to Freddie Mac s CreditSmart Initiative... 6 Program Structure...
This page intentionally left blank This page intentionally left blank. Table of Contents CreditSmart Module 2: Managing Your Money Welcome to Freddie Mac s CreditSmart Initiative... 6 Program Structure...
5 AGGREGATE DEMAND AND INFLATION. Part Review. Reading Between the Lines WHERE WILL INTEREST RATES GO IN 2002?
 Part Review 5 AGGREGATE DEMAND AND INFLATION Reading Between the Lines WHERE WILL INTEREST RATES GO IN 2002? On May 6, 2002 the FOMC met in Washington D.C. To combat the recession that started in 2001,
Part Review 5 AGGREGATE DEMAND AND INFLATION Reading Between the Lines WHERE WILL INTEREST RATES GO IN 2002? On May 6, 2002 the FOMC met in Washington D.C. To combat the recession that started in 2001,
How Hands on Banking / El futuro en tus manos aligns with Wisconsin Education Standards.
 How Hands on Banking / El futuro en tus manos aligns with. The Hands on Banking program is helping students across the United States grasp important mathematics concepts while gaining valuable skills for
How Hands on Banking / El futuro en tus manos aligns with. The Hands on Banking program is helping students across the United States grasp important mathematics concepts while gaining valuable skills for
Buy, Sell or Hold?: An Overview of Investing
 Buy, Sell or Hold?: An Overview of Investing LESSON 21: TE ACHER S GUIDE a new video game or smart phone in hopes that the price will go down. But when it comes to investments, gambling without knowing
Buy, Sell or Hold?: An Overview of Investing LESSON 21: TE ACHER S GUIDE a new video game or smart phone in hopes that the price will go down. But when it comes to investments, gambling without knowing
CH Lecture. McGraw-Hill/Irwin Colander, Economics 1-1
 CH 30+31 Lecture McGraw-Hill/Irwin Colander, Economics 1-1 Money 2 The Definition and Functions of Money Money is anything that is generally accepted as payment for goods or services Money is a highly
CH 30+31 Lecture McGraw-Hill/Irwin Colander, Economics 1-1 Money 2 The Definition and Functions of Money Money is anything that is generally accepted as payment for goods or services Money is a highly
Seven Steps of Constructing Projects
 I. Who are you? Seven Steps of Constructing Projects Agenda Assuming no responsibility, If you could immerse yourself for 4 hours doing something you love but never have 4 hours to do WHAT WOULD YOU DO?
I. Who are you? Seven Steps of Constructing Projects Agenda Assuming no responsibility, If you could immerse yourself for 4 hours doing something you love but never have 4 hours to do WHAT WOULD YOU DO?
The Role of the Federal Reserve in the Economy. I. Good morning. It s a pleasure to be with all of you today.
 Fed Focus Pocatello, Idaho For delivery June 2, 1998 9 a.m. MDT The Role of the Federal Reserve in the Economy I. Good morning. It s a pleasure to be with all of you today. A. I d like to try to answer
Fed Focus Pocatello, Idaho For delivery June 2, 1998 9 a.m. MDT The Role of the Federal Reserve in the Economy I. Good morning. It s a pleasure to be with all of you today. A. I d like to try to answer
Stock Market Project!
 Stock Market Project! How do stock brokers and financial analysts determine what stocks to buy? What do they investigate when looking at a company? As you work through the activities, you will collect
Stock Market Project! How do stock brokers and financial analysts determine what stocks to buy? What do they investigate when looking at a company? As you work through the activities, you will collect
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13)
 Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
Unit 6 Measuring and Monitoring Economics (Ch 12 and 13) -Macroeconomics 0 & Microeconomics- Government tries to prevent free enterprise from having wild swings in economic behavior. Microeconomics - analyzes
Lesson Plan: The U.S. Health Care Crisis
 Lesson Plan: The U.S. Health Care Crisis OVERVIEW This lesson plan is designed to be used with the film, Critical Condition, which tells the stories of four uninsured Americans as they battle illness over
Lesson Plan: The U.S. Health Care Crisis OVERVIEW This lesson plan is designed to be used with the film, Critical Condition, which tells the stories of four uninsured Americans as they battle illness over
How does the government stabilize the economy?
 How does the government stabilize the economy? The government has two different tool boxes it can use: 1. Fiscal Policy- Actions by Congress and the president to adjust to the G in aggregate demand. 2.
How does the government stabilize the economy? The government has two different tool boxes it can use: 1. Fiscal Policy- Actions by Congress and the president to adjust to the G in aggregate demand. 2.
Monetary Policy CHAPTER 31. Will Rogers. There have been three great inventions since the beginning of time: fire, the wheel and central banking.
 CHAPTER 31 Monetary Policy There have been three great inventions since the beginning of time: fire, the wheel and central banking. Will Rogers McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies,
CHAPTER 31 Monetary Policy There have been three great inventions since the beginning of time: fire, the wheel and central banking. Will Rogers McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2010 by the McGraw-Hill Companies,
Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Economics Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Economics 2.6A for Achievement Standard 91227 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Economics Level 2 Resource title: Government policies that could lift the
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Economics 2.6A for Achievement Standard 91227 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Economics Level 2 Resource title: Government policies that could lift the
Supply CHAPTER SUMMARY CHAPTER ASSESSMENT
 CHAPTER FOCUS SECTION 1 Organization and Functions of the Federal Reserve System SECTION 2 SECTION 3 Money Supply and the Economy Regulating the Money Supply CHAPTER SUMMARY CHAPTER ASSESSMENT 2 Click
CHAPTER FOCUS SECTION 1 Organization and Functions of the Federal Reserve System SECTION 2 SECTION 3 Money Supply and the Economy Regulating the Money Supply CHAPTER SUMMARY CHAPTER ASSESSMENT 2 Click
Chapter 17. The Conduct of Monetary Policy: Strategy and Tactics
 Chapter 17 The Conduct of Monetary Policy: Strategy and Tactics Six Goals of Central Banks Price stability High employment Economic growth Stability of financial markets Interest rate stability Stability
Chapter 17 The Conduct of Monetary Policy: Strategy and Tactics Six Goals of Central Banks Price stability High employment Economic growth Stability of financial markets Interest rate stability Stability
THE FEDERAL RESERVE AND MONETARY POLICY Macroeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.)
 Chapter 12 THE FEDERAL RESERVE AND MONETARY POLICY Macroeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview In this chapter, you will be introduced to a standard treatment of central banking and monetary
Chapter 12 THE FEDERAL RESERVE AND MONETARY POLICY Macroeconomics in Context (Goodwin, et al.) Chapter Overview In this chapter, you will be introduced to a standard treatment of central banking and monetary
Course Title: Fire Prevention Organization & Management (3082) ( )
 Course Title: Fire Prevention Organization & Management (3082) Course Number: FST - 3082 Course Credit Hours: (3) Three Semester Hours Instructor Information: Bernard W. Becker, III, MS (937-751-7371)
Course Title: Fire Prevention Organization & Management (3082) Course Number: FST - 3082 Course Credit Hours: (3) Three Semester Hours Instructor Information: Bernard W. Becker, III, MS (937-751-7371)
ECO 202 Final Project Guidelines and Rubric
 ECO 202 Final Project Guidelines and Rubric Overview The final project for this course is the creation of economic history analysis presentation. Macroeconomics is the part of the study of economics that
ECO 202 Final Project Guidelines and Rubric Overview The final project for this course is the creation of economic history analysis presentation. Macroeconomics is the part of the study of economics that
Instruction Guide. Teach your students the importance of saving and budgeting with this fun Marvel comic book.
 Instruction Guide Teach your students the importance of saving and budgeting with this fun Marvel comic book. OVERVIEW In this lesson based around the Practical Money Skills comic book, Saving the Day,
Instruction Guide Teach your students the importance of saving and budgeting with this fun Marvel comic book. OVERVIEW In this lesson based around the Practical Money Skills comic book, Saving the Day,
Profiles in Credit is designed to be flexible and meet the needs of learners in different educational settings. Examples include:
 Profiles in Credit Educator Resource Guide Module Summary Profiles in Credit is a self-paced, interactive learning module in which students visit the social media profiles of three young people facing
Profiles in Credit Educator Resource Guide Module Summary Profiles in Credit is a self-paced, interactive learning module in which students visit the social media profiles of three young people facing
How has money changed over the centuries? What are the functions of money? Where does our money come from?
 How has money changed over the centuries? What are the functions of money? Where does our money come from? Section Preview In this section, you will learn that money functions as a medium of exchange,
How has money changed over the centuries? What are the functions of money? Where does our money come from? Section Preview In this section, you will learn that money functions as a medium of exchange,
Algebra Success. LESSON 14: Discovering y = mx + b
 T282 Algebra Success [OBJECTIVE] The student will determine the slope and y-intercept of a line by examining the equation for the line written in slope-intercept form. [MATERIALS] Student pages S7 S Transparencies
T282 Algebra Success [OBJECTIVE] The student will determine the slope and y-intercept of a line by examining the equation for the line written in slope-intercept form. [MATERIALS] Student pages S7 S Transparencies
ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS
 ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Maple Grove Senior High School Jeff Rush rushj@district279.org, rushsocialstudies.weebly.com, aplia.com Social Studies Department Required textbook Economics, McConnell
ADVANCED PLACEMENT MACROECONOMICS Maple Grove Senior High School Jeff Rush rushj@district279.org, rushsocialstudies.weebly.com, aplia.com Social Studies Department Required textbook Economics, McConnell
Printable Lesson Materials
 Printable Lesson Materials Print these materials as a study guide These printable materials allow you to study away from your computer, which many students find beneficial. These materials consist of two
Printable Lesson Materials Print these materials as a study guide These printable materials allow you to study away from your computer, which many students find beneficial. These materials consist of two
Buying A Car. Mathematics Capstone Course
 Buying A Car Mathematics Capstone Course I. UNIT OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In this lesson the student will be asked to search the Internet and find a car that he/she would like to purchase. The student will
Buying A Car Mathematics Capstone Course I. UNIT OVERVIEW & PURPOSE: In this lesson the student will be asked to search the Internet and find a car that he/she would like to purchase. The student will
Current Economic Conditions and Selected Forecasts
 Order Code RL30329 Current Economic Conditions and Selected Forecasts Updated May 20, 2008 Gail E. Makinen Economic Policy Consultant Government and Finance Division Current Economic Conditions and Selected
Order Code RL30329 Current Economic Conditions and Selected Forecasts Updated May 20, 2008 Gail E. Makinen Economic Policy Consultant Government and Finance Division Current Economic Conditions and Selected
RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF
 RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF MARKET PARTICIPANTS Markets Group, Federal Reserve Bank of New York RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF a v JANUARY Distributed: 1/18/ Received by: 1/22/ The Survey of Market Participants is
RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF MARKET PARTICIPANTS Markets Group, Federal Reserve Bank of New York RESPONSES TO SURVEY OF a v JANUARY Distributed: 1/18/ Received by: 1/22/ The Survey of Market Participants is
The Federal Reserve & Monetary Policy
 The Federal Reserve & Monetary Policy Essential Standards SSEMA2B: Describe the organization of the Federal Reserve System (12 Districts, Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), and Board of Governors. SSEMA2C:
The Federal Reserve & Monetary Policy Essential Standards SSEMA2B: Describe the organization of the Federal Reserve System (12 Districts, Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), and Board of Governors. SSEMA2C:
AP Economics Pacing Guide
 AP Economics Pacing Guide Course Description: The purpose of AP Macroeconomics is to understand the principles of economics that apply to an economic system as a whole. The course will explore the study
AP Economics Pacing Guide Course Description: The purpose of AP Macroeconomics is to understand the principles of economics that apply to an economic system as a whole. The course will explore the study
Course Map Economics
 Course Title: Economics Course Map Text: Thinking Economics (National Council on Economic Education) Duration: one semester Frequency: one class period daily Year: 2013-2014 Other materials: Areas to be
Course Title: Economics Course Map Text: Thinking Economics (National Council on Economic Education) Duration: one semester Frequency: one class period daily Year: 2013-2014 Other materials: Areas to be
Monetary Policy: Regulating Money Supply
 Monetary Policy: Regulating Money Supply Review Quiz Trade Quiz #1: What are the two conflicting responsibilities of the Federal Reserve? Maximizing GDP & Employment while at the same time keeping inflation
Monetary Policy: Regulating Money Supply Review Quiz Trade Quiz #1: What are the two conflicting responsibilities of the Federal Reserve? Maximizing GDP & Employment while at the same time keeping inflation
Economics-in-Marketing CTE Lesson Plan
 Economics-in-Marketing CTE Lesson Plan Government Revenue and Services Lesson Title Lesson Objective At the completion of this lesson, students will be able to analyze how governments generate revenues
Economics-in-Marketing CTE Lesson Plan Government Revenue and Services Lesson Title Lesson Objective At the completion of this lesson, students will be able to analyze how governments generate revenues
Term used to refer to the Federal Reserve System/Bank.
 Federal Reserve The Fed Term used to refer to the Federal Reserve System/Bank. They are the government s fiscal agent Hold and set reserve requirements Clear checks Supervise member banks Supply paper
Federal Reserve The Fed Term used to refer to the Federal Reserve System/Bank. They are the government s fiscal agent Hold and set reserve requirements Clear checks Supervise member banks Supply paper
Saving, Investing, and Risk Management Extension Activity 4
 The Rule of 72 Students can quickly figure how long it would take to double their money by using the Rule of 72. Divide 72 by the interest rate to determine the number of years savers need for their money
The Rule of 72 Students can quickly figure how long it would take to double their money by using the Rule of 72. Divide 72 by the interest rate to determine the number of years savers need for their money
16-3: Monetary Policy. Notes
 16-3: Monetary Policy Notes I will gain an understanding of the three tools used by the Fed I will gain an understanding of when the Fed uses expansionary and contractionary monetary policy. Monetary Policy
16-3: Monetary Policy Notes I will gain an understanding of the three tools used by the Fed I will gain an understanding of when the Fed uses expansionary and contractionary monetary policy. Monetary Policy
Lesson 12 - Fiscal Policy: A Two-Act Play
 Lesson 12 - Fiscal Policy: A Two-Act Play INTRODUCTION Economics The government is often blamed when the economy experiences unemployment, decreasing gross domestic product or inflation. Many economists
Lesson 12 - Fiscal Policy: A Two-Act Play INTRODUCTION Economics The government is often blamed when the economy experiences unemployment, decreasing gross domestic product or inflation. Many economists
